



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (06): 1597-1608.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.050
杨元江1( ), 邓昌州2, 李成禄1, 杨文鹏1, 符安宗1, 郑博1, 袁茂文3, 张立东1
), 邓昌州2, 李成禄1, 杨文鹏1, 符安宗1, 郑博1, 袁茂文3, 张立东1
收稿日期:2022-09-14
修回日期:2023-04-17
出版日期:2023-12-10
发布日期:2024-01-24
作者简介:杨元江,男,高级工程师,1982年出生,地质学专业,主要从事地质矿产勘查及研究工作。Email:geolj@qq.com。
基金资助:
YANG Yuanjiang1( ), DENG Changzhou2, LI Chenglu1, YANG Wenpeng1, FU Anzong1, ZHENG Bo1, YUAN Maowen3, ZHANG Lidong1
), DENG Changzhou2, LI Chenglu1, YANG Wenpeng1, FU Anzong1, ZHENG Bo1, YUAN Maowen3, ZHANG Lidong1
Received:2022-09-14
Revised:2023-04-17
Online:2023-12-10
Published:2024-01-24
摘要:
小兴安岭伊春翠峦地区地处洋陆转换关键位置,受古亚洲洋和太平洋构造域的双重影响,是研究区域构造演化的重要部位。该区域中生代花岗岩形成构造环境与动力学机制长期存在分歧,一定程度上制约了区域构造演化历史的反演,也影响区域找矿工作的部署。本文对伊春翠峦地区碱长花岗岩进行全岩元素组成以及锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素组成分析,阐释岩石成因和源区属性,并探讨成岩构造环境。结果显示,岩浆锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(189.1 ± 1.6) Ma (MSWD=2.1,n=20),指示岩体侵位于早侏罗世。岩石富Si、K和Na元素,贫Ca、Mg元素;富集Th、Zr、Hf、Ce和Y元素,亏损Ba、Sr、Eu和Ti元素;锆石饱和温度高(804~ 810 ℃),显示岩石属于A型花岗岩。岩石稀土元素总量高(∑REE=192.60×10-6~232.80×10-6),Nb、Ta和Ti等元素亏损,Th元素富集,指示其具壳源特征。锆石的εHf(t)=1.46~2.27,对应的地壳模式年龄$T_{\mathrm{DM}}{ }^{\mathrm{C}}$=1133~1088 Ma,表明岩浆源区物质主要为中元古代新生下地壳。综合分析认为,伊春地区早侏罗世岩浆活动与太平洋板块俯冲及伸展作用密切相关。本研究成果为深入理解小兴安岭地区早侏罗世构造演化提供了新的年代学与岩石学约束。
中图分类号:
杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608.
YANG Yuanjiang, DENG Changzhou, LI Chenglu, YANG Wenpeng, FU Anzong, ZHENG Bo, YUAN Maowen, ZHANG Lidong. Genesis and Tectonic Significance of Early Jurassic Cuiluan A-type Granite in the Lesser Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608.

图1 中亚造山带构造简图(a)和中国东北地区大地构造单元划分图(b)(据文献[11]修改) EB.额尔古纳地块;HHS.黑河—贺根山断裂;JB.佳木斯地块;MYS.嘉荫—牡丹江断裂;SB.松嫩地块;XB.兴安地块;XXS.新林—喜桂图断裂
Fig.1 Tectonic map of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (a) and NE China (b) (modified after reference [11])

图2 伊春地区花岗岩分布简图(a)(据文献[31]修编)和研究区地质图(b) Qh.第四系;K2n.上白垩统嫩江组;K1n.下白垩统宁远村组;P3w.上二叠统五道岭组;P2t.中二叠统土门岭组;$\epsilon$1q.下寒武统铅山组;χργJ1.早侏罗世碱长花岗岩;γδO2.中奥陶世花岗闪长岩;ηγO2.中奥陶世二长花岗岩;γπ.花岗斑岩脉;δμ.闪长玢岩脉
Fig.2 Distribution map of granite in Yichun area (a) (modified after reference [31]) and geological map of the study area (b)

图3 翠峦碱长花岗岩(CL3号样品)岩石照片(a)和镜下图像(b)(c)(d) Bi.黑云母;Kfs.钾长石;Mc.微斜长石;Pl.斜长石;Pth.条纹长石;Qtz.石英
Fig.3 Rock specimen photos and microscopic photos of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite (Sample No.CL3)
| 测点号 | 元素含量(10-6) | Th/U | 比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||||||||
| CL3-01 | 7.71 | 117.0 | 223 | 0.52 | 0.0 554 | 0.0 033 | 0.2 212 | 0.0 290 | 0.0 004 | 427.8 | 133.3 200 | 202.9 | 10.8 979 | 184.6 | 2.4 853 | |||||||
| CL3-02 | 7.06 | 103.0 | 202 | 0.51 | 0.0 493 | 0.0 028 | 0.2 026 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 004 | 164.9 | 133.3 150 | 187.3 | 9.3 216 | 191.6 | 2.7 146 | |||||||
| CL3-03 | 8.26 | 139.0 | 234 | 0.59 | 0.0 529 | 0.0 025 | 0.2 161 | 0.0 297 | 0.0 003 | 327.8 | 105.5 425 | 198.6 | 8.1 512 | 188.7 | 2.1 670 | |||||||
| CL3-04 | 6.80 | 90.5 | 199 | 0.45 | 0.0 500 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 031 | 0.0 296 | 0.0 004 | 194.5 | 130.5 375 | 187.8 | 9.1 419 | 188.1 | 2.3 982 | |||||||
| CL3-05 | 8.05 | 106.0 | 232 | 0.46 | 0.0 514 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 143 | 0.0 303 | 0.0 004 | 257.5 | 122.2 050 | 197.2 | 9.2 817 | 192.3 | 2.4 385 | |||||||
| CL3-06 | 8.72 | 146.0 | 241 | 0.61 | 0.0 495 | 0.0 024 | 0.2 074 | 0.0 305 | 0.0 004 | 172.3 | 111.0 950 | 191.3 | 8.0 317 | 193.5 | 2.4 243 | |||||||
| CL3-07 | 11.32 | 181.0 | 330 | 0.55 | 0.0 537 | 0.0 021 | 0.2 123 | 0.0 287 | 0.0 003 | 366.7 | 95.3 600 | 195.5 | 6.7 753 | 182.6 | 1.9 873 | |||||||
| CL3-08 | 6.86 | 94.7 | 197 | 0.48 | 0.0 490 | 0.0 026 | 0.2 043 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 004 | 146.4 | 158.3 125 | 188.8 | 8.3 389 | 191.9 | 2.5 891 | |||||||
