



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (02): 277-293.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.062
出版日期:2025-04-10
发布日期:2025-05-08
作者简介:赖 静,男,工程师,1994年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,主要从事铀矿地质勘查与科研工作。Email: jinglai1994@163.com。
基金资助:
LAI Jing1,2,3( ), LIU Wenquan1,2,3, ZHONG Fujun4
), LIU Wenquan1,2,3, ZHONG Fujun4
Published:2025-04-10
Online:2025-05-08
摘要: 为进一步揭示华南中生代的地球动力学背景及其构造演化过程,本文对南岭东段上窖铀矿床花岗斑岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和地球化学特征开展研究。结果显示,岩浆锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(190.6±2.2) Ma和(190.6±1.3) Ma,表明花岗斑岩侵位于早侏罗世。岩石具有高硅(68.97%~69.56%),富碱(N2O+K2O为9.12%~9.28%),贫钙(0.50%~1.22%)、镁(0.09%~0.11%)和低磷(0.05%)的特征,属高钾钙碱性(里特曼指数σ为3.16~3.27)、准铝质-弱过铝质(A/CNK为0.98~1.09)系列。大离子亲石元素Rb、Th和U相对富集,高场强元素Zr、Hf、Nb、Ta、Ti相对亏损;富集轻稀土元素,亏损重稀土元素,呈负Eu异常。岩石地球化学特征综合指示上窑铀矿床的花岗斑岩为A型花岗岩。锆石εHf(t)值为+5.39~+9.07,平均+6.91,对应的地壳模式年龄(TDM2)为887~652 Ma,指示其主要物源为新元古代的新生镁铁质地壳。花岗斑岩形成于古太平洋俯冲构造背景下局部板内伸展构造环境,龙源坝岩体是古特提斯和古太平洋两大构造域的转换的地质体的证据展示。结合区域岩浆岩年代学特征和华南构造背景,认为古特提斯和古太平洋两大构造域的转换可能开始于190 Ma之前。
中图分类号:
赖静, 刘文泉, 钟福军. 南岭东段上窑铀矿床花岗斑岩脉岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 277-293.
LAI Jing, LIU Wenquan, ZHONG Fujun. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Granite Porphyry Veins in the Shangjiao Uranium Deposit, Eastern Nanling Range[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(02): 277-293.

图1 龙源坝岩体和上窖矿床位置及地质简图 (a)华南花岗岩带分布示意图(据文献[6]);(b)龙源坝岩体地质简图(据文献[2]);(c)上窖矿床地质简图(据核工业二九○研究所)
Fig.1 Location and geological sketch of Longyuanba pluton and Shangjiao deposit

图2 上窖矿床花岗斑岩野外照片及显微照片 (a)花岗斑岩脉野外照片;(b)石英斑晶特征;(c)斜长石、黑云母斑晶;(d)黑云母中见磁铁矿;Bt.黑云母;Kfs.钾长石;Mag.磁铁矿;Pl.斜长石;Qtz.石英
Fig.2 Filed and microscopic photographs of the porphyry in Shangjiao deposit
| 分析 点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/ 206Pb(σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(σ) | 207Pb/206Pb (σ)(Ma) | 207Pb/235U (σ)(Ma) | 206Pb/238U (σ)(Ma) | 谐和度 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (10-6) | |||||||||||
| HS84-1 | 93 | 303 | 0.31 | 0.05212(0.00331) | 0.21668(0.01085) | 0.03015(0.00071) | 300(144) | 199(9) | 191(4) | 0.96 | |
| HS84-2 | 104 | 258 | 0.40 | 0.05230(0.00270) | 0.21624(0.01227) | 0.02998(0.00090) | 298(119) | 199(10) | 190(6) | 0.99 | |
| HS84-3 | 41 | 159 | 0.26 | 0.05379(0.00388) | 0.22309(0.01693) | 0.03007(0.00078) | 361(163) | 204(14) | 191(5) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-4 | 152 | 378 | 0.40 | 0.04777(0.00382) | 0.19772(0.01570) | 0.03001(0.00098) | 87(246) | 183(13) | 191(6) | 0.93 | |
| HS84-5 | 110 | 274 | 0.40 | 0.05117(0.00184) | 0.21180(0.00837) | 0.03001(0.00067) | 256(81) | 195(7) | 191(4) | 0.94 | |
| HS84-6 | 88 | 258 | 0.34 | 0.05219(0.00211) | 0.21578(0.00868) | 0.02998(0.00049) | 295(93) | 198(7) | 190(3) | 0.96 | |
| HS84-7 | 301 | 576 | 0.52 | 0.05428(0.00272) | 0.22477(0.01511) | 0.03002(0.00088) | 383(118) | 206(13) | 191(6) | 0.96 | |
| HS84-8 | 129 | 278 | 0.46 | 0.05232(0.00281) | 0.21550(0.01438) | 0.02986(0.00101) | 298(122) | 198(12) | 190(6) | 0.97 | |
| HS84-9 | 95 | 278 | 0.34 | 0.05102(0.00271) | 0.21093(0.01146) | 0.02997(0.00053) | 243(119) | 194(10) | 190(3) | 0.93 | |
| HS84-10 | 168 | 341 | 0.49 | 0.05261(0.00420) | 0.21920(0.01193) | 0.03021(0.00090) | 322(181) | 201(10) | 192(6) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-11 | 105 | 289 | 0.36 | 0.05040(0.00321) | 0.20911(0.01237) | 0.03008(0.00106) | 213(148) | 193(10) | 191(7) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-12 | 94 | 300 | 0.31 | 0.05428(0.00342) | 0.22574(0.01149) | 0.03015(0.00085) | 383(141) | 207(10) | 191(5) | 0.91 | |
| HS84-13 | 96 | 244 | 0.39 | 0.05193(0.00233) | 0.21428(0.00991) | 0.02991(0.00064 ) | 283(106) | 197(8) | 190(4) | 0.92 | |
| HS84-14 | 71 | 224 | 0.32 | 0.04928(0.00191) | 0.20344(0.00743) | 0.02993(0.00054) | 161(86) | 188(6) | 190(3) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-15 | 100 | 288 | 0.35 | 0.05251(0.00258) | 0.21719(0.01094) | 0.02999(0.00066) | 309(113) | 200(9) | 190(4) | 0.97 | |
| HS85-1 | 199 | 497 | 0.40 | 0.051878(0.002058) | 0.214667(0.009675) | 0.030005(0.000439) | 280(91) | 197(8) | 191(3) | 0.89 | |
| HS85-2 | 81 | 302 | 0.27 | 0.054915(0.003502) | 0.223128(0.014475) | 0.029463(0.000528) | 409(143) | 205(12) | 187(3) | 0.87 | |
| HS85-3 | 375 | 774 | 0.48 | 0.053655(0.001485) | 0.225616(0.0067) | 0.030491(0.000445) | 367(58) | 207(6) | 194(3) | 0.91 | |
| HS85-4 | 98 | 307 | 0.32 | 0.049646(0.00302) | 0.205584(0.011211) | 0.030028(0.000526) | 189(145) | 190(9) | 191(3) | 0.85 | |
| HS85-5 | 278 | 554 | 0.50 | 0.052706(0.001871) | 0.218618(0.007578) | 0.030078(0.00036) | 317(81) | 201(6) | 191(2) | 0.097 | |
| HS85-6 | 172 | 498 | 0.35 | 0.04820(0.001683) | 0.199572(0.007025) | 0.030024(0.000394) | 109(79) | 185(6) | 191(2) | 0.95 | |
| HS85-7 | 64 | 217 | 0.30 | 0.051373(0.002832) | 0.211672(0.010994) | 0.029877(0.000463) | 257(132) | 195(9) | 190(3) | 0.99 | |
| HS85-8 | 129 | 342 | 0.38 | 0.050726(0.002005) | 0.209678(0.008078) | 0.029973(0.000447) | 228(58) | 193(7) | 190(3) | 0.92 | |
| HS85-9 | 53 | 203 | 0.26 | 0.047191(0.002886) | 0.194641(0.011236) | 0.029908(0.000391) | 58(141) | 181(10) | 190(2) | 0.90 | |
| HS85-10 | 147 | 366 | 0.40 | 0.052106(0.00258) | 0.216024(0.010695) | 0.030063(0.000531) | 300(113) | 199(9) | 191(3) | 0.96 | |
| HS85-11 | 68 | 242 | 0.28 | 0.04904(0.002576) | 0.201075(0.010676) | 0.029731(0.000448) | 150(156) | 186(9) | 189(3) | 0.96 | |
