



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (01): 154-168.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.080
收稿日期:2022-11-05
修回日期:2023-12-07
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
蒋孝君,男,高级工程师,1987年出生,构造地质学专业,主要从事构造及铀矿方面研究工作。Email: 作者简介:刘青占,男,硕士,工程师,1992年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学及铀矿方面研究工作。Email: 1531092309@qq.com。
基金资助:
LIU Qingzhan( ), JIANG Xiaojun(
), JIANG Xiaojun( ), WANG Guo, LI Tianyu, LI Dongpeng
), WANG Guo, LI Tianyu, LI Dongpeng
Received:2022-11-05
Revised:2023-12-07
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-03-20
摘要:
华北板块北缘中段多伦地区记录了强烈的早白垩世早期岩浆作用,构造环境的确立有助于解决其是受控于蒙古—鄂霍次克构造体系还是古太平洋板块俯冲上的争议。本文对多伦地区南炮台花岗斑岩进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成研究。结果显示,花岗斑岩岩浆锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(136±1) Ma,代表南炮台花岗斑岩形成于早白垩世早期。锆石$\varepsilon_{\mathrm{Hf}}$(t)值变化于-8.1~+1.9之间,Hf同位素地壳模式年龄($\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{DM}}{ }^{\mathrm{C}}$)为1044~1680 Ma。南炮台花岗斑岩属弱过铝质钾玄岩系列,富SiO2(70.53%~72.72%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O = 9.09%~9.48%)、贫MgO(0.19%~0.39%)、CaO(0.55%~0.67%)和P2O5(0.19%~0.39%),富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素(K、Cs和Rb)、亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta和Ti)及Sr、P元素,其(La/Yb)N介于22.10~57.67之间,Eu负异常(δEu=0.38~0.52)。综合地球化学特征,表明南炮台花岗斑岩为板内非造山伸展构造环境下的产物,属A型花岗岩,原始岩浆起源于古老下地壳物质的部分熔融,且存在幔源物质加入。结合区域构造演化,认为多伦地区早白垩世早期岩浆作用与蒙古—鄂霍次克洋闭合后的某个伸展环境有关,指示蒙古—鄂霍次克构造体系向南东的影响范围已波及至华北板块北缘中段内蒙古东南部地区。
中图分类号:
刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168.
LIU Qingzhan, JIANG Xiaojun, WANG Guo, LI Tianyu, LI Dongpeng. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of the Nanpaotai Granite Porphyry in Inner Mongolia: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Hf Isotopes, and Whole-rock Geochemistry[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(01): 154-168.

图1 内蒙古中部区域构造简图(a)和研究区地质简图(b)(分别据文献[5]和[37]修改)
Fig.1 Regional tectonic sketch of middle Inner Mongolia (a) and geological sketch of the study area (b) (modified after refs [5] and [37], respectively)
| 测点 号 | 含量(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||
| D025-02 | 193 | 366 | 0.53 | 0.0481 | 0.0010 | 0.1416 | 0.0034 | 0.0214 | 0.0003 | 103.6 | 47.8 | 134.5 | 3.0 | 136.5 | 1.7 | |
| D025-03 | 179 | 345 | 0.52 | 0.0488 | 0.0013 | 0.1451 | 0.0042 | 0.0216 | 0.0002 | 137.1 | 60.0 | 137.6 | 3.7 | 137.4 | 1.5 | |
| D025-04 | 364 | 471 | 0.77 | 0.0478 | 0.0010 | 0.1422 | 0.0038 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 90.6 | 50.5 | 135 | 3.4 | 137.4 | 1.7 | |
| D025-05 | 146 | 154 | 0.95 | 0.0482 | 0.0016 | 0.1391 | 0.0049 | 0.0211 | 0.0003 | 106.7 | 78.6 | 132.3 | 4.4 | 134.4 | 1.6 | |
| D025-06 | 133 | 262 | 0.51 | 0.0495 | 0.0014 | 0.1454 | 0.0043 | 0.0214 | 0.0003 | 173.7 | 66.3 | 137.8 | 3.8 | 136.3 | 1.7 | |
| D025-07 | 230 | 408 | 0.56 | 0.0496 | 0.0010 | 0.1457 | 0.0033 | 0.0214 | 0.0003 | 174.6 | 44.8 | 138.1 | 2.9 | 136.4 | 1.6 | |
| D025-08 | 310 | 610 | 0.51 | 0.0491 | 0.0011 | 0.1453 | 0.0033 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 153.8 | 50.7 | 137.7 | 3.0 | 137.0 | 1.8 | |
| D025-09 | 212 | 380 | 0.56 | 0.0481 | 0.0016 | 0.1426 | 0.0054 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 102.1 | 80.8 | 135.3 | 4.8 | 136.9 | 1.6 | |
| D025-10 | 550 | 569 | 0.97 | 0.0490 | 0.0008 | 0.1432 | 0.0028 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 149.8 | 38.6 | 135.9 | 2.5 | 135.2 | 1.4 | |
| D025-11 | 215 | 241 | 0.89 | 0.0490 | 0.0015 | 0.1442 | 0.0046 | 0.0213 | 0.0002 | 149.4 | 71.5 | 136.8 | 4.1 | 136.0 | 1.4 | |
| D025-12 | 233 | 572 | 0.41 | 0.0475 | 0.0014 | 0.1433 | 0.0051 | 0.0218 | 0.0004 | 74.9 | 70.1 | 136.0 | 4.6 | 138.8 | 2.3 | |
