



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (03): 547-561.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.011
韩飞1( ), 宋元宝1, 张伟1, 李道凌2, 黄永高1,3, 李应栩4, 贾小川1, 杨学俊1, 杨青松3, 宋旭波5, 卢柳5
), 宋元宝1, 张伟1, 李道凌2, 黄永高1,3, 李应栩4, 贾小川1, 杨学俊1, 杨青松3, 宋旭波5, 卢柳5
收稿日期:2022-05-12
修回日期:2023-04-10
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-07-20
作者简介:韩 飞,男,工程师,1988年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事区域地质调查和矿床成因研究。Email:cdhanfei7@163.com。
基金资助:
HAN Fei1( ), SONG Yuanbao1, ZHANG Wei1, LI Daoling2, HUANG Yonggao1,3, LI Yingxu4, JIA Xiaochuan1, YANG Xuejun1, YANG Qingsong3, SONG Xubo5, LU Liu5
), SONG Yuanbao1, ZHANG Wei1, LI Daoling2, HUANG Yonggao1,3, LI Yingxu4, JIA Xiaochuan1, YANG Xuejun1, YANG Qingsong3, SONG Xubo5, LU Liu5
Received:2022-05-12
Revised:2023-04-10
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-07-20
摘要:
拉萨地块新特提斯初期演化过程是构建特提斯时空格架的重要环节,受制于研究对象的匮乏,其认识尚待深入。为此,本研究选取中拉萨地块南木林甲措乡地区花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩,进行锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学分析,探讨岩石成因和源区,为新特提斯初期演化提供新的制约。分析结果表明,花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄分别为(214.3±1.1) Ma和(206.1±1.3) Ma,代表晚三叠世两期次岩浆事件。岩浆岩里特曼指数(σ)介于1.79~4.71,具有钙碱性-碱性特征,Al2O3含量为15.01%~17.57%,A/CNK=0.76~1.12,显示出准铝质-过铝质的特征,此外花岗闪长岩具有高硅(SiO2含量61.87%~73.72%,平均65.76%)、高钾(最高达4.25%)、较低的Mg#(31~46,均值为41)特征。二者微量元素均表现为强烈富集Rb、U、K、Pb等大离子亲石元素(LILE)以及La、Ce等轻稀土元素,而亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素(HFSE),表现出弧型岩浆岩的地球化学属性;Rb/Sr值(0.05~5.50,均值为2.54)指示壳源特征。(La/Yb)N值较高,平均12.05,反映了轻重稀土元素分馏显著的特征,Eu负异常不明显(δEu=0.57~1.01,平均0.73)。综合研究表明,南木林地区中酸性岩体为壳幔混合成因的I型花岗岩,其形成过程可能为:新特提斯洋北向俯冲导致地幔楔发生部分熔融,岩浆底侵形成新生下地壳,随后幔源岩浆热烘烤导致新生下地壳重熔,岩浆上升侵位形成甲措乡中酸性岩体。本研究指示新特提斯洋北向俯冲作用在晚三叠世(≈214 Ma)之前已经发生,早于新近发现的晚三叠世Be-Rb±(Nb-Ta)稀有金属矿化时限。
中图分类号:
韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561.
HAN Fei, SONG Yuanbao, ZHANG Wei, LI Daoling, HUANG Yonggao, LI Yingxu, JIA Xiaochuan, YANG Xuejun, YANG Qingsong, SONG Xubo, LU Liu. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of the Late Triassic Nanmulin Intermediate-felsic Magmatic Rocks in the Gangdese Batholith, Southern Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 547-561.

图1 拉萨地块大地构造位置图(a)与岩浆岩分布简图(b)(据文献[19,28]修改)
Fig.1 Tectonic sketch of the Lhasa terrane and the schematic diagram showing the distributions of magmatic rocks (modified from refs. [19,28])

图3 南木林中酸性岩石野外(a)(b)及镜下(正交偏光)岩相学照片(c)(d) (a)石英闪长岩侵入永珠组砂岩;(b)花岗闪长岩中中性包体;(c)花岗闪长岩显微照片;(d)石英闪长岩显微照片C1y.永珠组;οδT3.晚三叠世石英闪长岩;Qtz.石英;Pl.斜长石;Kfs.钾长石;Bt.黑云母;Chl.绿泥石;MME.包体
Fig.3 Field (a and b) and microscopic characteristics (c and d) of the Nanmulin intermediate-felsic rocks
| 测点号 | Th (10-6) | U (10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄(Ma) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||
| PM104-1-1 | 1275.8 | 2149.6 | 0.59 | 0.0560 | 0.0007 | 0.2606 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 213.9 | 4.4 |
| PM104-1-2 | 1506.7 | 3301.9 | 0.46 | 0.0494 | 0.0004 | 0.2302 | 0.0044 | 0.0338 | 0.0006 | 190.0 | 4.1 |
| PM104-1-3 | 777.3 | 2243.5 | 0.35 | 0.0544 | 0.0007 | 0.2536 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 189.6 | 4.4 |
| PM104-1-4 | 851.2 | 2875.8 | 0.30 | 0.0503 | 0.0005 | 0.2348 | 0.0027 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 185.8 | 6.3 |
| PM104-1-5 | 399.3 | 2337.1 | 0.17 | 0.0507 | 0.0003 | 0.2368 | 0.0024 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 208.4 | 2.1 |
| PM104-1-6 | 922.8 | 2391.1 | 0.39 | 0.0493 | 0.0004 | 0.2299 | 0.0033 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.3 | 2.7 |