| HS85-12 | 114 | 344 | 0.33 | 0.05406(0.002353) | 0.224155(0.010361) | 0.030068(0.000418) | 372(103) | 205(9) | 191(3) | 0.90 | |
| HS85-13 | 368 | 732 | 0.50 | 0.05511(0.001637) | 0.229598(0.006954) | 0.030211(0.000284) | 417(67) | 210(6) | 192(2) | 0.98 | |
| HS85-14 | 92 | 237 | 0.39 | 0.047874(0.003394) | 0.195332(0.012832) | 0.029587(0.000515) | 100(154) | 181(11) | 188(3) | 0.97 | |
| HS85-15 | 178 | 459 | 0.39 | 0.049037(0.002185) | 0.202944(0.008467) | 0.03001(0.000387) | 150(104) | 188(7) | 191(2) | 0.95 | |
表1 龙源坝岩体花岗斑岩中锆石的LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of zircons from granite porphyry of Longyuanba pluton
| 分析 点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/ 206Pb(σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(σ) | 207Pb/206Pb (σ)(Ma) | 207Pb/235U (σ)(Ma) | 206Pb/238U (σ)(Ma) | 谐和度 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (10-6) | |||||||||||
| HS84-1 | 93 | 303 | 0.31 | 0.05212(0.00331) | 0.21668(0.01085) | 0.03015(0.00071) | 300(144) | 199(9) | 191(4) | 0.96 | |
| HS84-2 | 104 | 258 | 0.40 | 0.05230(0.00270) | 0.21624(0.01227) | 0.02998(0.00090) | 298(119) | 199(10) | 190(6) | 0.99 | |
| HS84-3 | 41 | 159 | 0.26 | 0.05379(0.00388) | 0.22309(0.01693) | 0.03007(0.00078) | 361(163) | 204(14) | 191(5) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-4 | 152 | 378 | 0.40 | 0.04777(0.00382) | 0.19772(0.01570) | 0.03001(0.00098) | 87(246) | 183(13) | 191(6) | 0.93 | |
| HS84-5 | 110 | 274 | 0.40 | 0.05117(0.00184) | 0.21180(0.00837) | 0.03001(0.00067) | 256(81) | 195(7) | 191(4) | 0.94 | |
| HS84-6 | 88 | 258 | 0.34 | 0.05219(0.00211) | 0.21578(0.00868) | 0.02998(0.00049) | 295(93) | 198(7) | 190(3) | 0.96 | |
| HS84-7 | 301 | 576 | 0.52 | 0.05428(0.00272) | 0.22477(0.01511) | 0.03002(0.00088) | 383(118) | 206(13) | 191(6) | 0.96 | |
| HS84-8 | 129 | 278 | 0.46 | 0.05232(0.00281) | 0.21550(0.01438) | 0.02986(0.00101) | 298(122) | 198(12) | 190(6) | 0.97 | |
| HS84-9 | 95 | 278 | 0.34 | 0.05102(0.00271) | 0.21093(0.01146) | 0.02997(0.00053) | 243(119) | 194(10) | 190(3) | 0.93 | |
| HS84-10 | 168 | 341 | 0.49 | 0.05261(0.00420) | 0.21920(0.01193) | 0.03021(0.00090) | 322(181) | 201(10) | 192(6) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-11 | 105 | 289 | 0.36 | 0.05040(0.00321) | 0.20911(0.01237) | 0.03008(0.00106) | 213(148) | 193(10) | 191(7) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-12 | 94 | 300 | 0.31 | 0.05428(0.00342) | 0.22574(0.01149) | 0.03015(0.00085) | 383(141) | 207(10) | 191(5) | 0.91 | |
| HS84-13 | 96 | 244 | 0.39 | 0.05193(0.00233) | 0.21428(0.00991) | 0.02991(0.00064 ) | 283(106) | 197(8) | 190(4) | 0.92 | |
| HS84-14 | 71 | 224 | 0.32 | 0.04928(0.00191) | 0.20344(0.00743) | 0.02993(0.00054) | 161(86) | 188(6) | 190(3) | 0.95 | |
| HS84-15 | 100 | 288 | 0.35 | 0.05251(0.00258) | 0.21719(0.01094) | 0.02999(0.00066) | 309(113) | 200(9) | 190(4) | 0.97 | |
| HS85-1 | 199 | 497 | 0.40 | 0.051878(0.002058) | 0.214667(0.009675) | 0.030005(0.000439) | 280(91) | 197(8) | 191(3) | 0.89 | |
| HS85-2 | 81 | 302 | 0.27 | 0.054915(0.003502) | 0.223128(0.014475) | 0.029463(0.000528) | 409(143) | 205(12) | 187(3) | 0.87 | |
| HS85-3 | 375 | 774 | 0.48 | 0.053655(0.001485) | 0.225616(0.0067) | 0.030491(0.000445) | 367(58) | 207(6) | 194(3) | 0.91 | |
| HS85-4 | 98 | 307 | 0.32 | 0.049646(0.00302) | 0.205584(0.011211) | 0.030028(0.000526) | 189(145) | 190(9) | 191(3) | 0.85 | |
| HS85-5 | 278 | 554 | 0.50 | 0.052706(0.001871) | 0.218618(0.007578) | 0.030078(0.00036) | 317(81) | 201(6) | 191(2) | 0.097 | |
| HS85-6 | 172 | 498 | 0.35 | 0.04820(0.001683) | 0.199572(0.007025) | 0.030024(0.000394) | 109(79) | 185(6) | 191(2) | 0.95 | |
| HS85-7 | 64 | 217 | 0.30 | 0.051373(0.002832) | 0.211672(0.010994) | 0.029877(0.000463) | 257(132) | 195(9) | 190(3) | 0.99 | |
| HS85-8 | 129 | 342 | 0.38 | 0.050726(0.002005) | 0.209678(0.008078) | 0.029973(0.000447) | 228(58) | 193(7) | 190(3) | 0.92 | |
| HS85-9 | 53 | 203 | 0.26 | 0.047191(0.002886) | 0.194641(0.011236) | 0.029908(0.000391) | 58(141) | 181(10) | 190(2) | 0.90 | |
| HS85-10 | 147 | 366 | 0.40 | 0.052106(0.00258) | 0.216024(0.010695) | 0.030063(0.000531) | 300(113) | 199(9) | 191(3) | 0.96 | |
| HS85-11 | 68 | 242 | 0.28 | 0.04904(0.002576) | 0.201075(0.010676) | 0.029731(0.000448) | 150(156) | 186(9) | 189(3) | 0.96 | |
| HS85-12 | 114 | 344 | 0.33 | 0.05406(0.002353) | 0.224155(0.010361) | 0.030068(0.000418) | 372(103) | 205(9) | 191(3) | 0.90 | |
| HS85-13 | 368 | 732 | 0.50 | 0.05511(0.001637) | 0.229598(0.006954) | 0.030211(0.000284) | 417(67) | 210(6) | 192(2) | 0.98 | |
| HS85-14 | 92 | 237 | 0.39 | 0.047874(0.003394) | 0.195332(0.012832) | 0.029587(0.000515) | 100(154) | 181(11) | 188(3) | 0.97 | |
| HS85-15 | 178 | 459 | 0.39 | 0.049037(0.002185) | 0.202944(0.008467) | 0.03001(0.000387) | 150(104) | 188(7) | 191(2) | 0.95 | |
| 分析 点号 | 176Hf/177Hf(2σ) | 176Lu/177Hf(2σ) | 176Yb/177Hf(2σ) | 年龄 (Ma) | εHf(t) | TDM1 (Ma) | TDM2 (Ma) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS84-1 | 0.282827(0.000018) | 0.035444(0.000091) | 0.00131(0.0000042) | 191 | 5.98 | 608 | 850 |
| HS84-2 | 0.282847(0.000016) | 0.023351(0.000014) | 0.00090(0.0000007) | 190 | 6.71 | 573 | 803 |
| HS84-3 | 0.282837(0.000014) | 0.030009(0.000184) | 0.00114(0.0000047) | 191 | 6.34 | 591 | 826 |
| HS84-4 | 0.282840(0.000015) | 0.024463(0.000170) | 0.00090(0.0000065) | 191 | 6.48 | 582 | 817 |
| HS84-5 | 0.282916(0.000018) | 0.045125(0.000427) | 0.00165(0.0000169) | 191 | 9.07 | 485 | 652 |