| D025-13 | 290 | 639 | 0.45 | 0.0481 | 0.0011 | 0.1425 | 0.0036 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 101.8 | 55.5 | 135.3 | 3.2 | 137.2 | 1.9 | |
| D025-14 | 210 | 337 | 0.62 | 0.0494 | 0.0013 | 0.1453 | 0.0042 | 0.0215 | 0.0004 | 165.8 | 63.4 | 137.8 | 3.8 | 136.8 | 2.3 | |
| D025-15 | 259 | 453 | 0.57 | 0.0490 | 0.0009 | 0.1433 | 0.0029 | 0.0213 | 0.0002 | 147.6 | 44.5 | 136.0 | 2.6 | 135.6 | 1.3 | |
| D025-16 | 221 | 403 | 0.55 | 0.0486 | 0.0013 | 0.1438 | 0.0044 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 127.2 | 64.7 | 136.4 | 3.9 | 137.0 | 1.7 | |
| D025-17 | 133 | 312 | 0.43 | 0.0486 | 0.0009 | 0.1417 | 0.0030 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 129.2 | 45.2 | 134.5 | 2.6 | 135.1 | 1.5 | |
| D025-18 | 403 | 595 | 0.68 | 0.0498 | 0.0009 | 0.1455 | 0.0027 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 187.1 | 40.4 | 137.9 | 2.4 | 135.2 | 1.3 | |
| D025-19 | 155 | 198 | 0.78 | 0.0495 | 0.0012 | 0.1446 | 0.0038 | 0.0212 | 0.0003 | 172.5 | 58.2 | 137.1 | 3.4 | 135.5 | 1.6 | |
| D025-20 | 276 | 595 | 0.46 | 0.0487 | 0.0009 | 0.1436 | 0.0030 | 0.0214 | 0.0002 | 132.4 | 42.7 | 136.2 | 2.6 | 136.4 | 1.3 | |
| D025-21 | 173 | 284 | 0.61 | 0.0501 | 0.0014 | 0.1467 | 0.0039 | 0.0213 | 0.0002 | 200.9 | 64.5 | 139.0 | 3.5 | 135.8 | 1.4 | |
| D025-22 | 215 | 363 | 0.59 | 0.0495 | 0.0011 | 0.1443 | 0.0032 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 171.0 | 50.6 | 136.8 | 2.9 | 135.1 | 1.3 | |
| D025-23 | 400 | 603 | 0.66 | 0.0488 | 0.0008 | 0.1423 | 0.0024 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 136.1 | 37.4 | 135.0 | 2.2 | 135.1 | 1.3 | |
| D025-24 | 280 | 479 | 0.58 | 0.0493 | 0.0008 | 0.1443 | 0.0026 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 162.8 | 38.9 | 136.9 | 2.3 | 135.5 | 1.1 | |
| D025-25 | 252 | 508 | 0.50 | 0.0487 | 0.0011 | 0.1431 | 0.0033 | 0.0214 | 0.0002 | 133.0 | 52.6 | 135.8 | 2.9 | 136.2 | 1.5 | |
表1 南炮台花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating data for the Nanpaotai granite porphyry
| 测点 号 | 含量(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||
| D025-02 | 193 | 366 | 0.53 | 0.0481 | 0.0010 | 0.1416 | 0.0034 | 0.0214 | 0.0003 | 103.6 | 47.8 | 134.5 | 3.0 | 136.5 | 1.7 | |
| D025-03 | 179 | 345 | 0.52 | 0.0488 | 0.0013 | 0.1451 | 0.0042 | 0.0216 | 0.0002 | 137.1 | 60.0 | 137.6 | 3.7 | 137.4 | 1.5 | |
| D025-04 | 364 | 471 | 0.77 | 0.0478 | 0.0010 | 0.1422 | 0.0038 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 90.6 | 50.5 | 135 | 3.4 | 137.4 | 1.7 | |
| D025-05 | 146 | 154 | 0.95 | 0.0482 | 0.0016 | 0.1391 | 0.0049 | 0.0211 | 0.0003 | 106.7 | 78.6 | 132.3 | 4.4 | 134.4 | 1.6 | |
| D025-06 | 133 | 262 | 0.51 | 0.0495 | 0.0014 | 0.1454 | 0.0043 | 0.0214 | 0.0003 | 173.7 | 66.3 | 137.8 | 3.8 | 136.3 | 1.7 | |
| D025-07 | 230 | 408 | 0.56 | 0.0496 | 0.0010 | 0.1457 | 0.0033 | 0.0214 | 0.0003 | 174.6 | 44.8 | 138.1 | 2.9 | 136.4 | 1.6 | |
| D025-08 | 310 | 610 | 0.51 | 0.0491 | 0.0011 | 0.1453 | 0.0033 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 153.8 | 50.7 | 137.7 | 3.0 | 137.0 | 1.8 | |
| D025-09 | 212 | 380 | 0.56 | 0.0481 | 0.0016 | 0.1426 | 0.0054 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 102.1 | 80.8 | 135.3 | 4.8 | 136.9 | 1.6 | |
| D025-10 | 550 | 569 | 0.97 | 0.0490 | 0.0008 | 0.1432 | 0.0028 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 149.8 | 38.6 | 135.9 | 2.5 | 135.2 | 1.4 | |
| D025-11 | 215 | 241 | 0.89 | 0.0490 | 0.0015 | 0.1442 | 0.0046 | 0.0213 | 0.0002 | 149.4 | 71.5 | 136.8 | 4.1 | 136.0 | 1.4 | |
| D025-12 | 233 | 572 | 0.41 | 0.0475 | 0.0014 | 0.1433 | 0.0051 | 0.0218 | 0.0004 | 74.9 | 70.1 | 136.0 | 4.6 | 138.8 | 2.3 | |
