



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (02): 316-328.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.02.10
杨瀚文1,2( ), 申俊峰2(
), 申俊峰2( ), 魏立勇1, 张振1, 刘满年1, 冯博鑫1, 张洛宁3
), 魏立勇1, 张振1, 刘满年1, 冯博鑫1, 张洛宁3
收稿日期:2017-11-25
修回日期:2018-02-11
出版日期:2018-04-10
发布日期:2018-05-07
通讯作者:
申俊峰,男,教授,博士生导师,1962年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事成因矿物学与找矿矿物学方面的研究工作。Email:shenjf@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:杨瀚文,男,助理工程师,1992年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事环境与生命矿物学方面的研究工作。Email:306134832@qq.com。
基金资助:
YANG Hanwen1,2( ), SHEN Junfeng2(
), SHEN Junfeng2( ), WEI Liyong1, ZHANG Zhen1, LIU Mannian1, FENG Boxin1, ZHANG Luoning3
), WEI Liyong1, ZHANG Zhen1, LIU Mannian1, FENG Boxin1, ZHANG Luoning3
Received:2017-11-25
Revised:2018-02-11
Online:2018-04-10
Published:2018-05-07
摘要:
西功卡花岗闪长岩体位于西秦岭西段的共和盆地周缘。对该岩体进行了系统的岩相学、锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄为(227.2±7.3) Ma(MSWD=2.0),代表岩体侵位时间。西功卡岩体具有高硅(SiO2=69.86%~70.94%)、富钾(K2O= 3.20%~4.08%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O=5.61%~7.03%)、弱过铝质(A/CNK=0.99~1.20)特征,属于高钾钙碱性Ⅰ型花岗岩。西功卡岩体富集K、Rb、Ba、Th、U等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti、P等高场强元素,轻重稀土元素分馏较明显(LREE/HREE=11.04~13.13),具有中等Eu负异常(δEu=0.72~ 0.84)。岩石地球化学特征表明,西功卡花岗闪长岩主要由壳源物质熔融形成,结合前人研究成果,笔者认为,西功卡岩体形成于晚三叠世,与区域其他岩体年龄基本一致,均形成于后碰撞构造环境,为同一构造-岩浆事件的产物。研究表明,西秦岭造山带西段共和盆地周缘于晚三叠世进入后碰撞构造演化阶段,该认识对西秦岭造山带构造-岩浆事件演化过程提供了新的约束。
中图分类号:
杨瀚文, 申俊峰, 魏立勇, 张振, 刘满年, 冯博鑫, 张洛宁. 西秦岭西段共和盆地周缘西功卡花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 316-328.
YANG Hanwen, SHEN Junfeng, WEI Liyong, ZHANG Zhen, LIU Mannian, FENG Boxin, ZHANG Luoning. Zircon U-Pb Ages, Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Implications of Xigongka Granodiorite Around Gonghe Basin, West of Western Qinling Mountains[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(02): 316-328.

图1 兴海—同德一带区域地质简图(据陈岳龙等[4]改) 1.第四系;2.临夏组;3.羊曲组;4.古浪堤组第二岩性段;5.古浪堤组第一岩性段;6.隆务河组第三岩性段;7.隆务河组第二岩性段;8.隆务河组第一岩性段;9.甘家组上段;10.甘家组下段;11.岩体;12.不整合界线;13.地质界线;14.断层
Fig.1 Tectonic maps of Xinghai-Tongde area(modified after Chen Yuelong, et al[4])

图3 西功卡花岗闪长岩野外及镜下照片 (a)、(b)花岗闪长岩野外照片;(c)、(d)花岗闪长岩镜下照片;Qtz.石英;Amp.角闪石;Bt.黑云母;Pl.斜长石
Fig.3 Photos of Xigongka granodiorite in the field and microscopic photos
| 样号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 208Pb/ 232Th | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 208Pb/ 232Th | 1σ | |||||||||||||
| D3076-1-1 | 216.75 | 547.91 | 0.40 | 0.057 3 | 0.001 4 | 0.282 5 | 0.004 5 | 0.035 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.011 1 | 0.000 1 | 502 | 17 | 253 | 4 | 226 | 3 | 223 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-2 | 160.68 | 377.88 | 0.43 | 0.051 4 | 0.001 6 | 0.281 6 | 0.007 2 | 0.039 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 2 | 0.000 2 | 260 | 35 | 252 | 6 | 251 | 3 | 226 | 4 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-3 | 174.67 | 299.68 | 0.58 | 0.052 9 | 0.001 6 | 0.263 1 | 0.006 2 | 0.036 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.011 2 | 0.000 2 | 322 | 31 | 237 | 5 | 229 | 3 | 226 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-4 | 80.68 | 200.13 | 0.40 | 0.059 5 | 0.006 6 | 0.351 8 | 0.037 7 | 0.042 9 | 0.001 2 | 0.013 7 | 0.001 2 | 584 | 186 | 306 | 28 | 271 | 7 | 274 | 24 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-5 | 110.10 | 174.97 | 0.63 | 0.051 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.272 1 | 0.007 5 | 0.038 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.012 2 | 0.000 2 | 241 | 40 | 244 | 6 | 245 | 3 | 246 | 4 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-6 | 31.80 | 85.02 | 0.37 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 9 | 0.251 6 | 0.008 4 | 0.035 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.012 4 | 0.000 4 | 230 | 52 | 228 | 7 | 228 | 3 | 249 | 7 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-7 | 50.35 | 168.18 | 0.30 | 0.051 0 | 0.002 3 | 0.231 9 | 0.009 3 | 0.033 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.009 8 | 0.000 3 | 242 | 67 | 212 | 8 | 209 | 3 | 197 | 5 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-8 | 333.07 | 443.45 | 0.75 | 0.071 1 | 0.003 8 | 0.357 0 | 0.018 4 | 0.036 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.011 0 | 0.000 2 | 961 | 113 | 310 | 14 | 231 | 4 | 222 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-9 | 131.60 | 665.57 | 0.20 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.260 4 | 0.007 3 | 0.037 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 9 | 0.000 2 | 231 | 42 | 235 | 6 | 235 | 3 | 240 | 4 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-10 | 123.03 | 287.04 | 0.43 | 0.050 6 | 0.001 9 | 0.247 7 | 0.008 2 | 0.035 5 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 1 | 0.000 3 | 224 | 52 | 225 | 7 | 225 | 3 | 223 | 5 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-11 | 282.39 | 394.62 | 0.72 | 0.057 9 | 0.002 1 | 0.286 3 | 0.009 2 | 0.035 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 6 | 0.000 4 | 526 | 47 | 256 | 7 | 227 | 3 | 232 | 7 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-12 | 70.09 | 310.22 | 0.23 | 0.050 2 | 0.002 8 | 0.231 1 | 0.012 1 | 0.033 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.010 9 | 0.000 3 | 205 | 90 | 211 | 10 | 212 | 3 | 219 | 6 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-13 | 667.37 | 555.17 | 1.20 | 0.050 4 | 0.001 4 | 0.239 6 | 0.005 2 | 0.034 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.010 8 | 0.000 2 | 212 | 29 | 218 | 4 | 219 | 3 | 217 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-14 | 184.27 | 982.64 | 0.19 | 0.050 9 | 0.001 2 | 0.259 5 | 0.004 1 | 0.037 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.012 0 | 0.000 2 | 237 | 17 | 234 | 3 | 234 | 3 | 240 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-15 | 77.76 | 167.89 | 0.46 | 0.050 7 | 0.001 4 | 0.244 3 | 0.005 4 | 0.035 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.010 3 | 0.000 1 | 225 | 29 | 222 | 4 | 222 | 3 | 207 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-16 | 96.42 | 722.82 | 0.13 | 0.052 8 | 0.002 2 | 0.294 1 | 0.010 8 | 0.040 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.018 7 | 0.000 6 | 320 | 57 | 262 | 8 | 255 | 4 | 374 | 11 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-17 | 136.97 | 279.77 | 0.49 | 0.051 5 | 0.002 2 | 0.273 8 | 0.010 5 | 0.038 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.011 7 | 0.000 3 | 263 | 62 | 246 | 8 | 244 | 3 | 236 | 5 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-18 | 83.62 | 285.53 | 0.29 | 0.053 3 | 0.001 8 | 0.249 4 | 0.007 1 | 0.033 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.010 2 | 0.000 3 | 342 | 41 | 226 | 6 | 215 | 3 | 204 | 6 | |||||||||||
表1 西功卡花岗闪长岩(D3076-1)的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测试结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age dating of Late Triassic granitoids in Xigongka area
| 样号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 208Pb/ 232Th | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 208Pb/ 232Th | 1σ | |||||||||||||
| D3076-1-1 | 216.75 | 547.91 | 0.40 | 0.057 3 | 0.001 4 | 0.282 5 | 0.004 5 | 0.035 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.011 1 | 0.000 1 | 502 | 17 | 253 | 4 | 226 | 3 | 223 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-2 | 160.68 | 377.88 | 0.43 | 0.051 4 | 0.001 6 | 0.281 6 | 0.007 2 | 0.039 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 2 | 0.000 2 | 260 | 35 | 252 | 6 | 251 | 3 | 226 | 4 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-3 | 174.67 | 299.68 | 0.58 | 0.052 9 | 0.001 6 | 0.263 1 | 0.006 2 | 0.036 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.011 2 | 0.000 2 | 322 | 31 | 237 | 5 | 229 | 3 | 226 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-4 | 80.68 | 200.13 | 0.40 | 0.059 5 | 0.006 6 | 0.351 8 | 0.037 7 | 0.042 9 | 0.001 2 | 0.013 7 | 0.001 2 | 584 | 186 | 306 | 28 | 271 | 7 | 274 | 24 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-5 | 110.10 | 174.97 | 0.63 | 0.051 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.272 1 | 0.007 5 | 0.038 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.012 2 | 0.000 2 | 241 | 40 | 244 | 6 | 245 | 3 | 246 | 4 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-6 | 31.80 | 85.02 | 0.37 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 9 | 0.251 6 | 0.008 4 | 0.035 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.012 4 | 0.000 4 | 230 | 52 | 228 | 7 | 228 | 3 | 249 | 7 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-7 | 50.35 | 168.18 | 0.30 | 0.051 0 | 0.002 3 | 0.231 9 | 0.009 3 | 0.033 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.009 8 | 0.000 3 | 242 | 67 | 212 | 8 | 209 | 3 | 197 | 5 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-8 | 333.07 | 443.45 | 0.75 | 0.071 1 | 0.003 8 | 0.357 0 | 0.018 4 | 0.036 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.011 0 | 0.000 2 | 961 | 113 | 310 | 14 | 231 | 4 | 222 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-9 | 131.60 | 665.57 | 0.20 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.260 4 | 0.007 3 | 0.037 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 9 | 0.000 2 | 231 | 42 | 235 | 6 | 235 | 3 | 240 | 4 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-10 | 123.03 | 287.04 | 0.43 | 0.050 6 | 0.001 9 | 0.247 7 | 0.008 2 | 0.035 5 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 1 | 0.000 3 | 224 | 52 | 225 | 7 | 225 | 3 | 223 | 5 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-11 | 282.39 | 394.62 | 0.72 | 0.057 9 | 0.002 1 | 0.286 3 | 0.009 2 | 0.035 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.011 6 | 0.000 4 | 526 | 47 | 256 | 7 | 227 | 3 | 232 | 7 