| HS84-6 | 0.282841(0.000016) | 0.023863(0.000227) | 0.00088(0.0000059) | 190 | 6.50 | 581 | 816 |
| HS84-7 | 0.282881(0.000017) | 0.025421(0.000106) | 0.00094(0.0000056) | 191 | 7.91 | 526 | 726 |
| HS84-8 | 0.282857(0.000017) | 0.026894(0.000059) | 0.00101(0.0000022) | 190 | 7.05 | 560 | 780 |
| HS84-9 | 0.282839(0.000016) | 0.033561(0.000297) | 0.00124(0.0000133) | 190 | 6.40 | 589 | 822 |
| HS84-10 | 0.282850(0.000016) | 0.036102(0.000504) | 0.00138(0.0000176) | 192 | 6.78 | 576 | 799 |
| HS84-11 | 0.282845(0.000016) | 0.023576(0.000117) | 0.00090(0.0000043) | 191 | 6.66 | 576 | 806 |
| HS84-12 | 0.282882(0.000018) | 0.040274(0.000244) | 0.00147(0.0000112) | 191 | 7.92 | 531 | 726 |
| HS84-13 | 0.282832(0.000017) | 0.032946(0.000175) | 0.00123(0.0000075) | 190 | 6.16 | 598 | 837 |
| HS84-14 | 0.282821(0.000017) | 0.025838(0.000211) | 0.00096(0.0000064) | 190 | 5.79 | 610 | 861 |
| HS84-15 | 0.282858(0.000015) | 0.031726(0.000102) | 0.00116(0.0000019) | 190 | 7.09 | 560 | 778 |
| HS85-1 | 0.282852(0.000015) | 0.035941(0.000019) | 0.00135(0.0000008) | 191 | 6.83 | 573 | 795 |
| HS85-2 | 0.282862(0.000014) | 0.025235(0.000398) | 0.00093(0.0000125) | 187 | 7.16 | 552 | 771 |
| HS85-3 | 0.282849(0.000015) | 0.021763(0.000065) | 0.00080(0.0000014) | 194 | 6.86 | 569 | 795 |
| HS85-4 | 0.282899(0.000017) | 0.027905(0.000210) | 0.00107(0.0000064) | 191 | 8.54 | 502 | 686 |
| HS85-5 | 0.282809(0.000016) | 0.021743(0.000039) | 0.00082(0.0000014) | 191 | 5.39 | 625 | 887 |
| HS85-6 | 0.282819(0.000016) | 0.033548(0.000169) | 0.00123(0.0000055) | 191 | 5.69 | 618 | 867 |
| HS85-7 | 0.282866(0.000018) | 0.032393(0.000098) | 0.00122(0.0000034) | 190 | 7.35 | 550 | 761 |
| HS85-8 | 0.282844(0.000019) | 0.023586(0.000236) | 0.00090(0.0000070) | 190 | 6.63 | 576 | 807 |
| HS85-9 | 0.282862(0.000016) | 0.026947(0.000190) | 0.00098(0.0000058) | 190 | 7.24 | 552 | 768 |
| HS85-10 | 0.282844(0.000015) | 0.020426(0.000305) | 0.00008(0.0000109) | 191 | 6.71 | 565 | 802 |
| HS85-11 | 0.282865(0.000017) | 0.025375(0.000133) | 0.00090(0.0000007) | 189 | 7.33 | 547 | 762 |
| HS85-12 | 0.282848(0.000016) | 0.026230(0.000142) | 0.00098(0.0000053) | 191 | 6.75 | 573 | 800 |
| HS85-13 | 0.282874(0.000018) | 0.029777(0.000080) | 0.00113(0.0000046) | 192 | 7.67 | 538 | 742 |
| HS85-14 | 0.282857(0.000017) | 0.033489(0.000132) | 0.00124(0.0000048) | 188 | 6.99 | 563 | 783 |
| HS85-15 | 0.282859(0.000017) | 0.021200(0.000146) | 0.00080(0.0000035) | 191 | 7.16 | 554 | 774 |
表2 龙源坝岩体花岗斑岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2 Hf isotopic compositions of zircons from the granite porphyry of Longyuanba pluton
| 分析 点号 | 176Hf/177Hf(2σ) | 176Lu/177Hf(2σ) | 176Yb/177Hf(2σ) | 年龄 (Ma) | εHf(t) | TDM1 (Ma) | TDM2 (Ma) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS84-1 | 0.282827(0.000018) | 0.035444(0.000091) | 0.00131(0.0000042) | 191 | 5.98 | 608 | 850 |
| HS84-2 | 0.282847(0.000016) | 0.023351(0.000014) | 0.00090(0.0000007) | 190 | 6.71 | 573 | 803 |
| HS84-3 | 0.282837(0.000014) | 0.030009(0.000184) | 0.00114(0.0000047) | 191 | 6.34 | 591 | 826 |
| HS84-4 | 0.282840(0.000015) | 0.024463(0.000170) | 0.00090(0.0000065) | 191 | 6.48 | 582 | 817 |
| HS84-5 | 0.282916(0.000018) | 0.045125(0.000427) | 0.00165(0.0000169) | 191 | 9.07 | 485 | 652 |
| HS84-6 | 0.282841(0.000016) | 0.023863(0.000227) | 0.00088(0.0000059) | 190 | 6.50 | 581 | 816 |
| HS84-7 | 0.282881(0.000017) | 0.025421(0.000106) | 0.00094(0.0000056) | 191 | 7.91 | 526 | 726 |
| HS84-8 | 0.282857(0.000017) | 0.026894(0.000059) | 0.00101(0.0000022) | 190 | 7.05 | 560 | 780 |
| HS84-9 | 0.282839(0.000016) | 0.033561(0.000297) | 0.00124(0.0000133) | 190 | 6.40 | 589 | 822 |
| HS84-10 | 0.282850(0.000016) | 0.036102(0.000504) | 0.00138(0.0000176) | 192 | 6.78 | 576 | 799 |
| HS84-11 | 0.282845(0.000016) | 0.023576(0.000117) | 0.00090(0.0000043) | 191 | 6.66 | 576 | 806 |
| HS84-12 | 0.282882(0.000018) | 0.040274(0.000244) | 0.00147(0.0000112) | 191 | 7.92 | 531 | 726 |
| HS84-13 | 0.282832(0.000017) | 0.032946(0.000175) | 0.00123(0.0000075) | 190 | 6.16 | 598 | 837 |
| HS84-14 | 0.282821(0.000017) | 0.025838(0.000211) | 0.00096(0.0000064) | 190 | 5.79 | 610 | 861 |
| HS84-15 | 0.282858(0.000015) | 0.031726(0.000102) | 0.00116(0.0000019) | 190 | 7.09 | 560 | 778 |
| HS85-1 | 0.282852(0.000015) | 0.035941(0.000019) | 0.00135(0.0000008) | 191 | 6.83 | 573 | 795 |
| HS85-2 | 0.282862(0.000014) | 0.025235(0.000398) | 0.00093(0.0000125) | 187 | 7.16 | 552 | 771 |
| HS85-3 | 0.282849(0.000015) | 0.021763(0.000065) | 0.00080(0.0000014) | 194 | 6.86 | 569 | 795 |
| HS85-4 | 0.282899(0.000017) | 0.027905(0.000210) | 0.00107(0.0000064) | 191 | 8.54 | 502 | 686 |
| HS85-5 | 0.282809(0.000016) | 0.021743(0.000039) | 0.00082(0.0000014) | 191 | 5.39 | 625 | 887 |
| HS85-6 | 0.282819(0.000016) | 0.033548(0.000169) | 0.00123(0.0000055) | 191 | 5.69 | 618 | 867 |
| HS85-7 | 0.282866(0.000018) | 0.032393(0.000098) | 0.00122(0.0000034) | 190 | 7.35 | 550 | 761 |
| HS85-8 | 0.282844(0.000019) | 0.023586(0.000236) | 0.00090(0.0000070) | 190 | 6.63 | 576 | 807 |
| HS85-9 | 0.282862(0.000016) | 0.026947(0.000190) | 0.00098(0.0000058) | 190 | 7.24 | 552 | 768 |
| HS85-10 | 0.282844(0.000015) | 0.020426(0.000305) | 0.00008(0.0000109) | 191 | 6.71 | 565 | 802 |
| HS85-11 | 0.282865(0.000017) | 0.025375(0.000133) | 0.00090(0.0000007) | 189 | 7.33 | 547 | 762 |
| HS85-12 | 0.282848(0.000016) | 0.026230(0.000142) | 0.00098(0.0000053) | 191 | 6.75 | 573 | 800 |
