



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (01): 169-182.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.100
陈耀新1( ), 刘文恒1,2(
), 刘文恒1,2( ), 王凯兴1,2, 刘晓东2, 孙立强1, 尹冬华1
), 王凯兴1,2, 刘晓东2, 孙立强1, 尹冬华1
收稿日期:2023-06-25
修回日期:2023-12-20
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
刘文恒,男,副教授,1985年出生,国土资源信息工程专业,主要从事区域成矿学、地质矿产勘查工作。Email:作者简介:陈耀新,男,硕士研究生,1997年出生,地质资源与地质工程专业,主要从事地质矿产勘查工作。Email:1634164480@qq.com。
基金资助:
CHEN Yaoxin1( ), LIU Wenheng1,2(
), LIU Wenheng1,2( ), WANG Kaixing1,2, LIU Xiaodong2, SUN Liqiang1, YIN Donghua1
), WANG Kaixing1,2, LIU Xiaodong2, SUN Liqiang1, YIN Donghua1
Received:2023-06-25
Revised:2023-12-20
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-03-20
摘要:
龙首山铀成矿带位于北祁连造山带与阿拉善地块的结合部位,中志留世—早泥盆世受控于祁连造山带的构造演化而处于后碰撞伸展环境,然而关于龙首山铀成矿带在后碰撞伸展环境的结束时限尚缺乏精确的年代学约束。为此本文以该成矿带青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩为研究对象,开展了岩相学、锆石U-Pb年代学和全岩主微量元素组成分析,据此探讨了岩石类型及成因、源区特征及构造环境。结果显示,中牌细粒花岗岩成岩年龄为(413.7±3.0) Ma,为早泥盆世岩浆活动的产物,形成于碰撞后伸展环境。岩石具有高Si、富碱及低CaO、MgO和P2O5的特征,A/CNK=1.01~1.04;富集轻稀土元素,重稀土元素相对亏损,具有明显的负Eu异常;相对富集Th、U、Nd、K,亏损Ba、Sr、P、Ti等元素。岩石的地球化学特征指示,中牌细粒花岗岩应属于弱过铝质高分异I型花岗岩。中牌细粒花岗岩形成于碰撞后的伸展环境,岩浆来源于下地壳,岩浆源区主要残留相为角闪石,在岩浆演化过程中经历了显著的结晶分异作用。结合前人研究成果,提出龙首山地区早古生代形成的岩浆活动按照时间可划分为晚奥陶世—早志留世(452~438 Ma)和中志留世—早泥盆世(430~412 Ma)两个阶段,其分别对应于构造演化的俯冲阶段和后碰撞阶段。
中图分类号:
陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182.
CHEN Yaoxin, LIU Wenheng, WANG Kaixing, LIU Xiaodong, SUN Liqiang, YIN Donghua. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of the Zhongpai Fine-grained Granite in Qingshanbao, Gansu: Constraints from Geochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Chronology[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(01): 169-182.

图1 龙首山青山堡花岗岩类岩体地质图(图a据王增振等 [6],图b据刘文恒等[4])
Fig.1 Geological map of the Qingshanbao pluton in Longshoushan (modified after Wang et al.[6] and Liu et al.[4],respectively)

图2 中牌细粒花岗岩野外、镜下照片 (a)中牌细粒花岗岩野外照片;(b)中牌细粒花岗岩镜下照片(正交偏光);Q.石英;Pl.斜长石;Mic.微斜长石
Fig.2 Field and microscopic photographs of the Zhongpai fine-grained granites
| 样品 | 含量(10-6) | 232TH/ 238U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||
| QSB21-2-1 | 192 | 547 | 0.35 | 0.05638 | 0.0035 | 0.50206 | 0.0302 | 0.06462 | 0.00114 | 466.6 | 132.7 | 413.1 | 20.4 | 403.6 | 6.9 | |
| QSB21-2-2 | 469 | 1002 | 0.47 | 0.05283 | 0.00314 | 0.48336 | 0.02801 | 0.06637 | 0.00104 | 321.6 | 129.5 | 400.4 | 19.2 | 414.2 | 6.3 | |
| QSB21-2-3 | 76 | 227 | 0.33 | 0.05326 | 0.00537 | 0.48769 | 0.04774 | 0.06641 | 0.00177 | 340.0 | 213.5 | 403.3 | 32.6 | 414.5 | 10.7 | |
| QSB21-2-4 | 151 | 520 | 0.29 | 0.05545 | 0.00357 | 0.50919 | 0.03164 | 0.06659 | 0.00128 | 430.0 | 137.8 | 417.9 | 21.3 | 415.6 | 7.7 | |
| QSB21-2-8 | 171 | 919 | 0.19 | 0.05474 | 0.00164 | 0.51073 | 0.01372 | 0.06761 | 0.00097 | 401.5 | 64.9 | 418.9 | 9.2 | 421.8 | 5.9 | |
| QSB21-2-9 | 247 | 1169 | 0.21 | 0.05528 | 0.00197 | 0.50364 | 0.01647 | 0.06602 | 0.00101 | 423.4 | 77.2 | 414.2 | 11.1 | 412.1 | 6.1 | |
| QSB21-2-12 | 449 | 2407 | 0.19 | 0.06011 | 0.00182 | 0.54539 | 0.01477 | 0.06582 | 0.00089 | 607.5 | 64.1 | 442.0 | 9.7 | 411.0 | 5.4 | |
| QSB21-2-13 | 1232 | 3146 | 0.39 | 0.09385 | 0.00208 | 0.87823 | 0.01555 | 0.06791 | 0.00089 | 1505.0 | 41.3 | 640.0 | 8.4 | 423.6 | 5.4 | |
| QSB21-2-14 | 658 | 1418 | 0.46 | 0.05491 | 0.00193 | 0.50772 | 0.01634 | 0.06712 | 0.00095 | 408.6 | 76.3 | 416.9 | 11.0 | 418.8 | 5.8 | |
| QSB21-2-15 | 177 | 753 | 0.24 | 0.05748 | 0.00311 | 0.51905 | 0.02709 | 0.06558 | 0.00094 | 509.6 | 115.3 | 424.5 | 18.1 | 409.5 | 5.7 | |
| QSB21-2-16 | 111 | 271 | 0.41 | 0.05649 | 0.00339 | 0.50795 | 0.02926 | 0.06539 | 0.00107 | 471.0 | 128.2 | 417.1 | 19.7 | 408.3 | 6.5 | |
| QSB21-2-17 | 328 | 1254 | 0.26 | 0.05549 | 0.00157 | 0.50529 | 0.01223 | 0.06626 | 0.0009 | 431.6 | 61.4 | 415.3 | 8.3 | 413.6 | 5.5 | |
