



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (06): 1482-1494.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.016
宋彦博1( ), 王建平1(
), 王建平1( ), 沈存利2, 车东1, 杨文华2, 郭海蛟2
), 沈存利2, 车东1, 杨文华2, 郭海蛟2
收稿日期:2022-11-03
修回日期:2023-02-20
出版日期:2023-12-10
发布日期:2024-01-24
通讯作者:
王建平,男,教授,1972年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学的教学与科研工作。Email:jpwang@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:宋彦博,男,硕士研究生,1998年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学与矿床地球化学研究。Email:1339168830@qq.com。
基金资助:
SONG Yanbo1( ), WANG Jianping1(
), WANG Jianping1( ), SHEN Cunli2, CHE Dong1, YANG Wenhua2, GUO Haijiao2
), SHEN Cunli2, CHE Dong1, YANG Wenhua2, GUO Haijiao2
Received:2022-11-03
Revised:2023-02-20
Online:2023-12-10
Published:2024-01-24
摘要:
扎拉格阿木铜矿床位于锡林浩特古老地块东北部边缘,是内蒙古自治区也是大兴安岭中南段西坡富Zn-Pb-Ag成矿带新近发现的一处与花岗斑岩相关的中等规模热液型铜矿床,研究其成岩成矿机制能为区域找铜提供理论基础,并拓宽勘查方向。为查明花岗斑岩形成时代、岩浆源区特征及其与矿化之间的关系,本文对该岩体进行了岩相学、全岩元素组成、锆石U-Pb年代学和全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成研究。结果表明,岩体具高SiO2和Al2O3含量、低MgO含量,轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损,弱Eu负异常,亏损Ta、Nb、Ti和P等高场强元素,富集Rb、K、La和Th等大离子亲石元素。这些特征表明其属高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩。εNd(t)值为较小的正值,变化范围为2.1~3.3,对应的Nd同位素模式年龄TDM值在980~740 Ma之间,显示花岗斑岩岩浆的形成与壳幔物质的混合有关。岩浆锆石U-Pb年龄为(254.51±2.13) Ma,指示成岩及与其相关的成矿作用发生于晚二叠世。综合分析认为,扎拉格阿木铜矿床形成于晚二叠世岛弧构造环境,可能与贺根山洋盆俯冲作用有关。
中图分类号:
宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494.
SONG Yanbo, WANG Jianping, SHEN Cunli, CHE Dong, YANG Wenhua, GUO Haijiao. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics of Ore-forming Granite Porphyry and Its Metallogenic Significance in the Zhalageamu Copper Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494.

图1 扎拉格阿木铜矿床大地构造位置(a)和兴蒙造山带锡林浩特及额尔古纳地块铜、锡、钼、钨多金属矿床分布(b)(据文献 [2-3,13]修编)
Fig.1 Tectonic map of the Zhalageamu copper deposit (a) and geological map, showing the distribution of Cu,Zn,Mo and W polymetallic ore deposits in the Xilinhot and Erguna blocks of the Khingan metallogenic belt (b)(modified after references [2-3,13])

图2 扎拉格阿木铜矿床地质图(a)和15号勘探线钻孔剖面图(b)(据文献 [8]修编) 1.第四系沉积物;2.中二叠统哲斯组含碳质变质砂岩;3.中二叠统哲斯组褐灰色变质砂岩;4.中二叠统哲斯组砾岩和含砾砂岩;5.中二叠统哲斯组似千枚状板岩;6.中二叠统哲斯组紫灰色变质砂岩;7.中二叠统花岗闪长岩;8.橄榄玄武岩;9.花岗岩脉;10.闪长玢岩脉;11.断层;12.勘探线与钻孔编号;13.矿体;14.糜棱岩带
Fig.2 Geological map (a) and borehole profile along exploration line 15 (b) of the Zhalageamu copper deposit (after reference [8])

图3 扎拉格阿木铜矿床矿石手标本和显微照片 (a)块状构造(采自ZK1508下部);(b) 脉状构造(采自ZK704中下部);(c) 角砾状构造(采自ZK1505中部);(d) 自形-半自形粒状结构;(e) 乳滴结构;(f) 包含结构;Apy.毒砂;Ccp.黄铜矿;Sp.闪锌矿;Qtz.石英
Fig.3 Field photographs and microphotographs of the ore from the Zhalageamu copper deposit

图4 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩手标本和显微照片 Bt.黑云母;Ccp.黄铜矿;Kp.钾长石;Qtz.石英;Ser.绢云母
Fig.4 Field photographs and microphotographs (crossedpolar) of the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZLG-6-1 | 71.30 | 0.43 | 13.36 | 2.89 | 1.44 | 1.37 | 4.24 | 2.48 | 0.12 | 1.52 | 99.14 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 69.83 | 0.41 | 14.55 | 3.14 | 1.42 | 1.54 | 4.11 | 2.23 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 99.18 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 68.51 | 0.43 | 14.48 | 4.22 | 1.52 | 1.32 | 4.24 | 2.53 | 0.11 | 1.85 | 99.20 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 75.36 | 0.38 | 11.92 | 0.84 | 1.21 | 0.48 | 2.61 | 5.82 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 99.15 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 75.41 | 0.29 | 11.94 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 1.69 | 3.78 | 3.57 | 0.06 | 1.21 | 99.08 |
| ZLG-64 | 74.34 | 0.14 | 11.87 | 3.02 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 5.61 | 1.76 | 0.03 | 1.41 | 99.02 |