| HS85-13 | 0.282874(0.000018) | 0.029777(0.000080) | 0.00113(0.0000046) | 192 | 7.67 | 538 | 742 |
| HS85-14 | 0.282857(0.000017) | 0.033489(0.000132) | 0.00124(0.0000048) | 188 | 6.99 | 563 | 783 |
| HS85-15 | 0.282859(0.000017) | 0.021200(0.000146) | 0.00080(0.0000035) | 191 | 7.16 | 554 | 774 |
| 样号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | TFe2O3 | K2O | MgO | MnO | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | 烧失量 | 总量 | 里特曼 指数 | A/CNK | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-1 | 69.33 | 15.3 | 0.59 | 3.54 | 4.51 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 4.77 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.04 | 99.69 | 3.27 | 1.05 | 1.13 |
| SJ-2 | 69.50 | 15.24 | 0.6 | 3.42 | 4.58 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 4.69 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 1.09 | 99.64 | 3.24 | 1.05 | 1.13 |
| SJ-3 | 68.97 | 15.12 | 1.22 | 3.44 | 4.31 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 4.81 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 1.45 | 100.06 | 3.20 | 0.98 | 1.13 |
| SJ-4 | 69.48 | 15.42 | 0.52 | 3.50 | 4.57 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 4.60 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.17 | 99.61 | 3.18 | 1.09 | 1.16 |
| SJ-5 | 69.56 | 15.40 | 0.54 | 3.49 | 4.58 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 4.60 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.11 | 99.72 | 3.17 | 1.08 | 1.16 |
| SJ-6 | 69.49 | 15.32 | 0.52 | 3.6 | 4.33 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 4.83 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 1.04 | 99.78 | 3.17 | 1.07 | 1.14 |
| HS84 | 69.52 | 15.32 | 0.53 | 3.61 | 4.42 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 4.84 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.22 | 99.91 | 3.23 | 1.06 | 1.13 |
| HS85 | 69.53 | 15.45 | 0.50 | 3.71 | 4.46 | 0.11 | <0.01 | 4.69 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.20 | 99.95 | 3.16 | 1.09 | 1.16 |
表3 龙源坝岩体花岗斑岩主量元素分析结果
Table 3 Analytical results of major elements of granite porphyry from Longyuanba pluton
| 样号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | TFe2O3 | K2O | MgO | MnO | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | 烧失量 | 总量 | 里特曼 指数 | A/CNK | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-1 | 69.33 | 15.3 | 0.59 | 3.54 | 4.51 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 4.77 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.04 | 99.69 | 3.27 | 1.05 | 1.13 |
| SJ-2 | 69.50 | 15.24 | 0.6 | 3.42 | 4.58 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 4.69 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 1.09 | 99.64 | 3.24 | 1.05 | 1.13 |
| SJ-3 | 68.97 | 15.12 | 1.22 | 3.44 | 4.31 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 4.81 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 1.45 | 100.06 | 3.20 | 0.98 | 1.13 |
| SJ-4 | 69.48 | 15.42 | 0.52 | 3.50 | 4.57 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 4.60 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.17 | 99.61 | 3.18 | 1.09 | 1.16 |
| SJ-5 | 69.56 | 15.40 | 0.54 | 3.49 | 4.58 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 4.60 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.11 | 99.72 | 3.17 | 1.08 | 1.16 |
| SJ-6 | 69.49 | 15.32 | 0.52 | 3.6 | 4.33 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 4.83 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 1.04 | 99.78 | 3.17 | 1.07 | 1.14 |
| HS84 | 69.52 | 15.32 | 0.53 | 3.61 | 4.42 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 4.84 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.22 | 99.91 | 3.23 | 1.06 | 1.13 |
| HS85 | 69.53 | 15.45 | 0.50 | 3.71 | 4.46 | 0.11 | <0.01 | 4.69 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 1.20 | 99.95 | 3.16 | 1.09 | 1.16 |
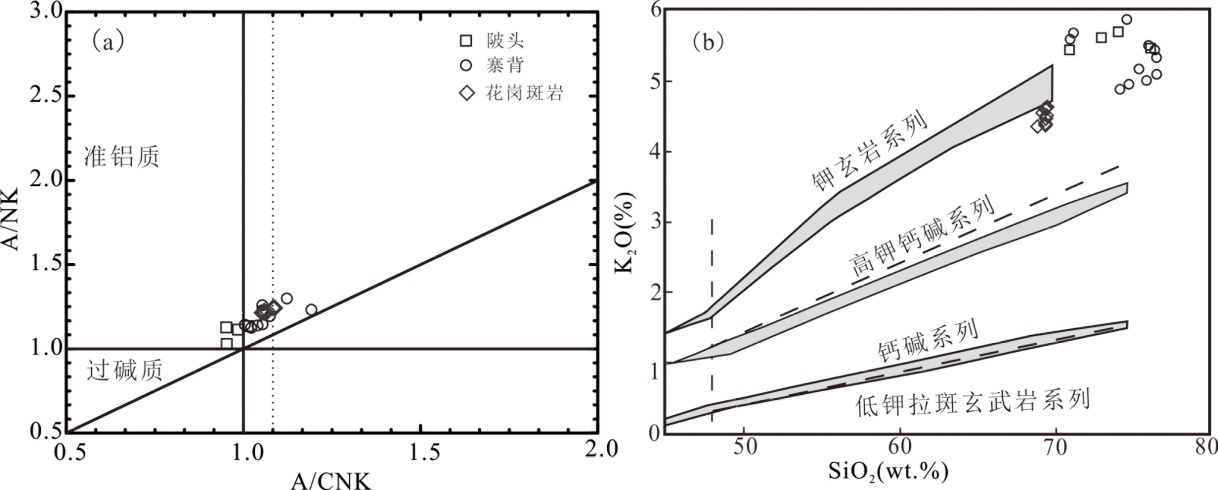
图6 花岗斑岩主量元素地球化学图解(寨背岩体陂头岩体数据分别引自文献[13]和[14])
Fig.6 Major element discrimination diagrams of the granite porphyry (data for the Zhaibei and Pitou plutons sourced from references [13] and [14], respectively)
| 样号 | Ni | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Ba | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-1 | 15.0 | 26.7 | 244 | 169 | 47.3 | 469 | 51.8 | 736 | 12 | 4.37 | 17.9 | 19.8 | 7.32 | 78.5 | |
| SJ-2 | 12.2 | 26.6 | 273 | 129 | 52.4 | 480 | 49.8 | 760 | 12.3 | 4.31 | 18.1 | 22.3 | 8.01 | 62.4 | |
| SJ-3 | 10.7 | 26.6 | 247 | 121 | 54.6 | 479 | 50.4 | 735 | 11.4 | 4.18 | 26.6 | 22.2 | 7.68 | 70.5 | |
| SJ-4 | 7.9 | 26.2 | 269 | 131 | 55.9 | 476 | 50.6 | 747 | 12.5 | 4.42 | 33.1 | 21.2 | 7.78 | 76.6 | |
| SJ-5 | 10.4 | 27.0 | 239 | 127 | 38.0 | 480 | 49 | 722 | 12.9 | 4.4 | 18.8 | 21.8 | 8.01 | 45.3 | |
| SJ-6 | 15.1 | 26.4 | 247 | 128 | 62.9 | 458 | 48.9 | 719 | 12.4 | 4.42 | 20.4 | 21.7 | 9.42 | 84.8 | |
| HS84 | 12.0 | 27.2 | 275 | 130 | 60.5 | 499 | 49.8 | 760 | 11.9 | 4.41 | 18 | 21.9 | 7.07 | 78.3 | |
| HS85 | 7.4 | 26.4 | 236 | 136 | 58.6 | 450 | 50 | 725 | 12.6 | 4.74 | 20.4 | 21.7 | 7.49 | 79.6 | |
| 样号 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | |
| SJ-1 | 120 | 18.3 | 68.9 | 13.4 | 2.64 | 11.7 | 1.73 | 9.55 | 1.85 | 4.99 | 0.71 | 4.53 | 0.70 | 337 | |
| SJ-2 | 84 | 15.8 | 59.6 | 11.8 | 2.24 | 10.7 | 1.6 | 9.16 | 1.89 | 5.14 | 0.75 | 4.91 | 0.74 | 271 | |
| SJ-3 | 91.2 | 16.9 | 63.8 | 11.7 | 2.19 | 10.5 | 1.61 | 9.29 | 1.87 | 5.27 | 0.76 | 4.95 | 0.73 | 291 | |
| SJ-4 | 107 | 18.4 | 69.5 | 13.6 | 2.64 | 12 | 1.8 | 10.4 | 2.01 | 5.62 | 0.77 | 4.89 | 0.74 | 326 | |