| D025-13 | 290 | 639 | 0.45 | 0.0481 | 0.0011 | 0.1425 | 0.0036 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 101.8 | 55.5 | 135.3 | 3.2 | 137.2 | 1.9 | |
| D025-14 | 210 | 337 | 0.62 | 0.0494 | 0.0013 | 0.1453 | 0.0042 | 0.0215 | 0.0004 | 165.8 | 63.4 | 137.8 | 3.8 | 136.8 | 2.3 | |
| D025-15 | 259 | 453 | 0.57 | 0.0490 | 0.0009 | 0.1433 | 0.0029 | 0.0213 | 0.0002 | 147.6 | 44.5 | 136.0 | 2.6 | 135.6 | 1.3 | |
| D025-16 | 221 | 403 | 0.55 | 0.0486 | 0.0013 | 0.1438 | 0.0044 | 0.0215 | 0.0003 | 127.2 | 64.7 | 136.4 | 3.9 | 137.0 | 1.7 | |
| D025-17 | 133 | 312 | 0.43 | 0.0486 | 0.0009 | 0.1417 | 0.0030 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 129.2 | 45.2 | 134.5 | 2.6 | 135.1 | 1.5 | |
| D025-18 | 403 | 595 | 0.68 | 0.0498 | 0.0009 | 0.1455 | 0.0027 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 187.1 | 40.4 | 137.9 | 2.4 | 135.2 | 1.3 | |
| D025-19 | 155 | 198 | 0.78 | 0.0495 | 0.0012 | 0.1446 | 0.0038 | 0.0212 | 0.0003 | 172.5 | 58.2 | 137.1 | 3.4 | 135.5 | 1.6 | |
| D025-20 | 276 | 595 | 0.46 | 0.0487 | 0.0009 | 0.1436 | 0.0030 | 0.0214 | 0.0002 | 132.4 | 42.7 | 136.2 | 2.6 | 136.4 | 1.3 | |
| D025-21 | 173 | 284 | 0.61 | 0.0501 | 0.0014 | 0.1467 | 0.0039 | 0.0213 | 0.0002 | 200.9 | 64.5 | 139.0 | 3.5 | 135.8 | 1.4 | |
| D025-22 | 215 | 363 | 0.59 | 0.0495 | 0.0011 | 0.1443 | 0.0032 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 171.0 | 50.6 | 136.8 | 2.9 | 135.1 | 1.3 | |
| D025-23 | 400 | 603 | 0.66 | 0.0488 | 0.0008 | 0.1423 | 0.0024 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 136.1 | 37.4 | 135.0 | 2.2 | 135.1 | 1.3 | |
| D025-24 | 280 | 479 | 0.58 | 0.0493 | 0.0008 | 0.1443 | 0.0026 | 0.0212 | 0.0002 | 162.8 | 38.9 | 136.9 | 2.3 | 135.5 | 1.1 | |
| D025-25 | 252 | 508 | 0.50 | 0.0487 | 0.0011 | 0.1431 | 0.0033 | 0.0214 | 0.0002 | 133.0 | 52.6 | 135.8 | 2.9 | 136.2 | 1.5 | |

图4 南炮台花岗斑岩锆石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分型式图(a)(标准化数值据文献[48])和锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)
Fig.4 Chondrite-normalized REE diagrams (a) (normalization values from ref [48]) and the U-Pb concordia diagram of zircons from the Nanpaotai granite porphyry (b)
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D025-02 | 7.63 | 40.30 | 2.23 | 10.39 | 4.33 | 0.23 | 15.53 | 5.33 | 68.42 | 25.57 | 126.99 | 29.22 | 298.87 | 47.63 |
| D025-03 | 2.85 | 21.27 | 1.09 | 7.23 | 7.16 | 0.07 | 31.70 | 10.31 | 119.58 | 41.07 | 178.95 | 36.23 | 322.66 | 46.99 |
| D025-04 | 0.03 | 21.96 | 0.35 | 5.46 | 10.76 | 0.07 | 52.13 | 15.47 | 183.00 | 60.99 | 257.97 | 50.92 | 447.62 | 63.81 |
| D025-05 | 0.04 | 23.59 | 0.35 | 5.74 | 9.92 | 1.59 | 43.32 | 13.21 | 156.50 | 52.34 | 230.79 | 48.46 | 450.69 | 69.86 |
| D025-06 | 18.44 | 61.46 | 5.22 | 22.51 | 6.07 | 0.32 | 17.10 | 5.11 | 66.11 | 24.24 | 119.31 | 27.61 | 280.01 | 45.61 |
| D025-07 | 0.03 | 16.09 | 0.42 | 7.32 | 13.51 | 0.09 | 64.31 | 20.16 | 234.07 | 78.43 | 325.71 | 63.37 | 541.14 | 78.22 |
| D025-08 | 0.05 | 24.88 | 0.22 | 3.69 | 9.38 | 0.07 | 52.39 | 17.65 | 212.39 | 69.83 | 304.78 | 59.89 | 522.94 | 70.46 |
| D025-09 | 0.02 | 15.04 | 0.13 | 2.89 | 6.59 | 0.02 | 34.68 | 10.86 | 126.36 | 43.39 | 188.24 | 37.21 | 340.16 | 47.22 |
| D025-10 | 0.05 | 29.46 | 0.54 | 8.45 | 17.45 | 0.13 | 84.83 | 24.68 | 281.26 | 91.49 | 379.15 | 72.89 | 613.00 | 90.45 |
| D025-11 | 8.14 | 65.70 | 2.46 | 12.79 | 7.08 | 0.94 | 26.06 | 8.06 | 99.47 | 35.01 | 162.53 | 35.64 | 339.91 | 52.20 |
| D025-12 | 93.53 | 233.69 | 32.05 | 145.69 | 37.44 | 0.57 | 52.94 | 12.58 | 132.56 | 44.18 | 198.97 | 42.11 | 387.32 | 54.80 |
| D025-13 | 0.03 | 27.87 | 0.10 | 2.23 | 5.27 | 0.16 | 31.08 | 10.73 | 138.07 | 49.57 | 231.93 | 50.53 | 465.84 | 68.77 |
| D025-14 | 4.36 | 37.19 | 1.31 | 6.58 | 4.65 | 0.39 | 20.26 | 6.85 | 85.92 | 31.38 | 148.80 | 33.03 | 328.02 | 50.60 |
