



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (02): 375-389.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.027
邓科1( ), 王金贵2(
), 王金贵2( ), 董玉杰1, 何林武1, 袁仁华1, 张泽国1, 陈守关1, 辛堂1
), 董玉杰1, 何林武1, 袁仁华1, 张泽国1, 陈守关1, 辛堂1
收稿日期:2021-04-07
修回日期:2022-03-21
出版日期:2023-04-10
发布日期:2023-05-23
通讯作者:
王金贵
作者简介:王金贵,男,高级工程师,1986年出生,构造地质学专业,主要从事区域地质调查与研究工作。Email:airstarry@163.com。基金资助:
DENG Ke1( ), WANG Jingui2(
), WANG Jingui2( ), DONG Yujie1, HE Linwu1, YUAN Renhua1, ZHANG Zeguo1, CHEN Shouguan1, XIN Tang1
), DONG Yujie1, HE Linwu1, YUAN Renhua1, ZHANG Zeguo1, CHEN Shouguan1, XIN Tang1
Received:2021-04-07
Revised:2022-03-21
Online:2023-04-10
Published:2023-05-23
Contact:
WANG Jingui
摘要:
冈底斯岩浆岩带呈近东西向沿雅鲁藏布江缝合带分布,是一条巨大的构造—岩浆岩带。南冈底斯中生代的岩浆活动经历了205~152 Ma、109~80 Ma、65~41 Ma和33~13 Ma 4个阶段,均是挤压环境的产物。但其触发机制一直存在争议。争议的焦点在于新特提斯洋和班公湖—怒江洋的俯冲方式。为解释冈底斯南缘中生代中酸性岩浆岩的成因及构造环境,本文以西藏自治区扎囊县桑耶地区的石英二长岩为研究对象,通过年代学、岩石地球化学、Lu-Hf同位素分析岩浆起源、岩石成因及其构造环境。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,岩体形成于晚白垩世(91~88 Ma)。岩石地球化学分析揭示其属准铝质高钾钙碱性系列,富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素和重稀土元素,无明显Eu负异常,锆石εHf(t)值为+10.6~+14.2。石英二长岩形成于斜长石和石榴石的过渡带,岩浆经历了角闪石、磷灰石及黑云母的分离结晶作用。其典型的微量元素比值特征指示岩浆来源于年轻俯冲洋壳的部分熔融,并有少量新生幔源物质加入,具典型的I型花岗岩特征,推断其形成于俯冲岛弧环境,表明晚白垩世时期冈底斯南缘处于新特提斯板块向北俯冲的构造背景之下。
中图分类号:
邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389.
DENG Ke, WANG Jingui, DONG Yujie, HE Linwu, YUAN Renhua, ZHANG Zeguo, CHEN Shouguan, XIN Tang. Genesis and Geological Significance of Late Cretaceous Intermediate Intrusions in Sangye, Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 375-389.

图1 冈底斯岩浆岩分布图(a)和研究区地质图(b)(据Zhu等[16]) 1. 晚全新世冲洪积物; 2. 中三叠统昌果组二段;3. 中三叠统昌果组一段; 4. 晚白垩世石英闪长岩;5. 晚白垩世二长岩、石英二长岩;6. 晚白垩世二长花岗岩;7. 晚白垩世花岗闪长岩;8. 测年样品位置;BNSZ.班公湖—怒江缝合带;LMF.洛巴堆—米拉山断裂带
Fig.1 Distribution of the Gangdese magmatic belt (a) and geological map of the study area (b) (after Zhu et al[16])

图2 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩野外及镜下显微照片 (a)(b) 野外宏观产出照片;(c)(d) 石英二长岩的镜下照片(正交偏光);Pl.斜长石;Kf.钾长石;Hb.角闪石;Qtz.石英
Fig.2 Field and microscopic photographs of the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet
| 测点号 | wB(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | ||||
| PM20-2 | 2.78 | 193.44 | 140.09 | 1.38 | 0.0507 | 0.0035 | 0.0974 | 0.0069 | 0.0140 | 0.00024 | 94.36 | 6.36 | 89.89 | 1.50 | ||
| PM20-3 | 1.85 | 112.68 | 103.95 | 1.08 | 0.0515 | 0.0054 | 0.0949 | 0.0098 | 0.0134 | 0.00031 | 92.10 | 9.12 | 86.10 | 2.00 | ||
| PM20-4 | 2.63 | 179.33 | 134.17 | 1.34 | 0.0555 | 0.0038 | 0.1026 | 0.0067 | 0.0138 | 0.00025 | 99.17 | 6.14 | 88.17 | 1.60 | ||
| PM20-5 | 2.19 | 142.37 | 121.19 | 1.17 | 0.0502 | 0.0044 | 0.0911 | 0.0077 | 0.0137 | 0.00042 | 88.55 | 7.18 | 87.69 | 2.68 | ||
| PM20-6 | 2.84 | 200.38 | 145.30 | 1.38 | 0.0477 | 0.0048 | 0.0908 | 0.0102 | 0.0135 | 0.00031 | 88.25 | 9.45 | 86.34 | 1.99 | ||
| PM20-7 | 2.93 | 199.68 | 147.58 | 1.35 | 0.0475 | 0.0039 | 0.0897 | 0.0074 | 0.0138 | 0.00025 | 87.18 | 6.93 | 88.10 | 1.59 | ||
| PM20-8 | 2.22 | 131.00 | 116.84 | 1.12 | 0.0539 | 0.0043 | 0.0978 | 0.0072 | 0.0138 | 0.00032 | 94.74 | 6.62 | 88.28 | 2.04 | ||
| PM20-9 | 2.34 | 157.27 | 125.17 | 1.26 | 0.0499 | 0.0050 | 0.0877 | 0.0080 | 0.0133 | 0.00031 | 85.33 | 7.47 | 85.34 | 2.00 | ||
| PM20-10 | 1.65 | 82.18 | 93.48 | 0.88 | 0.0506 | 0.0047 | 0.0910 | 0.0076 | 0.0137 | 0.00033 | 88.47 | 7.09 | 87.71 | 2.13 | ||
| PM20-11 | 2.97 | 202.83 | 150.93 | 1.34 | 0.0477 | 0.0033 | 0.0905 | 0.0065 | 0.0138 | 0.00027 | 87.94 | 6.09 | 88.06 | 1.74 | ||
| PM20-13 | 2.62 | 138.21 | 142.45 | 0.97 | 0.0460 | 0.0042 | 0.0868 | 0.0077 | 0.0139 | 0.00031 | 84.53 | 7.24 | 88.98 | 2.00 | ||
| PM20-15 | 2.80 | 196.74 | 144.21 | 1.36 | 0.0524 | 0.0059 | 0.0965 | 0.0104 | 0.0135 | 0.00033 | 93.59 | 9.63 | 86.31 | 2.07 | ||
| PM20-16 | 3.71 | 257.38 | 190.42 | 1.35 | 0.0524 | 0.0041 | 0.1017 | 0.0078 | 0.0141 | 0.00026 | 98.32 | 7.18 | 90.47 | 1.68 | ||
| PM20-17 | 3.30 | 228.79 | 168.25 | 1.36 | 0.0529 | 0.0037 | 0.0989 | 0.0068 | 0.0138 | 0.00026 | 95.73 | 6.25 | 88.31 | 1.66 | ||
| PM20-18 | 2.72 | 176.74 | 142.19 | 1.24 | 0.0498 | 0.0042 | 0.0929 | 0.0074 | 0.0140 | 0.00044 | 90.19 | 6.91 | 89.87 | 2.80 | ||
| PM20-21 | 3.19 | 214.30 | 164.84 | 1.30 | 0.0533 | 0.0040 | 0.0993 | 0.0072 | 0.0139 | 0.00024 | 96.15 | 6.69 | 88.93 | 1.50 | ||
| PM20-23 | 2.58 | 172.68 | 134.71 | 1.28 | 0.0505 | 0.0039 | 0.0938 | 0.0067 | 0.0138 | 0.00029 | 91.00 | 6.19 | 88.59 | 1.85 | ||
| PM20-24 | 1.82 | 94.76 | 96.28 | 0.98 | 0.0516 | 0.0064 | 0.1003 | 0.0130 | 0.0141 | 0.00037 | 97.06 | 11.95 | 90.01 | 2.33 | ||
| PM20-25 | 2.24 | 145.18 | 124.39 | 1.17 | 0.0511 | 0.0060 | 0.0930 | 0.0101 | 0.0134 | 0.00036 | 90.32 | 9.38 | 86.01 | 2.32 | ||
| PM06-1 | 3.10 | 158.02 | 156.18 | 1.01 | 0.0448 | 0.0040 | 0.0879 | 0.0074 | 0.0148 | 0.00043 | 85.57 | 6.91 | 94.77 | 2.71 | ||