| SJ-5 | 92.4 | 11.9 | 44.6 | 8.9 | 1.76 | 7.6 | 1.19 | 7.08 | 1.44 | 4.11 | 0.62 | 4.16 | 0.64 | 232 | |
| SJ-6 | 99.3 | 18.5 | 71.5 | 13.9 | 2.71 | 13.1 | 1.88 | 10.9 | 2.12 | 5.88 | 0.83 | 5.07 | 0.76 | 331 | |
| HS84 | 100 | 20.5 | 79 | 15.4 | 2.83 | 13.2 | 1.9 | 10.7 | 2.09 | 5.76 | 0.82 | 5.16 | 0.77 | 337 | |
| HS85 | 101 | 17.9 | 68.4 | 13.3 | 2.64 | 12.2 | 1.8 | 10.4 | 1.99 | 5.4 | 0.76 | 4.71 | 0.71 | 321 | |
| 样号 | LREE | HREE | L/H | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δEu | Nb/Ta | Nd/Th | Th/U | K/Rb | Nb/La | |||
| SJ-1 | 302 | 35.8 | 8.43 | 11.7 | 3.67 | 2.09 | 0.63 | 7.77 | 0.07 | 0.67 | 153 | 0.47 | |||
| SJ-2 | 236 | 34.9 | 6.75 | 8.6 | 3.32 | 1.77 | 0.6 | 11.9 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 139 | 0.66 | |||
| SJ-3 | 256 | 35.0 | 7.32 | 9.6 | 3.78 | 1.72 | 0.59 | 11.6 | 0.17 | 0.71 | 145 | 0.8 | |||
| SJ-4 | 288 | 38.2 | 7.54 | 10.6 | 3.54 | 1.99 | 0.62 | 12.1 | 0.18 | 0.67 | 141 | 0.71 | |||
| SJ-5 | 205 | 26.8 | 7.64 | 7.3 | 3.19 | 1.47 | 0.64 | 11.5 | 0.21 | 0.67 | 159 | 0.66 | |||
| SJ-6 | 291 | 40.6 | 7.17 | 11.3 | 3.83 | 2.09 | 0.6 | 11.1 | 0.13 | 0.57 | 146 | 1.08 | |||
| HS84 | 296 | 40.4 | 7.33 | 10.2 | 3.20 | 2.06 | 0.59 | 11.1 | 0.21 | 0.77 | 133 | 0.58 | |||
| HS85 | 283 | 38.0 | 7.46 | 11.4 | 3.77 | 2.09 | 0.62 | 11.3 | 0.23 | 0.72 | 157 | 0.64 | |||
表4 龙源坝岩体花岗斑岩微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 4 Aalytical results of trace and rare earth elements of granite porphyry from Longyuanba pluton
| 样号 | Ni | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Ba | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ-1 | 15.0 | 26.7 | 244 | 169 | 47.3 | 469 | 51.8 | 736 | 12 | 4.37 | 17.9 | 19.8 | 7.32 | 78.5 | |
| SJ-2 | 12.2 | 26.6 | 273 | 129 | 52.4 | 480 | 49.8 | 760 | 12.3 | 4.31 | 18.1 | 22.3 | 8.01 | 62.4 | |
| SJ-3 | 10.7 | 26.6 | 247 | 121 | 54.6 | 479 | 50.4 | 735 | 11.4 | 4.18 | 26.6 | 22.2 | 7.68 | 70.5 | |
| SJ-4 | 7.9 | 26.2 | 269 | 131 | 55.9 | 476 | 50.6 | 747 | 12.5 | 4.42 | 33.1 | 21.2 | 7.78 | 76.6 | |
| SJ-5 | 10.4 | 27.0 | 239 | 127 | 38.0 | 480 | 49 | 722 | 12.9 | 4.4 | 18.8 | 21.8 | 8.01 | 45.3 | |
| SJ-6 | 15.1 | 26.4 | 247 | 128 | 62.9 | 458 | 48.9 | 719 | 12.4 | 4.42 | 20.4 | 21.7 | 9.42 | 84.8 | |
| HS84 | 12.0 | 27.2 | 275 | 130 | 60.5 | 499 | 49.8 | 760 | 11.9 | 4.41 | 18 | 21.9 | 7.07 | 78.3 | |
| HS85 | 7.4 | 26.4 | 236 | 136 | 58.6 | 450 | 50 | 725 | 12.6 | 4.74 | 20.4 | 21.7 | 7.49 | 79.6 | |
| 样号 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | |
| SJ-1 | 120 | 18.3 | 68.9 | 13.4 | 2.64 | 11.7 | 1.73 | 9.55 | 1.85 | 4.99 | 0.71 | 4.53 | 0.70 | 337 | |
| SJ-2 | 84 | 15.8 | 59.6 | 11.8 | 2.24 | 10.7 | 1.6 | 9.16 | 1.89 | 5.14 | 0.75 | 4.91 | 0.74 | 271 | |
| SJ-3 | 91.2 | 16.9 | 63.8 | 11.7 | 2.19 | 10.5 | 1.61 | 9.29 | 1.87 | 5.27 | 0.76 | 4.95 | 0.73 | 291 | |
| SJ-4 | 107 | 18.4 | 69.5 | 13.6 | 2.64 | 12 | 1.8 | 10.4 | 2.01 | 5.62 | 0.77 | 4.89 | 0.74 | 326 | |
| SJ-5 | 92.4 | 11.9 | 44.6 | 8.9 | 1.76 | 7.6 | 1.19 | 7.08 | 1.44 | 4.11 | 0.62 | 4.16 | 0.64 | 232 | |
| SJ-6 | 99.3 | 18.5 | 71.5 | 13.9 | 2.71 | 13.1 | 1.88 | 10.9 | 2.12 | 5.88 | 0.83 | 5.07 | 0.76 | 331 | |
| HS84 | 100 | 20.5 | 79 | 15.4 | 2.83 | 13.2 | 1.9 | 10.7 | 2.09 | 5.76 | 0.82 | 5.16 | 0.77 | 337 | |
| HS85 | 101 | 17.9 | 68.4 | 13.3 | 2.64 | 12.2 | 1.8 | 10.4 | 1.99 | 5.4 | 0.76 | 4.71 | 0.71 | 321 | |
| 样号 | LREE | HREE | L/H | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δEu | Nb/Ta | Nd/Th | Th/U | K/Rb | Nb/La | |||
| SJ-1 | 302 | 35.8 | 8.43 | 11.7 | 3.67 | 2.09 | 0.63 | 7.77 | 0.07 | 0.67 | 153 | 0.47 | |||
| SJ-2 | 236 | 34.9 | 6.75 | 8.6 | 3.32 | 1.77 | 0.6 | 11.9 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 139 | 0.66 | |||
| SJ-3 | 256 | 35.0 | 7.32 | 9.6 | 3.78 | 1.72 | 0.59 | 11.6 | 0.17 | 0.71 | 145 | 0.8 | |||
| SJ-4 | 288 | 38.2 | 7.54 | 10.6 | 3.54 | 1.99 | 0.62 | 12.1 | 0.18 | 0.67 | 141 | 0.71 | |||
| SJ-5 | 205 | 26.8 | 7.64 | 7.3 | 3.19 | 1.47 | 0.64 | 11.5 | 0.21 | 0.67 | 159 | 0.66 | |||
| SJ-6 | 291 | 40.6 | 7.17 | 11.3 | 3.83 | 2.09 | 0.6 | 11.1 | 0.13 | 0.57 | 146 | 1.08 | |||
| HS84 | 296 | 40.4 | 7.33 | 10.2 | 3.20 | 2.06 | 0.59 | 11.1 | 0.21 | 0.77 | 133 | 0.58 | |||
| HS85 | 283 | 38.0 | 7.46 | 11.4 | 3.77 | 2.09 | 0.62 | 11.3 | 0.23 | 0.72 | 157 | 0.64 | |||

图7 花岗斑岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图和稀土元素球粒陨石化标准化配分曲线(标准化数据据文献[16];花岗岩数据引自文献[3]和[4])
Fig.7 Primitive mantle-normalized multi-element and chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the granite porphyry(Normalization values after reference [16], and granites samples data from references [3] and [4] )
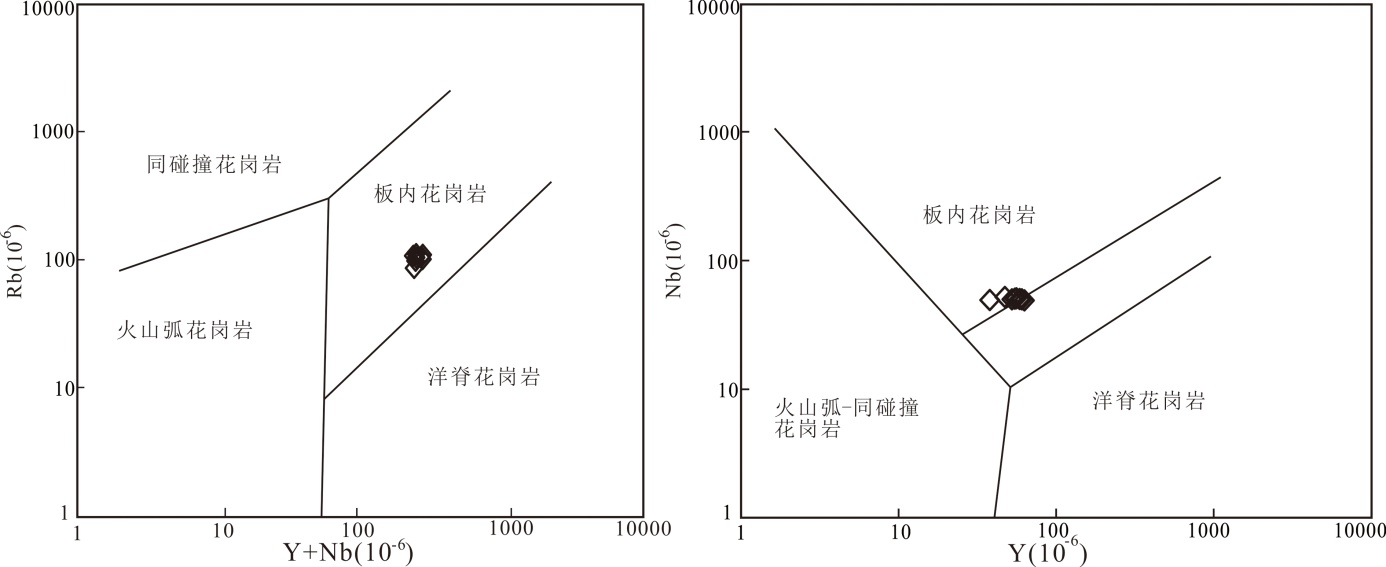
图11 上窖矿床花岗斑岩(Y+Nb)-Rb和Y-Nb构造判别图 (底图据文献[48])
Fig.11 (Y+Nb) vs.Rb and Y vs.Nb tectonic discrimination diagrams of granite porphyry in Shangjiao deposit(base map after reference [48])
| 序号 | 位置 | 岩石类型 | 年龄 (Ma) | 资料 来源 | 序号 | 位置 | 岩石类型 | 年龄 (Ma) | 资料 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 桂北圆石山 | A型花岗岩 | 179±2 | [ | 23 | 东坑盆地 | 辉长-辉绿岩 | 196±1 | [ |
| 2 | 宁远—新田 | 玄武岩 | 174~179 | [ | 24 | 临江盆地 | 玄武岩英安岩 | 173.7~174.9 | [ |
| 3 | 宜章 | 玄武岩 | 175 | [ | 25 | 车步 | 辉长岩 | 191 | [ |
| 4 | 长城岭 | 玄武岩 | 178 | [ | 26 | 寨背 | A型花岗岩 | 189 | [ |
| 5 | 下庄 | NWW辉绿岩 | 193±4 | [ | 27 | 柯树北 | A型花岗岩 | 189 | [ |
| 6 | 下庄 | 苦竹坑辉长岩 | 198±1 | [ | 28 | 隘高 | 辉绿岩 | 189 | [ |
| 7 | 下庄 | NWW基性岩 | 200~190 | [ | 29 | 白面石盆地 | 玄武岩 | 188 | [ |
| 8 | 船肚 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 175 | [ | 30 | 菖蒲盆地 | 玄武岩 | 191.9±2.2 | [ |
