



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (01): 128-153.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.082
何云龙1( ), 张国宾1,2(
), 张国宾1,2( ), 杨言辰3, 冯玥1, 孔金贵1, 陈兴凯4
), 杨言辰3, 冯玥1, 孔金贵1, 陈兴凯4
收稿日期:2023-05-08
修回日期:2023-08-15
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
张国宾,男,副教授,硕士生导师,1983年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,主要从事矿床学与矿产勘查方向的科研与教学。Email:作者简介:何云龙,男,硕士研究生,1999年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,主要从事岩石学、矿床学方面的研究。Email:hyl991206@163.com。
基金资助:
HE Yunlong1( ), ZHANG Guobin1,2(
), ZHANG Guobin1,2( ), YANG Yanchen3, FENG Yue1, KONG Jingui1, CHEN Xingkai4
), YANG Yanchen3, FENG Yue1, KONG Jingui1, CHEN Xingkai4
Received:2023-05-08
Revised:2023-08-15
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-03-20
摘要:
黑龙江省虎林市四平山金矿床位于那丹哈达地体东部,为该地体中规模最大的金矿床,已探明金资源量5.8 t,矿体赋存于四平山组硅质岩、硅质角砾岩以及大塔山林场组流纹岩中。为了进一步厘定成岩成矿时代,阐释成矿过程,查明成岩成矿地球动力学背景,本文在四平山金矿床进行详细的野外调查基础上,以四平山组硅质岩、硅质角砾岩和大塔山林场组流纹岩为研究对象,开展赋矿围岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和全岩主微量组成测试,以及含金石英脉流体包裹体热力学分析。结果表明,大塔山林场组流纹岩(SPS-H-002、SPS-H-009)的成岩年龄分别为(134±1)Ma和(123±1) Ma,金矿化时代略晚于流纹岩的成岩时代,属于早白垩世晚期;硅质岩和硅质角砾岩具有较高的SiO2含量,富集Cu、Ni、Ba元素而贫Co元素,ΣREE含量较低,轻重稀土分异程度不明显,具有铕正异常,形成于热水沉积作用;流纹岩具有高硅、富铝、贫钛锰磷和低Zr含量,为亚碱性过铝质钙碱性-高钾钙碱性系列岩石,轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损,具有明显的铕负异常,无铈异常,属于高分异S型花岗岩,可能为亏损地幔增生的年轻地壳物质部分熔融的产物;含金石英脉中流体包裹体大小介于5~12 μm之间,呈椭圆形和不规则形状成群或孤立分布,均一温度为118.7~223.4 ℃,盐度为0.40%~8.9%,密度为0.84~0.97 g/cm3,捕获压力为21.2~51.4 MPa, δD值为 -113.8‰~-84.0‰, δ18$O_{H_{2}O}$值为 -3.1‰~2.2‰,成矿流体以岩浆水为主,并显示出岩浆水与大气降水混合的特点。结合区域构造演化,认为四平山金矿床形成于碰撞后构造背景,成矿与古太平洋板块俯冲作用密切相关。
中图分类号:
何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153.
HE Yunlong, ZHANG Guobin, YANG Yanchen, FENG Yue, KONG Jingui, CHEN Xingkai. Genesis and Tectonics of the Sipingshan Gold Deposit in Nadanhada Terrane, Sikhote-Alin Orogen: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Chronology, Petrological and Fluid Geochemistry[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(01): 128-153.
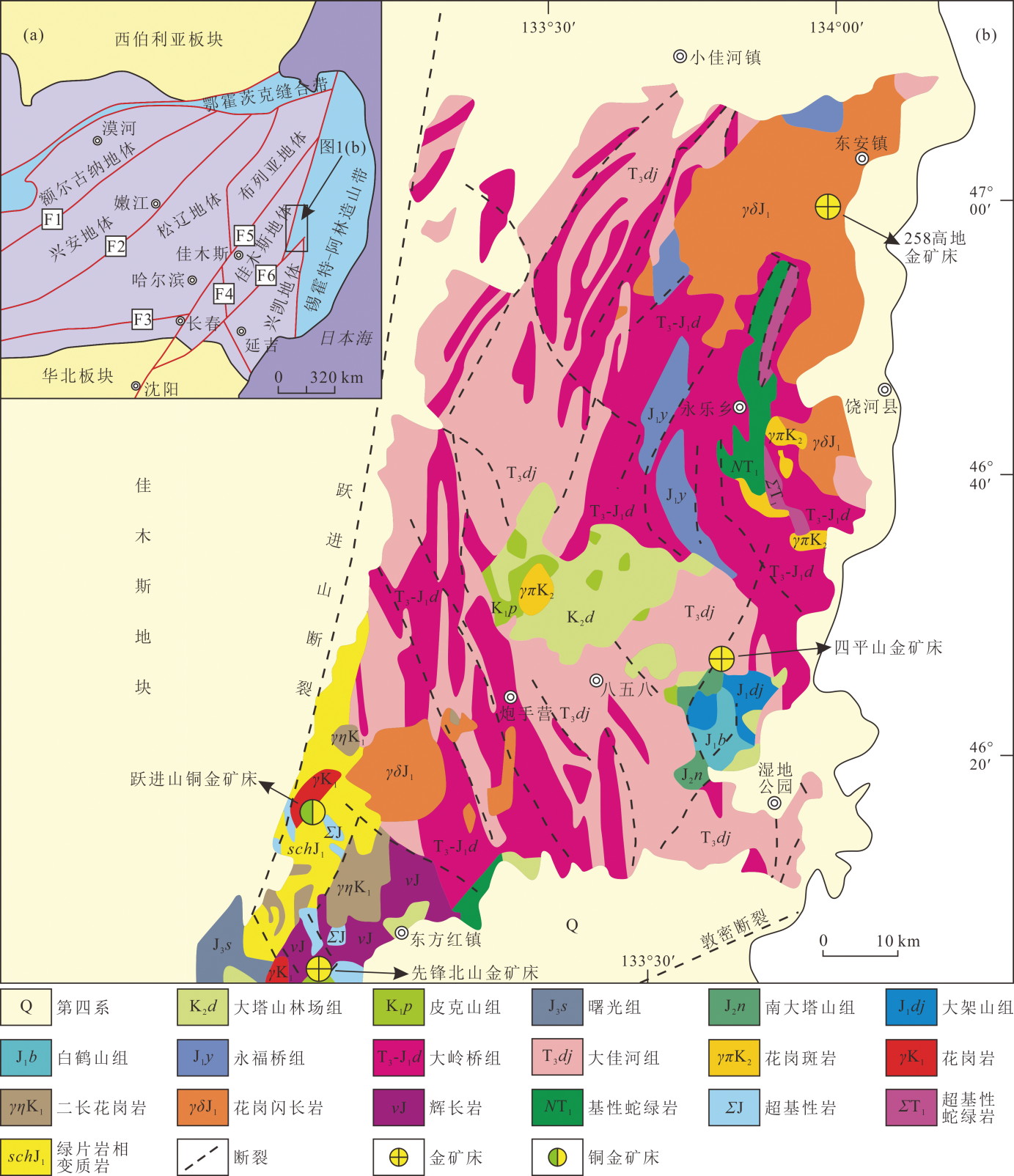
图1 东北地区大地构造单元划分图(a) (底图据文献[38]修改)和那丹哈达地体区域地质图(b) (底图据文献[39]修改) F1.新林—喜贵图缝合带;F2.贺根山—黑河缝合带;F3.索伦—西拉木伦—长春缝合带;F4.牡丹江断裂;F5.伊通—依兰断裂;F6.敦化—密山断裂
Fig.1 Division of tectonic units in Northeast China (a) (modified after reference [38]) and regional geological map of the Nadanhada terrane (b) (modified after reference [39])

图2 四平山金矿床大地构造位置图(a)、矿区地质图(b)和勘探线剖面图(c)(底图据文献[27]修改)
Fig.2 Tectonic map (a), geological map (b) and exploration line profile (c) of the Sipingshan gold deposit (modified after reference [27])

图3 四平山金矿床野外及显微镜下照片 (a) 灰白色硅质岩;(b) 硅质岩被晚期石英脉穿切,正交偏光;(c) 灰黄色硅质角砾岩;(d) 硅化角砾;(e) (f).灰-灰白色流纹岩;(g) 流纹岩正交镜下偏光照片;(h) 黄铁矿化硅质岩;(i) 含矿硅质角砾岩;(j) 团块状黄铁矿,反射光;(k) (l) 颗粒状黄铁矿,反射光。Qz.石英;Opl.蛋白石;Cln.玉髓;Pl.斜长石;Py.黄铁矿
Fig.3 Field and microscopic photos of the Sipingshan gold deposit
| 测点号 | wB(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | U-Pb年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1 σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1 σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1 σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1 σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1 σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1 σ | |||
| SPS-H-002-01 | 529 | 1972 | 0.27 | 0.07107 | 0.00474 | 0.22920 | 0.04211 | 0.02107 | 0.00036 | 959 | 136 | 210 | 35 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-02 | 358 | 1127 | 0.32 | 0.09041 | 0.00413 | 0.25974 | 0.01705 | 0.02115 | 0.00056 | 1433 | 87 | 234 | 14 | 135 | 4 | |
| SPS-H-002-03 | 418 | 1237 | 0.34 | 0.05271 | 0.00261 | 0.15180 | 0.01130 | 0.02106 | 0.00028 | 315 | 113 | 143 | 10 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-04 | 321 | 1215 | 0.26 | 0.06642 | 0.00174 | 0.19492 | 0.05620 | 0.02101 | 0.00018 | 819 | 55 | 181 | 48 | 134 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-002-05 | 308 | 1028 | 0.30 | 0.05314 | 0.00194 | 0.15739 | 0.06309 | 0.02112 | 0.00016 | 334 | 83 | 148 | 55 | 135 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-002-06 | 774 | 1567 | 0.49 | 0.06419 | 0.00309 | 0.18812 | 0.01067 | 0.02103 | 0.00018 | 747 | 102 | 175 | 9 | 134 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-002-07 | 308 | 1008 | 0.31 | 0.04735 | 0.00164 | 0.14023 | 0.06025 | 0.02107 | 0.00028 | 66 | 82 | 133 | 54 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-08 | 336 | 1095 | 0.31 | 0.05154 | 0.00162 | 0.14744 | 0.05626 | 0.02109 | 0.00035 | 264 | 72 | 140 | 50 | 135 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-09 | 223 | 1043 | 0.21 | 0.04405 | 0.00131 | 0.12805 | 0.01168 | 0.02108 | 0.00025 | 0.1 | 68 | 122 | 11 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-10 | 630 | 1384 | 0.46 | 0.03781 | 0.00100 | 0.11373 | 0.05315 | 0.02105 | 0.00017 | 0.1 | 52 | 109 | 48 | 134 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-01 | 101 | 342 | 0.30 | 0.06336 | 0.00278 | 0.16193 | 0.00685 | 0.01872 | 0.00021 | 719 | 93 | 152 | 6 | 120 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-02 | 303 | 1330 | 0.23 | 0.04782 | 0.00280 | 0.12740 | 0.00739 | 0.01932 | 0.00016 | 89 | 139 | 122 | 7 | 123 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-03 | 156 | 958 | 0.16 | 0.05489 | 0.00152 | 0.14750 | 0.00406 | 0.01947 | 0.00014 | 407 | 62 | 140 | 4 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-04 | 302 | 900 | 0.34 | 0.06263 | 0.01499 | 0.18169 | 0.03977 | 0.01957 | 0.00018 | 695 | 510 | 170 | 34 | 125 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-05 | 82 | 484 | 0.17 | 0.05438 | 0.00346 | 0.14554 | 0.00932 | 0.01939 | 0.00022 | 386 | 143 | 138 | 8 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-06 | 249 | 1038 | 0.24 | 0.05263 | 0.00259 | 0.14222 | 0.00685 | 0.01960 | 0.00020 | 312 | 112 | 135 | 6 | 125 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-07 | 107 | 448 | 0.24 | 0.05030 | 0.00293 | 0.13615 | 0.00632 | 0.01897 | 0.00021 | 208 | 135 | 130 | 6 | 121 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-08 | 97 | 477 | 0.20 | 0.04605 | 0.00355 | 0.11817 | 0.00902 | 0.01861 | 0.00020 | 0.1 | 184 | 113 | 8 | 119 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-09 | 172 | 551 | 0.31 | 0.05316 | 0.00328 | 0.13838 | 0.00843 | 0.01888 | 0.00019 | 335 | 140 | 132 | 8 | 121 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-10 | 608 | 1909 | 0.32 | 0.04665 | 0.00473 | 0.13694 | 0.00418 | 0.01935 | 0.00016 | 30 | 243 | 130 | 4 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-11 | 170 | 664 | 0.26 | 0.04939 | 0.00231 | 0.12763 | 0.00585 | 0.01874 | 0.00017 | 165 | 109 | 122 | 5 | 120 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-12 | 109 | 638 | 0.17 | 0.04658 | 0.00385 | 0.13376 | 0.00470 | 0.01946 | 0.00021 | 27 | 198 | 127 | 4 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-13 | 296 | 1164 | 0.25 | 0.05155 | 0.00257 | 0.13790 | 0.00674 | 0.01940 | 0.00020 | 264 | 114 | 131 | 6 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-14 | 101 | 418 | 0.24 | 0.04696 | 0.00255 | 0.12469 | 0.00633 | 0.01911 | 0.00022 | 46 | 130 | 119 | 6 | 122 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-15 | 159 | 984 | 0.16 | 0.04646 | 0.00477 | 0.13398 | 0.00487 | 0.01897 | 0.00018 | 20 | 247 | 128 | 4 | 121 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-16 | 112 | 281 | 0.40 | 0.05166 | 0.00394 | 0.14055 | 0.00725 | 0.01893 | 0.00023 | 269 | 175 | 134 | 6 | 121 | 1 | |