| PM06-3 | 3.91 | 191.79 | 194.27 | 0.99 | 0.0490 | 0.0051 | 0.0904 | 0.0087 | 0.0137 | 0.00030 | 87.88 | 8.08 | 87.65 | 1.88 | ||
| PM06-4 | 19.87 | 135.53 | 1318.74 | 0.10 | 0.0505 | 0.0025 | 0.0931 | 0.0043 | 0.0135 | 0.00022 | 90.40 | 4.03 | 86.47 | 1.42 | ||
| PM06-5 | 2.60 | 119.40 | 129.67 | 0.92 | 0.0582 | 0.0058 | 0.1078 | 0.0093 | 0.0138 | 0.00038 | 103.91 | 8.54 | 88.37 | 2.44 | ||
| PM06-6 | 4.48 | 237.46 | 211.82 | 1.12 | 0.0394 | 0.0088 | 0.0770 | 0.0160 | 0.0145 | 0.00046 | 75.36 | 15.05 | 93.03 | 2.94 | ||
| PM06-9 | 3.96 | 162.09 | 183.94 | 0.88 | 0.0647 | 0.0069 | 0.1222 | 0.0126 | 0.0145 | 0.00042 | 117.07 | 11.36 | 92.86 | 2.68 | ||
| PM06-10 | 2.45 | 103.61 | 112.43 | 0.92 | 0.0553 | 0.0070 | 0.1131 | 0.0145 | 0.0148 | 0.00049 | 108.78 | 13.24 | 94.45 | 3.09 | ||
| PM06-12 | 2.93 | 133.39 | 136.40 | 0.98 | 0.0686 | 0.0053 | 0.1328 | 0.0095 | 0.0150 | 0.00046 | 126.61 | 8.50 | 96.09 | 2.94 | ||
| PM06-15 | 4.90 | 246.13 | 220.04 | 1.12 | 0.0550 | 0.0049 | 0.1081 | 0.0094 | 0.0147 | 0.00038 | 104.23 | 8.60 | 94.08 | 2.43 | ||
| PM06-16 | 2.39 | 111.39 | 104.36 | 1.07 | 0.0494 | 0.0093 | 0.0943 | 0.0156 | 0.0151 | 0.00061 | 91.52 | 14.48 | 96.69 | 3.88 | ||
| PM06-17 | 4.05 | 158.08 | 199.89 | 0.79 | 0.0586 | 0.0049 | 0.1124 | 0.0080 | 0.0144 | 0.00039 | 108.18 | 7.34 | 92.03 | 2.48 | ||
| PM06-18 | 2.25 | 100.52 | 100.52 | 1.00 | 0.0567 | 0.0058 | 0.1148 | 0.0106 | 0.0150 | 0.00043 | 110.36 | 9.70 | 96.26 | 2.72 | ||
| PM06-19 | 3.72 | 167.03 | 173.58 | 0.96 | 0.0664 | 0.0056 | 0.1229 | 0.0106 | 0.0142 | 0.00034 | 117.71 | 9.61 | 91.03 | 2.18 | ||
| PM06-20 | 2.54 | 113.78 | 121.06 | 0.94 | 0.0456 | 0.0046 | 0.0879 | 0.0088 | 0.0143 | 0.00037 | 85.58 | 8.17 | 91.67 | 2.35 | ||
表1 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results for the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet
| 测点号 | wB(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | ||||
| PM20-2 | 2.78 | 193.44 | 140.09 | 1.38 | 0.0507 | 0.0035 | 0.0974 | 0.0069 | 0.0140 | 0.00024 | 94.36 | 6.36 | 89.89 | 1.50 | ||
| PM20-3 | 1.85 | 112.68 | 103.95 | 1.08 | 0.0515 | 0.0054 | 0.0949 | 0.0098 | 0.0134 | 0.00031 | 92.10 | 9.12 | 86.10 | 2.00 | ||
| PM20-4 | 2.63 | 179.33 | 134.17 | 1.34 | 0.0555 | 0.0038 | 0.1026 | 0.0067 | 0.0138 | 0.00025 | 99.17 | 6.14 | 88.17 | 1.60 | ||
| PM20-5 | 2.19 | 142.37 | 121.19 | 1.17 | 0.0502 | 0.0044 | 0.0911 | 0.0077 | 0.0137 | 0.00042 | 88.55 | 7.18 | 87.69 | 2.68 | ||
| PM20-6 | 2.84 | 200.38 | 145.30 | 1.38 | 0.0477 | 0.0048 | 0.0908 | 0.0102 | 0.0135 | 0.00031 | 88.25 | 9.45 | 86.34 | 1.99 | ||
| PM20-7 | 2.93 | 199.68 | 147.58 | 1.35 | 0.0475 | 0.0039 | 0.0897 | 0.0074 | 0.0138 | 0.00025 | 87.18 | 6.93 | 88.10 | 1.59 | ||
| PM20-8 | 2.22 | 131.00 | 116.84 | 1.12 | 0.0539 | 0.0043 | 0.0978 | 0.0072 | 0.0138 | 0.00032 | 94.74 | 6.62 | 88.28 | 2.04 | ||
| PM20-9 | 2.34 | 157.27 | 125.17 | 1.26 | 0.0499 | 0.0050 | 0.0877 | 0.0080 | 0.0133 | 0.00031 | 85.33 | 7.47 | 85.34 | 2.00 | ||
| PM20-10 | 1.65 | 82.18 | 93.48 | 0.88 | 0.0506 | 0.0047 | 0.0910 | 0.0076 | 0.0137 | 0.00033 | 88.47 | 7.09 | 87.71 | 2.13 | ||
| PM20-11 | 2.97 | 202.83 | 150.93 | 1.34 | 0.0477 | 0.0033 | 0.0905 | 0.0065 | 0.0138 | 0.00027 | 87.94 | 6.09 | 88.06 | 1.74 | ||
| PM20-13 | 2.62 | 138.21 | 142.45 | 0.97 | 0.0460 | 0.0042 | 0.0868 | 0.0077 | 0.0139 | 0.00031 | 84.53 | 7.24 | 88.98 | 2.00 | ||
| PM20-15 | 2.80 | 196.74 | 144.21 | 1.36 | 0.0524 | 0.0059 | 0.0965 | 0.0104 | 0.0135 | 0.00033 | 93.59 | 9.63 | 86.31 | 2.07 | ||
| PM20-16 | 3.71 | 257.38 | 190.42 | 1.35 | 0.0524 | 0.0041 | 0.1017 | 0.0078 | 0.0141 | 0.00026 | 98.32 | 7.18 | 90.47 | 1.68 | ||
| PM20-17 | 3.30 | 228.79 | 168.25 | 1.36 | 0.0529 | 0.0037 | 0.0989 | 0.0068 | 0.0138 | 0.00026 | 95.73 | 6.25 | 88.31 | 1.66 | ||
| PM20-18 | 2.72 | 176.74 | 142.19 | 1.24 | 0.0498 | 0.0042 | 0.0929 | 0.0074 | 0.0140 | 0.00044 | 90.19 | 6.91 | 89.87 | 2.80 | ||
| PM20-21 | 3.19 | 214.30 | 164.84 | 1.30 | 0.0533 | 0.0040 | 0.0993 | 0.0072 | 0.0139 | 0.00024 | 96.15 | 6.69 | 88.93 | 1.50 | ||
| PM20-23 | 2.58 | 172.68 | 134.71 | 1.28 | 0.0505 | 0.0039 | 0.0938 | 0.0067 | 0.0138 | 0.00029 | 91.00 | 6.19 | 88.59 | 1.85 | ||
| PM20-24 | 1.82 | 94.76 | 96.28 | 0.98 | 0.0516 | 0.0064 | 0.1003 | 0.0130 | 0.0141 | 0.00037 | 97.06 | 11.95 | 90.01 | 2.33 | ||
| PM20-25 | 2.24 | 145.18 | 124.39 | 1.17 | 0.0511 | 0.0060 | 0.0930 | 0.0101 | 0.0134 | 0.00036 | 90.32 | 9.38 | 86.01 | 2.32 | ||
| PM06-1 | 3.10 | 158.02 | 156.18 | 1.01 | 0.0448 | 0.0040 | 0.0879 | 0.0074 | 0.0148 | 0.00043 | 85.57 | 6.91 | 94.77 | 2.71 | ||
| PM06-3 | 3.91 | 191.79 | 194.27 | 0.99 | 0.0490 | 0.0051 | 0.0904 | 0.0087 | 0.0137 | 0.00030 | 87.88 | 8.08 | 87.65 | 1.88 | ||
| PM06-4 | 19.87 | 135.53 | 1318.74 | 0.10 | 0.0505 | 0.0025 | 0.0931 | 0.0043 | 0.0135 | 0.00022 | 90.40 | 4.03 | 86.47 | 1.42 | ||