| D025-15 | 6.38 | 46.39 | 2.24 | 10.27 | 5.36 | 0.32 | 18.63 | 6.34 | 81.54 | 30.22 | 148.59 | 34.66 | 350.36 | 56.18 |
| D025-16 | 0.04 | 15.67 | 0.34 | 6.07 | 13.86 | 0.09 | 70.56 | 21.97 | 257.05 | 84.66 | 354.50 | 67.23 | 569.64 | 84.02 |
| D025-17 | 0.06 | 11.77 | 0.08 | 1.64 | 4.03 | 0.03 | 21.68 | 7.20 | 90.66 | 31.60 | 141.54 | 29.12 | 261.53 | 39.21 |
| D025-18 | 64.17 | 192.44 | 24.45 | 119.29 | 39.71 | 0.20 | 83.15 | 21.97 | 239.78 | 76.37 | 317.10 | 60.91 | 509.11 | 74.45 |
| D025-19 | 25.76 | 82.04 | 7.07 | 31.90 | 9.95 | 0.73 | 27.90 | 8.11 | 97.93 | 34.22 | 157.22 | 34.45 | 325.58 | 52.15 |
| D025-20 | 0.01 | 17.79 | 0.10 | 2.09 | 5.61 | 0.04 | 31.76 | 10.79 | 135.96 | 47.24 | 209.04 | 43.02 | 370.90 | 54.05 |
| D025-21 | 30.69 | 89.40 | 8.60 | 36.24 | 8.94 | 0.42 | 19.83 | 5.62 | 70.10 | 25.07 | 119.43 | 27.12 | 271.06 | 44.14 |
| D025-22 | 3.95 | 32.42 | 1.14 | 6.06 | 3.99 | 0.17 | 18.92 | 6.18 | 79.08 | 28.84 | 136.10 | 29.92 | 283.96 | 44.30 |
| D025-23 | 7.29 | 43.61 | 2.69 | 15.90 | 12.56 | 0.07 | 55.12 | 17.23 | 203.38 | 67.52 | 285.43 | 56.47 | 483.43 | 68.85 |
| D025-24 | 37.77 | 112.48 | 9.79 | 41.98 | 10.82 | 0.66 | 25.34 | 7.87 | 100.57 | 38.39 | 191.16 | 44.67 | 457.81 | 75.74 |
| D025-25 | / | 24.66 | 0.06 | 1.22 | 3.08 | 0.13 | 17.69 | 6.34 | 82.31 | 31.27 | 153.03 | 34.74 | 341.51 | 53.49 |
表2 南炮台花岗斑岩锆石微量元素分析结果(10-6)
Table 2 Trace element (10-6) data for the zircon of the Nanpaotai granite porphyry
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D025-02 | 7.63 | 40.30 | 2.23 | 10.39 | 4.33 | 0.23 | 15.53 | 5.33 | 68.42 | 25.57 | 126.99 | 29.22 | 298.87 | 47.63 |
| D025-03 | 2.85 | 21.27 | 1.09 | 7.23 | 7.16 | 0.07 | 31.70 | 10.31 | 119.58 | 41.07 | 178.95 | 36.23 | 322.66 | 46.99 |
| D025-04 | 0.03 | 21.96 | 0.35 | 5.46 | 10.76 | 0.07 | 52.13 | 15.47 | 183.00 | 60.99 | 257.97 | 50.92 | 447.62 | 63.81 |
| D025-05 | 0.04 | 23.59 | 0.35 | 5.74 | 9.92 | 1.59 | 43.32 | 13.21 | 156.50 | 52.34 | 230.79 | 48.46 | 450.69 | 69.86 |
| D025-06 | 18.44 | 61.46 | 5.22 | 22.51 | 6.07 | 0.32 | 17.10 | 5.11 | 66.11 | 24.24 | 119.31 | 27.61 | 280.01 | 45.61 |
| D025-07 | 0.03 | 16.09 | 0.42 | 7.32 | 13.51 | 0.09 | 64.31 | 20.16 | 234.07 | 78.43 | 325.71 | 63.37 | 541.14 | 78.22 |
| D025-08 | 0.05 | 24.88 | 0.22 | 3.69 | 9.38 | 0.07 | 52.39 | 17.65 | 212.39 | 69.83 | 304.78 | 59.89 | 522.94 | 70.46 |
| D025-09 | 0.02 | 15.04 | 0.13 | 2.89 | 6.59 | 0.02 | 34.68 | 10.86 | 126.36 | 43.39 | 188.24 | 37.21 | 340.16 | 47.22 |
| D025-10 | 0.05 | 29.46 | 0.54 | 8.45 | 17.45 | 0.13 | 84.83 | 24.68 | 281.26 | 91.49 | 379.15 | 72.89 | 613.00 | 90.45 |
| D025-11 | 8.14 | 65.70 | 2.46 | 12.79 | 7.08 | 0.94 | 26.06 | 8.06 | 99.47 | 35.01 | 162.53 | 35.64 | 339.91 | 52.20 |
| D025-12 | 93.53 | 233.69 | 32.05 | 145.69 | 37.44 | 0.57 | 52.94 | 12.58 | 132.56 | 44.18 | 198.97 | 42.11 | 387.32 | 54.80 |
| D025-13 | 0.03 | 27.87 | 0.10 | 2.23 | 5.27 | 0.16 | 31.08 | 10.73 | 138.07 | 49.57 | 231.93 | 50.53 | 465.84 | 68.77 |
| D025-14 | 4.36 | 37.19 | 1.31 | 6.58 | 4.65 | 0.39 | 20.26 | 6.85 | 85.92 | 31.38 | 148.80 | 33.03 | 328.02 | 50.60 |
| D025-15 | 6.38 | 46.39 | 2.24 | 10.27 | 5.36 | 0.32 | 18.63 | 6.34 | 81.54 | 30.22 | 148.59 | 34.66 | 350.36 | 56.18 |
| D025-16 | 0.04 | 15.67 | 0.34 | 6.07 | 13.86 | 0.09 | 70.56 | 21.97 | 257.05 | 84.66 | 354.50 | 67.23 | 569.64 | 84.02 |
| D025-17 | 0.06 | 11.77 | 0.08 | 1.64 | 4.03 | 0.03 | 21.68 | 7.20 | 90.66 | 31.60 | 141.54 | 29.12 | 261.53 | 39.21 |
| D025-18 | 64.17 | 192.44 | 24.45 | 119.29 | 39.71 | 0.20 | 83.15 | 21.97 | 239.78 | 76.37 | 317.10 | 60.91 | 509.11 | 74.45 |
| D025-19 | 25.76 | 82.04 | 7.07 | 31.90 | 9.95 | 0.73 | 27.90 | 8.11 | 97.93 | 34.22 | 157.22 | 34.45 | 325.58 | 52.15 |