| CL3-09 | 8.28 | 107.0 | 238 | 0.45 | 0.0 510 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 089 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 004 | 239.0 | 128.6 850 | 192.6 | 8.4 208 | 191.8 | 2.4 298 | |||||||
| CL3-10 | 17.11 | 307.0 | 482 | 0.64 | 0.0 508 | 0.0 018 | 0.2 056 | 0.0 293 | 0.0 003 | 231.6 | 86.0 975 | 189.8 | 5.8 765 | 186.4 | 1.9 368 | |||||||
| CL3-11 | 15.87 | 202.0 | 457 | 0.44 | 0.0 513 | 0.0 020 | 0.2 141 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 003 | 253.8 | 90.7 275 | 197.0 | 6.8 858 | 191.7 | 2.0 755 | |||||||
| CL3-12 | 12.97 | 212.0 | 361 | 0.59 | 0.0 526 | 0.0 021 | 0.2 187 | 0.0 300 | 0.0 003 | 322.3 | 123.1 350 | 200.8 | 7.3 101 | 190.5 | 2.0 353 | |||||||
| CL3-13 | 11.80 | 153.0 | 342 | 0.45 | 0.0 517 | 0.0 022 | 0.2 138 | 0.0 299 | 0.0 004 | 276.0 | 98.1 325 | 196.8 | 7.7 240 | 189.8 | 2.2 624 | |||||||
| CL3-14 | 7.20 | 97.1 | 205 | 0.47 | 0.0 512 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 106 | 0.0 300 | 0.0 004 | 250.1 | 122.2 050 | 194.1 | 9.0 121 | 190.6 | 2.4 527 | |||||||
| CL3-15 | 4.70 | 65.4 | 133 | 0.49 | 0.0 484 | 0.0 037 | 0.2 034 | 0.0 306 | 0.0 005 | 120.5 | 179.6 000 | 188.0 | 12.0 015 | 194.4 | 3.2 822 | |||||||
| CL3-16 | 8.01 | 144.0 | 211 | 0.68 | 0.0 503 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 094 | 0.0 303 | 0.0 004 | 205.6 | 122.2 050 | 193.1 | 9.0 075 | 192.2 | 2.4 913 | |||||||
| CL3-17 | 8.51 | 146.0 | 235 | 0.62 | 0.0 500 | 0.0 030 | 0.2 018 | 0.0 294 | 0.0 004 | 198.2 | 140.7 225 | 186.6 | 9.8 710 | 186.5 | 2.7 089 | |||||||
| CL3-18 | 7.45 | 103.0 | 211 | 0.49 | 0.0 494 | 0.0 025 | 0.2 025 | 0.0 301 | 0.0 004 | 164.9 | 120.3 525 | 187.3 | 8.0 838 | 191.4 | 2.5 734 | |||||||
| CL3-19 | 6.20 | 93.4 | 178 | 0.52 | 0.0 462 | 0.0 033 | 0.1 820 | 0.0 288 | 0.0 004 | 5.7 | 166.6 500 | 169.7 | 10.4 249 | 183.0 | 2.4 091 | |||||||
| CL3-20 | 10.24 | 215.0 | 265 | 0.81 | 0.0 562 | 0.0 028 | 0.2 258 | 0.0 295 | 0.0 004 | 457.5 | 112.9 500 | 206.7 | 8.8 355 | 187.1 | 2.4 905 | |||||||
表1 翠峦碱长花岗岩锆石U-Pb测年分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating results of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite
| 测点号 | 元素含量(10-6) | Th/U | 比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||||||||
| CL3-01 | 7.71 | 117.0 | 223 | 0.52 | 0.0 554 | 0.0 033 | 0.2 212 | 0.0 290 | 0.0 004 | 427.8 | 133.3 200 | 202.9 | 10.8 979 | 184.6 | 2.4 853 | |||||||
| CL3-02 | 7.06 | 103.0 | 202 | 0.51 | 0.0 493 | 0.0 028 | 0.2 026 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 004 | 164.9 | 133.3 150 | 187.3 | 9.3 216 | 191.6 | 2.7 146 | |||||||
| CL3-03 | 8.26 | 139.0 | 234 | 0.59 | 0.0 529 | 0.0 025 | 0.2 161 | 0.0 297 | 0.0 003 | 327.8 | 105.5 425 | 198.6 | 8.1 512 | 188.7 | 2.1 670 | |||||||
| CL3-04 | 6.80 | 90.5 | 199 | 0.45 | 0.0 500 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 031 | 0.0 296 | 0.0 004 | 194.5 | 130.5 375 | 187.8 | 9.1 419 | 188.1 | 2.3 982 | |||||||
| CL3-05 | 8.05 | 106.0 | 232 | 0.46 | 0.0 514 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 143 | 0.0 303 | 0.0 004 | 257.5 | 122.2 050 | 197.2 | 9.2 817 | 192.3 | 2.4 385 | |||||||
| CL3-06 | 8.72 | 146.0 | 241 | 0.61 | 0.0 495 | 0.0 024 | 0.2 074 | 0.0 305 | 0.0 004 | 172.3 | 111.0 950 | 191.3 | 8.0 317 | 193.5 | 2.4 243 | |||||||
| CL3-07 | 11.32 | 181.0 | 330 | 0.55 | 0.0 537 | 0.0 021 | 0.2 123 | 0.0 287 | 0.0 003 | 366.7 | 95.3 600 | 195.5 | 6.7 753 | 182.6 | 1.9 873 | |||||||
| CL3-08 | 6.86 | 94.7 | 197 | 0.48 | 0.0 490 | 0.0 026 | 0.2 043 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 004 | 146.4 | 158.3 125 | 188.8 | 8.3 389 | 191.9 | 2.5 891 | |||||||
| CL3-09 | 8.28 | 107.0 | 238 | 0.45 | 0.0 510 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 089 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 004 | 239.0 | 128.6 850 | 192.6 | 8.4 208 | 191.8 | 2.4 298 | |||||||