| PM06-5 | 2.60 | 119.40 | 129.67 | 0.92 | 0.0582 | 0.0058 | 0.1078 | 0.0093 | 0.0138 | 0.00038 | 103.91 | 8.54 | 88.37 | 2.44 | ||
| PM06-6 | 4.48 | 237.46 | 211.82 | 1.12 | 0.0394 | 0.0088 | 0.0770 | 0.0160 | 0.0145 | 0.00046 | 75.36 | 15.05 | 93.03 | 2.94 | ||
| PM06-9 | 3.96 | 162.09 | 183.94 | 0.88 | 0.0647 | 0.0069 | 0.1222 | 0.0126 | 0.0145 | 0.00042 | 117.07 | 11.36 | 92.86 | 2.68 | ||
| PM06-10 | 2.45 | 103.61 | 112.43 | 0.92 | 0.0553 | 0.0070 | 0.1131 | 0.0145 | 0.0148 | 0.00049 | 108.78 | 13.24 | 94.45 | 3.09 | ||
| PM06-12 | 2.93 | 133.39 | 136.40 | 0.98 | 0.0686 | 0.0053 | 0.1328 | 0.0095 | 0.0150 | 0.00046 | 126.61 | 8.50 | 96.09 | 2.94 | ||
| PM06-15 | 4.90 | 246.13 | 220.04 | 1.12 | 0.0550 | 0.0049 | 0.1081 | 0.0094 | 0.0147 | 0.00038 | 104.23 | 8.60 | 94.08 | 2.43 | ||
| PM06-16 | 2.39 | 111.39 | 104.36 | 1.07 | 0.0494 | 0.0093 | 0.0943 | 0.0156 | 0.0151 | 0.00061 | 91.52 | 14.48 | 96.69 | 3.88 | ||
| PM06-17 | 4.05 | 158.08 | 199.89 | 0.79 | 0.0586 | 0.0049 | 0.1124 | 0.0080 | 0.0144 | 0.00039 | 108.18 | 7.34 | 92.03 | 2.48 | ||
| PM06-18 | 2.25 | 100.52 | 100.52 | 1.00 | 0.0567 | 0.0058 | 0.1148 | 0.0106 | 0.0150 | 0.00043 | 110.36 | 9.70 | 96.26 | 2.72 | ||
| PM06-19 | 3.72 | 167.03 | 173.58 | 0.96 | 0.0664 | 0.0056 | 0.1229 | 0.0106 | 0.0142 | 0.00034 | 117.71 | 9.61 | 91.03 | 2.18 | ||
| PM06-20 | 2.54 | 113.78 | 121.06 | 0.94 | 0.0456 | 0.0046 | 0.0879 | 0.0088 | 0.0143 | 0.00037 | 85.58 | 8.17 | 91.67 | 2.35 | ||
| 测点号 | 年龄(Ma) | 176Yb/177Hf | 2σ | 176Lu/177Hf | 2σ | 176Hf/177Hf | 2σ | εHf(t) | tDM1(Ma) | tDM2(Ma) | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM20-3 | 86.1 | 0.010741 | 0.000065 | 0.000399 | 0.000002 | 0.283065 | 0.000019 | 12.2 | 260.9 | 369.9 | -0.99 |
| PM20-5 | 87.69 | 0.022749 | 0.000103 | 0.000808 | 0.000006 | 0.283082 | 0.000021 | 12.9 | 238.6 | 330.1 | -0.98 |
| PM20-6 | 86.34 | 0.019553 | 0.000423 | 0.000691 | 0.000015 | 0.283063 | 0.000024 | 12.1 | 265.5 | 375.0 | -0.98 |
| PM20-7 | 88.1 | 0.017383 | 0.000174 | 0.000626 | 0.000007 | 0.283064 | 0.000019 | 12.2 | 263.7 | 371.6 | -0.98 |
| PM20-9 | 85.34 | 0.020284 | 0.000243 | 0.000704 | 0.000006 | 0.283039 | 0.000021 | 11.3 | 298.7 | 429.1 | -0.98 |
| PM20-10 | 87.71 | 0.010057 | 0.000083 | 0.000363 | 0.000002 | 0.283060 | 0.000021 | 12.1 | 266.6 | 378.5 | -0.99 |
| PM20-11 | 88.06 | 0.018632 | 0.000160 | 0.000640 | 0.000004 | 0.283050 | 0.000027 | 11.7 | 282.8 | 402.3 | -0.98 |
| PM20-13 | 88.98 | 0.018377 | 0.000138 | 0.000629 | 0.000005 | 0.283087 | 0.000023 | 13.1 | 230.9 | 318.0 | -0.98 |
| PM20-16 | 90.47 | 0.023509 | 0.000081 | 0.000798 | 0.000003 | 0.283054 | 0.000024 | 11.9 | 279.0 | 393.5 | -0.98 |
| PM20-17 | 88.31 | 0.021479 | 0.000068 | 0.000719 | 0.000001 | 0.283107 | 0.000020 | 13.8 | 202.8 | 272.7 | -0.98 |
| PM20-18 | 89.87 | 0.017991 | 0.000141 | 0.000614 | 0.000003 | 0.283091 | 0.000022 | 13.2 | 225.8 | 309.4 | -0.98 |
| PM20-20 | 96.22 | 0.016890 | 0.000319 | 0.000578 | 0.000008 | 0.283052 | 0.000021 | 12.0 | 280.7 | 394.3 | -0.98 |
| PM20-21 | 88.93 | 0.022531 | 0.000212 | 0.000765 | 0.000004 | 0.283067 | 0.000020 | 12.3 | 260.4 | 364.8 | -0.98 |
| PM20-23 | 88.59 | 0.015685 | 0.000091 | 0.000548 | 0.000003 | 0.283085 | 0.000023 | 13.0 | 233.6 | 323.2 | -0.98 |
| PM20-24 | 90.01 | 0.018729 | 0.000170 | 0.000634 | 0.000007 | 0.283076 | 0.000018 | 12.7 | 247.0 | 343.4 | -0.98 |
| PM06-1 | 94.77 | 0.012055 | 0.000218 | 0.000511 | 0.000009 | 0.283068 | 0.000020 | 12.5 | 257.5 | 358.2 | -0.98 |
| PM06-3 | 87.65 | 0.011490 | 0.000252 | 0.000477 | 0.000010 | 0.283018 | 0.000022 | 10.6 | 326.5 | 474.8 | -0.99 |
| PM06-4 | 86.47 | 0.015910 | 0.000215 | 0.000662 | 0.000010 | 0.283031 | 0.000023 | 11.0 | 309.8 | 446.6 | -0.98 |
| PM06-5 | 88.37 | 0.014593 | 0.001343 | 0.000615 | 0.000053 | 0.283065 | 0.000020 | 12.3 | 261.7 | 368.3 | -0.98 |
| PM06-6 | 93.03 | 0.011043 | 0.000074 | 0.000463 | 0.000002 | 0.283074 | 0.000022 | 12.7 | 248.4 | 344.9 | -0.99 |
| PM06-9 | 92.86 | 0.016204 | 0.000207 | 0.000677 | 0.000009 | 0.283041 | 0.000023 | 11.5 | 296.8 | 421.7 | -0.98 |
| PM06-10 | 94.45 | 0.017040 | 0.000535 | 0.000695 | 0.000023 | 0.283116 | 0.000024 | 14.2 | 190.8 | 249.7 | -0.98 |
| PM06-12 | 96.09 | 0.013220 | 0.000072 | 0.000547 | 0.000004 | 0.283107 | 0.000029 | 13.9 | 202.4 | 268.1 | -0.98 |
| PM06-15 | 94.08 | 0.011239 | 0.000117 | 0.000464 | 0.000003 | 0.283057 | 0.000023 | 12.1 | 271.6 | 381.9 | -0.99 |
| PM06-16 | 96.69 | 0.014018 | 0.000190 | 0.000577 | 0.000007 | 0.283046 | 0.000019 | 11.8 | 287.9 | 405.8 | -0.98 |
| PM06-17 | 92.03 | 0.011843 | 0.000122 | 0.000505 | 0.000005 | 0.283060 | 0.000022 | 12.2 | 268.6 | 378.0 | -0.98 |
| PM06-18 | 96.26 | 0.015116 | 0.000276 | 0.000623 | 0.000010 | 0.283045 | 0.000020 | 11.7 | 290.6 | 410.0 | -0.98 |