| ZLG-65 | 72.26 | 0.24 | 13.53 | 1.72 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 3.53 | 5.01 | 0.05 | 1.23 | 99.19 |
| ZLG-66 | 72.87 | 0.36 | 12.67 | 2.44 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 3.15 | 4.25 | 0.09 | 1.43 | 99.16 |
| 样品号 | Mg# | Sc | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb |
| ZLG-6-1 | 49.9 | 6.033 | 2571 | 33.77 | 5.046 | 9.91 | 133.2 | 238.1 | 11.098 | 163.15 | 4.77 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 47.4 | 6.278 | 2570 | 31.96 | 4.626 | 7.07 | 123.8 | 216.8 | 11.178 | 141.26 | 4.99 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 41.9 | 6.929 | 2654 | 35.15 | 5.109 | 7.47 | 157.8 | 258.1 | 10.635 | 135.28 | 5.08 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 70.4 | 5.513 | 2310 | 34.71 | 1.899 | 10.49 | 328.8 | 48.9 | 5.946 | 122.04 | 5.98 |
| 样品号 | Mg# | Sc | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb |
| ZLG-26-2 | 64.6 | 4.224 | 1750 | 22.69 | 2.448 | 15.37 | 204.3 | 62.4 | 10.583 | 100.56 | 4.52 |
| ZLG-64 | 23.2 | 3.557 | 881 | 3.41 | 9.403 | 8.46 | 105.6 | 78.3 | 29.971 | 77.34 | 4.39 |
| ZLG-65 | 45.2 | 4.865 | 1487 | 7.19 | 1.342 | 5.34 | 210.4 | 84.2 | 26.323 | 118.63 | 6.39 |
| ZLG-66 | 43.7 | 5.85 | 2156 | 12.99 | 3.632 | 7.93 | 243.2 | 96.4 | 19.516 | 123.91 | 6.96 |
| 样品号 | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
| ZLG-6-1 | 346.2 | 15.69 | 32.193 | 3.572 | 13.957 | 2.665 | 0.676 | 2.329 | 0.341 | 2.113 | 0.392 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 355.2 | 17.34 | 35.721 | 3.994 | 15.679 | 2.995 | 0.747 | 2.558 | 0.357 | 2.134 | 0.389 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 364.6 | 14.39 | 29.064 | 3.281 | 13.062 | 2.535 | 0.722 | 2.289 | 0.331 | 2.023 | 0.373 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 467.1 | 3.73 | 8.978 | 1.134 | 5.041 | 1.198 | 0.367 | 1.173 | 0.177 | 1.113 | 0.218 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 242.8 | 5.72 | 12.953 | 1.596 | 6.903 | 1.593 | 0.425 | 1.597 | 0.256 | 1.671 | 0.337 |
| ZLG-64 | 175.3 | 24.26 | 49.308 | 5.718 | 23.646 | 5.273 | 0.963 | 5.538 | 0.876 | 5.672 | 1.081 |
| ZLG-65 | 334.2 | 23.06 | 49.061 | 5.427 | 20.475 | 4.178 | 0.506 | 3.973 | 0.659 | 4.428 | 0.885 |
| ZLG-66 | 377.6 | 19.68 | 40.887 | 4.568 | 17.564 | 3.612 | 0.602 | 3.539 | 0.563 | 3.604 | 0.684 |
| 样品号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Hf | Lu | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Hf | Lu |
| ZLG-6-1 | 1.173 | 0.153 | 1.053 | 3.739 | 0.146 | 0.28 | 15.164 | 6.791 | 4.632 | 3.739 | 0.146 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 1.162 | 0.155 | 1.049 | 3.475 | 0.147 | 0.287 | 13.692 | 7.123 | 2.454 | 3.475 | 0.147 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 1.122 | 0.146 | 1.006 | 3.331 | 0.142 | 0.445 | 8.591 | 6.748 | 2.348 | 3.331 | 0.141 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 0.711 | 0.105 | 0.837 | 2.904 | 0.136 | 0.372 | 13.444 | 6.015 | 1.591 | 2.904 | 0.136 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 1.074 | 0.154 | 1.124 | 2.367 | 0.171 | 0.424 | 10.339 | 4.694 | 1.355 | 2.367 | 0.173 |
| ZLG-64 | 3.275 | 0.442 | 3.027 | 2.112 | 0.406 | 0.671 | 7.493 | 10.155 | 3.199 | 2.112 | 0.406 |
| ZLG-65 | 2.813 | 0.404 | 2.845 | 3.331 | 0.399 | 0.618 | 22.799 | 17.691 | 5.064 | 3.331 | 0.399 |
| ZLG-66 | 2.071 | 0.284 | 1.936 | 3.234 | 0.275 | 0.418 | 12.531 | 13.287 | 3.192 | 3.234 | 0.275 |
表1 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩全岩主量元素(%)、稀土元素和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 1 Major element (%), REE and trace element (10-6) compositions of the granite porphyry from the Zha-lageamu copper deposit