表1 大塔山林场组流纹岩锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 The U-Pb isotope analysis data of zircons for the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation
| 测点号 | wB(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | U-Pb年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1 σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1 σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1 σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1 σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1 σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1 σ | |||
| SPS-H-002-01 | 529 | 1972 | 0.27 | 0.07107 | 0.00474 | 0.22920 | 0.04211 | 0.02107 | 0.00036 | 959 | 136 | 210 | 35 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-02 | 358 | 1127 | 0.32 | 0.09041 | 0.00413 | 0.25974 | 0.01705 | 0.02115 | 0.00056 | 1433 | 87 | 234 | 14 | 135 | 4 | |
| SPS-H-002-03 | 418 | 1237 | 0.34 | 0.05271 | 0.00261 | 0.15180 | 0.01130 | 0.02106 | 0.00028 | 315 | 113 | 143 | 10 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-04 | 321 | 1215 | 0.26 | 0.06642 | 0.00174 | 0.19492 | 0.05620 | 0.02101 | 0.00018 | 819 | 55 | 181 | 48 | 134 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-002-05 | 308 | 1028 | 0.30 | 0.05314 | 0.00194 | 0.15739 | 0.06309 | 0.02112 | 0.00016 | 334 | 83 | 148 | 55 | 135 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-002-06 | 774 | 1567 | 0.49 | 0.06419 | 0.00309 | 0.18812 | 0.01067 | 0.02103 | 0.00018 | 747 | 102 | 175 | 9 | 134 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-002-07 | 308 | 1008 | 0.31 | 0.04735 | 0.00164 | 0.14023 | 0.06025 | 0.02107 | 0.00028 | 66 | 82 | 133 | 54 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-08 | 336 | 1095 | 0.31 | 0.05154 | 0.00162 | 0.14744 | 0.05626 | 0.02109 | 0.00035 | 264 | 72 | 140 | 50 | 135 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-09 | 223 | 1043 | 0.21 | 0.04405 | 0.00131 | 0.12805 | 0.01168 | 0.02108 | 0.00025 | 0.1 | 68 | 122 | 11 | 134 | 2 | |
| SPS-H-002-10 | 630 | 1384 | 0.46 | 0.03781 | 0.00100 | 0.11373 | 0.05315 | 0.02105 | 0.00017 | 0.1 | 52 | 109 | 48 | 134 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-01 | 101 | 342 | 0.30 | 0.06336 | 0.00278 | 0.16193 | 0.00685 | 0.01872 | 0.00021 | 719 | 93 | 152 | 6 | 120 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-02 | 303 | 1330 | 0.23 | 0.04782 | 0.00280 | 0.12740 | 0.00739 | 0.01932 | 0.00016 | 89 | 139 | 122 | 7 | 123 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-03 | 156 | 958 | 0.16 | 0.05489 | 0.00152 | 0.14750 | 0.00406 | 0.01947 | 0.00014 | 407 | 62 | 140 | 4 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-04 | 302 | 900 | 0.34 | 0.06263 | 0.01499 | 0.18169 | 0.03977 | 0.01957 | 0.00018 | 695 | 510 | 170 | 34 | 125 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-05 | 82 | 484 | 0.17 | 0.05438 | 0.00346 | 0.14554 | 0.00932 | 0.01939 | 0.00022 | 386 | 143 | 138 | 8 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-06 | 249 | 1038 | 0.24 | 0.05263 | 0.00259 | 0.14222 | 0.00685 | 0.01960 | 0.00020 | 312 | 112 | 135 | 6 | 125 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-07 | 107 | 448 | 0.24 | 0.05030 | 0.00293 | 0.13615 | 0.00632 | 0.01897 | 0.00021 | 208 | 135 | 130 | 6 | 121 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-08 | 97 | 477 | 0.20 | 0.04605 | 0.00355 | 0.11817 | 0.00902 | 0.01861 | 0.00020 | 0.1 | 184 | 113 | 8 | 119 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-09 | 172 | 551 | 0.31 | 0.05316 | 0.00328 | 0.13838 | 0.00843 | 0.01888 | 0.00019 | 335 | 140 | 132 | 8 | 121 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-10 | 608 | 1909 | 0.32 | 0.04665 | 0.00473 | 0.13694 | 0.00418 | 0.01935 | 0.00016 | 30 | 243 | 130 | 4 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-11 | 170 | 664 | 0.26 | 0.04939 | 0.00231 | 0.12763 | 0.00585 | 0.01874 | 0.00017 | 165 | 109 | 122 | 5 | 120 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-12 | 109 | 638 | 0.17 | 0.04658 | 0.00385 | 0.13376 | 0.00470 | 0.01946 | 0.00021 | 27 | 198 | 127 | 4 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-13 | 296 | 1164 | 0.25 | 0.05155 | 0.00257 | 0.13790 | 0.00674 | 0.01940 | 0.00020 | 264 | 114 | 131 | 6 | 124 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-14 | 101 | 418 | 0.24 | 0.04696 | 0.00255 | 0.12469 | 0.00633 | 0.01911 | 0.00022 | 46 | 130 | 119 | 6 | 122 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-15 | 159 | 984 | 0.16 | 0.04646 | 0.00477 | 0.13398 | 0.00487 | 0.01897 | 0.00018 | 20 | 247 | 128 | 4 | 121 | 1 | |
| SPS-H-009-16 | 112 | 281 | 0.40 | 0.05166 | 0.00394 | 0.14055 | 0.00725 | 0.01893 | 0.00023 | 269 | 175 | 134 | 6 | 121 | 1 | |

图5 大塔山林场组流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a) (c)和加权平均年龄图(b) (d)
Fig.5 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams (a) (c) and diagrams of their weighted mean (b) (d) from the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS-B-001 | 硅质岩 | 98.91 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 99.94 |
| SPS-B-002 | 97.84 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 99.71 | |
| SPS-B-003 | 96.87 | 0.02 | 1.67 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 99.96 | |
| SPS-B-004 | 98.50 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 100.25 | |
| SPS-B-005 | 98.20 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 100.50 | |
| SPS-B-006 | 97.50 | 0.06 | 0.78 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 100.15 | |
| SPS-B-007 | 硅质角 砾岩 | 87.70 | 0.18 | 4.41 | 1.33 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 2.21 | 0.02 | 1.40 | 97.90 |
| SPS-B-008 | 75.97 | 0.48 | 9.50 | 7.75 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 2.41 | 0.03 | 2.99 | 99.98 | |
| SPS-B-009 | 83.46 | 0.32 | 7.31 | 2.28 | 0.37 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 3.11 | 0.02 | 2.44 | 99.78 | |
| SPS-B-010 | 85.20 | 0.44 | 7.82 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 2.93 | 0.01 | 2.00 | 99.57 | |
| SPS-B-011 | 83.01 | 0.42 | 9.23 | 0.92 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 4.01 | 0.02 | 1.56 | 99.97 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb |
| SPS-B-001 | 硅质岩 | 0.83 | 1.52 | 0.17 | 0.61 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| SPS-B-002 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.02 | |
| SPS-B-003 | 0.96 | 1.89 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | |
| SPS-B-004 | 0.90 | 1.80 | 0.19 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| SPS-B-005 | 1.00 | 1.70 | 0.14 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.08 | |
| SPS-B-006 | 3.40 | 6.50 | 0.59 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.18 | |
| SPS-B-007 | 硅质角 砾岩 | 9.45 | 18.85 | 1.95 | 6.87 | 1.19 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.56 |