| PM104-1-7 | 627.1 | 1841.5 | 0.34 | 0.0507 | 0.0005 | 0.2366 | 0.0031 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 214.3 | 4.0 |
| PM104-1-8 | 1103.0 | 3219.6 | 0.34 | 0.0504 | 0.0004 | 0.2360 | 0.0035 | 0.0339 | 0.0004 | 214.1 | 2.0 |
| PM104-1-9 | 1196.8 | 2932.2 | 0.41 | 0.0521 | 0.0005 | 0.2432 | 0.0027 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 214.6 | 2.1 |
| PM104-1-10 | 521.3 | 2221.6 | 0.23 | 0.0506 | 0.0004 | 0.2360 | 0.0020 | 0.0338 | 0.0002 | 214.7 | 1.6 |
| PM104-1-11 | 922.1 | 2541.3 | 0.36 | 0.0505 | 0.0004 | 0.2359 | 0.0044 | 0.0338 | 0.0006 | 214.3 | 2.4 |
| PM104-1-12 | 799.2 | 2037.8 | 0.39 | 0.0540 | 0.0005 | 0.2524 | 0.0064 | 0.0338 | 0.0007 | 214.3 | 2.1 |
| PM104-1-13 | 549.3 | 1984.4 | 0.28 | 0.0522 | 0.0005 | 0.2436 | 0.0032 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.7 | 2.7 |
| PM104-1-14 | 974.7 | 2186.9 | 0.45 | 0.0495 | 0.0012 | 0.2309 | 0.0069 | 0.0337 | 0.0007 | 214.2 | 1.6 |
| PM104-1-15 | 588.1 | 2008.1 | 0.29 | 0.0501 | 0.0006 | 0.2351 | 0.0034 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.1 | 1.5 |
| PM104-1-16 | 465.0 | 1369.1 | 0.34 | 0.0491 | 0.0012 | 0.2296 | 0.0114 | 0.0336 | 0.0019 | 214.4 | 3.5 |
| PM104-1-17 | 1397.7 | 3039.6 | 0.46 | 0.0560 | 0.0007 | 0.2606 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.3 | 4.3 |
| PM104-1-18 | 737.0 | 2152.9 | 0.34 | 0.0494 | 0.0004 | 0.2302 | 0.0044 | 0.0338 | 0.0006 | 214.3 | 2.4 |
| PM104-1-19 | 244.9 | 399.3 | 0.61 | 0.0544 | 0.0007 | 0.2536 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 213.4 | 4.1 |
| PM104-1-20 | 417.9 | 1199.3 | 0.35 | 0.0503 | 0.0005 | 0.2348 | 0.0027 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 214.0 | 2.6 |
| PM104-1-21 | 612.6 | 2305.6 | 0.27 | 0.0507 | 0.0003 | 0.2368 | 0.0024 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 213.2 | 11.8 |
| D1268-1 | 201.2 | 253.9 | 0.79 | 0.0507 | 0.0011 | 0.2247 | 0.0056 | 0.0321 | 0.0005 | 203.7 | 3.2 |
| D1268-2 | 336.2 | 414.8 | 0.81 | 0.0504 | 0.0008 | 0.2210 | 0.0041 | 0.0318 | 0.0004 | 201.7 | 2.8 |
| D1268-3 | 458.8 | 453.4 | 1.01 | 0.0490 | 0.0008 | 0.2235 | 0.0049 | 0.0330 | 0.0005 | 209.6 | 3.0 |
| D1268-4 | 133.4 | 164.1 | 0.81 | 0.0558 | 0.0045 | 0.2516 | 0.0247 | 0.0323 | 0.0005 | 204.7 | 3.3 |
| D1268-5 | 909.5 | 603.4 | 1.51 | 0.0554 | 0.0010 | 0.2465 | 0.0057 | 0.0322 | 0.0005 | 204.3 | 3.3 |
| D1268-6 | 199.8 | 284.5 | 0.70 | 0.0495 | 0.0010 | 0.2253 | 0.0057 | 0.0329 | 0.0007 | 208.8 | 4.1 |
| D1268-7 | 212.6 | 293.9 | 0.72 | 0.0484 | 0.0011 | 0.2240 | 0.0063 | 0.0334 | 0.0007 | 211.9 | 4.4 |
| D1268-8 | 696.6 | 604.3 | 1.15 | 0.0502 | 0.0010 | 0.2302 | 0.0053 | 0.0332 | 0.0006 | 210.3 | 3.4 |
| D1268-9 | 481.9 | 447.2 | 1.08 | 0.0498 | 0.0010 | 0.2272 | 0.0053 | 0.0330 | 0.0006 | 209.5 | 3.6 |
| D1268-10 | 399.8 | 369.9 | 1.08 | 0.0508 | 0.0010 | 0.2261 | 0.0052 | 0.0322 | 0.0005 | 204.6 | 3.3 |
| D1268-11 | 443.1 | 379.6 | 1.17 | 0.0498 | 0.0009 | 0.2220 | 0.0049 | 0.0323 | 0.0005 | 204.8 | 3.0 |
| D1268-12 | 169.5 | 201.0 | 0.84 | 0.0485 | 0.0013 | 0.2124 | 0.0057 | 0.0318 | 0.0005 | 201.9 | 3.1 |
| D1268-13 | 417.2 | 542.4 | 0.77 | 0.0496 | 0.0007 | 0.2211 | 0.0053 | 0.0323 | 0.0007 | 204.9 | 4.3 |
| D1268-14 | 164.4 | 197.8 | 0.83 | 0.0501 | 0.0015 | 0.2420 | 0.0069 | 0.0351 | 0.0004 | 222.2 | 2.3 |
| D1268-15 | 235.2 | 280.5 | 0.84 | 0.0512 | 0.0011 | 0.2278 | 0.0051 | 0.0323 | 0.0005 | 205.0 | 2.9 |
| D1268-16 | 1188.3 | 1037.2 | 1.15 | 0.0504 | 0.0006 | 0.2266 | 0.0044 | 0.0326 | 0.0004 | 206.7 | 2.5 |
| D1268-17 | 236.0 | 313.5 | 0.75 | 0.0502 | 0.0011 | 0.2327 | 0.0061 | 0.0336 | 0.0005 | 213.1 | 3.3 |