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZLG-6-1 | 71.30 | 0.43 | 13.36 | 2.89 | 1.44 | 1.37 | 4.24 | 2.48 | 0.12 | 1.52 | 99.14 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 69.83 | 0.41 | 14.55 | 3.14 | 1.42 | 1.54 | 4.11 | 2.23 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 99.18 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 68.51 | 0.43 | 14.48 | 4.22 | 1.52 | 1.32 | 4.24 | 2.53 | 0.11 | 1.85 | 99.20 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 75.36 | 0.38 | 11.92 | 0.84 | 1.21 | 0.48 | 2.61 | 5.82 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 99.15 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 75.41 | 0.29 | 11.94 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 1.69 | 3.78 | 3.57 | 0.06 | 1.21 | 99.08 |
| ZLG-64 | 74.34 | 0.14 | 11.87 | 3.02 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 5.61 | 1.76 | 0.03 | 1.41 | 99.02 |
| ZLG-65 | 72.26 | 0.24 | 13.53 | 1.72 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 3.53 | 5.01 | 0.05 | 1.23 | 99.19 |
| ZLG-66 | 72.87 | 0.36 | 12.67 | 2.44 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 3.15 | 4.25 | 0.09 | 1.43 | 99.16 |
| 样品号 | Mg# | Sc | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb |
| ZLG-6-1 | 49.9 | 6.033 | 2571 | 33.77 | 5.046 | 9.91 | 133.2 | 238.1 | 11.098 | 163.15 | 4.77 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 47.4 | 6.278 | 2570 | 31.96 | 4.626 | 7.07 | 123.8 | 216.8 | 11.178 | 141.26 | 4.99 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 41.9 | 6.929 | 2654 | 35.15 | 5.109 | 7.47 | 157.8 | 258.1 | 10.635 | 135.28 | 5.08 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 70.4 | 5.513 | 2310 | 34.71 | 1.899 | 10.49 | 328.8 | 48.9 | 5.946 | 122.04 | 5.98 |
| 样品号 | Mg# | Sc | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb |
| ZLG-26-2 | 64.6 | 4.224 | 1750 | 22.69 | 2.448 | 15.37 | 204.3 | 62.4 | 10.583 | 100.56 | 4.52 |
| ZLG-64 | 23.2 | 3.557 | 881 | 3.41 | 9.403 | 8.46 | 105.6 | 78.3 | 29.971 | 77.34 | 4.39 |
| ZLG-65 | 45.2 | 4.865 | 1487 | 7.19 | 1.342 | 5.34 | 210.4 | 84.2 | 26.323 | 118.63 | 6.39 |
| ZLG-66 | 43.7 | 5.85 | 2156 | 12.99 | 3.632 | 7.93 | 243.2 | 96.4 | 19.516 | 123.91 | 6.96 |
| 样品号 | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
| ZLG-6-1 | 346.2 | 15.69 | 32.193 | 3.572 | 13.957 | 2.665 | 0.676 | 2.329 | 0.341 | 2.113 | 0.392 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 355.2 | 17.34 | 35.721 | 3.994 | 15.679 | 2.995 | 0.747 | 2.558 | 0.357 | 2.134 | 0.389 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 364.6 | 14.39 | 29.064 | 3.281 | 13.062 | 2.535 | 0.722 | 2.289 | 0.331 | 2.023 | 0.373 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 467.1 | 3.73 | 8.978 | 1.134 | 5.041 | 1.198 | 0.367 | 1.173 | 0.177 | 1.113 | 0.218 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 242.8 | 5.72 | 12.953 | 1.596 | 6.903 | 1.593 | 0.425 | 1.597 | 0.256 | 1.671 | 0.337 |
| ZLG-64 | 175.3 | 24.26 | 49.308 | 5.718 | 23.646 | 5.273 | 0.963 | 5.538 | 0.876 | 5.672 | 1.081 |
| ZLG-65 | 334.2 | 23.06 | 49.061 | 5.427 | 20.475 | 4.178 | 0.506 | 3.973 | 0.659 | 4.428 | 0.885 |
| ZLG-66 | 377.6 | 19.68 | 40.887 | 4.568 | 17.564 | 3.612 | 0.602 | 3.539 | 0.563 | 3.604 | 0.684 |
| 样品号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Hf | Lu | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Hf | Lu |
| ZLG-6-1 | 1.173 | 0.153 | 1.053 | 3.739 | 0.146 | 0.28 | 15.164 | 6.791 | 4.632 | 3.739 | 0.146 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 1.162 | 0.155 | 1.049 | 3.475 | 0.147 | 0.287 | 13.692 | 7.123 | 2.454 | 3.475 | 0.147 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 1.122 | 0.146 | 1.006 | 3.331 | 0.142 | 0.445 | 8.591 | 6.748 | 2.348 | 3.331 | 0.141 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 0.711 | 0.105 | 0.837 | 2.904 | 0.136 | 0.372 | 13.444 | 6.015 | 1.591 | 2.904 | 0.136 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 1.074 | 0.154 | 1.124 | 2.367 | 0.171 | 0.424 | 10.339 | 4.694 | 1.355 | 2.367 | 0.173 |