| CL3-10 | 17.11 | 307.0 | 482 | 0.64 | 0.0 508 | 0.0 018 | 0.2 056 | 0.0 293 | 0.0 003 | 231.6 | 86.0 975 | 189.8 | 5.8 765 | 186.4 | 1.9 368 | |||||||
| CL3-11 | 15.87 | 202.0 | 457 | 0.44 | 0.0 513 | 0.0 020 | 0.2 141 | 0.0 302 | 0.0 003 | 253.8 | 90.7 275 | 197.0 | 6.8 858 | 191.7 | 2.0 755 | |||||||
| CL3-12 | 12.97 | 212.0 | 361 | 0.59 | 0.0 526 | 0.0 021 | 0.2 187 | 0.0 300 | 0.0 003 | 322.3 | 123.1 350 | 200.8 | 7.3 101 | 190.5 | 2.0 353 | |||||||
| CL3-13 | 11.80 | 153.0 | 342 | 0.45 | 0.0 517 | 0.0 022 | 0.2 138 | 0.0 299 | 0.0 004 | 276.0 | 98.1 325 | 196.8 | 7.7 240 | 189.8 | 2.2 624 | |||||||
| CL3-14 | 7.20 | 97.1 | 205 | 0.47 | 0.0 512 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 106 | 0.0 300 | 0.0 004 | 250.1 | 122.2 050 | 194.1 | 9.0 121 | 190.6 | 2.4 527 | |||||||
| CL3-15 | 4.70 | 65.4 | 133 | 0.49 | 0.0 484 | 0.0 037 | 0.2 034 | 0.0 306 | 0.0 005 | 120.5 | 179.6 000 | 188.0 | 12.0 015 | 194.4 | 3.2 822 | |||||||
| CL3-16 | 8.01 | 144.0 | 211 | 0.68 | 0.0 503 | 0.0 027 | 0.2 094 | 0.0 303 | 0.0 004 | 205.6 | 122.2 050 | 193.1 | 9.0 075 | 192.2 | 2.4 913 | |||||||
| CL3-17 | 8.51 | 146.0 | 235 | 0.62 | 0.0 500 | 0.0 030 | 0.2 018 | 0.0 294 | 0.0 004 | 198.2 | 140.7 225 | 186.6 | 9.8 710 | 186.5 | 2.7 089 | |||||||
| CL3-18 | 7.45 | 103.0 | 211 | 0.49 | 0.0 494 | 0.0 025 | 0.2 025 | 0.0 301 | 0.0 004 | 164.9 | 120.3 525 | 187.3 | 8.0 838 | 191.4 | 2.5 734 | |||||||
| CL3-19 | 6.20 | 93.4 | 178 | 0.52 | 0.0 462 | 0.0 033 | 0.1 820 | 0.0 288 | 0.0 004 | 5.7 | 166.6 500 | 169.7 | 10.4 249 | 183.0 | 2.4 091 | |||||||
| CL3-20 | 10.24 | 215.0 | 265 | 0.81 | 0.0 562 | 0.0 028 | 0.2 258 | 0.0 295 | 0.0 004 | 457.5 | 112.9 500 | 206.7 | 8.8 355 | 187.1 | 2.4 905 | |||||||
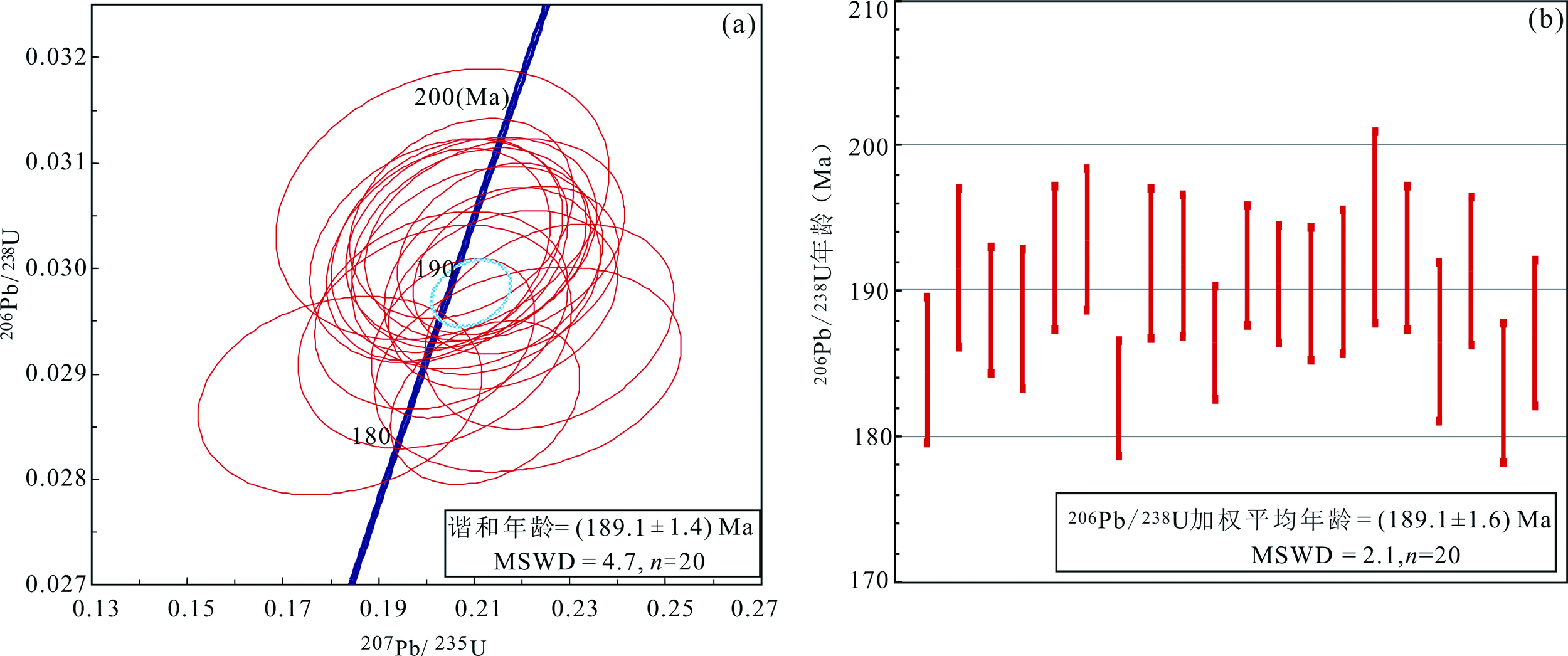
图5 翠峦碱长花岗岩锆石U-Pb谐和图(a)和206Pb/238U年龄分布图(b)
Fig.5 U-Pb concordant diagram (a) and 206Pb/238U age distribution diagram (b) of zircons from the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Mg# | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL3-25 | 72.39 | 0.26 | 13.91 | 1.79 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.99 | 3.83 | 5.43 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 16.42 | |||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 72.70 | 0.28 | 13.71 | 2.00 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 1.10 | 3.88 | 5.11 | 0.06 | 0.63 | 16.21 | |||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 74.04 | 0.24 | 13.13 | 1.74 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.94 | 3.72 | 4.88 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 14.44 | |||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 73.80 | 0.26 | 13.38 | 1.83 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 3.79 | 4.87 | 0.05 | 0.49 | 16.16 | |||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 73.65 | 0.25 | 13.56 | 1.63 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.94 | 3.44 | 5.87 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 18.18 | |||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 73.97 | 0.24 | 13.20 | 1.73 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.94 | 3.71 | 4.85 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 14.39 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Na2O+K2O | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | |||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 9.26 | 4.81 | 3.09 | 9.37 | 0.75 | 1.64 | 1.05 | 18.00 | 271 | 109.0 | 30.4 | 212 | |||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 8.98 | 4.00 | 3.28 | 11.30 | 2.48 | 1.92 | 1.50 | 17.80 | 246 | 109.0 | 38.6 | 247 | |||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 8.59 | 4.28 | 2.55 | 8.67 | 1.04 | 1.48 | 1.22 | 17.00 | 243 | 87.7 | 30.8 | 204 | |||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 8.66 | 4.26 | 2.99 | 9.73 | 1.28 | 1.58 | 1.27 | 17.40 | 225 | 98.8 | 37.1 | 221 | |||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 9.32 | 3.64 | 3.16 | 9.51 | 1.90 | 1.66 | 1.79 | 17.30 | 264 | 101.0 | 34.5 | 221 | |||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 8.56 | 3.89 | 2.96 | 9.07 | 0.86 | 1.49 | 1.13 | 17.50 | 221 | 96.7 | 36.5 | 229 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Nb | Sn | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | |||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 13.5 | 2.40 | 6.14 | 531 | 51.1 | 105.0 | 11.5 | 38.9 | 7.02 | 0.72 | 4.92 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 16.1 | 3.61 | 5.39 | 499 | 46.6 | 97.0 | 11.0 | 38.0 | 7.43 | 0.72 | 5.73 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 13.0 | 1.87 | 4.57 | 410 | 41.2 | 84.6 | 9.4 | 32.2 | 6.14 | 0.65 | 4.80 | 0.78 | |||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 15.0 | 4.75 | 3.80 | 432 | 44.8 | 93.6 | 10.5 | 36.7 | 7.01 | 0.63 | 5.95 | 0.96 | |||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 13.5 | 3.73 | 3.58 | 470 | 48.7 | 98.6 | 10.8 | 36.7 | 6.73 | 0.66 | 5.20 | 0.87 | |||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 15.4 | 4.73 | 3.78 | 423 | 44.1 | 92.1 | 10.3 | 36.8 | 7.11 | 0.69 | 5.91 | 0.96 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Tl | Pb | Th | U | A/NK | ||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 5.13 | 0.99 | 2.91 | 0.46 | 2.90 | 0.45 | 6.23 | 1.08 | 1.94 | 21.1 | 30.9 | 11.3 | 1.14 | ||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 6.22 | 1.21 | 3.58 | 0.60 | 3.64 | 0.53 | 7.32 | 1.44 | 1.73 | 18.9 | 39.4 | 14.7 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 5.07 | 0.97 | 2.91 | 0.46 | 3.02 | 0.42 | 6.24 | 1.14 | 1.76 | 18.5 | 55.1 | 15.1 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 6.30 | 1.22 | 3.62 | 0.59 | 3.53 | 0.56 | 6.62 | 1.19 | 1.56 | 15.3 | 35.9 | 12.1 | 1.16 | ||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 5.31 | 1.11 | 3.31 | 0.54 | 3.43 | 0.53 | 6.48 | 1.14 | 1.87 | 17.3 | 37.3 | 12.9 | 1.13 | ||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 6.00 | 1.21 | 3.74 | 0.59 | 3.50 | 0.54 | 7.05 | 1.17 | 1.46 | 15.0 | 36.7 | 12.3 | 1.16 | ||||||||||
| 样品编号 | A/CNK | ∑REE | ∑LREE | ∑HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | Zr+Nb+Ce+Y | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 1.00 | 232.80 | 214.24 | 18.56 | 11.54 | 0.36 | 11.88 | 361.23 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 0.99 | 223.23 | 200.75 | 22.48 | 8.93 | 0.33 | 8.63 | 398.70 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 1.00 | 192.60 | 174.17 | 18.43 | 9.45 | 0.35 | 9.20 | 332.22 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 1.00 | 215.97 | 193.24 | 22.73 | 8.50 | 0.29 | 8.56 | 366.38 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 0.99 | 222.49 | 202.19 | 20.30 | 9.96 | 0.33 | 9.57 | 367.37 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 1.01 | 213.55 | 191.10 | 22.45 | 8.51 | 0.32 | 8.49 | 373.19 | |||||||||||||||
表2 翠峦碱长花岗岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果及特征参数
Table 2 Major element(%) and trace element (10-6) compositions and characteristic parameters of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granites
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Mg# | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL3-25 | 72.39 | 0.26 | 13.91 | 1.79 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.99 | 3.83 | 5.43 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 16.42 | |||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 72.70 | 0.28 | 13.71 | 2.00 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 1.10 | 3.88 | 5.11 | 0.06 | 0.63 | 16.21 | |||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 74.04 | 0.24 | 13.13 | 1.74 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.94 | 3.72 | 4.88 