



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 1129-1142.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.144
程先钰1,2( ), 张天福1,2, 张云1,2, 何鹏1, 孙立新1,2, 马海林3, 鲁超4
), 张天福1,2, 张云1,2, 何鹏1, 孙立新1,2, 马海林3, 鲁超4
出版日期:2025-08-10
发布日期:2025-08-27
作者简介:程先钰,男,硕士,工程师,1991年出生,主要从事地质矿产调查与研究工作。Email:chengxianyu_601@163.com。
基金资助:
CHENG Xianyu1,2( ), ZHANG Tianfu1,2, ZHANG Yun1,2, HE Peng1, SUN Lixin1,2, MA Hailin3, LU Chao4
), ZHANG Tianfu1,2, ZHANG Yun1,2, HE Peng1, SUN Lixin1,2, MA Hailin3, LU Chao4
Published:2025-08-10
Online:2025-08-27
摘要:
鄂尔多斯盆地南部侏罗系泥岩地球化学证据记录了古沉积环境演化,中侏罗世古沉积环境演化是鄂尔多斯盆地铀元素沉积富集的基础。然而,有关鄂尔多斯东南部直罗组沉积环境的认识仍然薄弱,制约了砂岩型铀矿形成条件的深入理解。本文对黄陵店头地区中侏罗统直罗组及延安组顶部泥岩进行主、微量元素分析,然后根据泥岩典型地球化学参数的垂向变化对其古沉积环境进行了恢复。结果表明,B、相当B含量、Sr/Ba组合指示直罗组沉积水体为半咸水到微咸水环境;U/Th、V/(V+Ni)、V/Cr、Ni/Co组合指示直罗组及延安组顶部的古水体介质富氧;Fe2+/Fe3+指示延安组形成稳定的还原层,直罗组下段上亚段底部逐渐向弱还原环境过渡,上段为强氧化环境;古气候指标Sr、Sr/Cu、A12O3/MgO、FeO/MnO指示直罗组沉积期经历了半干旱逐渐向干旱环境转变;化学蚀变指数(CIA)、成分变异指数(ICV)反映直罗组上段相对于下段的化学风化程度有所减弱,表明鄂尔多斯盆地周缘构造活动性逐渐增强。物源输送的逐渐增多与直罗期古气候的转变,还原环境向氧化环境转换的古水体条件对本区铀元素富集成矿具有关键制约作用。
中图分类号:
程先钰, 张天福, 张云, 何鹏, 孙立新, 马海林, 鲁超. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘直罗组顶部古沉积环境恢复:来自泥岩元素组成的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 1129-1142.
CHENG Xianyu, ZHANG Tianfu, ZHANG Yun, HE Peng, SUN Lixin, MA Hailin, LU Chao. Restoration of Paleosedimentary Environment of the Top of Zhiluo Formation in the Southern Margin of Ordos Basin: Evidence from Geochemical Characteristics of Mudstone[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(04): 1129-1142.

图1 研究区地质简图(b)及构造位置图(a)(据文献[16]修改) 1.第四系;2.白垩系—新近系;3.安定组;4.直罗组;5.延安组;6.三叠系;7.奥陶系—二叠系; 8.断裂;9.钻井位置
Fig.1 Simplified geological map (b) and tectonic location map (a) of the study area (modified after reference[16])
| 层位 | 样品序号 | 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直罗组上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 63.52 | 17.88 | 3.99 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 2.13 | 5.75 | 1.85 | 0.83 | 0.055 | |||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 60.45 | 12.96 | 12.08 | 0.49 | 2.26 | 1.24 | 3.20 | 2.90 | 0.61 | 0.350 | ||||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 紫红色泥岩 | 52.56 | 22.00 | 8.21 | 0.75 | 0.33 | 2.95 | 6.52 | 0.37 | 0.78 | 0.049 | ||||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 暗紫红色粉砂质泥岩 | 68.43 | 15.77 | 3.41 | 0.31 | 0.51 | 1.43 | 3.97 | 2.36 | 0.81 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 暗紫红色钙质粉砂岩 | 74.99 | 8.82 | 3.00 | 0.16 | 3.52 | 0.41 | 2.63 | 2.38 | 0.38 | 0.054 | ||||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 杂色泥岩 | 60.09 | 13.59 | 13.35 | 0.40 | 1.10 | 1.17 | 3.54 | 1.86 | 0.63 | 0.470 | ||||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 紫红色泥岩 | 68.24 | 15.47 | 4.15 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 1.50 | 4.28 | 1.92 | 0.80 | 0.110 | ||||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 56.49 | 21.15 | 6.56 | 0.82 | 0.42 | 2.35 | 6.05 | 0.33 | 0.92 | 0.092 | ||||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 紫红色细粉砂岩 | 67.65 | 11.54 | 4.81 | 0.37 | 2.97 | 1.77 | 2.75 | 2.20 | 0.87 | 0.190 | ||||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 73.66 | 12.26 | 2.13 | 0.19 | 1.34 | 0.74 | 3.28 | 2.16 | 0.66 | 0.055 | ||||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 紫红色泥岩 | 62.55 | 18.59 | 5.06 | 0.92 | 0.38 | 1.85 | 4.59 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.140 | ||||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 紫红色泥岩 | 62.83 | 18.97 | 4.25 | 1.02 | 0.39 | 1.87 | 4.65 | 0.62 | 0.95 | 0.120 | ||||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 66.71 | 16.36 | 4.33 | 0.75 | 0.34 | 1.65 | 3.85 | 1.35 | 0.94 | 0.110 | ||||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 紫红色粉砂岩 | 71.17 | 14.32 | 2.61 | 0.43 | 0.88 | 1.15 | 4.09 | 1.25 | 0.72 | 0.480 | ||||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 紫红色泥岩 | 58.24 | 19.04 | 7.90 | 0.56 | 0.32 | 2.25 | 5.62 | 0.41 | 1.04 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 71.57 | 10.54 | 2.40 | 0.51 | 3.27 | 1.19 | 3.07 | 1.71 | 0.47 | 0.048 | ||||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 63.61 | 18.39 | 4.41 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 1.82 | 4.39 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.094 | ||||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 63.25 | 11.91 | 4.15 | 0.56 | 3.84 | 3.11 | 3.13 | 1.58 | 0.77 | 0.120 | ||||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 51.43 | 17.64 | 9.74 | 0.82 | 3.31 | 3.07 | 4.25 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.170 | ||||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 62.58 | 12.30 | 4.57 | 0.66 | 3.58 | 3.22 | 3.24 | 1.48 | 0.82 | 0.140 | ||||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 杂色泥岩 | 57.47 | 19.59 | 7.94 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 2.09 | 5.51 | 0.49 | 0.92 | 0.082 | ||||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 灰色泥岩 | 63.08 | 19.23 | 3.68 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 1.93 | 4.65 | 0.56 | 0.92 | 0.092 | ||||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 69.35 | 14.43 | 4.53 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 1.59 | 3.42 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.035 | ||||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 59.41 | 19.17 | 7.56 | 0.61 | 0.34 | 1.79 | 5.12 | 0.51 | 0.93 | 0.077 | ||||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 65.37 | 7.74 | 4.61 | 0.34 | 5.72 | 2.96 | 1.50 | 2.71 | 0.47 | 0.110 | ||||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 54.59 | 8.37 | 3.66 | 0.59 | 9.53 | 4.78 | 1.55 | 2.51 | 0.62 | 0.140 | ||||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 51.55 | 16.22 | 9.69 | 1.01 | 3.59 | 3.50 | 3.92 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.050 | ||||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 52.81 | 20.97 | 7.23 | 1.17 | 1.72 | 2.48 | 5.43 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 0.310 | ||||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 73.75 | 12.87 | 3.40 | 0.67 | 0.12 | 1.03 | 3.64 | 1.25 | 0.66 | 0.033 | ||||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 紫红色泥岩 | 58.62 | 19.36 | 8.42 | 0.76 | 0.20 | 1.61 | 5.28 | 0.56 | 0.80 | 0.057 | ||||||||
| 31 | FX9-b39 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 63.44 | 19.12 | 2.26 | 1.25 | 0.53 | 2.14 | 4.93 | 0.58 | 0.87 | 0.064 | ||||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 43.63 | 13.35 | 1.29 | 1.42 | 10.38 | 7.06 | 3.33 | 0.50 | 0.65 | 0.033 | ||||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 62.34 | 17.01 | 7.92 | 1.10 | 0.17 | 1.62 | 4.60 | 0.55 | 0.79 | 0.044 | ||||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 暗红色粉砂岩 | 76.61 | 10.24 | 1.16 | 0.77 | 1.77 | 0.65 | 3.49 | 1.16 | 0.45 | 0.054 | ||||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 65.86 | 16.91 | 1.62 | 1.66 | 0.88 | 1.94 | 4.72 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.054 | ||||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 灰黑色粉砂质泥岩 | 67.91 | 16.12 | 1.31 | 1.72 | 0.92 | 1.51 | 4.63 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.560 | ||||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 灰绿色粉砂岩 | 74.34 | 12.68 | 1.11 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 1.25 | 4.06 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 62.30 | 19.89 | 2.17 | 1.76 | 0.23 | 1.80 | 5.40 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.058 | ||||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 64.35 | 17.17 | 1.64 | 3.11 | 0.25 | 1.65 | 4.54 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 灰绿色泥质粉砂质 | 51.17 | 12.63 | 1.16 | 12.52 | 0.86 | 3.28 | 3.28 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 0.220 | ||||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 62.55 | 21.65 | 1.40 | 1.04 | 0.16 | 1.17 | 5.44 | 0.56 | 1.08 | 0.066 | ||||||||
| 42 | FX9-b75 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 56.65 | 18.06 | 0.79 | 5.02 | 0.53 | 1.84 | 3.89 | 0.52 | 0.87 | 0.260 | ||||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 48.57 | 16.77 | 1.46 | 10.06 | 0.66 | 2.70 | 3.57 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.170 | ||||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 55.39 | 18.78 | 0.51 | 5.32 | 0.49 | 2.12 | 3.87 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 0.150 | ||||||||