| ZLG-64 | 3.275 | 0.442 | 3.027 | 2.112 | 0.406 | 0.671 | 7.493 | 10.155 | 3.199 | 2.112 | 0.406 |
| ZLG-65 | 2.813 | 0.404 | 2.845 | 3.331 | 0.399 | 0.618 | 22.799 | 17.691 | 5.064 | 3.331 | 0.399 |
| ZLG-66 | 2.071 | 0.284 | 1.936 | 3.234 | 0.275 | 0.418 | 12.531 | 13.287 | 3.192 | 3.234 | 0.275 |

图5 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩K2O-SiO2图解(a)与A/NK-A/CNK图解(b)(底图据文献 [18-19])
Fig.5 Diagrams of K2O-SiO2 (a) and A/NK-A/CNK (b) for the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit (after references [18-19])
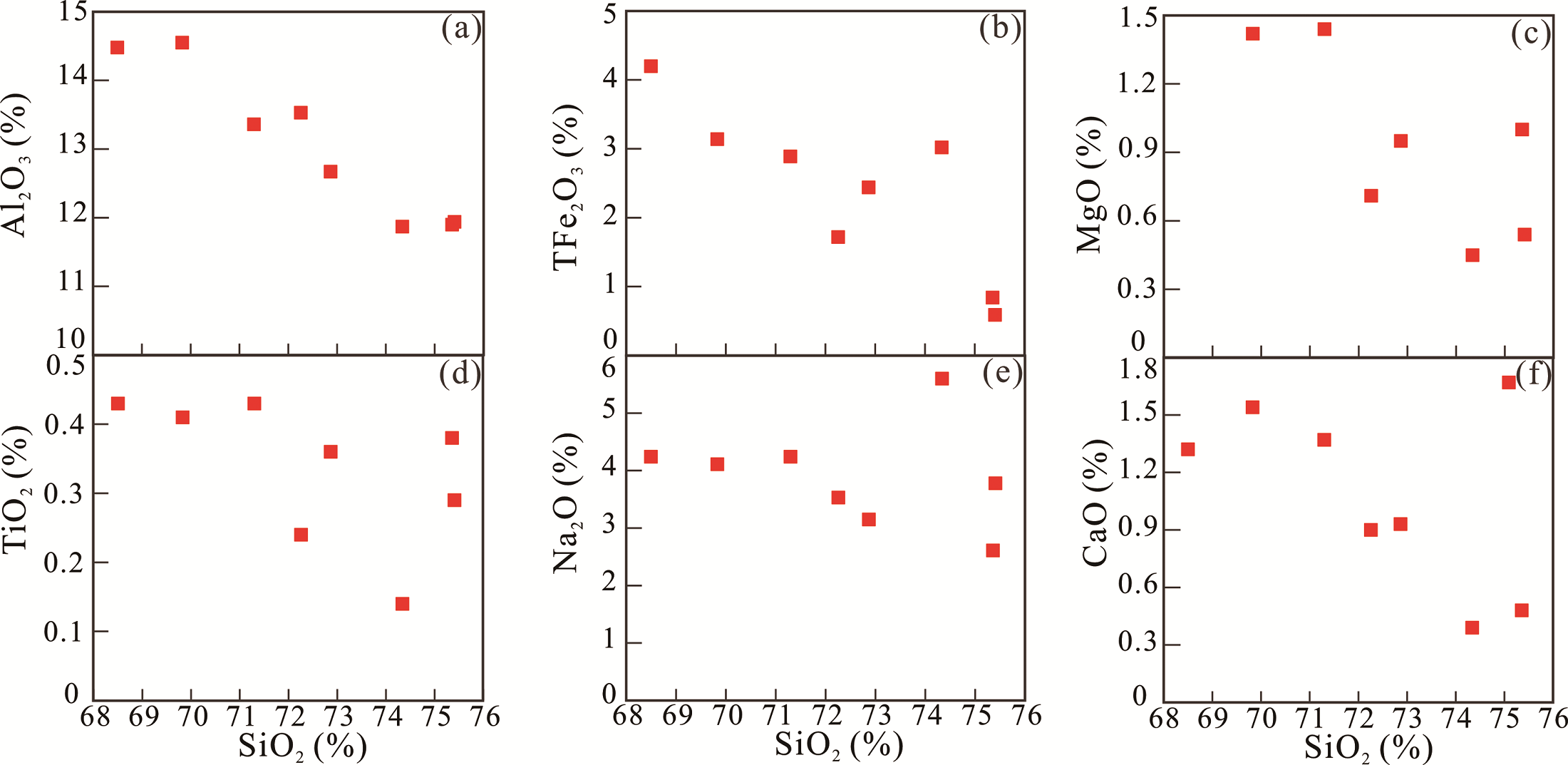
图6 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩哈克图解 (a)Al2O3-SiO2协变图;(b) TFe2O3-SiO2协变图;(c) MgO-SiO2协变图;(d) TiO2-SiO2协变图;(e) Na2O-SiO2协变图;(f) CaO-SiO2协变图
Fig.6 Harker diagrams for the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit

图7 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准值和原始地幔标准化值据文献 [19])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized multi-elements spidergram (b) of the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit (chondrite- and primitive mantle-normalizing values from reference [19])

图8 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩典型锆石测点CL图像(标示年龄为锆石206Pb/238U年龄)
Fig.8 Zircon cathodoluminescence (CL) images of the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit (the zircon 206Pb/238U are indicated)
| 样品编号 | 元素含量 (10-6) | 232Th/ 238U | 同位素比值 | 年龄 (Ma) | 谐和度 (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb | 238U | 232Th | 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ | 207Pb/235U ±1σ | 206Pb/238U ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ | 207Pb/235U ±1σ | 206Pb/238U ±1σ | ||||||
| ZLG-22-4 | 2.0817 | 484.09 | 214.53 | 0.44 | 0.0531± 0.0036 | 0.2956± 0.0181 | 0.0402± 0.0008 | 331.54± 153.6830 | 262.94± 14.2592 | 254.46± 4.8230 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-6 | 0.0917 | 332.75 | 171.95 | 0.52 | 0.0544± 0.0074 | 0.2949± 0.0354 | 0.0395± 0.0011 | 387.09± 307.3680 | 262.43± 27.0588 | 250.11± 7.0920 | 95 | |||
| ZLG-22-7 | 0.7494 | 458.93 | 233.51 | 0.51 | 0.0529± 0.0032 | 0.2932± 0.0165 | 0.0399± 0.0006 | 324.13± 132.3900 | 261.07± 12.6790 | 252.22± 3.9420 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-8 | 1.1862 | 407.11 | 244.18 | 0.60 | 0.0503± 0.0042 | 0.2909± 0.0241 | 0.0411± 0.0008 | 209.33± 4.6300 | 259.31± 18.8419 | 259.78± 5.1700 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-9 | 0.5036 | 448.42 | 199.59 | 0.45 | 0.0518± 0.0029 | 0.2883± 0.0165 | 0.0401± 0.0007 | 279.69± 160.1650 | 257.28± 12.2389 | 253.47± 4.1580 | 98 | |||
| ZLG-22-11 | 0.0917 | 351.28 | 243.92 | 0.69 | 0.0538± 0.0050 | 0.2936± 0.0257 | 0.0398± 0.0010 | 361.17± 213.8630 | 261.46± 19.3354 | 251.86± 6.4871 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-12 | 1.1402 | 335.09 | 146.00 | 0.44 | 0.0522± 0.0040 | 0.2907± 0.0224 | 0.0403± 0.0008 | 294.51± 175.9030 | 259.16± 17.5984 | 254.79± 5.1493 | 98 | |||
| ZLG-22-13 | 0.7494 | 416.34 | 222.29 | 0.53 | 0.0530± 0.0033 | 0.2912± 0.0175 | 0.0396± 0.0007 | 327.84± 136.0930 | 259.55± 13.5015 | 250.43± 4.2806 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-14 | 0.5042 | 351.60 | 185.95 | 0.53 | 0.0528± 0.0035 | 0.2877± 0.0177 | 0.0400± 0.0008 | 320.43± 151.8330 | 256.78± 13.4575 | 253.29± 4.7386 | 98 | |||