| QSB21-2-19 | 381 | 1134 | 0.34 | 0.05448 | 0.00176 | 0.48773 | 0.01381 | 0.06522 | 0.00093 | 390.7 | 70.0 | 403.4 | 9.4 | 407.3 | 5.7 | |
| QSB21-2-20 | 211 | 947 | 0.22 | 0.05783 | 0.00224 | 0.52039 | 0.01859 | 0.0656 | 0.00091 | 523.2 | 83.1 | 425.4 | 12.4 | 409.6 | 5.5 | |
| QSB21-2-21 | 277 | 1030 | 0.27 | 0.05713 | 0.00292 | 0.52523 | 0.02562 | 0.06707 | 0.00092 | 496.0 | 109.3 | 428.6 | 17.1 | 418.5 | 5.5 | |
表1 中牌细粒花岗岩锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb isotopic analysis results for the Zhongpai fine-grained granites
| 样品 | 含量(10-6) | 232TH/ 238U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||
| QSB21-2-1 | 192 | 547 | 0.35 | 0.05638 | 0.0035 | 0.50206 | 0.0302 | 0.06462 | 0.00114 | 466.6 | 132.7 | 413.1 | 20.4 | 403.6 | 6.9 | |
| QSB21-2-2 | 469 | 1002 | 0.47 | 0.05283 | 0.00314 | 0.48336 | 0.02801 | 0.06637 | 0.00104 | 321.6 | 129.5 | 400.4 | 19.2 | 414.2 | 6.3 | |
| QSB21-2-3 | 76 | 227 | 0.33 | 0.05326 | 0.00537 | 0.48769 | 0.04774 | 0.06641 | 0.00177 | 340.0 | 213.5 | 403.3 | 32.6 | 414.5 | 10.7 | |
| QSB21-2-4 | 151 | 520 | 0.29 | 0.05545 | 0.00357 | 0.50919 | 0.03164 | 0.06659 | 0.00128 | 430.0 | 137.8 | 417.9 | 21.3 | 415.6 | 7.7 | |
| QSB21-2-8 | 171 | 919 | 0.19 | 0.05474 | 0.00164 | 0.51073 | 0.01372 | 0.06761 | 0.00097 | 401.5 | 64.9 | 418.9 | 9.2 | 421.8 | 5.9 | |
| QSB21-2-9 | 247 | 1169 | 0.21 | 0.05528 | 0.00197 | 0.50364 | 0.01647 | 0.06602 | 0.00101 | 423.4 | 77.2 | 414.2 | 11.1 | 412.1 | 6.1 | |
| QSB21-2-12 | 449 | 2407 | 0.19 | 0.06011 | 0.00182 | 0.54539 | 0.01477 | 0.06582 | 0.00089 | 607.5 | 64.1 | 442.0 | 9.7 | 411.0 | 5.4 | |
| QSB21-2-13 | 1232 | 3146 | 0.39 | 0.09385 | 0.00208 | 0.87823 | 0.01555 | 0.06791 | 0.00089 | 1505.0 | 41.3 | 640.0 | 8.4 | 423.6 | 5.4 | |
| QSB21-2-14 | 658 | 1418 | 0.46 | 0.05491 | 0.00193 | 0.50772 | 0.01634 | 0.06712 | 0.00095 | 408.6 | 76.3 | 416.9 | 11.0 | 418.8 | 5.8 | |
| QSB21-2-15 | 177 | 753 | 0.24 | 0.05748 | 0.00311 | 0.51905 | 0.02709 | 0.06558 | 0.00094 | 509.6 | 115.3 | 424.5 | 18.1 | 409.5 | 5.7 | |
| QSB21-2-16 | 111 | 271 | 0.41 | 0.05649 | 0.00339 | 0.50795 | 0.02926 | 0.06539 | 0.00107 | 471.0 | 128.2 | 417.1 | 19.7 | 408.3 | 6.5 | |
| QSB21-2-17 | 328 | 1254 | 0.26 | 0.05549 | 0.00157 | 0.50529 | 0.01223 | 0.06626 | 0.0009 | 431.6 | 61.4 | 415.3 | 8.3 | 413.6 | 5.5 | |
| QSB21-2-19 | 381 | 1134 | 0.34 | 0.05448 | 0.00176 | 0.48773 | 0.01381 | 0.06522 | 0.00093 | 390.7 | 70.0 | 403.4 | 9.4 | 407.3 | 5.7 | |
| QSB21-2-20 | 211 | 947 | 0.22 | 0.05783 | 0.00224 | 0.52039 | 0.01859 | 0.0656 | 0.00091 | 523.2 | 83.1 | 425.4 | 12.4 | 409.6 | 5.5 | |
| QSB21-2-21 | 277 | 1030 | 0.27 | 0.05713 | 0.00292 | 0.52523 | 0.02562 | 0.06707 | 0.00092 | 496.0 | 109.3 | 428.6 | 17.1 | 418.5 | 5.5 | |
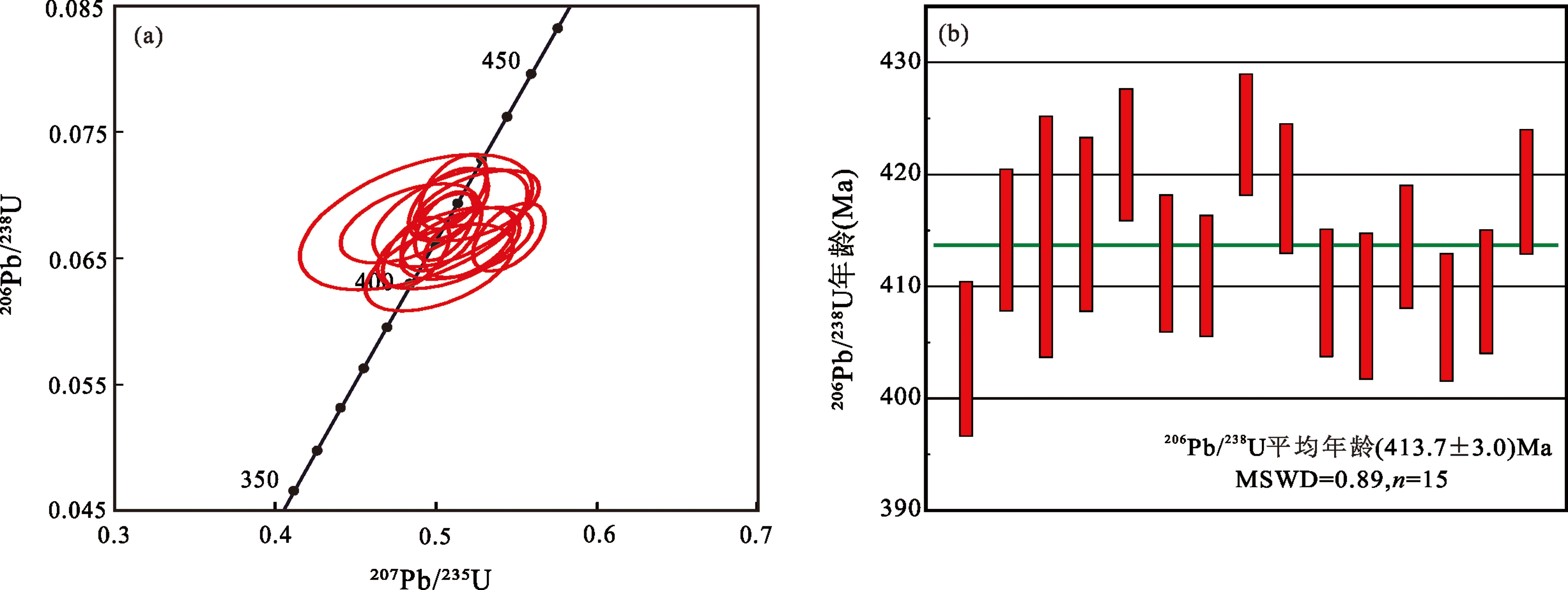
图4 中牌细粒花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)、加权平均年龄图(b)
Fig.4 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagram (a) and the weighted average age diagram (b) of the Zhongpai fine-grained granites
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | A/ CNK | A/ NK | AKI | Mg# | K2O+ Na2O | K2O/ Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSB21-2 | 76.48 | 0.11 | 12.15 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 3.36 | 5.41 | 0.01 | 0.77 | 98.82 | 1.01 | 1.07 | 0.94 | 34.89 | 8.77 | 1.61 |
| QSB21-3 | 76.08 | 0.10 | 12.32 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 3.43 | 5.11 | 0.01 | 0.87 | 98.34 | 1.02 | 1.10 | 0.91 | 28.99 | 8.54 | 1.49 |
| QSB21-4 | 76.26 | 0.14 | 12.41 | 0.86 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 3.43 | 4.94 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 98.83 | 1.03 | 1.13 | 0.89 | 39.45 | 8.37 | 1.44 |