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-12 | 70.09 | 310.22 | 0.23 | 0.050 2 | 0.002 8 | 0.231 1 | 0.012 1 | 0.033 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.010 9 | 0.000 3 | 205 | 90 | 211 | 10 | 212 | 3 | 219 | 6 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-13 | 667.37 | 555.17 | 1.20 | 0.050 4 | 0.001 4 | 0.239 6 | 0.005 2 | 0.034 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.010 8 | 0.000 2 | 212 | 29 | 218 | 4 | 219 | 3 | 217 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-14 | 184.27 | 982.64 | 0.19 | 0.050 9 | 0.001 2 | 0.259 5 | 0.004 1 | 0.037 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.012 0 | 0.000 2 | 237 | 17 | 234 | 3 | 234 | 3 | 240 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-15 | 77.76 | 167.89 | 0.46 | 0.050 7 | 0.001 4 | 0.244 3 | 0.005 4 | 0.035 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.010 3 | 0.000 1 | 225 | 29 | 222 | 4 | 222 | 3 | 207 | 3 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-16 | 96.42 | 722.82 | 0.13 | 0.052 8 | 0.002 2 | 0.294 1 | 0.010 8 | 0.040 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.018 7 | 0.000 6 | 320 | 57 | 262 | 8 | 255 | 4 | 374 | 11 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-17 | 136.97 | 279.77 | 0.49 | 0.051 5 | 0.002 2 | 0.273 8 | 0.010 5 | 0.038 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.011 7 | 0.000 3 | 263 | 62 | 246 | 8 | 244 | 3 | 236 | 5 | |||||||||||
| D3076-1-18 | 83.62 | 285.53 | 0.29 | 0.053 3 | 0.001 8 | 0.249 4 | 0.007 1 | 0.033 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.010 2 | 0.000 3 | 342 | 41 | 226 | 6 | 215 | 3 | 204 | 6 | |||||||||||
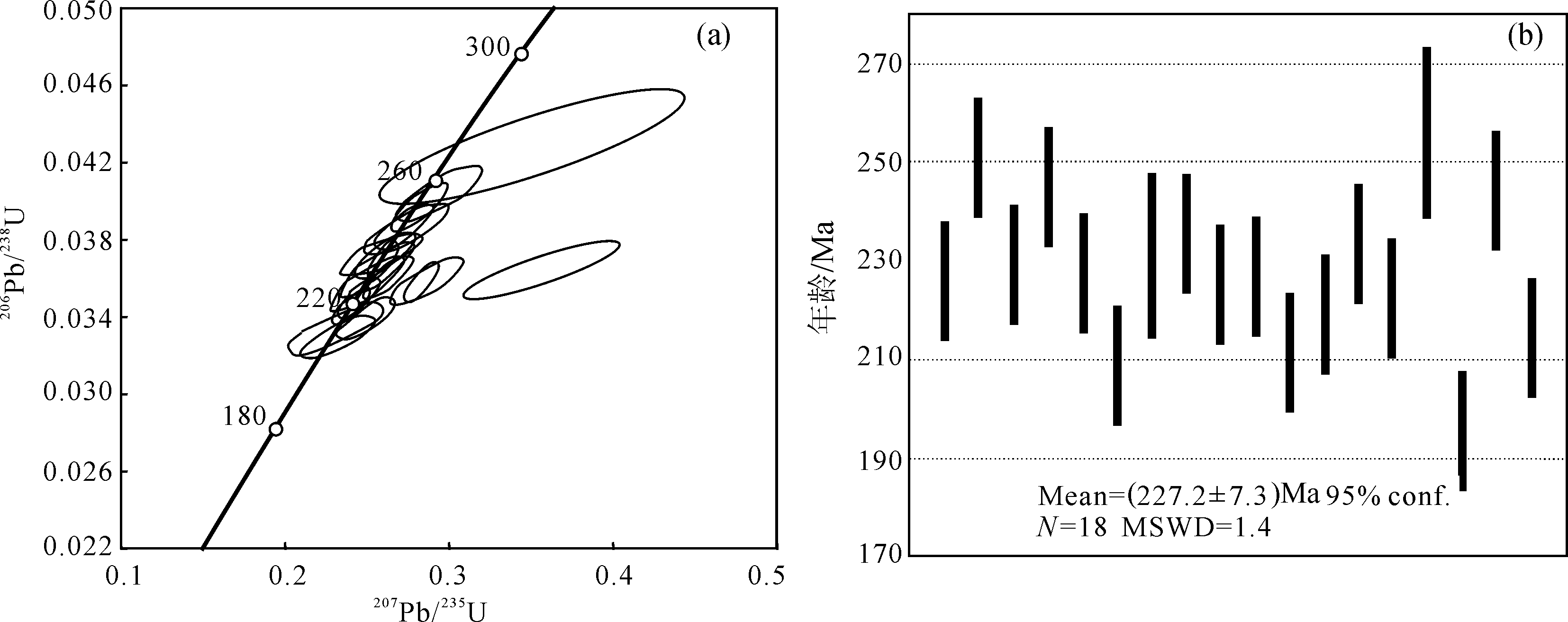
图5 西功卡花岗闪长岩体(D3076-1)中LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)与加权直方图(b)
Fig.5 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb concordant age diagram (a) and weighted histogram (b) of Xigongka granodiorite(D3076-1)
| 样品 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | K2O+ Na2O | K2O/ Na2O | A/ CNK | A/ NK | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D3076HX2-1 | 70.10 | 0.28 | 14.81 | 2.46 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 3.03 | 3.42 | 3.48 | 0.11 | 1.95 | 100.23 | 0.34 | 6.90 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.58 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 70.11 | 0.28 | 14.94 | 2.44 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 2.71 | 3.12 | 3.55 | 0.10 | 1.54 | 99.39 | 0.33 | 6.67 | 1.14 | 1.07 | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 70.56 | 0.26 | 15.02 | 2.25 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 2.54 | 2.95 | 4.08 | 0.10 | 1.38 | 99.63 | 0.30 | 7.03 | 1.38 | 1.08 | 1.62 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 70.08 | 0.27 | 15.01 | 2.39 | 0.06 | 0.58 | 2.76 | 3.13 | 3.64 | 0.10 | 2.04 | 100.06 | 0.36 | 6.77 | 1.16 | 1.06 | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 70.22 | 0.28 | 14.85 | 2.45 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 2.89 | 3.06 | 3.50 | 0.11 | 1.37 | 99.32 | 0.33 | 6.56 | 1.15 | 1.03 | 1.61 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 70.91 | 0.27 | 15.15 | 2.49 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 2.38 | 2.98 | 3.49 | 0.10 | 1.75 | 100.02 | 0.29 | 6.47 | 1.17 | 1.15 | 1.72 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 70.55 | 0.28 | 15.09 | 2.54 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 2.39 | 3.12 | 3.49 | 0.11 | 1.62 | 99.65 | 0.27 | 6.61 | 1.12 | 1.14 | 1.69 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 70.93 | 0.27 | 15.25 | 2.56 | 0.07 | 0.41 | 2.38 | 3.13 | 3.48 | 0.11 | 1.18 | 99.77 | 0.27 | 6.62 | 1.11 | 1.15 | 1.71 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 69.86 | 0.29 | 14.81 | 2.37 | 0.17 | 0.66 | 3.44 | 3.05 | 3.20 | 0.10 | 2.26 | 100.21 | 0.39 | 6.25 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 1.74 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 70.56 | 0.27 | 14.98 | 2.45 | 0.09 | 0.63 | 2.81 | 2.77 | 3.66 | 0.10 | 1.14 | 99.46 | 0.37 | 6.43 | 1.32 | 1.11 | 1.78 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 70.94 | 0.27 | 15.04 | 2.31 | 0.11 | 0.52 | 2.90 | 2.03 | 3.57 | 0.11 | 1.84 | 99.65 | 0.35 | 5.61 | 1.76 | 1.20 | 2.08 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 70.30 | 0.27 | 15.02 | 2.42 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 2.65 | 3.11 | 3.68 | 0.10 | 1.26 | 99.48 | 0.36 | 6.79 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 1.69 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品 | δ | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX2-1 | 1.76 | 26.09 | 49.97 | 5.49 | 20.10 | 3.91 | 0.96 | 3.33 | 0.45 | 2.42 | 0.42 | 1.10 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 13.27 | 115.51 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 1.72 | 23.74 | 45.78 | 5.09 | 18.58 | 3.71 | 0.93 | 3.20 | 0.45 | 2.38 | 0.42 | 1.11 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.18 | 106.67 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 1.79 | 25.30 | 49.03 | 5.38 | 19.66 | 3.88 | 0.92 | 3.29 | 0.46 | 2.47 | 0.43 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 1.01 | 0.15 | 13.46 | 113.28 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 1.69 | 27.03 | 51.61 | 5.72 | 20.91 | 4.08 | 0.95 | 3.43 | 0.48 | 2.52 | 0.44 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.61 | 119.59 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 1.73 | 30.94 | 58.24 | 6.32 | 22.67 | 4.29 | 0.98 | 3.56 | 0.48 | 2.50 | 0.44 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.76 | 132.84 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 1.55 | 29.92 | 56.99 | 6.26 | 22.60 | 4.24 | 0.98 | 3.55 | 0.48 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.12 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.54 | 130.35 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 1.58 | 29.03 | 55.61 | 6.13 | 22.15 | 4.24 | 0.94 | 3.51 | 0.47 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.38 | 127.42 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 1.57 | 29.92 | 57.12 | 6.30 | 22.76 | 4.27 | 0.94 | 3.56 | 0.47 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 13.49 | 130.67 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 1.45 | 27.03 | 51.83 | 5.79 | 21.19 | 4.20 | 1.10 | 3.66 | 0.51 | 2.72 | 0.48 | 1.27 | 0.17 | 1.10 | 0.16 | 15.19 | 121.21 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 1.50 | 26.71 | 51.61 | 5.70 | 20.76 | 4.02 | 0.93 | 3.38 | 0.47 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.42 | 118.92 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 1.13 | 28.88 | 54.95 | 6.06 | 22.02 | 4.20 | 0.98 | 3.52 | 0.48 | 2.50 | 0.44 | 1.15 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 13.71 | 126.48 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 1.69 | 28.89 | 55.33 | 6.09 | 22.01 | 4.20 | 0.96 | 3.53 | 0.48 | 2.52 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.45 | 126.85 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品 | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Co | Ni | Cs | Ga | Hf | Rb | Nb | Sr | Ba | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX2-1 | 106.52 | 8.99 | 11.85 | 19.29 | 4.31 | 2.84 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 5.71 | 2.28 | 8.46 | 17.79 | 3.43 | 115.52 | 10.88 | 337.77 | 590.66 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 97.83 | 8.84 | 11.07 | 17.38 | 4.13 | 2.70 | 0.81 | 0.97 | 5.34 | 2.34 | 8.17 | 17.84 | 3.43 | 120.15 | 11.20 | 344.87 | 690.22 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 104.17 | 9.11 | 11.43 | 17.97 | 4.21 | 2.69 | 0.77 | 0.98 | 5.46 | 6.19 | 8.58 | 17.93 | 3.75 | 129.75 | 11.22 | 349.83 | 786.23 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 110.30 | 9.29 | 11.87 | 19.78 | 4.28 | 2.90 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 4.80 | 2.71 | 8.13 | 17.82 | 3.34 | 120.52 | 11.22 | 314.97 | 690.96 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 123.44 | 9.40 | 13.13 | 22.65 | 4.66 | 3.01 | 0.74 | 0.97 | 4.89 | 2.71 | 7.53 | 17.80 | 3.42 | 116.06 | 11.35 | 344.68 | 647.00 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 120.99 | 9.36 | 12.93 | 21.90 | 4.56 | 3.00 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 4.67 | 3.40 | 7.12 | 18.05 | 3.56 | 111.18 | 11.17 | 292.26 | 593.03 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 118.10 | 9.32 | 12.67 | 21.25 | 4.42 | 2.96 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 6.04 | 3.27 | 6.52 | 18.14 | 3.59 | 109.87 | 11.08 | 291.45 | 559.94 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 121.31 | 9.36 | 12.96 | 22.13 | 4.52 | 3.04 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 6.08 | 2.51 | 6.59 | 18.47 | 3.51 | 111.03 | 11.45 | 293.41 | 560.98 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 111.14 | 10.07 | 11.04 | 17.63 | 4.15 | 2.75 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 7.26 | 3.73 | 9.13 | 23.17 | 4.06 | 140.14 | 14.98 | 262.52 | 382.96 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 109.73 | 9.19 | 11.94 | 19.55 | 4.29 | 2.85 | 0.75 | 0.98 | 5.55 | 2.09 | 7.91 | 17.96 | 3.55 | 127.86 | 11.62 | 267.88 | 554.99 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 117.09 | 9.39 | 12.47 | 20.72 | 4.44 | 2.91 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 5.55 | 2.09 | 5.98 | 18.22 | 3.71 | 126.51 | 11.27 | 201.84 | 525.22 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 117.48 | 9.37 | 12.54 | 21.15 | 4.44 | 2.98 | 0.74 | 0.97 | 4.71 | 2.12 | 7.69 | 17.91 | 3.46 | 129.86 | 11.33 | 282.71 | 681.88 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Ta | Th | V | U | Cu | Zr | Pb | Zn | Sc | Cr | Ge | Li | Be | Sr/Y | Nb/Ta | La/Nb | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX2-1 | 0.97 | 10.41 | 25.93 | 3.87 | 3.46 | 121.32 | 13.02 | 30.33 | 3.69 | 4.72 | 1.29 | 27.67 | 3.05 | 25.45 | 11.22 | 2.40 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 1.00 | 9.87 | 24.94 | 4.00 | 2.20 | 120.75 | 14.58 | 30.55 | 3.57 | 4.87 | 1.22 | 33.13 | 3.09 | 26.17 | 11.20 | 2.12 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 1.02 | 10.55 | 25.34 | 4.03 | 4.16 | 133.55 | 14.83 | 31.54 | 3.69 | 10.85 | 1.29 | 24.58 | 2.95 | 25.99 | 11.00 | 2.