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 14.44 | |||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 73.80 | 0.26 | 13.38 | 1.83 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 3.79 | 4.87 | 0.05 | 0.49 | 16.16 | |||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 73.65 | 0.25 | 13.56 | 1.63 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.94 | 3.44 | 5.87 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 18.18 | |||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 73.97 | 0.24 | 13.20 | 1.73 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.94 | 3.71 | 4.85 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 14.39 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Na2O+K2O | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | |||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 9.26 | 4.81 | 3.09 | 9.37 | 0.75 | 1.64 | 1.05 | 18.00 | 271 | 109.0 | 30.4 | 212 | |||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 8.98 | 4.00 | 3.28 | 11.30 | 2.48 | 1.92 | 1.50 | 17.80 | 246 | 109.0 | 38.6 | 247 | |||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 8.59 | 4.28 | 2.55 | 8.67 | 1.04 | 1.48 | 1.22 | 17.00 | 243 | 87.7 | 30.8 | 204 | |||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 8.66 | 4.26 | 2.99 | 9.73 | 1.28 | 1.58 | 1.27 | 17.40 | 225 | 98.8 | 37.1 | 221 | |||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 9.32 | 3.64 | 3.16 | 9.51 | 1.90 | 1.66 | 1.79 | 17.30 | 264 | 101.0 | 34.5 | 221 | |||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 8.56 | 3.89 | 2.96 | 9.07 | 0.86 | 1.49 | 1.13 | 17.50 | 221 | 96.7 | 36.5 | 229 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Nb | Sn | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | |||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 13.5 | 2.40 | 6.14 | 531 | 51.1 | 105.0 | 11.5 | 38.9 | 7.02 | 0.72 | 4.92 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 16.1 | 3.61 | 5.39 | 499 | 46.6 | 97.0 | 11.0 | 38.0 | 7.43 | 0.72 | 5.73 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 13.0 | 1.87 | 4.57 | 410 | 41.2 | 84.6 | 9.4 | 32.2 | 6.14 | 0.65 | 4.80 | 0.78 | |||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 15.0 | 4.75 | 3.80 | 432 | 44.8 | 93.6 | 10.5 | 36.7 | 7.01 | 0.63 | 5.95 | 0.96 | |||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 13.5 | 3.73 | 3.58 | 470 | 48.7 | 98.6 | 10.8 | 36.7 | 6.73 | 0.66 | 5.20 | 0.87 | |||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 15.4 | 4.73 | 3.78 | 423 | 44.1 | 92.1 | 10.3 | 36.8 | 7.11 | 0.69 | 5.91 | 0.96 | |||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Tl | Pb | Th | U | A/NK | ||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 5.13 | 0.99 | 2.91 | 0.46 | 2.90 | 0.45 | 6.23 | 1.08 | 1.94 | 21.1 | 30.9 | 11.3 | 1.14 | ||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 6.22 | 1.21 | 3.58 | 0.60 | 3.64 | 0.53 | 7.32 | 1.44 | 1.73 | 18.9 | 39.4 | 14.7 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 5.07 | 0.97 | 2.91 | 0.46 | 3.02 | 0.42 | 6.24 | 1.14 | 1.76 | 18.5 | 55.1 | 15.1 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 6.30 | 1.22 | 3.62 | 0.59 | 3.53 | 0.56 | 6.62 | 1.19 | 1.56 | 15.3 | 35.9 | 12.1 | 1.16 | ||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 5.31 | 1.11 | 3.31 | 0.54 | 3.43 | 0.53 | 6.48 | 1.14 | 1.87 | 17.3 | 37.3 | 12.9 | 1.13 | ||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 6.00 | 1.21 | 3.74 | 0.59 | 3.50 | 0.54 | 7.05 | 1.17 | 1.46 | 15.0 | 36.7 | 12.3 | 1.16 | ||||||||||
