



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (06): 1651-1676.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.119
任廷仙1,2( ), 李小伟1,2(
), 李小伟1,2( ), 王可1,2, 葛涵云1,2, 关瑞1,2
), 王可1,2, 葛涵云1,2, 关瑞1,2
收稿日期:2021-06-02
修回日期:2021-09-02
出版日期:2021-12-10
发布日期:2022-02-14
通讯作者:
李小伟
作者简介:李小伟,男,副教授,博士生导师,1985年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事成因矿物学与岩石学研究。Email: xwli@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
REN Tingxian1,2( ), LI Xiaowei1,2(
), LI Xiaowei1,2( ), WANG Ke1,2, GE Hanyun1,2, GUAN Rui1,2
), WANG Ke1,2, GE Hanyun1,2, GUAN Rui1,2
Received:2021-06-02
Revised:2021-09-02
Online:2021-12-10
Published:2022-02-14
Contact:
LI Xiaowei
摘要:
不同成因类型的花岗岩组合,反映出不同的物源组成或迥异的岩浆演化过程。为了进一步探讨西秦岭造山带中生代花岗质侵入岩的成因、矿物结晶条件和地球动力学背景,选择西秦岭东部碌础坝岩体内的石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩为研究对象,对其开展详细的野外地质调查以及系统的岩相学、矿物学和岩石地球化学研究。研究结果表明:碌础坝石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩的SiO2含量范围为59.65%~67.36%,A/CNK为0.82~1.04,K2O/Na2O=1.11~1.74,Mg#值为47~53,显示出准铝质-弱过铝质特征,属于高钾钙碱性岩石,其中花岗闪长岩为I型花岗岩;岩体具有富集Rb、Th、U、K和Pb等元素,亏损Nb、Ta、P和Ti等元素的特征,具有中等Eu负异常(δEu=0.50~0.77),轻重稀土分馏明显((La/Yb)N=9.43~30.37)。碌础坝花岗质岩石中斜长石的An值介于18~53之间,以中长石为主,部分斜长石显示振荡环带;角闪石为镁角闪石,部分角闪石具有环带结构,且核部Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)值较高(0.88~0.91)并具有富钙特征(CaO含量为17.80%~22.67%),但Al2O3含量较低,指示角闪石核部与边部的形成环境具有明显差异;黑云母Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)值为0.44~0.57,为镁质黑云母。碌础坝花岗质岩石中全岩和各类矿物的温度计算结果显示,全岩锆饱和温度为736~795 ℃,角闪石结晶温度为704~824 ℃,黑云母结晶温度为700~746 ℃。三种方法计算的结晶温度相近,表明岩体形成于中温环境。碌础坝岩体角闪石全铝压力计结果为1.0~3.5 kbar(1 bar=100 kPa),平均形成深度为6.8 km;黑云母结晶压力为0.9~1.4 kbar,平均形成深度为4.1 km。角闪石湿度及氧逸度计显示其相对氧逸度为ΔNNO=0.1~1.3,含水量为3.9%~6.3%。结合前人资料,认为西秦岭碌础坝岩体由角闪岩为主的变基性岩部分熔融形成,幔源组分的参与导致其具有高Mg#值、高Cr和Ni等元素含量的特征。碌础坝岩体形成于洋-陆俯冲向陆-陆碰撞转换的阶段。
中图分类号:
任廷仙, 李小伟, 王可, 葛涵云, 关瑞. 西秦岭碌础坝石英闪长岩-花岗闪长岩的地球化学、矿物学研究及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1651-1676.
REN Tingxian, LI Xiaowei, WANG Ke, GE Hanyun, GUAN Rui. Geochemistry, Mineralogy, and Geological Significance of the Luchuba Quartz Diorite-Granodiorite in the West Qinling Orogen[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1651-1676.
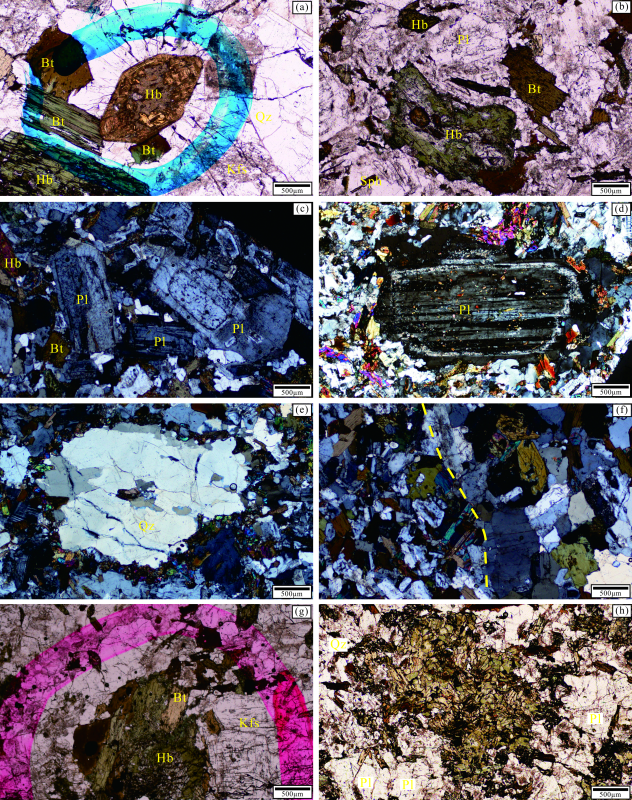
图3 西秦岭碌础坝岩体显微镜下照片 (a)自形角闪石颗粒;(b)半自形角闪石颗粒;(c)斜长石筛状结构;(d)斜长石斑晶;(e)眼球状石英;(f)矿物粒径不一;(g)角闪石黑云母化;(h)暗色矿物聚晶。矿物代号:Hb. 角闪石;Bt. 黑云母;Pl. 斜长石;Kfs. 钾长石;Qz. 石英;Sph. 榍石
Fig.3 Photomicrographs of the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3T | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | A/CNK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 66.48 | 0.51 | 15.29 | 3.54 | 0.06 | 1.69 | 2.73 | 3.06 | 5.21 | 0.17 | 0.77 | 99.51 | 48.68 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 67.36 | 0.47 | 15.13 | 3.23 | 0.05 | 1.50 | 2.80 | 3.19 | 5.00 | 0.16 | 0.67 | 99.57 | 47.96 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 64.45 | 0.57 | 14.96 | 4.65 | 0.07 | 2.69 | 3.65 | 3.17 | 4.19 | 0.17 | 1.10 | 99.67 | 53.35 | 0.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 63.80 | 0.58 | 15.40 | 4.67 | 0.07 | 2.69 | 3.98 | 3.47 | 3.86 | 0.17 | 0.96 | 99.65 | 53.27 | 0.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 64.72 | 0.55 | 15.45 | 4.35 | 0.06 | 2.47 | 3.82 | 3.39 | 4.18 | 0.16 | 0.94 | 100.09 | 52.99 | 0.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 67.04 | 0.47 | 15.03 | 3.68 | 0.06 | 1.91 | 3.07 | 3.28 | 4.58 | 0.14 | 0.56 | 99.81 | 50.64 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 64.00 | 0.60 | 15.42 | 4.58 | 0.07 | 2.49 | 3.91 | 3.27 | 3.95 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 99.33 | 51.82 | 0.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 62.45 | 0.69 | 16.20 | 5.16 | 0.08 | 2.29 | 3.97 | 3.42 | 4.11 | 0.28 | 0.89 | 99.54 | 46.81 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 67.10 | 0.52 | 15.65 | 3.47 | 0.06 | 1.53 | 2.99 | 3.11 | 4.18 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 99.44 | 46.69 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 59.65 | 0.74 | 15.94 | 5.91 | 0.13 | 3.05 | 4.73 | 3.10 | 5.40 | 0.24 | 0.86 | 99.76 | 50.58 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | Li | P | K | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 69.8 | 768 | 40 680 | 7.89 | 3 166 | 55.0 | 53.3 | 450 | 8.54 | 14.0 | 5.55 | 58.2 | 20.0 | 193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 68.4 | 723 | 39 720 | 7.02 | 3 036 | 50.9 | 47.1 | 427 | 7.88 | 12.2 | 3.67 | 57.1 | 20.4 | 187 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 33.4 | 732 | 32 540 | 11.50 | 3 638 | 91.0 | 90.1 | 538 | 13.80 | 32.4 | 20.60 | 44.1 | 19.7 | 140 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 36.2 | 786 | 32 000 | 12.00 | 3 870 | 94.6 | 90.7 | 545 | 15.50 | 34.3 | 11.40 | 51.1 | 21.1 | 143 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 34.5 | 340 | 19 260 | 3.60 | 3 164 | 81.5 | 77.8 | 409 | 12.30 | 29.9 | 29.40 | 34.7 | 16.7 | 27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 47.8 | 619 | 35 540 | 8.11 | 2 878 | 61.4 | 61.7 | 465 | 9.97 | 21.7 | 11.50 | 49.0 | 18.6 | 151 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 37.5 | 719 | 31 452 | 10.80 | 3 724 | 88.6 | 87.9 | 541 | 14.40 | 33.5 | 12.90 | 60.7 | 20.1 | 139 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 27.8 | 1 195 | 31 380 | 9.35 | 4 204 | 81.1 | 56.3 | 592 | 12.30 | 20.4 | 17.20 | 69.8 | 20.6 | 131 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 74.1 | 782 | 34 200 | 7.73 | 3 150 | 53.2 | 37.8 | 455 | 7.79 | 10.2 | 3.86 | 58.2 | 20.0 | 169 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 70.6 | 1 081 | 41 860 | 14.2 | 4 592 | 116 | 34.5 | 964 | 14.9 | 12.7 | 32.7 | 85.9 | 21.4 | 226 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 370 | 18.40 | 210 | 14.9 | 13.00 | 1 105 | 37.4 | 77.5 | 7.77 | 28.2 | 5.44 | 1.18 | 4.57 | 0.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 368 | 16.50 | 203 | 14.2 | 11.20 | 876 | 37.7 | 79.2 | 7.68 | 27.6 | 5.11 | 1.09 | 4.24 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 448 | 18.00 | 206 | 14.9 | 10.20 | 1 202 | 42.3 | 81.8 | 8.53 | 30.9 | 5.47 | 1.17 | 4.44 | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 502 | 18.50 | 215 | 16.2 | 13.40 | 1 226 | 44.9 | 84.0 | 8.53 | 30.4 | 5.38 | 1.20 | 4.41 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 272 | 8.72 | 166 | 13.6 | 14.30 | 274 | 15.3 | 43.1 | 4.12 | 15.8 | 3.15 | 0.72 | 2.65 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 411 | 15.30 | 158 | 14.0 | 11.20 | 1 174 | 50.5 | 88.6 | 8.46 | 28.4 | 4.67 | 1.06 | 3.75 | 0.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 458 | 17.00 | 169 | 14.4 | 8.29 | 1 201 | 38.0 | 76.8 | 7.83 | 28.2 | 5.07 | 1.16 | 4.15 | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 574 | 18.60 | 184 | 15.1 | 14.20 | 1 487 | 52.6 | 93.8 | 9.63 | 34.5 | 5.98 | 1.39 | 4.77 | 0.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 360 | 16.30 | 195 | 13.6 | 10.90 | 771 | 58.7 | 107.3 | 10.79 | 37.0 | 5.92 | 1.07 | 4.49 | 0.57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 359 | 22.10 | 199 | 17.5 | 10.10 | 871 | 49.0 | 90.6 | 9.45 | 34.3 | 6.54 | 1.02 | 5.59 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (Gd/Yb)N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 3.42 | 0.65 | 1.79 | 0.27 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 4.87 | 1.08 | 32.68 | 16.92 | 2.55 | 0.70 | 16.25 | 2.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 3.07 | 0.57 | 1.58 | 0.23 | 1.44 | 0.22 | 5.00 | 0.91 | 32.70 | 25.50 | 5.25 | 0.70 | 18.82 | 2.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 3.25 | 0.62 | 1.74 | 0.25 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 4.93 | 0.93 | 21.30 | 19.41 | 4.39 | 0.70 | 18.98 | 2.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 3.29 | 0.63 | 1.79 | 0.27 | 1.66 | 0.26 | 4.88 | 1.13 | 25.94 | 17.87 | 6.94 | 0.73 | 19.40 | 2.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 2.21 | 0.43 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 1.17 | 0.18 | 3.98 | 0.81 | 13.25 | 7.00 | 1.93 | 0.74 | 9.43 | 1.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 2.70 | 0.52 | 1.48 | 0.22 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 3.68 | 1.04 | 30.14 | 25.44 | 5.74 | 0.75 | 26.02 | 2.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 3.10 | 0.59 | 1.63 | 0.24 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 4.00 | 0.88 | 24.34 | 16.45 | 3.58 | 0.75 | 18.30 | 2.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 3.38 | 0.64 | 1.78 | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 4.20 | 0.89 | 25.36 | 17.15 | 4.48 | 0.77 | 23.66 | 2.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 3.01 | 0.56 | 1.52 | 0.23 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 4.58 | 0.97 | 28.02 | 17.16 | 5.02 | 0.61 | 30.37 | 2.68 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 4.07 | 0.76 | 2.08 | 0.29 | 1.87 | 0.29 | 4.67 | 1.10 | 34.60 | 15.07 | 3.82 | 0.50 | 18.84 | 2.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表1 西秦岭碌础坝岩体的主量元素(%)和微量元素组成(10-6)
Table 1 Major (%) and trace (10-6) element contents of the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3T | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | A/CNK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 66.48 | 0.51 | 15.29 | 3.54 | 0.06 | 1.69 | 2.73 | 3.06 | 5.21 | 0.17 | 0.77 | 99.51 | 48.68 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 67.36 | 0.47 | 15.13 | 3.23 | 0.05 | 1.50 | 2.80 | 3.19 | 5.00 | 0.16 | 0.67 | 99.57 | 47.96 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 64.45 | 0.57 | 14.96 | 4.65 | 0.07 | 2.69 | 3.65 | 3.17 | 4.19 | 0.17 | 1.10 | 99.67 | 53.35 | 0.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 63.80 | 0.58 | 15.40 | 4.67 | 0.07 | 2.69 | 3.98 | 3.47 | 3.86 | 0.17 | 0.96 | 99.65 | 53.27 | 0.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 64.72 | 0.55 | 15.45 | 4.35 | 0.06 | 2.47 | 3.82 | 3.39 | 4.18 | 0.16 | 0.94 | 100.09 | 52.99 | 0.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 67.04 | 0.47 | 15.03 | 3.68 | 0.06 | 1.91 | 3.07 | 3.28 | 4.58 | 0.14 | 0.56 | 99.81 | 50.64 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 64.00 | 0.60 | 15.42 | 4.58 | 0.07 | 2.49 | 3.91 | 3.27 | 3.95 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 99.33 | 51.82 | 0.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 62.45 | 0.69 | 16.20 | 5.16 | 0.08 | 2.29 | 3.97 | 3.42 | 4.11 | 0.28 | 0.89 | 99.54 | 46.81 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 67.10 | 0.52 | 15.65 | 3.47 | 0.06 | 1.53 | 2.99 | 3.11 | 4.18 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 99.44 | 46.69 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 59.65 | 0.74 | 15.94 | 5.91 | 0.13 | 3.05 | 4.73 | 3.10 | 5.40 | 0.24 | 0.86 | 99.76 | 50.58 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | Li | P | K | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 69.8 | 768 | 40 680 | 7.89 | 3 166 | 55.0 | 53.3 | 450 | 8.54 | 14.0 | 5.55 | 58.2 | 20.0 | 193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 68.4 | 723 | 39 720 | 7.02 | 3 036 | 50.9 | 47.1 | 427 | 7.88 | 12.2 | 3.67 | 57.1 | 20.4 | 187 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 33.4 | 732 | 32 540 | 11.50 | 3 638 | 91.0 | 90.1 | 538 | 13.80 | 32.4 | 20.60 | 44.1 | 19.7 | 140 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 36.2 | 786 | 32 000 | 12.00 | 3 870 | 94.6 | 90.7 | 545 | 15.50 | 34.3 | 11.40 | 51.1 | 21.1 | 143 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 34.5 | 340 | 19 260 | 3.60 | 3 164 | 81.5 | 77.8 | 409 | 12.30 | 29.9 | 29.40 | 34.7 | 16.7 | 27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 47.8 | 619 | 35 540 | 8.11 | 2 878 | 61.4 | 61.7 | 465 | 9.97 | 21.7 | 11.50 | 49.0 | 18.6 | 151 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 37.5 | 719 | 31 452 | 10.80 | 3 724 | 88.6 | 87.9 | 541 | 14.40 | 33.5 | 12.90 | 60.7 | 20.1 | 139 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 27.8 | 1 195 | 31 380 | 9.35 | 4 204 | 81.1 | 56.3 | 592 | 12.30 | 20.4 | 17.20 | 69.8 | 20.6 | 131 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 74.1 | 782 | 34 200 | 7.73 | 3 150 | 53.2 | 37.8 | 455 | 7.79 | 10.2 | 3.86 | 58.2 | 20.0 | 169 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 70.6 | 1 081 | 41 860 | 14.2 | 4 592 | 116 | 34.5 | 964 | 14.9 | 12.7 | 32.7 | 85.9 | 21.4 | 226 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 370 | 18.40 | 210 | 14.9 | 13.00 | 1 105 | 37.4 | 77.5 | 7.77 | 28.2 | 5.44 | 1.18 | 4.57 | 0.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 368 | 16.50 | 203 | 14.2 | 11.20 | 876 | 37.7 | 79.2 | 7.68 | 27.6 | 5.11 | 1.09 | 4.24 | 0.56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 448 | 18.00 | 206 | 14.9 | 10.20 | 1 202 | 42.3 | 81.8 | 8.53 | 30.9 | 5.47 | 1.17 | 4.44 | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 502 | 18.50 | 215 | 16.2 | 13.40 | 1 226 | 44.9 | 84.0 | 8.53 | 30.4 | 5.38 | 1.20 | 4.41 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 272 | 8.72 | 166 | 13.6 | 14.30 | 274 | 15.3 | 43.1 | 4.12 | 15.8 | 3.15 | 0.72 | 2.65 | 0.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 411 | 15.30 | 158 | 14.0 | 11.20 | 1 174 | 50.5 | 88.6 | 8.46 | 28.4 | 4.67 | 1.06 | 3.75 | 0.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 458 | 17.00 | 169 | 14.4 | 8.29 | 1 201 | 38.0 | 76.8 | 7.83 | 28.2 | 5.07 | 1.16 | 4.15 | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 574 | 18.60 | 184 | 15.1 | 14.20 | 1 487 | 52.6 | 93.8 | 9.63 | 34.5 | 5.98 | 1.39 | 4.77 | 0.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 360 | 16.30 | 195 | 13.6 | 10.90 | 771 | 58.7 | 107.3 | 10.79 | 37.0 | 5.92 | 1.07 | 4.49 | 0.57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 359 | 22.10 | 199 | 17.5 | 10.10 | 871 | 49.0 | 90.6 | 9.45 | 34.3 | 6.54 | 1.02 | 5.59 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩石类型 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (Gd/Yb)N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 3.42 | 0.65 | 1.79 | 0.27 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 4.87 | 1.08 | 32.68 | 16.92 | 2.55 | 0.70 | 16.25 | 2.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-3 | 3.07 | 0.57 | 1.58 | 0.23 | 1.44 | 0.22 | 5.00 | 0.91 | 32.70 | 25.50 | 5.25 | 0.70 | 18.82 | 2.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-7 | 3.25 | 0.62 | 1.74 | 0.25 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 4.93 | 0.93 | 21.30 | 19.41 | 4.39 | 0.70 | 18.98 | 2.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 3.29 | 0.63 | 1.79 | 0.27 | 1.66 | 0.26 | 4.88 | 1.13 | 25.94 | 17.87 | 6.94 | 0.73 | 19.40 | 2.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-12 | 2.21 | 0.43 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 1.17 | 0.18 | 3.98 | 0.81 | 13.25 | 7.00 | 1.93 | 0.74 | 9.43 | 1.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 2.70 | 0.52 | 1.48 | 0.22 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 3.68 | 1.04 | 30.14 | 25.44 | 5.74 | 0.75 | 26.02 | 2.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 3.10 | 0.59 | 1.63 | 0.24 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 4.00 | 0.88 | 24.34 | 16.45 | 3.58 | 0.75 | 18.30 | 2.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 3.38 | 0.64 | 1.78 | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.25 | 4.20 | 0.89 | 25.36 | 17.15 | 4.48 | 0.77 | 23.66 | 2.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-25 | 3.01 | 0.56 | 1.52 | 0.23 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 4.58 | 0.97 | 28.02 | 17.16 | 5.02 | 0.61 | 30.37 | 2.68 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 石英闪长岩 | 4.07 | 0.76 | 2.08 | 0.29 | 1.87 | 0.29 | 4.67 | 1.10 | 34.60 | 15.07 | 3.82 | 0.50 | 18.84 | 2.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
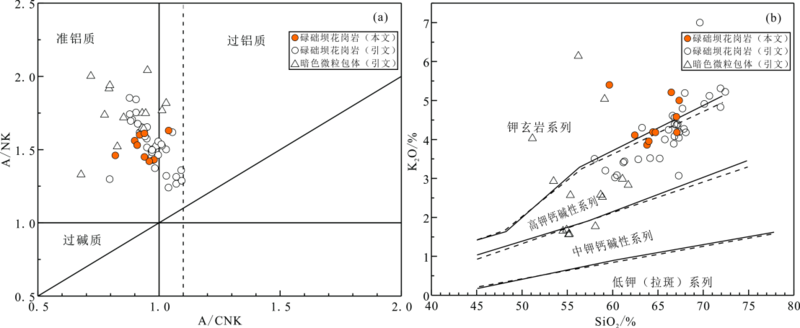
图4 碌础坝岩体的岩石分类和系列图解 (a)A/CNK-A/NK图解(底图据文献[39]);(b)SiO2-K2O图解(底图据文献[40])。引文数据来自文献[18,19,20,21,22,23],下文相同
Fig.4 Rock classification and series diagrams of the Luchuba pluton
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | 总量 /% | Si | Al | Ca | Na | K | An | Ab | Or | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB15-7 | 3-9 | 59.20 | 0.04 | 25.76 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 7.22 | 7.24 | 0.19 | 99.81 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.69 | 65.36 | 1.95 | ||||||||||
| 1-3 | 59.57 | 0 | 25.41 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | 6.83 | 7.55 | 0.34 | 100.02 | 2.66 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.58 | 65.46 | 1.95 | |||||||||||
| 1-4 | 59.64 | 0.03 | 25.72 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 6.83 | 7.58 | 0.34 | 100.46 | 2.66 | 1.35 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.36 | 65.86 | 1.78 | |||||||||||
| 1-5 | 59.52 | 0.06 | 25.68 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0 | 6.73 | 7.57 | 0.31 | 100.24 | 2.69 | 1.32 | 0.31 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 31.19 | 67.37 | 1.43 | |||||||||||
| 1-6 | 60.18 | 0 | 25.12 | 0.22 | 0 | 0.01 | 6.42 | 7.67 | 0.25 | 99.86 | 2.80 | 1.20 | 0.18 | 0.83 | 0 | 17.77 | 81.84 | 0.39 | |||||||||||
| 2-5 | 63.42 | 0 | 23.09 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 3.82 | 9.71 | 0.07 | 100.19 | 2.59 | 1.42 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 39.88 | 59.13 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 2-6 | 57.67 | 0 | 26.81 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.03 | 8.25 | 6.76 | 0.17 | 99.88 | 2.63 | 1.38 | 0.36 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 37.05 | 61.69 | 1.26 | |||||||||||
| 2-7 | 59.41 | 0 | 26.43 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.17 | 7.53 | 6.93 | 0.22 | 101.05 | 2.69 | 1.31 | 0.31 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 30.75 | 68.07 | 1.18 | |||||||||||
| 2-8 | 60.27 | 0 | 24.82 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 6.46 | 7.90 | 0.21 | 99.88 | 2.76 | 1.25 | 0.23 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 23.11 | 76.08 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| 2-9 | 62.24 | 0 | 23.86 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.01 | 4.81 | 8.75 | 0.14 | 99.92 | 2.65 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 35.12 | 63.77 | 1.11 | |||||||||||
| 4-8 | 57.38 | 0.05 | 25.64 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0 | 7.76 | 6.78 | 0.30 | 98.17 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.34 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 33.63 | 65.18 | 1.19 | |||||||||||
| 4-9 | 55.99 | 0.03 | 27.00 | 0.23 | 0 | 0 | 9.21 | 6.25 | 0.25 | 99.05 | 2.57 | 1.43 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 42.64 | 55.50 | 1.86 | |||||||||||
| 4-10 | 59.27 | 0.01 | 25.41 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.01 | 7.02 | 7.52 | 0.21 | 99.61 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 32.53 | 64.61 | 2.86 | |||||||||||
| 4-11 | 56.92 | 0.03 | 26.82 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 8.80 | 6.33 | 0.32 | 99.51 | 2.69 | 1.31 | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 31.28 | 66.94 | 1.78 | |||||||||||
| 4-12 | 59.04 | 0 | 25.13 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0 | 6.76 | 7.41 | 0.50 | 99.04 | 2.61 | 1.40 | 0.38 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 38.70 | 60.15 | 1.15 | |||||||||||