| SPS-B-008 | 11.86 | 28.63 | 3.10 | 10.90 | 1.91 | 0.39 | 1.23 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 0.85 | 0.13 | 0.93 | |
| SPS-B-009 | 12.59 | 26.76 | 2.81 | 9.64 | 1.64 | 0.37 | 1.31 | 0.20 | 1.04 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 0.79 | |
| SPS-B-010 | 17.80 | 35.70 | 3.71 | 12.60 | 3.13 | 0.43 | 1.63 | 0.26 | 1.77 | 0.36 | 1.07 | 0.20 | 1.23 | |
| SPS-B-011 | 20.73 | 39.95 | 4.43 | 16.07 | 2.86 | 0.56 | 2.44 | 0.42 | 2.40 | 0.48 | 1.51 | 0.26 | 1.63 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Lu | Y | Th | U | Nb | Sr | Hf | Ta | Zr | Rb | Ba | Co | Ni |
| SPS-B-001 | 硅质岩 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 19.80 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 13.80 | 7.4 | 41.4 | 0.38 | 1.26 |
| SPS-B-002 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 40.90 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 9.10 | 12.3 | 169.3 | 0.39 | 1.71 | |
| SPS-B-003 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 37.50 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 9.40 | 15.6 | 188.7 | 0.51 | 1.46 | |
| SPS-B-004 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 1.40 | 6.20 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 2.00 | 4.0 | 36.3 | 1.00 | 3.00 | |
| SPS-B-005 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 1.28 | 2.30 | 13.20 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 2.00 | 7.3 | 66.2 | 1.00 | 2.00 | |
| SPS-B-006 | 0.03 | 1.90 | 0.66 | 0.30 | 2.00 | 17.30 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 17.00 | 13.2 | 106.0 | 1.00 | 2.00 | |
| SPS-B-007 | 硅质角 砾岩 | 0.09 | 5.43 | 2.54 | 0.81 | 4.68 | 26.30 | 1.59 | 0.33 | 57.60 | 96.3 | 432.4 | 2.53 | 7.97 |
| SPS-B-008 | 0.14 | 6.78 | 7.88 | 2.13 | 13.77 | 33.50 | 3.31 | 1.06 | 123.2 | 156.0 | 922.5 | 1.11 | 2.31 | |
| SPS-B-009 | 0.12 | 6.21 | 4.72 | 0.99 | 8.17 | 30.10 | 2.02 | 0.47 | 72.90 | 131.8 | 794.7 | 3.65 | 13.83 | |
| SPS-B-010 | 0.20 | 8.90 | 6.55 | 2.42 | 7.30 | 26.60 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 104.0 | 164.5 | 415.0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| SPS-B-011 | 0.24 | 14.41 | 8.72 | 1.96 | 12.83 | 41.20 | 4.43 | 1.07 | 145.2 | 304.9 | 345.1 | 1.29 | 4.56 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
| SPS-H-001 | 流纹岩 | 77.23 | 0.34 | 7.40 | 3.49 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 3.92 | 0.02 | 3.45 | 96.84 |
| SPS-H-002 | 84.21 | 0.46 | 7.62 | 2.22 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 2.58 | 0.03 | 1.80 | 99.90 | |
| SPS-H-003 | 81.16 | 0.42 | 8.03 | 2.20 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 4.04 | 0.02 | 2.75 | 99.71 | |
| SPS-H-004 | 84.55 | 0.46 | 7.55 | 1.01 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 3.82 | 0.01 | 1.64 | 99.84 | |
| SPS-H-005 | 86.00 | 0.41 | 5.68 | 2.09 | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 2.96 | 0.03 | 1.63 | 99.76 | |
| SPS-H-006 | 81.50 | 0.31 | 8.06 | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 4.65 | 0.01 | 3.86 | 100.80 | |
| SPS-H-007 | 82.14 | 0.34 | 8.77 | 1.31 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 4.89 | 0.02 | 1.79 | 99.88 | |
| SPS-H-008 | 86.80 | 0.45 | 6.29 | 2.13 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 1.28 | 0.03 | 2.04 | 99.84 | |
| SPS-H-009 | 75.28 | 0.26 | 4.54 | 8.10 | 1.19 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 2.03 | 0.03 | 7.86 | 99.71 | |
| SPS-H-010 | 83.06 | 0.53 | 10.45 | 0.71 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 2.70 | 0.02 | 1.83 | 99.96 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb |
| SPS-H-001 | 流纹岩 | 17.35 | 37.05 | 3.91 | 14.02 | 2.53 | 0.50 | 1.94 | 0.33 | 2.11 | 0.41 | 1.26 | 0.20 | 1.32 |
| SPS-H-002 | 8.20 | 17.59 | 2.03 | 7.64 | 1.78 | 0.42 | 1.94 | 0.41 | 2.65 | 0.52 | 1.58 | 0.28 | 1.67 | |
| SPS-H-003 | 16.42 | 32.90 | 3.49 | 11.91 | 2.08 | 0.42 | 1.66 | 0.27 | 1.54 | 0.32 | 1.04 | 0.20 | 1.21 | |
| SPS-H-004 | 16.45 | 32.58 | 3.67 | 13.35 | 2.73 | 0.55 | 2.40 | 0.44 | 2.47 | 0.49 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 1.56 | |
| SPS-H-005 | 15.58 | 31.38 | 3.57 | 12.92 | 2.57 | 0.55 | 2.30 | 0.39 | 2.16 | 0.42 | 1.25 | 0.21 | 1.35 | |
| SPS-H-006 | 17.90 | 38.10 | 3.61 | 13.20 | 3.05 | 0.38 | 2.13 | 0.30 | 1.98 | 0.38 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.41 | |
| SPS-H-007 | 15.96 | 30.22 | 3.46 | 12.43 | 2.39 | 0.51 | 2.03 | 0.33 | 1.78 | 0.35 | 1.04 | 0.18 | 1.18 | |
| SPS-H-008 | 7.17 | 12.77 | 1.49 | 5.37 | 1.15 | 0.28 | 1.12 | 0.24 | 1.52 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 1.12 | |
| SPS-H-009 | 14.19 | 30.85 | 3.58 | 12.77 | 2.39 | 0.49 | 1.83 | 0.28 | 1.33 | 0.24 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 0.79 | |
| SPS-H-010 | 17.52 | 34.19 | 3.82 | 13.82 | 2.60 | 0.51 | 2.34 | 0.40 | 2.33 | 0.47 | 1.44 | 0.26 | 1.59 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Lu | Y | Th | U | Nb | Sr | Hf | Ta | Zr | Rb | Ba | Co | Ni |
| SPS-H-001 | 流纹岩 | 0.20 | 11.03 | 5.45 | 1.69 | 9.95 | 31.10 | 2.82 | 0.71 | 107.00 | 212.0 | 942.4 | 34.96 | 52.86 |
| SPS-H-002 | 0.24 | 15.44 | 6.84 | 1.85 | 10.20 | 42.70 | 3.96 | 0.85 | 133.60 | 126.4 | 989.3 | 0.66 | 2.33 | |
| SPS-H-003 | 0.18 | 9.12 | 5.71 | 1.45 | 10.86 | 36.10 | 3.58 | 0.66 | 123.60 | 209.2 | 799.1 | 4.27 | 12.69 | |
| SPS-H-004 | 0.24 | 14.78 | 7.30 | 2.07 | 11.61 | 27.00 | 4.38 | 0.76 | 149.00 | 237.8 | 608.9 | 1.73 | 6.94 | |
| SPS-H-005 | 0.19 | 12.68 | 5.85 | 1.43 | 9.39 | 26.00 | 3.35 | 0.67 | 114.00 | 129.6 | 542.1 | 0.83 | 3.26 | |
| SPS-H-006 | 0.24 | 10.40 | 9.14 | 4.00 | 10.70 | 24.70 | 3.70 | 0.90 | 108.00 | 256.0 | 1475 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| SPS-H-007 | 0.17 | 10.52 | 4.53 | 1.27 | 9.65 | 31.20 | 3.22 | 0.57 | 117.20 | 278.6 | 411.7 | 3.12 | 6.99 | |
| SPS-H-008 | 0.15 | 8.88 | 5.21 | 1.22 | 11.31 | 32.20 | 3.14 | 0.73 | 112.70 | 68.2 | 249.2 | 1.11 | 3.26 | |
| SPS-H-009 | 0.12 | 6.87 | 4.70 | 1.08 | 8.38 | 49.40 | 2.47 | 0.52 | 85.60 | 101.2 | 393.8 | 8.33 | 16.23 | |
| SPS-H-010 | 0.25 | 13.96 | 6.70 | 1.73 | 13.37 | 20.40 | 5.16 | 0.82 | 183.60 | 164.9 | 158.2 | 1.62 | 6.36 |
表2 四平山组硅质岩、硅质角砾岩主量(%)、稀土和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Analysis results of the major (%), rare earth and trace (10-6) elements of the chert and silicified breccia in Sipingshan Formation
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS-B-001 | 硅质岩 | 98.91 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 99.94 |
| SPS-B-002 | 97.84 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 99.71 | |
| SPS-B-003 | 96.87 | 0.02 | 1.67 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 99.96 | |
| SPS-B-004 | 98.50 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 100.25 | |
| SPS-B-005 | 98.20 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 100.50 | |
| SPS-B-006 | 97.50 | 0.06 | 0.78 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 100.15 | |
| SPS-B-007 | 硅质角 砾岩 | 87.70 | 0.18 | 4.41 | 1.33 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 2.21 | 0.02 | 1.40 | 97.90 |
| SPS-B-008 | 75.97 | 0.48 | 9.50 | 7.75 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 2.41 | 0.03 | 2.99 | 99.98 | |