| D1268-18 | 401.6 | 501.5 | 0.80 | 0.0503 | 0.0010 | 0.2216 | 0.0046 | 0.0320 | 0.0004 | 202.8 | 2.3 |
| D1268-19 | 273.5 | 260.0 | 1.05 | 0.0517 | 0.0013 | 0.2345 | 0.0063 | 0.0329 | 0.0004 | 208.5 | 2.6 |
| D1268-20 | 300.2 | 355.9 | 0.84 | 0.0505 | 0.0014 | 0.2269 | 0.0070 | 0.0325 | 0.0003 | 206.2 | 1.9 |
| D1268-21 | 240.0 | 241.7 | 0.99 | 0.0508 | 0.0012 | 0.2402 | 0.0057 | 0.0343 | 0.0003 | 217.5 | 2.1 |
表1 南木林地区中酸性岩体锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb dating results for the Nanmulin intermediate-felsic rocks
| 测点号 | Th (10-6) | U (10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄(Ma) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||
| PM104-1-1 | 1275.8 | 2149.6 | 0.59 | 0.0560 | 0.0007 | 0.2606 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 213.9 | 4.4 |
| PM104-1-2 | 1506.7 | 3301.9 | 0.46 | 0.0494 | 0.0004 | 0.2302 | 0.0044 | 0.0338 | 0.0006 | 190.0 | 4.1 |
| PM104-1-3 | 777.3 | 2243.5 | 0.35 | 0.0544 | 0.0007 | 0.2536 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 189.6 | 4.4 |
| PM104-1-4 | 851.2 | 2875.8 | 0.30 | 0.0503 | 0.0005 | 0.2348 | 0.0027 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 185.8 | 6.3 |
| PM104-1-5 | 399.3 | 2337.1 | 0.17 | 0.0507 | 0.0003 | 0.2368 | 0.0024 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 208.4 | 2.1 |
| PM104-1-6 | 922.8 | 2391.1 | 0.39 | 0.0493 | 0.0004 | 0.2299 | 0.0033 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.3 | 2.7 |
| PM104-1-7 | 627.1 | 1841.5 | 0.34 | 0.0507 | 0.0005 | 0.2366 | 0.0031 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 214.3 | 4.0 |
| PM104-1-8 | 1103.0 | 3219.6 | 0.34 | 0.0504 | 0.0004 | 0.2360 | 0.0035 | 0.0339 | 0.0004 | 214.1 | 2.0 |
| PM104-1-9 | 1196.8 | 2932.2 | 0.41 | 0.0521 | 0.0005 | 0.2432 | 0.0027 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 214.6 | 2.1 |
| PM104-1-10 | 521.3 | 2221.6 | 0.23 | 0.0506 | 0.0004 | 0.2360 | 0.0020 | 0.0338 | 0.0002 | 214.7 | 1.6 |
| PM104-1-11 | 922.1 | 2541.3 | 0.36 | 0.0505 | 0.0004 | 0.2359 | 0.0044 | 0.0338 | 0.0006 | 214.3 | 2.4 |
| PM104-1-12 | 799.2 | 2037.8 | 0.39 | 0.0540 | 0.0005 | 0.2524 | 0.0064 | 0.0338 | 0.0007 | 214.3 | 2.1 |
| PM104-1-13 | 549.3 | 1984.4 | 0.28 | 0.0522 | 0.0005 | 0.2436 | 0.0032 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.7 | 2.7 |
| PM104-1-14 | 974.7 | 2186.9 | 0.45 | 0.0495 | 0.0012 | 0.2309 | 0.0069 | 0.0337 | 0.0007 | 214.2 | 1.6 |
| PM104-1-15 | 588.1 | 2008.1 | 0.29 | 0.0501 | 0.0006 | 0.2351 | 0.0034 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.1 | 1.5 |
| PM104-1-16 | 465.0 | 1369.1 | 0.34 | 0.0491 | 0.0012 | 0.2296 | 0.0114 | 0.0336 | 0.0019 | 214.4 | 3.5 |
| PM104-1-17 | 1397.7 | 3039.6 | 0.46 | 0.0560 | 0.0007 | 0.2606 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0004 | 214.3 | 4.3 |
| PM104-1-18 | 737.0 | 2152.9 | 0.34 | 0.0494 | 0.0004 | 0.2302 | 0.0044 | 0.0338 | 0.0006 | 214.3 | 2.4 |
| PM104-1-19 | 244.9 | 399.3 | 0.61 | 0.0544 | 0.0007 | 0.2536 | 0.0041 | 0.0338 | 0.0003 | 213.4 | 4.1 |
| PM104-1-20 | 417.9 | 1199.3 | 0.35 | 0.0503 | 0.0005 | 0.2348 | 0.0027 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 214.0 | 2.6 |
| PM104-1-21 | 612.6 | 2305.6 | 0.27 | 0.0507 | 0.0003 | 0.2368 | 0.0024 | 0.0339 | 0.0003 | 213.2 | 11.8 |
| D1268-1 | 201.2 | 253.9 | 0.79 | 0.0507 | 0.0011 | 0.2247 | 0.0056 | 0.0321 | 0.0005 | 203.7 | 3.2 |
| D1268-2 | 336.2 | 414.8 | 0.81 | 0.0504 | 0.0008 | 0.2210 | 0.0041 | 0.0318 | 0.0004 | 201.7 | 2.8 |
| D1268-3 | 458.8 | 453.4 | 1.01 | 0.0490 | 0.0008 | 0.2235 | 0.0049 | 0.0330 | 0.0005 | 209.6 | 3.0 |
| D1268-4 | 133.4 | 164.1 | 0.81 | 0.0558 | 0.0045 | 0.2516 | 0.0247 | 0.0323 | 0.0005 | 204.7 | 3.3 |