| ZLG-22-16 | 0.3047 | 247.92 | 97.98 | 0.40 | 0.0548± 0.0051 | 0.2973± 0.0268 | 0.0396± 0.0008 | 466.71± 211.0800 | 264.31± 20.6215 | 250.41± 4.7054 | 94 | |||
| ZLG-22-17 | 2.1587 | 461.24 | 327.07 | 0.71 | 0.0538± 0.0034 | 0.2954± 0.0181 | 0.0396± 0.0007 | 364.87± 144.4280 | 262.81± 14.0484 | 250.68± 4.2119 | 95 | |||
| ZLG-22-20 | 2.4374 | 227.64 | 102.24 | 0.45 | 0.0547± 0.0067 | 0.2916± 0.0303 | 0.0401± 0.0010 | 466.71± 275.8900 | 259.82± 23.4196 | 253.60± 6.3016 | 97 | |||
| ZLG-22-22 | 0.6650 | 346.50 | 178.91 | 0.52 | 0.0506± 0.0045 | 0.2891± 0.0262 | 0.0408± 0.0009 | 220.44± 196.2750 | 257.88± 20.1280 | 258.22± 5.7015 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-23 | 0.2382 | 379.90 | 132.01 | 0.35 | 0.0524± 0.0045 | 0.2805± 0.0211 | 0.0400± 0.0010 | 305.62± 202.7530 | 251.13± 16.3184 | 253.34± 6.2258 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-25 | 0.6496 | 362.72 | 146.31 | 0.40 | 0.0539± 0.0044 | 0.2887± 0.0215 | 0.0399± 0.0009 | 368.57± 183.3100 | 257.58± 16.2335 | 252.39± 5.5236 | 97 | |||
| ZLG-22-26 | 1.5691 | 376.49 | 212.50 | 0.56 | 0.0507± 0.0046 | 0.2911± 0.0251 | 0.0413± 0.0008 | 227.85± 16.6650 | 259.49± 19.3279 | 261.40± 4.9738 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-27 | 1.9669 | 414.77 | 176.72 | 0.43 | 0.0521± 0.0034 | 0.2937± 0.0195 | 0.0410± 0.0008 | 300.06± 115.7280 | 261.48± 14.8045 | 259.13± 4.9481 | 99 | |||
表2 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb同位素 LA-ICP-MS 定年结果
Table 2 Results of LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating for the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit
| 样品编号 | 元素含量 (10-6) | 232Th/ 238U | 同位素比值 | 年龄 (Ma) | 谐和度 (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb | 238U | 232Th | 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ | 207Pb/235U ±1σ | 206Pb/238U ±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ | 207Pb/235U ±1σ | 206Pb/238U ±1σ | ||||||
| ZLG-22-4 | 2.0817 | 484.09 | 214.53 | 0.44 | 0.0531± 0.0036 | 0.2956± 0.0181 | 0.0402± 0.0008 | 331.54± 153.6830 | 262.94± 14.2592 | 254.46± 4.8230 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-6 | 0.0917 | 332.75 | 171.95 | 0.52 | 0.0544± 0.0074 | 0.2949± 0.0354 | 0.0395± 0.0011 | 387.09± 307.3680 | 262.43± 27.0588 | 250.11± 7.0920 | 95 | |||
| ZLG-22-7 | 0.7494 | 458.93 | 233.51 | 0.51 | 0.0529± 0.0032 | 0.2932± 0.0165 | 0.0399± 0.0006 | 324.13± 132.3900 | 261.07± 12.6790 | 252.22± 3.9420 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-8 | 1.1862 | 407.11 | 244.18 | 0.60 | 0.0503± 0.0042 | 0.2909± 0.0241 | 0.0411± 0.0008 | 209.33± 4.6300 | 259.31± 18.8419 | 259.78± 5.1700 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-9 | 0.5036 | 448.42 | 199.59 | 0.45 | 0.0518± 0.0029 | 0.2883± 0.0165 | 0.0401± 0.0007 | 279.69± 160.1650 | 257.28± 12.2389 | 253.47± 4.1580 | 98 | |||
| ZLG-22-11 | 0.0917 | 351.28 | 243.92 | 0.69 | 0.0538± 0.0050 | 0.2936± 0.0257 | 0.0398± 0.0010 | 361.17± 213.8630 | 261.46± 19.3354 | 251.86± 6.4871 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-12 | 1.1402 | 335.09 | 146.00 | 0.44 | 0.0522± 0.0040 | 0.2907± 0.0224 | 0.0403± 0.0008 | 294.51± 175.9030 | 259.16± 17.5984 | 254.79± 5.1493 | 98 | |||
| ZLG-22-13 | 0.7494 | 416.34 | 222.29 | 0.53 | 0.0530± 0.0033 | 0.2912± 0.0175 | 0.0396± 0.0007 | 327.84± 136.0930 | 259.55± 13.5015 | 250.43± 4.2806 | 96 | |||
| ZLG-22-14 | 0.5042 | 351.60 | 185.95 | 0.53 | 0.0528± 0.0035 | 0.2877± 0.0177 | 0.0400± 0.0008 | 320.43± 151.8330 | 256.78± 13.4575 | 253.29± 4.7386 | 98 | |||
| ZLG-22-16 | 0.3047 | 247.92 | 97.98 | 0.40 | 0.0548± 0.0051 | 0.2973± 0.0268 | 0.0396± 0.0008 | 466.71± 211.0800 | 264.31± 20.6215 | 250.41± 4.7054 | 94 | |||
| ZLG-22-17 | 2.1587 | 461.24 | 327.07 | 0.71 | 0.0538± 0.0034 | 0.2954± 0.0181 | 0.0396± 0.0007 | 364.87± 144.4280 | 262.81± 14.0484 | 250.68± 4.2119 | 95 | |||