| 4-13 | 60.35 | 0.06 | 24.95 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.02 | 6.56 | 7.76 | 0.31 | 100.33 | 2.80 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 17.58 | 80.23 | 2.19 | |||||||||||
| 4-15 | 61.75 | 0.01 | 22.78 | 0.18 | 0 | 0.04 | 3.55 | 8.96 | 0.37 | 97.67 | 2.62 | 1.38 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 38.06 | 60.20 | 1.73 | |||||||||||
| 4-16 | 65.62 | 0.02 | 20.33 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 10.67 | 0.14 | 98.46 | 2.55 | 1.45 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 44.22 | 54.35 | 1.44 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 2-7 | 59.56 | 0.03 | 24.78 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 6.72 | 7.42 | 0.20 | 98.84 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 36.34 | 61.93 | 1.73 | ||||||||||
| 2-9 | 59.88 | 0 | 24.73 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 | 6.74 | 7.54 | 0.38 | 99.65 | 2.67 | 1.33 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.55 | 65.36 | 2.10 | |||||||||||
| 2-10 | 58.10 | 0.03 | 25.50 | 0.30 | 0 | 0.01 | 7.46 | 7.02 | 0.30 | 98.77 | 2.78 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 22.21 | 76.52 | 1.27 | |||||||||||
| 2-11 | 59.65 | 0.02 | 25.20 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 6.69 | 7.43 | 0.36 | 99.68 | 2.68 | 1.32 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 32.81 | 65.49 | 1.69 | |||||||||||
| 2-12 | 63.04 | 0.04 | 23.90 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 4.54 | 8.64 | 0.22 | 100.50 | 2.81 | 1.19 | 0.19 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 20.05 | 79.31 | 0.64 | |||||||||||
| 2-13 | 59.46 | 0 | 24.81 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 6.85 | 7.56 | 0.30 | 99.24 | 2.69 | 1.32 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 32.97 | 65.88 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| 2-14 | 62.75 | 0.01 | 22.55 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.71 | 4.05 | 8.85 | 0.11 | 99.51 | 2.69 | 1.31 | 0.32 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 32.32 | 65.50 | 2.18 | |||||||||||
| 2P-1 | 57.32 | 0.04 | 26.81 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0 | 8.54 | 6.36 | 0.22 | 99.44 | 2.58 | 1.42 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 42.07 | 56.65 | 1.28 | |||||||||||
| 2P-2 | 56.12 | 0.02 | 24.78 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 7.66 | 6.54 | 0.19 | 95.71 | 2.63 | 1.37 | 0.38 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 38.84 | 59.99 | 1.17 | |||||||||||
| 2P-3 | 59.18 | 0 | 25.05 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0 | 6.88 | 7.66 | 0.32 | 99.40 | 2.67 | 1.33 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 32.59 | 65.64 | 1.78 | |||||||||||
| 2P-4 | 57.34 | 0 | 26.32 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.01 | 8.07 | 6.82 | 0.20 | 98.88 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 39.09 | 59.77 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| 2P-5 | 61.84 | 0 | 23.04 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0 | 4.29 | 8.95 | 0.37 | 98.81 | 2.78 | 1.22 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 0.02 | 20.49 | 77.40 | 2.12 | |||||||||||
| 3-1 | 55.13 | 0.04 | 28.21 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 10.51 | 5.60 | 0.16 | 99.97 | 2.49 | 1.50 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 50.48 | 48.61 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
| 3-2 | 55.50 | 0.01 | 27.91 | 0.23 | 0 | 0.01 | 10.01 | 5.83 | 0.17 | 99.66 | 2.51 | 1.49 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 48.24 | 50.79 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 3-3 | 54.14 | 0 | 28.30 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0 | 11.04 | 5.20 | 0.17 | 99.15 | 2.47 | 1.52 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 53.44 | 45.56 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 3-4 | 57.05 | 0.02 | 26.43 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0 | 8.60 | 6.40 | 0.21 | 98.94 | 2.59 | 1.41 | 0.42 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 42.11 | 56.67 | 1.22 | |||||||||||
| 3-5 | 56.46 | 0.01 | 26.87 | 0.21 | 0 | 0 | 9.17 | 6.43 | 0.21 | 99.40 | 2.56 | 1.43 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 43.55 | 55.26 | 1.19 | |||||||||||
| 3-6 | 54.18 | 0.05 | 26.02 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.32 | 10.69 | 5.93 | 0.25 | 98.51 | 2.52 | 1.43 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 49.24 | 49.42 | 1.34 | |||||||||||
| 3-7 | 54.98 | 0.03 | 27.58 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0 | 9.89 | 5.71 | 0.22 | 98.70 | 2.51 | 1.49 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 48.31 | 50.43 | 1.27 | |||||||||||
| 3-8 | 58.89 | 0 | 25.99 | 0.20 | 0 | 0 | 7.83 | 7.00 | 0.27 | 100.18 | 2.63 | 1.37 | 0.37 | 0.61 | 0.02 | 37.62 | 60.84 | 1.54 | |||||||||||
| 3-9 | 58.01 | 0 | 25.36 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 7.74 | 6.81 | 0.26 | 98.44 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 37.98 | 60.48 | 1.54 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 4-3 | 56.52 | 0.05 | 26.35 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.01 | 9.38 | 5.87 | 0.24 | 98.79 | 2.58 | 1.42 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 46.25 | 52.35 | 1.40 | ||||||||||
| 4-4 | 57.84 | 0 | 25.39 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.02 | 8.09 | 6.21 | 0.92 | 98.67 | 2.63 | 1.36 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 39.58 | 55.04 | 5.39 | |||||||||||
| 4-5 | 55.99 | 0.02 | 25.63 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 8.57 | 6.45 | 0.26 | 97.29 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.42 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 41.71 | 56.76 | 1.53 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 1-19 | 58.37 | 0.02 | 25.59 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0 | 7.31 | 7.30 | 0.16 | 99.02 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 35.30 | 63.80 | 0.90 | ||||||||||
| 1-20 | 57.24 | 0.04 | 26.27 | 0.32 | 0 | 0.01 | 8.12 | 6.75 | 0.10 | 98.86 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 39.73 | 59.69 | 0.59 | |||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | 总量 /% | Si | Al | Ca | Na | K | An | Ab | Or | ||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 3-1 | 58.47 | 0 | 25.40 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.02 | 7.20 | 7.17 | 0.31 | 98.89 | 2.65 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 35.03 | 63.19 | 1.78 | ||||||||||
| 3-2 | 58.59 | 0.02 | 24.78 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0 | 7.09 | 7.13 | 0.26 | 98.11 | 2.70 | 1.30 | 0.29 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 29.14 | 69.68 | 1.18 | |||||||||||
| 3-3 | 59.53 | 0.02 | 24.80 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 6.59 | 7.63 | 0.35 | 99.04 | 2.61 | 1.39 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 40.14 | 58.27 | 1.59 | |||||||||||
| 3-4 | 55.84 | 0 | 27.36 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0 | 9.54 | 6.10 | 0.18 | 99.25 | 2.67 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 34.90 | 63.57 | 1.52 | |||||||||||
| 3-5 | 56.57 | 0 | 26.50 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0 | 8.94 | 6.26 | 0.20 | 98.78 | 2.68 | 1.32 | 0.32 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 31.67 | 66.31 | 2.02 | |||||||||||
| 3-6 | 55.81 | 0 | 26.88 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | 9.17 | 6.07 | 0.15 | 98.40 | 2.53 | 1.46 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 45.91 | 53.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 3-9 | 56.99 | 0 | 26.79 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.01 | 8.77 | 6.34 | 0.34 | 99.41 | 2.57 | 1.42 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 43.61 | 55.25 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| 3-10 | 60.54 | 0.02 | 24.69 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 6.12 | 8.09 | 0.21 | 99.83 | 2.55 | 1.45 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 45.10 | 54.03 | 0.87 | |||||||||||
| 3-11 | 57.79 | 0.02 | 26.19 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0 | 8.11 | 6.50 | 0.27 | 99.14 | 2.57 | 1.43 | 0.42 | 0.56 | 0.02 | 42.45 | 55.57 | 1.98 | |||||||||||
| 4-6 | 59.53 | 0.02 | 25.48 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 6.92 | 7.41 | 0.22 | 99.84 | 2.65 | 1.35 | 0.34 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 34.17 | 64.98 | 0.85 | |||||||||||
| 4-7 | 55.93 | 0.02 | 28.56 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0 | 10.40 | 5.64 | 0.14 | 101.05 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 33.62 | 65.10 | 1.28 | |||||||||||
| 4-8 | 57.04 | 0.01 | 27.95 | 0.18 | 0 | 0.01 | 9.72 | 6.06 | 0.13 | 101.14 | 2.50 | 1.50 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 50.06 | 49.15 | 0.79 | |||||||||||
| 4-9 | 55.86 | 0 | 27.63 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 | 9.37 | 6.14 | 0.14 | 99.32 | 2.54 | 1.47 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 46.65 | 52.62 | 0.73 | |||||||||||
| 4-10 | 59.76 | 0 | 25.92 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 7.21 | 7.58 | 0.15 | 100.82 | 2.53 | 1.47 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 45.38 | 53.83 | 0.79 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 2-1 | 58.90 | 0 | 26.26 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.03 | 7.94 | 7.08 | 0.12 | 100.52 | 2.62 | 1.38 | 0.38 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 38.01 | 61.33 | 0.66 | ||||||||||
| 2-2 | 59.44 | 0.04 | 25.87 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 7.19 | 7.69 | 0.13 | 100.45 | 2.68 | 1.31 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 31.58 | 67.41 | 1.02 | |||||||||||
| 2-3 | 62.11 | 0 | 24.15 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 5.04 | 8.87 | 0.10 | 100.32 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 33.83 | 65.43 | 0.73 | |||||||||||
| 2-4 | 59.98 | 0.04 | 25.60 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 7.14 | 7.70 | 0.09 | 100.65 | 2.75 | 1.26 | 0.24 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 23.75 | 75.67 | 0.58 | |||||||||||
| 2-5 | 59.13 | 0.01 | 24.97 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 6.72 | 7.32 | 0.16 | 99.04 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 33.72 | 65.75 | 0.53 | |||||||||||
| 2-6 | 61.17 | 0.01 | 24.77 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 5.94 | 8.36 | 0.09 | 100.43 | 2.68 | 1.33 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 33.36 | 65.72 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| 2-8 | 58.33 | 0 | 23.96 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 6.47 | 7.40 | 0.28 | 96.69 | 2.71 | 1.29 | 0.28 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 28.04 | 71.46 | 0.50 | |||||||||||
| 2-12 | 60.19 | 0.03 | 24.99 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0 | 6.63 | 7.82 | 0.18 | 99.97 | 2.69 | 1.30 | 0.32 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 32.03 | 66.29 | 1.67 | |||||||||||
表2 西秦岭碌础坝岩体斜长石电子探针数据
Table 2 EPMA data of plagioclase from the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | 总量 /% | Si | Al | Ca | Na | K | An | Ab | Or | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB15-7 | 3-9 | 59.20 | 0.04 | 25.76 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 7.22 | 7.24 | 0.19 | 99.81 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.69 | 65.36 | 1.95 | ||||||||||
| 1-3 | 59.57 | 0 | 25.41 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | 6.83 | 7.55 | 0.34 | 100.02 | 2.66 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.58 | 65.46 | 1.95 | |||||||||||
| 1-4 | 59.64 | 0.03 | 25.72 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 6.83 | 7.58 | 0.34 | 100.46 | 2.66 | 1.35 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.36 | 65.86 | 1.78 | |||||||||||
| 1-5 | 59.52 | 0.06 | 25.68 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0 | 6.73 | 7.57 | 0.31 | 100.24 | 2.69 | 1.32 | 0.31 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 31.19 | 67.37 | 1.43 | |||||||||||
| 1-6 | 60.18 | 0 | 25.12 | 0.22 | 0 | 0.01 | 6.42 | 7.67 | 0.25 | 99.86 | 2.80 | 1.20 | 0.18 | 0.83 | 0 | 17.77 | 81.84 | 0.39 | |||||||||||
| 2-5 | 63.42 | 0 | 23.09 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 3.82 | 9.71 | 0.07 | 100.19 | 2.59 | 1.42 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 39.88 | 59.13 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 2-6 | 57.67 | 0 | 26.81 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.03 | 8.25 | 6.76 | 0.17 | 99.88 | 2.63 | 1.38 | 0.36 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 37.05 | 61.69 | 1.26 | |||||||||||
| 2-7 | 59.41 | 0 | 26.43 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.17 | 7.53 | 6.93 | 0.22 | 101.05 | 2.69 | 1.31 | 0.31 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 30.75 | 68.07 | 1.18 | |||||||||||
| 2-8 | 60.27 | 0 | 24.82 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 6.46 | 7.90 | 0.21 | 99.88 | 2.76 | 1.25 | 0.23 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 23.11 | 76.08 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| 2-9 | 62.24 | 0 | 23.86 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.01 | 4.81 | 8.75 | 0.14 | 99.92 | 2.65 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 35.12 | 63.77 | 1.11 | |||||||||||
| 4-8 | 57.38 | 0.05 | 25.64 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0 | 7.76 | 6.78 | 0.30 | 98.17 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.34 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 33.63 | 65.18 | 1.19 | |||||||||||
| 4-9 | 55.99 | 0.03 | 27.00 | 0.23 | 0 | 0 | 9.21 | 6.25 | 0.25 | 99.05 | 2.57 | 1.43 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 42.64 | 55.50 | 1.86 | |||||||||||
| 4-10 | 59.27 | 0.01 | 25.41 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.01 | 7.02 | 7.52 | 0.21 | 99.61 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 32.53 | 64.61 | 2.86 | |||||||||||
| 4-11 | 56.92 | 0.03 | 26.82 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 8.80 | 6.33 | 0.32 | 99.51 | 2.69 | 1.31 | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 31.28 | 66.94 | 1.78 | |||||||||||
| 4-12 | 59.04 | 0 | 25.13 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0 | 6.76 | 7.41 | 0.50 | 99.04 | 2.61 | 1.40 | 0.38 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 38.70 | 60.15 | 1.15 | |||||||||||
| 4-13 | 60.35 | 0.06 | 24.95 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.02 | 6.56 | 7.76 | 0.31 | 100.33 | 2.80 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 17.58 | 80.23 | 2.19 | |||||||||||
| 4-15 | 61.75 | 0.01 | 22.78 | 0.18 | 0 | 0.04 | 3.55 | 8.96 | 0.37 | 97.67 | 2.62 | 1.38 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 38.06 | 60.20 | 1.73 | |||||||||||
| 4-16 | 65.62 | 0.02 | 20.33 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 10.67 | 0.14 | 98.46 | 2.55 | 1.45 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 44.22 | 54.35 | 1.44 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-9 | 2-7 | 59.56 | 0.03 | 24.78 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 6.72 | 7.42 | 0.20 | 98.84 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 36.34 | 61.93 | 1.73 | ||||||||||
| 2-9 | 59.88 | 0 | 24.73 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 | 6.74 | 7.54 | 0.38 | 99.65 | 2.67 | 1.33 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 32.55 | 65.36 | 2.10 | |||||||||||
| 2-10 | 58.10 | 0.03 | 25.50 | 0.30 | 0 | 0.01 | 7.46 | 7.02 | 0.30 | 98.77 | 2.78 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 22.21 | 76.52 | 1.27 | |||||||||||
| 2-11 | 59.65 | 0.02 | 25.20 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 6.69 | 7.43 | 0.36 | 99.68 | 2.68 | 1.32 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 32.81 | 65.49 | 1.69 | |||||||||||
| 2-12 | 63.04 | 0.04 | 23.90 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 4.54 | 8.64 | 0.22 | 100.50 | 2.81 | 1.19 | 0.19 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 20.05 | 79.31 | 0.64 | |||||||||||
| 2-13 | 59.46 | 0 | 24.81 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 6.85 | 7.56 | 0.30 | 99.24 | 2.69 | 1.32 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 32.97 | 65.88 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| 2-14 | 62.75 | 0.01 | 22.55 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.71 | 4.05 | 8.85 | 0.11 | 99.51 | 2.69 | 1.31 | 0.32 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 32.32 | 65.50 | 2.18 | |||||||||||
| 2P-1 | 57.32 | 0.04 | 26.81 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0 | 8.54 | 6.36 | 0.22 | 99.44 | 2.58 | 1.42 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 42.07 | 56.65 | 1.28 | |||||||||||
| 2P-2 | 56.12 | 0.02 | 24.78 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 7.66 | 6.54 | 0.19 | 95.71 | 2.63 | 1.37 | 0.38 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 38.84 | 59.99 | 1.17 | |||||||||||
| 2P-3 | 59.18 | 0 | 25.05 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0 | 6.88 | 7.66 | 0.32 | 99.40 | 2.67 | 1.33 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 32.59 | 65.64 | 1.78 | |||||||||||
| 2P-4 | 57.34 | 0 | 26.32 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.01 | 8.07 | 6.82 | 0.20 | 98.88 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 39.09 | 59.77 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| 2P-5 | 61.84 | 0 | 23.04 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0 | 4.29 | 8.95 | 0.37 | 98.81 | 2.78 | 1.22 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 0.02 | 20.49 | 77.40 | 2.12 | |||||||||||
| 3-1 | 55.13 | 0.04 | 28.21 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 10.51 | 5.60 | 0.16 | 99.97 | 2.49 | 1.50 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 50.48 | 48.61 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
| 3-2 | 55.50 | 0.01 | 27.91 | 0.23 | 0 | 0.01 | 10.01 | 5.83 | 0.17 | 99.66 | 2.51 | 1.49 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 48.24 | 50.79 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 3-3 | 54.14 | 0 | 28.30 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0 | 11.04 | 5.20 | 0.17 | 99.15 | 2.47 | 1.52 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 53.44 | 45.56 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 3-4 | 57.05 | 0.02 | 26.43 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0 | 8.60 | 6.40 | 0.21 | 98.94 | 2.59 | 1.41 | 0.42 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 42.11 | 56.67 | 1.22 | |||||||||||
| 3-5 | 56.46 | 0.01 | 26.87 | 0.21 | 0 | 0 | 9.17 | 6.43 | 0.21 | 99.40 | 2.56 | 1.43 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 43.55 | 55.26 | 1.19 | |||||||||||
| 3-6 | 54.18 | 0.05 | 26.02 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.32 | 10.69 | 5.93 | 0.25 | 98.51 | 2.52 | 1.43 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 49.24 | 49.42 | 1.34 | |||||||||||