| 直罗组 上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.026 | 3.37 | 99.96 | 0.08 | 8.19 | 8.39 | 11.54 | 69.46 | 0.83 | ||||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.11 | 3.30 | 99.95 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 10.45 | 4.45 | 60.79 | 1.72 | |||||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.037 | 5.36 | 99.92 | 0.10 | 8.94 | 7.46 | 20.27 | 75.29 | 0.87 | |||||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 暗紫红色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.021 | 2.85 | 99.97 | 0.10 | 2.80 | 11.03 | 14.76 | 69.75 | 0.79 | |||||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 暗紫红色钙质粉砂岩 | 0.046 | 3.59 | 99.98 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 21.51 | 3.48 | 50.84 | 1.40 | |||||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 杂色泥岩 | 0.130 | 3.63 | 99.96 | 0.03 | 1.06 | 11.62 | 3.08 | 67.65 | 1.59 | |||||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.025 | 2.72 | 99.97 | 0.11 | 4.55 | 10.31 | 16.80 | 70.32 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 0.032 | 4.69 | 99.90 | 0.14 | 5.60 | 9.00 | 25.63 | 75.67 | 0.79 | |||||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 紫红色细粉砂岩 | 0.150 | 4.70 | 99.97 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 6.52 | 2.47 | 59.30 | 1.33 | |||||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.036 | 3.46 | 99.97 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 16.57 | 5.28 | 64.39 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.044 | 3.93 | 99.89 | 0.20 | 4.87 | 10.05 | 20.91 | 76.06 | 0.74 | |||||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.040 | 4.17 | 99.88 | 0.27 | 4.79 | 10.14 | 25.50 | 77.02 | 0.67 | |||||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 0.039 | 3.49 | 99.92 | 0.19 | 4.85 | 9.92 | 19.23 | 74.70 | 0.76 | |||||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.025 | 2.84 | 99.97 | 0.18 | 1.31 | 12.45 | 17.20 | 69.72 | 0.75 | |||||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.028 | 4.43 | 99.94 | 0.08 | 7.03 | 8.46 | 20.00 | 74.99 | 0.92 | |||||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.100 | 5.07 | 99.95 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 8.86 | 5.10 | 56.70 | 1.15 | |||||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.033 | 4.38 | 99.95 | 0.18 | 4.55 | 10.10 | 21.21 | 76.59 | 0.69 | |||||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.210 | 7.31 | 99.94 | 0.15 | 0.81 | 3.83 | 2.67 | 58.21 | 1.39 | |||||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.220 | 7.85 | 99.92 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 5.75 | 3.73 | 68.29 | 1.24 | |||||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.180 | 7.18 | 99.95 | 0.16 | 0.90 | 3.82 | 3.67 | 59.71 | 1.37 | |||||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 杂色泥岩 | 0.026 | 4.53 | 99.89 | 0.13 | 6.33 | 9.37 | 35.00 | 75.58 | 0.88 | |||||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 灰色泥岩 | 0.034 | 4.45 | 99.90 | 0.27 | 5.22 | 9.96 | 26.47 | 77.51 | 0.63 | |||||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.051 | 3.70 | 99.95 | 0.15 | 2.79 | 9.08 | 11.76 | 74.88 | 0.82 | |||||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.020 | 4.41 | 99.95 | 0.09 | 5.26 | 10.71 | 30.50 | 76.25 | 0.85 | |||||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.280 | 8.18 | 99.99 | 0.08 | 0.52 | 2.61 | 1.21 | 43.80 | 2.32 | |||||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.520 | 13.09 | 99.95 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 1.75 | 1.13 | 38.11 | 2.71 | |||||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.240 | 8.56 | 99.90 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 4.63 | 4.21 | 66.07 | 1.37 | |||||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.140 | 6.28 | 99.88 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 8.46 | 8.36 | 72.99 | 0.87 | |||||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.018 | 2.49 | 99.93 | 0.22 | 8.58 | 12.50 | 37.22 | 71.98 | 0.78 | |||||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.018 | 4.24 | 99.93 | 0.10 | 8.05 | 12.02 | 42.22 | 76.22 | 0.87 | |||||||||
| 直罗组 下段上 亚段 | 31 | FX9-b39 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.048 | 4.63 | 99.86 | 0.61 | 4.04 | 8.93 | 26.04 | 75.99 | 0.59 | ||||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.370 | 17.83 | 99.84 | 1.22 | 0.68 | 1.89 | 3.84 | 48.44 | 1.74 | |||||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.024 | 3.72 | 99.89 | 0.15 | 9.53 | 10.50 | 45.83 | 76.18 | 0.92 | |||||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 暗红色粉砂岩 | 0.027 | 3.52 | 99.90 | 0.74 | 0.37 | 15.75 | 28.52 | 61.46 | 0.85 | |||||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.064 | 4.76 | 99.83 | 1.14 | 2.20 | 8.72 | 25.94 | 73.11 | 0.62 | |||||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 灰黑色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.026 | 3.71 | 99.82 | 1.46 | 1.64 | 10.68 | 66.15 | 72.25 | 0.61 | |||||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 灰绿色粉砂岩 | 0.032 | 2.73 | 99.80 | 1.77 | 3.05 | 10.14 | 55.31 | 71.00 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.037 | 4.67 | 99.81 | 0.90 | 7.83 | 11.05 | 47.57 | 76.06 | 0.56 | |||||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.087 | 5.10 | 99.64 | 2.11 | 6.60 | 10.41 | 35.75 | 75.44 | 0.57 | |||||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 灰绿色泥质粉砂质 | 0.340 | 12.02 | 98.61 | 12.00 | 3.81 | 3.85 | 36.82 | 73.13 | 0.77 | |||||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.012 | 4.76 | 99.89 | 0.83 | 7.31 | 18.50 | 86.67 | 77.85 | 0.45 | |||||||||
| 延安组 | 42 | FX9-b75 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 0.19 | 10.82 | 99.44 | 7.06 | 3.47 | 9.82 | 26.42 | 78.52 | 0.47 | ||||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 0.47 | 13.09 | 98.88 | 7.66 | 4.09 | 6.21 | 21.40 | 77.67 | 0.58 | |||||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 0.15 | 11.07 | 99.41 | 11.59 | 4.33 | 8.86 | 35.47 | 78.87 | 0.46 | |||||||||
表1 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘延安组、直罗组泥岩常量元素(%)分析及计算结果
Table 1 Major elements (%) contents and calculation results of mudstones from the Yan’an Formation and Zhiluo Formation in the southern margin of the Ordos Basin
| 层位 | 样品序号 | 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直罗组上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 63.52 | 17.88 | 3.99 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 2.13 | 5.75 | 1.85 | 0.83 | 0.055 | |||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 60.45 | 12.96 | 12.08 | 0.49 | 2.26 | 1.24 | 3.20 | 2.90 | 0.61 | 0.350 | ||||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 紫红色泥岩 | 52.56 | 22.00 | 8.21 | 0.75 | 0.33 | 2.95 | 6.52 | 0.37 | 0.78 | 0.049 | ||||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 暗紫红色粉砂质泥岩 | 68.43 | 15.77 | 3.41 | 0.31 | 0.51 | 1.43 | 3.97 | 2.36 | 0.81 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 暗紫红色钙质粉砂岩 | 74.99 | 8.82 | 3.00 | 0.16 | 3.52 | 0.41 | 2.63 | 2.38 | 0.38 | 0.054 | ||||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 杂色泥岩 | 60.09 | 13.59 | 13.35 | 0.40 | 1.10 | 1.17 | 3.54 | 1.86 | 0.63 | 0.470 | ||||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 紫红色泥岩 | 68.24 | 15.47 | 4.15 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 1.50 | 4.28 | 1.92 | 0.80 | 0.110 | ||||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 56.49 | 21.15 | 6.56 | 0.82 | 0.42 | 2.35 | 6.05 | 0.33 | 0.92 | 0.092 | ||||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 紫红色细粉砂岩 | 67.65 | 11.54 | 4.81 | 0.37 | 2.97 | 1.77 | 2.75 | 2.20 | 0.87 | 0.190 | ||||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 73.66 | 12.26 | 2.13 | 0.19 | 1.34 | 0.74 | 3.28 | 2.16 | 0.66 | 0.055 | ||||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 紫红色泥岩 | 62.55 | 18.59 | 5.06 | 0.92 | 0.38 | 1.85 | 4.59 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.140 | ||||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 紫红色泥岩 | 62.83 | 18.97 | 4.25 | 1.02 | 0.39 | 1.87 | 4.65 | 0.62 | 0.95 | 0.120 | ||||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 66.71 | 16.36 | 4.33 | 0.75 | 0.34 | 1.65 | 3.85 | 1.35 | 0.94 | 0.110 | ||||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 紫红色粉砂岩 | 71.17 | 14.32 | 2.61 | 0.43 | 0.88 | 1.15 | 4.09 | 1.25 | 0.72 | 0.480 | ||||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 紫红色泥岩 | 58.24 | 19.04 | 7.90 | 0.56 | 0.32 | 2.25 | 5.62 | 0.41 | 1.04 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 71.57 | 10.54 | 2.40 | 0.51 | 3.27 | 1.19 | 3.07 | 1.71 | 0.47 | 0.048 | ||||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 63.61 | 18.39 | 4.41 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 1.82 | 4.39 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.094 | ||||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 63.25 | 11.91 | 4.15 | 0.56 | 3.84 | 3.11 | 3.13 | 1.58 | 0.77 | 0.120 | ||||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 51.43 | 17.64 | 9.74 | 0.82 | 3.31 | 3.07 | 4.25 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.170 | ||||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 62.58 | 12.30 | 4.57 | 0.66 | 3.58 | 3.22 | 3.24 | 1.48 | 0.82 | 0.140 | ||||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 杂色泥岩 | 57.47 | 19.59 | 7.94 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 2.09 | 5.51 | 0.49 | 0.92 | 0.082 | ||||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 灰色泥岩 | 63.08 | 19.23 | 3.68 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 1.93 | 4.65 | 0.56 | 0.92 | 0.092 | ||||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 69.35 | 14.43 | 4.53 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 1.59 | 3.42 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.035 | ||||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 59.41 | 19.17 | 7.56 | 0.61 | 0.34 | 1.79 | 5.12 | 0.51 | 0.93 | 0.077 | ||||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 65.37 | 7.74 | 4.61 | 0.34 | 5.72 | 2.96 | 1.50 | 2.71 | 0.47 | 0.110 | ||||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 54.59 | 8.37 | 3.66 | 0.59 | 9.53 | 4.78 | 1.55 | 2.51 | 0.62 | 0.140 | ||||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 51.55 | 16.22 | 9.69 | 1.01 | 3.59 | 3.50 | 3.92 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.050 | ||||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 52.81 | 20.97 | 7.23 | 1.17 | 1.72 | 2.48 | 5.43 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 0.310 | ||||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 73.75 | 12.87 | 3.40 | 0.67 | 0.12 | 1.03 | 3.64 | 1.25 | 0.66 | 0.033 | ||||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 紫红色泥岩 | 58.62 | 19.36 | 8.42 | 0.76 | 0.20 | 1.61 | 5.28 | 0.56 | 0.80 | 0.057 | ||||||||
| 31 | FX9-b39 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 63.44 | 19.12 | 2.26 | 1.25 | 0.53 | 2.14 | 4.93 | 0.58 | 0.87 | 0.064 | ||||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 43.63 | 13.35 | 1.29 | 1.42 | 10.38 | 7.06 | 3.33 | 0.50 | 0.65 | 0.033 | ||||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 62.34 | 17.01 | 7.92 | 1.10 | 0.17 | 1.62 | 4.60 | 0.55 | 0.79 | 0.044 | ||||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 暗红色粉砂岩 | 76.61 | 10.24 | 1.16 | 0.77 | 1.77 | 0.65 | 3.49 | 1.16 | 0.45 | 0.054 | ||||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 65.86 | 16.91 | 1.62 | 1.66 | 0.88 | 1.94 | 4.72 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.054 | ||||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 灰黑色粉砂质泥岩 | 67.91 | 16.12 | 1.31 | 1.72 | 0.92 | 1.51 | 4.63 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.560 | ||||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 灰绿色粉砂岩 | 74.34 | 12.68 | 1.11 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 1.25 | 4.06 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 62.30 | 19.89 | 2.17 | 1.76 | 0.23 | 1.80 | 5.40 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.058 | ||||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 64.35 | 17.17 | 1.64 | 3.11 | 0.25 | 1.65 | 4.54 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.100 | ||||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 灰绿色泥质粉砂质 | 51.17 | 12.63 | 1.16 | 12.52 | 0.86 | 3.28 | 3.28 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 0.220 | ||||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 62.55 | 21.65 | 1.40 | 1.04 | 0.16 | 1.17 | 5.44 | 0.56 | 1.08 | 0.066 | ||||||||
| 42 | FX9-b75 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 56.65 | 18.06 | 0.79 | 5.02 | 0.53 | 1.84 | 3.89 | 0.52 | 0.87 | 0.260 | ||||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 48.57 | 16.77 | 1.46 | 10.06 | 0.66 | 2.70 | 3.57 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.170 | ||||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 55.39 | 18.78 | 0.51 | 5.32 | 0.49 | 2.12 | 3.87 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 0.150 | ||||||||
| 直罗组 上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.026 | 3.37 | 99.96 | 0.08 | 8.19 | 8.39 | 11.54 | 69.46 | 0.83 | ||||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.11 | 3.30 | 99.95 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 10.45 | 4.45 | 60.79 | 1.72 | |||||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.037 | 5.36 | 99.92 | 0.10 | 8.94 | 7.46 | 20.27 | 75.29 | 0.87 | |||||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 暗紫红色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.021 | 2.85 | 99.97 | 0.10 | 2.80 | 11.03 | 14.76 | 69.75 | 0.79 | |||||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 暗紫红色钙质粉砂岩 | 0.046 | 3.59 | 99.98 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 21.51 | 3.48 | 50.84 | 1.40 | |||||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 杂色泥岩 | 0.130 | 3.63 | 99.96 | 0.03 | 1.06 | 11.62 | 3.08 | 67.65 | 1.59 | |||||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.025 | 2.72 | 99.97 | 0.11 | 4.55 | 10.31 | 16.80 | 70.32 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 0.032 | 4.69 | 99.90 | 0.14 | 5.60 | 9.00 | 25.63 | 75.67 | 0.79 | |||||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 紫红色细粉砂岩 | 0.150 | 4.70 | 99.97 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 6.52 | 2.47 | 59.30 | 1.33 | |||||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.036 | 3.46 | 99.97 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 16.57 | 5.28 | 64.39 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.044 | 3.93 | 99.89 | 0.20 | 4.87 | 10.05 | 20.91 | 76.06 | 0.74 | |||||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.040 | 4.17 | 99.88 | 0.27 | 4.79 | 10.14 | 25.50 | 77.02 | 0.67 | |||||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 0.039 | 3.49 | 99.92 | 0.19 | 4.85 | 9.92 | 19.23 | 74.70 | 0.76 | |||||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.025 | 2.84 | 99.97 | 0.18 | 1.31 | 12.45 | 17.20 | 69.72 | 0.75 | |||||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.028 | 4.43 | 99.94 | 0.08 | 7.03 | 8.46 | 20.00 | 74.99 | 0.92 | |||||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.100 | 5.07 | 99.95 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 8.86 | 5.10 | 56.70 | 1.15 | |||||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.033 | 4.38 | 99.95 | 0.18 | 4.55 | 10.10 | 21.21 | 76.59 | 0.69 | |||||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.210 | 7.31 | 99.94 | 0.15 | 0.81 | 3.83 | 2.67 | 58.21 | 1.39 | |||||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.220 | 7.85 | 99.92 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 5.75 | 3.73 | 68.29 | 1.24 | |||||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.180 | 7.18 | 99.95 | 0.16 | 0.90 | 3.82 | 3.67 | 59.71 | 1.37 | |||||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 杂色泥岩 | 0.026 | 4.53 | 99.89 | 0.13 | 6.33 | 9.37 | 35.00 | 75.58 | 0.88 | |||||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 灰色泥岩 | 0.034 | 4.45 | 99.90 | 0.27 | 5.22 | 9.96 | 26.47 | 77.51 | 0.63 | |||||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.051 | 3.70 | 99.95 | 0.15 | 2.79 | 9.08 | 11.76 | 74.88 | 0.82 | |||||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.020 | 4.41 | 99.95 | 0.09 | 5.26 | 10.71 | 30.50 | 76.25 | 0.85 | |||||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.280 | 8.18 | 99.99 | 0.08 | 0.52 | 2.61 | 1.21 | 43.80 | 2.32 | |||||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.520 | 13.09 | 99.95 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 1.75 | 1.13 | 38.11 | 2.71 | |||||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.240 | 8.56 | 99.90 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 4.63 | 4.21 | 66.07 | 1.37 | |||||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.140 | 6.28 | 99.88 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 8.46 | 8.36 | 72.99 | 0.87 | |||||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 暗紫红色粉砂岩 | 0.018 | 2.49 | 99.93 | 0.22 | 8.58 | 12.50 | 37.22 | 71.98 | 0.78 | |||||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 紫红色泥岩 | 0.018 | 4.24 | 99.93 | 0.10 | 8.05 | 12.02 | 42.22 | 76.22 | 0.87 | |||||||||