| ZLG-22-20 | 2.4374 | 227.64 | 102.24 | 0.45 | 0.0547± 0.0067 | 0.2916± 0.0303 | 0.0401± 0.0010 | 466.71± 275.8900 | 259.82± 23.4196 | 253.60± 6.3016 | 97 | |||
| ZLG-22-22 | 0.6650 | 346.50 | 178.91 | 0.52 | 0.0506± 0.0045 | 0.2891± 0.0262 | 0.0408± 0.0009 | 220.44± 196.2750 | 257.88± 20.1280 | 258.22± 5.7015 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-23 | 0.2382 | 379.90 | 132.01 | 0.35 | 0.0524± 0.0045 | 0.2805± 0.0211 | 0.0400± 0.0010 | 305.62± 202.7530 | 251.13± 16.3184 | 253.34± 6.2258 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-25 | 0.6496 | 362.72 | 146.31 | 0.40 | 0.0539± 0.0044 | 0.2887± 0.0215 | 0.0399± 0.0009 | 368.57± 183.3100 | 257.58± 16.2335 | 252.39± 5.5236 | 97 | |||
| ZLG-22-26 | 1.5691 | 376.49 | 212.50 | 0.56 | 0.0507± 0.0046 | 0.2911± 0.0251 | 0.0413± 0.0008 | 227.85± 16.6650 | 259.49± 19.3279 | 261.40± 4.9738 | 99 | |||
| ZLG-22-27 | 1.9669 | 414.77 | 176.72 | 0.43 | 0.0521± 0.0034 | 0.2937± 0.0195 | 0.0410± 0.0008 | 300.06± 115.7280 | 261.48± 14.8045 | 259.13± 4.9481 | 99 | |||

图9 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb谐和年龄图(a)与206Pb/238U加权平均年龄图(b)
Fig.9 Zircon U-Pb concordia (a) and weighted average age (b) diagrams of the granite porphyry from the Zha-lageamu copper deposit
| 样品号 | T (Ma) | Rb (10-6) | Sr (10-6) | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr | (87Sr/ 86Sr)i | Sm (10-6) | Nd (10-6) | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd | (143Nd/ 144Nd)i | εNd(t) | TDM (Ga) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZLG-6-1 | 255 | 133.216 | 238.080 | 1.667 | 0.708 | 0.702 | 2.664 | 13.951 | 0.115 | 0.51264 | 0.51241 | 3.3 | 0.74 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 255 | 204.320 | 62.400 | 9.760 | 0.706 | 0.670 | 1.592 | 6.902 | 0.139 | 0.51268 | 0.51248 | 2.5 | 0.98 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 255 | 157.760 | 258.080 | 1.822 | 0.708 | 0.701 | 2.534 | 13.062 | 0.117 | 0.51267 | 0.51244 | 3.2 | 0.77 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 255 | 328.800 | 48.880 | 20.052 | 0.745 | 0.672 | 1.198 | 5.040 | 0.143 | 0.51267 | 0.51248 | -0.6 | 1.37 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 255 | 123.840 | 216.800 | 1.702 | 0.707 | 0.701 | 2.994 | 15.673 | 0.115 | 0.51265 | 0.51246 | 3.0 | 0.76 |
| ZLG-64 | 255 | 105.616 | 78.304 | 4.020 | 0.705 | 0.691 | 5.273 | 23.640 | 0.134 | 0.51266 | 0.51247 | 2.1 | 0.98 |
| ZLG-65 | 255 | 210.450 | 84.244 | 7.446 | 0.707 | 0.680 | 4.178 | 20.474 | 0.123 | 0.51252 | 0.51228 | 3.3 | 0.78 |
表3 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic compositions for the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit
| 样品号 | T (Ma) | Rb (10-6) | Sr (10-6) | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr | (87Sr/ 86Sr)i | Sm (10-6) | Nd (10-6) | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd | (143Nd/ 144Nd)i | εNd(t) | TDM (Ga) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZLG-6-1 | 255 | 133.216 | 238.080 | 1.667 | 0.708 | 0.702 | 2.664 | 13.951 | 0.115 | 0.51264 | 0.51241 | 3.3 | 0.74 |
| ZLG-6-2 | 255 | 204.320 | 62.400 | 9.760 | 0.706 | 0.670 | 1.592 | 6.902 | 0.139 | 0.51268 | 0.51248 | 2.5 | 0.98 |
| ZLG-6-3 | 255 | 157.760 | 258.080 | 1.822 | 0.708 | 0.701 | 2.534 | 13.062 | 0.117 | 0.51267 | 0.51244 | 3.2 | 0.77 |
| ZLG-26-1 | 255 | 328.800 | 48.880 | 20.052 | 0.745 | 0.672 | 1.198 | 5.040 | 0.143 | 0.51267 | 0.51248 | -0.6 | 1.37 |
| ZLG-26-2 | 255 | 123.840 | 216.800 | 1.702 | 0.707 | 0.701 | 2.994 | 15.673 | 0.115 | 0.51265 | 0.51246 | 3.0 | 0.76 |
| ZLG-64 | 255 | 105.616 | 78.304 | 4.020 | 0.705 | 0.691 | 5.273 | 23.640 | 0.134 | 0.51266 | 0.51247 | 2.1 | 0.98 |