| PM06-19 | 91.03 | 0.010779 | 0.000319 | 0.000457 | 0.000013 | 0.283068 | 0.000019 | 12.4 | 257.3 | 360.6 | -0.99 |
| PM06-20 | 91.67 | 0.009409 | 0.000130 | 0.000406 | 0.000006 | 0.283030 | 0.000022 | 11.1 | 309.2 | 444.9 | -0.99 |
表2 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2 Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic analysis results for the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet
| 测点号 | 年龄(Ma) | 176Yb/177Hf | 2σ | 176Lu/177Hf | 2σ | 176Hf/177Hf | 2σ | εHf(t) | tDM1(Ma) | tDM2(Ma) | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM20-3 | 86.1 | 0.010741 | 0.000065 | 0.000399 | 0.000002 | 0.283065 | 0.000019 | 12.2 | 260.9 | 369.9 | -0.99 |
| PM20-5 | 87.69 | 0.022749 | 0.000103 | 0.000808 | 0.000006 | 0.283082 | 0.000021 | 12.9 | 238.6 | 330.1 | -0.98 |
| PM20-6 | 86.34 | 0.019553 | 0.000423 | 0.000691 | 0.000015 | 0.283063 | 0.000024 | 12.1 | 265.5 | 375.0 | -0.98 |
| PM20-7 | 88.1 | 0.017383 | 0.000174 | 0.000626 | 0.000007 | 0.283064 | 0.000019 | 12.2 | 263.7 | 371.6 | -0.98 |
| PM20-9 | 85.34 | 0.020284 | 0.000243 | 0.000704 | 0.000006 | 0.283039 | 0.000021 | 11.3 | 298.7 | 429.1 | -0.98 |
| PM20-10 | 87.71 | 0.010057 | 0.000083 | 0.000363 | 0.000002 | 0.283060 | 0.000021 | 12.1 | 266.6 | 378.5 | -0.99 |
| PM20-11 | 88.06 | 0.018632 | 0.000160 | 0.000640 | 0.000004 | 0.283050 | 0.000027 | 11.7 | 282.8 | 402.3 | -0.98 |
| PM20-13 | 88.98 | 0.018377 | 0.000138 | 0.000629 | 0.000005 | 0.283087 | 0.000023 | 13.1 | 230.9 | 318.0 | -0.98 |
| PM20-16 | 90.47 | 0.023509 | 0.000081 | 0.000798 | 0.000003 | 0.283054 | 0.000024 | 11.9 | 279.0 | 393.5 | -0.98 |
| PM20-17 | 88.31 | 0.021479 | 0.000068 | 0.000719 | 0.000001 | 0.283107 | 0.000020 | 13.8 | 202.8 | 272.7 | -0.98 |
| PM20-18 | 89.87 | 0.017991 | 0.000141 | 0.000614 | 0.000003 | 0.283091 | 0.000022 | 13.2 | 225.8 | 309.4 | -0.98 |
| PM20-20 | 96.22 | 0.016890 | 0.000319 | 0.000578 | 0.000008 | 0.283052 | 0.000021 | 12.0 | 280.7 | 394.3 | -0.98 |
| PM20-21 | 88.93 | 0.022531 | 0.000212 | 0.000765 | 0.000004 | 0.283067 | 0.000020 | 12.3 | 260.4 | 364.8 | -0.98 |
| PM20-23 | 88.59 | 0.015685 | 0.000091 | 0.000548 | 0.000003 | 0.283085 | 0.000023 | 13.0 | 233.6 | 323.2 | -0.98 |
| PM20-24 | 90.01 | 0.018729 | 0.000170 | 0.000634 | 0.000007 | 0.283076 | 0.000018 | 12.7 | 247.0 | 343.4 | -0.98 |
| PM06-1 | 94.77 | 0.012055 | 0.000218 | 0.000511 | 0.000009 | 0.283068 | 0.000020 | 12.5 | 257.5 | 358.2 | -0.98 |
| PM06-3 | 87.65 | 0.011490 | 0.000252 | 0.000477 | 0.000010 | 0.283018 | 0.000022 | 10.6 | 326.5 | 474.8 | -0.99 |
| PM06-4 | 86.47 | 0.015910 | 0.000215 | 0.000662 | 0.000010 | 0.283031 | 0.000023 | 11.0 | 309.8 | 446.6 | -0.98 |
| PM06-5 | 88.37 | 0.014593 | 0.001343 | 0.000615 | 0.000053 | 0.283065 | 0.000020 | 12.3 | 261.7 | 368.3 | -0.98 |
| PM06-6 | 93.03 | 0.011043 | 0.000074 | 0.000463 | 0.000002 | 0.283074 | 0.000022 | 12.7 | 248.4 | 344.9 | -0.99 |
| PM06-9 | 92.86 | 0.016204 | 0.000207 | 0.000677 | 0.000009 | 0.283041 | 0.000023 | 11.5 | 296.8 | 421.7 | -0.98 |
| PM06-10 | 94.45 | 0.017040 | 0.000535 | 0.000695 | 0.000023 | 0.283116 | 0.000024 | 14.2 | 190.8 | 249.7 | -0.98 |
| PM06-12 | 96.09 | 0.013220 | 0.000072 | 0.000547 | 0.000004 | 0.283107 | 0.000029 | 13.9 | 202.4 | 268.1 | -0.98 |
| PM06-15 | 94.08 | 0.011239 | 0.000117 | 0.000464 | 0.000003 | 0.283057 | 0.000023 | 12.1 | 271.6 | 381.9 | -0.99 |
| PM06-16 | 96.69 | 0.014018 | 0.000190 | 0.000577 | 0.000007 | 0.283046 | 0.000019 | 11.8 | 287.9 | 405.8 | -0.98 |
| PM06-17 | 92.03 | 0.011843 | 0.000122 | 0.000505 | 0.000005 | 0.283060 | 0.000022 | 12.2 | 268.6 | 378.0 | -0.98 |
| PM06-18 | 96.26 | 0.015116 | 0.000276 | 0.000623 | 0.000010 | 0.283045 | 0.000020 | 11.7 | 290.6 | 410.0 | -0.98 |
| PM06-19 | 91.03 | 0.010779 | 0.000319 | 0.000457 | 0.000013 | 0.283068 | 0.000019 | 12.4 | 257.3 | 360.6 | -0.99 |
| PM06-20 | 91.67 | 0.009409 | 0.000130 | 0.000406 | 0.000006 | 0.283030 | 0.000022 | 11.1 | 309.2 | 444.9 | -0.99 |
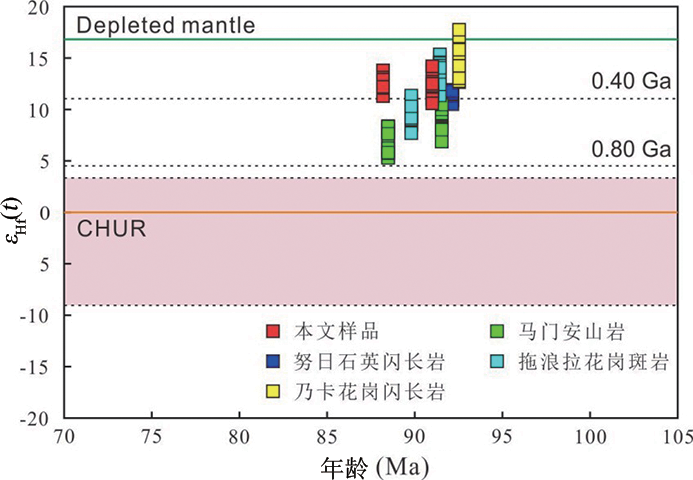
图5 冈底斯南缘晚白垩世花岗岩εHf(t)与U-Pb年龄图解(底图据Amelin等[24])
Fig.5 εHf(t) vs. U-Pb age plot for the Late Cretaceous granites in the southern Gangdese margin (after Amelin et al[24])