| 直罗组 下段上 亚段 | 31 | FX9-b39 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.048 | 4.63 | 99.86 | 0.61 | 4.04 | 8.93 | 26.04 | 75.99 | 0.59 | ||||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.370 | 17.83 | 99.84 | 1.22 | 0.68 | 1.89 | 3.84 | 48.44 | 1.74 | |||||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 暗紫红色泥岩 | 0.024 | 3.72 | 99.89 | 0.15 | 9.53 | 10.50 | 45.83 | 76.18 | 0.92 | |||||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 暗红色粉砂岩 | 0.027 | 3.52 | 99.90 | 0.74 | 0.37 | 15.75 | 28.52 | 61.46 | 0.85 | |||||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.064 | 4.76 | 99.83 | 1.14 | 2.20 | 8.72 | 25.94 | 73.11 | 0.62 | |||||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 灰黑色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.026 | 3.71 | 99.82 | 1.46 | 1.64 | 10.68 | 66.15 | 72.25 | 0.61 | |||||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 灰绿色粉砂岩 | 0.032 | 2.73 | 99.80 | 1.77 | 3.05 | 10.14 | 55.31 | 71.00 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.037 | 4.67 | 99.81 | 0.90 | 7.83 | 11.05 | 47.57 | 76.06 | 0.56 | |||||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 灰绿色粉砂质泥岩 | 0.087 | 5.10 | 99.64 | 2.11 | 6.60 | 10.41 | 35.75 | 75.44 | 0.57 | |||||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 灰绿色泥质粉砂质 | 0.340 | 12.02 | 98.61 | 12.00 | 3.81 | 3.85 | 36.82 | 73.13 | 0.77 | |||||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 灰绿色泥岩 | 0.012 | 4.76 | 99.89 | 0.83 | 7.31 | 18.50 | 86.67 | 77.85 | 0.45 | |||||||||
| 延安组 | 42 | FX9-b75 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 0.19 | 10.82 | 99.44 | 7.06 | 3.47 | 9.82 | 26.42 | 78.52 | 0.47 | ||||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 0.47 | 13.09 | 98.88 | 7.66 | 4.09 | 6.21 | 21.40 | 77.67 | 0.58 | |||||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 灰黑色泥页岩 | 0.15 | 11.07 | 99.41 | 11.59 | 4.33 | 8.86 | 35.47 | 78.87 | 0.46 | |||||||||

图2 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘店头地区FX9钻井岩性综合柱状图 1.含砾砂岩;2.粗砂岩;3.细砂岩;4.粉砂岩;5.泥质粉砂岩;6.泥岩;7.铀矿化
Fig.2 Comprehensive lithological column of Well FX9 in Diantou area, southern margin of the Ordos Basin
| 层位 | 样品顺序 | 样号 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Ni | Co | Cd | Li | Rb | Cs | Mo | Sr | Ba | V | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直罗组上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 14.1 | 14.9 | 111 | 98.1 | 46.9 | 18.9 | 0.05 | 49.5 | 203 | 14 | 2.82 | 103 | 474 | 91 | ||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 10.8 | 55.5 | 45.5 | 52.4 | 25.5 | 14.1 | 0.05 | 18.7 | 101 | 5.63 | 5.76 | 159 | 513 | 184 | |||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 14.3 | 18.6 | 108 | 82.4 | 41.4 | 17.7 | 0.02 | 48.5 | 263 | 20.3 | 2.56 | 150 | 355 | 143 | |||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 16.3 | 24.3 | 70.1 | 78.2 | 34.7 | 11.4 | 0.06 | 24.6 | 165 | 13 | 2.54 | 174 | 468 | 82 | |||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 7.58 | 23.6 | 11.8 | 27.9 | 7.79 | 3.49 | 0.04 | 7.44 | 82 | 2.94 | 3.31 | 556 | 662 | 53.3 | |||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 19.4 | 49.6 | 75.5 | 48.9 | 39 | 17.1 | 0.06 | 16.3 | 136 | 9.27 | 4.45 | 799 | 614 | 265 | |||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 15.8 | 20 | 90.9 | 69.7 | 37.3 | 15.9 | 0.05 | 27.4 | 169 | 13 | 2.12 | 152 | 491 | 73.9 | |||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 14.9 | 31.2 | 144 | 100 | 63.2 | 30.4 | 0.04 | 56.2 | 245 | 22.8 | 4 | 219 | 464 | 119 | |||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 7.84 | 36.3 | 29.5 | 52.9 | 14.6 | 7.58 | 0.09 | 10.8 | 98 | 4.73 | 3.31 | 1430 | 753 | 136 | |||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 12.2 | 24.3 | 40.6 | 56.6 | 14.3 | 6.58 | 0.1 | 43 | 127 | 11.6 | 3.9 | 187 | 1070 | 70.2 | |||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 18.7 | 32 | 109 | 105 | 54.3 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 76.3 | 201 | 16.9 | 3.24 | 158 | 516 | 125 | |||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 22.5 | 29 | 119 | 119 | 57.5 | 20 | 0.05 | 88.3 | 208 | 20.1 | 4.6 | 161 | 536 | 152 | |||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 20.6 | 25.2 | 104 | 111 | 50.2 | 18.2 | 0.05 | 89 | 172 | 16 | 2.91 | 127 | 475 | 119 | |||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 19 | 20.7 | 81.3 | 64.2 | 35.2 | 13.1 | 0.06 | 45.5 | 178 | 13.6 | 1.21 | 206 | 568 | 71.5 | |||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 25 | 37.6 | 188 | 105 | 55.4 | 26.9 | 0.05 | 71.7 | 265 | 31.6 | 2.68 | 173 | 588 | 142 | |||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 13.4 | 21.2 | 43.4 | 41.7 | 17.9 | 8.8 | 0.05 | 19.4 | 117 | 8.42 | 2.74 | 141 | 682 | 54.2 | |||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 22.5 | 25 | 114 | 86.3 | 42.4 | 17.3 | 0.04 | 77.9 | 198 | 17.5 | 2.1 | 126 | 640 | 100 | |||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 15.4 | 27.2 | 67.6 | 58 | 26.1 | 12.8 | 0.09 | 29.3 | 130 | 11.3 | 1.92 | 111 | 457 | 85.8 | |||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 17.6 | 32.4 | 96.2 | 95.2 | 41 | 17.3 | 0.08 | 67.8 | 187 | 16 | 3.12 | 182 | 427 | 182 | |||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 15.2 | 30 | 69.6 | 61 | 28.4 | 13.2 | 0.09 | 37.2 | 139 | 11.5 | 2.62 | 106 | 473 | 84 | |||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 18.9 | 41.8 | 168 | 100 | 51.1 | 21.3 | 0.05 | 83.7 | 276 | 28.2 | 3.87 | 136 | 444 | 157 | |||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 17.6 | 23 | 124 | 110 | 53.7 | 18.9 | 0.05 | 94.3 | 221 | 19.5 | 1.97 | 171 | 520 | 114 | |||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 20.7 | 19.4 | 91.3 | 94.1 | 46.8 | 16.8 | 0.06 | 88.4 | 154 | 14.9 | 1.86 | 127 | 555 | 107 | |||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 17.2 | 32.1 | 127 | 92.7 | 44.9 | 17 | 0.04 | 94.4 | 249 | 24.3 | 3.17 | 194 | 418 | 150 | |||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 9.4 | 16.5 | 28.4 | 23.8 | 8.82 | 8.15 | 0.06 | 11.8 | 67 | 9 | 1.45 | 85 | 521 | 72.6 | |||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 10 | 21 | 56.9 | 41.2 | 15.3 | 14 | 0.11 | 15.1 | 70 | 6.24 | 1.59 | 122 | 430 | 75.2 | |||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 17.4 | 41.1 | 94.1 | 85.8 | 40.6 | 18.1 | 0.08 | 60.1 | 186 | 16.1 | 3.95 | 206 | 404 | 171 | |||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 12.3 | 30.4 | 106 | 84 | 44.5 | 20.1 | 0.04 | 73.9 | 273 | 28.3 | 2.94 | 404 | 481 | 133 | |||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 13.1 | 20.3 | 61.6 | 59.4 | 26.7 | 11.4 | 0.04 | 46.8 | 155 | 13.9 | 2.19 | 109 | 470 | 57.7 | |||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 21.4 | 32.3 | 98.2 | 81.7 | 35 | 12.1 | 0.04 | 55.5 | 286 | 31.7 | 1.91 | 140 | 402 | 143 | |||||||
| 31 | FX9-b39 | 38.9 | 23 | 102 | 87.9 | 41.2 | 15.4 | 0.05 | 74 | 244 | 22.4 | 1.34 | 145 | 502 | 105 | |||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 101 | 24.5 | 75.6 | 68.8 | 27 | 12.9 | 0.13 | 50.7 | 161 | 16.6 | 2 | 407 | 373 | 77.5 | |||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 12.1 | 36.4 | 90.1 | 81.3 | 37.9 | 15.1 | 0.05 | 68.3 | 219 | 24 | 4.58 | 119 | 524 | 112 | |||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 21 | 19.6 | 28.5 | 33.1 | 13.4 | 6.25 | 0.06 | 17.6 | 133 | 9.17 | 1.33 | 214 | 579 | 39 | |||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 80.1 | 17.4 | 72.6 | 69 | 36.6 | 11.6 | 0.05 | 53 | 233 | 36.4 | 1.88 | 128 | 544 | 88.4 | |||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 28.6 | 17.5 | 73.2 | 76 | 41.9 | 14.9 | 0.05 | 47.7 | 227 | 25.8 | 1.42 | 131 | 600 | 98.3 | |||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 29.2 | 18.2 | 59.2 | 55.3 | 29.6 | 11.2 | 0.06 | 36.9 | 170 | 17.4 | 0.74 | 149 | 711 | 66.2 | |||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 38.1 | 16.6 | 66.2 | 78.7 | 38.7 | 10.7 | 0.04 | 58.3 | 297 | 30.6 | 1.22 | 151 | 717 | 112 | |||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 32.1 | 18.5 | 56.5 | 76.7 | 36.4 | 18.7 | 0.05 | 54.8 | 220 | 23.7 | 2.01 | 159 | 531 | 108 | |||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 10.9 | 13.3 | 39.7 | 59 | 25.9 | 13.8 | 0.04 | 47 | 147 | 13.6 | 3.17 | 164 | 410 | 86.2 | |||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 13.2 | 20.4 | 28.9 | 91.3 | 64.8 | 25.2 | 0.06 | 114 | 272 | 32.4 | 2.22 | 237 | 532 | 118 | |||||||