| D1268-5 | 909.5 | 603.4 | 1.51 | 0.0554 | 0.0010 | 0.2465 | 0.0057 | 0.0322 | 0.0005 | 204.3 | 3.3 |
| D1268-6 | 199.8 | 284.5 | 0.70 | 0.0495 | 0.0010 | 0.2253 | 0.0057 | 0.0329 | 0.0007 | 208.8 | 4.1 |
| D1268-7 | 212.6 | 293.9 | 0.72 | 0.0484 | 0.0011 | 0.2240 | 0.0063 | 0.0334 | 0.0007 | 211.9 | 4.4 |
| D1268-8 | 696.6 | 604.3 | 1.15 | 0.0502 | 0.0010 | 0.2302 | 0.0053 | 0.0332 | 0.0006 | 210.3 | 3.4 |
| D1268-9 | 481.9 | 447.2 | 1.08 | 0.0498 | 0.0010 | 0.2272 | 0.0053 | 0.0330 | 0.0006 | 209.5 | 3.6 |
| D1268-10 | 399.8 | 369.9 | 1.08 | 0.0508 | 0.0010 | 0.2261 | 0.0052 | 0.0322 | 0.0005 | 204.6 | 3.3 |
| D1268-11 | 443.1 | 379.6 | 1.17 | 0.0498 | 0.0009 | 0.2220 | 0.0049 | 0.0323 | 0.0005 | 204.8 | 3.0 |
| D1268-12 | 169.5 | 201.0 | 0.84 | 0.0485 | 0.0013 | 0.2124 | 0.0057 | 0.0318 | 0.0005 | 201.9 | 3.1 |
| D1268-13 | 417.2 | 542.4 | 0.77 | 0.0496 | 0.0007 | 0.2211 | 0.0053 | 0.0323 | 0.0007 | 204.9 | 4.3 |
| D1268-14 | 164.4 | 197.8 | 0.83 | 0.0501 | 0.0015 | 0.2420 | 0.0069 | 0.0351 | 0.0004 | 222.2 | 2.3 |
| D1268-15 | 235.2 | 280.5 | 0.84 | 0.0512 | 0.0011 | 0.2278 | 0.0051 | 0.0323 | 0.0005 | 205.0 | 2.9 |
| D1268-16 | 1188.3 | 1037.2 | 1.15 | 0.0504 | 0.0006 | 0.2266 | 0.0044 | 0.0326 | 0.0004 | 206.7 | 2.5 |
| D1268-17 | 236.0 | 313.5 | 0.75 | 0.0502 | 0.0011 | 0.2327 | 0.0061 | 0.0336 | 0.0005 | 213.1 | 3.3 |
| D1268-18 | 401.6 | 501.5 | 0.80 | 0.0503 | 0.0010 | 0.2216 | 0.0046 | 0.0320 | 0.0004 | 202.8 | 2.3 |
| D1268-19 | 273.5 | 260.0 | 1.05 | 0.0517 | 0.0013 | 0.2345 | 0.0063 | 0.0329 | 0.0004 | 208.5 | 2.6 |
| D1268-20 | 300.2 | 355.9 | 0.84 | 0.0505 | 0.0014 | 0.2269 | 0.0070 | 0.0325 | 0.0003 | 206.2 | 1.9 |
| D1268-21 | 240.0 | 241.7 | 0.99 | 0.0508 | 0.0012 | 0.2402 | 0.0057 | 0.0343 | 0.0003 | 217.5 | 2.1 |

图5 南木林地区中酸性岩体锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图和206Pb/238U加权平均年龄 (a)花岗闪长岩年龄谐和图;(b)花岗闪长岩加权平均年龄图;(c)石英闪长岩年龄谐和图;(d)石英闪长岩加权平均年龄图
Fig.5 Zircon U-Pb concordia and weighted average age diagram for the Nanmulin intermediate-felsic rocks
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | TFeO | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM104-6H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 61.87 | 0.92 | 15.93 | 6.40 | 0.09 | 2.28 | 4.23 | 3.01 | 3.72 | 0.24 | 1.42 | 99.54 | 5.87 | 0.70 |
| PM104-3H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 62.85 | 0.85 | 15.82 | 6.03 | 0.09 | 2.20 | 4.05 | 3.35 | 3.59 | 0.22 | 1.05 | 99.59 | 5.51 | 0.90 |
| PM104-10H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 63.41 | 0.94 | 15.27 | 6.43 | 0.10 | 2.27 | 4.01 | 2.90 | 3.66 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 99.56 | 5.87 | 0.94 |
| PM104-1H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 64.46 | 0.73 | 15.22 | 5.72 | 0.09 | 2.02 | 3.43 | 3.24 | 4.25 | 0.22 | 0.75 | 99.60 | 5.21 | 0.65 |
| D9015H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 68.24 | 0.41 | 15.01 | 4.35 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 1.14 | 4.48 | 3.68 | 0.13 | 1.65 | 99.76 | 3.99 | 1.54 |
| PM104-D0001H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 73.72 | 0.28 | 13.37 | 2.21 | 0.05 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 3.92 | 4.18 | 0.07 | 1.03 | 99.91 | 2.01 | 0.73 |
| D1267H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 53.09 | 1.71 | 17.57 | 9.01 | 0.14 | 3.78 | 6.63 | 3.36 | 2.91 | 0.34 | 1.51 | 99.33 | 8.30 | 1.84 |
| D1268H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 53.53 | 1.76 | 15.23 | 9.61 | 0.16 | 5.36 | 7.84 | 2.77 | 1.23 | 0.12 | 2.45 | 99.27 | 8.94 | 1.80 |