| QSB21-5 | 75.99 | 0.10 | 12.14 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 3.45 | 5.02 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 98.10 | 1.01 | 1.09 | 0.92 | 33.63 | 8.47 | 1.46 |
| QSB21-6 | 76.74 | 0.11 | 12.20 | 0.80 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.61 | 3.53 | 4.74 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 98.92 | 1.01 | 1.11 | 0.90 | 33.09 | 8.27 | 1.34 |
| QSB21-7 | 77.12 | 0.09 | 12.44 | 0.74 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 3.36 | 5.30 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 99.62 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 0.91 | 30.00 | 8.66 | 1.58 |
| QSB21-8 | 75.84 | 0.18 | 12.56 | 1.36 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.60 | 3.35 | 5.09 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 99.31 | 1.04 | 1.14 | 0.88 | 36.93 | 8.44 | 1.52 |
| QSB21-9 | 76.62 | 0.10 | 12.42 | 0.85 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 3.32 | 5.43 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 99.31 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 0.91 | 24.10 | 8.75 | 1.63 |
| 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | (La/ Yb)N | δEu | ΣREE | LREE/ HREE |
| QSB21-2 | 23.1 | 54.7 | 5.46 | 19.5 | 4.31 | 0.34 | 3.76 | 0.65 | 4.23 | 0.86 | 2.71 | 0.45 | 3.27 | 0.50 | 5.07 | 0.25 | 123.84 | 6.54 |
| QSB21-3 | 25.5 | 56.9 | 6.30 | 22.6 | 4.98 | 0.38 | 4.23 | 0.70 | 4.48 | 0.90 | 2.73 | 0.44 | 3.01 | 0.45 | 6.08 | 0.25 | 133.60 | 6.89 |
| QSB21-4 | 32.3 | 66.6 | 7.25 | 25.1 | 5.08 | 0.49 | 4.17 | 0.68 | 4.24 | 0.86 | 2.61 | 0.41 | 2.71 | 0.41 | 8.55 | 0.32 | 152.91 | 8.50 |
| QSB21-5 | 23.8 | 51.5 | 5.68 | 20.7 | 4.64 | 0.37 | 4.01 | 0.66 | 4.27 | 0.87 | 2.66 | 0.44 | 2.94 | 0.45 | 5.81 | 0.26 | 122.99 | 6.55 |
| QSB21-6 | 26.3 | 56.5 | 6.25 | 22.2 | 5.09 | 0.41 | 4.55 | 0.75 | 4.73 | 0.97 | 2.97 | 0.46 | 3.10 | 0.46 | 6.09 | 0.26 | 134.74 | 6.49 |
| QSB21-7 | 24.7 | 55.3 | 6.16 | 22.1 | 5.26 | 0.30 | 4.58 | 0.78 | 5.20 | 1.07 | 3.44 | 0.58 | 4.18 | 0.67 | 4.24 | 0.18 | 134.32 | 5.55 |
| QSB21-8 | 28.2 | 57.3 | 6.77 | 24.5 | 5.54 | 0.48 | 4.75 | 0.79 | 4.95 | 0.99 | 2.95 | 0.49 | 3.38 | 0.53 | 5.98 | 0.28 | 141.62 | 6.52 |
| QSB21-9 | 25.7 | 59.0 | 6.78 | 24.9 | 6.58 | 0.26 | 6.41 | 1.11 | 7.63 | 1.55 | 4.81 | 0.78 | 5.24 | 0.79 | 3.52 | 0.12 | 151.54 | 4.35 |
| 样品号 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Cs | Co | Ni | Cu | Ga | Sr | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | P |
| QSB21-2 | 3.50 | 2.42 | 2.80 | 9.00 | 2.00 | 3.07 | 1.00 | 1.40 | 1.50 | 13.60 | 61.40 | 208.00 | 226.00 | 37.40 | 5.72 | 2.55 | 23.20 | 60.00 |
| QSB21-3 | 4.30 | 2.94 | 2.60 | 6.00 | 1.00 | 3.10 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 15.85 | 47.30 | 218.00 | 169.50 | 42.10 | 5.43 | 1.74 | 17.40 | 50.00 |
| QSB21-4 | 7.60 | 4.06 | 2.80 | 8.00 | 3.00 | 3.39 | 1.30 | 1.90 | 8.50 | 15.10 | 57.40 | 222.00 | 228.00 | 27.40 | 5.42 | 1.85 | 18.10 | 80.00 |
| QSB21-5 | 4.90 | 2.98 | 2.70 | 6.00 | 1.00 | 3.67 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 1.40 | 15.90 | 47.40 | 215.00 | 151.50 | 36.50 | 4.94 | 1.81 | 17.10 | 50.00 |
| QSB21-6 | 8.00 | 3.70 | 3.50 | 6.00 | 2.00 | 4.54 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 1.40 | 15.25 | 51.40 | 229.00 | 168.00 | 34.10 | 6.71 | 1.90 | 20.70 | 60.00 |
| QSB21-7 | 8.00 | 4.84 | 3.60 | 5.00 | 2.00 | 5.09 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 2.20 | 16.90 | 36.70 | 219.00 | 135.50 | 48.40 | 9.63 | 3.36 | 26.70 | 40.00 |
| QSB21-8 | 18.30 | 4.44 | 4.80 | 14.00 | 8.00 | 7.08 | 1.70 | 2.70 | 1.40 | 16.60 | 57.50 | 238.00 | 197.00 | 39.30 | 7.52 | 2.55 | 25.60 | 120.00 |