| 3-7 | 54.98 | 0.03 | 27.58 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0 | 9.89 | 5.71 | 0.22 | 98.70 | 2.51 | 1.49 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 48.31 | 50.43 | 1.27 | |||||||||||
| 3-8 | 58.89 | 0 | 25.99 | 0.20 | 0 | 0 | 7.83 | 7.00 | 0.27 | 100.18 | 2.63 | 1.37 | 0.37 | 0.61 | 0.02 | 37.62 | 60.84 | 1.54 | |||||||||||
| 3-9 | 58.01 | 0 | 25.36 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 7.74 | 6.81 | 0.26 | 98.44 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 37.98 | 60.48 | 1.54 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-15 | 4-3 | 56.52 | 0.05 | 26.35 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.01 | 9.38 | 5.87 | 0.24 | 98.79 | 2.58 | 1.42 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 46.25 | 52.35 | 1.40 | ||||||||||
| 4-4 | 57.84 | 0 | 25.39 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.02 | 8.09 | 6.21 | 0.92 | 98.67 | 2.63 | 1.36 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 39.58 | 55.04 | 5.39 | |||||||||||
| 4-5 | 55.99 | 0.02 | 25.63 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 8.57 | 6.45 | 0.26 | 97.29 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.42 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 41.71 | 56.76 | 1.53 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-18 | 1-19 | 58.37 | 0.02 | 25.59 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0 | 7.31 | 7.30 | 0.16 | 99.02 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 35.30 | 63.80 | 0.90 | ||||||||||
| 1-20 | 57.24 | 0.04 | 26.27 | 0.32 | 0 | 0.01 | 8.12 | 6.75 | 0.10 | 98.86 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 39.73 | 59.69 | 0.59 | |||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | 总量 /% | Si | Al | Ca | Na | K | An | Ab | Or | ||||||||||
| YDB15-19 | 3-1 | 58.47 | 0 | 25.40 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.02 | 7.20 | 7.17 | 0.31 | 98.89 | 2.65 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 35.03 | 63.19 | 1.78 | ||||||||||
| 3-2 | 58.59 | 0.02 | 24.78 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0 | 7.09 | 7.13 | 0.26 | 98.11 | 2.70 | 1.30 | 0.29 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 29.14 | 69.68 | 1.18 | |||||||||||
| 3-3 | 59.53 | 0.02 | 24.80 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 6.59 | 7.63 | 0.35 | 99.04 | 2.61 | 1.39 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 40.14 | 58.27 | 1.59 | |||||||||||
| 3-4 | 55.84 | 0 | 27.36 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0 | 9.54 | 6.10 | 0.18 | 99.25 | 2.67 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 34.90 | 63.57 | 1.52 | |||||||||||
| 3-5 | 56.57 | 0 | 26.50 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0 | 8.94 | 6.26 | 0.20 | 98.78 | 2.68 | 1.32 | 0.32 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 31.67 | 66.31 | 2.02 | |||||||||||
| 3-6 | 55.81 | 0 | 26.88 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | 9.17 | 6.07 | 0.15 | 98.40 | 2.53 | 1.46 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 45.91 | 53.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 3-9 | 56.99 | 0 | 26.79 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.01 | 8.77 | 6.34 | 0.34 | 99.41 | 2.57 | 1.42 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 43.61 | 55.25 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| 3-10 | 60.54 | 0.02 | 24.69 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 6.12 | 8.09 | 0.21 | 99.83 | 2.55 | 1.45 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 45.10 | 54.03 | 0.87 | |||||||||||
| 3-11 | 57.79 | 0.02 | 26.19 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0 | 8.11 | 6.50 | 0.27 | 99.14 | 2.57 | 1.43 | 0.42 | 0.56 | 0.02 | 42.45 | 55.57 | 1.98 | |||||||||||
| 4-6 | 59.53 | 0.02 | 25.48 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 6.92 | 7.41 | 0.22 | 99.84 | 2.65 | 1.35 | 0.34 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 34.17 | 64.98 | 0.85 | |||||||||||
| 4-7 | 55.93 | 0.02 | 28.56 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0 | 10.40 | 5.64 | 0.14 | 101.05 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 33.62 | 65.10 | 1.28 | |||||||||||
| 4-8 | 57.04 | 0.01 | 27.95 | 0.18 | 0 | 0.01 | 9.72 | 6.06 | 0.13 | 101.14 | 2.50 | 1.50 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 50.06 | 49.15 | 0.79 | |||||||||||
| 4-9 | 55.86 | 0 | 27.63 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 | 9.37 | 6.14 | 0.14 | 99.32 | 2.54 | 1.47 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 46.65 | 52.62 | 0.73 | |||||||||||
| 4-10 | 59.76 | 0 | 25.92 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 7.21 | 7.58 | 0.15 | 100.82 | 2.53 | 1.47 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 45.38 | 53.83 | 0.79 | |||||||||||
| YDB15-27 | 2-1 | 58.90 | 0 | 26.26 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.03 | 7.94 | 7.08 | 0.12 | 100.52 | 2.62 | 1.38 | 0.38 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 38.01 | 61.33 | 0.66 | ||||||||||
| 2-2 | 59.44 | 0.04 | 25.87 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 7.19 | 7.69 | 0.13 | 100.45 | 2.68 | 1.31 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 31.58 | 67.41 | 1.02 | |||||||||||
| 2-3 | 62.11 | 0 | 24.15 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 5.04 | 8.87 | 0.10 | 100.32 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 33.83 | 65.43 | 0.73 | |||||||||||
| 2-4 | 59.98 | 0.04 | 25.60 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 7.14 | 7.70 | 0.09 | 100.65 | 2.75 | 1.26 | 0.24 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 23.75 | 75.67 | 0.58 | |||||||||||
| 2-5 | 59.13 | 0.01 | 24.97 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 6.72 | 7.32 | 0.16 | 99.04 | 2.66 | 1.34 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 33.72 | 65.75 | 0.53 | |||||||||||
| 2-6 | 61.17 | 0.01 | 24.77 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 5.94 | 8.36 | 0.09 | 100.43 | 2.68 | 1.33 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 33.36 | 65.72 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| 2-8 | 58.33 | 0 | 23.96 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 6.47 | 7.40 | 0.28 | 96.69 | 2.71 | 1.29 | 0.28 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 28.04 | 71.46 | 0.50 | |||||||||||
| 2-12 | 60.19 | 0.03 | 24.99 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0 | 6.63 | 7.82 | 0.18 | 99.97 | 2.69 | 1.30 | 0.32 | 0.66 | 0.02 | 32.03 | 66.29 | 1.67 | |||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB 15-7 | 3-3 | 49.39 | 0.86 | 3.75 | 14.43 | 0.45 | 13.87 | 12.19 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 95.98 | 7.35 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 0.24 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 3.08 | 1.94 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.66 | - | 727.9 | 1.65 | -13.88 | 4.45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-10 | 47.81 | 0.82 | 5.32 | 14.57 | 0.43 | 13.70 | 11.70 | 1.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 95.82 | 7.12 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 0.40 | 1.41 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 1.87 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 1.43 | 762.6 | 1.55 | -13.14 | 4.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-11 | 50.91 | 0.46 | 3.38 | 15.29 | 0.39 | 14.45 | 12.12 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 97.95 | 7.42 | 0.05 | 0.58 | 0.25 | 1.61 | 0.05 | 3.14 | 1.89 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.66 | - | 728.1 | 1.81 | -13.71 | 4.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 48.02 | 0.76 | 5.21 | 14.21 | 0.51 | 13.40 | 11.41 | 1.02 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 94.96 | 7.22 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 0.28 | 1.51 | 0.07 | 3.00 | 1.84 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.38 | 749.5 | 1.50 | -13.50 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 47.85 | 0.87 | 5.69 | 14.60 | 0.45 | 14.09 | 11.25 | 1.04 | 0.39 | 0 | 96.24 | 7.07 | 0.10 | 0.99 | 0.52 | 1.28 | 0.06 | 3.10 | 1.78 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.70 | 770.2 | 1.77 | -12.75 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-1 | 48.90 | 0.69 | 4.96 | 14.00 | 0.43 | 14.88 | 11.34 | 1.02 | 0.36 | 0 | 96.58 | 7.18 | 0.08 | 0.86 | 0.42 | 1.30 | 0.05 | 3.26 | 1.78 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.08 | 764.8 | 2.11 | -12.54 | 4.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 46.55 | 0.82 | 5.75 | 14.89 | 0.45 | 13.86 | 11.38 | 1.04 | 0.47 | 0.02 | 95.26 | 7.00 | 0.09 | 1.02 | 0.46 | 1.41 | 0.06 | 3.10 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.84 | 802.7 | 1.87 | -11.94 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 48.06 | 1.00 | 5.40 | 14.34 | 0.46 | 14.20 | 11.53 | 1.12 | 0.43 | 0.02 | 96.56 | 7.10 | 0.11 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 1.39 | 0.06 | 3.13 | 1.83 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.46 | 775.3 | 1.72 | -12.69 | 4.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-4 | 48.57 | 0.78 | 5.37 | 14.64 | 0.49 | 14.53 | 11.31 | 1.12 | 0.39 | 0 | 97.27 | 7.11 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 0.43 | 1.36 | 0.06 | 3.17 | 1.77 | 0.32 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.40 | 775.7 | 1.97 | -12.43 | 4.49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-10 | 49.89 | 0.57 | 3.58 | 14.28 | 0.38 | 14.68 | 11.82 | 0.81 | 0.28 | 0 | 96.31 | 7.38 | 0.06 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 1.55 | 0.05 | 3.24 | 1.87 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.68 | - | 744.8 | 1.87 | -13.25 | 3.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-11 | 47.22 | 0.88 | 5.58 | 14.56 | 0.48 | 14.40 | 11.29 | 1.11 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 96.09 | 7.03 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.39 | 1.42 | 0.06 | 3.20 | 1.80 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 1.65 | 820.8 | 1.69 | -11.75 | 4.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-12 | 48.27 | 0.82 | 5.15 | 14.25 | 0.48 | 14.40 | 11.50 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 96.37 | 7.13 | 0.09 | 0.90 | 0.42 | 1.35 | 0.06 | 3.17 | 1.82 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 1.26 | 771.2 | 1.91 | -12.59 | 4.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-13 | 50.56 | 0.36 | 2.83 | 13.27 | 0.43 | 15.27 | 12.09 | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 95.56 | 7.49 | 0.04 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 1.43 | 0.05 | 3.37 | 1.92 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.70 | - | 726.3 | 2.23 | -13.33 | 4.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-14 | 48.81 | 0.75 | 4.85 | 13.84 | 0.47 | 14.74 | 11.36 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0 | 96.17 | 7.20 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 0.41 | 1.29 | 0.06 | 3.24 | 1.80 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 758.9 | 2.05 | -12.74 | 4.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-15 | 47.94 | 0.97 | 5.54 | 14.39 | 0.45 | 14.12 | 11.65 | 1.03 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 96.52 | 7.08 | 0.11 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 1.34 | 0.06 | 3.11 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.57 | 774.9 | 1.68 | -12.73 | 4.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 48.43 | 0.88 | 5.42 | 15.07 | 0.40 | 14.14 | 11.85 | 1.07 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 97.74 | 7.09 | 0.10 | 0.93 | 0.39 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 3.08 | 1.86 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.44 | 779.0 | 1.71 | -12.61 | 4.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | 47.92 | 1.04 | 5.60 | 14.26 | 0.48 | 13.67 | 11.76 | 0.99 | 0.51 | 0.04 | 96.27 | 7.11 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.33 | 1.45 | 0.06 | 3.02 | 1.87 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.65 | 769.4 | 1.45 | -13.09 | 4.55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | 51.96 | 0.16 | 0.96 | 9.73 | 0.56 | 13.91 | 22.53 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.11 | 100.31 | 7.35 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 2.93 | 3.41 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-4 | 47.23 | 0.96 | 5.41 | 14.72 | 0.44 | 14.12 | 11.46 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 95.84 | 7.05 | 0.11 | 0.95 | 0.38 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 3.14 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.52 | 798.8 | 1.93 | -11.97 | 4.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-18 | 1-1 | 47.74 | 0.50 | 3.33 | 12.97 | 0.39 | 14.73 | 11.90 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 92.38 | 7.39 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0 | 1.68 | 0.05 | 3.40 | 1.97 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.67 | - | 766.0 | 2.24 | -12.39 | 4.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 48.85 | 0.66 | 4.99 | 14.47 | 0.43 | 13.57 | 12.05 | 0.86 | 0.40 | 0 | 96.37 | 7.25 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.26 | 1.54 | 0.05 | 3.00 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.15 | 746.6 | 1.49 | -13.58 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 46.21 | 0.98 | 5.57 | 15.50 | 0.45 | 12.91 | 11.68 | 1.02 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 94.81 | 7.02 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.92 | 1.90 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.74 | 788.2 | 1.42 | -12.70 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 46.10 | 0.95 | 5.80 | 15.77 | 0.48 | 12.89 | 11.64 | 1.07 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 95.25 | 6.98 | 0.11 | 1.04 | 0.43 | 1.57 | 0.06 | 2.91 | 1.89 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.92 | 796.6 | 1.43 | -12.51 | 4.88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-5 | 47.25 | 1.08 | 6.14 | 15.67 | 0.46 | 12.97 | 11.60 | 1.10 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 96.86 | 7.01 | 0.12 | 1.07 | 0.43 | 1.52 | 0.06 | 2.87 | 1.84 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.10 | 778.5 | 1.25 | -13.08 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 47.08 | 1.00 | 5.98 | 15.73 | 0.43 | 12.94 | 11.33 | 1.18 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 96.26 | 7.03 | 0.11 | 1.05 | 0.43 | 1.53 | 0.06 | 2.88 | 1.81 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.65 | 2.00 | 773.1 | 1.31 | -13.14 | 4.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 48.27 | 0.72 | 4.47 | 14.43 | 0.56 | 14.29 | 11.40 | 0.91 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 95.45 | 7.22 | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.31 | 1.49 | 0.07 | 3.19 | 1.83 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.68 | - | 780.1 | 1.75 | -12.55 | 4.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-9 | 46.92 | 0.93 | 5.51 | 15.75 | 0.52 | 13.12 | 11.02 | 1.10 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 95.35 | 7.06 | 0.11 | 0.98 | 0.43 | 1.55 | 0.07 | 2.94 | 1.78 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.65 | 1.65 | 776.1 | 1.60 | -12.79 | 4.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-10 | 47.59 | 0.79 | 5.21 | 14.99 | 0.42 | 13.61 | 11.88 | 0.87 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 95.80 | 7.10 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 0.45 | 1.42 | 0.05 | 3.03 | 1.90 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.35 | 768.2 | 1.61 | -12.95 | 4.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-13 | 47.87 | 0.95 | 5.65 | 15.30 | 0.46 | 13.42 | 11.35 | 1.17 | 0.44 | 0.03 | 96.62 | 7.09 | 0.11 | 0.99 | 0.42 | 1.47 | 0.06 | 2.96 | 1.80 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.68 | 763.3 | 1.45 | -13.22 | 4.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-18 | 1-14 | 47.66 | 0.71 | 5.68 | 15.82 | 0.43 | 13.32 | 11.67 | 0.98 | 0.39 | 0 | 96.69 | 7.05 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 0.55 | 1.41 | 0.05 | 2.94 | 1.85 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.71 | 766.0 | 1.51 | -13.11 | 4.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-15 | 46.99 | 1.04 | 6.05 | 15.42 | 0.47 | 13.16 | 11.27 | 1.12 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 95.98 | 7.01 | 0.12 | 1.06 | 0.49 | 1.43 | 0.06 | 2.92 | 1.80 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.67 | 2.05 | 775.5 | 1.39 | -13.00 | 4.78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-16 | 46.56 | 1.09 | 6.04 | 14.84 | 0.44 | 12.62 | 11.67 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 94.84 | 7.05 | 0.13 | 1.08 | 0.28 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 2.85 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.12 | 779.2 | 1.13 | -13.18 | 5.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-17 | 47.68 | 0.90 | 5.47 | 15.38 | 0.38 | 13.34 | 11.52 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 96.31 | 7.10 | 0.10 | 0.96 | 0.42 | 1.50 | 0.05 | 2.96 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.55 | 762.4 | 1.44 | -13.26 | 4.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | 48.16 | 0.78 | 4.94 | 14.35 | 0.47 | 14.04 | 11.30 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 95.33 | 7.18 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.44 | 1.35 | 0.06 | 3.12 | 1.81 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.12 | 753.2 | 1.82 | -13.10 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-3 | 46.24 | 1.16 | 5.87 | 15.93 | 0.43 | 12.57 | 11.52 | 1.11 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 95.43 | 6.99 | 0.13 | 1.05 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 2.83 | 1.87 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.64 | 1.97 | 782.3 | 1.19 | -13.06 | 4.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-4 | 47.25 | 0.95 | 5.46 | 14.84 | 0.53 | 13.14 | 11.52 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 95.13 | 7.11 | 0.11 | 0.97 | 0.38 | 1.49 | 0.07 | 2.95 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.60 | 763.5 | 1.39 | -13.28 | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-6 | 48.21 | 0.84 | 4.99 | 14.07 | 0.58 | 14.18 | 11.32 | 1.06 | 0.35 | 0 | 95.65 | 7.17 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.39 | 1.36 | 0.07 | 3.14 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.15 | 758.4 | 1.80 | -12.99 | 4.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-7 | 48.37 | 0.80 | 4.97 | 14.44 | 0.40 | 13.98 | 11.52 | 0.95 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 95.82 | 7.18 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 1.37 | 0.05 | 3.09 | 1.83 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.13 | 748.8 | 1.70 | -13.32 | 4.51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 46.89 | 1.04 | 5.61 | 15.13 | 0.42 | 13.18 | 11.80 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 95.55 | 7.04 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.44 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 2.95 | 1.90 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.71 | 775.3 | 1.37 | -13.04 | 4.68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | 46.64 | 0.96 | 5.68 | 15.19 | 0.49 | 12.97 | 11.31 | 1.08 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 94.83 | 7.05 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 0.44 | 1.48 | 0.06 | 2.92 | 1.83 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.81 | 770.1 | 1.38 | -13.14 | 4.