| D025-20 | 0.01 | 17.79 | 0.10 | 2.09 | 5.61 | 0.04 | 31.76 | 10.79 | 135.96 | 47.24 | 209.04 | 43.02 | 370.90 | 54.05 |
| D025-21 | 30.69 | 89.40 | 8.60 | 36.24 | 8.94 | 0.42 | 19.83 | 5.62 | 70.10 | 25.07 | 119.43 | 27.12 | 271.06 | 44.14 |
| D025-22 | 3.95 | 32.42 | 1.14 | 6.06 | 3.99 | 0.17 | 18.92 | 6.18 | 79.08 | 28.84 | 136.10 | 29.92 | 283.96 | 44.30 |
| D025-23 | 7.29 | 43.61 | 2.69 | 15.90 | 12.56 | 0.07 | 55.12 | 17.23 | 203.38 | 67.52 | 285.43 | 56.47 | 483.43 | 68.85 |
| D025-24 | 37.77 | 112.48 | 9.79 | 41.98 | 10.82 | 0.66 | 25.34 | 7.87 | 100.57 | 38.39 | 191.16 | 44.67 | 457.81 | 75.74 |
| D025-25 | / | 24.66 | 0.06 | 1.22 | 3.08 | 0.13 | 17.69 | 6.34 | 82.31 | 31.27 | 153.03 | 34.74 | 341.51 | 53.49 |
| 测点号 | 年龄 (Ma) | 176Yb/ 177Hf | 176Lu/ 177Hf | 176Hf/ 177Hf | 2σ | εHf(0) | εHf (t) | 2σ | TDM (Ma) | (Ma) | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND025-1-02 | 134.5 | 0.021489 | 0.000710 | 0.282504 | 0.000016 | -9.9 | -7.0 | 0.6 | 1050 | 1610 | -0.98 |
| ND025-1-03 | 137.6 | 0.060029 | 0.001814 | 0.282727 | 0.000019 | -2.0 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 760 | 1111 | -0.95 |
| ND025-1-04 | 135.0 | 0.087223 | 0.002627 | 0.282702 | 0.000024 | -3.0 | -0.2 | 0.8 | 815 | 1175 | -0.92 |
| ND025-1-05 | 132.3 | 0.037801 | 0.001231 | 0.282558 | 0.000018 | -8.0 | -5.2 | 0.6 | 988 | 1492 | -0.96 |
| ND025-1-06 | 137.8 | 0.024288 | 0.000806 | 0.282472 | 0.000018 | -11.1 | -8.1 | 0.6 | 1098 | 1680 | -0.98 |
| ND025-1-07 | 138.1 | 0.037787 | 0.001153 | 0.282594 | 0.000017 | -6.7 | -3.8 | 0.6 | 935 | 1407 | -0.97 |
| ND025-1-08 | 137.7 | 0.089925 | 0.002680 | 0.282641 | 0.000018 | -5.1 | -2.3 | 0.6 | 906 | 1311 | -0.92 |
| ND025-1-09 | 135.3 | 0.331457 | 0.008975 | 0.282770 | 0.000071 | -0.5 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 867 | 1059 | -0.73 |
| ND025-1-10 | 135.9 | 0.117371 | 0.003438 | 0.282761 | 0.000021 | -0.8 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 743 | 1044 | -0.90 |
| ND025-1-11 | 136.8 | 0.044135 | 0.001452 | 0.282605 | 0.000019 | -6.4 | -3.4 | 0.7 | 927 | 1385 | -0.96 |
表3 南炮台花岗斑岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of the Nanpaotai granite porphyry
| 测点号 | 年龄 (Ma) | 176Yb/ 177Hf | 176Lu/ 177Hf | 176Hf/ 177Hf | 2σ | εHf(0) | εHf (t) | 2σ | TDM (Ma) | (Ma) | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND025-1-02 | 134.5 | 0.021489 | 0.000710 | 0.282504 | 0.000016 | -9.9 | -7.0 | 0.6 | 1050 | 1610 | -0.98 |
| ND025-1-03 | 137.6 | 0.060029 | 0.001814 | 0.282727 | 0.000019 | -2.0 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 760 | 1111 | -0.95 |
| ND025-1-04 | 135.0 | 0.087223 | 0.002627 | 0.282702 | 0.000024 | -3.0 | -0.2 | 0.8 | 815 | 1175 | -0.92 |
| ND025-1-05 | 132.3 | 0.037801 | 0.001231 | 0.282558 | 0.000018 | -8.0 | -5.2 | 0.6 | 988 | 1492 | -0.96 |
| ND025-1-06 | 137.8 | 0.024288 | 0.000806 | 0.282472 | 0.000018 | -11.1 | -8.1 | 0.6 | 1098 | 1680 | -0.98 |
| ND025-1-07 | 138.1 | 0.037787 | 0.001153 | 0.282594 | 0.000017 | -6.7 | -3.8 | 0.6 | 935 | 1407 | -0.97 |
| ND025-1-08 | 137.7 | 0.089925 | 0.002680 | 0.282641 | 0.000018 | -5.1 | -2.3 | 0.6 | 906 | 1311 | -0.92 |
| ND025-1-09 | 135.3 | 0.331457 | 0.008975 | 0.282770 | 0.000071 | -0.5 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 867 | 1059 | -0.73 |
| ND025-1-10 | 135.9 | 0.117371 | 0.003438 | 0.282761 | 0.000021 | -0.8 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 743 | 1044 | -0.90 |
| ND025-1-11 | 136.8 | 0.044135 | 0.001452 | 0.282605 | 0.000019 | -6.4 | -3.4 | 0.7 | 927 | 1385 | -0.96 |
| 样品号 | D025-1 | D025-2 | D025-3 | D025-4 | D025-5 | 样品号 | D025-1 | D025-2 | D025-3 | D025-4 | D025-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 14.31 | 13.76 | 13.84 | 14.17 | 14.11 | Zr | 442.25 | 451.98 | 459.65 | 468.25 | 433.78 |