| SPS-B-009 | 83.46 | 0.32 | 7.31 | 2.28 | 0.37 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 3.11 | 0.02 | 2.44 | 99.78 | |
| SPS-B-010 | 85.20 | 0.44 | 7.82 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 2.93 | 0.01 | 2.00 | 99.57 | |
| SPS-B-011 | 83.01 | 0.42 | 9.23 | 0.92 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 4.01 | 0.02 | 1.56 | 99.97 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb |
| SPS-B-001 | 硅质岩 | 0.83 | 1.52 | 0.17 | 0.61 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| SPS-B-002 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.02 | |
| SPS-B-003 | 0.96 | 1.89 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | |
| SPS-B-004 | 0.90 | 1.80 | 0.19 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| SPS-B-005 | 1.00 | 1.70 | 0.14 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.08 | |
| SPS-B-006 | 3.40 | 6.50 | 0.59 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.18 | |
| SPS-B-007 | 硅质角 砾岩 | 9.45 | 18.85 | 1.95 | 6.87 | 1.19 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.56 |
| SPS-B-008 | 11.86 | 28.63 | 3.10 | 10.90 | 1.91 | 0.39 | 1.23 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 0.85 | 0.13 | 0.93 | |
| SPS-B-009 | 12.59 | 26.76 | 2.81 | 9.64 | 1.64 | 0.37 | 1.31 | 0.20 | 1.04 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 0.79 | |
| SPS-B-010 | 17.80 | 35.70 | 3.71 | 12.60 | 3.13 | 0.43 | 1.63 | 0.26 | 1.77 | 0.36 | 1.07 | 0.20 | 1.23 | |
| SPS-B-011 | 20.73 | 39.95 | 4.43 | 16.07 | 2.86 | 0.56 | 2.44 | 0.42 | 2.40 | 0.48 | 1.51 | 0.26 | 1.63 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Lu | Y | Th | U | Nb | Sr | Hf | Ta | Zr | Rb | Ba | Co | Ni |
| SPS-B-001 | 硅质岩 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 19.80 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 13.80 | 7.4 | 41.4 | 0.38 | 1.26 |
| SPS-B-002 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 40.90 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 9.10 | 12.3 | 169.3 | 0.39 | 1.71 | |
| SPS-B-003 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 37.50 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 9.40 | 15.6 | 188.7 | 0.51 | 1.46 | |
| SPS-B-004 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 1.40 | 6.20 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 2.00 | 4.0 | 36.3 | 1.00 | 3.00 | |
| SPS-B-005 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 1.28 | 2.30 | 13.20 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 2.00 | 7.3 | 66.2 | 1.00 | 2.00 | |
| SPS-B-006 | 0.03 | 1.90 | 0.66 | 0.30 | 2.00 | 17.30 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 17.00 | 13.2 | 106.0 | 1.00 | 2.00 | |
| SPS-B-007 | 硅质角 砾岩 | 0.09 | 5.43 | 2.54 | 0.81 | 4.68 | 26.30 | 1.59 | 0.33 | 57.60 | 96.3 | 432.4 | 2.53 | 7.97 |
| SPS-B-008 | 0.14 | 6.78 | 7.88 | 2.13 | 13.77 | 33.50 | 3.31 | 1.06 | 123.2 | 156.0 | 922.5 | 1.11 | 2.31 | |
| SPS-B-009 | 0.12 | 6.21 | 4.72 | 0.99 | 8.17 | 30.10 | 2.02 | 0.47 | 72.90 | 131.8 | 794.7 | 3.65 | 13.83 | |
| SPS-B-010 | 0.20 | 8.90 | 6.55 | 2.42 | 7.30 | 26.60 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 104.0 | 164.5 | 415.0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| SPS-B-011 | 0.24 | 14.41 | 8.72 | 1.96 | 12.83 | 41.20 | 4.43 | 1.07 | 145.2 | 304.9 | 345.1 | 1.29 | 4.56 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
| SPS-H-001 | 流纹岩 | 77.23 | 0.34 | 7.40 | 3.49 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 3.92 | 0.02 | 3.45 | 96.84 |
| SPS-H-002 | 84.21 | 0.46 | 7.62 | 2.22 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 2.58 | 0.03 | 1.80 | 99.90 | |
| SPS-H-003 | 81.16 | 0.42 | 8.03 | 2.20 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 4.04 | 0.02 | 2.75 | 99.71 | |
| SPS-H-004 | 84.55 | 0.46 | 7.55 | 1.01 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 3.82 | 0.01 | 1.64 | 99.84 | |
| SPS-H-005 | 86.00 | 0.41 | 5.68 | 2.09 | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 2.96 | 0.03 | 1.63 | 99.76 | |
| SPS-H-006 | 81.50 | 0.31 | 8.06 | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 4.65 | 0.01 | 3.86 | 100.80 | |
| SPS-H-007 | 82.14 | 0.34 | 8.77 | 1.31 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 4.89 | 0.02 | 1.79 | 99.88 | |
| SPS-H-008 | 86.80 | 0.45 | 6.29 | 2.13 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 1.28 | 0.03 | 2.04 | 99.84 | |
| SPS-H-009 | 75.28 | 0.26 | 4.54 | 8.10 | 1.19 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 2.03 | 0.03 | 7.86 | 99.71 | |
| SPS-H-010 | 83.06 | 0.53 | 10.45 | 0.71 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 2.70 | 0.02 | 1.83 | 99.96 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb |
| SPS-H-001 | 流纹岩 | 17.35 | 37.05 | 3.91 | 14.02 | 2.53 | 0.50 | 1.94 | 0.33 | 2.11 | 0.41 | 1.26 | 0.20 | 1.32 |
| SPS-H-002 | 8.20 | 17.59 | 2.03 | 7.64 | 1.78 | 0.42 | 1.94 | 0.41 | 2.65 | 0.52 | 1.58 | 0.28 | 1.67 | |
| SPS-H-003 | 16.42 | 32.90 | 3.49 | 11.91 | 2.08 | 0.42 | 1.66 | 0.27 | 1.54 | 0.32 | 1.04 | 0.20 | 1.21 | |
| SPS-H-004 | 16.45 | 32.58 | 3.67 | 13.35 | 2.73 | 0.55 | 2.40 | 0.44 | 2.47 | 0.49 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 1.56 | |
| SPS-H-005 | 15.58 | 31.38 | 3.57 | 12.92 | 2.57 | 0.55 | 2.30 | 0.39 | 2.16 | 0.42 | 1.25 | 0.21 | 1.35 | |
| SPS-H-006 | 17.90 | 38.10 | 3.61 | 13.20 | 3.05 | 0.38 | 2.13 | 0.30 | 1.98 | 0.38 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.41 | |
| SPS-H-007 | 15.96 | 30.22 | 3.46 | 12.43 | 2.39 | 0.51 | 2.03 | 0.33 | 1.78 | 0.35 | 1.04 | 0.18 | 1.18 | |
| SPS-H-008 | 7.17 | 12.77 | 1.49 | 5.37 | 1.15 | 0.28 | 1.12 | 0.24 | 1.52 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 1.12 | |
| SPS-H-009 | 14.19 | 30.85 | 3.58 | 12.77 | 2.39 | 0.49 | 1.83 | 0.28 | 1.33 | 0.24 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 0.79 | |
| SPS-H-010 | 17.52 | 34.19 | 3.82 | 13.82 | 2.60 | 0.51 | 2.34 | 0.40 | 2.33 | 0.47 | 1.44 | 0.26 | 1.59 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Lu | Y | Th | U | Nb | Sr | Hf | Ta | Zr | Rb | Ba | Co | Ni |
| SPS-H-001 | 流纹岩 | 0.20 | 11.03 | 5.45 | 1.69 | 9.95 | 31.10 | 2.82 | 0.71 | 107.00 | 212.0 | 942.4 | 34.96 | 52.86 |
| SPS-H-002 | 0.24 | 15.44 | 6.84 | 1.85 | 10.20 | 42.70 | 3.96 | 0.85 | 133.60 | 126.4 | 989.3 | 0.66 | 2.33 | |
| SPS-H-003 | 0.18 | 9.12 | 5.71 | 1.45 | 10.86 | 36.10 | 3.58 | 0.66 | 123.60 | 209.2 | 799.1 | 4.27 | 12.69 | |
| SPS-H-004 | 0.24 | 14.78 | 7.30 | 2.07 | 11.61 | 27.00 | 4.38 | 0.76 | 149.00 | 237.8 | 608.9 | 1.73 | 6.94 | |
| SPS-H-005 | 0.19 | 12.68 | 5.85 | 1.43 | 9.39 | 26.00 | 3.35 | 0.67 | 114.00 | 129.6 | 542.1 | 0.83 | 3.26 | |
| SPS-H-006 | 0.24 | 10.40 | 9.14 | 4.00 | 10.70 | 24.70 | 3.70 | 0.90 | 108.00 | 256.0 | 1475 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| SPS-H-007 | 0.17 | 10.52 | 4.53 | 1.27 | 9.65 | 31.20 | 3.22 | 0.57 | 117.20 | 278.6 | 411.7 | 3.12 | 6.99 | |
| SPS-H-008 | 0.15 | 8.88 | 5.21 | 1.22 | 11.31 | 32.20 | 3.14 | 0.73 | 112.70 | 68.2 | 249.2 | 1.11 | 3.26 | |
| SPS-H-009 | 0.12 | 6.87 | 4.70 | 1.08 | 8.38 | 49.40 | 2.47 | 0.52 | 85.60 | 101.2 | 393.8 | 8.33 | 16.23 | |