| 样品编号 | A/CNK | ∑REE | ∑LREE | ∑HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | Zr+Nb+Ce+Y | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-25 | 1.00 | 232.80 | 214.24 | 18.56 | 11.54 | 0.36 | 11.88 | 361.23 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-31 | 0.99 | 223.23 | 200.75 | 22.48 | 8.93 | 0.33 | 8.63 | 398.70 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-32 | 1.00 | 192.60 | 174.17 | 18.43 | 9.45 | 0.35 | 9.20 | 332.22 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-33 | 1.00 | 215.97 | 193.24 | 22.73 | 8.50 | 0.29 | 8.56 | 366.38 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-34 | 0.99 | 222.49 | 202.19 | 20.30 | 9.96 | 0.33 | 9.57 | 367.37 | |||||||||||||||
| CL3-35 | 1.01 | 213.55 | 191.10 | 22.45 | 8.51 | 0.32 | 8.49 | 373.19 | |||||||||||||||

图6 翠峦碱长花岗岩TAS图解(a)(底图据参考文献[39])、K2O-SiO2图解(b)(底图据参考文献[40])和A/NK-A/CNK图解(c)(底图据参考文献[41])
Fig.6 TAS diagram (a)(modified after reference [39]), K2O-SiO2 diagram (b) (modified after reference [40])and A/NK-A/CNK diagram (c)(modified after reference [41])of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite

图7 翠峦碱长花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram (b) of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite
| 序 号 | 点号 | U-Pb年 龄(Ma) | 176Yb/ 177Hf | 1σ | 176Lu/ 177Hf | 1σ | 176Hf/ 177Hf | 1σ | εHf(0) | εHf(t) | 1σ | TDM1 (Ma) | (Ma) | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CL3-01 | 185 | 0.031048 | 0.000009 | 0.000889 | 0.000011 | 0.282712 | 0.000462 | -2.11 | 1.840 | 16.36 | 763 | 1110 | -0.973222 |
| 2 | CL3-02 | 192 | 0.027737 | 0.000010 | 0.000824 | 0.000007 | 0.282720 | 0.000309 | -1.84 | 2.268 | 10.92 | 751 | 1088 | -0.975196 |
| 3 | CL3-03 | 189 | 0.035169 | 0.000009 | 0.001000 | 0.000013 | 0.282715 | 0.000640 | -2.02 | 2.000 | 22.65 | 762 | 1103 | -0.969886 |
| 4 | CL3-04 | 188 | 0.025450 | 0.000009 | 0.000738 | 0.000006 | 0.282707 | 0.000273 | -2.28 | 1.757 | 9.66 | 767 | 1118 | -0.977759 |
| 5 | CL3-05 | 192 | 0.031139 | 0.000009 | 0.000875 | 0.000006 | 0.282716 | 0.000277 | -1.98 | 2.132 | 9.81 | 758 | 1098 | -0.973655 |
| 6 | CL3-06 | 194 | 0.038944 | 0.000009 | 0.001091 | 0.000008 | 0.282718 | 0.000310 | -1.91 | 2.200 | 10.98 | 759 | 1094 | -0.967127 |
| 7 | CL3-07 | 183 | 0.041288 | 0.000009 | 0.001171 | 0.000021 | 0.282704 | 0.000811 | -2.41 | 1.463 | 28.68 | 781 | 1133 | -0.964720 |
| 8 | CL3-08 | 192 | 0.035492 | 0.000009 | 0.001001 | 0.000039 | 0.282718 | 0.001419 | -1.91 | 2.179 | 50.21 | 757 | 1094 | -0.969837 |
| 9 | CL3-09 | 192 | 0.036861 | 0.000009 | 0.001050 | 0.000011 | 0.282711 | 0.000431 | -2.15 | 1.929 | 15.25 | 768 | 1110 | -0.968380 |
| 10 | CL3-10 | 186 | 0.049822 | 0.000010 | 0.001389 | 0.000023 | 0.282708 | 0.001064 | -2.26 | 1.663 | 37.63 | 779 | 1123 | -0.958164 |
表3 翠峦碱长花岗岩锆石Hf同位素组成
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotope analysis results of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite
| 序 号 | 点号 | U-Pb年 龄(Ma) | 176Yb/ 177Hf | 1σ | 176Lu/ 177Hf | 1σ | 176Hf/ 177Hf | 1σ | εHf(0) | εHf(t) | 1σ | TDM1 (Ma) | (Ma) | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CL3-01 | 185 | 0.031048 | 0.000009 | 0.000889 | 0.000011 | 0.282712 | 0.000462 | -2.11 | 1.840 | 16.36 | 763 | 1110 | -0.973222 |
| 2 | CL3-02 | 192 | 0.027737 | 0.000010 | 0.000824 | 0.000007 | 0.282720 | 0.000309 | -1.84 | 2.268 | 10.92 | 751 | 1088 | -0.975196 |
| 3 | CL3-03 | 189 | 0.035169 | 0.000009 | 0.001000 | 0.000013 | 0.282715 | 0.000640 | -2.02 | 2.000 | 22.65 | 762 | 1103 | -0.969886 |
| 4 | CL3-04 | 188 | 0.025450 | 0.000009 | 0.000738 | 0.000006 | 0.282707 | 0.000273 | -2.28 | 1.757 | 9.66 | 767 | 1118 | -0.977759 |
| 5 | CL3-05 | 192 | 0.031139 | 0.000009 | 0.000875 | 0.000006 | 0.282716 | 0.000277 | -1.98 | 2.132 | 9.81 | 758 | 1098 | -0.973655 |
| 6 | CL3-06 | 194 | 0.038944 | 0.000009 | 0.001091 | 0.000008 | 0.282718 | 0.000310 | -1.91 | 2.200 | 10.98 | 759 | 1094 | -0.967127 |
| 7 | CL3-07 | 183 | 0.041288 | 0.000009 | 0.001171 | 0.000021 | 0.282704 | 0.000811 | -2.41 | 1.463 | 28.68 | 781 | 1133 | -0.964720 |
| 8 | CL3-08 | 192 | 0.035492 | 0.000009 | 0.001001 | 0.000039 | 0.282718 | 0.001419 | -1.91 | 2.179 | 50.21 | 757 | 1094 | -0.969837 |