| 9 | 大宝山 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 175.8±1.5 | [ | 31 | 菖蒲盆地 | 流纹岩 | 195.2±2.8 | [ |
| 10 | 笋洞岩体 | S型花岗岩 | 189.1±0.7 | [ | 32 | 寻乌盆地 | 玄武岩 | 173 | [ |
| 11 | 含湖 | 花岗闪长岩辉长岩 | 193 196 | [ | 33 | 霞岚岩体 | 辉长岩 | 194±1 | [ |
| 12 | 黄埠 | 正长岩 | 179.3 | [ | 34 | 霞岚岩体 | 闪长岩 | 191~192 | [ |
| 13 | 龙源坝 | 正长岩 | 196.3±1.4 | [ | 35 | 霞岚岩体 | A型花岗岩 | 190~195 | [ |
| 14 | 陂头 | A型花岗岩 | 186.3±1.1 | [ | 36 | 梅州 | 辉长岩 | 178 | [ |
| 15 | 塔背 | 正长岩 | 188.6±2.2 | [ | 37 | 温公 | A型花岗岩 | 192 | [ |
| 16 | 龙源坝花岗斑岩 | A型花岗岩 | 190.6 | 本文 | 38 | 田东花岗岩 | 中粒花岗岩 | 191.5±0.9 | [ |
| 17 | 龙南盆地 | 英安岩 | 191±1.7 | [ | 39 | 田东花岗岩 | 细粒斑状钾长花岗岩(I型) | 188 | [ |
| 18 | 程龙 | 辉长岩 | 197 | [ | 40 | 会昌盆地 | 粗面玄武岩 | 181 | [ |
| 19 | 石背 | A型花岗岩 | 189.0±1.5 | [ | 41 | 永定盆地 | 流纹岩、花岗斑岩 | 179~188 | [ |
| 20 | 石背 | 二长花岗岩 | 187.5±1.8 | [ | 42 | 永定盆地 | 玄武岩 | 178 | [ |
| 21 | 石背 | 花岗闪长岩 | 186.9±2.0 | [ | 43 | 光泽 | A型花岗岩 | 189 | [ |
| 22 | 东坑盆地 | 玄武岩 | 194.4±2.0 | [ | 44 | 大坪花岗斑岩 | A型花岗岩 | 186.7±1.2 190.7±1.1 | [ |
| 23 | 东坑盆地 | 花岗闪长岩 | 193±2 | [ | 45 | 福建锦城 | I型花岗岩 | 187 | [ |
表5 华南地区EW向岩浆岩带200~170 Ma岩石统计
Table 5 200~170 Ma magmatic rocks from the EW magmatic belt in South China
| 序号 | 位置 | 岩石类型 | 年龄 (Ma) | 资料 来源 | 序号 | 位置 | 岩石类型 | 年龄 (Ma) | 资料 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 桂北圆石山 | A型花岗岩 | 179±2 | [ | 23 | 东坑盆地 | 辉长-辉绿岩 | 196±1 | [ |
| 2 | 宁远—新田 | 玄武岩 | 174~179 | [ | 24 | 临江盆地 | 玄武岩英安岩 | 173.7~174.9 | [ |
| 3 | 宜章 | 玄武岩 | 175 | [ | 25 | 车步 | 辉长岩 | 191 | [ |
| 4 | 长城岭 | 玄武岩 | 178 | [ | 26 | 寨背 | A型花岗岩 | 189 | [ |
| 5 | 下庄 | NWW辉绿岩 | 193±4 | [ | 27 | 柯树北 | A型花岗岩 | 189 | [ |
| 6 | 下庄 | 苦竹坑辉长岩 | 198±1 | [ | 28 | 隘高 | 辉绿岩 | 189 | [ |
| 7 | 下庄 | NWW基性岩 | 200~190 | [ | 29 | 白面石盆地 | 玄武岩 | 188 | [ |
| 8 | 船肚 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 175 | [ | 30 | 菖蒲盆地 | 玄武岩 | 191.9±2.2 | [ |
| 9 | 大宝山 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 175.8±1.5 | [ | 31 | 菖蒲盆地 | 流纹岩 | 195.2±2.8 | [ |
| 10 | 笋洞岩体 | S型花岗岩 | 189.1±0.7 | [ | 32 | 寻乌盆地 | 玄武岩 | 173 | [ |
| 11 | 含湖 | 花岗闪长岩辉长岩 | 193 196 | [ | 33 | 霞岚岩体 | 辉长岩 | 194±1 | [ |
| 12 | 黄埠 | 正长岩 | 179.3 | [ | 34 | 霞岚岩体 | 闪长岩 | 191~192 | [ |
| 13 | 龙源坝 | 正长岩 | 196.3±1.4 | [ | 35 | 霞岚岩体 | A型花岗岩 | 190~195 | [ |
| 14 | 陂头 | A型花岗岩 | 186.3±1.1 | [ | 36 | 梅州 | 辉长岩 | 178 | [ |
| 15 | 塔背 | 正长岩 | 188.6±2.2 | [ | 37 | 温公 | A型花岗岩 | 192 | [ |
| 16 | 龙源坝花岗斑岩 | A型花岗岩 | 190.6 | 本文 | 38 | 田东花岗岩 | 中粒花岗岩 | 191.5±0.9 | [ |
| 17 | 龙南盆地 | 英安岩 | 191±1.7 | [ | 39 | 田东花岗岩 | 细粒斑状钾长花岗岩(I型) | 188 | [ |
| 18 | 程龙 | 辉长岩 | 197 | [ | 40 | 会昌盆地 | 粗面玄武岩 | 181 | [ |
| 19 | 石背 | A型花岗岩 | 189.0±1.5 | [ | 41 | 永定盆地 | 流纹岩、花岗斑岩 | 179~188 | [ |
| 20 | 石背 | 二长花岗岩 | 187.5±1.8 | [ | 42 | 永定盆地 | 玄武岩 | 178 | [ |
| 21 | 石背 | 花岗闪长岩 | 186.9±2.0 | [ | 43 | 光泽 | A型花岗岩 | 189 | [ |
| 22 | 东坑盆地 | 玄武岩 | 194.4±2.0 | [ | 44 | 大坪花岗斑岩 | A型花岗岩 | 186.7±1.2 190.7±1.1 | [ |
| 23 | 东坑盆地 | 花岗闪长岩 | 193±2 | [ | 45 | 福建锦城 | I型花岗岩 | 187 | [ |
| [1] | 赖静, 祁家明, 陈军军, 等. 粤北青嶂山岩体江头矿区铀矿微区矿物学、年代学特征及其成矿动力背景制约[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(4): 1128-1142. |
| [2] | 张敏, 陈培荣, 黄国龙, 等. 南岭东段龙源坝复式岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(7): 984-994. |
| [3] | 张敏, 陈培荣, 黄国龙, 等. 南岭龙源坝复式岩体的地球化学特征研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 2006, 22(6): 336-344. |
| [4] | 陶继华, 李武显, 李献华, 等. 赣南龙源坝地区燕山期高分异花岗岩年代学、地球化学及锆石Hf-O同位素研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(5):770-788. |
| [5] | 聂斌, 张万良. 赣南黄沙矿区辉绿岩Ar-Ar年龄及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 矿产与地质, 2018, 32(3): 390-396. |
| [6] | 周新民. 南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. |
| [7] | BOUVIER A, VERVOORT J D, PATCHETT P J. The Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(1/2): 48-57. |
| [8] | SÖDERLUND U, PATCHETT P J, VERVOORT J D, et al. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219(3/4): 311-324. |
| [9] | GRIFFIN W L, PEARSON N J, BELOUSOVA E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1): 133-147. |
| [10] | GRIFFIN W L, WANG X, JACKSON S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: in situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3/4): 237-269. |
| [11] | ELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622. |
| [12] | SMITH R E, SMITH S E. Comments on the use of Ti, Zr, Y, Sr, K, P and Nb in classification of basaltic magmas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 32(2): 114-120. |
| [13] | LI X H, CHEN Z, LIU D Y, et al. Jurassic gabbro-granitesyenitesuites from southern Jiangxi Province, SE China: Age,origin,and tectonic significance[J]. International Geology Review, 2003, 45: 898-921. |
| [14] | 陈培荣, 周新民, 张文兰, 等. 南岭东段燕山早期正长岩-花岗岩杂岩的成因和意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2004, 34(6):493-503. |
| [15] | 桑隆康, 马昌前. 岩石学[M]. 2版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012. |
| [16] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. |
| [17] | WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. |
| [18] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Eerth and Enviromental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1992, 83(1/2): 1-26. |
| [19] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America, Abstracts with Programs, 1979, 11: 468. |
| [20] | BREITER K, LAMARÃO C N, BORGES R M K, et al. Chemical characteristics of zircon from A-type granites and comparison to zircon of S-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2014, 192: 208-225. |
| [21] | 李小伟, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 关于A型花岗岩判别过程中若干问题的讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(S1): 278-285. |