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-4 | 46.49 | 1.08 | 6.06 | 16.39 | 0.49 | 12.69 | 11.40 | 1.20 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 96.38 | 6.96 | 0.12 | 1.07 | 0.44 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 2.83 | 1.83 | 0.35 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.08 | 791.1 | 1.30 | -12.75 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-5 | 46.61 | 1.06 | 6.28 | 16.01 | 0.42 | 12.95 | 11.52 | 1.18 | 0.50 | 0 | 96.60 | 6.94 | 0.12 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 2.88 | 1.84 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.66 | 2.24 | 789.9 | 1.30 | -12.77 | 4.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 47.16 | 1.00 | 6.03 | 15.91 | 0.48 | 12.89 | 11.59 | 1.14 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 96.78 | 7.01 | 0.11 | 1.06 | 0.44 | 1.53 | 0.06 | 2.85 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.02 | 777.0 | 1.26 | -13.11 | 4.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 47.01 | 0.94 | 5.68 | 15.63 | 0.46 | 13.31 | 11.23 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 95.91 | 7.03 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 1.52 | 0.06 | 2.97 | 1.80 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 1.76 | 783.1 | 1.60 | -12.64 | 4.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-5 | 46.17 | 1.04 | 6.58 | 16.41 | 0.39 | 12.30 | 11.91 | 1.09 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 96.45 | 6.91 | 0.12 | 1.16 | 0.46 | 1.60 | 0.05 | 2.74 | 1.91 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.63 | 2.52 | 795.4 | 1.03 | -12.93 | 5.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-19 | 5-1 | 47.69 | 0.95 | 5.93 | 14.92 | 0.39 | 13.74 | 11.40 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 96.58 | 7.04 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 0.50 | 1.35 | 0.05 | 3.02 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 1.90 | 772.4 | 1.56 | -12.91 | 4.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-2 | 47.61 | 0.91 | 5.25 | 14.73 | 0.45 | 13.61 | 11.31 | 1.01 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 95.32 | 7.12 | 0.10 | 0.93 | 0.44 | 1.40 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 1.81 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.40 | 758.7 | 1.61 | -13.17 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-3 | 47.69 | 0.96 | 5.63 | 15.44 | 0.51 | 13.69 | 11.20 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 96.66 | 7.06 | 0.11 | 0.98 | 0.45 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 3.02 | 1.78 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.66 | 778.9 | 1.71 | -12.62 | 4.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-4 | 47.37 | 1.09 | 5.83 | 14.38 | 0.35 | 14.07 | 11.33 | 1.09 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 96.02 | 7.03 | 0.12 | 1.02 | 0.45 | 1.34 | 0.04 | 3.11 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 1.85 | 784.1 | 1.70 | -12.51 | 4.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-5 | 47.04 | 1.01 | 5.75 | 15.57 | 0.39 | 13.62 | 11.35 | 1.08 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 96.34 | 7.01 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 0.42 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 3.03 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 1.80 | 797.4 | 1.73 | -12.19 | 4.76 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-6 | 46.39 | 1.00 | 6.46 | 15.61 | 0.42 | 12.76 | 11.38 | 1.15 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 95.83 | 6.96 | 0.11 | 1.14 | 0.45 | 1.51 | 0.05 | 2.85 | 1.83 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.43 | 787.7 | 1.24 | -12.88 | 4.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-7 | 47.16 | 1.03 | 5.74 | 15.65 | 0.41 | 13.21 | 11.39 | 1.02 | 0.44 | 0.02 | 96.07 | 7.03 | 0.12 | 1.01 | 0.47 | 1.48 | 0.05 | 2.94 | 1.82 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.80 | 774.8 | 1.47 | -12.94 | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-8 | 48.08 | 1.03 | 5.32 | 15.64 | 0.50 | 13.47 | 11.32 | 1.08 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 96.98 | 7.11 | 0.12 | 0.93 | 0.37 | 1.57 | 0.06 | 2.97 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.65 | 1.41 | 767.3 | 1.57 | -13.02 | 4.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-9 | 46.95 | 0.99 | 5.81 | 15.04 | 0.40 | 13.26 | 11.46 | 1.12 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 95.64 | 7.04 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 0.43 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 2.96 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 1.87 | 774.8 | 1.41 | -13.01 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-10 | 48.17 | 1.13 | 4.93 | 15.16 | 0.47 | 13.74 | 11.29 | 1.06 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 96.41 | 7.16 | 0.13 | 0.87 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 3.05 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.11 | 769.4 | 1.70 | -12.84 | 4.52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 51.16 | 0.32 | 1.82 | 11.06 | 0.59 | 13.31 | 20.81 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 99.71 | 7.28 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.92 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 2.82 | 3.17 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | 49.27 | 0.81 | 4.25 | 10.55 | 0.33 | 14.07 | 17.80 | 0.84 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 98.46 | 7.05 | 0.09 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 3.00 | 2.73 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-4 | 46.33 | 1.10 | 7.85 | 15.91 | 0.46 | 12.64 | 11.19 | 1.48 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 97.69 | 6.83 | 0.12 | 1.36 | 0.43 | 1.53 | 0.06 | 2.78 | 1.77 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.65 | 3.48 | 814.3 | 1.07 | -12.48 | 5.19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-5 | 46.40 | 1.39 | 6.59 | 16.56 | 0.46 | 12.34 | 11.29 | 1.29 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 96.83 | 6.91 | 0.16 | 1.16 | 0.45 | 1.62 | 0.06 | 2.74 | 1.80 | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.63 | 2.50 | 789.6 | 1.01 | -13.08 | 4.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-25 | 2-1 | 47.22 | 0.94 | 6.10 | 18.23 | 0.62 | 11.03 | 11.84 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 97.56 | 7.06 | 0.11 | 1.07 | 0.34 | 1.94 | 0.08 | 2.46 | 1.90 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.56 | 2.10 | 762.1 | 0.67 | -14.03 | 5.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 47.97 | 0.81 | 4.88 | 17.36 | 0.67 | 11.49 | 11.63 | 0.95 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 96.17 | 7.24 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.25 | 1.94 | 0.09 | 2.58 | 1.88 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.57 | 1.12 | 730.9 | 0.91 | -14.54 | 5.32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 47.50 | 0.91 | 5.76 | 17.63 | 0.66 | 11.00 | 11.80 | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0 | 96.61 | 7.15 | 0.10 | 1.02 | 0.23 | 1.99 | 0.08 | 2.47 | 1.90 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.55 | 1.85 | 749.8 | 0.67 | -14.31 | 5.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-4 | 47.17 | 0.83 | 5.84 | 18.08 | 0.68 | 11.05 | 11.67 | 1.07 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 96.92 | 7.09 | 0.09 | 1.04 | 0.32 | 1.95 | 0.09 | 2.48 | 1.88 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.56 | 1.92 | 755.9 | 0.72 | -14.12 | 5.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-5 | 49.65 | 0.33 | 4.39 | 17.34 | 0.62 | 11.76 | 12.36 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 97.33 | 7.37 | 0.04 | 0.77 | 0.23 | 1.92 | 0.08 | 2.60 | 1.97 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.58 | - | 709.7 | 1.05 | -14.93 | 6.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-7 | 48.65 | 0.76 | 5.44 | 16.27 | 0.52 | 12.36 | 12.42 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.08 | 97.69 | 7.18 | 0.08 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 1.96 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 1.49 | 752.3 | 1.04 | -13.89 | 5.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-8 | 48.70 | 0.69 | 4.82 | 17.14 | 0.58 | 11.68 | 11.72 | 0.82 | 0.36 | 0 | 96.54 | 7.30 | 0.08 | 0.85 | 0.22 | 1.93 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 1.88 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.58 | 1.05 | 722.3 | 0.98 | -14.67 | 5.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 48.38 | 0.37 | 4.49 | 16.76 | 0.59 | 11.41 | 12.16 | 0.72 | 0.35 | 0.74 | 95.97 | 7.32 | 0.04 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 1.97 | 0.08 | 2.57 | 1.97 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.57 | - | 720.8 | 0.92 | -14.77 | 5.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 46.96 | 0.93 | 6.29 | 17.81 | 0.62 | 11.08 | 11.94 | 0.91 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 97.21 | 7.03 | 0.11 | 1.11 | 0.34 | 1.89 | 0.08 | 2.47 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 2.27 | 769.6 | 0.67 | -13.85 | 5.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 47.49 | 0.84 | 6.00 | 17.60 | 0.63 | 11.19 | 11.91 | 0.98 | 0.51 | 0.04 | 97.29 | 7.11 | 0.10 | 1.06 | 0.25 | 1.95 | 0.08 | 2.50 | 1.91 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 2.03 | 759.4 | 0.71 | -14.06 | 5.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 48.42 | 0.66 | 5.01 | 16.82 | 0.62 | 11.51 | 12.05 | 0.80 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 96.36 | 7.28 | 0.07 | 0.89 | 0.15 | 1.97 | 0.08 | 2.58 | 1.94 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 1.22 | 731.7 | 0.86 | -14.56 | 5.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 47.08 | 0.92 | 5.86 | 17.91 | 0.57 | 11.18 | 11.72 | 1.04 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 96.84 | 7.08 | 0.10 | 1.04 | 0.31 | 1.95 | 0.07 | 2.50 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.56 | 1.93 | 759.1 | 0.74 | -14.03 | 5.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 47.27 | 0.97 | 6.04 | 17.47 | 0.64 | 11.26 | 11.92 | 0.89 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 97.01 | 7.08 | 0.11 | 1.07 | 0.29 | 1.90 | 0.08 | 2.51 | 1.91 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.57 | 2.07 | 763.0 | 0.72 | -13.96 | 5.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 47.59 | 0.85 | 5.99 | 17.47 | 0.59 | 11.14 | 11.75 | 0.66 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 96.50 | 7.14 | 0.10 | 1.06 | 0.31 | 1.88 | 0.08 | 2.49 | 1.89 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.57 | 2.03 | 749.5 | 0.79 | -14.21 | 6.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-27 | 1-1 | 48.91 | 0.65 | 5.34 | 17.29 | 0.59 | 11.88 | 12.35 | 0.74 | 0.40 | 0 | 98.19 | 7.21 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.28 | 1.85 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 1.95 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.58 | 1.41 | 741.6 | 0.95 | -14.24 | 5.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 50.30 | 0.39 | 4.16 | 16.01 | 0.49 | 12.85 | 12.71 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.04 | 97.70 | 7.39 | 0.04 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 1.73 | 0.06 | 2.81 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.62 | - | 714.1 | 1.31 | -14.55 | 5.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 49.03 | 0.63 | 5.51 | 16.55 | 0.54 | 12.39 | 12.06 | 0.85 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 98.08 | 7.21 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.07 | 2.71 | 1.90 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.61 | 1.54 | 744.4 | 1.12 | -14.00 | 5.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-5 | 49.10 | 0.74 | 5.29 | 16.94 | 0.53 | 11.84 | 12.45 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0 | 98.04 | 7.25 | 0.08 | 0.92 | 0.18 | 1.91 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 1.97 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.58 | 1.37 | 739.4 | 0.88 | -14.36 | 5.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 49.94 | 0.38 | 3.86 | 16.59 | 0.55 | 12.62 | 12.26 | 0.52 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 97.05 | 7.40 | 0.04 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 1.76 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 1.95 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.61 | - | 704.0 | 1.35 | -14.77 | 5.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 49.76 | 0.42 | 4.39 | 16.34 | 0.57 | 12.74 | 12.42 | 0.59 | 0.30 | 0 | 97.59 | 7.33 | 0.05 | 0.76 | 0.30 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 2.80 | 1.96 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.62 | - | 720.8 | 1.31 | -14.38 | 5.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 48.79 | 0.64 | 5.29 | 17.10 | 0.57 | 12.13 | 12.15 | 0.80 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 97.89 | 7.20 | 0.07 | 0.92 | 0.32 | 1.79 | 0.07 | 2.67 | 1.92 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.60 | 1.37 | 741.9 | 1.06 | -14.11 | 5.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-9 | 2P-6 | 47.96 | 0.84 | 5.64 | 14.25 | 0.43 | 14.46 | 10.84 | 1.13 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 96.01 | 7.09 | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.05 | 3.18 | 1.72 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.72 | 1.66 | 771.7 | 1.97 | -12.52 | 4.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 48.89 | 0.67 | 5.02 | 14.08 | 0.47 | 14.80 | 11.17 | 1.09 | 0.35 | 0 | 96.58 | 7.18 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 1.30 | 0.06 | 3.24 | 1.76 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.13 | 761.7 | 2.09 | -12.63 | 4.38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 48.07 | 0.89 | 5.60 | 14.59 | 0.47 | 13.89 | 11.20 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 96.30 | 7.11 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.46 | 1.34 | 0.06 | 3.06 | 1.77 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.63 | 760.6 | 1.65 | -13.09 | 4.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 47.98 | 0.91 | 5.78 | 14.51 | 0.40 | 13.95 | 11.29 | 1.12 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 96.44 | 7.08 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 0.45 | 1.34 | 0.05 | 3.07 | 1.79 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 1.78 | 767.0 | 1.63 | -12.96 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 48.79 | 0.76 | 5.10 | 14.59 | 0.42 | 14.00 | 11.17 | 0.99 | 0.36 | 0 | 96.22 | 7.20 | 0.08 | 0.89 | 0.44 | 1.37 | 0.05 | 3.08 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.21 | 742.0 | 1.74 | -13.43 | 4.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-9 | 49.44 | 0.71 | 4.20 | 13.97 | 0.39 | 14.60 | 11.59 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 96.10 | 7.30 | 0.08 | 0.73 | 0.34 | 1.39 | 0.05 | 3.21 | 1.84 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.70 | - | 738.8 | 1.99 | -13.26 | 4.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-10 | 48.74 | 0.78 | 4.54 | 13.96 | 0.51 | 14.34 | 11.41 | 0.95 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 95.68 | 7.24 | 0.09 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 1.39 | 0.07 | 3.18 | 1.82 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.70 | - | 748.3 | 1.89 | -13.14 | 4.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-15 | 2-1 | 47.20 | 1.23 | 5.93 | 15.11 | 0.26 | 13.13 | 11.52 | 1.15 | 0.55 | 0.13 | 96.27 | 7.04 | 0.14 | 1.04 | 0.32 | 1.57 | 0.03 | 2.92 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 1.95 | 776.6 | 1.26 | -13.12 | 4.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 52.28 | 0.13 | 0.85 | 10.45 | 0.55 | 12.99 | 22.67 | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 100.32 | 7.40 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.87 | 0.37 | 0.07 | 2.74 | 3.44 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 52.29 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 10.19 | 0.29 | 14.05 | 22.08 | 0.36 | 0 | 0.07 | 100.55 | 7.36 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 2.95 | 3.33 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-4 | 51.59 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 9.11 | 0.29 | 13.97 | 22.05 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 98.78 | 7.38 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 2.98 | 3.38 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.90 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-5 | 46.94 | 0.55 | 6.17 | 14.98 | 0.36 | 12.66 | 11.48 | 0.99 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 94.83 | 7.10 | 0.06 | 1.10 | 0.31 | 1.58 | 0.05 | 2.85 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.22 | 769.8 | 1.31 | -13.22 | 5.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-6 | 46.76 | 1.00 | 6.45 | 15.29 | 0.41 | 12.97 | 11.81 | 1.17 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 96.50 | 6.97 | 0.11 | 1.13 | 0.38 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 2.88 | 1.89 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.38 | 792.7 | 1.21 | -12.81 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-7 | 48.72 | 0.64 | 4.35 | 15.17 | 0.38 | 13.74 | 12.02 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 96.19 | 7.25 | 0.07 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 1.55 | 0.05 | 3.05 | 1.92 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.66 | - | 746.5 | 1.71 | -13.37 | 4.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-8 | 50.00 | 0.52 | 3.72 | 14.81 | 0.47 | 13.94 | 11.95 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 96.48 | 7.38 | 0.06 | 0.65 | 0.32 | 1.51 | 0.06 | 3.07 | 1.89 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.67 | - | 712.2 | 1.74 | -14.18 | 4.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-1 | 53.49 | 0.31 | 2.80 | 7.98 | 0.38 | 12.84 | 18.19 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 97.12 | 7.63 | 0.03 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 2.73 | 2.78 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.91 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | 52.06 | 0.21 | 1.28 | 8.85 | 0.33 | 14.40 | 21.71 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.20 | 99.38 | 7.38 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 3.04 | 3.30 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.91 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-3 | 51.19 | 0.38 | 2.43 | 11.13 | 0.49 | 13.53 | 18.64 | 0.61 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 98.71 | 7.31 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.93 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 2.88 | 2.85 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-4 | 46.79 | 1.07 | 6.22 | 15.99 | 0.44 | 12.53 | 11.62 | 1.10 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 96.41 | 6.99 | 0.12 | 1.10 | 0.39 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 2.79 | 1.86 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 2.21 | 781.1 | 1.12 | -13.16 | 4.90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-6 | 46.16 | 0.88 | 6.27 | 14.98 | 0.41 | 12.83 | 11.77 | 1.15 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 95.10 | 6.98 | 0.10 | 1.12 | 0.37 | 1.53 | 0.05 | 2.89 | 1.91 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.31 | 792.2 | 1.23 | -12.80 | 4.