| SPS-H-010 | 0.25 | 13.96 | 6.70 | 1.73 | 13.37 | 20.40 | 5.16 | 0.82 | 183.60 | 164.9 | 158.2 | 1.62 | 6.36 |
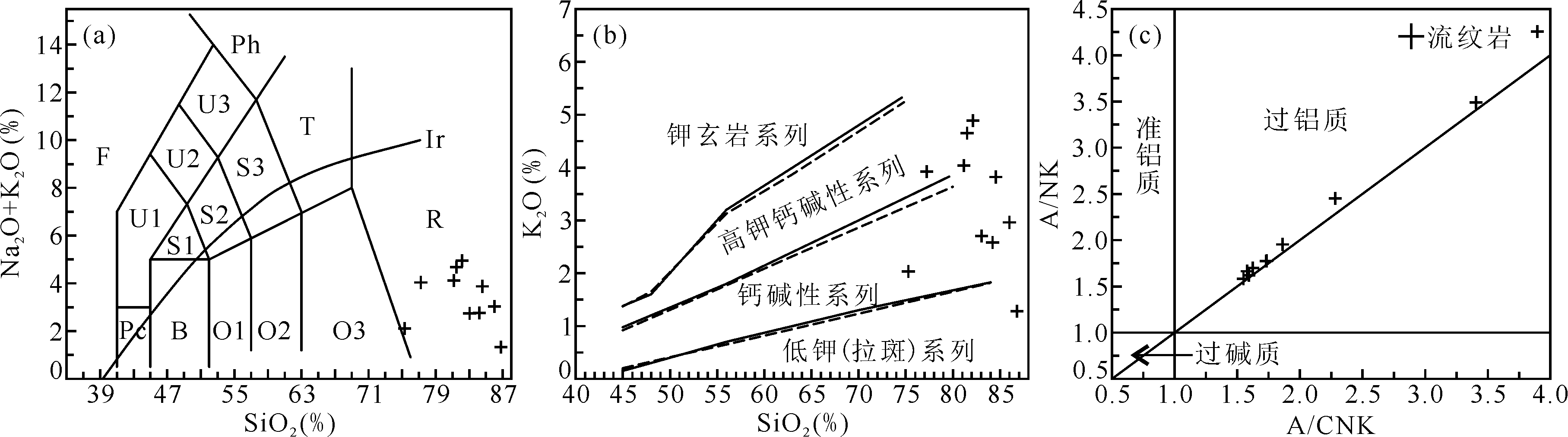
图6 大塔山林场组流纹岩TAS图解(a) [44]、K2O-SiO2图解(b) [45]和A/NK-A/CNK图解(c) [46] Pc.苦橄玄武岩;B.玄武岩;O1.玄武安山岩;O2.安山岩;O3.英安岩;R.流纹岩;S1.粗面玄武岩;S2.玄武质粗面安山岩;S3.粗面安山岩;T.粗面岩、粗面英安岩;F.副长石岩;U1.碱玄岩、碧玄岩;U2.响岩质碱玄岩;U3.碱玄质响岩;Ph.响岩;Ir.Irvine 分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性
Fig.6 TAS (a) [44], K2O-SiO2(b) [45] and A/NK-A/CNK (c) [46] diagrams of the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation
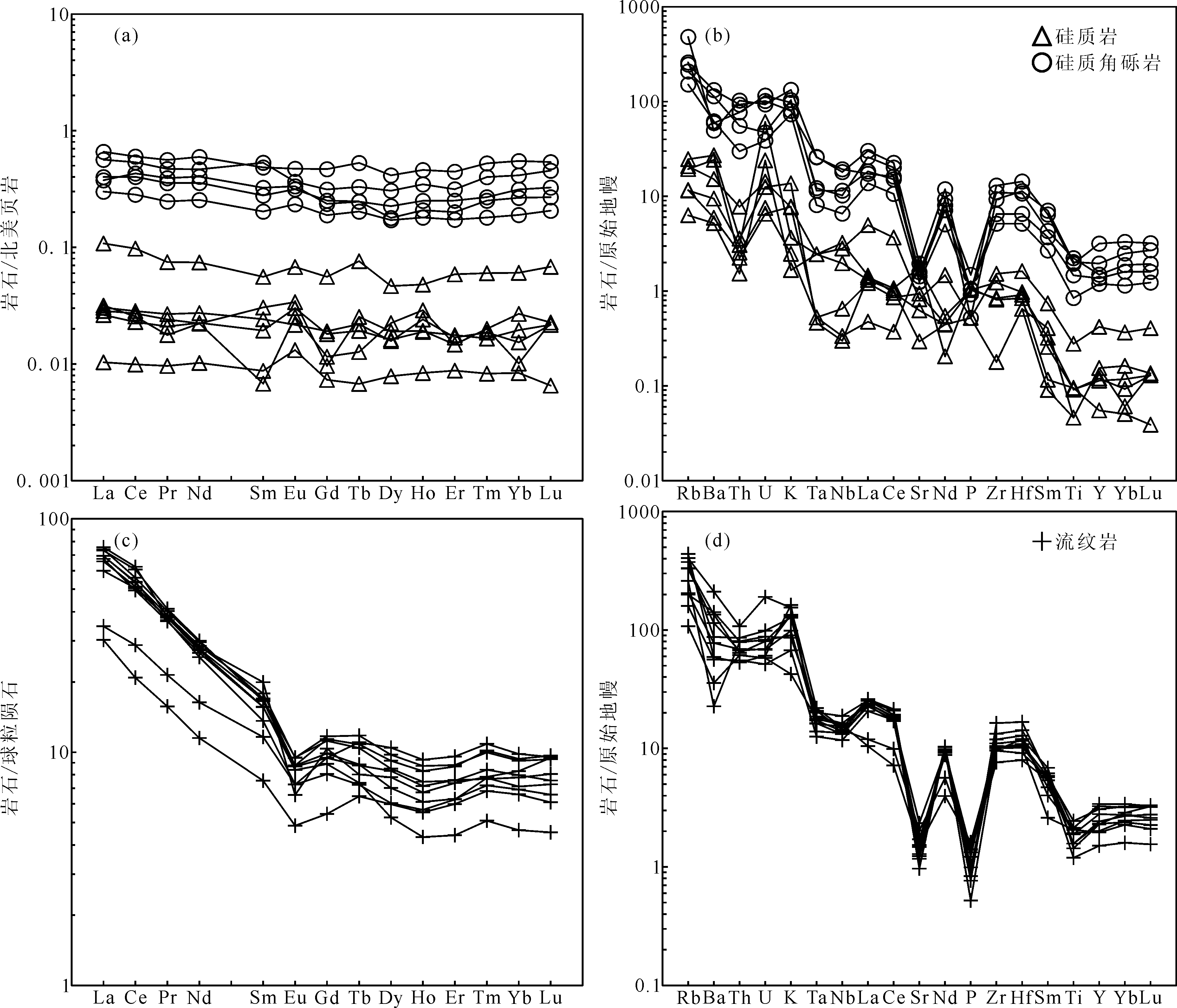
图7 四平山组硅质岩、硅质角砾岩稀土元素北美页岩标准化配分型式图(a)、微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)和大塔山林场组流纹岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分型式图(c)以及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(d)(北美页岩标准化值据文献[47],球粒陨石和原始地幔标准化值据文献[48])
Fig.7 NASC-normalized REE distribution patterns (a), primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spider diagrams (b) of the chert, silicified breccia in Sipingshan Formation and chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (c), primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spider diagrams (d) of the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation
| 序 号 | 类型 | 大小 (μm) | 气液比 (%) | 均一温度 (℃) | 冰点温度 (℃) | 资料 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 气液两相 | 5×8 | 15 | 157.2 | -3.4 | 本文 |
| 2 | 气液两相 | 6×8 | 25 | 181.7 | -5.8 | |
| 3 | 气液两相 | 3×6 | 10 | 126.7 | -1.8 | |
| 4 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 20 | 159.3 | -0.5 | |
| 5 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 20 | 131.3 | -3.7 | |
| 6 | 气液两相 | 4×6 | 15 | 129.8 | -0.2 | |
| 7 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 15 | 134.6 | -2.9 | |
| 8 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 30 | 162.8 | -3.6 | |
| 9 | 气液两相 | 4×6 | 20 | 161.9 | -0.7 | |
| 10 | 气液两相 | 4×8 | 15 | 170.3 | -1.5 | |
| 11 | 气液两相 | 7×8 | 20 | 223.4 | -2.8 | |
| 12 | 气液两相 | 5×5 | 15 | 118.7 | -3.2 | |
| 13 | 气液两相 | 4×6 | 15 | 120.3 | -3.1 | |
| 14 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 25 | 167.5 | -2.6 | |
| 15 | 气液两相 | 4×7 | 20 | 172.2 | -2.3 | |
| 16 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 30 | 193.2 | -4.6 | |
| 17 | 气液两相 | 4×5 | 25 | 146.3 | -1.3 | |
| 18 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 20 | 180.7 | -4.3 | |
| 19 | 气液两相 | 6×10 | 20 | 191.7 | -0.6 | |
| 20 | 气液两相 | 6×12 | 20 | 201.6 | -3.1 | |
| 21 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 35 | 169.6 | -2.3 | |
| 22 | 气液两相 | 4×7 | 20 | 185.3 | -0.8 | |
| 23 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 35 | 179.0 | -3.6 | |
| 24 | 气液两相 | 5×7 | 25 | 196.1 | -3.9 | |
| 25 | 气液两相 | 6×9 | 25 | 194.3 | -2.5 | |
| 26 | 气液两相 | 3×5 | 25 | 142.8 | -1.9 | |
| 27 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 30 | 173.2 | -1.4 |
表3 四平山金矿床流体包裹体分析结果
Table 3 Analysis results of fluid inclusions in the Siping-shan gold deposit
| 序 号 | 类型 | 大小 (μm) | 气液比 (%) | 均一温度 (℃) | 冰点温度 (℃) | 资料 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 气液两相 | 5×8 | 15 | 157.2 | -3.4 | 本文 |
| 2 | 气液两相 | 6×8 | 25 | 181.7 | -5.8 | |
| 3 | 气液两相 | 3×6 | 10 | 126.7 | -1.8 | |
| 4 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 20 | 159.3 | -0.5 | |
| 5 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 20 | 131.3 | -3.7 | |
| 6 | 气液两相 | 4×6 | 15 | 129.8 | -0.2 | |
| 7 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 15 | 134.6 | -2.9 | |
| 8 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 30 | 162.8 | -3.6 | |
| 9 | 气液两相 | 4×6 | 20 | 161.9 | -0.7 | |
| 10 | 气液两相 | 4×8 | 15 | 170.3 | -1.5 | |
| 11 | 气液两相 | 7×8 | 20 | 223.4 | -2.8 | |
| 12 | 气液两相 | 5×5 | 15 | 118.7 | -3.2 | |
| 13 | 气液两相 | 4×6 | 15 | 120.3 | -3.1 | |
| 14 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 25 | 167.5 | -2.6 | |
| 15 | 气液两相 | 4×7 | 20 | 172.2 | -2.3 | |
| 16 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 30 | 193.2 | -4.6 | |
| 17 | 气液两相 | 4×5 | 25 | 146.3 | -1.3 | |
| 18 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 20 | 180.7 | -4.3 | |
| 19 | 气液两相 | 6×10 | 20 | 191.7 | -0.6 | |
| 20 | 气液两相 | 6×12 | 20 | 201.6 | -3.1 | |
| 21 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 35 | 169.6 | -2.3 | |
| 22 | 气液两相 | 4×7 | 20 | 185.3 | -0.8 | |
| 23 | 气液两相 | 6×6 | 35 | 179.0 | -3.6 | |
| 24 | 气液两相 | 5×7 | 25 | 196.1 | -3.9 | |
| 25 | 气液两相 | 6×9 | 25 | 194.3 | -2.5 | |
| 26 | 气液两相 | 3×5 | 25 | 142.8 | -1.9 | |
| 27 | 气液两相 | 5×6 | 30 | 173.2 | -1.4 |
| 样品 编号 | 岩性 | 矿物 | δ18OV-SMOW (‰) | δD (‰) | δ18 (‰) | 资料 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWLZ-1 | 硅质脉 | 石英 | 15.3 | -103.3 | 2.23 | 文献 [ |
| DWLZ-2 | 硅质脉 | 石英 | 15.2 | -106.5 | 2.13 | |
| DWLZ-3 | 硅质脉 | 石英 | 15.1 | -113.8 | 2.03 | |
| SP31 | 黑色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.3 | -95.0 | -3.10 | 文献 [ |
| SP89 | 黑色硅质脉 | 石英 | 11.3 | -94.0 | -2.10 | |
| SP82 | 黑灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.3 | -95.0 | -3.10 | |
| SP18 | 黑灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 11.5 | -106.0 | -1.90 | |
| SP89 | 灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 12.6 | -95.0 | -0.80 | |
| SP20 | 灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.3 | -95.0 | -3.10 | |
| SP47 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 9.9 | -106.0 | 0.10 | |
| SP84 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 11.2 | -94.0 | 1.30 | |
| SP39 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 9.0 | -86.0 | -0.80 | |
| SP64 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.8 | -84.0 | 0.90 |
表4 四平山金矿床H-O同位素分析结果
Table 4 Hydrogen and oxygen isotope data of the Siping-shan gold deposit
| 样品 编号 | 岩性 | 矿物 | δ18OV-SMOW (‰) | δD (‰) | δ18 (‰) | 资料 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWLZ-1 | 硅质脉 | 石英 | 15.3 | -103.3 | 2.23 | 文献 [ |
| DWLZ-2 | 硅质脉 | 石英 | 15.2 | -106.5 | 2.13 | |
| DWLZ-3 | 硅质脉 | 石英 | 15.1 | -113.8 | 2.03 | |
| SP31 | 黑色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.3 | -95.0 | -3.10 | 文献 [ |
| SP89 | 黑色硅质脉 | 石英 | 11.3 | -94.0 | -2.10 | |
| SP82 | 黑灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.3 | -95.0 | -3.10 | |
| SP18 | 黑灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 11.5 | -106.0 | -1.90 | |
| SP89 | 灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 12.6 | -95.0 | -0.80 | |
| SP20 | 灰色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.3 | -95.0 | -3.10 | |
| SP47 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 9.9 | -106.0 | 0.10 | |
| SP84 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 11.2 | -94.0 | 1.30 | |
| SP39 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 9.0 | -86.0 | -0.80 | |
| SP64 | 白色硅质脉 | 石英 | 10.8 | -84.0 | 0.90 |

图9 四平山金矿床含金石英脉中流体包裹体均一温度(a)、盐度(b)、盐度-均一温度关系图(c)和 δD- δ18 O H 2 O图(d)[27,50]
Fig.9 Diagrams of the homogeneous temperature (a), salinity (b) of fluid inclusions trapped in the gold-bearing quartz veins in the Sipingshan gold deposit, and diagrams of salinity vs.homogeneous temperature (c) and δD-δ18 O H 2 O(d)
| 矿床名称 | 岩性 | 年龄(Ma) | 测试方法 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 先锋北山 金矿床 | 硅化流纹岩 | 116.98±0.47 | LA- ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 岩屑晶屑 凝灰岩 | 116.98±0.42 | |||