| 42 | FX9-b75 | 27.2 | 21 | 145 | 76.2 | 26.2 | 11.6 | 0.13 | 86.5 | 164 | 14.6 | 2.75 | 386 | 510 | 117 | |||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 25.1 | 23.4 | 92.6 | 72.6 | 29.8 | 15.5 | 0.06 | 77.9 | 152 | 14.2 | 3.05 | 231 | 510 | 110 | |||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 32.2 | 34.1 | 126 | 71.5 | 36.3 | 20.6 | 0.1 | 86 | 168 | 15.5 | 2.71 | 286 | 507 | 109 | |||||||
| 层位 | 样品顺序 | 样号 | Sc | B | Ga | U | Th | 校正B 含量 | 相当B 含量 | Sr/Ba | U/Th | V/ (V+Ni) | V/Cr | Ni/Co | Sr/Cu | |||||||
| 直罗组上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 15.7 | 152 | 27.3 | 3.01 | 15.9 | 224.70 | 257.79 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 0.93 | 2.48 | 7.30 | |||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 13.4 | 83.1 | 15 | 4.51 | 9.76 | 220.73 | 178.16 | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.88 | 3.51 | 1.81 | 14.72 | ||||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 14.5 | 261 | 26.8 | 3.59 | 14.9 | 340.26 | 447.31 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.78 | 1.74 | 2.34 | 10.49 | ||||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 13.6 | 154 | 20.6 | 2.77 | 14.9 | 329.72 | 292.29 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 1.05 | 3.04 | 10.67 | ||||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 6.74 | 36.7 | 8.26 | 1.66 | 8.31 | 118.61 | 89.78 | 0.84 | 0.20 | 0.87 | 1.91 | 2.23 | 73.35 | ||||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 13 | 104 | 19.7 | 3.76 | 13.4 | 249.72 | 209.85 | 1.30 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 5.42 | 2.28 | 41.19 | ||||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 1.5 | 142 | 20 | 2.76 | 14.5 | 28.01 | 260.30 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 1.06 | 2.35 | 9.62 | ||||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 16.3 | 264 | 29.8 | 4.14 | 18 | 370.91 | 447.75 | 0.47 | 0.23 | 0.65 | 1.19 | 2.08 | 14.70 | ||||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 13.8 | 50.9 | 14.6 | 6.88 | 13.5 | 157.33 | 120.67 | 1.90 | 0.51 | 0.90 | 2.57 | 1.93 | 182.40 | ||||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 10.8 | 114 | 13.3 | 4.62 | 17.4 | 295.43 | 240.68 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.83 | 1.24 | 2.17 | 15.33 | ||||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 15.7 | 222 | 25.1 | 3.95 | 18.9 | 411.11 | 395.78 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.70 | 1.19 | 2.84 | 8.45 | ||||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 18 | 248 | 28 | 3.92 | 20.5 | 453.33 | 440.09 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.73 | 1.28 | 2.88 | 7.16 | ||||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 15.2 | 221 | 21 | 3.29 | 15.8 | 487.92 | 426.01 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.70 | 1.07 | 2.76 | 6.17 | ||||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 11.5 | 158 | 19.1 | 2.84 | 13.8 | 328.36 | 295.62 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.67 | 1.11 | 2.69 | 10.84 | ||||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 19.2 | 219 | 27.1 | 4.37 | 28.7 | 331.23 | 372.02 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.72 | 1.35 | 2.06 | 6.92 | ||||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 9.64 | 73.1 | 12.1 | 2.64 | 9.79 | 202.39 | 160.92 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.75 | 1.30 | 2.03 | 10.52 | ||||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 14.2 | 156 | 23.8 | 3.76 | 17.1 | 302.05 | 282.94 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.70 | 1.16 | 2.45 | 5.60 | ||||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 11.7 | 103 | 15.4 | 2.37 | 12.7 | 279.71 | 223.94 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.77 | 1.48 | 2.04 | 7.21 | ||||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 18.9 | 177 | 24.6 | 3.28 | 16.4 | 354.00 | 325.45 | 0.43 | 0.20 | 0.82 | 1.91 | 2.37 | 10.34 | ||||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 6.13 | 102 | 15.7 | 2.56 | 11.3 | 267.59 | 216.99 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.75 | 1.38 | 2.15 | 6.97 | ||||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 17.9 | 219 | 28.3 | 3.8 | 26.6 | 337.84 | 372.82 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.75 | 1.57 | 2.40 | 7.20 | ||||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 16.5 | 193 | 25.6 | 3.39 | 19.1 | 352.80 | 342.49 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 1.04 | 2.84 | 9.72 | ||||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 13.3 | 162 | 18.9 | 2.59 | 15 | 402.63 | 333.50 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 1.14 | 2.79 | 6.14 | ||||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 16.4 | 188 | 25.8 | 3.31 | 23.3 | 312.11 | 324.31 | 0.46 | 0.14 | 0.77 | 1.62 | 2.64 | 11.28 | ||||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 8.31 | 55.4 | 6.9 | 3.22 | 8.65 | 313.93 | 211.56 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 0.89 | 3.05 | 1.08 | 9.04 | ||||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 9.58 | 54.2 | 10.1 | 1.76 | 8.66 | 297.23 | 201.28 | 0.28 | 0.2 | 0.83 | 1.83 | 1.09 | 12.20 | ||||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 15.9 | 147 | 20.7 | 5.10 | 14.30 | 318.75 | 280.77 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.81 | 1.99 | 2.24 | 11.84 | ||||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 17.2 | 198 | 29.5 | 4.90 | 19.80 | 309.94 | 337.74 | 0.84 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 1.58 | 2.21 | 32.85 | ||||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 9.97 | 106 | 14.6 | 2.55 | 11.40 | 247.53 | 210.56 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 2.34 | 8.32 | ||||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 14.6 | 190 | 24.7 | 4.77 | 20.30 | 305.87 | 325.63 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.80 | 1.75 | 2.89 | 6.54 | ||||||||
| 31 | FX9-b39 | 14 | 183 | 25.1 | 3.99 | 20.2 | 315.52 | 318.79 | 0.29 | 0.20 | 0.72 | 1.19 | 2.68 | 3.73 | ||||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 14.9 | 147 | 17.3 | 4.70 | 14.2 | 375.23 | 307.50 | 1.09 | 0.33 | 0.74 | 1.13 | 2.09 | 4.03 | ||||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 13.9 | 191 | 23.6 | 5.02 | 18.4 | 352.93 | 340.25 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.75 | 1.38 | 2.51 | 9.83 | ||||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 6.89 | 63.1 | 11.2 | 2.35 | 9.66 | 153.68 | 128.37 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.74 | 1.18 | 2.14 | 10.19 | ||||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 11.4 | 150 | 21.6 | 4.49 | 17.0 | 270.13 | 264.83 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.71 | 1.28 | 3.16 | 1.60 | ||||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 12.7 | 163 | 22.5 | 4.35 | 17.9 | 299.24 | 289.69 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 1.29 | 2.81 | 4.58 | ||||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 8.84 | 103 | 16.0 | 3.77 | 12.8 | 215.64 | 193.38 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.69 | 1.20 | 2.64 | 5.10 | ||||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 11.9 | 197 | 25.1 | 2.85 | 15.2 | 310.09 | 336.31 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 1.42 | 3.62 | 3.96 | ||||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 14.7 | 222 | 23.5 | 2.81 | 16.8 | 415.64 | 397.39 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.75 | 1.41 | 1.95 | 4.95 | ||||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 11.4 | 126 | 17.0 | 2.56 | 11.8 | 326.52 | 266.02 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 1.46 | 1.88 | 15.05 | ||||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 13.7 | 248 | 32.2 | 7.78 | 17.7 | 387.50 | 422.91 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.65 | 1.29 | 2.57 | 17.95 | ||||||||