| SiO2 | 72.27 | 71.76 | 71.81 | 71.24 | 70.53 | Nb | 22.26 | 26.61 | 24.39 | 25.81 | 22.88 |
| CaO | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.56 | Cs | 3.79 | 3.46 | 2.70 | 3.87 | 3.33 |
| K2O | 5.45 | 5.02 | 5.33 | 5.17 | 4.97 | Ba | 895.82 | 677.81 | 845.03 | 816.33 | 930.30 |
| TFe2O3 | 1.79 | 2.52 | 2.28 | 2.90 | 2.94 | La | 95.58 | 44.72 | 109.21 | 56.35 | 81.68 |
| MgO | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.39 | Ce | 175.25 | 169.99 | 181.31 | 171.99 | 166.91 |
| MnO | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | Pr | 13.85 | 10.86 | 17.14 | 12.14 | 13.80 |
| Na2O | 3.96 | 4.07 | 4.13 | 4.16 | 4.51 | Nd | 46.09 | 38.44 | 63.67 | 46.06 | 52.86 |
| P2O5 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.11 | Sm | 6.58 | 6.36 | 10.21 | 8.29 | 9.35 |
| TiO2 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.42 | Eu | 1.10 | 0.92 | 1.25 | 1.13 | 1.27 |
| LOI | 1.00 | 1.11 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 1.20 | Gd | 6.31 | 5.87 | 9.59 | 7.54 | 8.08 |
| Total | 99.99 | 99.71 | 99.62 | 100.12 | 99.77 | Tb | 0.77 | 0.82 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 1.19 |
| Mg# | 17 | 16 | 21 | 19 | 21 | Dy | 3.75 | 4.43 | 6.91 | 5.99 | 6.27 |
| A/CNK | 1.06 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.05 | 1.02 | Ho | 0.75 | 0.83 | 1.30 | 1.06 | 1.15 |
| Na2O+K2O | 9.41 | 9.09 | 9.46 | 9.33 | 9.48 | Er | 2.31 | 2.69 | 4.06 | 3.35 | 3.53 |
| Li | 22.09 | 24.82 | 25.58 | 27.29 | 25.94 | Tm | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.53 |
| Be | 3.30 | 4.09 | 4.33 | 4.28 | 4.47 | Yb | 2.64 | 3.22 | 3.88 | 3.64 | 3.59 |
| Sc | 4.02 | 4.40 | 4.24 | 4.89 | 4.72 | Lu | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.53 |
| V | 18.88 | 17.52 | 14.01 | 17.61 | 18.57 | Hf | 11.34 | 11.84 | 11.84 | 11.65 | 10.84 |
| Cr | 0.66 | 0.74 | 1.23 | 0.43 | 0.55 | Ta | 1.57 | 1.73 | 1.70 | 1.68 | 1.52 |
| Co | 1.40 | 1.49 | 1.82 | 2.60 | 2.75 | Th | 39.19 | 40.91 | 39.92 | 35.11 | 33.88 |
| Ni | 2.05 | 2.69 | 1.08 | 2.61 | 3.62 | U | 2.89 | 4.68 | 5.55 | 9.44 | 2.51 |
| Pb | 23.54 | 24.13 | 24.22 | 27.41 | 16.87 | δEu | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.44 |
| Ga | 25.67 | 25.43 | 26.93 | 25.84 | 25.33 | (La/Yb)N | 24.45 | 9.37 | 18.97 | 10.43 | 15.33 |
| Rb | 216.37 | 208.55 | 225.54 | 208.95 | 183.94 | ∑REE | 371.66 | 308.84 | 442.72 | 344.27 | 375.98 |
| Sr | 136.57 | 127.31 | 141.01 | 149.59 | 130.98 | LREE/HREE | 10.19 | 7.23 | 6.39 | 6.13 | 6.50 |
| Y | 15.95 | 18.80 | 31.64 | 24.63 | 25.23 | Tzr(℃) | 884 | 883 | 883 | 887 | 875 |
表4 南炮台花岗斑岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)组成
Table 4 Major (%) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the Nanpaotai granite porphyry
| 样品号 | D025-1 | D025-2 | D025-3 | D025-4 | D025-5 | 样品号 | D025-1 | D025-2 | D025-3 | D025-4 | D025-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 14.31 | 13.76 | 13.84 | 14.17 | 14.11 | Zr | 442.25 | 451.98 | 459.65 | 468.25 | 433.78 |
| SiO2 | 72.27 | 71.76 | 71.81 | 71.24 | 70.53 | Nb | 22.26 | 26.61 | 24.39 | 25.81 | 22.88 |
| CaO | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.56 | Cs | 3.79 | 3.46 | 2.70 | 3.87 | 3.33 |
| K2O | 5.45 | 5.02 | 5.33 | 5.17 | 4.97 | Ba | 895.82 | 677.81 | 845.03 | 816.33 | 930.30 |
| TFe2O3 | 1.79 | 2.52 | 2.28 | 2.90 | 2.94 | La | 95.58 | 44.72 | 109.21 | 56.35 | 81.68 |
| MgO | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.39 | Ce | 175.25 | 169.99 | 181.31 | 171.99 | 166.91 |
| MnO | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | Pr | 13.85 | 10.86 | 17.14 | 12.14 | 13.80 |
| Na2O | 3.96 | 4.07 | 4.13 | 4.16 | 4.51 | Nd | 46.09 | 38.44 | 63.67 | 46.06 | 52.86 |