| 样品号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM20-1 | 60.03 | 16.20 | 0.89 | 3.27 | 2.56 | 4.62 | 2.97 | 3.18 | 3.97 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 1.71 | 99.82 | 50.20 | 36.77 | 74.99 | 9.11 | 34.94 | 6.20 | 1.55 | 5.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM20-2 | 59.58 | 16.62 | 0.86 | 2.51 | 3.39 | 5.39 | 3.33 | 2.65 | 4.02 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 1.05 | 99.81 | 52.80 | 37.60 | 77.80 | 9.66 | 38.14 | 6.90 | 1.75 | 5.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9415 | 64.89 | 15.59 | 0.59 | 1.98 | 2.12 | 3.63 | 2.25 | 3.64 | 4.00 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.89 | 99.85 | 52.10 | 32.07 | 59.52 | 6.69 | 23.87 | 3.84 | 0.99 | 3.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9416 | 66.83 | 15.22 | 0.51 | 1.82 | 1.73 | 3.14 | 1.86 | 4.05 | 3.85 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 99.85 | 50.90 | 27.53 | 54.35 | 6.40 | 22.93 | 3.78 | 0.97 | 3.12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9389 | 62.24 | 15.93 | 0.75 | 2.31 | 2.56 | 4.36 | 2.78 | 3.72 | 3.94 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.89 | 99.81 | 53.10 | 33.33 | 66.99 | 8.02 | 30.32 | 5.14 | 1.35 | 4.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3816 | 62.21 | 15.88 | 0.80 | 2.71 | 2.45 | 4.35 | 2.71 | 3.77 | 3.93 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.67 | 99.82 | 51.00 | 30.56 | 61.72 | 7.59 | 28.72 | 4.93 | 1.22 | 4.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3015 | 61.74 | 15.94 | 0.90 | 2.64 | 2.70 | 4.16 | 2.58 | 4.13 | 3.98 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.67 | 99.82 | 48.90 | 37.80 | 78.38 | 9.57 | 36.21 | 6.18 | 1.41 | 5.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D0219 | 63.90 | 16.68 | 0.74 | 1.91 | 2.00 | 3.62 | 1.36 | 4.43 | 4.13 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.74 | 99.86 | 40.80 | 39.85 | 76.04 | 9.51 | 36.32 | 6.58 | 1.38 | 5.56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM06 | 64.20 | 15.55 | 0.69 | 2.00 | 2.18 | 3.88 | 2.23 | 3.91 | 3.90 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 1.02 | 99.85 | 51.40 | 31.74 | 63.94 | 7.55 | 28.76 | 4.71 | 1.07 | 3.84 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | ∑REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | δEu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM20-1 | 0.73 | 3.94 | 0.72 | 2.07 | 0.36 | 2.23 | 0.33 | 18.31 | 89.69 | 481.50 | 8.43 | 2.71 | 0.61 | 10.80 | 197.33 | 4.84 | 11.16 | 3.73 | 1.86 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM20-2 | 0.80 | 4.55 | 0.83 | 2.41 | 0.41 | 2.58 | 0.37 | 20.96 | 110.96 | 569.60 | 6.69 | 2.42 | 0.58 | 8.79 | 210.41 | 4.46 | 9.86 | 3.43 | 1.77 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9415 | 0.44 | 2.36 | 0.44 | 1.29 | 0.23 | 1.49 | 0.22 | 11.51 | 123.55 | 437.60 | 21.78 | 6.32 | 0.72 | 9.29 | 148.30 | 5.96 | 14.58 | 5.26 | 1.82 | 0.83 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9416 | 0.43 | 2.31 | 0.42 | 1.25 | 0.22 | 1.42 | 0.21 | 12.13 | 133.45 | 497.80 | 14.25 | 4.48 | 0.57 | 8.62 | 137.46 | 5.39 | 13.10 | 4.59 | 1.78 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9389 | 0.59 | 3.15 | 0.57 | 1.68 | 0.30 | 1.87 | 0.28 | 15.56 | 145.02 | 597.00 | 24.26 | 7.08 | 0.66 | 9.86 | 173.37 | 5.14 | 12.02 | 4.08 | 1.83 | 0.86 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3816 | 0.56 | 3.04 | 0.54 | 1.58 | 0.27 | 1.70 | 0.25 | 15.14 | 126.68 | 460.90 | 12.86 | 2.48 | 0.45 | 10.13 | 161.83 | 4.97 | 12.11 | 3.90 | 1.90 | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3015 | 0.72 | 3.92 | 0.71 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 18.04 | 151.92 | 470.00 | 20.68 | 3.19 | 0.70 | 12.72 | 202.99 | 5.07 | 11.58 | 3.85 | 1.88 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D0219 | 0.83 | 4.64 | 0.87 | 2.56 | 0.45 | 2.87 | 0.42 | 22.23 | 139.39 | 415.20 | 14.52 | 3.74 | 0.66 | 13.83 | 210.11 | 4.20 | 9.39 | 3.81 | 1.57 | 0.68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM06 | 0.54 | 2.89 | 0.53 | 1.51 | 0.23 | 1.44 | 0.23 | 15.40 | 123.00 | 416.00 | 17.80 | 4.61 | 0.67 | 10.40 | 164.39 | 5.18 | 14.94 | 4.24 | 2.17 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表3 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩全岩主量(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 3 Results of whole-rock major (%) and trace elements (10-6) analyses for the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet
| 样品号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM20-1 | 60.03 | 16.20 | 0.89 | 3.27 | 2.56 | 4.62 | 2.97 | 3.18 | 3.97 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 1.71 | 99.82 | 50.20 | 36.77 | 74.99 | 9.11 | 34.94 | 6.20 | 1.55 | 5.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM20-2 | 59.58 | 16.62 | 0.86 | 2.51 | 3.39 | 5.39 | 3.33 | 2.65 | 4.02 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 1.05 | 99.81 | 52.80 | 37.60 | 77.80 | 9.66 | 38.14 | 6.90 | 1.75 | 5.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9415 | 64.89 | 15.59 | 0.59 | 1.98 | 2.12 | 3.63 | 2.25 | 3.64 | 4.00 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.89 | 99.85 | 52.10 | 32.07 | 59.52 | 6.69 | 23.87 | 3.84 | 0.99 | 3.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9416 | 66.83 | 15.22 | 0.51 | 1.82 | 1.73 | 3.14 | 1.86 | 4.05 | 3.85 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 99.85 | 50.90 | 27.53 | 54.35 | 6.40 | 22.93 | 3.78 | 0.97 | 3.12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9389 | 62.24 | 15.93 | 0.75 | 2.31 | 2.56 | 4.36 | 2.78 | 3.72 | 3.94 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.89 | 99.81 | 53.10 | 33.33 | 66.99 | 8.02 | 30.32 | 5.14 | 1.35 | 4.