| QSB21-9 | 8.30 | 3.62 | 3.30 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 2.48 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 8.30 | 16.90 | 33.80 | 220.00 | 103.50 | 53.70 | 11.80 | 2.71 | 30.20 | 50.00 |
| 样品号 | Zr | Hf | Y | Ti | Zn | Mo | Bi | Sn | Pb | K | Nb/U | Rb/Sr | Ti/Zr | Nb/Ta | K/ Rb | TZr (℃) | Zr+Nb+ Ce+Y | 10000 Ga/Al |
| QSB21-2 | 105.00 | 4.30 | 24.4 | 680 | 11.00 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 1.70 | 32.0 | 43800 | 4.06 | 3.40 | 6.48 | 9.10 | 210.58 | 792.00 | 207.30 | 2.11 |
| QSB21-3 | 85.00 | 3.70 | 26.0 | 640 | 13.00 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 1.70 | 34.6 | 42800 | 3.20 | 4.60 | 7.53 | 10.00 | 196.33 | 774.00 | 185.30 | 2.43 |
| QSB21-4 | 80.00 | 3.30 | 25.3 | 880 | 14.00 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 1.60 | 33.1 | 41300 | 3.34 | 3.90 | 11.00 | 9.78 | 186.04 | 769.00 | 190.00 | 2.30 |
| QSB21-5 | 91.00 | 3.80 | 25.2 | 680 | 12.00 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 1.90 | 33.6 | 42400 | 3.46 | 4.50 | 7.47 | 9.45 | 197.21 | 779.00 | 184.80 | 2.47 |
| QSB21-6 | 77.00 | 3.20 | 26.8 | 700 | 15.00 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 2.30 | 34.7 | 39000 | 3.08 | 4.50 | 9.09 | 10.89 | 170.31 | 764.00 | 181.00 | 2.36 |
| QSB21-7 | 127.00 | 5.50 | 31.1 | 620 | 11.00 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 2.10 | 37.1 | 45100 | 2.77 | 6.00 | 4.88 | 7.95 | 205.94 | 811.00 | 240.10 | 2.57 |
| QSB21-8 | 122.00 | 4.90 | 27.9 | 1160 | 23.00 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 4.40 | 35.8 | 41600 | 3.40 | 4.10 | 9.51 | 10.04 | 174.79 | 805.00 | 232.80 | 2.50 |
| QSB21-9 | 147.00 | 6.00 | 43.0 | 660 | 11.00 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 1.50 | 35.0 | 45500 | 2.56 | 6.50 | 4.49 | 11.14 | 206.82 | 823.00 | 279.20 | 2.57 |
表2 中牌细粒花岗岩的主量元素(%)、微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major (%) and trace (10-6) element data for the Zhongpai fine-grained granites
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | A/ CNK | A/ NK | AKI | Mg# | K2O+ Na2O | K2O/ Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSB21-2 | 76.48 | 0.11 | 12.15 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 3.36 | 5.41 | 0.01 | 0.77 | 98.82 | 1.01 | 1.07 | 0.94 | 34.89 | 8.77 | 1.61 |
| QSB21-3 | 76.08 | 0.10 | 12.32 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 3.43 | 5.11 | 0.01 | 0.87 | 98.34 | 1.02 | 1.10 | 0.91 | 28.99 | 8.54 | 1.49 |
| QSB21-4 | 76.26 | 0.14 | 12.41 | 0.86 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 3.43 | 4.94 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 98.83 | 1.03 | 1.13 | 0.89 | 39.45 | 8.37 | 1.44 |
| QSB21-5 | 75.99 | 0.10 | 12.14 | 0.76 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 3.45 | 5.02 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 98.10 | 1.01 | 1.09 | 0.92 | 33.63 | 8.47 | 1.46 |
| QSB21-6 | 76.74 | 0.11 | 12.20 | 0.80 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.61 | 3.53 | 4.74 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 98.92 | 1.01 | 1.11 | 0.90 | 33.09 | 8.27 | 1.34 |
| QSB21-7 | 77.12 | 0.09 | 12.44 | 0.74 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 3.36 | 5.30 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 99.62 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 0.91 | 30.00 | 8.66 | 1.58 |
| QSB21-8 | 75.84 | 0.18 | 12.56 | 1.36 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.60 | 3.35 | 5.09 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 99.31 | 1.04 | 1.14 | 0.88 | 36.93 | 8.44 | 1.52 |
| QSB21-9 | 76.62 | 0.10 | 12.42 | 0.85 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 3.32 | 5.43 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 99.31 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 0.91 | 24.10 | 8.75 | 1.63 |