| P2O5 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.11 | Sm | 6.58 | 6.36 | 10.21 | 8.29 | 9.35 |
| TiO2 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.42 | Eu | 1.10 | 0.92 | 1.25 | 1.13 | 1.27 |
| LOI | 1.00 | 1.11 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 1.20 | Gd | 6.31 | 5.87 | 9.59 | 7.54 | 8.08 |
| Total | 99.99 | 99.71 | 99.62 | 100.12 | 99.77 | Tb | 0.77 | 0.82 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 1.19 |
| Mg# | 17 | 16 | 21 | 19 | 21 | Dy | 3.75 | 4.43 | 6.91 | 5.99 | 6.27 |
| A/CNK | 1.06 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.05 | 1.02 | Ho | 0.75 | 0.83 | 1.30 | 1.06 | 1.15 |
| Na2O+K2O | 9.41 | 9.09 | 9.46 | 9.33 | 9.48 | Er | 2.31 | 2.69 | 4.06 | 3.35 | 3.53 |
| Li | 22.09 | 24.82 | 25.58 | 27.29 | 25.94 | Tm | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.53 |
| Be | 3.30 | 4.09 | 4.33 | 4.28 | 4.47 | Yb | 2.64 | 3.22 | 3.88 | 3.64 | 3.59 |
| Sc | 4.02 | 4.40 | 4.24 | 4.89 | 4.72 | Lu | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.53 |
| V | 18.88 | 17.52 | 14.01 | 17.61 | 18.57 | Hf | 11.34 | 11.84 | 11.84 | 11.65 | 10.84 |
| Cr | 0.66 | 0.74 | 1.23 | 0.43 | 0.55 | Ta | 1.57 | 1.73 | 1.70 | 1.68 | 1.52 |
| Co | 1.40 | 1.49 | 1.82 | 2.60 | 2.75 | Th | 39.19 | 40.91 | 39.92 | 35.11 | 33.88 |
| Ni | 2.05 | 2.69 | 1.08 | 2.61 | 3.62 | U | 2.89 | 4.68 | 5.55 | 9.44 | 2.51 |
| Pb | 23.54 | 24.13 | 24.22 | 27.41 | 16.87 | δEu | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.44 |
| Ga | 25.67 | 25.43 | 26.93 | 25.84 | 25.33 | (La/Yb)N | 24.45 | 9.37 | 18.97 | 10.43 | 15.33 |
| Rb | 216.37 | 208.55 | 225.54 | 208.95 | 183.94 | ∑REE | 371.66 | 308.84 | 442.72 | 344.27 | 375.98 |
| Sr | 136.57 | 127.31 | 141.01 | 149.59 | 130.98 | LREE/HREE | 10.19 | 7.23 | 6.39 | 6.13 | 6.50 |
| Y | 15.95 | 18.80 | 31.64 | 24.63 | 25.23 | Tzr(℃) | 884 | 883 | 883 | 887 | 875 |

图5 南炮台花岗斑岩TAS图(a)、K2O-SiO2图(b)和A/NK-A/CNK图(c)(底图分别据文献[49]、[50]和[51],研究区及周边岩浆岩数据引自文献[31-32,36,52⇓-54])
Fig.5 Diagrams of TAS (a), K2O versus SiO2 (b) and A/NK versus A/CNK (c) for the Nanpaotai granite porphyry(base maps after refs[49], [50]and [51], respectively; data from refs.[31-32,36,52⇓-54])

图6 南炮台花岗斑岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分型式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化数值分别据文献[48]和[55],研究区及周边岩浆岩数据引自文献[31-32,36,52⇓-54])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE spider diagrams (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagrams of trace elements (b) for the Nanpaotai granite porphyry (normalization values from ref.[48] and [55], respectively; data from refs.[31-32,36,52⇓-54])

图7 南炮台花岗斑岩成因类型判别图(底图据文献[58],研究区及周边岩浆岩数据引自文献[31-32,36,52⇓-54])
Fig.7 Genetic type discrimination for the Nanpaotai granite porphyry (basemap after ref.[58]; data from refs.[31-32,36,52⇓-54])

图9 南炮台花岗斑岩Nb-Y-Ce图解(a)和R1-R2构造环境判别图解(b)(底图分别据文献[56]和[77],研究区及周边岩浆岩数据引自文献[31-32,36,52⇓-54])
Fig.9 Discrimination diagrams of A-type granite (a) and R1-R2 tectonic environment (b) for the Nanpaotai granite porphyry (base maps after refs.[56]and [77], respectively; data from refs.[31-32,36,52⇓-54])
| 序号 | 样品号 | 纬度 | 经度 | 采样位置 | 岩性 | 年龄(Ma) | 测试方法 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 侵入岩 | ||||||||
| 1 | WB08-N3 | 42°20'10″ | 144°55'05″ | 那仁乌拉 | 碱长花岗岩 | 144.9±1.3 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 2 | 729-2S | — | — | 姚五沟 | 花岗斑岩 | 141.6±1.3 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 3 | LQ-67 | 42°22'29″ | 115°44'22″ | 正蓝旗 | 花岗斑岩 | 140.9±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 4 | DH-23 | 42°15'00″ | 114°12'16″ | 道郎呼都格 | 钾长花岗岩 | 139.6±1.7 | SHRIMP | 文献[ |