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-7 | 46.63 | 0.83 | 6.46 | 14.68 | 0.41 | 12.62 | 11.31 | 1.05 | 0.81 | 0.11 | 94.96 | 7.06 | 0.09 | 1.15 | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.05 | 2.85 | 1.83 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.47 | 780.2 | 1.21 | -13.08 | 4.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 46.38 | 0.97 | 7.12 | 15.17 | 0.51 | 12.78 | 10.80 | 1.49 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 95.98 | 6.94 | 0.11 | 1.26 | 0.41 | 1.49 | 0.06 | 2.85 | 1.73 | 0.43 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 2.96 | 794.7 | 1.22 | -12.74 | 4.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | 44.20 | 1.05 | 7.30 | 15.33 | 0.49 | 12.69 | 11.00 | 1.38 | 0.64 | 0.12 | 94.24 | 6.74 | 0.12 | 1.31 | 0.62 | 1.33 | 0.06 | 2.89 | 1.80 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 3.24 | 824.0 | 1.28 | -12.07 | 4.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-6 | 47.76 | 0.68 | 4.16 | 15.07 | 0.52 | 13.53 | 11.93 | 0.77 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 94.79 | 7.24 | 0.08 | 0.74 | 0.27 | 1.65 | 0.07 | 3.06 | 1.94 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.65 | - | 763.2 | 1.80 | -12.89 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-7 | 47.75 | 1.05 | 5.58 | 15.49 | 0.54 | 13.01 | 11.21 | 1.16 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 96.36 | 7.11 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.36 | 1.57 | 0.07 | 2.89 | 1.79 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.65 | 758.3 | 1.32 | -13.47 | 4.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-8 | 48.16 | 0.71 | 3.68 | 13.61 | 0.51 | 13.75 | 11.84 | 0.71 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 93.46 | 7.35 | 0.08 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 1.51 | 0.07 | 3.13 | 1.94 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.68 | - | 729.4 | 1.72 | -13.77 | 4.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 46.07 | 1.09 | 7.32 | 14.95 | 0.44 | 12.42 | 11.00 | 1.50 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 95.55 | 6.93 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 1.58 | 0.06 | 2.78 | 1.77 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 3.17 | 802.0 | 1.01 | -12.80 | 5.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 45.16 | 1.19 | 6.80 | 15.34 | 0.41 | 12.65 | 10.91 | 1.35 | 0.78 | 0.03 | 94.68 | 6.87 | 0.14 | 1.22 | 0.45 | 1.51 | 0.05 | 2.87 | 1.78 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0 | 0.66 | 2.80 | 803.0 | 1.21 | -12.58 | 4.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 45.99 | 1.12 | 7.41 | 14.49 | 0.41 | 12.86 | 10.90 | 1.43 | 0.71 | 0.08 | 95.42 | 6.91 | 0.13 | 1.31 | 0.35 | 1.47 | 0.05 | 2.88 | 1.75 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 3.23 | 806.2 | 1.18 | -12.54 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 45.12 | 1.13 | 7.16 | 15.91 | 0.50 | 12.28 | 11.15 | 1.26 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 95.19 | 6.83 | 0.13 | 1.28 | 0.51 | 1.50 | 0.06 | 2.77 | 1.81 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.65 | 3.07 | 808.2 | 1.09 | -12.59 | 4.97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-5 | 47.79 | 0.72 | 5.09 | 15.11 | 0.50 | 13.17 | 11.89 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 95.76 | 7.16 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 0.33 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.94 | 1.91 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.65 | 1.26 | 756.0 | 1.39 | -13.46 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 46.45 | 1.04 | 7.71 | 15.60 | 0.44 | 12.49 | 11.09 | 1.58 | 0.82 | 0.06 | 97.29 | 6.88 | 0.12 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 2.76 | 1.76 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 3.40 | 808.9 | 1.00 | -12.66 | 4.86 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 45.31 | 0.96 | 7.30 | 15.61 | 0.47 | 12.76 | 11.03 | 1.40 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 95.51 | 6.81 | 0.11 | 1.29 | 0.57 | 1.40 | 0.06 | 2.86 | 1.78 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.67 | 3.15 | 811.5 | 1.27 | -12.34 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 45.15 | 0.93 | 7.22 | 15.92 | 0.48 | 12.40 | 10.65 | 1.42 | 0.58 | 0 | 94.75 | 6.85 | 0.11 | 1.29 | 0.56 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 1.73 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.66 | 3.13 | 801.8 | 1.23 | -12.58 | 5.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表3 西秦岭碌础坝岩体角闪石电子探针数据
Table 3 EPMA data of amphibole from the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB 15-7 | 3-3 | 49.39 | 0.86 | 3.75 | 14.43 | 0.45 | 13.87 | 12.19 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 95.98 | 7.35 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 0.24 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 3.08 | 1.94 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.66 | - | 727.9 | 1.65 | -13.88 | 4.45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-10 | 47.81 | 0.82 | 5.32 | 14.57 | 0.43 | 13.70 | 11.70 | 1.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 95.82 | 7.12 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 0.40 | 1.41 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 1.87 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 1.43 | 762.6 | 1.55 | -13.14 | 4.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-11 | 50.91 | 0.46 | 3.38 | 15.29 | 0.39 | 14.45 | 12.12 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 97.95 | 7.42 | 0.05 | 0.58 | 0.25 | 1.61 | 0.05 | 3.14 | 1.89 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.66 | - | 728.1 | 1.81 | -13.71 | 4.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 48.02 | 0.76 | 5.21 | 14.21 | 0.51 | 13.40 | 11.41 | 1.02 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 94.96 | 7.22 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 0.28 | 1.51 | 0.07 | 3.00 | 1.84 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.38 | 749.5 | 1.50 | -13.50 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 47.85 | 0.87 | 5.69 | 14.60 | 0.45 | 14.09 | 11.25 | 1.04 | 0.39 | 0 | 96.24 | 7.07 | 0.10 | 0.99 | 0.52 | 1.28 | 0.06 | 3.10 | 1.78 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.70 | 770.2 | 1.77 | -12.75 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-1 | 48.90 | 0.69 | 4.96 | 14.00 | 0.43 | 14.88 | 11.34 | 1.02 | 0.36 | 0 | 96.58 | 7.18 | 0.08 | 0.86 | 0.42 | 1.30 | 0.05 | 3.26 | 1.78 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.08 | 764.8 | 2.11 | -12.54 | 4.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 46.55 | 0.82 | 5.75 | 14.89 | 0.45 | 13.86 | 11.38 | 1.04 | 0.47 | 0.02 | 95.26 | 7.00 | 0.09 | 1.02 | 0.46 | 1.41 | 0.06 | 3.10 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.84 | 802.7 | 1.87 | -11.94 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 48.06 | 1.00 | 5.40 | 14.34 | 0.46 | 14.20 | 11.53 | 1.12 | 0.43 | 0.02 | 96.56 | 7.10 | 0.11 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 1.39 | 0.06 | 3.13 | 1.83 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.46 | 775.3 | 1.72 | -12.69 | 4.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-4 | 48.57 | 0.78 | 5.37 | 14.64 | 0.49 | 14.53 | 11.31 | 1.12 | 0.39 | 0 | 97.27 | 7.11 | 0.09 | 0.93 | 0.43 | 1.36 | 0.06 | 3.17 | 1.77 | 0.32 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.40 | 775.7 | 1.97 | -12.43 | 4.49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-10 | 49.89 | 0.57 | 3.58 | 14.28 | 0.38 | 14.68 | 11.82 | 0.81 | 0.28 | 0 | 96.31 | 7.38 | 0.06 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 1.55 | 0.05 | 3.24 | 1.87 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.68 | - | 744.8 | 1.87 | -13.25 | 3.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-11 | 47.22 | 0.88 | 5.58 | 14.56 | 0.48 | 14.40 | 11.29 | 1.11 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 96.09 | 7.03 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.39 | 1.42 | 0.06 | 3.20 | 1.80 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 1.65 | 820.8 | 1.69 | -11.75 | 4.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-12 | 48.27 | 0.82 | 5.15 | 14.25 | 0.48 | 14.40 | 11.50 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 96.37 | 7.13 | 0.09 | 0.90 | 0.42 | 1.35 | 0.06 | 3.17 | 1.82 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 1.26 | 771.2 | 1.91 | -12.59 | 4.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-13 | 50.56 | 0.36 | 2.83 | 13.27 | 0.43 | 15.27 | 12.09 | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 95.56 | 7.49 | 0.04 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 1.43 | 0.05 | 3.37 | 1.92 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.70 | - | 726.3 | 2.23 | -13.33 | 4.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-14 | 48.81 | 0.75 | 4.85 | 13.84 | 0.47 | 14.74 | 11.36 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0 | 96.17 | 7.20 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 0.41 | 1.29 | 0.06 | 3.24 | 1.80 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 758.9 | 2.05 | -12.74 | 4.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-15 | 47.94 | 0.97 | 5.54 | 14.39 | 0.45 | 14.12 | 11.65 | 1.03 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 96.52 | 7.08 | 0.11 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 1.34 | 0.06 | 3.11 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.57 | 774.9 | 1.68 | -12.73 | 4.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 48.43 | 0.88 | 5.42 | 15.07 | 0.40 | 14.14 | 11.85 | 1.07 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 97.74 | 7.09 | 0.10 | 0.93 | 0.39 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 3.08 | 1.86 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.44 | 779.0 | 1.71 | -12.61 | 4.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | 47.92 | 1.04 | 5.60 | 14.26 | 0.48 | 13.67 | 11.76 | 0.99 | 0.51 | 0.04 | 96.27 | 7.11 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.33 | 1.45 | 0.06 | 3.02 | 1.87 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.65 | 769.4 | 1.45 | -13.09 | 4.55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | 51.96 | 0.16 | 0.96 | 9.73 | 0.56 | 13.91 | 22.53 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.11 | 100.31 | 7.35 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 2.93 | 3.41 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-4 | 47.23 | 0.96 | 5.41 | 14.72 | 0.44 | 14.12 | 11.46 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 95.84 | 7.05 | 0.11 | 0.95 | 0.38 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 3.14 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.52 | 798.8 | 1.93 | -11.97 | 4.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-18 | 1-1 | 47.74 | 0.50 | 3.33 | 12.97 | 0.39 | 14.73 | 11.90 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 92.38 | 7.39 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0 | 1.68 | 0.05 | 3.40 | 1.97 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.67 | - | 766.0 | 2.24 | -12.39 | 4.30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 48.85 | 0.66 | 4.99 | 14.47 | 0.43 | 13.57 | 12.05 | 0.86 | 0.40 | 0 | 96.37 | 7.25 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.26 | 1.54 | 0.05 | 3.00 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.15 | 746.6 | 1.49 | -13.58 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 46.21 | 0.98 | 5.57 | 15.50 | 0.45 | 12.91 | 11.68 | 1.02 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 94.81 | 7.02 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.92 | 1.90 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.74 | 788.2 | 1.42 | -12.70 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 46.10 | 0.95 | 5.80 | 15.77 | 0.48 | 12.89 | 11.64 | 1.07 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 95.25 | 6.98 | 0.11 | 1.04 | 0.43 | 1.57 | 0.06 | 2.91 | 1.89 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.92 | 796.6 | 1.43 | -12.51 | 4.88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-5 | 47.25 | 1.08 | 6.14 | 15.67 | 0.46 | 12.97 | 11.60 | 1.10 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 96.86 | 7.01 | 0.12 | 1.07 | 0.43 | 1.52 | 0.06 | 2.87 | 1.84 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.10 | 778.5 | 1.25 | -13.08 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 47.08 | 1.00 | 5.98 | 15.73 | 0.43 | 12.94 | 11.33 | 1.18 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 96.26 | 7.03 | 0.11 | 1.05 | 0.43 | 1.53 | 0.06 | 2.88 | 1.81 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.65 | 2.00 | 773.1 | 1.31 | -13.14 | 4.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 48.27 | 0.72 | 4.47 | 14.43 | 0.56 | 14.29 | 11.40 | 0.91 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 95.45 | 7.22 | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.31 | 1.49 | 0.07 | 3.19 | 1.83 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.68 | - | 780.1 | 1.75 | -12.55 | 4.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-9 | 46.92 | 0.93 | 5.51 | 15.75 | 0.52 | 13.12 | 11.02 | 1.10 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 95.35 | 7.06 | 0.11 | 0.98 | 0.43 | 1.55 | 0.07 | 2.94 | 1.78 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.65 | 1.65 | 776.1 | 1.60 | -12.79 | 4.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-10 | 47.59 | 0.79 | 5.21 | 14.99 | 0.42 | 13.61 | 11.88 | 0.87 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 95.80 | 7.10 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 0.45 | 1.42 | 0.05 | 3.03 | 1.90 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.35 | 768.2 | 1.61 | -12.95 | 4.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-13 | 47.87 | 0.95 | 5.65 | 15.30 | 0.46 | 13.42 | 11.35 | 1.17 | 0.44 | 0.03 | 96.62 | 7.09 | 0.11 | 0.99 | 0.42 | 1.47 | 0.06 | 2.96 | 1.80 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.68 | 763.3 | 1.45 | -13.22 | 4.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-18 | 1-14 | 47.66 | 0.71 | 5.68 | 15.82 | 0.43 | 13.32 | 11.67 | 0.98 | 0.39 | 0 | 96.69 | 7.05 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 0.55 | 1.41 | 0.05 | 2.94 | 1.85 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.71 | 766.0 | 1.51 | -13.11 | 4.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-15 | 46.99 | 1.04 | 6.05 | 15.42 | 0.47 | 13.16 | 11.27 | 1.12 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 95.98 | 7.01 | 0.12 | 1.06 | 0.49 | 1.43 | 0.06 | 2.92 | 1.80 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.67 | 2.05 | 775.5 | 1.39 | -13.00 | 4.78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-16 | 46.56 | 1.09 | 6.04 | 14.84 | 0.44 | 12.62 | 11.67 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 94.84 | 7.05 | 0.13 | 1.08 | 0.28 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 2.85 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.12 | 779.2 | 1.13 | -13.18 | 5.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-17 | 47.68 | 0.90 | 5.47 | 15.38 | 0.38 | 13.34 | 11.52 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 96.31 | 7.10 | 0.10 | 0.96 | 0.42 | 1.50 | 0.05 | 2.96 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.55 | 762.4 | 1.44 | -13.26 | 4.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | 48.16 | 0.78 | 4.94 | 14.35 | 0.47 | 14.04 | 11.30 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 95.33 | 7.18 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.44 | 1.35 | 0.06 | 3.12 | 1.81 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.12 | 753.2 | 1.82 | -13.10 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-3 | 46.24 | 1.16 | 5.87 | 15.93 | 0.43 | 12.57 | 11.52 | 1.11 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 95.43 | 6.99 | 0.13 | 1.05 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 2.83 | 1.87 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.64 | 1.97 | 782.3 | 1.19 | -13.06 | 4.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-4 | 47.25 | 0.95 | 5.46 | 14.84 | 0.53 | 13.14 | 11.52 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 95.13 | 7.11 | 0.11 | 0.97 | 0.38 | 1.49 | 0.07 | 2.95 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.60 | 763.5 | 1.39 | -13.28 | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-6 | 48.21 | 0.84 | 4.99 | 14.07 | 0.58 | 14.18 | 11.32 | 1.06 | 0.35 | 0 | 95.65 | 7.17 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.39 | 1.36 | 0.07 | 3.14 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.70 | 1.15 | 758.4 | 1.80 | -12.99 | 4.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-7 | 48.37 | 0.80 | 4.97 | 14.44 | 0.40 | 13.98 | 11.52 | 0.95 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 95.82 | 7.18 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 1.37 | 0.05 | 3.09 | 1.83 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.13 | 748.8 | 1.70 | -13.32 | 4.51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 46.89 | 1.04 | 5.61 | 15.13 | 0.42 | 13.18 | 11.80 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 95.55 | 7.04 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.44 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 2.95 | 1.90 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.71 | 775.3 | 1.37 | -13.04 | 4.68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | 46.64 | 0.96 | 5.68 | 15.19 | 0.49 | 12.97 | 11.31 | 1.08 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 94.83 | 7.05 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 0.44 | 1.48 | 0.06 | 2.92 | 1.83 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.81 | 770.1 | 1.38 | -13.14 | 4.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-4 | 46.49 | 1.08 | 6.06 | 16.39 | 0.49 | 12.69 | 11.40 | 1.20 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 96.38 | 6.96 | 0.12 | 1.07 | 0.44 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 2.83 | 1.83 | 0.35 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.08 | 791.1 | 1.30 | -12.75 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-5 | 46.61 | 1.06 | 6.28 | 16.01 | 0.42 | 12.95 | 11.52 | 1.18 | 0.50 | 0 | 96.60 | 6.94 | 0.12 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 2.88 | 1.84 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.66 | 2.24 | 789.9 | 1.30 | -12.77 | 4.