| 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | (La/ Yb)N | δEu | ΣREE | LREE/ HREE |
| QSB21-2 | 23.1 | 54.7 | 5.46 | 19.5 | 4.31 | 0.34 | 3.76 | 0.65 | 4.23 | 0.86 | 2.71 | 0.45 | 3.27 | 0.50 | 5.07 | 0.25 | 123.84 | 6.54 |
| QSB21-3 | 25.5 | 56.9 | 6.30 | 22.6 | 4.98 | 0.38 | 4.23 | 0.70 | 4.48 | 0.90 | 2.73 | 0.44 | 3.01 | 0.45 | 6.08 | 0.25 | 133.60 | 6.89 |
| QSB21-4 | 32.3 | 66.6 | 7.25 | 25.1 | 5.08 | 0.49 | 4.17 | 0.68 | 4.24 | 0.86 | 2.61 | 0.41 | 2.71 | 0.41 | 8.55 | 0.32 | 152.91 | 8.50 |
| QSB21-5 | 23.8 | 51.5 | 5.68 | 20.7 | 4.64 | 0.37 | 4.01 | 0.66 | 4.27 | 0.87 | 2.66 | 0.44 | 2.94 | 0.45 | 5.81 | 0.26 | 122.99 | 6.55 |
| QSB21-6 | 26.3 | 56.5 | 6.25 | 22.2 | 5.09 | 0.41 | 4.55 | 0.75 | 4.73 | 0.97 | 2.97 | 0.46 | 3.10 | 0.46 | 6.09 | 0.26 | 134.74 | 6.49 |
| QSB21-7 | 24.7 | 55.3 | 6.16 | 22.1 | 5.26 | 0.30 | 4.58 | 0.78 | 5.20 | 1.07 | 3.44 | 0.58 | 4.18 | 0.67 | 4.24 | 0.18 | 134.32 | 5.55 |
| QSB21-8 | 28.2 | 57.3 | 6.77 | 24.5 | 5.54 | 0.48 | 4.75 | 0.79 | 4.95 | 0.99 | 2.95 | 0.49 | 3.38 | 0.53 | 5.98 | 0.28 | 141.62 | 6.52 |
| QSB21-9 | 25.7 | 59.0 | 6.78 | 24.9 | 6.58 | 0.26 | 6.41 | 1.11 | 7.63 | 1.55 | 4.81 | 0.78 | 5.24 | 0.79 | 3.52 | 0.12 | 151.54 | 4.35 |
| 样品号 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Cs | Co | Ni | Cu | Ga | Sr | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | P |
| QSB21-2 | 3.50 | 2.42 | 2.80 | 9.00 | 2.00 | 3.07 | 1.00 | 1.40 | 1.50 | 13.60 | 61.40 | 208.00 | 226.00 | 37.40 | 5.72 | 2.55 | 23.20 | 60.00 |
| QSB21-3 | 4.30 | 2.94 | 2.60 | 6.00 | 1.00 | 3.10 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 15.85 | 47.30 | 218.00 | 169.50 | 42.10 | 5.43 | 1.74 | 17.40 | 50.00 |
| QSB21-4 | 7.60 | 4.06 | 2.80 | 8.00 | 3.00 | 3.39 | 1.30 | 1.90 | 8.50 | 15.10 | 57.40 | 222.00 | 228.00 | 27.40 | 5.42 | 1.85 | 18.10 | 80.00 |
| QSB21-5 | 4.90 | 2.98 | 2.70 | 6.00 | 1.00 | 3.67 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 1.40 | 15.90 | 47.40 | 215.00 | 151.50 | 36.50 | 4.94 | 1.81 | 17.10 | 50.00 |
| QSB21-6 | 8.00 | 3.70 | 3.50 | 6.00 | 2.00 | 4.54 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 1.40 | 15.25 | 51.40 | 229.00 | 168.00 | 34.10 | 6.71 | 1.90 | 20.70 | 60.00 |
| QSB21-7 | 8.00 | 4.84 | 3.60 | 5.00 | 2.00 | 5.09 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 2.20 | 16.90 | 36.70 | 219.00 | 135.50 | 48.40 | 9.63 | 3.36 | 26.70 | 40.00 |
| QSB21-8 | 18.30 | 4.44 | 4.80 | 14.00 | 8.00 | 7.08 | 1.70 | 2.70 | 1.40 | 16.60 | 57.50 | 238.00 | 197.00 | 39.30 | 7.52 | 2.55 | 25.60 | 120.00 |
| QSB21-9 | 8.30 | 3.62 | 3.30 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 2.48 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 8.30 | 16.90 | 33.80 | 220.00 | 103.50 | 53.70 | 11.80 | 2.71 | 30.20 | 50.00 |
| 样品号 | Zr | Hf | Y | Ti | Zn | Mo | Bi | Sn | Pb | K | Nb/U | Rb/Sr | Ti/Zr | Nb/Ta | K/ Rb | TZr (℃) | Zr+Nb+ Ce+Y | 10000 Ga/Al |
| QSB21-2 | 105.00 | 4.30 | 24.4 | 680 | 11.00 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 1.70 | 32.0 | 43800 | 4.06 | 3.40 | 6.48 | 9.10 | 210.58 | 792.00 | 207.30 | 2.11 |
| QSB21-3 | 85.00 | 3.70 | 26.0 | 640 | 13.00 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 1.70 | 34.6 | 42800 | 3.20 | 4.60 | 7.53 | 10.00 | 196.33 | 774.00 | 185.30 | 2.43 |
| QSB21-4 | 80.00 | 3.30 | 25.3 | 880 | 14.00 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 1.60 | 33.1 | 41300 | 3.34 | 3.90 | 11.00 | 9.78 | 186.04 | 769.00 | 190.00 | 2.30 |
| QSB21-5 | 91.00 | 3.80 | 25.2 | 680 | 12.00 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 1.90 | 33.6 | 42400 | 3.46 | 4.50 | 7.47 | 9.45 | 197.21 | 779.00 | 184.80 | 2.47 |