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3816 | 62.21 | 15.88 | 0.80 | 2.71 | 2.45 | 4.35 | 2.71 | 3.77 | 3.93 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.67 | 99.82 | 51.00 | 30.56 | 61.72 | 7.59 | 28.72 | 4.93 | 1.22 | 4.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3015 | 61.74 | 15.94 | 0.90 | 2.64 | 2.70 | 4.16 | 2.58 | 4.13 | 3.98 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.67 | 99.82 | 48.90 | 37.80 | 78.38 | 9.57 | 36.21 | 6.18 | 1.41 | 5.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D0219 | 63.90 | 16.68 | 0.74 | 1.91 | 2.00 | 3.62 | 1.36 | 4.43 | 4.13 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.74 | 99.86 | 40.80 | 39.85 | 76.04 | 9.51 | 36.32 | 6.58 | 1.38 | 5.56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM06 | 64.20 | 15.55 | 0.69 | 2.00 | 2.18 | 3.88 | 2.23 | 3.91 | 3.90 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 1.02 | 99.85 | 51.40 | 31.74 | 63.94 | 7.55 | 28.76 | 4.71 | 1.07 | 3.84 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | ∑REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | δEu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM20-1 | 0.73 | 3.94 | 0.72 | 2.07 | 0.36 | 2.23 | 0.33 | 18.31 | 89.69 | 481.50 | 8.43 | 2.71 | 0.61 | 10.80 | 197.33 | 4.84 | 11.16 | 3.73 | 1.86 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM20-2 | 0.80 | 4.55 | 0.83 | 2.41 | 0.41 | 2.58 | 0.37 | 20.96 | 110.96 | 569.60 | 6.69 | 2.42 | 0.58 | 8.79 | 210.41 | 4.46 | 9.86 | 3.43 | 1.77 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9415 | 0.44 | 2.36 | 0.44 | 1.29 | 0.23 | 1.49 | 0.22 | 11.51 | 123.55 | 437.60 | 21.78 | 6.32 | 0.72 | 9.29 | 148.30 | 5.96 | 14.58 | 5.26 | 1.82 | 0.83 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9416 | 0.43 | 2.31 | 0.42 | 1.25 | 0.22 | 1.42 | 0.21 | 12.13 | 133.45 | 497.80 | 14.25 | 4.48 | 0.57 | 8.62 | 137.46 | 5.39 | 13.10 | 4.59 | 1.78 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9389 | 0.59 | 3.15 | 0.57 | 1.68 | 0.30 | 1.87 | 0.28 | 15.56 | 145.02 | 597.00 | 24.26 | 7.08 | 0.66 | 9.86 | 173.37 | 5.14 | 12.02 | 4.08 | 1.83 | 0.86 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3816 | 0.56 | 3.04 | 0.54 | 1.58 | 0.27 | 1.70 | 0.25 | 15.14 | 126.68 | 460.90 | 12.86 | 2.48 | 0.45 | 10.13 | 161.83 | 4.97 | 12.11 | 3.90 | 1.90 | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3015 | 0.72 | 3.92 | 0.71 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 18.04 | 151.92 | 470.00 | 20.68 | 3.19 | 0.70 | 12.72 | 202.99 | 5.07 | 11.58 | 3.85 | 1.88 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D0219 | 0.83 | 4.64 | 0.87 | 2.56 | 0.45 | 2.87 | 0.42 | 22.23 | 139.39 | 415.20 | 14.52 | 3.74 | 0.66 | 13.83 | 210.11 | 4.20 | 9.39 | 3.81 | 1.57 | 0.68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM06 | 0.54 | 2.89 | 0.53 | 1.51 | 0.23 | 1.44 | 0.23 | 15.40 | 123.00 | 416.00 | 17.80 | 4.61 | 0.67 | 10.40 | 164.39 | 5.18 | 14.94 | 4.24 | 2.17 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

图6 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩TAS图解((a),据Middlemost[25])、SiO2-K2O图解((b),据Rickwood[26])、A/NK-A/CNK图解((c),据Maniar和Piccoli[27])和SiO2-AR图解((d),据Wright[28]) (a)图中:1.橄榄辉长岩;2a.碱性辉长岩;2b.亚碱性辉长岩;3.辉长闪长岩;4.闪长岩;5.花岗闪长岩;6.花岗岩;7.硅英岩;8.二长辉长岩;9.二长闪长岩;10.二长岩;11.石英二长岩;12.正长岩;13.副长石辉长岩;14.副长石二长闪长岩;15.副长石二长正长岩;16.副长正长岩;17.副长深成岩;18.霓方钠岩/磷霞岩/粗白榴岩
Fig.6 TAS diagram of the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet ((a) modified after Middcemost[25], (b) modified after Rickwood[26], (c) modified after Maniar and piccoli[27] and (d) modified after Wright[28])

图7 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图((a),标准化值据Boynton[32])和原始地幔标准化微量元素蜘蛛图((b),标准化值据Sun和Mc Donough[33])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns ((a),normalizing values after Boynton[32]) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns ((b),normalizing values after Sun and McDonough[33]) for the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet

图8 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩岩石成因类型判别图解 (a) P2O5-SiO2图解(据Li等 [47]);(b) K2O-Na2O图解(据Collins等 [48]);(c) (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(FeOT/MgO)图解(据Whalen [49]);(d) Zr-SiO2图解(据Collins等 [48])
Fig.8 Petrogenetic discrimination diagrams of the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet

图9 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩双变量图解 (a) La/Sm-La图解(据Allégr和Hart [50]);(b) LREE-SiO2图解;(c) Y-SiO2图解;(d) Er-Dy图解;(e) Rb-Sr图解(据Zhang等 [57]);(f) Ba-Sr图解(据Zhang等 [57])
Fig. 9 Bivariate plots of the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet