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| PM104-6H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 53.67 | 116.95 | 13.18 | 41.46 | 6.89 | 1.55 | 6.82 | 0.91 | 4.31 | 0.78 | 2.21 | 0.28 | 1.70 | 0.25 |
| PM104-3H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 43.28 | 96.40 | 11.42 | 37.31 | 6.78 | 1.47 | 6.55 | 1.00 | 5.79 | 1.16 | 3.49 | 0.56 | 3.54 | 0.55 |
| PM104-10H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 53.38 | 114.98 | 13.31 | 42.88 | 7.24 | 1.59 | 7.42 | 1.03 | 5.36 | 1.00 | 2.71 | 0.37 | 2.42 | 0.31 |
| PM104-1H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 49.37 | 108.45 | 12.62 | 40.15 | 7.10 | 1.33 | 7.00 | 1.04 | 5.40 | 1.00 | 2.93 | 0.40 | 2.59 | 0.39 |
| D9015H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 30.78 | 71.48 | 9.58 | 32.44 | 6.26 | 1.31 | 5.51 | 0.86 | 4.60 | 0.83 | 2.32 | 0.34 | 1.89 | 0.26 |
| PM104-D0001H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 31.19 | 65.77 | 7.44 | 23.22 | 4.25 | 0.88 | 4.08 | 0.60 | 3.39 | 0.70 | 2.09 | 0.32 | 2.21 | 0.33 |
| D1267H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 33.34 | 75.6 | 9.25 | 32.49 | 6.48 | 2.04 | 6.24 | 0.88 | 4.65 | 0.81 | 2.23 | 0.31 | 1.95 | 0.26 |
| D1268H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 19.77 | 42.41 | 5.32 | 18.89 | 4.03 | 1.40 | 4.39 | 0.67 | 3.69 | 0.68 | 1.90 | 0.28 | 1.87 | 0.26 |
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Nb | Ta | Hf | Y | Th | U | FeO | A/CNK | A/NK | δEu |
| PM104-6H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 105.0 | 215.0 | 569.0 | 327.00 | 18.10 | 1.45 | 6.74 | 20.13 | 27.90 | 3.42 | 5.13 | 0.96 | 1.77 | 0.68 |
| PM104-3H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 175.0 | 230.0 | 522.0 | 293.00 | 18.20 | 3.20 | 7.12 | 32.78 | 28.00 | 4.78 | 4.62 | 0.94 | 1.68 | 0.67 |
| PM104-10H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 133.0 | 196.0 | 497.0 | 343.00 | 20.30 | 1.91 | 7.04 | 24.74 | 28.70 | 3.03 | 4.94 | 0.95 | 1.75 | 0.66 |
| PM104-1H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 220.0 | 162.0 | 575.0 | 284.00 | 23.30 | 2.78 | 5.60 | 27.19 | 26.10 | 5.14 | 4.56 | 0.94 | 1.53 | 0.57 |
| D9015H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 116.4 | 175.4 | 654.2 | 257.27 | 12.14 | 1.01 | 6.76 | 21.03 | 11.72 | 1.41 | 2.53 | 1.12 | 1.32 | 0.67 |
| PM104-D0001H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 110.1 | 150.4 | 533.4 | 135.65 | 6.59 | 0.97 | 4.49 | 18.97 | 14.67 | 1.53 | 1.33 | 1.09 | 1.22 | 0.64 |
| D1267H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 53.07 | 347.9 | 643.9 | 299.00 | 22.76 | 1.65 | 6.50 | 21.44 | 11.07 | 1.80 | 6.46 | 0.85 | 2.03 | 0.97 |
| D1268H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 19.07 | 318.6 | 274.1 | 119.38 | 11.85 | 1.16 | 3.28 | 17.98 | 8.46 | 2.83 | 7.03 | 0.76 | 2.59 | 1.01 |
表2 南木林晚三叠世岩体主量元素(%)、稀土和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Compositions of major elements (%), REE and trace elements (10-6) of the Late Triassic Nanmulin rocks
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | TFeO | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM104-6H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 61.87 | 0.92 | 15.93 | 6.40 | 0.09 | 2.28 | 4.23 | 3.01 | 3.72 | 0.24 | 1.42 | 99.54 | 5.87 | 0.70 |
| PM104-3H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 62.85 | 0.85 | 15.82 | 6.03 | 0.09 | 2.20 | 4.05 | 3.35 | 3.59 | 0.22 | 1.05 | 99.59 | 5.51 | 0.90 |
| PM104-10H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 63.41 | 0.94 | 15.27 | 6.43 | 0.10 | 2.27 | 4.01 | 2.90 | 3.66 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 99.56 | 5.87 | 0.94 |