| QSB21-6 | 77.00 | 3.20 | 26.8 | 700 | 15.00 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 2.30 | 34.7 | 39000 | 3.08 | 4.50 | 9.09 | 10.89 | 170.31 | 764.00 | 181.00 | 2.36 |
| QSB21-7 | 127.00 | 5.50 | 31.1 | 620 | 11.00 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 2.10 | 37.1 | 45100 | 2.77 | 6.00 | 4.88 | 7.95 | 205.94 | 811.00 | 240.10 | 2.57 |
| QSB21-8 | 122.00 | 4.90 | 27.9 | 1160 | 23.00 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 4.40 | 35.8 | 41600 | 3.40 | 4.10 | 9.51 | 10.04 | 174.79 | 805.00 | 232.80 | 2.50 |
| QSB21-9 | 147.00 | 6.00 | 43.0 | 660 | 11.00 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 1.50 | 35.0 | 45500 | 2.56 | 6.50 | 4.49 | 11.14 | 206.82 | 823.00 | 279.20 | 2.57 |

图5 中牌细粒花岗岩A/CNK-A/NK图解(a) (据Maniar 等[14] )和SiO2-K2O图解(b) (据Peccerillo 等[15])
Fig.5 A/CNK-A/N K(a) (after Maniar et al.[14] ) and SiO2-K2O (b) (after Peccerillo et al.[15]) diagrams of the Zhongpai fine-grained granites

图6 中牌细粒花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据McDonough和Sun [16])
Fig.6 Spider diagrams of chondrite-normalized REE (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements (b) of the Zhongpai fine-grained granites (after McDonough and Sun [16])
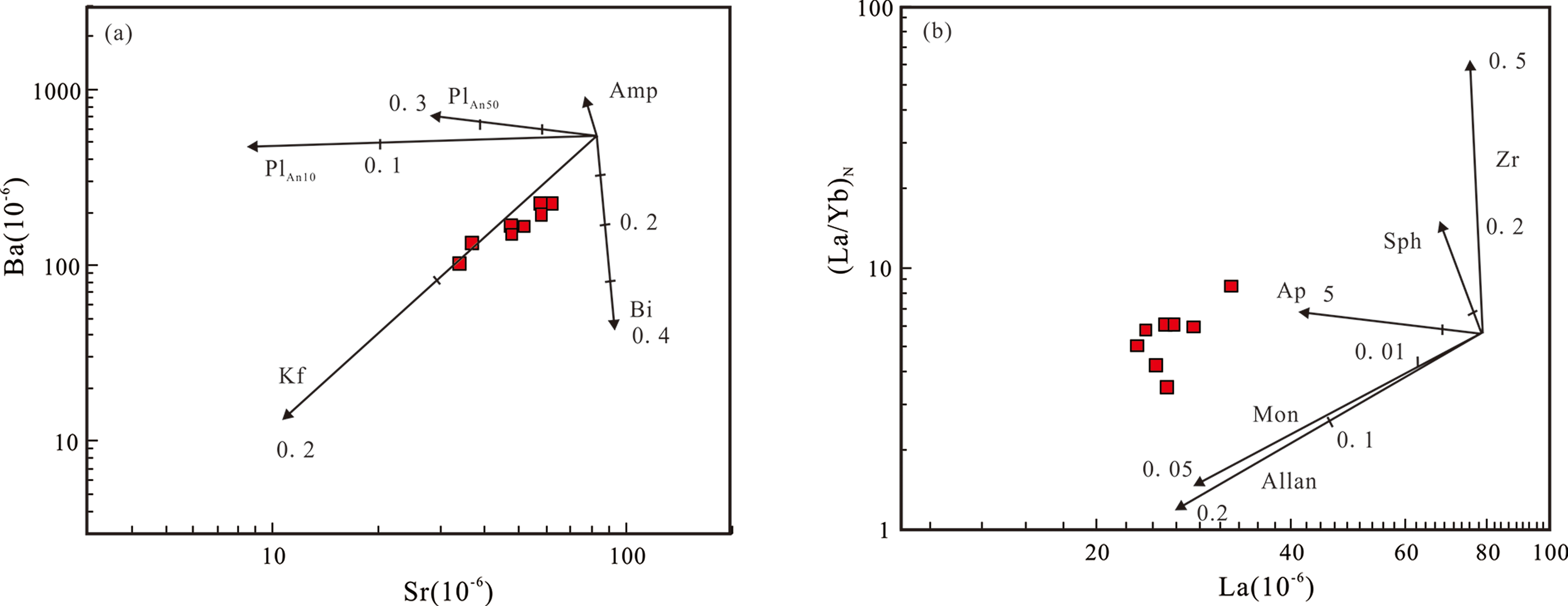
图8 中牌细粒花岗岩Sr-Ba(a)和La-(La/Yb)N(b)关系图及分离结晶趋势 图(a)中Sr、Ba在斜长石中的分配系数据Blundy and Shimizu [38],在其余矿物中的分配系数据Ewart and Griffin [39],图(b)中的副矿物结晶分离趋势线,据Wu et al.[28];分异趋势线上的数字代表分离结晶程度,PlAn10.斜长石(An=10),PlAn50.斜长石(An=50),Kf.钾长石,Bi.黑云母,Amp.角闪石,Zr.锆石,Sph.榍石,Ap.磷灰石,Mon.独居石,Allan.褐帘石。
Fig.8 Sr-Ba (a) and La-(LA/Yb)N (b) diagrams showing the fractional crystallization trends of the Zhongpai fine-grained granites Partition coefficients of Sr and Ba used in Fig.(a) are from Blundy and Shimizu[38] for plagioclase,and from Ewart and Griffin[39] for other minerals.The fractionation trends for accessory minerals shown in Fig.(b) are from Wu et al. [28], and the data on the lines represent the fractionation degree.Plan10.plagioclase with An = 10; Plan50.plagioclase with An = 50; Kf.K-feldspar; Bi.biotite; Amp.amphibole, Zr.zircon, Sph.sphene, Ap.apatite;Mon.monazite; Allan.allanite

图9 龙首山地区早古生代侵入岩的构造环境判别图解(据Pearce等[43]; 俯冲花岗岩数据据文献[2-3,44⇓⇓-47];后碰撞花岗岩数据据文献[4,6⇓-8,19⇓-21,31,41-42])
Fig.9 Tectonic environment discrimination diagrams of Early Paleozoic intrusive rocks in Longshoushan Subduction (data of granites from refs.[2-3,44⇓⇓-47], and post-collision granites from refs[4,6⇓-8,19⇓-21,31,41-42])
| 位置 | 岩性 | 年龄(Ma) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 龙首山芨岭 | 肉红色中粗粒花岗岩 | 426.4±2.0 | 陈云杰等[ |
| 龙首山牛角沟 | 石英二长花岗岩 | 447.0±5.2 | 陈云杰等[ |
| 青山堡 | 灰绿色闪长玢岩 | 422.3±3.6 | 陈云杰等[ |
| 龙首山西井 | 橄榄辉石和辉长岩 | 421±9.0 | 段俊等[ |
| 青山堡 | 花岗闪长岩 | 451.5±3.2 | 何佳军等[ |
| 龙首山红石泉 | 正长岩 | 416±0.17 | 冷天赐等[ |
| 青山堡 | 中粗粒钾长花岗岩 | 441.6±4.2 | 刘文恒等[ |
| 青山堡 | 细晶花岗岩 | 430.1±5.6 | 刘文恒等[ |
| 龙首山青山堡 | 细粒闪长岩 | 438.6±4.7 | 牛宇奔[ |
| 大佛寺 | 花岗岩 | 426.1±2.8 | 孙宝璐等[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 花岗岩 | 428.6±8.1 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 425.2±3.0 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 二长花岗斑岩 | 416.6±9.2 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 | 412.8±9 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山大佛寺 | 碱性长石花岗岩 | 426±2.0 | 王增振等[ |
| 河西堡孟家大湾 | 花岗岩 | 444±2.0 | 魏俏巧等[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | A型似斑状花岗岩 | 458.3±2.3 | 张甲民等[ |
| 龙首山莲花山 | 花岗闪长岩 | 441±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山孟家大湾 | 花岗闪长岩 | 441±3 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 角闪辉长岩 | 441±2 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山西井 | 二长岩 | 438±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 杨前大山 | 花岗闪长岩 | 427±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山孟家大湾 | 石英闪长岩 | 424±2 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山圣容寺 | 钾长花岗岩 | 422±2 | 张丽琪[ |