图10 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世石英二长岩构造环境判别图解 (a) Ta-Yb图解(据Pearce等[70] );(b) (FeOT+MgO)-CaO图解(据Maniar和Piccoli[71] );(c) Rb-(Yb+Ta)图解(据Pearce等[70] );(d) Rb-Hf-Ta图解(据Batchelor和Bowdden[72] )
Fig.10 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of the Late Cretaceous quartz monzonite in Sangye area, Tibet
| [1] |
YIN A, HARRISON T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28(1): 211-280.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 印度—亚洲碰撞大地构造[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(1): 1-33. |
| [3] | 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 牛耀龄, 等. 拉萨地体的起源和古生代构造演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2012, 18(1): 1-15. |
| [4] |
ZHU D C, ZHAO Z D, NIU Y L, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 1429-1454.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 莫宣学, 潘桂棠. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆事件的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 43-51. |
| [6] | 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 521-533. |
| [7] | 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等. 西藏冈底斯带中生代岩浆岩的时空分布和相关问题的讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(9): 1535-1550. |
| [8] | 莫宣学. 岩浆作用与青藏高原演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2011, 17(3): 351-367. |
| [9] | 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 等. 冈底斯岩浆弧的形成与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(2): 275-294. |
| [10] | 纪伟强, 吴福元, 锺孙霖, 等. 西藏南部冈底斯岩基花岗岩时代与岩石成因[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2009, 39(7): 849-871. |
| [11] | 杨宗耀, 胡古月, 肖洪天, 等. 西藏汤白矿区下白垩统比马组砂岩地球化学特征:对冈底斯南缘构造演化的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(7):2189-2205. |
| [12] | 唐演, 赵志丹, 齐宁远, 等. 西藏冈底斯岩基南木林晚白垩世岩体和脉岩地球化学与岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(2): 387-404. |
| [13] | 吴浩, 李才, 胡培远. 达查沟地区多样性岩浆作用:对班公湖—怒江洋早白垩世俯冲闭合指示[M]//中国地球物理学会,全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会组委会,中国地质学会构造地质学与地球动力学专业委员会,中国地质学会区域地质与成矿专业委员会.2014年中国地球科学联合学术年会——专题36: 羌塘—三江特提斯造山带形成演化与成矿效应论文集.北京:中国地球物理学会,全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会组委会,中国地质学会构造地质学与地球动力学专业委员会,中国地质学会区域地质与成矿专业委员会, 2014: 2. |
| [14] | 刘畅, 杨竹森, 徐培言, 等. 冈底斯西段麻木矽卡岩型铅锌矿化区岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 466-476. |
| [15] |
COULON C, MALUSKI H, BOLLINGER C, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic rocks from central and southern Tibet: 39Ar/40Ar dating, petrological characteristics and geodynamic significance[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79: 281-302.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHU D C, ZHAO Z D, NIU Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301: 241-255.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51: 537-571.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10): 2595-2604. |
| [20] |
WU F Y, YANG Y H, XIE L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochrono-logy[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234(1/2): 105-126.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 高剑峰, 陆建军, 赖鸣远, 等. 岩石样品中微量元素的高分辨率等离子质谱分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 39(6): 844-850. |
| [22] |
BELOUSOVA E A, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. |
| [24] |
AMELIN Y, LEE D, HALLIDAY A N, et al. Nature of Earth’s earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons[J]. Nature, 1999, 399: 252-255.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37: 215-244.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WRIGHT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969, 106(4): 370-384.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33: 241-265.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
POLAT A, HOFMANN A W, ROSING M T. Boninite-like volcanic rocks in the 3.7-3.8 Ga Isua greenstone belt, West Greenland: geochemical evidence for intra-oceanic subduction zone processes in the early Earth[J]. Chemical geology, 2002, 184: 231-254.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 王中刚, 欧阳婞薇. 多阶段部分熔融-花岗岩成矿的一种模式[R]. 贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所年报, 1986:234-235. |
| [32] | BOYNTON W V. Geochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies[M]//HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [33] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
KINNY P D, MAAS R. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53: 327-341.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
FALLOON T J, DANYUSHEVSKY L V. Melting of refractory mantle at 1.5, 2 and 2.5 GPa under anhydrous and H2O-undersaturated conditions: Implications for the petrogenesis of high-Ca boninites and the influence of subduction components on mantle melting[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41: 257-283.