| 9 | CL3-09 | 192 | 0.036861 | 0.000009 | 0.001050 | 0.000011 | 0.282711 | 0.000431 | -2.15 | 1.929 | 15.25 | 768 | 1110 | -0.968380 |
| 10 | CL3-10 | 186 | 0.049822 | 0.000010 | 0.001389 | 0.000023 | 0.282708 | 0.001064 | -2.26 | 1.663 | 37.63 | 779 | 1123 | -0.958164 |
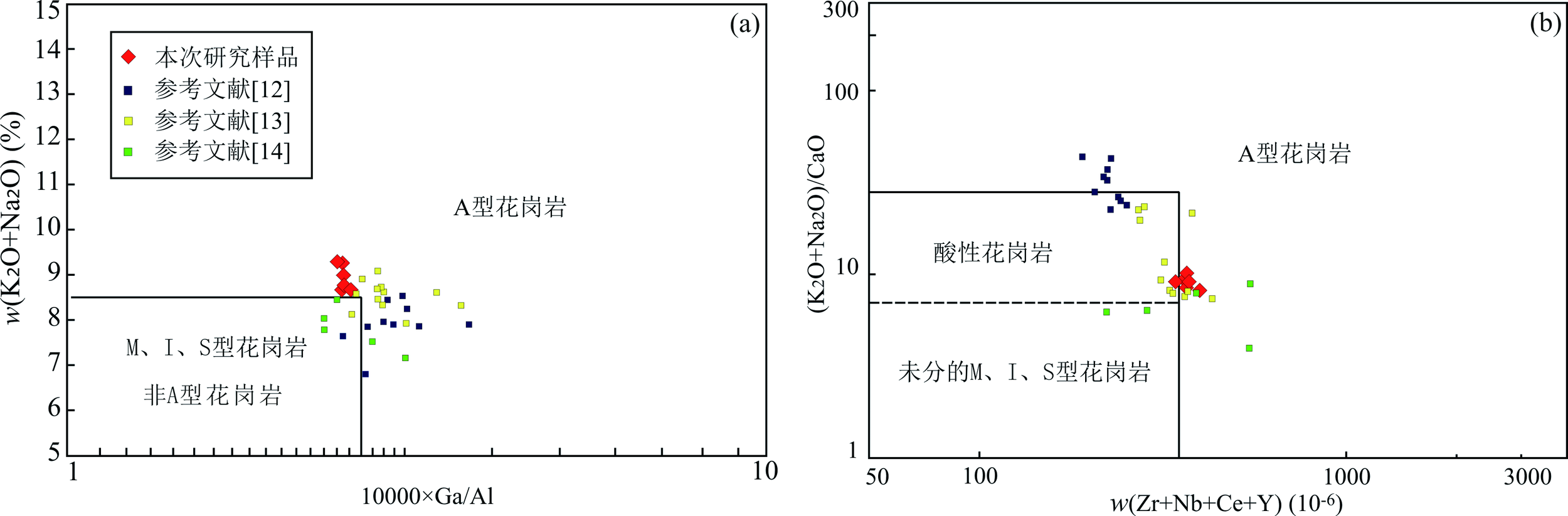
图8 翠峦碱长花岗岩10000×Ga/Al-(K2O+Na2O)图解(a)和(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(K2O+Na2O)/CaO图解(b)(底图据参考文献[54])
Fig.8 10000×Ga/Al-(K2O+Na2O)(a) and (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(K2O+Na2O)/CaO (b) discrimination diagrams of the Cuiluan alkali feldspar granite (basemap modified after reference [54])
| [1] | 周若. 花岗岩混合作用[J]. 地学前缘, 1994, 1(增): 87-97. |
| [2] | 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邓晋福, 等. 中国花岗岩与大陆地壳生长方式初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 2005, 32(3): 343-352. |
| [3] | 陈会军, 付俊彧, 钱程, 等. 东北地区前中生代花岗岩类年龄与时空分布[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(6): 827-844. |
| [4] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J]. 岩石学报, 1999, 15(2): 181-189. |
| [5] | 韩振新, 郝正平, 侯敏. 小兴安岭地区与加里东期花岗岩类有关的矿床成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 1995, 14(4): 293-302. |
| [6] | 张海驲, 栾慧敏, 陈乐国. 黑龙江省印支期花岗岩的确定及其意义[J]. 中国区域地质, 1991(1): 25-27, 9. |
| [7] | 谭红艳, 舒广龙, 吕骏超, 等. 小兴安岭鹿鸣大型钼矿LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(6): 1757-1770. |
| [8] | 韩振哲, 赵海玲, 苏士杰, 等. 小兴安岭东南金山屯一带晚三叠世二长花岗岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 197-206. |
| [9] | 许文良, 王枫, 孟恩, 等. 黑龙江省东部古生代—早中生代的构造演化: 火成岩组合与碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(5): 1378-1389. |
| [10] | 董玉. 佳木斯地块与松嫩—张广才岭地块拼合历史:年代学与地球化学证据[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018. |
| [11] | 李伟民, 刘永江, 赵英利, 等. 佳木斯地块构造演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(3): 665-684. |
| [12] | 牛延宏, 王兴, 董国臣, 等. 伊春地区斑状二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2012, 31(2): 247-254. |
| [13] | 姜浩杰. 伊春西部新第二林场-跃进林场中生代花岗岩特征及地质意义[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017. |
| [14] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 吉林中部晚三叠世和早侏罗世两期铝质A型花岗岩的厘定及对吉黑东部构造格局的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(2): 263-275. |
| [15] | 王玉净, 樊志勇. 内蒙古西拉木伦河北部蛇绿岩带中二叠纪放射虫的发现及其地质意义[J]. 古生物学报, 1997, 36(1): 58-69. |
| [16] | 赵春荆, 彭玉鲸, 党增欣, 等. 吉黑东部构造格架及地壳演化[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学出版社, 1996. |
| [17] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山. 小兴安岭东部清水岩体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定[J]. 地球学报, 2004, 25(2): 213-218. |
| [18] | 杨长江, 王亚春. 小兴安岭东南部伊春中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 吉林地质, 2010, 29(4):1-5. |
| [19] | 梁本胜. 黑龙江省二股铁多金属矿田矿床地质特征及成因[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014. |
| [20] | 程国华, 王瑞良, 曾庆栋, 等. 黑龙江鹿鸣钼矿区花岗质杂岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素、辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(8): 2450-2464. |
| [21] | 陈静, 孙丰月, 潘彤, 等. 黑龙江霍吉河钼矿成矿地质特征及花岗闪长岩年代学、地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(增): 207-215. |
| [22] | 刘瑞萍. 黑龙江伊春地区斑岩—浅成低温热液金矿床岩浆、流体与成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [23] | 孙喜德. 黑龙江省东安—汤旺河地区花岗岩地球化学及热年代学[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [24] | 吴智平, 侯旭波, 李伟. 华北东部地区中生代盆地格局及演化过程探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(4): 385-399. |
| [25] | 裴福萍, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 松辽盆地南部中生代火山岩: 锆石U-Pb年代学及其对基底性质的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2008, 33(5): 603-617. |
| [26] | 周建波, 张兴洲, WILDE Simon A, 等. 黑龙江杂岩的碎屑锆石年代及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(8): 1924-1936. |
| [27] |
XU W L, JI W Q, PEI F P, et al. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, NE China: Chronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 392-402.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 1-30.