| PM104-1H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 64.46 | 0.73 | 15.22 | 5.72 | 0.09 | 2.02 | 3.43 | 3.24 | 4.25 | 0.22 | 0.75 | 99.60 | 5.21 | 0.65 |
| D9015H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 68.24 | 0.41 | 15.01 | 4.35 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 1.14 | 4.48 | 3.68 | 0.13 | 1.65 | 99.76 | 3.99 | 1.54 |
| PM104-D0001H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 73.72 | 0.28 | 13.37 | 2.21 | 0.05 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 3.92 | 4.18 | 0.07 | 1.03 | 99.91 | 2.01 | 0.73 |
| D1267H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 53.09 | 1.71 | 17.57 | 9.01 | 0.14 | 3.78 | 6.63 | 3.36 | 2.91 | 0.34 | 1.51 | 99.33 | 8.30 | 1.84 |
| D1268H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 53.53 | 1.76 | 15.23 | 9.61 | 0.16 | 5.36 | 7.84 | 2.77 | 1.23 | 0.12 | 2.45 | 99.27 | 8.94 | 1.80 |
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| PM104-6H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 53.67 | 116.95 | 13.18 | 41.46 | 6.89 | 1.55 | 6.82 | 0.91 | 4.31 | 0.78 | 2.21 | 0.28 | 1.70 | 0.25 |
| PM104-3H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 43.28 | 96.40 | 11.42 | 37.31 | 6.78 | 1.47 | 6.55 | 1.00 | 5.79 | 1.16 | 3.49 | 0.56 | 3.54 | 0.55 |
| PM104-10H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 53.38 | 114.98 | 13.31 | 42.88 | 7.24 | 1.59 | 7.42 | 1.03 | 5.36 | 1.00 | 2.71 | 0.37 | 2.42 | 0.31 |
| PM104-1H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 49.37 | 108.45 | 12.62 | 40.15 | 7.10 | 1.33 | 7.00 | 1.04 | 5.40 | 1.00 | 2.93 | 0.40 | 2.59 | 0.39 |
| D9015H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 30.78 | 71.48 | 9.58 | 32.44 | 6.26 | 1.31 | 5.51 | 0.86 | 4.60 | 0.83 | 2.32 | 0.34 | 1.89 | 0.26 |
| PM104-D0001H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 31.19 | 65.77 | 7.44 | 23.22 | 4.25 | 0.88 | 4.08 | 0.60 | 3.39 | 0.70 | 2.09 | 0.32 | 2.21 | 0.33 |
| D1267H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 33.34 | 75.6 | 9.25 | 32.49 | 6.48 | 2.04 | 6.24 | 0.88 | 4.65 | 0.81 | 2.23 | 0.31 | 1.95 | 0.26 |
| D1268H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 19.77 | 42.41 | 5.32 | 18.89 | 4.03 | 1.40 | 4.39 | 0.67 | 3.69 | 0.68 | 1.90 | 0.28 | 1.87 | 0.26 |
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Nb | Ta | Hf | Y | Th | U | FeO | A/CNK | A/NK | δEu |
| PM104-6H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 105.0 | 215.0 | 569.0 | 327.00 | 18.10 | 1.45 | 6.74 | 20.13 | 27.90 | 3.42 | 5.13 | 0.96 | 1.77 | 0.68 |
| PM104-3H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 175.0 | 230.0 | 522.0 | 293.00 | 18.20 | 3.20 | 7.12 | 32.78 | 28.00 | 4.78 | 4.62 | 0.94 | 1.68 | 0.67 |
| PM104-10H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 133.0 | 196.0 | 497.0 | 343.00 | 20.30 | 1.91 | 7.04 | 24.74 | 28.70 | 3.03 | 4.94 | 0.95 | 1.75 | 0.66 |
| PM104-1H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 220.0 | 162.0 | 575.0 | 284.00 | 23.30 | 2.78 | 5.60 | 27.19 | 26.10 | 5.14 | 4.56 | 0.94 | 1.53 | 0.57 |
| D9015H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 116.4 | 175.4 | 654.2 | 257.27 | 12.14 | 1.01 | 6.76 | 21.03 | 11.72 | 1.41 | 2.53 | 1.12 | 1.32 | 0.67 |
| PM104-D0001H1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 110.1 | 150.4 | 533.4 | 135.65 | 6.59 | 0.97 | 4.49 | 18.97 | 14.67 | 1.53 | 1.33 | 1.09 | 1.22 | 0.64 |
| D1267H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 53.07 | 347.9 | 643.9 | 299.00 | 22.76 | 1.65 | 6.50 | 21.44 | 11.07 | 1.80 | 6.46 | 0.85 | 2.03 | 0.97 |