| [22] | WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2): 295-304. |
| [23] | EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641. |
| [24] | BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1/2):1-29. |
| [25] | YANG J H, WU F Y, CHUNG S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, NorthEast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1/2): 89-106. |
| [26] | CHEN Y X, LI H, SUN W D, et al. Generation of late Mesozoic qianlishan A2-type granite in Nanling range, South China: Implications for Shizhuyuan W-Sn mineralization and tectonic evolution[J]. Lithos, 2016, 266: 435-452. |
| [27] | SKJERLIE K P, JOHNSTON A D. Vapor-absent melting at 10 kbar of a biotite- and amphibole-bearing tonalitic gneiss: Implications for the generation of A-type granites[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(3): 263. |
| [28] | KING P L, WHITE A J R, CHAPPELL B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt,southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3): 371-391. |
| [29] | PATIÑO DOUCE A E. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8): 743. |
| [30] | ANDERSON D L. Large igneous provinces, delamination, and fertile mantle[J]. Elements, 2005, 1(5): 271-275. |
| [31] | BEA F, ARZAMASTSEV A, MONTERO P, et al. Anomalous alkaline rocks of soustov, kola: Evidence of mantle-derived metasomatic fluids affecting crustal materials[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2001, 140(5): 554-566. |
| [32] | BARTH M G, MCDONOUGH W F, RUDNICK R L. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 165(3/4): 197-213. |
| [33] | HOFMANN A W, JOCHUM K P, SEUFERT M, et al. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: New constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(1/2): 33-45. |
| [34] | GAN C S, WANG Y J, QIAN X, et al. Constraints of the Xialan gabbroic intrusion in the eastern Nanling Range on the Early Jurassic intra-continental extension in eastern South China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 145: 576-590. |
| [35] | 刘潜, 于津海, 苏斌, 等. 福建锦城187Ma花岗岩的发现: 对华南沿海早侏罗世构造演化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(12): 3575-3589. |
| [36] | 舒徐洁. 华南南岭地区中生代花岗岩成因与地壳演化[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. |
| [37] | 周佐民. 华南晚中生代多旋回构造-岩浆演化及地热成因机制: 来自广东省典型岩体的制约[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2015. |
| [38] | WYLIIE P J. Constraints imposed by experimental petrology on possible and impossible magma sources and products[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1984, 310(1514): 439-456. |
| [39] | 毛建仁, 厉子龙, 叶海敏. 华南中生代构造-岩浆活动研究: 现状与前景[J]. 中国科学( 地球科学), 2014, 44 (12): 2593-2617. |
| [40] | COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200. |
| [41] | FROST C D, FROST B R, CHAMBERLAIN K R, et al. Petrogenesis of the 1.43 Ga Sherman batholith, SE Wyoming, USA: A reduced, rapakivi-type anorogenic granite[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1999, 40(12): 1771-1802. |
| [42] | FROST C D, FROST B R. On ferroan (A-type) granitoids: Their compositional variability and modes of origin[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2011, 52(1): 39-53. |
| [43] | ZHOU Y Y, ZHAI M G, ZHAO T P, et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of the early Paleoproterozoic potassic granite in the Lushan area, southern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 94: 190-204. |
| [44] | ZHENG Y F. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328: 5-48. |
| [45] | LÓPEZ S, CASTRO A. Determination of the fluid—absent solidus and supersolidus phase relationships of MORB-derived amphibolites in the range 4-14 kbar[J]. American Mineralogist, 2001, 86(11/12): 1396-1403. |
| [46] | XIAO L, CLEMENS J D. Origin of potassic (C-type) adakite magmas: Experimental and field constraints[J]. Lithos, 2007, 95(3/4): 399-414. |
| [47] | 舒良树. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(7): 1035-1053. |
| [48] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. |
| [49] | JAHN B M. Mesozoic thermal events in Southeast China[J]. Nature, 1974, 248: 480-483. |
| [50] | ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 326(3/4): 269-287. |
| [51] | ZHOU X M, SUN T, SHEN W Z, et al. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 2006, 29(1): 26-33. |
| [52] | LI Z X, LI X H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(2): 179. |
| [53] | CHEN L, ZHAO Z F, ZHENG Y F. Origin of andesitic rocks: Geochemical constraints from Mesozoic volcanics in the Luzong basin, South China[J]. Lithos, 2014, 190: 220-239. |
| [54] | 谢昕, 徐夕生, 邹海波, 等. 中国东南部晚中生代大规模岩浆作用序幕: J2早期玄武岩[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2005, 35(7): 587-605. |
| [55] | 丁兴, 陈培荣, 陈卫锋, 等. 湖南沩山花岗岩中锆石LA-ICP MS U-Pb定年: 成岩启示和意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2005(7): 606-616. |
| [56] | HE Z Y, XU X S, NIU Y L. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic granite-syenite-gabbro association from inland South China[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(3/4):621-641. |
| [57] | 余心起, 狄永军, 吴淦国, 等. 粤北存在早侏罗世的岩浆活动:来自霞岚杂岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2009, 39(6): 681-693. |
| [58] | 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(3): 257-279. |
| [59] | 许美辉. 福建省永定地区早侏罗世双峰式火山岩及其构造环境[J]. 福建地质, 1992, 11(2): 115-125. |
| [60] | 陈迪, 马爱军, 刘伟, 等. 湖南锡田花岗岩体锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 819-830. |