| 42 | FX9-b75 | 14.3 | 147 | 23.5 | 3.92 | 15.5 | 321.21 | 281.87 | 0.76 | 0.25 | 0.82 | 1.54 | 2.26 | 14.19 | ||||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 14.6 | 111 | 22.6 | 3.33 | 14.8 | 264.29 | 222.9 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.79 | 1.52 | 1.92 | 9.20 | ||||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 13.7 | 110 | 23.8 | 4.11 | 16.4 | 241.60 | 211.48 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 1.52 | 1.76 | 8.88 | ||||||||
表2 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘延安组、直罗组泥岩微量元素(10-6)分析及比值结果
Table 2 Trace elements contents (10-6) and ratio results of mudstones from the Yan’an Formation and Zhiluo Formation in the southern margin of the Ordos Basin
| 层位 | 样品顺序 | 样号 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Ni | Co | Cd | Li | Rb | Cs | Mo | Sr | Ba | V | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直罗组上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 14.1 | 14.9 | 111 | 98.1 | 46.9 | 18.9 | 0.05 | 49.5 | 203 | 14 | 2.82 | 103 | 474 | 91 | ||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 10.8 | 55.5 | 45.5 | 52.4 | 25.5 | 14.1 | 0.05 | 18.7 | 101 | 5.63 | 5.76 | 159 | 513 | 184 | |||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 14.3 | 18.6 | 108 | 82.4 | 41.4 | 17.7 | 0.02 | 48.5 | 263 | 20.3 | 2.56 | 150 | 355 | 143 | |||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 16.3 | 24.3 | 70.1 | 78.2 | 34.7 | 11.4 | 0.06 | 24.6 | 165 | 13 | 2.54 | 174 | 468 | 82 | |||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 7.58 | 23.6 | 11.8 | 27.9 | 7.79 | 3.49 | 0.04 | 7.44 | 82 | 2.94 | 3.31 | 556 | 662 | 53.3 | |||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 19.4 | 49.6 | 75.5 | 48.9 | 39 | 17.1 | 0.06 | 16.3 | 136 | 9.27 | 4.45 | 799 | 614 | 265 | |||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 15.8 | 20 | 90.9 | 69.7 | 37.3 | 15.9 | 0.05 | 27.4 | 169 | 13 | 2.12 | 152 | 491 | 73.9 | |||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 14.9 | 31.2 | 144 | 100 | 63.2 | 30.4 | 0.04 | 56.2 | 245 | 22.8 | 4 | 219 | 464 | 119 | |||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 7.84 | 36.3 | 29.5 | 52.9 | 14.6 | 7.58 | 0.09 | 10.8 | 98 | 4.73 | 3.31 | 1430 | 753 | 136 | |||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 12.2 | 24.3 | 40.6 | 56.6 | 14.3 | 6.58 | 0.1 | 43 | 127 | 11.6 | 3.9 | 187 | 1070 | 70.2 | |||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 18.7 | 32 | 109 | 105 | 54.3 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 76.3 | 201 | 16.9 | 3.24 | 158 | 516 | 125 | |||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 22.5 | 29 | 119 | 119 | 57.5 | 20 | 0.05 | 88.3 | 208 | 20.1 | 4.6 | 161 | 536 | 152 | |||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 20.6 | 25.2 | 104 | 111 | 50.2 | 18.2 | 0.05 | 89 | 172 | 16 | 2.91 | 127 | 475 | 119 | |||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 19 | 20.7 | 81.3 | 64.2 | 35.2 | 13.1 | 0.06 | 45.5 | 178 | 13.6 | 1.21 | 206 | 568 | 71.5 | |||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 25 | 37.6 | 188 | 105 | 55.4 | 26.9 | 0.05 | 71.7 | 265 | 31.6 | 2.68 | 173 | 588 | 142 | |||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 13.4 | 21.2 | 43.4 | 41.7 | 17.9 | 8.8 | 0.05 | 19.4 | 117 | 8.42 | 2.74 | 141 | 682 | 54.2 | |||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 22.5 | 25 | 114 | 86.3 | 42.4 | 17.3 | 0.04 | 77.9 | 198 | 17.5 | 2.1 | 126 | 640 | 100 | |||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 15.4 | 27.2 | 67.6 | 58 | 26.1 | 12.8 | 0.09 | 29.3 | 130 | 11.3 | 1.92 | 111 | 457 | 85.8 | |||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 17.6 | 32.4 | 96.2 | 95.2 | 41 | 17.3 | 0.08 | 67.8 | 187 | 16 | 3.12 | 182 | 427 | 182 | |||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 15.2 | 30 | 69.6 | 61 | 28.4 | 13.2 | 0.09 | 37.2 | 139 | 11.5 | 2.62 | 106 | 473 | 84 | |||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 18.9 | 41.8 | 168 | 100 | 51.1 | 21.3 | 0.05 | 83.7 | 276 | 28.2 | 3.87 | 136 | 444 | 157 | |||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 17.6 | 23 | 124 | 110 | 53.7 | 18.9 | 0.05 | 94.3 | 221 | 19.5 | 1.97 | 171 | 520 | 114 | |||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 20.7 | 19.4 | 91.3 | 94.1 | 46.8 | 16.8 | 0.06 | 88.4 | 154 | 14.9 | 1.86 | 127 | 555 | 107 | |||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 17.2 | 32.1 | 127 | 92.7 | 44.9 | 17 | 0.04 | 94.4 | 249 | 24.3 | 3.17 | 194 | 418 | 150 | |||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 9.4 | 16.5 | 28.4 | 23.8 | 8.82 | 8.15 | 0.06 | 11.8 | 67 | 9 | 1.45 | 85 | 521 | 72.6 | |||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 10 | 21 | 56.9 | 41.2 | 15.3 | 14 | 0.11 | 15.1 | 70 | 6.24 | 1.59 | 122 | 430 | 75.2 | |||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 17.4 | 41.1 | 94.1 | 85.8 | 40.6 | 18.1 | 0.08 | 60.1 | 186 | 16.1 | 3.95 | 206 | 404 | 171 | |||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 12.3 | 30.4 | 106 | 84 | 44.5 | 20.1 | 0.04 | 73.9 | 273 | 28.3 | 2.94 | 404 | 481 | 133 | |||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 13.1 | 20.3 | 61.6 | 59.4 | 26.7 | 11.4 | 0.04 | 46.8 | 155 | 13.9 | 2.19 | 109 | 470 | 57.7 | |||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 21.4 | 32.3 | 98.2 | 81.7 | 35 | 12.1 | 0.04 | 55.5 | 286 | 31.7 | 1.91 | 140 | 402 | 143 | |||||||
| 31 | FX9-b39 | 38.9 | 23 | 102 | 87.9 | 41.2 | 15.4 | 0.05 | 74 | 244 | 22.4 | 1.34 | 145 | 502 | 105 | |||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 101 | 24.5 | 75.6 | 68.8 | 27 | 12.9 | 0.13 | 50.7 | 161 | 16.6 | 2 | 407 | 373 | 77.5 | |||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 12.1 | 36.4 | 90.1 | 81.3 | 37.9 | 15.1 | 0.05 | 68.3 | 219 | 24 | 4.58 | 119 | 524 | 112 | |||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 21 | 19.6 | 28.5 | 33.1 | 13.4 | 6.25 | 0.06 | 17.6 | 133 | 9.17 | 1.33 | 214 | 579 | 39 | |||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 80.1 | 17.4 | 72.6 | 69 | 36.6 | 11.6 | 0.05 | 53 | 233 | 36.4 | 1.88 | 128 | 544 | 88.4 | |||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 28.6 | 17.5 | 73.2 | 76 | 41.9 | 14.9 | 0.05 | 47.7 | 227 | 25.8 | 1.42 | 131 | 600 | 98.3 | |||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 29.2 | 18.2 | 59.2 | 55.3 | 29.6 | 11.2 | 0.06 | 36.9 | 170 | 17.4 | 0.74 | 149 | 711 | 66.2 | |||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 38.1 | 16.6 | 66.2 | 78.7 | 38.7 | 10.7 | 0.04 | 58.3 | 297 | 30.6 | 1.22 | 151 | 717 | 112 | |||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 32.1 | 18.5 | 56.5 | 76.7 | 36.4 | 18.7 | 0.05 | 54.8 | 220 | 23.7 | 2.01 | 159 | 531 | 108 | |||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 10.9 | 13.3 | 39.7 | 59 | 25.9 | 13.8 | 0.04 | 47 | 147 | 13.6 | 3.17 | 164 | 410 | 86.2 | |||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 13.2 | 20.4 | 28.9 | 91.3 | 64.8 | 25.2 | 0.06 | 114 | 272 | 32.4 | 2.22 | 237 | 532 | 118 | |||||||
| 42 | FX9-b75 | 27.2 | 21 | 145 | 76.2 | 26.2 | 11.6 | 0.13 | 86.5 | 164 | 14.6 | 2.75 | 386 | 510 | 117 | |||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 25.1 | 23.4 | 92.6 | 72.6 | 29.8 | 15.5 | 0.06 | 77.9 | 152 | 14.2 | 3.05 | 231 | 510 | 110 | |||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 32.2 | 34.1 | 126 | 71.5 | 36.3 | 20.6 | 0.1 | 86 | 168 | 15.5 | 2.71 | 286 | 507 | 109 | |||||||
| 层位 | 样品顺序 | 样号 | Sc | B | Ga | U | Th | 校正B 含量 | 相当B 含量 | Sr/Ba | U/Th | V/ (V+Ni) | V/Cr | Ni/Co | Sr/Cu | |||||||
| 直罗组上段 | 1 | FX9-b1 | 15.7 | 152 | 27.3 | 3.01 | 15.9 | 224.70 | 257.79 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 0.93 | 2.48 | 7.30 | |||||||
| 2 | FX9-b2 | 13.4 | 83.1 | 15 | 4.51 | 9.76 | 220.73 | 178.16 | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.88 | 3.51 | 1.81 | 14.72 | ||||||||
| 3 | FX9-b3 | 14.5 | 261 | 26.8 | 3.59 | 14.9 | 340.26 | 447.31 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.78 | 1.74 | 2.34 | 10.49 | ||||||||