| D1268H1 | 石英闪长岩 | 19.07 | 318.6 | 274.1 | 119.38 | 11.85 | 1.16 | 3.28 | 17.98 | 8.46 | 2.83 | 7.03 | 0.76 | 2.59 | 1.01 |
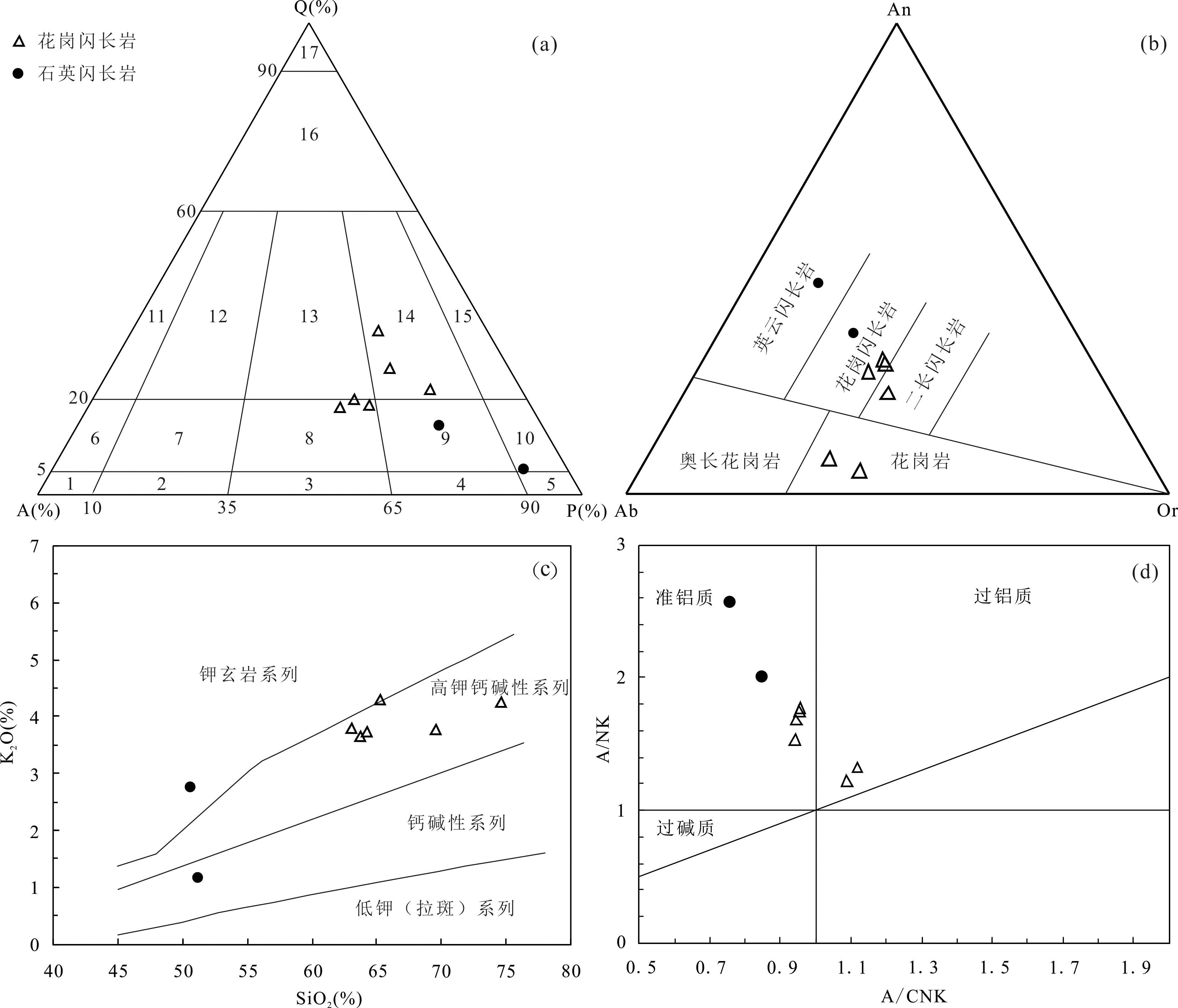
图6 南木林地区中酸性岩体Q-A-P(a)、An-Ab-Or分类图解(b)、SiO2-K2O(c)和A/CNK-A/NK(d)判别图解(下文图例同) 1.碱长正长岩;2.正长岩;3.二长岩;4.二长闪长岩;5.闪长岩;6.碱长石英正长岩;7.石英正长岩;8.石英二长岩;9.石英二长闪长岩;10.石英闪长岩、石英辉长岩、石英斜长岩;11.碱长花岗岩;12.花岗岩;13.花岗岩(二长花岗岩);14.花岗闪长岩;15.英云闪长岩、斜长花岗岩;16.富石英花岗岩;17.硅英岩
Fig.6 Q-A-P(a), An-Ab-Or (b), SiO2-K2O (c), and A/CNK-A/NK (d) diagrams for the Nanmulin intermediate-felsic rocks
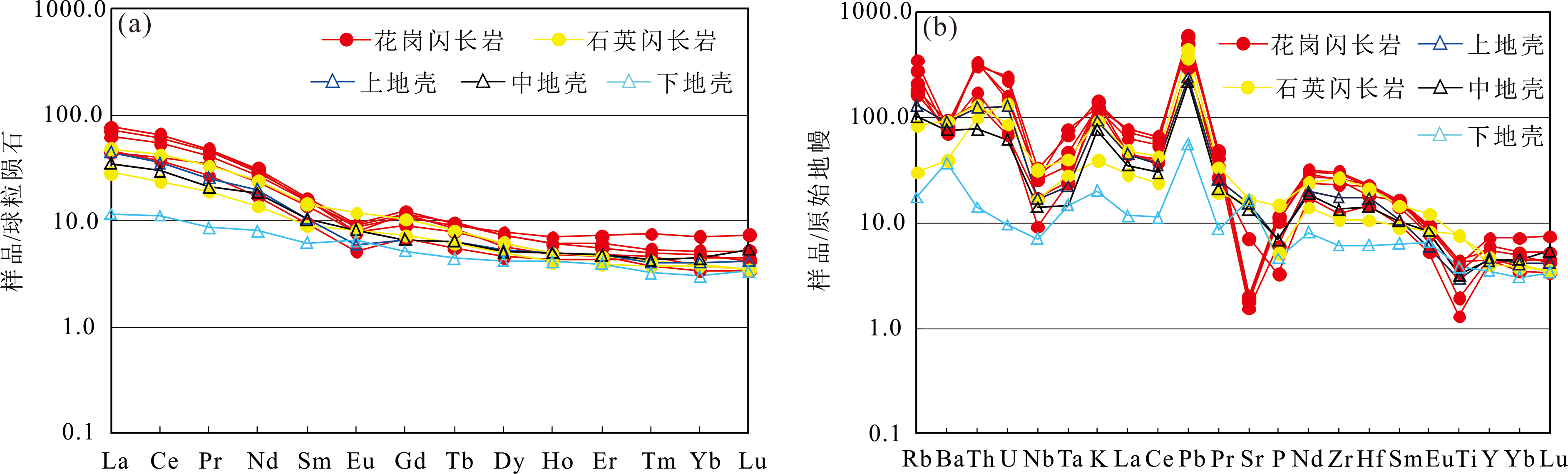
图7 南木林地区中酸性岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据文献[36-37])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element diagram (b) of the Nanmulin intermediate-felsic rocks (basemap after refs. [36-37])
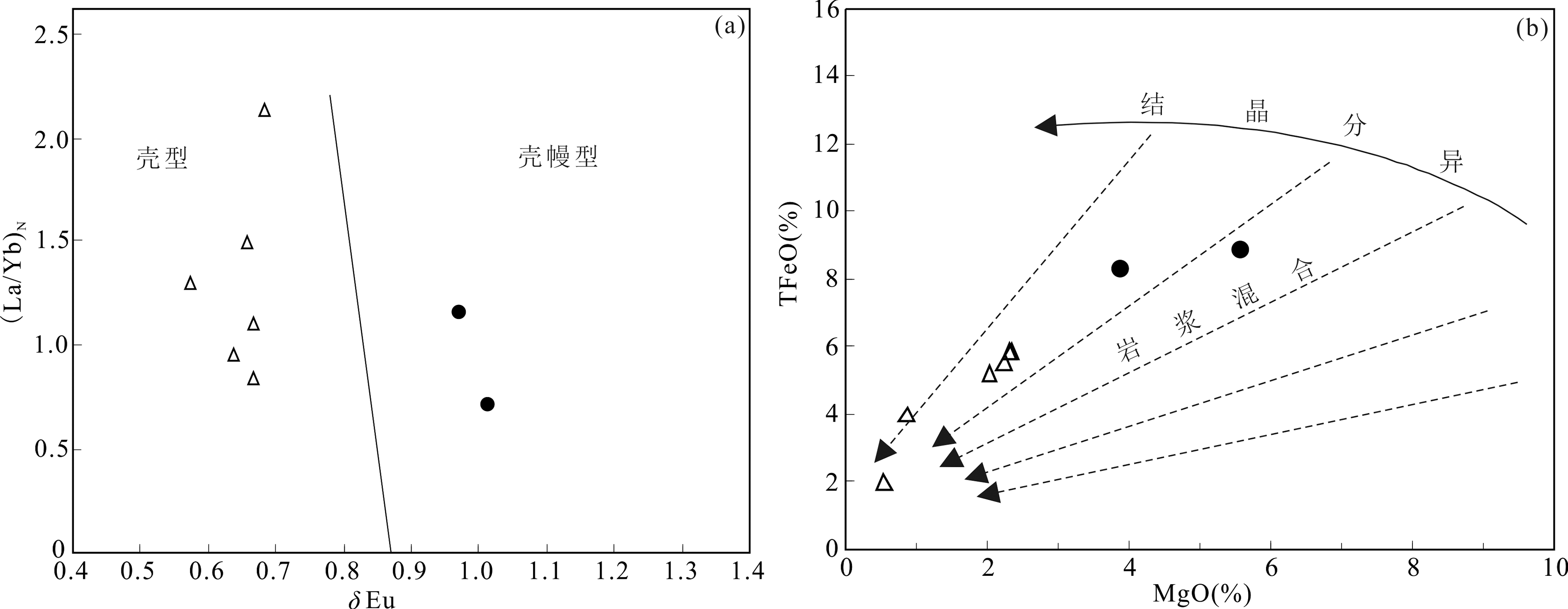
图8 南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩体δEu-(La/Yb)N(a)和MgO-TFeO(b)图解(底图据文献[51])
Fig.8 δEu vs. (La/Yb)N(a) and MgO vs. ΤFeO (b) diagrams of the Late Triassic Nanmulin intermediate-felsic rocks (basemap after ref. [51])
| [1] | 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):521-533. |
| [2] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 印度—亚洲碰撞大地构造[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(1):1-33. |
| [3] |
YIN A. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2006, 76(1/2): 1-131.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KAPP P, DECELLES P G. Mesozoic-Cenozoic geological evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen and working tectonic hypotheses[J]. American Journal of Science, 2019, 319(3): 159-254.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 莫宣学, 董国臣, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏冈底斯带花岗岩的时空分布特征及地壳生长演化信息[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3):281-290. |
| [6] | 许志琴, 姜枚, 杨经绥, 等. 青藏高原的地幔结构:地幔羽、地幔剪切带及岩石圈俯冲板片的拆沉[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4):329-343. |
| [7] |
PAN G T, WANG L Q, LI R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the qinghai-tibet plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 3-14.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 吴福元, 黄宝春, 叶凯, 等. 青藏高原造山带的垮塌与高原隆升[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(1):1-30. |
| [9] | DING L, KAPP P, WAN X Q. Paleocene-Eocene record of ophiolite obduction and initial India-Asia collision,south central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2005, 24(3): TC3001. |
| [10] | 韩飞, 黄永高, 李应栩, 等. 西藏冈底斯中段南木林地区始新世岩浆作用的厘定及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(9):1403-1416. |
| [11] | 朱弟成, 王青, 赵志丹. 岩浆岩定量限定陆-陆碰撞时间和过程的方法和实例[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(6):657-673. |
| [12] | 李才, 董永胜, 翟庆国, 等. 青藏高原羌塘高压变质带的特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(1):27-35. |
| [13] | 李才, 王天武, 李惠民, 等. 冈底斯地区发现印支期巨斑花岗闪长岩——古冈底斯造山的存在证据[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(5):364-366. |
| [14] | 张宏飞, 徐旺春, 郭建秋, 等. 冈底斯南缘变形花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成:新特提斯洋早侏罗世俯冲作用的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1347-1353. |
| [15] | 水新芳, 贺振宇, 张泽明, 等. 西藏冈底斯带东段早侏罗世英云闪长岩的岩浆起源及其对拉萨地体地壳演化的意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(11):3129-3152. |
| [16] | 王旭辉, 郎兴海, 邓煜霖, 等. 西藏冈底斯南缘汤白斑状花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(1):41-55. |
| [17] | 宋绍玮, 刘泽, 朱弟成, 等. 西藏打加错晚三叠世安山质岩浆作用的锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(10):3100-3112. |
| [18] |
朱弟成, 王青, 赵志丹, 等. 大陆边缘弧岩浆成因与大陆地壳形成[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(6):67-77.