DOI URL |
| [29] | XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HAO J E, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6): 1069-1087. |
| [30] | 翟明见. 依兰—伊通断裂新构造活动规律[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016. |
| [31] |
YU J J, WANG F, XU W L, et al. Early Jurassic mafic magmatism in the lesser Xing'an-Zhangguangcai range, NE China, and its tectonic implications: Constraints from zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry[J]. Lithos, 2012, 142/143: 256-266.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 徐平, 吴福元, 谢烈文, 等. U-Pb同位素定年标准锆石的Hf同位素[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(14): 1403-1410. |
| [34] | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第28部分:16个主次成分量测定(GB/T 14506.28—2010)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. |
| [35] | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第30部分:44个元素量测定(GB/T 14506.30—2010)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. |
| [36] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 等. 大兴安岭大洋山钼矿区侵入岩年代学、岩石地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(4): 1064-1081. |
| [37] | 杨元江, 李成禄, 邓昌州, 等. 大兴安岭大洋山钼矿成矿岩体地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及构造背景[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5): 1092-1102. |
| [38] | 韩振哲, 赵海玲, 王盘喜, 等. 黑龙江伊春地区晚三叠世—早侏罗世铝质A型正长-碱长花岗岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 97-108. |
| [39] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [40] | PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogyand Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81. |
| [41] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZINDLER A, HART S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14: 493-571.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
GRIFFIN W L, PEARSON N J, BELOUSOVA E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1): 133-147.
DOI URL |
| [44] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America, 1979, 11: 468. |
| [45] | PITCHER W S. The Nature and Origin of Granite[M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1993, 193-291. |
| [46] |
KING P L, WHITE A J R, CHAPPELL B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan fold belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3): 371-391.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002. |
| [48] | 吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静. A型花岗岩研究现状及其述评[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1): 57-66. |
| [49] | 苏玉平, 唐红峰. A型花岗岩的微量元素地球化学[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2005, 24(3): 245-251. |
| [50] | 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等. 福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(11): 2468-2484. |
| [51] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, JAHN B M, et al. A Jurassic garnet-bearing granitic pluton from NE China showing tetrad REE patterns[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5): 731-744.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
BOEHNKE P, WATSON E B, TRAIL D, et al. Zircon saturation re-revisited[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 351: 324-334.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 等. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003, 9(4): 573-591. |
| [54] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type gra-nites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DICKIN A P, HALLIDAY A N, BOWDEN P. A Pb, Sr and Nd isotope study of the basement and Mesozoic ring complexes of the Jos Plateau, Nigeria[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 94(1):23-32.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
LANDENBERGER B, COLLINS W J. Derivation of A-type granites from a dehydrated charnockitic lower crust: Evidence from the Chaelundi complex, eastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(1): 145-170.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
DICKIN A P. Nd isotope chemistry of Tertiary igneous rocks from Arran, Scotland: Implications for magma evolution and crustal structure[J]. Geological Magazine, 1994, 131(3): 329-333.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 杨帆, 肖荣阁, 李娜, 等. 内蒙古宝音图钼矿床花岗岩稀土元素地球化学特征及花岗岩成因[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 831-840. |
| [60] |
MCDONOUGH W F, SUN S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223-253.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
HANS WEDEPOHL K. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217-1232.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
AMELIN Y, LEE D C, HALLIDAY A N. Early-Middle Archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(24): 4205-4225.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [5] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [6] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [7] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [8] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [9] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [10] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [11] | 王战永, 隆兆笃, 解波, 孙悦, 李巨初, 向杰, 范永宏. 四川冕西岩体岩石地球化学特征及铀成矿条件分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1465-1474. |
| [12] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [13] | 吕云鹤, 董国臣, 赵丽玮, 苏麟, 殷国栋, 汤家辉. 内蒙古沙章土矿区闪长玢岩成岩时代及岩浆源区探讨:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 836-847. |
| [14] | 李秀章, 王立功, 李衣鑫, 王英鹏, 于晓卫, 张文, 郭瑞朋, 刘汉栋. 胶东艾山岩体二长花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Lu-Hf同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 333-346. |
| [15] | 任廷仙, 李小伟, 王可, 葛涵云, 关瑞. 西秦岭碌础坝石英闪长岩-花岗闪长岩的地球化学、矿物学研究及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1651-1676. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||