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 47.16 | 1.00 | 6.03 | 15.91 | 0.48 | 12.89 | 11.59 | 1.14 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 96.78 | 7.01 | 0.11 | 1.06 | 0.44 | 1.53 | 0.06 | 2.85 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.02 | 777.0 | 1.26 | -13.11 | 4.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 47.01 | 0.94 | 5.68 | 15.63 | 0.46 | 13.31 | 11.23 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 95.91 | 7.03 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 1.52 | 0.06 | 2.97 | 1.80 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 1.76 | 783.1 | 1.60 | -12.64 | 4.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-5 | 46.17 | 1.04 | 6.58 | 16.41 | 0.39 | 12.30 | 11.91 | 1.09 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 96.45 | 6.91 | 0.12 | 1.16 | 0.46 | 1.60 | 0.05 | 2.74 | 1.91 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.63 | 2.52 | 795.4 | 1.03 | -12.93 | 5.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-19 | 5-1 | 47.69 | 0.95 | 5.93 | 14.92 | 0.39 | 13.74 | 11.40 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 96.58 | 7.04 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 0.50 | 1.35 | 0.05 | 3.02 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 1.90 | 772.4 | 1.56 | -12.91 | 4.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-2 | 47.61 | 0.91 | 5.25 | 14.73 | 0.45 | 13.61 | 11.31 | 1.01 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 95.32 | 7.12 | 0.10 | 0.93 | 0.44 | 1.40 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 1.81 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.68 | 1.40 | 758.7 | 1.61 | -13.17 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-3 | 47.69 | 0.96 | 5.63 | 15.44 | 0.51 | 13.69 | 11.20 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 96.66 | 7.06 | 0.11 | 0.98 | 0.45 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 3.02 | 1.78 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.67 | 1.66 | 778.9 | 1.71 | -12.62 | 4.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-4 | 47.37 | 1.09 | 5.83 | 14.38 | 0.35 | 14.07 | 11.33 | 1.09 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 96.02 | 7.03 | 0.12 | 1.02 | 0.45 | 1.34 | 0.04 | 3.11 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 1.85 | 784.1 | 1.70 | -12.51 | 4.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-5 | 47.04 | 1.01 | 5.75 | 15.57 | 0.39 | 13.62 | 11.35 | 1.08 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 96.34 | 7.01 | 0.11 | 1.01 | 0.42 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 3.03 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 1.80 | 797.4 | 1.73 | -12.19 | 4.76 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-6 | 46.39 | 1.00 | 6.46 | 15.61 | 0.42 | 12.76 | 11.38 | 1.15 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 95.83 | 6.96 | 0.11 | 1.14 | 0.45 | 1.51 | 0.05 | 2.85 | 1.83 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.43 | 787.7 | 1.24 | -12.88 | 4.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-7 | 47.16 | 1.03 | 5.74 | 15.65 | 0.41 | 13.21 | 11.39 | 1.02 | 0.44 | 0.02 | 96.07 | 7.03 | 0.12 | 1.01 | 0.47 | 1.48 | 0.05 | 2.94 | 1.82 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.66 | 1.80 | 774.8 | 1.47 | -12.94 | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-8 | 48.08 | 1.03 | 5.32 | 15.64 | 0.50 | 13.47 | 11.32 | 1.08 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 96.98 | 7.11 | 0.12 | 0.93 | 0.37 | 1.57 | 0.06 | 2.97 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.65 | 1.41 | 767.3 | 1.57 | -13.02 | 4.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-9 | 46.95 | 0.99 | 5.81 | 15.04 | 0.40 | 13.26 | 11.46 | 1.12 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 95.64 | 7.04 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 0.43 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 2.96 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 1.87 | 774.8 | 1.41 | -13.01 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-10 | 48.17 | 1.13 | 4.93 | 15.16 | 0.47 | 13.74 | 11.29 | 1.06 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 96.41 | 7.16 | 0.13 | 0.87 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 3.05 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.11 | 769.4 | 1.70 | -12.84 | 4.52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 51.16 | 0.32 | 1.82 | 11.06 | 0.59 | 13.31 | 20.81 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 99.71 | 7.28 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.92 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 2.82 | 3.17 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-3 | 49.27 | 0.81 | 4.25 | 10.55 | 0.33 | 14.07 | 17.80 | 0.84 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 98.46 | 7.05 | 0.09 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 3.00 | 2.73 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-4 | 46.33 | 1.10 | 7.85 | 15.91 | 0.46 | 12.64 | 11.19 | 1.48 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 97.69 | 6.83 | 0.12 | 1.36 | 0.43 | 1.53 | 0.06 | 2.78 | 1.77 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.65 | 3.48 | 814.3 | 1.07 | -12.48 | 5.19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-5 | 46.40 | 1.39 | 6.59 | 16.56 | 0.46 | 12.34 | 11.29 | 1.29 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 96.83 | 6.91 | 0.16 | 1.16 | 0.45 | 1.62 | 0.06 | 2.74 | 1.80 | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.63 | 2.50 | 789.6 | 1.01 | -13.08 | 4.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-25 | 2-1 | 47.22 | 0.94 | 6.10 | 18.23 | 0.62 | 11.03 | 11.84 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 97.56 | 7.06 | 0.11 | 1.07 | 0.34 | 1.94 | 0.08 | 2.46 | 1.90 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.56 | 2.10 | 762.1 | 0.67 | -14.03 | 5.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 47.97 | 0.81 | 4.88 | 17.36 | 0.67 | 11.49 | 11.63 | 0.95 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 96.17 | 7.24 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.25 | 1.94 | 0.09 | 2.58 | 1.88 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.57 | 1.12 | 730.9 | 0.91 | -14.54 | 5.32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 47.50 | 0.91 | 5.76 | 17.63 | 0.66 | 11.00 | 11.80 | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0 | 96.61 | 7.15 | 0.10 | 1.02 | 0.23 | 1.99 | 0.08 | 2.47 | 1.90 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.55 | 1.85 | 749.8 | 0.67 | -14.31 | 5.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-4 | 47.17 | 0.83 | 5.84 | 18.08 | 0.68 | 11.05 | 11.67 | 1.07 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 96.92 | 7.09 | 0.09 | 1.04 | 0.32 | 1.95 | 0.09 | 2.48 | 1.88 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.56 | 1.92 | 755.9 | 0.72 | -14.12 | 5.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-5 | 49.65 | 0.33 | 4.39 | 17.34 | 0.62 | 11.76 | 12.36 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 97.33 | 7.37 | 0.04 | 0.77 | 0.23 | 1.92 | 0.08 | 2.60 | 1.97 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.58 | - | 709.7 | 1.05 | -14.93 | 6.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-7 | 48.65 | 0.76 | 5.44 | 16.27 | 0.52 | 12.36 | 12.42 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.08 | 97.69 | 7.18 | 0.08 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 1.96 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 1.49 | 752.3 | 1.04 | -13.89 | 5.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-8 | 48.70 | 0.69 | 4.82 | 17.14 | 0.58 | 11.68 | 11.72 | 0.82 | 0.36 | 0 | 96.54 | 7.30 | 0.08 | 0.85 | 0.22 | 1.93 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 1.88 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.58 | 1.05 | 722.3 | 0.98 | -14.67 | 5.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 48.38 | 0.37 | 4.49 | 16.76 | 0.59 | 11.41 | 12.16 | 0.72 | 0.35 | 0.74 | 95.97 | 7.32 | 0.04 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 1.97 | 0.08 | 2.57 | 1.97 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.57 | - | 720.8 | 0.92 | -14.77 | 5.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 46.96 | 0.93 | 6.29 | 17.81 | 0.62 | 11.08 | 11.94 | 0.91 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 97.21 | 7.03 | 0.11 | 1.11 | 0.34 | 1.89 | 0.08 | 2.47 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 2.27 | 769.6 | 0.67 | -13.85 | 5.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 47.49 | 0.84 | 6.00 | 17.60 | 0.63 | 11.19 | 11.91 | 0.98 | 0.51 | 0.04 | 97.29 | 7.11 | 0.10 | 1.06 | 0.25 | 1.95 | 0.08 | 2.50 | 1.91 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 2.03 | 759.4 | 0.71 | -14.06 | 5.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 48.42 | 0.66 | 5.01 | 16.82 | 0.62 | 11.51 | 12.05 | 0.80 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 96.36 | 7.28 | 0.07 | 0.89 | 0.15 | 1.97 | 0.08 | 2.58 | 1.94 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 1.22 | 731.7 | 0.86 | -14.56 | 5.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 47.08 | 0.92 | 5.86 | 17.91 | 0.57 | 11.18 | 11.72 | 1.04 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 96.84 | 7.08 | 0.10 | 1.04 | 0.31 | 1.95 | 0.07 | 2.50 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.56 | 1.93 | 759.1 | 0.74 | -14.03 | 5.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 47.27 | 0.97 | 6.04 | 17.47 | 0.64 | 11.26 | 11.92 | 0.89 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 97.01 | 7.08 | 0.11 | 1.07 | 0.29 | 1.90 | 0.08 | 2.51 | 1.91 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.57 | 2.07 | 763.0 | 0.72 | -13.96 | 5.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 47.59 | 0.85 | 5.99 | 17.47 | 0.59 | 11.14 | 11.75 | 0.66 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 96.50 | 7.14 | 0.10 | 1.06 | 0.31 | 1.88 | 0.08 | 2.49 | 1.89 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.57 | 2.03 | 749.5 | 0.79 | -14.21 | 6.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-27 | 1-1 | 48.91 | 0.65 | 5.34 | 17.29 | 0.59 | 11.88 | 12.35 | 0.74 | 0.40 | 0 | 98.19 | 7.21 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.28 | 1.85 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 1.95 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.58 | 1.41 | 741.6 | 0.95 | -14.24 | 5.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 50.30 | 0.39 | 4.16 | 16.01 | 0.49 | 12.85 | 12.71 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.04 | 97.70 | 7.39 | 0.04 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 1.73 | 0.06 | 2.81 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.62 | - | 714.1 | 1.31 | -14.55 | 5.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 49.03 | 0.63 | 5.51 | 16.55 | 0.54 | 12.39 | 12.06 | 0.85 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 98.08 | 7.21 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.07 | 2.71 | 1.90 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.61 | 1.54 | 744.4 | 1.12 | -14.00 | 5.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-5 | 49.10 | 0.74 | 5.29 | 16.94 | 0.53 | 11.84 | 12.45 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0 | 98.04 | 7.25 | 0.08 | 0.92 | 0.18 | 1.91 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 1.97 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.58 | 1.37 | 739.4 | 0.88 | -14.36 | 5.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 49.94 | 0.38 | 3.86 | 16.59 | 0.55 | 12.62 | 12.26 | 0.52 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 97.05 | 7.40 | 0.04 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 1.76 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 1.95 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.61 | - | 704.0 | 1.35 | -14.77 | 5.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 49.76 | 0.42 | 4.39 | 16.34 | 0.57 | 12.74 | 12.42 | 0.59 | 0.30 | 0 | 97.59 | 7.33 | 0.05 | 0.76 | 0.30 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 2.80 | 1.96 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.62 | - | 720.8 | 1.31 | -14.38 | 5.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 48.79 | 0.64 | 5.29 | 17.10 | 0.57 | 12.13 | 12.15 | 0.80 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 97.89 | 7.20 | 0.07 | 0.92 | 0.32 | 1.79 | 0.07 | 2.67 | 1.92 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.60 | 1.37 | 741.9 | 1.06 | -14.11 | 5.53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-9 | 2P-6 | 47.96 | 0.84 | 5.64 | 14.25 | 0.43 | 14.46 | 10.84 | 1.13 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 96.01 | 7.09 | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.05 | 3.18 | 1.72 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.72 | 1.66 | 771.7 | 1.97 | -12.52 | 4.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 48.89 | 0.67 | 5.02 | 14.08 | 0.47 | 14.80 | 11.17 | 1.09 | 0.35 | 0 | 96.58 | 7.18 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 1.30 | 0.06 | 3.24 | 1.76 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.71 | 1.13 | 761.7 | 2.09 | -12.63 | 4.38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 48.07 | 0.89 | 5.60 | 14.59 | 0.47 | 13.89 | 11.20 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 96.30 | 7.11 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.46 | 1.34 | 0.06 | 3.06 | 1.77 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.63 | 760.6 | 1.65 | -13.09 | 4.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 47.98 | 0.91 | 5.78 | 14.51 | 0.40 | 13.95 | 11.29 | 1.12 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 96.44 | 7.08 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 0.45 | 1.34 | 0.05 | 3.07 | 1.79 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 1.78 | 767.0 | 1.63 | -12.96 | 4.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 48.79 | 0.76 | 5.10 | 14.59 | 0.42 | 14.00 | 11.17 | 0.99 | 0.36 | 0 | 96.22 | 7.20 | 0.08 | 0.89 | 0.44 | 1.37 | 0.05 | 3.08 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.69 | 1.21 | 742.0 | 1.74 | -13.43 | 4.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-9 | 49.44 | 0.71 | 4.20 | 13.97 | 0.39 | 14.60 | 11.59 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 96.10 | 7.30 | 0.08 | 0.73 | 0.34 | 1.39 | 0.05 | 3.21 | 1.84 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.70 | - | 738.8 | 1.99 | -13.26 | 4.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-10 | 48.74 | 0.78 | 4.54 | 13.96 | 0.51 | 14.34 | 11.41 | 0.95 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 95.68 | 7.24 | 0.09 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 1.39 | 0.07 | 3.18 | 1.82 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.70 | - | 748.3 | 1.89 | -13.14 | 4.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Ti | Al | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg# | p/kbar | T/℃ | ΔNNO | lg | H2Omelt/% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YDB 15-15 | 2-1 | 47.20 | 1.23 | 5.93 | 15.11 | 0.26 | 13.13 | 11.52 | 1.15 | 0.55 | 0.13 | 96.27 | 7.04 | 0.14 | 1.04 | 0.32 | 1.57 | 0.03 | 2.92 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 1.95 | 776.6 | 1.26 | -13.12 | 4.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-2 | 52.28 | 0.13 | 0.85 | 10.45 | 0.55 | 12.99 | 22.67 | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 100.32 | 7.40 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.87 | 0.37 | 0.07 | 2.74 | 3.44 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-3 | 52.29 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 10.19 | 0.29 | 14.05 | 22.08 | 0.36 | 0 | 0.07 | 100.55 | 7.36 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 2.95 | 3.33 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-4 | 51.59 | 0.24 | 1.03 | 9.11 | 0.29 | 13.97 | 22.05 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 98.78 | 7.38 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 2.98 | 3.38 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.90 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-5 | 46.94 | 0.55 | 6.17 | 14.98 | 0.36 | 12.66 | 11.48 | 0.99 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 94.83 | 7.10 | 0.06 | 1.10 | 0.31 | 1.58 | 0.05 | 2.85 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.22 | 769.8 | 1.31 | -13.22 | 5.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-6 | 46.76 | 1.00 | 6.45 | 15.29 | 0.41 | 12.97 | 11.81 | 1.17 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 96.50 | 6.97 | 0.11 | 1.13 | 0.38 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 2.88 | 1.89 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.38 | 792.7 | 1.21 | -12.81 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-7 | 48.72 | 0.64 | 4.35 | 15.17 | 0.38 | 13.74 | 12.02 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 96.19 | 7.25 | 0.07 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 1.55 | 0.05 | 3.05 | 1.92 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.66 | - | 746.5 | 1.71 | -13.37 | 4.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-8 | 50.00 | 0.52 | 3.72 | 14.81 | 0.47 | 13.94 | 11.95 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 96.48 | 7.38 | 0.06 | 0.65 | 0.32 | 1.51 | 0.06 | 3.07 | 1.89 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.67 | - | 712.2 | 1.74 | -14.18 | 4.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-1 | 53.49 | 0.31 | 2.80 | 7.98 | 0.38 | 12.84 | 18.19 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 97.12 | 7.63 | 0.03 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 2.73 | 2.78 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.91 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-2 | 52.06 | 0.21 | 1.28 | 8.85 | 0.33 | 14.40 | 21.71 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.20 | 99.38 | 7.38 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 3.04 | 3.30 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.91 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-3 | 51.19 | 0.38 | 2.43 | 11.13 | 0.49 | 13.53 | 18.64 | 0.61 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 98.71 | 7.31 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.93 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 2.88 | 2.85 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-4 | 46.79 | 1.07 | 6.22 | 15.99 | 0.44 | 12.53 | 11.62 | 1.10 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 96.41 | 6.99 | 0.12 | 1.10 | 0.39 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 2.79 | 1.86 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 2.21 | 781.1 | 1.12 | -13.16 | 4.90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-6 | 46.16 | 0.88 | 6.27 | 14.98 | 0.41 | 12.83 | 11.77 | 1.15 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 95.10 | 6.98 | 0.10 | 1.12 | 0.37 | 1.53 | 0.05 | 2.89 | 1.91 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 2.31 | 792.2 | 1.23 | -12.80 | 4.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-7 | 46.63 | 0.83 | 6.46 | 14.68 | 0.41 | 12.62 | 11.31 | 1.05 | 0.81 | 0.11 | 94.96 | 7.06 | 0.09 | 1.15 | 0.26 | 1.60 | 0.05 | 2.85 | 1.83 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2.47 | 780.2 | 1.21 | -13.08 | 4.