DOI |
| [19] | 刘洪, 张林奎, 黄瀚霄, 等. 西藏冈底斯西段鲁尔玛晚三叠世二长闪长岩的成因[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(7):2339-2356. |
| [20] | 和钟铧, 杨德明, 郑常青, 等. 西藏冈底斯带门巴地区印支期花岗岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(4):354-359. |
| [21] | 杨志明, 侯增谦, 江迎飞, 等. 西藏驱龙矿区早侏罗世斑岩的Sr-Nd-Pb及锆石Hf同位素研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7):2003-2010. |
| [22] | 唐菊兴, 黎风佶, 李志军, 等. 西藏谢通门县雄村铜金矿主要地质体形成的时限:锆石U-Pb、辉钼矿Re-Os年龄的证据[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(3):461-475. |
| [23] | 黄瀚霄, 张林奎, 刘洪, 等. 西藏冈底斯成矿带西段矿床类型、成矿作用和找矿方向[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(6):1876-1887. |
| [24] |
LIU H, LI G M, HUANG H X, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous Jiangla’angzong I-type granite in central Lhasa terrane, Tibet,China:Constraints from whole-rock geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(4):1396-1414.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MENG Y K, DONG H W, CONG Y, et al. The early-stage evolution of the Neo-Tethys Ocean: Evidence from granitoids in the middle Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2016, 94/95: 34-49.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 纪伟强. 藏南冈底斯岩基东段花岗岩时代与成因[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2010. |
| [27] |
GUO L S, LIU Y L, LIU S W, et al. Petrogenesis of Early to Middle Jurassic granitoid rocks from the Gangdese belt, Southern Tibet:Implications for early history of the Neo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2013, 179: 320-333.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHU D C, ZHAO Z D, NIU Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane:Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1/2): 241-255.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHANG Z M, DONG X, SANTOSH M, et al. Metamorphism and tectonic evolution of the Lhasa terrane,Central Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(1): 170-189.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 董昕, 张泽明. 拉萨地体南部早侏罗世岩浆岩的成因和构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(6):1933-1948. |
| [31] | 李应栩, 李光明, 黄永高, 等. 西藏中冈底斯成矿带晚三叠世铍铷稀有金属矿化:独居石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(7):2379-2393. |
| [32] |
HAN Y G, ZHANG S H, PIRAJNO F, et al. Evolution of the Mesozoic granites in the Xiong’ershan-Waifangshan region, western Henan Province, China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(2): 253-265.
DOI URL |
| [33] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00, A Geochronologi-cal Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geo-chronological Center Special Publication, 2003: 25-27. |
| [34] |
HOSKIN P W O. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 27-62.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WU Y B, ZHENG Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15):1554-1569.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
MCDONOUGH W F, SUN S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223-253.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 孟元库, 许志琴, 徐扬, 等. 藏南冈底斯带中段早侏罗世岩浆作用的厘定及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(6):1196-1215. |
| [39] | 高强, 闫茂强, 魏俊浩, 等. 西藏切琼地区钾长花岗岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(11):3272-3292. |
| [40] | 西藏自治区地矿局. 西藏自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993:1-50. |
| [41] |
GUYNN J H, KAPP P, PULLEN A, et al. Tibetan basement rocks near Amdo reveal “missing” Mesozoic tectonism along the Bangong suture,central Tibet[J]. Geology, 2006, 34(6): 505.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
RAPP R P, WATSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
HARRIS N B W, INGER S. Trace element modelling of pelite-derived granites[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1992, 110(1): 46-56.
DOI URL |
| [44] | COLEMAN R G, DONATO M M. Oceanic plagiogranite revisited[M]// Developments in Petrology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1979: 149-168. |
| [45] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
BEA F, ARZAMASTSEV A, MONTERO P, et al. Anomalous alkaline rocks of Soustov,Kola:Evidence of mantle-derived metasomatic fluids affecting crustal materials[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2001, 140(5): 554-566.
DOI URL |
| [47] | KELEMEN P B, HANGHØJ K, GREENE A R. One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[M]// Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 749-806. |
| [48] | 钟华明, 童劲松, 鲁如魁, 等. 西藏日土县松西地区过铝质花岗岩的地球化学特征及构造背景[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2):183-188. |
| [49] |
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
WOLF M B, LONDON D. Apatite dissolution into peraluminous haplogranitic melts: An experimental study of solubilities and mechanisms[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(19): 4127-4145.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
ZORPI M J, COULON C, ORSINI J B. Hybridization between felsic and mafic magmas in calc-alkaline granitoids—a case study in northern Sardinia, Italy[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 92(1/2/3): 45-86.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
PITCHER W S. The nature ascent and emplacement of granitic magmas[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1979, 136(6): 627-662.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 董国臣, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 冈底斯岩浆带中段岩浆混合作用:来自花岗杂岩的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(4):835-844. |
| [54] |
GORTON M P, SCHANDL E S. From continents to island arcs: A geochemical index of tectonic setting for arc-related and within-plate felsic to intermediate volcanic rocks[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2000, 38(5): 1065-1073.
DOI URL |
| [55] | 陈耀飞, 侯恩刚, 高金汉, 等. 西藏荣玛地区上三叠统日干配错组沉积环境及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(1):48-57. |
| [56] | 朱杰, 刘早学, 杜远生, 等. 拉孜县幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(增):471-474. |
| [57] | 朱杰, 杜远生, 刘早学, 等. 西藏雅鲁藏布江缝合带中段中生代放射虫硅质岩成因及其大地构造意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2005, 35(12):1131-1139. |
| [58] | 高洪学, 李海平, 周青山. 雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩地层新知[J]. 中国区域地质, 1993(3):282. |
| [59] |
JU Q, ZHANG Y C, QIAO F, et al. A Middle Permian assemblage of smaller foraminifera (Shanita-Hemigordiopsis assemblage) from the central Lhasa Block and its paleobiogeographic implications[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 572: 110417.
DOI URL |
| [60] | 郑来林, 廖光宇, 耿全如, 等. 墨脱县幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(增):458-462. |
| [61] | 尹集祥, 徐均涛, 刘成杰, 等. 拉萨至格尔木的区域地层:青藏高原地质演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990:1-49. |
| [62] | 曲永贵, 王永胜, 张树岐, 等. 西藏申扎地区晚三叠世多布日组地层剖面的启示: 对冈底斯印支运动的地层学制约[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(7):470-473. |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [5] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [6] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [7] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [8] | 杨文鹏, 李成禄, 杨元江, 符安宗, 郑博, 周腾飞, 赵瑞君. 黑龙江塔溪地区中侏罗世侵入岩地球化学特征、成因及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 390-403. |
| [9] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [10] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [11] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| [12] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [13] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [14] | 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 王建田, 王利鹏, 赵鹏飞. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 876-897. |
| [15] | 刘建栋, 李五福, 王国良, 董进生, 曹锦山, 李红刚, 赵忠国. 北祁连东段柏木峡—门岗峡地区蛇绿岩的识别及其区域构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 244-258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||