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Ta | Th | V | U | Cu | Zr | Pb | Zn | Sc | Cr | Ge | Li | Be | Sr/Y | Nb/Ta | La/Nb | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 1.01 | 11.17 | 24.71 | 3.92 | 3.01 | 114.64 | 15.34 | 28.18 | 3.58 | 5.15 | 1.27 | 36.02 | 3.07 | 23.14 | 11.11 | 2.41 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 1.00 | 11.94 | 24.42 | 4.03 | 2.34 | 120.56 | 15.26 | 28.61 | 3.63 | 5.99 | 1.19 | 25.75 | 2.99 | 25.05 | 11.35 | 2.73 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 1.00 | 11.69 | 25.55 | 4.10 | 7.10 | 126.95 | 15.59 | 33.61 | 3.68 | 7.54 | 1.35 | 50.99 | 3.07 | 21.58 | 11.17 | 2.68 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 1.01 | 11.38 | 25.86 | 4.16 | 8.08 | 126.61 | 16.21 | 32.33 | 3.65 | 5.83 | 1.26 | 39.66 | 3.02 | 21.78 | 10.97 | 2.62 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 1.02 | 11.92 | 26.40 | 4.14 | 8.25 | 124.38 | 16.23 | 32.22 | 3.68 | 4.44 | 1.34 | 39.95 | 3.05 | 21.75 | 11.23 | 2.61 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 1.28 | 11.10 | 36.12 | 4.50 | 10.35 | 143.63 | 14.97 | 166.77 | 4.22 | 9.13 | 1.74 | 16.45 | 3.58 | 17.28 | 11.70 | 1.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 1.01 | 10.76 | 25.56 | 4.11 | 12.45 | 126.82 | 9.05 | 41.58 | 3.55 | 4.29 | 1.39 | 16.57 | 3.02 | 19.96 | 11.50 | 2.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 1.02 | 11.39 | 26.06 | 3.89 | 4.83 | 132.43 | 11.57 | 49.38 | 3.44 | 3.83 | 1.37 | 41.60 | 2.81 | 14.72 | 11.05 | 2.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 1.01 | 11.30 | 25.33 | 4.07 | 11.24 | 120.95 | 9.61 | 28.13 | 3.62 | 4.34 | 1.39 | 19.36 | 2.91 | 21.02 | 11.22 | 2.55 | ||||||||||||||||
表2 西功卡花岗闪长岩体主量元素(wB/%)、微量元素和稀土元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Contents of major elements(%),trace elements and REE(10-6 ) of Late Triassic granitoids in Xigongka area
| 样品 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | K2O+ Na2O | K2O/ Na2O | A/ CNK | A/ NK | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D3076HX2-1 | 70.10 | 0.28 | 14.81 | 2.46 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 3.03 | 3.42 | 3.48 | 0.11 | 1.95 | 100.23 | 0.34 | 6.90 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.58 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 70.11 | 0.28 | 14.94 | 2.44 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 2.71 | 3.12 | 3.55 | 0.10 | 1.54 | 99.39 | 0.33 | 6.67 | 1.14 | 1.07 | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 70.56 | 0.26 | 15.02 | 2.25 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 2.54 | 2.95 | 4.08 | 0.10 | 1.38 | 99.63 | 0.30 | 7.03 | 1.38 | 1.08 | 1.62 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 70.08 | 0.27 | 15.01 | 2.39 | 0.06 | 0.58 | 2.76 | 3.13 | 3.64 | 0.10 | 2.04 | 100.06 | 0.36 | 6.77 | 1.16 | 1.06 | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 70.22 | 0.28 | 14.85 | 2.45 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 2.89 | 3.06 | 3.50 | 0.11 | 1.37 | 99.32 | 0.33 | 6.56 | 1.15 | 1.03 | 1.61 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 70.91 | 0.27 | 15.15 | 2.49 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 2.38 | 2.98 | 3.49 | 0.10 | 1.75 | 100.02 | 0.29 | 6.47 | 1.17 | 1.15 | 1.72 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 70.55 | 0.28 | 15.09 | 2.54 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 2.39 | 3.12 | 3.49 | 0.11 | 1.62 | 99.65 | 0.27 | 6.61 | 1.12 | 1.14 | 1.69 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 70.93 | 0.27 | 15.25 | 2.56 | 0.07 | 0.41 | 2.38 | 3.13 | 3.48 | 0.11 | 1.18 | 99.77 | 0.27 | 6.62 | 1.11 | 1.15 | 1.71 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 69.86 | 0.29 | 14.81 | 2.37 | 0.17 | 0.66 | 3.44 | 3.05 | 3.20 | 0.10 | 2.26 | 100.21 | 0.39 | 6.25 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 1.74 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 70.56 | 0.27 | 14.98 | 2.45 | 0.09 | 0.63 | 2.81 | 2.77 | 3.66 | 0.10 | 1.14 | 99.46 | 0.37 | 6.43 | 1.32 | 1.11 | 1.78 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 70.94 | 0.27 | 15.04 | 2.31 | 0.11 | 0.52 | 2.90 | 2.03 | 3.57 | 0.11 | 1.84 | 99.65 | 0.35 | 5.61 | 1.76 | 1.20 | 2.08 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 70.30 | 0.27 | 15.02 | 2.42 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 2.65 | 3.11 | 3.68 | 