| [61] | 贾小辉, 王晓地, 杨文强, 等. 桂北圆石山早侏罗世A型花岗岩的岩石成因及意义[J]. 地球科学, 2014, 39(1): 21-36. |
| [62] | LI X H, CHUNG S L, ZHOU H W, et al. Jurassic intraplate magmatism in southern Hunan-eastern Guangxi:40Ar/39Ar dating, geochemistry, Sr-Nd isotopes and implications for the tectonic evolution of SE China[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2004, 226(1): 193-215. |
| [63] | 赵振华, 包志伟, 张伯友. 湘南中生代玄武岩类地球化学特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 1998, 28(S2): 7-14. |
| [64] | WANG L X, MA C Q, LAI Z X, et al. Early Jurassic mafic dykes from the Xiazhuang ore district (South China): Implications for tectonic evolution and uranium metallogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2015, 239: 71-85. |
| [65] | 骆金诚, 齐有强, 王连训, 等. 粤北下庄铀矿田基性岩脉Ar-Ar定年及其与铀成矿关系新认识[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(9): 2660-2678. |
| [66] | 王磊, 胡明安, 杨振, 等. 粤北大宝山矿区花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2010, 35(2): 175-185. |
| [67] | 凌洪飞, 沈渭洲, 邓平, 等. 粤北笋洞花岗岩的形成时代、地球化学特征与成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(3): 413-424. |
| [68] | YU X Q, WU G G, ZHAO X X, et al. The Early Jurassic tectono-magmatic events in southern Jiangxi and northern Guangdong provinces, SE China: Constraints from the SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 39(5): 408-422. |
| [69] | HE Zhenyu, XU Xisheng, CHEN Rong, et al. Genesis of Middle Jurassic syenite-gabbro in southern Jiangxi Province and their geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(6):1457-1469. |
| [70] | YANG J H, ZHANG J H, CHEN J Y, et al. Mesozoic continental crustal rejuvenation of South China: Insights from zircon HfO isotopes of Early Jurassic gabbros, syenites and A-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2021, 402: 105678. |
| [71] | 冀春雨, 巫建华. 江西南部余田群长英质火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 33(2): 131-138. |
| [72] | 王国昌. 闽西北与赣南地区中生代侵入岩成因及其地球动力学意义研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2016. |
| [73] | ZHAO P L, ZHAO H J, YUAN S D, et al. The Early Jurassic Fe-Sn metallogenic event and its geodynamic setting in South China: Evidence from Re-Os, U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Dading magnesian skarn Fe-Sn deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 111: 102970. |
| [74] | 程顺波, 付建明, 马丽艳, 等. 南岭地区早侏罗世成矿作用: 来自粤北大顶铁锡矿床LA-ICP-MS和Ar-Ar年代学证据[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(1): 163-176. |
| [75] | 项媛馨, 巫建华. 赣南龙南地区余田群玄武岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(5): 716-725. |
| [76] | 章邦桐, 陈培荣, 孔兴功. 赣南临江盆地余田群双峰式火山岩的Rb-Sr年代学研究[J]. 中国地质, 2002, 29(4): 351-354. |
| [77] | ZHANG D, ZHAO K D, CHEN W, et al. Early Jurassic mafic dykes from the Aigao uranium ore deposit in South China: Geochronology, petrogenesis and relationship with uranium mineralization[J]. Lithos, 2018, 308: 118-133. |
| [78] | CEN T, LI W X, WANG X C, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Jurassic basalts in southern Jiangxi Province, South China: Implications for the thermal state of the Mesozoic mantle beneath South China[J]. Lithos, 2016, 256: 311-330. |
| [79] | 陈培荣, 孔兴功, 王银喜, 等. 赣南燕山早期双峰式火山-侵入杂岩的Rb-Sr同位素定年及意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 1999, 5(4): 378-383. |
| [80] | 邢光福, 杨祝良, 孙强辉, 等. 广东梅州早侏罗世层状基性-超基性岩体研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(3): 172-175. |
| [81] | ZHU W G, ZHONG H, LI X H, et al. The Early Jurassic mafic-ultramafic intrusion and A-type granite from northeastern Guangdong, SE China: Age, origin, and tectonic significance[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(3/4): 313-329. |
| [82] | 刘鹏, 程彦博, 毛景文, 等. 粤东田东钨锡多金属矿床花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(7): 1244-1257. |
| [83] | 周金城, 陈荣. 闽东南晚中生代壳幔作用地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 2001, 30(6): 547-558. |
| [84] | 王锦荣, 张哲坤, 凌明星, 等. 南岭早侏罗世稀有金属成矿作用研究: 以闽西南大坪花岗斑岩为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1): 125-140. |
| [85] | GILDER S A, GILL J, COE R S, et al. Isotopic and paleomagnetic constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of South China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1996, 101(B7): 16137-16154. |
| [1] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 王翠彭, 史宏江, 鞠楠, 何云龙. 大兴安岭北段呼玛地区晚石炭世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征:对古亚洲洋构造演化的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 62-82. |
| [2] | 刘孝锐, 路俊刚, 谭开俊, 廖建波, 龙礼文, 陈世加, 李勇, 肖正录. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部HQ地区长7段烃源岩地球化学特征与长8段原油来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1306-1324. |
| [3] | 郑英, 韩杰, 张小永, 缑明亮, 王明, 袁博武. 柴达木盆地东北部拉合根地区中生代火山岩的发现及其地质意义:来自地球化学与锆石年代学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1147-1161. |
| [4] | 张德富, 王先广, 何涛, 曹明轩, 吕婷婷, 龚良信, 徐进. 赣南加里东期重稀土矿赋矿母岩岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 959-976. |
| [5] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [6] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [7] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [8] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [9] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [10] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [11] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [12] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [13] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [14] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [15] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||