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-1 | 46.38 | 0.97 | 7.12 | 15.17 | 0.51 | 12.78 | 10.80 | 1.49 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 95.98 | 6.94 | 0.11 | 1.26 | 0.41 | 1.49 | 0.06 | 2.85 | 1.73 | 0.43 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 2.96 | 794.7 | 1.22 | -12.74 | 4.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-2 | 44.20 | 1.05 | 7.30 | 15.33 | 0.49 | 12.69 | 11.00 | 1.38 | 0.64 | 0.12 | 94.24 | 6.74 | 0.12 | 1.31 | 0.62 | 1.33 | 0.06 | 2.89 | 1.80 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 3.24 | 824.0 | 1.28 | -12.07 | 4.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-6 | 47.76 | 0.68 | 4.16 | 15.07 | 0.52 | 13.53 | 11.93 | 0.77 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 94.79 | 7.24 | 0.08 | 0.74 | 0.27 | 1.65 | 0.07 | 3.06 | 1.94 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.65 | - | 763.2 | 1.80 | -12.89 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-7 | 47.75 | 1.05 | 5.58 | 15.49 | 0.54 | 13.01 | 11.21 | 1.16 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 96.36 | 7.11 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.36 | 1.57 | 0.07 | 2.89 | 1.79 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 1.65 | 758.3 | 1.32 | -13.47 | 4.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-8 | 48.16 | 0.71 | 3.68 | 13.61 | 0.51 | 13.75 | 11.84 | 0.71 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 93.46 | 7.35 | 0.08 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 1.51 | 0.07 | 3.13 | 1.94 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.68 | - | 729.4 | 1.72 | -13.77 | 4.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-1 | 46.07 | 1.09 | 7.32 | 14.95 | 0.44 | 12.42 | 11.00 | 1.50 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 95.55 | 6.93 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 1.58 | 0.06 | 2.78 | 1.77 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 3.17 | 802.0 | 1.01 | -12.80 | 5.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2 | 45.16 | 1.19 | 6.80 | 15.34 | 0.41 | 12.65 | 10.91 | 1.35 | 0.78 | 0.03 | 94.68 | 6.87 | 0.14 | 1.22 | 0.45 | 1.51 | 0.05 | 2.87 | 1.78 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0 | 0.66 | 2.80 | 803.0 | 1.21 | -12.58 | 4.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 45.99 | 1.12 | 7.41 | 14.49 | 0.41 | 12.86 | 10.90 | 1.43 | 0.71 | 0.08 | 95.42 | 6.91 | 0.13 | 1.31 | 0.35 | 1.47 | 0.05 | 2.88 | 1.75 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 3.23 | 806.2 | 1.18 | -12.54 | 4.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 | 45.12 | 1.13 | 7.16 | 15.91 | 0.50 | 12.28 | 11.15 | 1.26 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 95.19 | 6.83 | 0.13 | 1.28 | 0.51 | 1.50 | 0.06 | 2.77 | 1.81 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.65 | 3.07 | 808.2 | 1.09 | -12.59 | 4.97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-5 | 47.79 | 0.72 | 5.09 | 15.11 | 0.50 | 13.17 | 11.89 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 95.76 | 7.16 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 0.33 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.94 | 1.91 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.65 | 1.26 | 756.0 | 1.39 | -13.46 | 4.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-6 | 46.45 | 1.04 | 7.71 | 15.60 | 0.44 | 12.49 | 11.09 | 1.58 | 0.82 | 0.06 | 97.29 | 6.88 | 0.12 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 2.76 | 1.76 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 3.40 | 808.9 | 1.00 | -12.66 | 4.86 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-7 | 45.31 | 0.96 | 7.30 | 15.61 | 0.47 | 12.76 | 11.03 | 1.40 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 95.51 | 6.81 | 0.11 | 1.29 | 0.57 | 1.40 | 0.06 | 2.86 | 1.78 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.67 | 3.15 | 811.5 | 1.27 | -12.34 | 4.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-8 | 45.15 | 0.93 | 7.22 | 15.92 | 0.48 | 12.40 | 10.65 | 1.42 | 0.58 | 0 | 94.75 | 6.85 | 0.11 | 1.29 | 0.56 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 1.73 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.66 | 3.13 | 801.8 | 1.23 | -12.58 | 5.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Altot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB15-7 | 3-1 | 34.61 | 3.31 | 13.34 | 20.61 | 0.21 | 10.94 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 8.91 | 1.17 | 93.24 | 5.46 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-4 | 34.54 | 4.43 | 13.73 | 21.56 | 0.23 | 10.26 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 8.82 | 0.04 | 93.74 | 5.44 | 2.55 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-5 | 34.94 | 4.48 | 13.57 | 20.95 | 0.18 | 11.62 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 8.76 | 0.01 | 94.64 | 5.40 | 2.47 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-6 | 35.00 | 4.10 | 13.54 | 20.59 | 0.20 | 11.56 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 8.77 | 0.08 | 94.04 | 5.44 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-12 | 34.56 | 4.21 | 13.11 | 20.17 | 0.24 | 11.25 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 8.90 | 0.04 | 92.59 | 5.48 | 2.45 |
| YDB15-7 | 1-1 | 33.49 | 4.05 | 13.40 | 20.50 | 0.19 | 11.51 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 8.50 | 0.04 | 91.89 | 5.33 | 2.52 |
| YDB15-7 | 1-2 | 33.19 | 4.25 | 13.55 | 21.53 | 0.21 | 11.45 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 8.30 | 0.06 | 92.65 | 5.26 | 2.53 |
| YDB15-7 | 4-17 | 32.66 | 4.05 | 13.46 | 21.21 | 0.22 | 11.57 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 8.87 | 0.07 | 92.21 | 5.22 | 2.54 |
| YDB15-18 | 1-12 | 34.96 | 3.70 | 13.34 | 19.44 | 0.18 | 11.67 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 8.93 | 0.07 | 92.42 | 5.52 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-18 | 1-21 | 33.82 | 4.53 | 13.34 | 19.74 | 0.28 | 11.39 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 8.41 | 0.03 | 91.65 | 5.38 | 2.50 |
| YDB15-18 | 4-2 | 33.77 | 3.73 | 13.29 | 19.17 | 0.27 | 11.74 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 8.33 | 0.06 | 90.47 | 5.42 | 2.51 |
| YDB15-18 | 2-1 | 34.51 | 4.36 | 13.37 | 19.67 | 0.26 | 11.57 | 0 | 0.08 | 8.91 | 0.07 | 92.93 | 5.44 | 2.49 |
| YDB15-25 | 3-3 | 35.64 | 3.78 | 14.22 | 21.44 | 0.34 | 9.34 | 0 | 0.06 | 8.88 | 0.02 | 93.71 | 5.60 | 2.63 |
| YDB15-9 | 3-13 | 34.18 | 3.41 | 13.70 | 18.59 | 0.24 | 11.93 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 8.14 | 0 | 90.33 | 5.46 | 2.58 |
| YDB15-9 | 1-3 | 33.13 | 3.86 | 12.85 | 20.57 | 0.20 | 10.59 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 8.05 | 0.03 | 89.34 | 5.42 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-9 | 1-6 | 32.51 | 3.99 | 13.32 | 21.43 | 0.19 | 10.20 | 0 | 0.08 | 8.03 | 0.06 | 89.87 | 5.32 | 2.57 |
| YDB15-15 | 3-5 | 30.16 | 3.97 | 12.57 | 19.28 | 0.34 | 11.46 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 7.59 | 0.11 | 85.63 | 5.17 | 2.54 |
| 样品号 | 点号 | Ti | Fe2+ | Fe3+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg/(Mg+Fe2+) | T/℃ | P/kbar | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-1 | 0.39 | 2.48 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 2.57 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.79 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 700.06 | 1.06 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-4 | 0.52 | 2.73 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 2.41 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.77 | 0 | 0.47 | 734.69 | 1.18 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-5 | 0.52 | 2.37 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 2.68 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.73 | 0 | 0.53 | 740.05 | 0.97 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-6 | 0.48 | 2.40 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 2.68 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 729.62 | 0.99 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-12 | 0.50 | 2.52 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 2.66 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 735.23 | 0.88 | |
| YDB15-7 | 1-1 | 0.49 | 2.32 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 2.73 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.73 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 731.29 | 1.16 | |
| YDB15-7 | 1-2 | 0.51 | 2.43 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 2.70 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.68 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 734.29 | 1.22 | |
| YDB15-7 | 4-17 | 0.49 | 2.41 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 2.76 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 730.59 | 1.24 | |
| YDB15-18 | 1-12 | 0.44 | 2.42 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 2.75 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 721.03 | 0.97 | |
| YDB15-18 | 1-21 | 0.54 | 2.33 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 2.70 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.71 | 0 | 0.54 | 746.44 | 1.09 | |
| YDB15-18 | 4-2 | 0.45 | 2.19 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 2.81 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.71 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 724.96 | 1.14 | |
| YDB15-18 | 2-1 | 0.52 | 2.42 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 2.72 | 0 | 0.03 | 1.79 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 741.04 | 0.99 | |
| YDB15-25 | 3-3 | 0.45 | 2.82 | 0 | 0.05 | 2.19 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.78 | 0 | 0.44 | 709.91 | 1.37 | |
| YDB15-9 | 3-13 | 0.41 | 2.11 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 2.84 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.66 | 0 | 0.57 | 714.65 | 1.32 | |
| YDB15-9 | 1-3 | 0.47 | 2.39 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 2.58 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.68 | 0 | 0.52 | 724.39 | 1.05 | |
| YDB15-9 | 1-6 | 0.49 | 2.49 | 0.44 | 0.03 | 2.49 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.68 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 726.40 | 1.33 | |
| YDB15-15 | 3-5 | 0.51 | 2.35 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 2.93 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.66 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 740.52 | 1.25 | |
表4 西秦岭碌础坝岩体黑云母电子探针数据
Table 4 Electron probe data of biotite in the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling
| 样品号 | 点号 | SiO2 /% | TiO2 /% | Al2O3 /% | FeO /% | MnO /% | MgO /% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | Cr2O3 /% | 总量 /% | Si | Altot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDB15-7 | 3-1 | 34.61 | 3.31 | 13.34 | 20.61 | 0.21 | 10.94 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 8.91 | 1.17 | 93.24 | 5.46 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-4 | 34.54 | 4.43 | 13.73 | 21.56 | 0.23 | 10.26 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 8.82 | 0.04 | 93.74 | 5.44 | 2.55 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-5 | 34.94 | 4.48 | 13.57 | 20.95 | 0.18 | 11.62 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 8.76 | 0.01 | 94.64 | 5.40 | 2.47 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-6 | 35.00 | 4.10 | 13.54 | 20.59 | 0.20 | 11.56 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 8.77 | 0.08 | 94.04 | 5.44 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-7 | 3-12 | 34.56 | 4.21 | 13.11 | 20.17 | 0.24 | 11.25 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 8.90 | 0.04 | 92.59 | 5.48 | 2.45 |
| YDB15-7 | 1-1 | 33.49 | 4.05 | 13.40 | 20.50 | 0.19 | 11.51 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 8.50 | 0.04 | 91.89 | 5.33 | 2.52 |
| YDB15-7 | 1-2 | 33.19 | 4.25 | 13.55 | 21.53 | 0.21 | 11.45 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 8.30 | 0.06 | 92.65 | 5.26 | 2.53 |
| YDB15-7 | 4-17 | 32.66 | 4.05 | 13.46 | 21.21 | 0.22 | 11.57 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 8.87 | 0.07 | 92.21 | 5.22 | 2.54 |
| YDB15-18 | 1-12 | 34.96 | 3.70 | 13.34 | 19.44 | 0.18 | 11.67 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 8.93 | 0.07 | 92.42 | 5.52 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-18 | 1-21 | 33.82 | 4.53 | 13.34 | 19.74 | 0.28 | 11.39 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 8.41 | 0.03 | 91.65 | 5.38 | 2.50 |
| YDB15-18 | 4-2 | 33.77 | 3.73 | 13.29 | 19.17 | 0.27 | 11.74 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 8.33 | 0.06 | 90.47 | 5.42 | 2.51 |
| YDB15-18 | 2-1 | 34.51 | 4.36 | 13.37 | 19.67 | 0.26 | 11.57 | 0 | 0.08 | 8.91 | 0.07 | 92.93 | 5.44 | 2.49 |
| YDB15-25 | 3-3 | 35.64 | 3.78 | 14.22 | 21.44 | 0.34 | 9.34 | 0 | 0.06 | 8.88 | 0.02 | 93.71 | 5.60 | 2.63 |
| YDB15-9 | 3-13 | 34.18 | 3.41 | 13.70 | 18.59 | 0.24 | 11.93 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 8.14 | 0 | 90.33 | 5.46 | 2.58 |
| YDB15-9 | 1-3 | 33.13 | 3.86 | 12.85 | 20.57 | 0.20 | 10.59 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 8.05 | 0.03 | 89.34 | 5.42 | 2.48 |
| YDB15-9 | 1-6 | 32.51 | 3.99 | 13.32 | 21.43 | 0.19 | 10.20 | 0 | 0.08 | 8.03 | 0.06 | 89.87 | 5.32 | 2.57 |
| YDB15-15 | 3-5 | 30.16 | 3.97 | 12.57 | 19.28 | 0.34 | 11.46 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 7.59 | 0.11 | 85.63 | 5.17 | 2.54 |
| 样品号 | 点号 | Ti | Fe2+ | Fe3+ | Mn | Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cr | Mg/(Mg+Fe2+) | T/℃ | P/kbar | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-1 | 0.39 | 2.48 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 2.57 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.79 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 700.06 | 1.06 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-4 | 0.52 | 2.73 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 2.41 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.77 | 0 | 0.47 | 734.69 | 1.18 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-5 | 0.52 | 2.37 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 2.68 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.73 | 0 | 0.53 | 740.05 | 0.97 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-6 | 0.48 | 2.40 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 2.68 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.74 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 729.62 | 0.99 | |
| YDB15-7 | 3-12 | 0.50 | 2.52 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 2.66 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 735.23 | 0.88 | |
| YDB15-7 | 1-1 | 0.49 | 2.32 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 2.73 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.73 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 731.29 | 1.16 | |
| YDB15-7 | 1-2 | 0.51 | 2.43 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 2.70 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.68 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 734.29 | 1.22 | |
| YDB15-7 | 4-17 | 0.49 | 2.41 | 0.43 | 0.03 | 2.76 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 730.59 | 1.24 | |
| YDB15-18 | 1-12 | 0.44 | 2.42 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 2.75 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 721.03 | 0.97 | |
| YDB15-18 | 1-21 | 0.54 | 2.33 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 2.70 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.71 | 0 | 0.54 | 746.44 | 1.09 | |
| YDB15-18 | 4-2 | 0.45 | 2.19 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 2.81 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.71 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 724.96 | 1.14 | |
| YDB15-18 | 2-1 | 0.52 | 2.42 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 2.72 | 0 | 0.03 | 1.79 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 741.04 | 0.99 | |
| YDB15-25 | 3-3 | 0.45 | 2.82 | 0 | 0.05 | 2.19 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.78 | 0 | 0.44 | 709.91 | 1.37 | |
| YDB15-9 | 3-13 | 0.41 | 2.11 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 2.84 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.66 | 0 | 0.57 | 714.65 | 1.32 | |
| YDB15-9 | 1-3 | 0.47 | 2.39 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 2.58 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.68 | 0 | 0.52 | 724.39 | 1.05 | |
| YDB15-9 | 1-6 | 0.49 | 2.49 | 0.44 | 0.03 | 2.49 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.68 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 726.40 | 1.33 | |
| YDB15-15 | 3-5 | 0.51 | 2.35 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 2.93 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.66 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 740.52 | 1.25 | |

图6 西秦岭碌础坝岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准值据文献[41],下地壳数据来自文献[42])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram (b) of the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling (normalizing values after ref. [41], lower crust data from ref. [42])

图8 斜长石的显微照片(a)(b)、 背散射电子图像(c)(d)以及An值成分剖面(e)(f)
Fig.8 Optical micrographs(a)(b), SEM-BSE (backscattered-electron) images (c)(d) and An content profiles (e)(f) of plagioclase
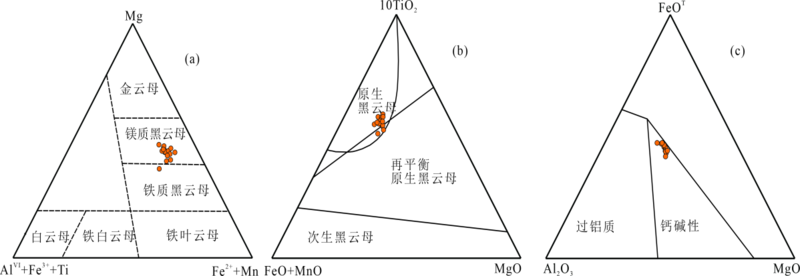
图11 黑云母分类判别图 (a)(Fe2++Mn)-Mg-(AlⅥ+Fe3++Ti)图解(底图据文献[45]);(b)MgO-10TiO2-(FeO+MnO)图解(底图据文献[46]);(c)MgO-FeOT-Al2O3图解(底图据文献[47])
Fig.11 Ternary biotite classification diagrams
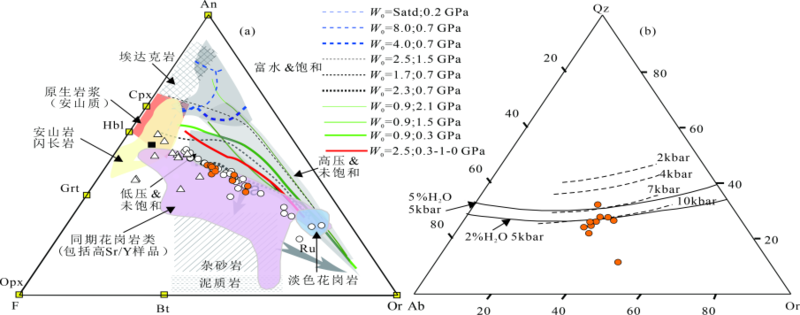
图14 西秦岭碌础坝岩体的岩浆含水量图 (a)F-An-Or 图解(底图据文献[59]);(b)Qz-Ab-Or相图(底图据文献[60]);F = FeO + MgO + MnO,a为混染,Ru为残留-未混合,W0为初始含水量(%);数据来源同图4
Fig.14 Ternary magma water content discrimination diagrams of the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling
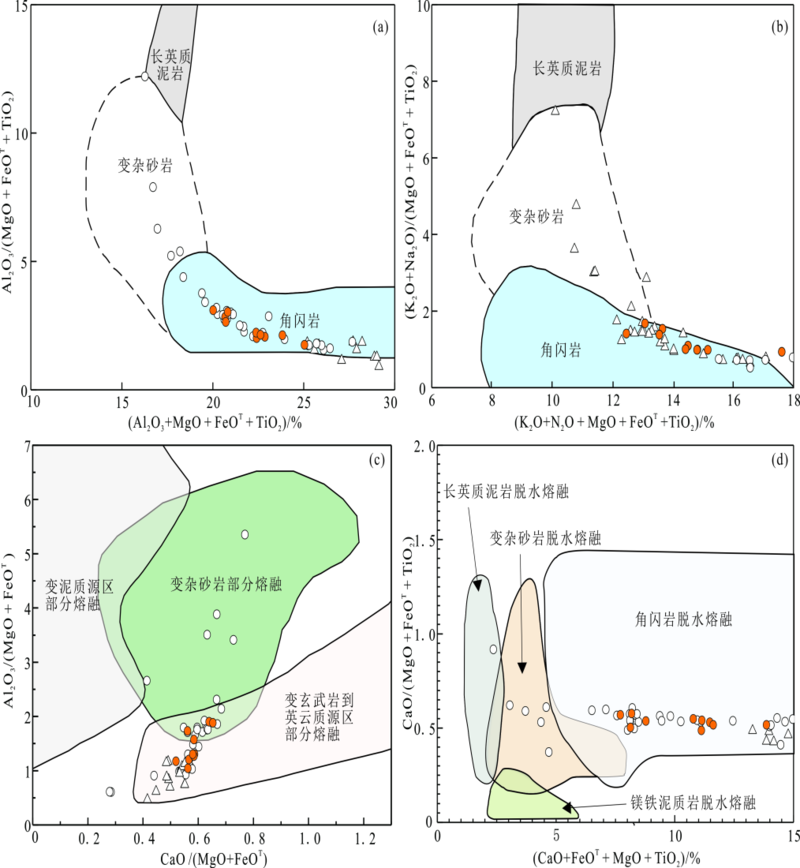
图16 西秦岭碌础坝岩体化学组成图解((a)和(b)底图据文献[62],(c)底图据文献[63];(d)底图据文献[64])
Fig.16 Chemical discrimination plots for the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling (base map (a)(b) after ref. [62]; base map (c) after ref. [63]; base map (d) after ref. [64])
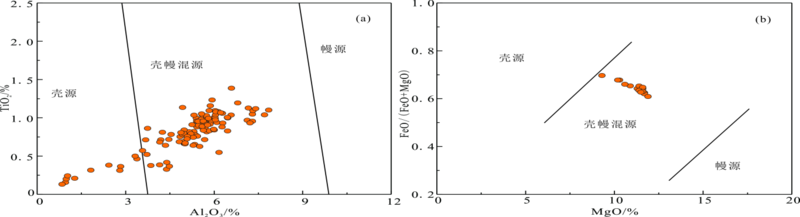
图18 西秦岭碌础坝岩体角闪石Al2O3-TiO2(a)和黑云母MgO-FeO/(FeO+MgO)图解(b)((a)底图据文献[48];(b)底图据文献[84])
Fig. 18 Amphibole Al2O3 vs.TiO2 (a) and biotite MgO vs.FeO/(FeO+MgO) (b) plots for the Luchuba pluton in West Qinling (base map (a) after ref. [48];base map (b) after ref. [84])

图19 西秦岭碌础坝岩体Y-Sr/Y图解和YbN-(La/Yb)N图解(据文献[87],引文数据据文献[17,18,19,20,21,22,23],下文相同)
Fig.19 Y vs.Sr/Y (a) and YbN vs.(La/Yb)N (b) plots for the Luchuba pluton in the West Qinling (base map after ref.[87];cited data from refs.[17-23]; the same below)
| [1] |
HOANG N, UTO K. Geochemistry of Cenozoic basalts in the Fukuoka district (northern Kyushu, Japan): Implications for asthenosphere and lithospheric mantle interaction[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 198(3/4):249-268.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邢作云, 等. 花岗岩成因研究前沿的认识[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(增):17-27. |
| [3] | 徐夕生, 王孝磊, 赵凯, 等. 新时期花岗岩研究的进展和趋势[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(5):899-911, 1069. |
| [4] | 黄雄飞. 西秦岭印支期花岗质岩浆作用与造山带演化[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [5] | 喻晓. 青海省同仁县江里沟花岗岩地球化学及其与成矿关系[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [6] |