| 新开沟 | 似斑状花岗岩 | 419±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 新开沟 | 细粒花岗岩 | 414±3 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 正长岩 | 427.2±3.6 | 张志强等[ |
| 龙首山牛角沟 | 中粗粒花岗岩 | 445.2±7.8 | 赵如意等[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 纳长岩 | 442.9±5.7 | 赵如意等[ |
表3 龙首山地区早古生代侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄统计结果
Table 3 Statistical data of zircon U-Pb ages of the Early Paleozoic intrusive rocks in Longshoushan
| 位置 | 岩性 | 年龄(Ma) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 龙首山芨岭 | 肉红色中粗粒花岗岩 | 426.4±2.0 | 陈云杰等[ |
| 龙首山牛角沟 | 石英二长花岗岩 | 447.0±5.2 | 陈云杰等[ |
| 青山堡 | 灰绿色闪长玢岩 | 422.3±3.6 | 陈云杰等[ |
| 龙首山西井 | 橄榄辉石和辉长岩 | 421±9.0 | 段俊等[ |
| 青山堡 | 花岗闪长岩 | 451.5±3.2 | 何佳军等[ |
| 龙首山红石泉 | 正长岩 | 416±0.17 | 冷天赐等[ |
| 青山堡 | 中粗粒钾长花岗岩 | 441.6±4.2 | 刘文恒等[ |
| 青山堡 | 细晶花岗岩 | 430.1±5.6 | 刘文恒等[ |
| 龙首山青山堡 | 细粒闪长岩 | 438.6±4.7 | 牛宇奔[ |
| 大佛寺 | 花岗岩 | 426.1±2.8 | 孙宝璐等[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 花岗岩 | 428.6±8.1 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 黑云母二长花岗岩 | 425.2±3.0 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 二长花岗斑岩 | 416.6±9.2 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 | 412.8±9 | 汤琳[ |
| 龙首山大佛寺 | 碱性长石花岗岩 | 426±2.0 | 王增振等[ |
| 河西堡孟家大湾 | 花岗岩 | 444±2.0 | 魏俏巧等[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | A型似斑状花岗岩 | 458.3±2.3 | 张甲民等[ |
| 龙首山莲花山 | 花岗闪长岩 | 441±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山孟家大湾 | 花岗闪长岩 | 441±3 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 角闪辉长岩 | 441±2 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山西井 | 二长岩 | 438±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 杨前大山 | 花岗闪长岩 | 427±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山孟家大湾 | 石英闪长岩 | 424±2 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山圣容寺 | 钾长花岗岩 | 422±2 | 张丽琪[ |
| 新开沟 | 似斑状花岗岩 | 419±4 | 张丽琪[ |
| 新开沟 | 细粒花岗岩 | 414±3 | 张丽琪[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 正长岩 | 427.2±3.6 | 张志强等[ |
| 龙首山牛角沟 | 中粗粒花岗岩 | 445.2±7.8 | 赵如意等[ |
| 龙首山芨岭 | 纳长岩 | 442.9±5.7 | 赵如意等[ |
| [1] | 周立发. 阿拉善地块南缘早古生代大地构造特征和演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 1992, 22(1): 107-115. |
| [2] | 何佳军, 邵东, 王刚, 等. 甘肃龙首山青山堡花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 2022, 36(3): 596-606. |
| [3] | 陈云杰, 赵如意, 王刚, 等. 甘肃龙首山牛角沟地区中粗粒石英二长花岗岩年代学与元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(1): 21-29. |
| [4] | 刘文恒, 潘家永, 刘晓东, 等. 甘肃龙首山青山堡花岗岩成因及其构造意义: 元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Sr-Nd同位素约束[J]. 矿物岩石, 2019, 39(4): 26-40. |
| [5] | 牛宇奔. 甘肃龙首山青山堡岩体地质地球化学特征与成岩因研究[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2019. |
| [6] | 王增振, 陈宣华, 邵兆刚, 等. 甘肃龙首山—合黎山晚志留世—早泥盆世花岗岩类的成因及其对阿拉善地块西南缘早古生代构造演化的约束[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(8): 2243-2261. |
| [7] | 冷天赐, 刘文恒, 余驰达, 等. 甘肃龙首山红石泉正长岩地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 矿物岩石, 2021, 41(3): 72-83. |
| [8] | 张丽琪. 北祁连—阿拉善地块南缘古生代碰撞后岩浆作用及深部过程[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2019. |
| [9] | 邱检生, 胡建, 王孝磊, 等. 广东河源白石冈岩体: 一个高分异的I型花岗岩[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(4): 503-514. |
| [10] | 苏扣林. 广东良口黄田埔高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩地球化学特征及大地构造意义[J]. 地质学刊, 2018, 42(2): 197-205. |
| [11] | 黄孔文, 郭敏, 林杰春, 等. 粤北白沙地区晚侏罗世高分异Ⅰ型细粒花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(5): 926-944. |
| [12] | 李响, 王令占, 涂兵, 等. 广东连山地区禾洞高分异花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(10):3577-3596. |
| [13] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MCDONOUGH W F, SUN S S. The composition of the earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223-253.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2): 295-304.