0.10 | 1.26 | 99.48 | 0.36 | 6.79 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 1.69 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品 | δ | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX2-1 | 1.76 | 26.09 | 49.97 | 5.49 | 20.10 | 3.91 | 0.96 | 3.33 | 0.45 | 2.42 | 0.42 | 1.10 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 13.27 | 115.51 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 1.72 | 23.74 | 45.78 | 5.09 | 18.58 | 3.71 | 0.93 | 3.20 | 0.45 | 2.38 | 0.42 | 1.11 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.18 | 106.67 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 1.79 | 25.30 | 49.03 | 5.38 | 19.66 | 3.88 | 0.92 | 3.29 | 0.46 | 2.47 | 0.43 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 1.01 | 0.15 | 13.46 | 113.28 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 1.69 | 27.03 | 51.61 | 5.72 | 20.91 | 4.08 | 0.95 | 3.43 | 0.48 | 2.52 | 0.44 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.61 | 119.59 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 1.73 | 30.94 | 58.24 | 6.32 | 22.67 | 4.29 | 0.98 | 3.56 | 0.48 | 2.50 | 0.44 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.76 | 132.84 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 1.55 | 29.92 | 56.99 | 6.26 | 22.60 | 4.24 | 0.98 | 3.55 | 0.48 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.12 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.54 | 130.35 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 1.58 | 29.03 | 55.61 | 6.13 | 22.15 | 4.24 | 0.94 | 3.51 | 0.47 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.38 | 127.42 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 1.57 | 29.92 | 57.12 | 6.30 | 22.76 | 4.27 | 0.94 | 3.56 | 0.47 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 13.49 | 130.67 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 1.45 | 27.03 | 51.83 | 5.79 | 21.19 | 4.20 | 1.10 | 3.66 | 0.51 | 2.72 | 0.48 | 1.27 | 0.17 | 1.10 | 0.16 | 15.19 | 121.21 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 1.50 | 26.71 | 51.61 | 5.70 | 20.76 | 4.02 | 0.93 | 3.38 | 0.47 | 2.50 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.42 | 118.92 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 1.13 | 28.88 | 54.95 | 6.06 | 22.02 | 4.20 | 0.98 | 3.52 | 0.48 | 2.50 | 0.44 | 1.15 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 13.71 | 126.48 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 1.69 | 28.89 | 55.33 | 6.09 | 22.01 | 4.20 | 0.96 | 3.53 | 0.48 | 2.52 | 0.43 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 13.45 | 126.85 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品 | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Co | Ni | Cs | Ga | Hf | Rb | Nb | Sr | Ba | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX2-1 | 106.52 | 8.99 | 11.85 | 19.29 | 4.31 | 2.84 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 5.71 | 2.28 | 8.46 | 17.79 | 3.43 | 115.52 | 10.88 | 337.77 | 590.66 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 97.83 | 8.84 | 11.07 | 17.38 | 4.13 | 2.70 | 0.81 | 0.97 | 5.34 | 2.34 | 8.17 | 17.84 | 3.43 | 120.15 | 11.20 | 344.87 | 690.22 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 104.17 | 9.11 | 11.43 | 17.97 | 4.21 | 2.69 | 0.77 | 0.98 | 5.46 | 6.19 | 8.58 | 17.93 | 3.75 | 129.75 | 11.22 | 349.83 | 786.23 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 110.30 | 9.29 | 11.87 | 19.78 | 4.28 | 2.90 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 4.80 | 2.71 | 8.13 | 17.82 | 3.34 | 120.52 | 11.22 | 314.97 | 690.96 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 123.44 | 9.40 | 13.13 | 22.65 | 4.66 | 3.01 | 0.74 | 0.97 | 4.89 | 2.71 | 7.53 | 17.80 | 3.42 | 116.06 | 11.35 | 344.68 | 647.00 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 120.99 | 9.36 | 12.93 | 21.90 | 4.56 | 3.00 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 4.67 | 3.40 | 7.12 | 18.05 | 3.56 | 111.18 | 11.17 | 292.26 | 593.03 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 118.10 | 9.32 | 12.67 | 21.25 | 4.42 | 2.96 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 6.04 | 3.27 | 6.52 | 18.14 | 3.59 | 109.87 | 11.08 | 291.45 | 559.94 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 121.31 | 9.36 | 12.96 | 22.13 | 4.52 | 3.04 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 6.08 | 2.51 | 6.59 | 18.47 | 3.51 | 111.03 | 11.45 | 293.41 | 560.98 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 111.14 | 10.07 | 11.04 | 17.63 | 4.15 | 2.75 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 7.26 | 3.73 | 9.13 | 23.17 | 4.06 | 140.14 | 14.98 | 262.52 | 382.96 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 109.73 | 9.19 | 11.94 | 19.55 | 4.29 | 2.85 | 0.75 | 0.98 | 5.55 | 2.09 | 7.91 | 17.96 | 3.55 | 127.86 | 11.62 | 267.88 | 554.99 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 117.09 | 9.39 | 12.47 | 20.72 | 4.44 | 2.91 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 5.55 | 2.09 | 5.98 | 18.22 | 3.71 | 126.51 | 11.27 | 201.84 | 525.22 | |||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 117.48 | 9.37 | 12.54 | 21.15 | 4.44 | 2.98 | 0.74 | 0.97 | 4.71 | 2.12 | 7.69 | 17.91 | 3.46 | 129.86 | 11.33 | 282.71 | 681.88 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Ta | Th | V | U | Cu | Zr | Pb | Zn | Sc | Cr | Ge | Li | Be | Sr/Y | Nb/Ta | La/Nb | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX2-1 | 0.97 | 10.41 | 25.93 | 3.87 | 3.46 | 121.32 | 13.02 | 30.33 | 3.69 | 4.72 | 1.29 | 27.67 | 3.05 | 25.45 | 11.22 | 2.40 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX3-1 | 1.00 | 9.87 | 24.94 | 4.00 | 2.20 | 120.75 | 14.58 | 30.55 | 3.57 | 4.87 | 1.22 | 33.13 | 3.09 | 26.17 | 11.20 | 2.12 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX4-1 | 1.02 | 10.55 | 25.34 | 4.03 | 4.16 | 133.55 | 14.83 | 31.54 | 3.69 | 10.85 | 1.29 | 24.58 | 2.95 | 25.99 | 11.00 | 2.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Ta | Th | V | U | Cu | Zr | Pb | Zn | Sc | Cr | Ge | Li | Be | Sr/Y | Nb/Ta | La/Nb | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX5-1 | 1.01 | 11.17 | 24.71 | 3.92 | 3.01 | 114.64 | 15.34 | 28.18 | 3.58 | 5.15 | 1.27 | 36.02 | 3.07 | 23.14 | 11.11 | 2.41 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX6-1 | 1.00 | 11.94 | 24.42 | 4.03 | 2.34 | 120.56 | 15.26 | 28.61 | 3.63 | 5.99 | 1.19 | 25.75 | 2.99 | 25.05 | 11.35 | 2.73 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX7-1 | 1.00 | 11.69 | 25.55 | 4.10 | 7.10 | 126.95 | 15.59 | 33.61 | 3.68 | 7.54 | 1.35 | 50.99 | 3.07 | 21.58 | 11.17 | 2.68 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1 | 1.01 | 11.38 | 25.86 | 4.16 | 8.08 | 126.61 | 16.21 | 32.33 | 3.65 | 5.83 | 1.26 | 39.66 | 3.02 | 21.78 | 10.97 | 2.62 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX8-1R | 1.02 | 11.92 | 26.40 | 4.14 | 8.25 | 124.38 | 16.23 | 32.22 | 3.68 | 4.44 | 1.34 | 39.95 | 3.05 | 21.75 | 11.23 | 2.61 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX9-1 | 1.28 | 11.10 | 36.12 | 4.50 | 10.35 | 143.63 | 14.97 | 166.77 | 4.22 | 9.13 | 1.74 | 16.45 | 3.58 | 17.28 | 11.70 | 1.80 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX110-1 | 1.01 | 10.76 | 25.56 | 4.11 | 12.45 | 126.82 | 9.05 | 41.58 | 3.55 | 4.29 | 1.39 | 16.57 | 3.02 | 19.96 | 11.50 | 2.30 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX11-1 | 1.02 | 11.39 | 26.06 | 3.89 | 4.83 | 132.43 | 11.57 | 49.38 | 3.44 | 3.83 | 1.37 | 41.60 | 2.81 | 14.72 | 11.05 | 2.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3076HX12-1 | 1.01 | 11.30 | 25.33 | 4.07 | 11.24 | 120.95 | 9.61 | 28.13 | 3.62 | 4.34 | 1.39 | 19.36 | 2.91 | 21.02 | 11.22 | 2.55 | ||||||||||||||||

图6 西功卡花岗岩闪长岩SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)图解(底图据MIDDLEMOST E A K [13])
Fig.6 SiO2-(K2O+Na2O) plot for the Xigongka granitoid pluton(Base map after MIDDLEMOST E A K [13])
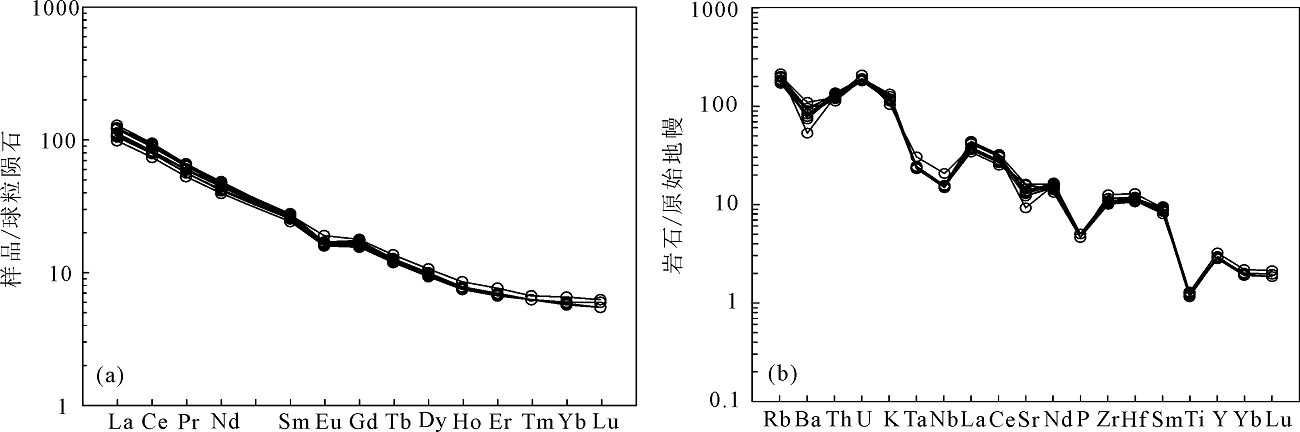
图8 西功卡花岗闪长岩球粒陨石标准化REE配分模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b) (球粒陨石、原始地幔标准化值据参考文献[14])
Fig.8 Chondrite-normalized REE pattern and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram for Xigongka granodiorite(primitive mantle and chondrite after reference[14])
| [1] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-855. |
| [2] | 张宏飞, 靳兰兰, 张利, 等. 西秦岭花岗岩类地球化学和Pb-Sr-Nd同位素组成对基底性质及其构造属性的限制[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2005, 35(10):914-926. |
| [3] | 李佐臣, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 西秦岭糜署岭花岗岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 29(8):2617-2634. |
| [4] | 陈岳龙, 周建, 皮桥辉, 等. 青海共和-花石峡三叠纪碎屑沉积岩的地球化学特征与锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2):161-174. |
| [5] | 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭-松潘大陆构造结[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):23-32. |
| [6] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化、构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1):1-10. |
| [7] | LUDWIG K R. Users Manual for Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 1-71. |
| [8] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2):59-79.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 李远友, 刘国仁, 于秀斌, 等. 新疆准噶尔北缘加玛特金铜矿区辉长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(4):651-661. |
| [10] | 司志发, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 等. 江西相山铀矿田河元背地区流纹斑岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf-Sr-Nd同位素特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(1):45-55. |
| [11] |
BELOUSOVA E A, SUZANNE G W, FISHER Y. Igneous zircon: trace element compositions as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 吴元保, 郑永飞, 龚冰, 等. 北淮阳庐镇关岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄和氧同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(5): 1007-1024. |