| ZLG-65 | 255 | 210.450 | 84.244 | 7.446 | 0.707 | 0.680 | 4.178 | 20.474 | 0.123 | 0.51252 | 0.51228 | 3.3 | 0.78 |

图10 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩成因类型判别图解 (a)花岗岩Zr-SiO2判别图解(底图据文献 [21,24-25]);(b) I型花岗岩P2O5-SiO2图解(底图据文献 [27])
Fig.10 Granite discrimination diagrams for the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit

图11 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩εNd(t)值与侵位时代的关系(底图据文献 [24]) CHUR.球粒陨石均一储存库;DM.亏损地幔
Fig.11 Plot of εNd(t) vs. intrusive age of the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit(basemap after reference [24])

图12 扎拉格阿木铜矿床花岗斑岩微量元素构造环境判别图解(底图据文献 [39]) (a) Nb-Y构造判别图解;(b) Ta-Yb构造判别图解;(c) Rb/30-Hf-3Ta构造判别图解;(d) TiO2-Zr构造判别图解
Fig.12 Trace element tectonic discrimination diagrams for the granite porphyry from the Zhalageamu copper deposit(basemap after reference [39])

图13 扎拉格阿木铜矿床成岩成矿模式图(底图据文献 [40]) (a) 扎拉格阿木地区晚二叠世构造演化;(b) 来自交代板片的岩浆在下地壳经历了MASH(熔融、同化、均一和存储)过程,形成高分异和相对低密度岩浆,向上运移定位并成矿;(c) 含矿热液运移并沉淀成矿于花岗闪长岩体与上覆地层的接触带及裂隙中
Fig.13 Magmatic and metallogenic models of the Zhalageamu copper deposit (basemap after reference [40])
| [1] | 张广范. 大兴安岭中段地球物理特征及地质解释[J]. 地质与资源, 2005, 14(4): 287-292. |
| [2] | 赵一鸣, 毕承思, 孟昭君. 内蒙古甲乌拉银多金属矿床分带特征[M]//中国地质科学院地质研究所文集(29-30). 北京: 中国地质科学院, 1997: 206-215. |
| [3] | 张德全. 敖瑙达巴斑岩型锡多金属矿床地质特征[J]. 矿床地质, 1993, 12(1): 10-19. |
| [4] | 杜青松. 内蒙古大兴安岭地区银多金属矿床找矿模型与成矿预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. |
| [5] | 刘建明, 张锐, 张庆洲. 大兴安岭地区的区域成矿特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 269-277. |
| [6] | 王长明, 张寿庭, 邓军. 大兴安岭南段铜多金属矿成矿时空结构[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 33(5): 478-484. |
| [7] | 张璟, 邵军, 贺锋, 等. 大兴安岭中南段布敦化铜矿床地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 地质与资源, 2017, 26(1): 5-12. |
| [8] | 沈存利, 刘玉堂, 高月元, 等. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜多金属矿床地质特征及发现启示[J]. 矿产勘查, 2016, 7(3): 380-390. |
| [9] | 聂凤军, 温银维, 赵元艺, 等. 内蒙古白音查干银多金属矿化区地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质, 2007, 26(2): 213-220. |
| [10] | 刘翼飞, 樊志勇, 蒋胡灿, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托-拜仁达坝斑岩-热液脉状成矿体系研究[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12): 2373-2385. |
| [11] | 李双林, 欧阳自远. 兴蒙造山带及邻区的构造格局与构造演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18(3): 45-54. |
| [12] | 贾盼盼, 魏俊浩, 巩庆伟, 等. 大兴安岭地区铜钼矿床成矿区带背景及找矿前景分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(2):151-162. |
| [13] | REN J S, WANG Z X, CHEN B W, et al. The Tectonics of China from A Global View:A Guide to Tectonic Map of China and Region[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999: 1-3. |
| [14] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, ZONG K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LING W L, DUAN R C, XIE X J, et al. Contrasting geoche-mistry of the Cretaceous volcanic suites in Shandong Province and its implications for the Mesozoic lower crust delamination in the eastern North China craton[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4): 640-658.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 王梁, 王根厚, 雷时斌, 等. 内蒙古乌拉山大桦背岩体成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(7): 1977-1994. |
| [17] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area,Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 等. 西拉木伦河—长春—延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间——来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004, 34(2):174-181. |
| [21] | 张本仁. 区域成矿作用的地球化学分析:壳幔系统与地质作用的成矿机制[M]//中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第十届学术年会论文集. 武汉, 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会, 2005:100-101. |