| 258高地 金矿床 | 闪长玢岩 | 119.5±1.30 | 文献[ | |
| 107.4±2.20 | ||||
| 110.7±1.00 | 文献[ | |||
| 二长花岗岩 | 130.5±0.80 | 文献[ | ||
| 122.1±0.7 | ||||
| 118.0±0.9 | ||||
| 花岗闪长岩 | 118.3±1.1 | |||
| 358高地 金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 128±1.0 | 文献[ | |
| 闪长玢岩 | 108.4±0.9 | 文献[ | ||
| 跃进山铜 金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 109.17±0.91 | 文献[ | |
| 115.8±1.0 | 文献[ | |||
| 101.9±1.1 | 文献[ | |||
| 111.8±2.9 | 文献[ | |||
| 河口林场锡 多金属矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 121.4±0.5 | 文献[ | |
| 118.0±1.1 | 文献[ | |||
| 115.4±1.0 | 文献[ | |||
| 锡石 | 101.4±7.9 | LA-MC- ICP-MS | ||
| 四平山 金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 113.5±0.7 | LA- ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 硅质岩 | 121.8±1.1 | 文献[ | ||
| 117.6±1.0 | ||||
| 硅质角砾岩 | 122.3±1.1 | |||
| 黄铁矿 | 106±3 | Rb-Sr | ||
| 流纹岩 | 134±1 | LA- ICP-MS | 本文 | |
| 123±1 |
表5 那丹哈达地体燕山期金多金属矿床成矿岩体年龄
Table 5 Age of ore-forming rock mass of the Yanshanian gold polymetallic deposit in the Nadanhada terrane
| 矿床名称 | 岩性 | 年龄(Ma) | 测试方法 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 先锋北山 金矿床 | 硅化流纹岩 | 116.98±0.47 | LA- ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 岩屑晶屑 凝灰岩 | 116.98±0.42 | |||
| 258高地 金矿床 | 闪长玢岩 | 119.5±1.30 | 文献[ | |
| 107.4±2.20 | ||||
| 110.7±1.00 | 文献[ | |||
| 二长花岗岩 | 130.5±0.80 | 文献[ | ||
| 122.1±0.7 | ||||
| 118.0±0.9 | ||||
| 花岗闪长岩 | 118.3±1.1 | |||
| 358高地 金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 128±1.0 | 文献[ | |
| 闪长玢岩 | 108.4±0.9 | 文献[ | ||
| 跃进山铜 金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 109.17±0.91 | 文献[ | |
| 115.8±1.0 | 文献[ | |||
| 101.9±1.1 | 文献[ | |||
| 111.8±2.9 | 文献[ | |||
| 河口林场锡 多金属矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 121.4±0.5 | 文献[ | |
| 118.0±1.1 | 文献[ | |||
| 115.4±1.0 | 文献[ | |||
| 锡石 | 101.4±7.9 | LA-MC- ICP-MS | ||
| 四平山 金矿床 | 花岗斑岩 | 113.5±0.7 | LA- ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 硅质岩 | 121.8±1.1 | 文献[ | ||
| 117.6±1.0 | ||||
| 硅质角砾岩 | 122.3±1.1 | |||
| 黄铁矿 | 106±3 | Rb-Sr | ||
| 流纹岩 | 134±1 | LA- ICP-MS | 本文 | |
| 123±1 |

图10 四平山组硅质岩和硅质角砾岩SiO2-Al2O3图解(a)[59]、Al-Fe-Mn图解(b)[60]、10(Cu+Ni+Co)-Fe-Mn图解(c)[61]和lgU-lgTh图解(d)[62]
Fig.10 SiO2-Al2O3(a) [59], Al-Fe-Mn(b) [60], 10(Cu+Ni+Co)-Fe-Mn (c) [61] and lgU-lgTh (d) [62] diagrams of the chert and silicified breccia in Sipingshan Formation
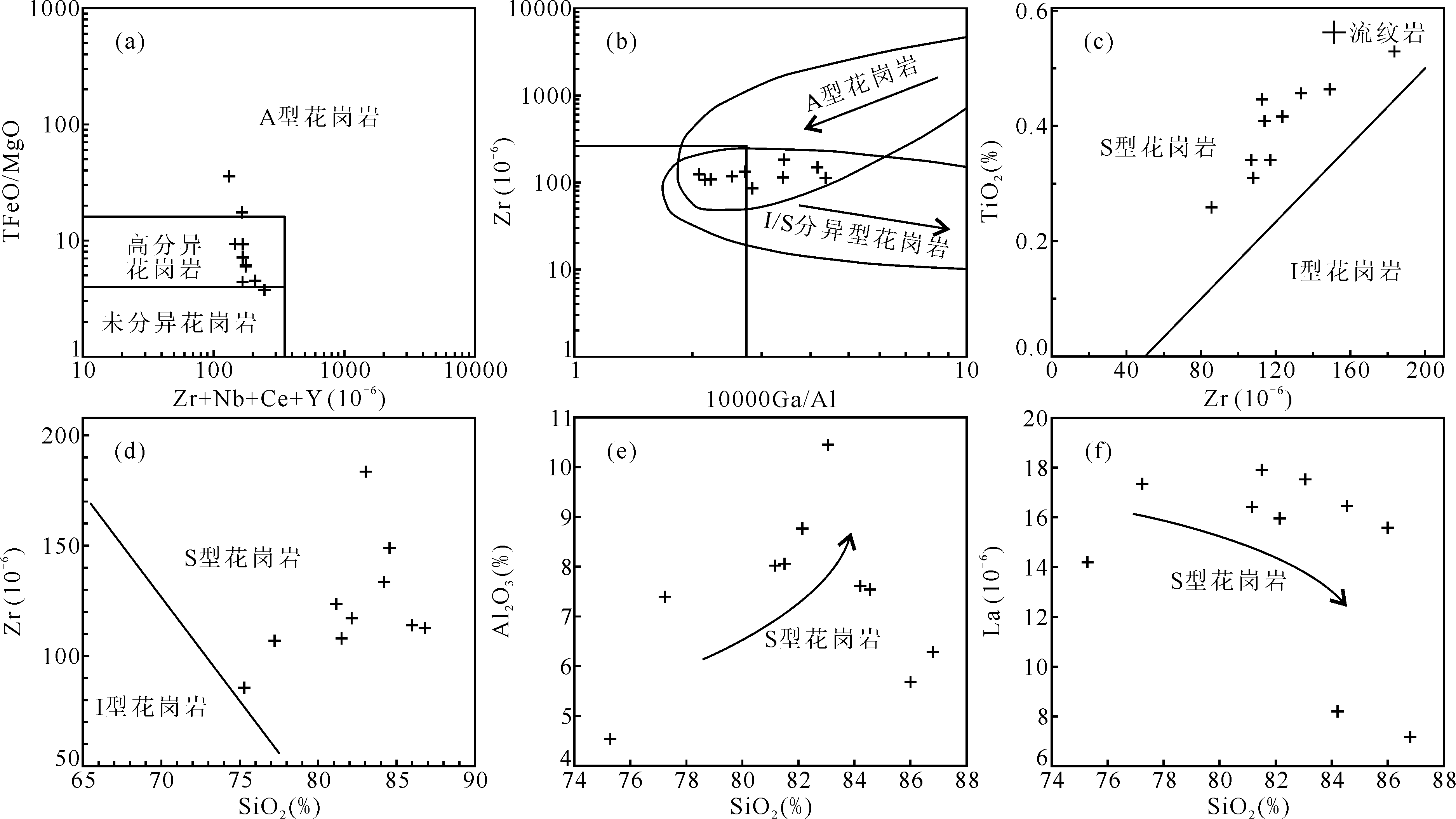
图11 大塔山林场组流纹岩TFeO/MgO-(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)图解(a)[69]、Zr-10000Ga/Al图解(b)[76]、TiO2-Zr图解(c)[77]、Zr-SiO2图解(d)[69]、Al2O3-SiO2图解(e)和La- SiO2图解(f)
Fig.11 TFeO/MgO-(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) (a) [69], Zr-10000Ga/Al (b) [76], TiO2-Zr(c) [77], Zr-SiO2(d) [69], Al2O3-SiO2(e), and La-SiO2(f) diagrams of the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation
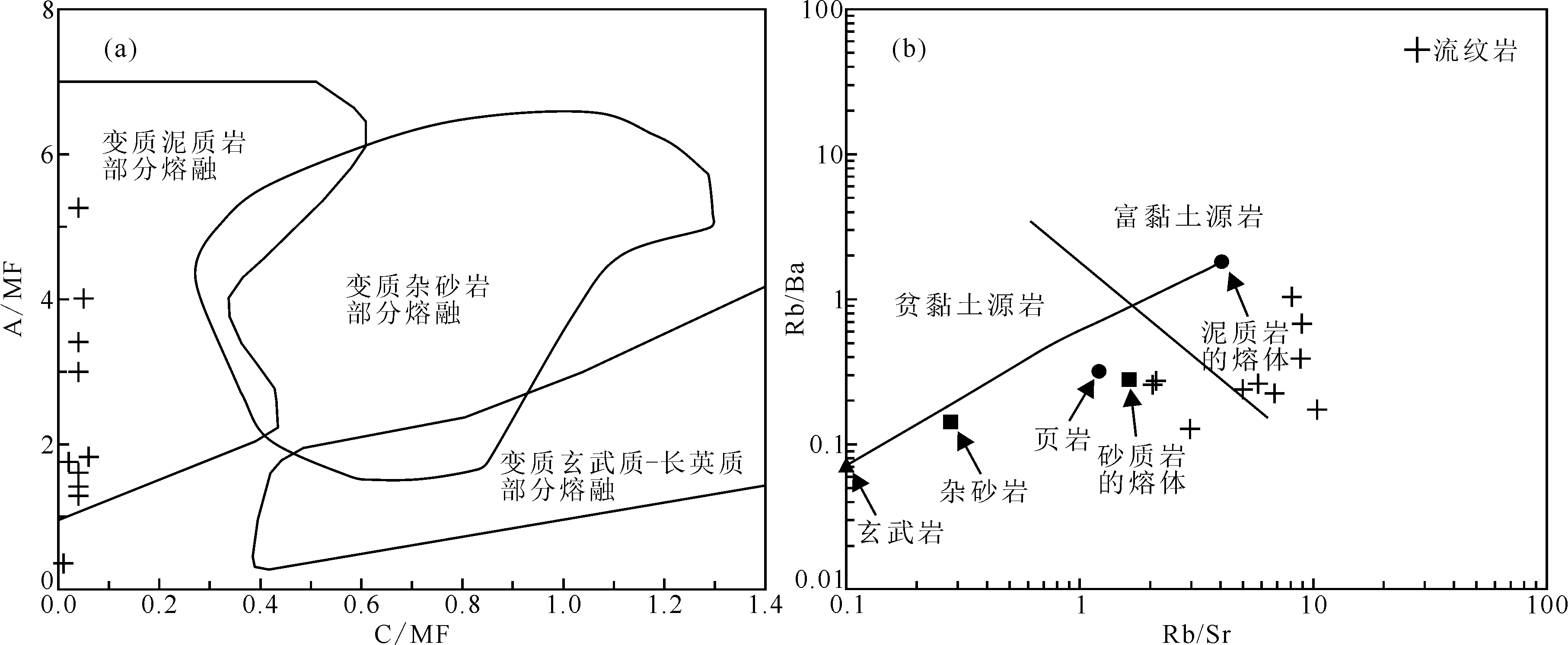
图12 大塔山林场组流纹岩A/MF-C/MF图解(a)[84]和Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr图解(b)[78]
Fig.12 A/MF-C/MF (a) [84] and Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr (b) [78] diagrams of the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation
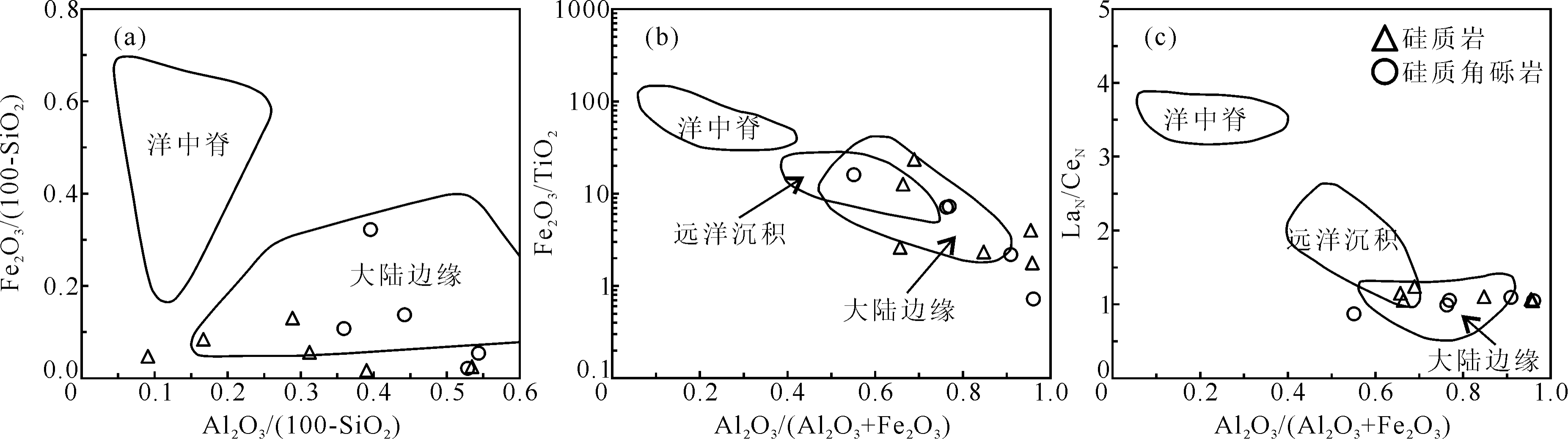
图14 四平山组硅质岩、硅质角砾岩Fe2O3/(100-SiO2)-Al2O3/(100-SiO2)图解(a)、Fe2O3/TiO2-Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3)图解(b)和LaN/CeN-Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3)图解(c)[129]
Fig.14 Fe2O3/(100-SiO2)-Al2O3/(100-SiO2) (a), Fe2O3/TiO2-Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3) (b) and LaN/CeN-Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3) (c) diagrams of the chert and silicified breccia in Sipingshan Formation[129]
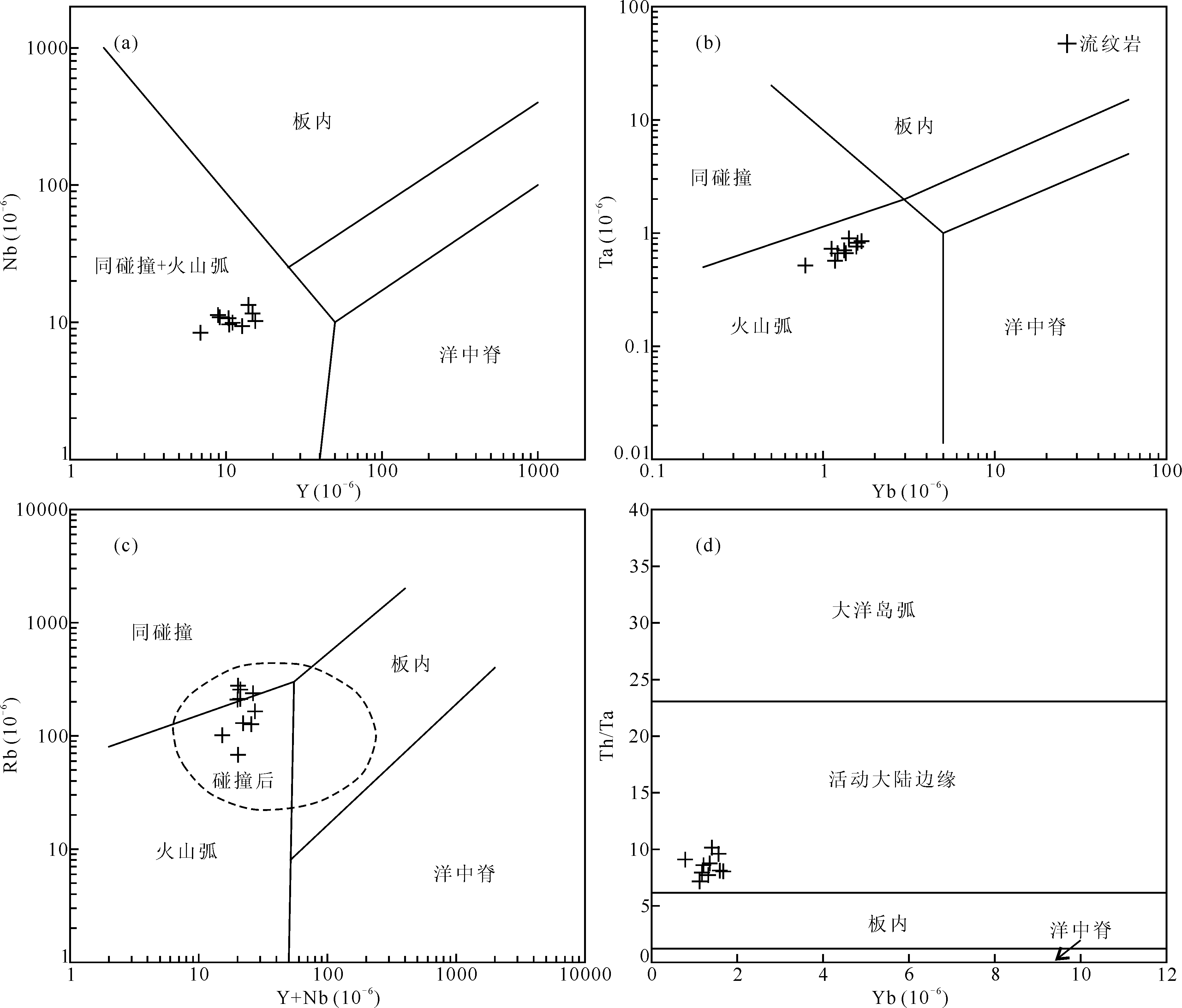
图15 大塔山林场组流纹岩Nb-Y图解(a)、Ta-Yb图解(b)、Rb-(Y+Nb)图解(c)、Th/Ta-Yb图解(d)[131-132]
Fig.15 Nb-Y (a), Ta-Yb (b), Rb-(Y+Nb) (c), and Th/Ta-Yb (d) diagrams of the rhyolite in Datashanlinchang Formation [131-132]

图16 那丹哈达地体早白垩世地球动力学背景重建图(底图据文献[25]修改)
Fig.16 Reconstruction diagram of the Early Cretaceous geodynamic background in the Nadanhada terrane (modified after reference [25])
| [1] |
BI J H, GE W C, YANG H, et al. Geochemistry of MORB and OIB in the Yuejinshan complex, NE China: Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 145: 475-493.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHENG H, SUN X M, WAN K, et al. Structure and tectonic evolution of the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Wandashan accretionary complex, NE China[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(1): 17-38.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 田东江, 周建波, 郑常青, 等. 完达山造山带蛇绿混杂岩中变质基性岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2006, 26(3): 64-70. |
| [4] |
ZHOU J B, CAO J L, WILDE S A, et al. Paleo-pacific subduction-accretion: Evidence from geochemical and U-Pb zircon dating of the nadanhada accretionary complex, NE China[J]. Tectonics, 2014, 33(12): 2444-2466.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 王继尧, 杨言辰, 黄永卫, 等. 黑龙江东部完达山地体蛇绿岩形成时代及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2016, 38(2): 182-195. |
| [6] | 刘永江, 冯志强, 蒋立伟, 等. 中国东北地区蛇绿岩[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(10): 3017-3047. |
| [7] | 李伟民, 刘永江, 赵英利, 等. 佳木斯地块构造演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(3): 665-684. |
| [8] |
LIANG Y, ZHENG H, LI H, et al. Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic subduction and accretion of the Paleo-Pacific Plate: Insights from ophiolitic rocks in the Wandashan accretionary complex, NE China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2021, 12(6): 101242.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIANG Y, ZHENG H, LI H A, et al. Late paleozoic-mesozoic subduction and accretion of the paleo-pacific plate: Insights from the ocean plate stratigraphy of the Wandashan accretionary complex, NE China[J]. International Geology Review, 2023, 65(1): 114-132.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 周建波, 石爱国, 景妍. 东北地块群: 构造演化与古大陆重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(4): 1042-1055. |
| [11] | 周建波, 蒲先刚, 侯贺晟, 等. 东北中生代增生杂岩及对古太平洋向欧亚大陆俯冲历史的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(10): 2845-2856. |
| [12] |
李三忠, 张勇, 郭玲莉, 等. 那丹哈达地体及周缘中生代变形与增生造山过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 200-212.
DOI |
| [13] | 曾振. 佳木斯地块与完达山杂岩的构造性质及其演化[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. |
| [14] |
ZHOU J B, LI L. The Mesozoic accretionary complex in Northeast China: Evidence for the accretion history of Paleo-Pacific subduction[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 145: 91-100.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG D, LIU Y J, LI W M, et al. Marginal accretion processes of Jiamusi Block in NE China: Evidences from detrital zircon U-Pb age and deformation of the Wandashan Terrane[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 78: 92-109.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 韩伟, 周建波. 古太平洋板块俯冲—增生时限:饶河增生杂岩的地球化学和年代学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(3): 703-725. |
| [17] |