| 4 | FX9-b4 | 13.6 | 154 | 20.6 | 2.77 | 14.9 | 329.72 | 292.29 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 1.05 | 3.04 | 10.67 | ||||||||
| 5 | FX9-b5 | 6.74 | 36.7 | 8.26 | 1.66 | 8.31 | 118.61 | 89.78 | 0.84 | 0.20 | 0.87 | 1.91 | 2.23 | 73.35 | ||||||||
| 6 | FX9-b6 | 13 | 104 | 19.7 | 3.76 | 13.4 | 249.72 | 209.85 | 1.30 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 5.42 | 2.28 | 41.19 | ||||||||
| 7 | FX9-b8 | 1.5 | 142 | 20 | 2.76 | 14.5 | 28.01 | 260.30 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 1.06 | 2.35 | 9.62 | ||||||||
| 8 | FX9-b11 | 16.3 | 264 | 29.8 | 4.14 | 18 | 370.91 | 447.75 | 0.47 | 0.23 | 0.65 | 1.19 | 2.08 | 14.70 | ||||||||
| 9 | FX9-b12 | 13.8 | 50.9 | 14.6 | 6.88 | 13.5 | 157.33 | 120.67 | 1.90 | 0.51 | 0.90 | 2.57 | 1.93 | 182.40 | ||||||||
| 10 | FX9-b13 | 10.8 | 114 | 13.3 | 4.62 | 17.4 | 295.43 | 240.68 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.83 | 1.24 | 2.17 | 15.33 | ||||||||
| 11 | FX9-b15 | 15.7 | 222 | 25.1 | 3.95 | 18.9 | 411.11 | 395.78 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.70 | 1.19 | 2.84 | 8.45 | ||||||||
| 12 | FX9-b16 | 18 | 248 | 28 | 3.92 | 20.5 | 453.33 | 440.09 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.73 | 1.28 | 2.88 | 7.16 | ||||||||
| 13 | FX9-b17 | 15.2 | 221 | 21 | 3.29 | 15.8 | 487.92 | 426.01 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.70 | 1.07 | 2.76 | 6.17 | ||||||||
| 14 | FX9-b18 | 11.5 | 158 | 19.1 | 2.84 | 13.8 | 328.36 | 295.62 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.67 | 1.11 | 2.69 | 10.84 | ||||||||
| 15 | FX9-b19 | 19.2 | 219 | 27.1 | 4.37 | 28.7 | 331.23 | 372.02 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.72 | 1.35 | 2.06 | 6.92 | ||||||||
| 16 | FX9-b20 | 9.64 | 73.1 | 12.1 | 2.64 | 9.79 | 202.39 | 160.92 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.75 | 1.30 | 2.03 | 10.52 | ||||||||
| 17 | FX9-b21 | 14.2 | 156 | 23.8 | 3.76 | 17.1 | 302.05 | 282.94 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.70 | 1.16 | 2.45 | 5.60 | ||||||||
| 18 | FX9-b22 | 11.7 | 103 | 15.4 | 2.37 | 12.7 | 279.71 | 223.94 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.77 | 1.48 | 2.04 | 7.21 | ||||||||
| 19 | FX9-b23 | 18.9 | 177 | 24.6 | 3.28 | 16.4 | 354.00 | 325.45 | 0.43 | 0.20 | 0.82 | 1.91 | 2.37 | 10.34 | ||||||||
| 20 | FX9-b24 | 6.13 | 102 | 15.7 | 2.56 | 11.3 | 267.59 | 216.99 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.75 | 1.38 | 2.15 | 6.97 | ||||||||
| 21 | FX9-b25 | 17.9 | 219 | 28.3 | 3.8 | 26.6 | 337.84 | 372.82 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.75 | 1.57 | 2.40 | 7.20 | ||||||||
| 22 | FX9-b26 | 16.5 | 193 | 25.6 | 3.39 | 19.1 | 352.80 | 342.49 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 1.04 | 2.84 | 9.72 | ||||||||
| 23 | FX9-b27 | 13.3 | 162 | 18.9 | 2.59 | 15 | 402.63 | 333.50 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 1.14 | 2.79 | 6.14 | ||||||||
| 24 | FX9-b28 | 16.4 | 188 | 25.8 | 3.31 | 23.3 | 312.11 | 324.31 | 0.46 | 0.14 | 0.77 | 1.62 | 2.64 | 11.28 | ||||||||
| 25 | FX9-b29 | 8.31 | 55.4 | 6.9 | 3.22 | 8.65 | 313.93 | 211.56 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 0.89 | 3.05 | 1.08 | 9.04 | ||||||||
| 26 | FX9-b32 | 9.58 | 54.2 | 10.1 | 1.76 | 8.66 | 297.23 | 201.28 | 0.28 | 0.2 | 0.83 | 1.83 | 1.09 | 12.20 | ||||||||
| 27 | FX9-b33 | 15.9 | 147 | 20.7 | 5.10 | 14.30 | 318.75 | 280.77 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.81 | 1.99 | 2.24 | 11.84 | ||||||||
| 28 | FX9-b36 | 17.2 | 198 | 29.5 | 4.90 | 19.80 | 309.94 | 337.74 | 0.84 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 1.58 | 2.21 | 32.85 | ||||||||
| 29 | FX9-b37 | 9.97 | 106 | 14.6 | 2.55 | 11.40 | 247.53 | 210.56 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 2.34 | 8.32 | ||||||||
| 30 | FX9-b38 | 14.6 | 190 | 24.7 | 4.77 | 20.30 | 305.87 | 325.63 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.80 | 1.75 | 2.89 | 6.54 | ||||||||
| 31 | FX9-b39 | 14 | 183 | 25.1 | 3.99 | 20.2 | 315.52 | 318.79 | 0.29 | 0.20 | 0.72 | 1.19 | 2.68 | 3.73 | ||||||||
| 32 | FX9-b40 | 14.9 | 147 | 17.3 | 4.70 | 14.2 | 375.23 | 307.50 | 1.09 | 0.33 | 0.74 | 1.13 | 2.09 | 4.03 | ||||||||
| 33 | FX9-b41 | 13.9 | 191 | 23.6 | 5.02 | 18.4 | 352.93 | 340.25 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.75 | 1.38 | 2.51 | 9.83 | ||||||||
| 34 | FX9-b42 | 6.89 | 63.1 | 11.2 | 2.35 | 9.66 | 153.68 | 128.37 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.74 | 1.18 | 2.14 | 10.19 | ||||||||
| 35 | FX9-b44 | 11.4 | 150 | 21.6 | 4.49 | 17.0 | 270.13 | 264.83 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.71 | 1.28 | 3.16 | 1.60 | ||||||||
| 36 | FX9-b45 | 12.7 | 163 | 22.5 | 4.35 | 17.9 | 299.24 | 289.69 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 1.29 | 2.81 | 4.58 | ||||||||
| 37 | FX9-b46 | 8.84 | 103 | 16.0 | 3.77 | 12.8 | 215.64 | 193.38 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.69 | 1.20 | 2.64 | 5.10 | ||||||||
| 38 | FX9-b47 | 11.9 | 197 | 25.1 | 2.85 | 15.2 | 310.09 | 336.31 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 1.42 | 3.62 | 3.96 | ||||||||
| 39 | FX9-b48 | 14.7 | 222 | 23.5 | 2.81 | 16.8 | 415.64 | 397.39 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.75 | 1.41 | 1.95 | 4.95 | ||||||||
| 40 | FX9-b49 | 11.4 | 126 | 17.0 | 2.56 | 11.8 | 326.52 | 266.02 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 1.46 | 1.88 | 15.05 | ||||||||
| 41 | FX9-b51 | 13.7 | 248 | 32.2 | 7.78 | 17.7 | 387.50 | 422.91 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.65 | 1.29 | 2.57 | 17.95 | ||||||||
| 42 | FX9-b75 | 14.3 | 147 | 23.5 | 3.92 | 15.5 | 321.21 | 281.87 | 0.76 | 0.25 | 0.82 | 1.54 | 2.26 | 14.19 | ||||||||
| 43 | FX9-b76 | 14.6 | 111 | 22.6 | 3.33 | 14.8 | 264.29 | 222.9 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.79 | 1.52 | 1.92 | 9.20 | ||||||||
| 44 | FX9-b77 | 13.7 | 110 | 23.8 | 4.11 | 16.4 | 241.60 | 211.48 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 1.52 | 1.76 | 8.88 | ||||||||

图3 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘延安组、直罗组泥岩微量元素比值判别图
Fig.3 Discrimination diagram of trace element ratios of mudstones from the Yan’an Formation and Zhiluo Formation in the southern margin of the Ordos Basin
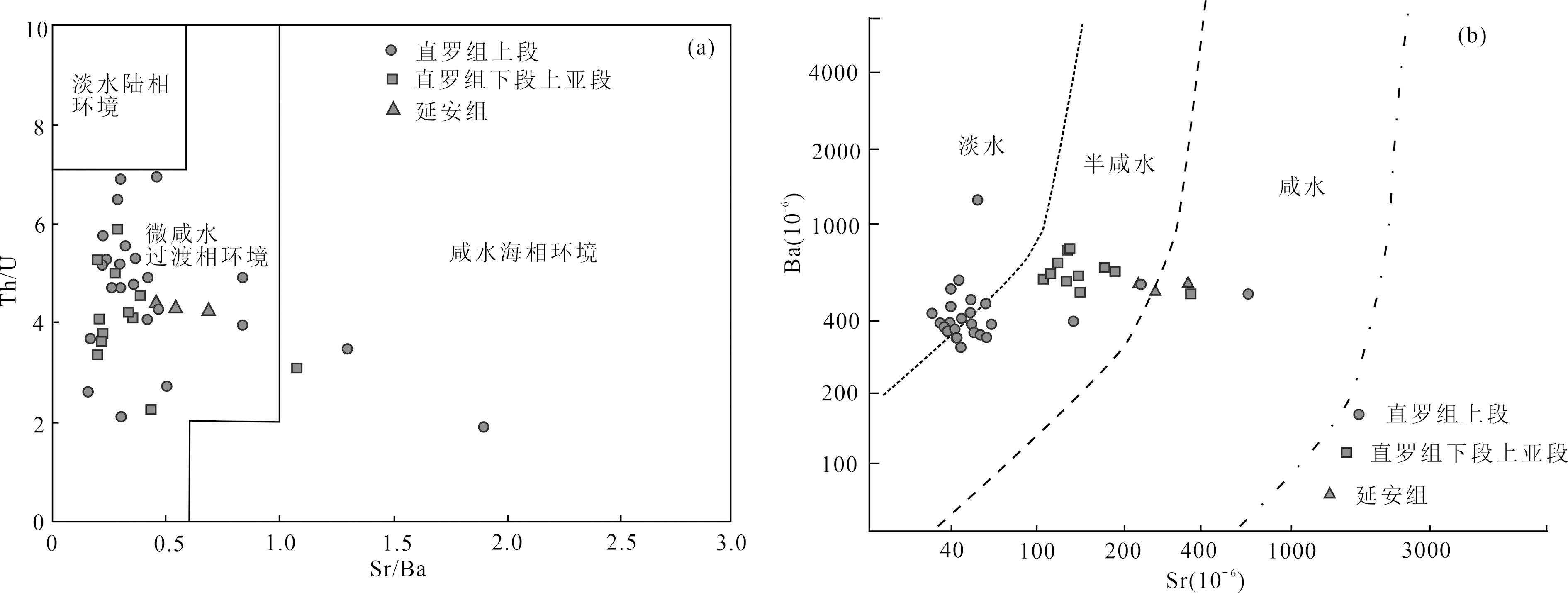
图4 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘FX9井泥岩Sr/Ba与Th/U相关关系图(a)、Ba-Sr图解(b)[28]
Fig.4 Correlation diagrams of Sr/Ba-Th/U (a) and Ba-Sr (b) of mudstones from Well FX9 in the southern margin of the Ordos Basin[28]
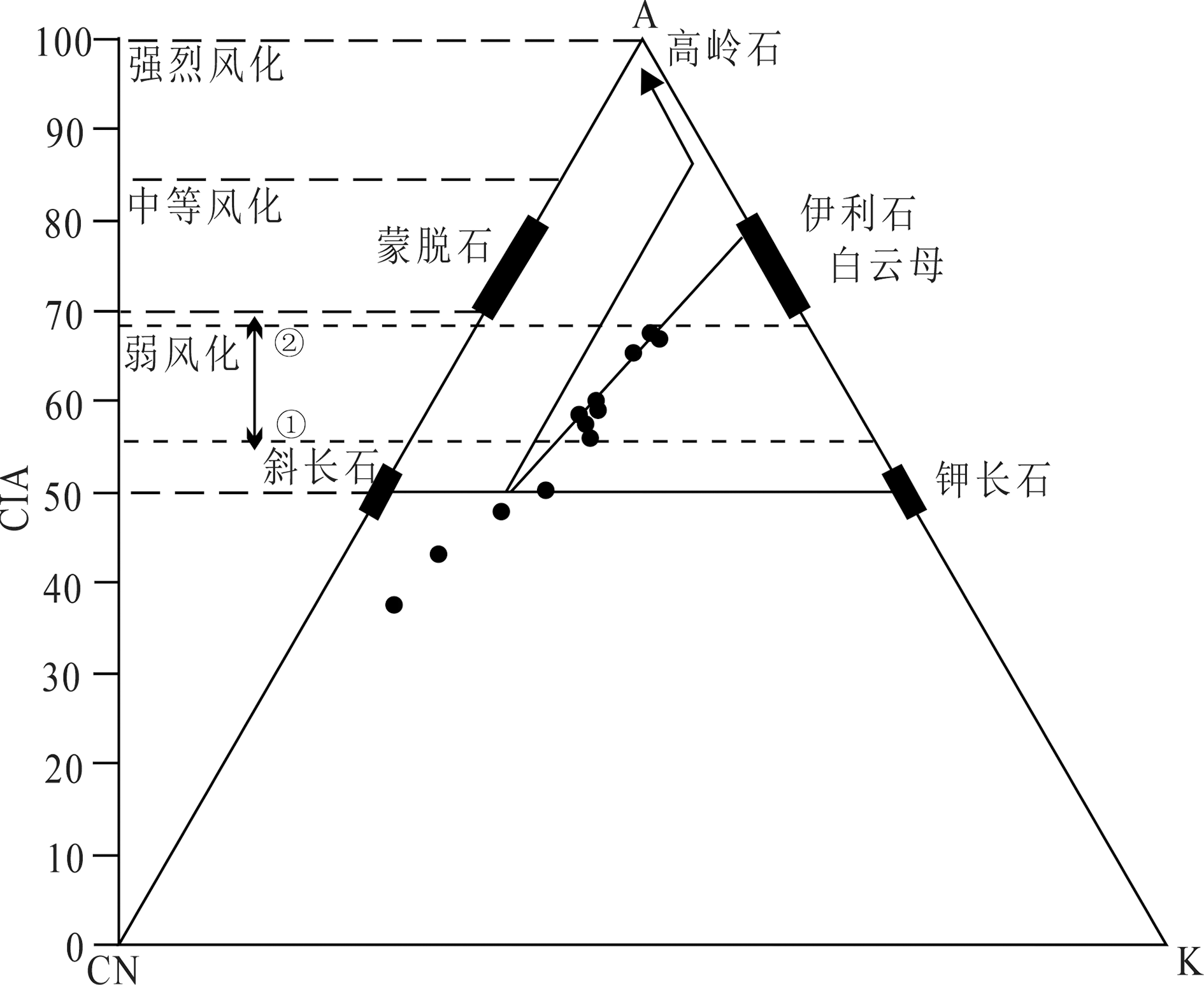
图7 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘延安组、直罗组ICV和CIA指数垂向上变化趋势图
Fig.7 Vertical variation trend diagram of ICV and CIA indices for the Yan’an Formation and Zhiluo Formation in the southern margin of the Ordos Basin
| [1] | LI S T, YANG S G, JERZYKIEWICZ T. Upper Triassic-Jurassic foreland sequences of the Ordos basin in China[M]// Stratigraphic Evolution of Foreland Basins. Calgary: SEPM(Society for Sedimentary Geology), 1995: 233-241. |
| [2] | YANG X Y, LING M X, SUN W, et al. Study on the ore-forming condition and occurrence of uranium minerals in sandstone-type uranium deposits from Ordos basin, Northwest China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(18): A720. |
| [3] | WU B L, WEI A J, LIU C Y, et al. Stable isotope tracer of white sandstone formation in Yan’an Formation in Northern Ordos Basin and its geological signifcance[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2015, 22(3):205-214. |
| [4] | 叶晓东, 陈军, 陈曦, 等. “双碳”目标下的中国CCUS技术挑战及对策[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2024, 14(1):1-9. |
| [5] | 张迈, 宋到福, 王铁冠, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区天然气地球化学特征及气源探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1):124-135. |
| [6] | MIAO P S, CHEN Y, CHENG Y H, et al. New deep exploration discoveries of sandstonetype uranium deposits in North China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia 2020, 44(4):563-575. |
| [7] | MIAO P S, JIN R S, LI J G, et al. The first discovery of a large sandstone-type uranium deposit in aeolian depositional environment[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2020, 94(2): 583-584. |
| [8] | 张天福, 孙立新, 张云, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组、直罗组泥岩微量、稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3454-3472. |