DOI URL |
| [18] | PITCHER W S. The Nature and Origin of Granite[M]. 2nd Edi.London: Chapman & Hall, 1997. |
| [19] | 张志强, 王凯兴, 王刚, 等. 甘肃龙首山芨岭地区古生代正长岩成因及构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2018, 64(4): 1017-1029. |
| [20] | 汤琳. 甘肃龙首山芨岭地区花岗岩特征及锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2015. |
| [21] | 陈云杰, 王刚, 王伟, 等. 龙首山芨岭地区中粗粒花岗岩地质特征及其地质意义[J]. 铀矿地质, 2022, 38(6): 1111-1121. |
| [22] | 刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 等. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003, 9(4): 573-591. |
| [23] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type gra-nites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(7): 745-765. |
| [25] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [26] |
PICHAVANT M, MONTEL J M, RICHARD L R. Apatite solubility in peraluminous liquids: Experimental data and an extension of the Harrison-Watson model[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(10): 3855-3861.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 535-551.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I): Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003, 66(3/4): 241-273.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG X S, BI X W, LENG C B, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Cretaceous igneous intrusions and Mo-Cu-(W) mineralization in the southern Yidun Arc, SW China: Implications for metallogenesis and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 61: 73-95.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等. 福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(11): 2468-2484. |
| [31] | 段俊, 钱壮志, 焦建刚, 等. 甘肃龙首山岩带西井镁铁质岩体成因及其构造意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(3): 832-846. |
| [32] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subductedlithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347(6294): 662-665.
DOI |
| [33] | 许逢明, 孙巍, 吴大天, 等. 大兴安岭北段免渡河地区晚石炭世二长花岗岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和地球化学证据[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(8): 2839-2855. |
| [34] |
HOFMANN A W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3): 297-314.
DOI URL |
| [35] | WILSON M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London: Unwin Hyman, 1989. |
| [36] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution:An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary rocks[M]. Boston: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985:209-230. |
| [37] | BAS M J L. Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1994, 58:523-523. |
| [38] |
BLUNDY J D, SHIMIZU N. Trace element evidence for plagioclase recycling in calc-alkaline magmas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 102(2): 178-197.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
EWART A, GRIFFIN W L. Application of proton-microprobe data to trace-element partitioning in volcanic rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 117(1/2/3/4): 251-284.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩构造环境问题:关于花岗岩研究的思考之三[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(11): 2683-2698. |
| [41] | 孙宝璐, 钱青, 张建新. 甘肃大佛寺、金佛寺花岗岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf-O同位素和全岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(10): 3091-3108. |
| [42] | 陈云杰, 王刚, 赵如意, 等. 甘肃龙首山成矿带东段闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 铀矿地质, 2021, 37(1): 38-50, 111. |
| [43] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 张甲民, 赵如意, 王刚, 等. 甘肃龙首山芨岭铀矿区A型似斑状花岗岩地质特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017, 36(5): 813-823. |
| [45] | 赵如意, 王博, 陈毓川, 等. 甘肃省龙首山牛角沟铀矿点钾钠混合交代作用研究[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(12): 2469-2484. |
| [46] | 魏俏巧, 郝立波, 陆继龙, 等. 甘肃河西堡花岗岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(6): 729-735. |
| [47] | 赵如意, 姜常义, 陈旭, 等. 甘肃省龙首山成矿带中段钠长岩脉地质特征及其与铀矿化关系研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(6): 1069-1078. |
| [48] | 相振群, 陆松年, 李怀坤, 等. 北祁连西段熬油沟辉长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12): 1686-1691. |
| [49] | 曾建元, 杨怀仁, 杨宏仪, 等. 北祁连东草河蛇绿岩: 一个早古生代的洋壳残片[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(7): 825-835. |
| [50] | 孟繁聪, 张建新, 郭春满, 等. 大岔大坂MOR型和SSZ型蛇绿岩对北祁连洋演化的制约[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(5): 453-466. |
| [51] | 武鹏, 李向民, 徐学义, 等. 北祁连山扎麻什地区东沟蛇绿岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(6): 896-906. |
| [52] | 夏小洪, 孙楠, 宋述光, 等. 北祁连西段熬油沟二只哈拉达坂蛇绿岩的形成环境和时代[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(5): 757-769. |
| [53] | 宋述光, 张立飞, NIU Y, 等. 北祁连山榴辉岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(6): 592-595. |
| [54] |
ZHANG J X, MENG F C, WAN Y S. A cold Early Palaeozoic subduction zone in the North Qilian Mountains, NW China: Petrological and U-Pb geochronological constraints[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2007, 25(3): 285-304.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHANG L, CHEN R X, ZHENG Y F, et al. Geochemical constraints on the protoliths of eclogites and blueschists from North Qilian, northern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 421: 26-43.
DOI URL |
| [56] | 喻星星, 张建新. 北祁连香子沟榴辉岩相变沉积岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(5): 1437-1451. |
| [57] |
SONG S G, NIU Y L, SU L, et al. Tectonics of the North Qilian orogen, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1378-1401.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
XU Y J, DU Y S, CAWOOD P A, et al. Provenance record of a foreland basin: Detrital zircon U-Pb ages from Devonian strata in the North Qilian Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 495(3/4): 337-347.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [2] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [3] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [4] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [5] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| [6] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [7] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [8] | 朱德全, 唐名鹰, 丁正江, 朱海波, 王炜晓, 张宇, 何宗围, 吴洪彬. 柴北缘赛坝沟金矿床花岗斑岩脉的成因及动力学背景: 来自年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 898-910. |
| [9] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [10] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [11] | 欧伟程, 李承东, 张永清, 赵利刚, 许腾, 许雅雯, 孙烜烨. 北秦岭二郎坪群抱树坪组碎屑锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及物源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 347-361. |
| [12] | 吴小雷, 常晋阳, 曾南石, 徐文杰, 陶明荣, 赵刚, 韩建. 辽宁红透山铜锌矿床含矿岩系地球化学特征及找矿指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 362-377. |
| [13] | 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 郑艳荣, 李晓东, 武海文, 张龙. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1633-1650. |
| [14] | 谢亘, 喻光明, 路英川, 冯欣, 田光昊, 王然, 王建. 华北克拉通南缘小秦岭地区花岗质片麻岩年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712. |
| [15] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||