DOI URL |
| [36] | NICHOLLS J, CARMICHEAL I S E. The equilibration temperature and pressure of various lava types with spinel- and garnet-peridotite[J]. American Mineralogist, 1972, 57: 941-959. |
| [37] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENANN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Blackwell: Oxford Press, 1985: 1-312. |
| [38] |
HOFMANN A W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: the relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3): 297-314.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
GREEN T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120: 347-359.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ATHERTON M P, PETFORD N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362: 144-146.
DOI |
| [41] |
MCCARRON J J, SMELLIE J. Tectonic implications of fore-arc magmatism and generation of high-magnesian andesites: Alexander Island, Antarctica[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1998, 155: 269-280.
DOI URL |
| [42] | DODGER F C W, KISTLER R W. Some additional observations on inclusions in the granitic rocks of the Sierra Nevada[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth and Planets), 1990, 95(11): 17841-17848. |
| [43] |
CHAPPELL B W. Magma mixing and the production of compositional variation within granite suites: Evidence from the granites of southeasternAustralia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(3): 449-470.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 刘亮, 邱检生, 李真, 等. 浙江龙游沐尘早白垩世石英二长岩体的成因:镁铁质包体及寄主岩的元素与 Sr-Nd 同位素地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(12): 3993-4006. |
| [45] | 雷传扬, 唐菊兴, 李威, 等. 班公湖—怒江缝合带西段阿翁错复式岩体的岩浆混合成因: 地球化学、年代学和暗色微粒包体证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(3): 665-686. |
| [46] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in Lachlan fold belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 1992, 83(1/2): 1-26. |
| [47] |
LI X H, LI W X, LI Z H. On the genetic classification and tectonic implications of the Early Yanshanian granitoids in the Nanling Range, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(14): 1873-1885.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J H, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
WHALEN J B, CURROE K L, CHAPPEL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95: 420-436.
DOI URL |
| [50] | ALLEGRE C J, HART S R. Trace elements in igneous petrology[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1978, 86(6): 773-774. |
| [51] | WHITE W M. Geochemistry[M]. Washington: John Wiley & Sons, 2020. |
| [52] |
BEDARD J H. A catalytic delamination-driven model for coupled genesis of Archean crust and sub-continental lithospheric mantle[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70: 1188-1214.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
GREEN T H. Island arc and continent-building magmatism: A review of petrogenic models based on experimental petrology and geochemistry[J]. Tectonophysics, 1980, 63(1/4): 367-385.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
SISSON T W. Hornblende-melt trace-element partitioning measured by ion microprobe[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 117(1/4): 331-344.
DOI URL |
| [55] | 高永丰, 侯增谦, 魏瑞华. 冈底斯晚第三纪斑岩的岩石学、地球化学及其地球动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(3): 418-428. |
| [56] | 张祥信, 高永丰, 雷世和. 内蒙古中部红格尔地区白音高老组流纹岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 950-960. |
| [57] |
BARKER F, ARTH J G. Generation of trondhjemitic-tonalitic liquids and Archean bimodal trondhjemitic-basalt suites[J]. Geology, 1976, 4: 596-600.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 魏永峰, 肖倩茹, 李有波, 等. 西藏纳木错早白垩世流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(3): 487-500. |
| [59] |
ZHANG J H, YANG J H, CHEN J Y, et al. Genesis of late Early Cretaceous high-silica rhyolites in eastern Zhejiang Province, southeast China: A crystal mush origin with mantle input[J]. Lithos, 2018, 296/299: 482-495.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
ENGLANG P, HOUSEMAN G A. Finite strain calculations of continental deformation: Comparition with the Indi-Asia collision[J]. Geophysical Research, 1986, 91: 3664-3667.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
MURPHY M A, YIN A, HARRISON T M, et al. Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8): 719.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
WANG B D, WANG L Q, CHUNG S L, et al. Evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean: Insights from the geochronology and geochemistry of mafic rocks within ophiolites[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245: 18-33.
DOI URL |
| [63] | 宋绍玮, 刘泽, 朱弟成, 等. 西藏打加错晚三叠世安山质岩浆作用的锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(10): 3100-3112. |
| [64] |
GUTSCHER M A, MUAIY R C, EISSEN J P, et al. Can slab melting be caused by flat subduction?[J]. Geology, 2000, 28: 535-538.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
ZHENG Y C, HOU Z Q, GONG Y L, et al. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakite-like intrusions of the Gangdese Plutonic Belt, southern Tibet: Implications for mid-ocean ridge subduction and crustal growth[J]. Lithos, 2014, 190/191: 240-263.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
GUYNN J H, KAPP P, PULLENA, et al. Tibetan basement rocks near Amdo reveal “missing” Mesozoic tectonism along the Bangong suture, central Tibet[J]. Geology, 2006, 34: 505-508.
DOI URL |
| [67] | 潘桂棠, 王立全, 朱弟成. 青藏高原区域地质调查中几个重大科学问题的思考[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(1): 12-19. |
| [68] | 翟文建, 崔霄峰, 岳国利, 等. 西藏扎雪—门巴韧性剪切带变形时代及机制研究:来自同构造花岗岩体的证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(2):8. |
| [69] | 高家昊, 曾令森, 郭春丽, 等. 藏南冈底斯岩基晚白垩世构造岩浆作用:以拉萨白堆复合岩体中-基性岩脉群为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(8): 2412-2436. |
| [70] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. |
| [71] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multi-cationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1/4): 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [3] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [4] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [5] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [6] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [7] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [8] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [9] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [10] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [11] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [12] | 刘阳, 姜冰, 张海瑞, 孙增兵, 王松涛. 山东省青州市表层土壤硒元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 933-940. |
| [13] | 王美华. 浙西典型石煤矿山周边耕地富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [14] | 朱必清, 陈世加, 白艳军, 雷俊杰, 尹相东. 鄂尔多斯盆地甘泉地区延长组长8段原油地球化学特征及来源[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 742-754. |
| [15] | 刘建栋, 李五福, 王国良, 董进生, 曹锦山, 李红刚, 赵忠国. 北祁连东段柏木峡—门岗峡地区蛇绿岩的识别及其区域构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 244-258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||