WANG Y N, XU W L, WANG F, et al. Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the northeastern Asian continental margin revealed by sedimentary formations and fossil accretionary complexes[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 225: 103908.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG G B, YANG Y C, WANG J A, et al. Geology, geochemistry, and genesis of the hot-spring-type Sipingshan gold deposit, eastern Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(4): 482-495.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 王庆双, 杨言辰, 韩世炯, 等. 黑龙江先锋北山金矿床火山岩地球化学特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(4): 675-691. |
| [20] | 韦延兰, 杨言辰, 刘娜, 等. 黑龙江省跃进山铜金矿床花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(1): 169-179. |
| [21] | 王庆磊, 杨言辰, 李骞, 等. 黑龙江完达山地区358高地岩金矿床花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(12): 2171-2180. |
| [22] | 谈艳, 杨言辰, 王建, 等. 黑龙江258高地金矿区侵入岩锆石U-Pb年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2016, 35(4): 737-757. |
| [23] | 王硕, 孙丰月, 王冠, 等. 黑龙江河口林场锡多金属矿床地质特征及矿床成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(3): 312-328. |
| [24] | 郝宇杰, 任云生, 史雨凡, 等. 黑龙江省完达山地区河口林场斑岩型锡多金属矿床花岗斑岩的形成年代、岩石成因及构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(3): 837-855. |
| [25] |
WANG Q S, WEI Y L, YANG Y C, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of granitoid in the Yuejinshan copper-gold deposit, NE China: Constraints on petrogenesis and metallogenesis[J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(11): 1206.
DOI URL |
| [26] | ZHANG Y, SONG Q H, HAN S J, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hekoulinchang Sn polymetallic deposit in Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. China Geology, 2021, 4(3): 1-14. |
| [27] |
HAN S J, YANG Y C, BO J W, et al. New insights into the genesis of the Sipingshan gold deposit in eastern Heilongjiang, north-eastern China: Evidence from geology, U-Pb and Rb-Sr geochronology, geochemistry, and H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2023, 154: 105325.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 孙荣祥, 柏志佳, 史建民, 等. 虎林市四平山金矿热泉成因特征[J]. 黄金, 2000, 21(3): 9-15. |
| [29] | 黄永卫. 黑龙江省东南部完达山—太平岭一带浅成低温热液矿床区域成矿规律及找矿前景研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010. |
| [30] | 孙甲富, 王连国, 迟晓彬, 等. 黑龙江虎林四平山热泉型金矿床地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 世界地质, 2012, 31(2): 271-280. |
| [31] | 王硕, 孙丰月, 王冠, 等. 黑龙江省四平山金矿床成矿作用及矿床成因: 来自矿床地质、地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及H-O-S同位素的制约[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(5): 1626-1648. |
| [32] | 张传恒, 张世红. 完达山造山带原型盆地及可能的造山机制[J]. 现代地质, 1999, 13(1): 25-31. |
| [33] | 张国宾, 杨言辰, 梁冰, 等. 黑龙江东部完达山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及成矿预测[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(3): 588-603. |
| [34] | 杨云宝, 柳永清. 黑龙江完达山造山带填图方法实践及意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1919-1926. |
| [35] | 黄迪颖, 房亚男, 李建国, 等. 中国侏罗纪岩石地层划分和对比[J]. 地层学杂志, 2021, 45(3): 364-374. |
| [36] |
LAN H Y, LI S Z, GUO L L, et al. Mesozoic deformation of the nadanhada terrane (NE China) and its implications on the subduction of the paleo-pacific plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 232: 105166.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 万阔. 完达山地体构造特征、结构及增生过程[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. |
| [38] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 1-30.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 任云生, 郝宇杰, 王崇一, 等. 黑龙江省完达山地区金铜成矿作用时代、构造背景及物质源区[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(3): 644-664. |
| [40] | 张国宾. 黑龙江省东部完达山地块区域成矿系统研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014. |
| [41] | LUDWIG K R. Isoplot V.3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003: 70. |
| [42] |
GAO S, LIU X, YUAN H, et al. Determination of forty two major and trace elements in USGS and NIST SRM glasses by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards Newsletter, 2002, 26(2): 181-196.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
VAVRA G, SCHMID R, GEBAUER D. Internal morphology, habit and U-Th-Pb microanalysis of amphibolite-to-granulite facies zircons: Geochronology of the ivrea zone (southern Alps)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1999, 134(4): 380-404.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene cal-calkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
HASKIN M A, HASKIN L A. Rare earths in European shales: A redetermination[J]. Science, 1966, 154: 507-509.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [49] | POTTER R W, BROWN D L. Volumetric properties of aqueous sodium chloride solutions from 0 to 500 ℃ at pressures up to 2000 bars based on a regression of available data in the literature[R]. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1977: 1-36. |
| [50] | 张理刚. 两阶段水-岩同位素交换理论及其勘查应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995: 174-188. |
| [51] | 张国宾, 韩超, 杨言辰, 等. 完达山地块跃进山矽卡岩型铜金矿区酸性侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(5): 977-991. |
| [52] |
DUHIG N C, STOLZ J, DAVIDSON G J, et al. Cambrian microbial and silica gel textures in silica iron exhalites from the Mount Windsor volcanic belt, Australia: their petrography, chemistry, and origin[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87(3): 764-784.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 潘家永, 张乾, 马东升, 等. 滇西学拉铜矿区硅质岩特征及与成矿的关系[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(1): 10-16. |
| [54] | 杨恩林, 陈恨水, 陈焕, 等. 黔东留茶坡组硅质岩元素地球化学特征与形成环境[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 31(3): 406-411. |
| [55] | HØGDAHL O T, MELSOM S, BOWEN V T. Neutron activation analysis of lanthanide elements in sea water[M]// Trace in Organics in Water. WASHINGTON: American Chemical Society, 1968: 308-325. |
| [56] |
MURRAY R W, TENBRINK M R B, JONES D L, et al. Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environments in chert and shale[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(3): 268-271.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
MARCHIG V, GUNDLACH H, MÖLLER P, et al. Some geochemical indicators for discrimination between diagenetic and hydrothermal metalliferous sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1982, 50(3): 241-256.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 周永章. 丹池盆地热水成因硅岩的沉积地球化学特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1990, 8(3): 75-83. |
| [59] |
WONDER J D, SPRY P G, WINDOM K E. Geochemistry and origin of manganese-rich rocks related to iron-formation and sulfide deposits, western Georgia[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(5): 1070-1081.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
ADACHI M, YAMAMOTO K, SUGISAKI R. Hydrothermal chert and associated siliceous rocks from the northern Pacific their geological significance as indication of ocean ridge activity[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 47(1/2): 125-148.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
BOSTRÖM K, KRAEMER T, GARTNER S. Provenance and accumulation rates of opaline silica, Al, Ti, Fe, Mn, Cu, Ni and Co in Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1973, 11(2): 123-148.