LI X W, MO X X, HUANG X F, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of the Early Indosinian Tongren Pluton in West Qinling: Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97:38-50.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LUO B J, ZHANG H F, XU W C, et al. The Middle Triassic Meiwu batholith, West Qinling, central China: implications for the evolution of compositional diversity in a composite batholith[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2015, 56(6):1139-1172.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LUO B J, ZHANG H F, XU W C, et al. The magmatic plumbing system for Mesozoic high-Mg andesites, garnet-bearing dacites and porphyries, rhyolites and leucogranites from West Qinling, central China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2018, 59(3):447-482.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 豆敬兆. 西秦岭造山带早中生代花岗质岩浆作用与成分多样性研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2020. |
| [10] |
REN L, LIANG H Y, BAO Z W, et al. Genesis of the high Sr/Y rocks in Qinling orogenic belt, central China[J]. Lithos, 2018, 314/315:337-349.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 张宏飞, 陈岳龙, 徐旺春, 等. 青海共和盆地周缘印支期花岗岩类的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12):2910-2922. |
| [12] | 李佐臣, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 西秦岭糜署岭花岗岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2617-2634. |
| [13] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest earth[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723):841-844.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 王建中, 赵玉梅, 钱壮志, 等. 甘肃岷—礼成矿带钨矿地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 华东地质, 2017, 38(4):296-305. |
| [15] | 欧春生, 杨永春, 王虎, 等. 礼县碌础坝花岗岩体特征及其成矿作用[J]. 甘肃科技, 2010, 26(17):37-41. |
| [16] |
KONG J J, NIU Y L, DUAN M, et al. Petrogenesis of Luchuba and Wuchaba granitoids in western Qinling: Geochronological and geochemical evidence[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2017, 111(6):887-908.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
XIONG X, ZHU L M, ZHANG G W, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Indosinian granitoids from Western Qinling Orogen, China: Products of magma-mixing and fractionation[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(4):1305-1321.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 杨阳, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 西秦岭碌础坝岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(10):1735-1761. |
| [19] | 彭璇. 西秦岭二长花岗岩岩体群同源性研究[J]. 西北地质, 2013, 46:63-80. |
| [20] | 姜航. 西秦岭礼—岷矿集区“五朵金花”花岗质岩浆作用及其成岩大地构造背景研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2016. |
| [21] | 杨尚松. 西秦岭中川地区中酸性岩浆活动与金成矿作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. |
| [22] | 孔娟娟. 西秦岭三叠纪同碰撞花岗岩及中国东部中生代岩脉成因与洋壳的关系[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2018. |
| [23] |
ZENG Q T, MCCUAIG T C, TOHVER E, et al. Episodic Triassic magmatism in the western South Qinling Orogen, central China, and its implications[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49(4/5):402-423.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化、构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1):1-10. |
| [25] | 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭—松潘大陆构造结[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):23-32. |
| [26] | 霍福臣, 李永军. 西秦岭造山带的演化[J]. 甘肃地质学报, 1996, 5(1): 3-4, 6-17. |
| [27] | 苏春乾, 李勇, 赵欣, 等. 西秦岭礼县—武山杨河一带石炭纪地层的重新厘定[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2009, 31(2):135-141, 147. |
| [28] | 杜远生, 殷鸿福, 王治平. 秦岭造山带晚加里东—早海西期的盆地格局与构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 1997, 22(4):65-69. |
| [29] | 喻学惠, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 西秦岭新生代双峰式火山作用及南北构造带成因初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7):2195-2202. |
| [30] | 黄雄飞, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 西秦岭宕昌地区晚三叠世酸性火山岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11):3968-3980. |
| [31] | LI X W, MO X X, YU X H, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of the early Mesozoic pyroxene andesites in the Maixiu Area, West Qinling, China: Products of subduction or syn-collision?[J]. Lithos, 2013, 172:158-174. |
| [32] | 王天刚, 倪培, 孙卫东, 等. 西秦岭勉略带北部黄渚关和厂坝花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及源区性质[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(36):3493-3505. |
| [33] | 骆必继, 张宏飞, 肖尊奇. 西秦岭印支早期美武岩体的岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(3):199-213. |
| [34] | 王顺安, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 西秦岭闾井花岗岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学及其意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(1):33-51. |
| [35] | 刘树文, 杨朋涛, 李秋根, 等. 秦岭中段印支期花岗质岩浆作用与造山过程[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(6):1928-1943. |
| [36] | 张涛. 青海岗察花岗岩体地球化学特征及其成矿系列[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [37] | 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 高婷, 等. 西秦岭北缘花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2):371-389. |
| [38] |
LI X H, LI Z X, WINGATE M T D, et al. Geochemistry of the 755 Ma Mundine Well dyke swarm, northwestern Australia: Part of a Neoproterozoic mantle superplume beneath Rodinia?[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 146(1/2):1-15.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4):247-263.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [42] | RUDNICK RL, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3:659. |
| [43] | DEER W, HOWIE R, ZUSSMAN J. An introduction to the rock-forming minerals[M]. England: Longman Scientific and Technology, 1992: 509-517. |
| [44] |
LEAKE B E, WOOLLEY A R, ARPS C E S, et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles report of the subcommittee on amphiboles of the international mineralogical association commission on new minerals and mineral names[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 1997, 9(3):623-651.
DOI URL |
| [45] | FROSTER M. Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral mica[R]. Tulsa:US Geological Survey, 1960:11-49. |
| [46] |
NACHIT H, IBHI A, ABIA E H, et al. Discrimination between primary magmatic biotites, reequilibrated biotites and neoformed biotites[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2005, 337(16):1415-1420.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
ABDEL-RAHMAN A F M. Nature of biotites from alkaline, calc-alkaline, and peraluminous magmas[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1994, 35(2):525-541.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 刘春花, 吴才来, 雷敏, 等. 秦岭沙河湾I型花岗岩岩石学、矿物学特征及岩浆形成的温压条件[J]. 地质与勘探, 2013, 49(4):595-608. |
| [49] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
HENRY D J. The Ti-saturation surface for low-to-medium pressuremetapelitic biotites: Implications for geothermometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms[J]. American Mineralogist, 2005, 90(2/3):316-328.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 李清, 梁贤, 吴伟哲, 等. 黑云母温压计在岩浆系统中的适用性研究[J]. 河北地质大学学报, 2020, 43(4):12-18. |
| [52] | RIDOLFI F, RENZULLI A, PUERINI M. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: an overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2010, 160(1):45-66. |
| [53] |
UCHIDA E, ENDO S, MAKINO M. Relationship between solidification depth of granitic rocks and formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Resource Geology, 2007, 57(1):47-56.
DOI URL |
| [54] | 刘行, 邹灏, 李阳, 等. 川西新元古代灯杆坪花岗岩成因与岩浆演化:来自斜长石和黑云母矿物学依据[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5):1043-1057. |
| [55] | 李小伟, 黄雄飞, 黄丹峰. 花岗岩中常用压力计的应用评述[J]. 高校地质学报, 2011, 17(3):415-422. |
| [56] |
SCHMIDT M W. Amphibole composition in tonalite as a function of pressure: An experimental calibration of the Al-in-hornblende barometer[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1992, 110(2/3):304-310.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
KOHN M J. Titanite petrochronology[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2017, 83(1):419-441.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ANDERSON J L, SMITH D R. The effects of temperature and fO2 on the Al-in-hornblende barometer[J]. American Mineralogist, 1995, 80(5/6):549-559.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
CASTRO A. Tonalite-granodiorite suites as cotectic systems: A review of experimental studies with applications to granitoid petrogenesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 124:68-95.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
LI S, CHUNG S L, WANG T, et al. Water-fluxed crustal melting and petrogenesis of large-scale Early Cretaceous intracontinental granitoids in the southern Great Xing'an Range, North China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2018, 130(3/4):580-597.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
MOYEN J F, LAURENT O, CHELLE-MICHOU C, et al. Collision vs. subduction-related magmatism: Two contrasting ways of granite formation and implications for crustal growth[J]. Lithos, 2017, 277:154-177.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
KAYGUSUZ A, SIEBEL W, ILBEYLI N, et al. Insight into magma genesis at convergent plate margins-a case study from the eastern Pontides (NE Turkey)[J]. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie-Abhandlungen, 2010, 187(3):265-287.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ALTHERR R, HOLL A, HEGNER E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides: Northern Vosges (France) and northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(1/2/3):51-73.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
PATIÑO DOUCE A E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas?[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1999, 168(1):55-75.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
SOESOO A. Fractional crystallization of mantle-derived melts as a mechanism for some I-type granite petrogenesis: an example from Lachlan Fold Belt, Australia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2000, 157(1):135-149.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
JAGOUTZ O, KLEIN B. On the importance of crystallization-differentiation for the generation of SiO2-rich melts and the compositional build-up of arc (and continental) crust[J]. American Journal of Science, 2018, 318(1):29-63.
DOI URL |
| [67] | NANDEDKAR R H, ULMER P, MüNTENER O. Fractional crystallization of primitive, hydrous arc magmas: An experimental study at 0.7 GPa[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2014, 167(6):1-27. |
| [68] |
MüNTENER O, ULMER P. Arc crust formation and differentiation constrained by experimental petrology[J]. American Journal of Science, 2018, 318(1):64-89.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
ULMER P, KAEGI R, MüNTENER O. Experimentally derived intermediate to silica-rich arc magmas by fractional and equilibrium crystallization at 1.0 GPa: An evaluation of phase relationships, compositions, liquid lines of descent and oxygen fugacity[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2018, 59(1):11-58.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
BROWNM. Granite: From genesis to emplacement[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2013, 125(7/8):1079-1113.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
STUCK T J, DIENER J F A. Mineral equilibria constraints on open-system melting in metamafic compositions[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2018, 36(2):255-281.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
BARBARIN B. Mafic magmatic enclaves and mafic rocks associated with some granitoids of the central Sierra Nevada batholith, California: nature, origin, and relations with the hosts[J]. Lithos, 2005, 80(1/2/3/4):155-177.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, WILDE S A, et al. Tracing magma mixing in granite genesis: in situ U-Pb dating and Hf-isotope analysis of zircons[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 153(2):177-190.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
KEMP A I S, HAWKESWORTH C J, FOSTER G L, et al. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon[J]. Science, 2007, 315(5814):980-983.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
REUBI O, BLUNDY J. A dearth of intermediate melts at subduction zone volcanoes and the petrogenesis of arc andesites[J]. Nature, 2009, 461:1269-1273.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
FOLEY S, TIEPOLO M, VANNUCCI R. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones[J]. Nature, 2002, 417(6891):837-840.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
SISSON T W. Hornblende-melt trace-element partitioning measured by ion microprobe[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 117(1/2/3/4):331-344.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
TIEPOLO M, BOTTAZZI P, FOLEYS F, et al. Fractionation of Nb and Ta from Zr and Hf at mantle depths: The role of titanian pargasite and kaersutite[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(1):221-232.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
STEPANOV A S, HERMANN J. Fractionation of Nb and Ta by biotite and phengite: Implications for the “missing Nb paradox”[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(3):303-306.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
BEA F, PEREIRA M D, STROH A. Mineral/leucosome trace-element partitioning in a peraluminous migmatite (a laser ablation-ICP-MS study)[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 117(1/2/3/4):291-312.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
RAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
RAPP R P, SHIMIZU N, NORMAN M D, et al. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(4):335-356.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
XIONG X L, ADAM J, GREEN T H. Rutile stability and rutile/melt HFSE partitioning during partial melting of hydrous basalt: Implications for TTG genesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 218(3/4):339-359.
DOI URL |
| [84] | 周作侠. 侵入岩的镁铁云母化学成分特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1988, 4(3):63-73. |
| [85] | ROLLINSON HUGH R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation[M]. London:Taylor and Francis, 2014: 384. |
| [86] | 秦江锋. 秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩类成因机制及深部动力学背景[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2010. |
| [87] |
OU Q, WANG Q, WYMAN D A, et al. Eocene adakitic porphyries in the central-northern Qiangtang Block, central Tibet: Partial melting of thickened lower crust and implications for initial surface uplifting of the plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2017, 122(2):1025-1053.
DOI URL |
| [88] | 熊富浩, 马昌前, 张金阳, 等. 东昆仑造山带早中生代镁铁质岩墙群LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年, 元素和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11):3350-3364. |
| [89] |
ZHANG Z, ZHANG G, TANG S, et al. Age of Anzishan granulites in the Mianxian-Lueyang suture zone of Qingling orogen:With a discussion of the timing of final assembly of Yangtze and North China craton blocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(22):1925-1930.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
JIANG Y H, JIN G D, LIAO S Y, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Triassic granitoids from the Qinling orogen, central China: implications for a continental arc to continent-continent collision[J]. Lithos, 2010, 117(1/2/3/4):183-197.
DOI URL |
| [91] | 陈衍景. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4):854-865. |
| [92] | 李曙光, 孙卫东, 张国伟, 等. 南秦岭勉略构造带黑沟峡变质火山岩的年代学和地球化学: 古生代洋盆及其闭合时代的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 1996, 26(3):223-230. |
| [93] |
ZHANG H F, GAO S, ZHONG Z Q, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Cretaceous granitoids: Constraints on tectonic framework and crustal structure of the Dabieshan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 186(3/4):281-299.
DOI URL |
| [94] | 赖绍聪, 秦江锋. 南秦岭勉略缝合带蛇绿岩与火山岩[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. |
| [95] | 王晓霞, 王涛, 张成立. 秦岭造山带花岗质岩浆作用与造山带演化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45(8):1109-1125. |
| [96] | 王绘清, 朱云海, 林启祥, 等. 青海尖扎—同仁地区隆务峡蛇绿岩的形成时代及意义: 来自辉长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(1):86-92. |
| [97] |
LI X W, MO XX, YU X H, et al. Geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of the Cretaceous intraplate volcanism in West Qinling, Central China: Implications for asthenosphere-lithosphere interaction[J]. Lithos, 2013, 177:381-401.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
HU F Y, DUCEA M N, LIU S W, et al. Quantifying crustal thickness in continental collisional belts: Global perspective and a geologic application[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):7058.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
HU F Y, LIU S W, DUCEA M N, et al. Early Mesozoic magmatism and tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen: Implications for oblique continental collision[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 88:296-332.
DOI URL |
| [100] | 魏春景. 麻粒岩相变质作用与花岗岩成因-Ⅱ:变质泥质岩高温-超高温变质相平衡与S型花岗岩成因的定量模拟[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(6):1625-1643. |
| [1] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [2] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [3] | 高银虎, 尹刚, 龚泽强, 郭明春. 甘肃两当湘潭子金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| [4] | 胡博心, 周鸿飞, 屈海浪, 曹易刚, 白会良, 王凌童, 王立新, 杨昭克, 李元申. 陕西铧厂沟金矿南矿带构造叠加晕特征及深部找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1515-1522. |
| [5] | 缪广, 董国臣, 屈海浪, 刘舒飞, 艾忠林, 史鹏亮, 曹雪峰. 西秦岭大店沟金矿成矿流体演化及矿床成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1565-1575. |
| [6] | 第鹏飞, 汤庆艳, 刘聪, 宋宏, 张家和, 刘东晓, 王玉玺, 蒲万峰. 西秦岭夏河—合作地区早子沟和加甘滩金矿床石英微量元素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1608-1621. |
| [7] | 严镜, 刘景显, 蒲万峰, 魏学平, 李智斌. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世构造属性:来自将其那梁侵入杂岩体的年代学及地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1677-1690. |
| [8] | 杨维刚, 李永胜, 李通元, 张俊, 任鹏飞. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世板块碰撞事件的记录:来自合作地区火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1691-1701. |
| [9] | 寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260. |
| [10] | 李林积, 李堂积, 王丹. 西秦岭大水金矿床方解石Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 469-475. |
| [11] | 赵胜金, 高利东, 于海洋, 朴丽丽, 柳志辉, 周颖帅, 张猛, 张玉龙, 杨海星, 赵万莉. 大兴安岭北段上侏罗统哈日陶勒盖玄武岩的厘定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 718-726. |
| [12] | 刘伯崇, 李康宁, 史海龙, 蒲万峰, 汪宏涛, 王舒恒. 西秦岭甘青交界一带晚三叠世火山岩岩石成因及构造指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 704-717. |
| [13] | 杨瀚文, 申俊峰, 魏立勇, 张振, 刘满年, 冯博鑫, 张洛宁. 西秦岭西段共和盆地周缘西功卡花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 316-328. |
| [14] | 孙载波, 李静, 周坤, 曾文涛, 段向东, 赵江泰, 徐桂香, 樊岳华. 滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩的岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 746-756. |
| [15] | 李金春,申俊峰,刘海明,彭自栋,魏竹君,王冬丽, 窦润吾,蓸卫东. 西秦岭岗岔金矿赋矿围岩成岩时代及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 36-49. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||