| [13] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42 (1) :313-345.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 张宏飞, 陈岳龙, 徐旺春, 等. 青海共和盆地周缘印支期花岗岩类的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12):2910-2922. |
| [18] | 李小江, 李佐臣, 杨拴海, 等. 西秦岭西段然果儿岗花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2015, 33(3):393-398. |
| [19] | 杨拴海, 李瑞保, 王伟峰, 等. 西秦岭西段曲如沟花岗闪长岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义研究[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(2):57-72. |
| [20] | CHAPPELL B W. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974, 8: 173-174. |
| [21] | 王德滋, 刘昌实. 桐庐Ⅰ型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(1):44-54. |
| [22] |
LI X H, LI Z X, SINCLAIR J A, et al. Revisiting the “Yanbian Terrane”: Implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the western Yangtze, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 151(1/2): 14-30.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 孟繁聪, 薛怀民, 李天福, 等. 苏鲁造山带晚中生代地幔的富集特征——来自辉长岩的地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(6):1583-1592. |
| [25] |
DEPAOLO D J, DALEY E E. Neodymium isotopes in basalts of the southwest basin and range and lithospheric thinning during continental extension[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 169(1/2): 157-185.
DOI URL |
| [26] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution, An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 1-132. |
| [27] |
PATIÑO-DOUCE A E, JOHNSTON A D. Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the pelitic system: Implications for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1991, 107(2): 202-218.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
GREEN T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120 (3/4): 347-359.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
BARTH M G, MCDONOUGH W F, RUDNICK R L. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 165(3/4): 197-213.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHAO X X, COE R S, GILDER S A, et al. Palaeomagnetic constraints on the palaeogeography of China: Implications for Gondwanaland[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1996, 43(6): 643-672.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 王秉璋, 张智勇, 张森琦, 等. 东昆仑东端苦海—塞什塘地区晚古生代蛇绿岩的特征[J]. 地球科学, 2000, 25(6):592-598. |
| [32] | 赖绍聪, 秦江锋. 勉略缝合带三岔子辉绿岩墙锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素组成——古特提斯洋壳俯冲的年代学证据[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2010, 32(1):27-33. |
| [33] | 李曙光, 孙卫东, 张国伟, 等. 南秦岭勉略构造带黑沟峡变质火山岩的年代学和地球化学: 生代洋盆及其闭合时代的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(3):223-230. |
| [34] | ZHENG Y F, YE K, ZHANG L F. Developing the plate tectonics from oceanic subduction to continental collision[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54: 2549-2555. |
| [35] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
PEARCE J. Sources and setting of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19(4): 120-125.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 陈衍景. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4):854-865. |
| [38] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 李继亮, 等. 西秦岭楔的构造属性及其增生造山过程[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(6):1808-1828. |
| [39] | 李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑东段晚古生代-中生代若干不整合面特征及其对重大构造事件的响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5):244-254. |
| [40] | 李碧乐, 孙丰月, 于晓飞, 等. 东昆中隆起带东段闪长岩U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4):1163-1172. |
| [41] | 马昌前, 熊富浩, 张金阳, 等. 从板块俯冲到造山后阶段俯冲板片对岩浆作用的影响:东昆仑早二叠世—晚三叠世镁铁质岩墙群的证据[M]// 中国地质学会.第七届世界华人地质科学讨论会专辑. 成都: 中国地质学会, 2014:79-81. |
| [42] | 李瑞保. 东昆仑造山带(东段)晚古生代-早中生代造山作用研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012:1-185. |
| [43] | 闫臻, 边千韬, KORCHAGIN O A, 等. 东昆仑南缘早三叠世洪水川组的源区特征:来自碎屑组成、重矿物和岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(5):1068-1078. |
| [44] | 孙延贵. 西秦岭—东昆仑造山带的衔接转换与共和坳拉谷[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2004:1-206. |
| [45] | 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑洪水川地区科科鄂阿龙岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(2):178-196. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [4] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [5] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [6] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [7] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [8] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [9] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [10] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [11] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [12] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [13] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [14] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [15] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||