DOI URL |
| [62] | BOSTROM K. Genesis of ferromanganese deposits-diagnostic criteria for recent and old deposits[M]// RONAP A, BOSTRÖMK, LAUBIERL, et al. Hydrothermal Processes at Seafloor Spreading Centers. Boston: Springer, 1983: 473-489. |
| [63] |
COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
WHALEN J B. Geochemistry of an island-arc plutonic suite: The Uasilau-Yau Yau intrusive complex, new Britain, PNG[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1985, 26(3): 603-632.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
BARBARIN B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 605-626.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
CLEMENS J D. S-type granitic magmas—Petrogenetic issues, models and evidence[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 61(1/2): 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1/2): 1-29.
DOI URL |
| [68] | 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等. 福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(11): 2468-2484. |
| [69] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type gra-nites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [70] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [71] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974, 8(2): 173-174. |
| [72] |
CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1992, 83(1/2): 1-26.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 535-551.
DOI URL |
| [74] | 王德滋, 刘昌实, 沈渭洲, 等. 桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(1): 44-54. |
| [75] |
MILLER C F. Are strongly peraluminous magmas derived from pelitic sedimentary sources?[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 93(6): 673-689.
DOI URL |
| [76] | 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2017, 47(7): 745-765. |
| [77] |
FLOYD P A, WINCHESTER J A. Magma type and tectonic setting discrimination using immobile elements[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1975, 27(2): 211-218.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/2/3/4): 29-44.
DOI URL |
| [79] | RUDNICK R, GAO S. The role of lower crustal recycling in continent formation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(18): 403. |
| [80] |
HOFMANN A W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3): 297-314.
DOI URL |
| [81] | 寇林林, 张朋, 赵岩, 等. 辽东半岛早白垩世黑云母二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(11): 3950-3961. |
| [82] |
RAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931.
DOI URL |
| [83] | 王崇一, 郝宇杰, 商青青, 等. 黑龙江跃进山矽卡岩型铜金矿床花岗闪长岩的年代学和地球化学特征[J]. 世界地质, 2021, 40(1): 29-40. |
| [84] |
ALTHERR R, HOLL A, HEGNER E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides: Northern Vosges (France) and northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(1/2/3): 51-73.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
XU W L, PEI F P, WANG F, et al. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74: 167-193.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
TANG J, XU W L, WANG F, et al. Subduction history of the Paleo-Pacific slab beneath Eurasian continent: Mesozoic-Paleogene magmatic records in Northeast Asia[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 527-559.
DOI |
| [87] | 许文良, 王旖旎, 王枫, 等. 西太平洋俯冲带的演变:来自东北亚陆缘增生杂岩的制约[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(1): 1-17. |
| [88] |
ŞENGÖR A M C, NATAL’IN B A, BURTMAN V S. Evolution of the altaid tectonic collage and palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364(6435): 299-307.
DOI |
| [89] |
LIU Y J, LI W M, FENG Z Q, et al. A review of the Paleozoic tectonics in the eastern part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 43: 123-148.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
METELKIN D V, VERNIKOVSKY V A, KAZANSKY A Y, et al. Late Mesozoic tectonics of Central Asia based on paleomagnetic evidence[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 18(2/3): 400-419.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
COCKS L R M, TORSVIK T H. The dynamic evolution of the Palaeozoic geography of eastern Asia[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 117: 40-79.
DOI URL |
| [92] | 张祥信, 高永丰, 雷世和. 内蒙古中部红格尔地区白音高老组流纹岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 950-960. |
| [93] | WU L, KRAVCHINSKY V A, GU Y J, et al. Absolute reconstruction of the closing of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean in the Mesozoic elucidates the genesis of the slab geometry underneath Eurasia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2017, 122(7): 4831-4851. |
| [94] |
SOROKIN A A, ZAIKA V A, KOVACH V P, et al. Timing of closure of the eastern Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean: Constraints from U-Pb and Hf isotopic data of detrital zircons from metasediments along the Dzhagdy Transect[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 81: 58-78.
DOI URL |
| [95] | 杨智荔, 张晓晖, 袁玲玲. 辽—蒙交界地区晚侏罗世高硅花岗岩:岩石成因与地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(4): 1061-1081. |
| [96] | 杨文鹏, 李成禄, 杨元江, 等. 黑龙江塔溪地区中侏罗世侵入岩地球化学特征、成因及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(2): 390-403. |
| [97] |
XU W L, JI W Q, PEI F P, et al. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, NE China: Chronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 392-402.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
ZHOU J B, WILDE S A. The crustal accretion history and tectonic evolution of the NE China segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1365-1377.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
JAHN B M, VALUI G, KRUK N, et al. Emplacement ages, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characterization of Mesozoic to Early Cenozoic granitoids of the Sikhote-Alin Orogenic Belt, Russian Far East: Crustal growth and regional tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 111: 872-918.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
MA X H, CAO R, ZHOU Z H, et al. Early Cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Yanji area, northeastern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 393-405.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
MA X H, ZHU W P, ZHOU Z H, et al. Transformation from Paleo-Asian Ocean closure to Paleo-Pacific subduction: New constraints from granitoids in the eastern Jilin-Heilongjiang Belt, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 144: 261-286.
DOI URL |
| [102] | 乔石磊, 马星华, 陈忠新. 吉黑东部两类侏罗纪长英质岩体的成因及成矿潜力分析: 以东宁和福洞岩体为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 799-816. |
| [103] | 杨雪叶, 尹继元, 肖文交, 等. 东北那丹哈达岭中—新生代构造-热演化史:来自(U-Th)/He和裂变径迹热年代学的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(12): 3660-3675. |
| [104] | 杨文采. 中—新生代东北和华北的洋陆转换作用[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(3): 769-780. |
| [105] | 吴福元, 徐义刚, 高山, 等. 华北岩石圈减薄与克拉通破坏研究的主要学术争论[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1145-1174. |
| [106] | 王玉平, 吴文彬, 刘永俊, 等. 辽东岫岩地区晚侏罗世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(4): 955-967. |
| [107] | 张兴洲, 杨宝俊, 吴福元, 等. 中国兴蒙—吉黑地区岩石圈结构基本特征[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(4): 816-823. |
| [108] | 陈衍景, 肖文交, 张进江. 成矿系统: 地球动力学的有效探针[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(6): 1059-1073. |
| [109] | 葛肖虹, 刘俊来, 任收麦, 等. 中国东部中—新生代大陆构造的形成与演化[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1): 19-38. |
| [110] |
SAFONOVA I Y, SANTOSH M. Accretionary complexes in the Asia-Pacific region: Tracing archives of ocean plate stratigraphy and tracking mantle plumes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(1): 126-158.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
KHANCHUK A I, KEMKIN I V, KRUK N N. The Sikhote-Alin orogenic belt, Russian South East: Terranes and the formation of continental lithosphere based on geological and isotopic data[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 120: 117-138.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
WANG Z H, GE W C, YANG H, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Early Jurassic volcanic rocks of the Raohe accretionary complex, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 134: 262-280.
DOI URL |
| [113] | SUN M D, XU Y G, WILDE S A, et al. Provenance of Cretaceous trench slope sediments from the Mesozoic Wandashan Orogen, NE China: Implications for determining ancient drainage systems and tectonics of the Paleo-Pacific[J]. Tectonics, 2015, 34(6): 1269-1289. |
| [114] | DMITRIENKO LIUDMILA Valer'evna, 王鹏程, 李三忠, 等. 东亚大汇聚与中—新生代地球表层系统演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(4): 33-64. |
| [115] | WU M Q, TIAN B F, ZHANG D H, et al. Zircon of the No. 782 deposit from the Great Xing’an Range in NE China: Implications for Nb-REE-Zr mineralization during magmatic-hydrothermal evolution[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 102: 284-299. |
| [116] | 肖文交, 宋东方, BRIAN F Windley, 等. 中亚增生造山过程与成矿作用研究进展[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2019, 49(10): 1512-1545. |
| [117] | LI G, MATSUOKA A, YANG Q, et al. Middle and Late Jurassic radiolarians from Nadanhada terrane of eastern Heilongjiang Province, northeastern China[J]. Paleontological Research, 2019, 23(4): 291. |
| [118] | 韩伟, 冯志强, 刘永江, 等. 跃进山杂岩的地质年代学和地球化学证据及其构造演化意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(8): 2489-2509. |
| [119] | 周建波. 增生杂岩: 从大洋俯冲到大陆深俯冲的地质记录[J]. 中国科学(地球科学,) 2020, 50(12): 1709-1726. |
| [120] | 杜兵盈, 刘飞, 刘勇, 等. 黑龙江省中东部地区二叠纪—早侏罗世洋陆演化过程及成矿动力学背景探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(2): 431-451. |
| [121] | 水谷伸治郎, 邵济安, 张庆龙. 那丹哈达地体与东亚大陆边缘中生代构造的关系[J]. 地质学报, 1989, 63(3): 204-216. |
| [122] | 邵济安, 唐克东, 王成源, 等. 那丹哈达地体的构造特征及演化[J]. 中国科学 (B辑), 1991, 21(7): 744-751. |
| [123] | 刘德来, 马莉. 中生代东亚大陆边缘构造演化[J]. 现代地质, 1997, 11(4): 444-451. |
| [124] | 任收麦, 朱日祥, 邱海峻, 等. 黑龙江省饶河枕状玄武岩古地磁学研究及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(4): 1269-1283. |
| [125] | KOJIMA S. Mesozoic terrane accretion in Northeast China, Sikhote-Alin and Japan regions[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1989, 69: 213-232. |
| [126] | MIZUTANI S, KOJIMA S. Mesozoic radiolarian biostratigraphy of Japan and collage tectonics along the eastern continental margin of Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1992, 96(1/2): 3-22. |
| [127] | KIRILLOVA G L. Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary basins of active continental margin of Southeast Russia: Paleogeography, tectonics, and coal-oil-gas presence[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(3/4): 385-397. |
| [128] | 周丽云, 王瑜, 王娜. 中国东北完达山地区早白垩世同构造岩浆侵位: 对晚中生代左行走滑作用的响应[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(增): 400-418. |
| [129] | MURRAY R W. Chemical criteria to identify the depositional environment of chert: General principles and applications[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3/4): 213-232. |
| [130] | MURRAY R W, BUCHHOLTZ TEN BRINK M R, GERLACH D C, et al. Rare earth, major, and trace elements in chert from the Franciscan Complex and Monterey Group, California: Assessing REE sources to fine-grained marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(7): 1875-1895. |
| [131] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. |
| [132] | GORTON M P, SCHANDL E S. From continents to island arcs: A geochemical index of tectonic setting for arc-related and within-plate felsic to intermediate volcanic rocks[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2000, 38(5): 1065-1073. |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [5] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [6] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [7] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [8] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [9] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [10] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [11] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [12] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [13] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| [14] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [15] | 李成禄, 符安宗, 徐文喜, 袁茂文, 刘宝山, 杨文鹏, 赵瑞君, 赵忠海. 黑龙江多宝山地区永新金矿床构造叠加晕特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 674-689. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||