| [22] | 施光海, 苗来成, 张福勤, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特A型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(4): 384-389. |
| [23] | 郭志军, 周振华, 李贵涛, 等. 内蒙古敖尔盖铜矿中-酸性侵入岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年与岩石地球化学特征研究[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6): 1486-1500. |
| [24] | 洪大卫, 王式, 谢锡林, 等. 兴蒙造山带正εNd(t)值花岗岩的成因和大陆地壳生长[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(2): 441-456. |
| [25] |
CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1992, 83(1/2): 1-26.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Li S R, SUN L, ZHANG H F, et al. Magma mixing genesis of the Qushui collisional granitoids, Tibet, China:Evidences from genetic mineralogy[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(4): 884-894. |
| [27] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [28] | 王珍珍, 刘栋, 赵志丹, 等. 冈底斯带南部桑日高分异I型花岗岩的岩石成因及其动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(8): 2479-2493. |
| [29] |
GAO S, WEREPOHL K H. The negative Eu anomaly in Archean sedimentary rocks: Implications for decomposition, age and importance of their granitic sources[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 133(1/2): 81-94.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
HANS WEDEPOHL K. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217-1232.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BEA F, FERSHTATER G B, MONTERO P, et al. Recycling of continental crust into the mantle as revealed by Kytlym dunite zircons,Ural Mts,Russia[J]. Terra Nova, 2001, 13(6): 407-412.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 童英, 洪大卫, 王涛, 等. 中蒙边境中段花岗岩时空分布特征及构造和找矿意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 395-412. |
| [33] | 苏美霞, 赵文涛, 张慧聪, 等. 华北板块与西伯利亚板块缝合带之地球物理特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(5): 949-955. |
| [34] | 黄波, 付冬, 李树才, 等. 内蒙古贺根山蛇绿岩形成时代及构造启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(1): 158-176. |
| [35] | 尚庆华. 北方造山带内蒙古中、东部地区二叠纪放射虫的发现及意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(24): 2574-2579. |
| [36] | 张晓晖, 张宏福, 汤艳杰, 等. 内蒙古中部锡林浩特—西乌旗早三叠世A型酸性火山岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(11): 2769-2780. |
| [37] | 李益龙, 周汉文, 肖文交, 等. 古亚洲构造域和西太平洋构造域在索伦缝合带东段的叠加:来自内蒙古林西县西拉木伦断裂带内变形闪长岩的岩石学、地球化学和年代学证据[J]. 地球科学, 2012, 37(3): 433-450. |
| [38] | 和钟铧, 王启智, 王强. 大兴安岭索伦地区哲斯组碎屑岩地球化学特征和锆石U-Pb年龄对沉积物源属性约束[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 405-424. |
| [39] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination andpetrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-19.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 毛景文, 罗茂澄, 谢桂青, 等. 斑岩铜矿床的基本特征和研究勘查新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12): 2153-2175. |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [3] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [4] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [5] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [6] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [7] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [8] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [9] | 王战永, 隆兆笃, 解波, 孙悦, 李巨初, 向杰, 范永宏. 四川冕西岩体岩石地球化学特征及铀成矿条件分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1465-1474. |
| [10] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [11] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [12] | 杨瀚文, 王建中, 赵军, 段俊, 王荣敏, 高文彬, 魏文昊, 郑延河. 新疆温泉地区晚石炭世古老地壳重熔: 花岗斑岩脉侵位年龄及其Sr、Nd同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 824-835. |
| [13] | 朱德全, 唐名鹰, 丁正江, 朱海波, 王炜晓, 张宇, 何宗围, 吴洪彬. 柴北缘赛坝沟金矿床花岗斑岩脉的成因及动力学背景: 来自年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 898-910. |
| [14] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [15] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||