| [9] | 汤超, 肖鹏, 魏佳林, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地志丹地区安定组铀矿化地质地球化学特征[J]. 华北地质, 2021, 44(2): 4-13. |
| [10] | 金若时, 滕雪明. 中国北方砂岩型铀矿大规模成矿作用[J]. 华北地质, 20, 45(1):42-57. |
| [11] | WU B L, WEI A J, HU L, et al. Stable isotope characteristics and geological signifcance of epigenetic alteration in Dongsheng Uranium Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology Bulletin, 2016, 35(12), 2133-2145. |
| [12] | AKHTAR S, YANG X Y, PIRAJNO F. Sandstone type uranium deposits in the Ordos basin, northwest China: A case study and an overview[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 146: 367-382. |
| [13] | 许中杰, 程日辉, 王嘹亮, 等. 闽西南地区晚三叠-中侏罗世沉积岩矿物和元素地球化学特征: 对盆地构造背景转变的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8): 2913-2924. |
| [14] | SAGEM AN B B, MURPHY A E, WERNE J P, et al. A tale of shales: the relative roles of production, deco mposition, and dilution in the accumulation of organic-rich strata,Middle Upper Devonian, Appalachian Basin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003,195:229-273. |
| [15] | 刘池洋, 赵红格, 桂小军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地演化-改造的时空坐标及其成藏(矿)响应[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(5): 617-638. |
| [16] | 黄少华, 刘章月, 秦明宽, 等. 基于便携式色度、X荧光及高光谱的砂岩铀成矿环境研究——以鄂尔多斯盆地西北部特拉敖包铀矿产地为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(6):1182-1193. |
| [17] | 张字龙, 范洪海, 蔡煜琦, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地黄陵地区直罗组有机地球化学特征及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3408-3423. |
| [18] | 刘孝锐, 路俊刚, 谭开俊, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部HQ地区长7段烃源岩地球化学特征与长8段原油来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5): 1306-1324. |
| [19] | 马明, 刘池洋, 王建强, 等. 鄂尔多斯地块庆阳—鄂托克旗古隆起地质特征及其形成与演化[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(6): 1431-1444. |
| [20] | RIMMER S M, THOMPSON J A, GOODNIGHT S A, et al. Multiple controls on the preservation of organic matter in Devonian-Mississippian marine black shales: Geochemical and petrographic evidence[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 215(1/2): 125-154. |
| [21] | ALGEO T J, MAYNARD J B. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 289-318. |
| [22] | 雷开宇, 刘池洋, 张龙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部侏罗系泥岩地球化学特征: 物源与古沉积环境恢复[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(3): 621-636. |
| [23] | RUSSELL A D, MORFORD J L. The behavior of redox-sensitive metals across a laminated-massive-laminated transition in Saanich Inlet, British Columbia[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 174(1/2/3/4): 341-354. |
| [24] | ZHANG T F, CHENG X Y, WANG S Y, et al. Middle Jurassic-Early Cretaceous drastic paleoenvironmental changes in the Ordos Basin: Constraints on sandstone-type uranium mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 20,142:1-22. |
| [25] | 李得路, 刘福田, 程敬华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部三叠系陆相油页岩稀土元素特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017, 36(Supp):1172. |
| [26] | 郑荣才, 柳梅青. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组古盐度研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(1): 20-25. |
| [27] | 刘刚, 周东升. 微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用: 以江汉盆地潜江组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3): 307-310, 314. |
| [28] | 王仁民. 变质岩原岩图解判别法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987. |
| [29] | COUCH E L. Calculation of paleosalinities from boron and clay mineral data[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1971, 55(10):1829-1837. |
| [30] | 邓宏文, 钱凯. 沉积地球化学与环境分析[M]. 兰州: 甘肃科学技术出版社, 1999. |
| [31] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continenta1 crust:Its composition and evolution[J]. Oxford:Blackwell,1985:312. |
| [32] |
HASKIN L A, FREY F A. Dispersed and not-so-rare earths[J]. Science, 1966, 152: 299-314.
PMID |
| [33] | HATCH J R. LEVENTHAL J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the upper pennsylvanian(Missourian) stark shale member of the dennis limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U.S.A[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/2/3):65-82. |
| [34] | TRIBOVILLARD N, BIALKOWSKI A, TYSON R V, et al. Organic facies variation in the late Kimmeridgian of the Boulonnais area(northernmost France)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2001, 18(3): 371-389. |
| [35] | SCHEFFLER K, BUEHMANN D, SCHWARK L. Analysis of late Palaeozoic glacial to postglacial sedimentary successions in South Africa by geochemical proxies-Response to climate evolution and sedimentary environment[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 240(1/2): 184-203. |
| [36] |
DING J H, ZHANG J C, HUO Z P, et al. Controlling factors and formation models of organic matter accumulation for the upper Permian dalong formation black shale in the Lower Yangtze Region, South China: Constraints from geochemical evidence[J]. ACS Omega, 2021, 6(5): 3681-3692.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | ROY D K, ROSER B P. Climatic control on the composition of Carboniferous-Permian Gondwana sediments, Khalaspir basin, Bangladesh[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(3): 1163-1171. |
| [38] | JONES B, MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of Palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/2/3/4): 111-129. |
| [39] |
徐小涛, 邵龙义. 利用泥质岩化学蚀变指数分析物源区风化程度时的限制因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(3): 515-522.
DOI |
| [40] | LEMRMANM A. Lakes:Chemistry,Geology, Physics[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1978:79-89. |
| [41] | COX R, LOWE D R, CULLERS R L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(14): 2919-2940. |
| [42] |
白洁, 郑栋宇, 侯明才, 等. 全球硅酸盐化学风化-二氧化碳消耗定量模型研究进展[J]. 古地球学报, 2024, 26(2): 460-474.
DOI |
| [43] | PANAHI A, YOUNG G M, RAINBIRD R H. Behavior of major and trace elements(including REE) during Paleoproterozoic pedogenesis and diagenetic alteration of an Archean granite near Ville Marie, Québec, Canada[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(13): 2199-2220. |
| [1] | 武将伟, 胡浩, 张富臣, 牛毅, 周志广, 张达. 内蒙古集宁地区小大青山中生代花岗岩岩石特征及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 995-1015. |
| [2] | 刘立芬, 栾欣婷, 李瑛, 杨兴, 姜清龙, 高博, 刘晓兰. 黑龙江省农业主产区土壤地球化学基准值与背景值[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 1068-1082. |
| [3] | 刘婷, 张立, 吕石佳, 张思宇, 王刚, 孙振伟. 黑龙江省庆安地区土壤-作物系统硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 1098-1107. |
| [4] | 恽虎, 官军, 王成, 林世莉, 费光春. 海南岛西部抱板杂岩中伟晶岩矿物学与全岩地球化学特征及成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 715-727. |
| [5] | 吴晓贺, 张聚全, 段站站, 张乐民, 温雨菁, 郭子桤, 李清. 华北克拉通中部菅等岩体的成因及构造意义: 锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 728-751. |
| [6] | 娄元林, 成明, 陈武, 唐侥, 曾昊, 陈坤, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区锑多金属矿床成矿流体热力学与地球化学特征及其成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 263-266. |
| [7] | 赖静, 刘文泉, 钟福军. 南岭东段上窑铀矿床花岗斑岩脉岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 277-293. |
| [8] | 韩慧萍, 马嘉, 张怡, 潘莹露. 塔里木盆地塔中地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层成岩流体性质及分布[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 312-326. |
| [9] | 杨宇婷, 白峰, 温宇航, 张启东, 张道元, 王雯. 吉林“磐龙玉”的地球化学特征及颜色成因探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 167-182. |
| [10] | 安雯静, 白峰, 刘孟松, 张道元, 黄甜甜, 王雯. 吉林“磐龙墨玉”的宝石矿物学、年代学及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 183-193. |
| [11] | 刘帆, 程志国, 郭祝芳, 冀文涛. 西南天山托云盆地古近纪熔积岩成因及其古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 46-61. |
| [12] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 王翠彭, 史宏江, 鞠楠, 何云龙. 大兴安岭北段呼玛地区晚石炭世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征:对古亚洲洋构造演化的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 62-82. |
| [13] | 张美诺, 石康兴, 邱昆峰, 邓军. 冀东司家营BIF铁矿床磁铁矿类型与成因及其对高品位铁矿化成矿机制的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 96-114. |
| [14] | 李辉, 张涛, 侯雨庭, 喻健, 何鑫, 陈世加, 李勇. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段陆相页岩层系致密储层充注物性下限及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(06): 1498-1510. |
| [15] | 刘孝锐, 路俊刚, 谭开俊, 廖建波, 龙礼文, 陈世加, 李勇, 肖正录. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部HQ地区长7段烃源岩地球化学特征与长8段原油来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1306-1324. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||