| 5 | TW03 | — | — | 多伦县 | 石英二长斑岩 | 138.4±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 6 | Sample-5 | 43°07'30″ | 119°01'49″ | 勃隆克 | 花岗岩 | 134.9±4.1 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 7 | WB08-N8 | 42°20'10″ | 144°55'05″ | 白旗 | 花岗斑岩 | 134.6±1.1 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 8 | BQ-05 | — | — | 伊和 | 花岗斑岩 | 135.8±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 9 | BQ-07 | — | — | 三面井 | 正长花岗岩 | 136.8±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 10 | BQ-04 | — | — | 八一牧场 | 似斑状花岗岩 | 138.8±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 11 | BQ-06 | — | — | 食品牧场 | 二长花岗岩 | 139.0±1.3 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 12 | DB1901-7 | 42°23'16″ | 114°47'41″ | 都比 | 花岗斑岩 | 128.8±0.8 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 13 | DB1901-2 | 42°23'8″ | 114°47'39″ | 都比 | 石英斑岩 | 127.8±2.1 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 火山岩 | ||||||||
| 1 | N3 | — | — | 羊盘沟 | 流纹斑岩 | 144.2±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 2 | TW01 | — | — | 多伦县 | 石英粗面岩 | 144.2±0.4 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 3 | HB14-454 | 42°18'14″ | 115°41'13″ | 正蓝旗 | 霏细碎斑熔岩 | 141.6±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 4 | N-1 | — | — | 正蓝旗丹金 | 流纹斑岩 | 141.5±0.5 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 5 | HB14-449 | 42°15'12″ | 115°44'44″ | 正蓝旗 | 流纹岩 | 141.4±0.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
表5 多伦及邻近地区早白垩世年代学数据
Table 5 Early Cretaceous geochronology data of Duolun and its adjacent areas
| 序号 | 样品号 | 纬度 | 经度 | 采样位置 | 岩性 | 年龄(Ma) | 测试方法 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 侵入岩 | ||||||||
| 1 | WB08-N3 | 42°20'10″ | 144°55'05″ | 那仁乌拉 | 碱长花岗岩 | 144.9±1.3 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 2 | 729-2S | — | — | 姚五沟 | 花岗斑岩 | 141.6±1.3 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 3 | LQ-67 | 42°22'29″ | 115°44'22″ | 正蓝旗 | 花岗斑岩 | 140.9±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 4 | DH-23 | 42°15'00″ | 114°12'16″ | 道郎呼都格 | 钾长花岗岩 | 139.6±1.7 | SHRIMP | 文献[ |
| 5 | TW03 | — | — | 多伦县 | 石英二长斑岩 | 138.4±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 6 | Sample-5 | 43°07'30″ | 119°01'49″ | 勃隆克 | 花岗岩 | 134.9±4.1 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 7 | WB08-N8 | 42°20'10″ | 144°55'05″ | 白旗 | 花岗斑岩 | 134.6±1.1 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 8 | BQ-05 | — | — | 伊和 | 花岗斑岩 | 135.8±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 9 | BQ-07 | — | — | 三面井 | 正长花岗岩 | 136.8±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 10 | BQ-04 | — | — | 八一牧场 | 似斑状花岗岩 | 138.8±1.0 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 11 | BQ-06 | — | — | 食品牧场 | 二长花岗岩 | 139.0±1.3 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 12 | DB1901-7 | 42°23'16″ | 114°47'41″ | 都比 | 花岗斑岩 | 128.8±0.8 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 13 | DB1901-2 | 42°23'8″ | 114°47'39″ | 都比 | 石英斑岩 | 127.8±2.1 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 火山岩 | ||||||||
| 1 | N3 | — | — | 羊盘沟 | 流纹斑岩 | 144.2±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 2 | TW01 | — | — | 多伦县 | 石英粗面岩 | 144.2±0.4 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 3 | HB14-454 | 42°18'14″ | 115°41'13″ | 正蓝旗 | 霏细碎斑熔岩 | 141.6±0.6 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 4 | N-1 | — | — | 正蓝旗丹金 | 流纹斑岩 | 141.5±0.5 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
| 5 | HB14-449 | 42°15'12″ | 115°44'44″ | 正蓝旗 | 流纹岩 | 141.4±0.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 文献[ |
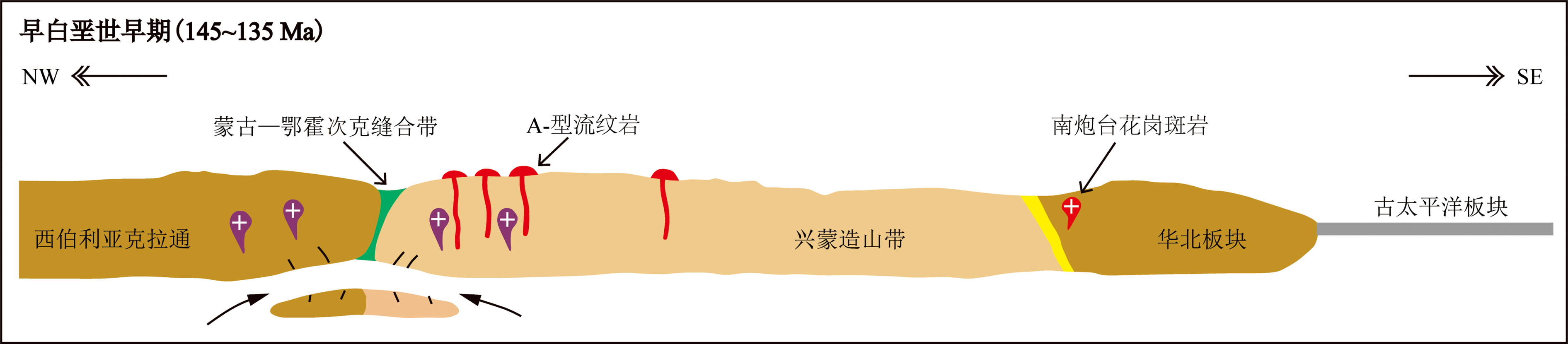
图10 早白垩世早期华北板块北缘中段地区构造示意图(据文献[12]修改)
Fig.10 Schematic tectonic evolution of the middle area of the northern margin of North China Plate during early Early Cretaceous (modified after ref.[12])
| [1] | 张拴宏, 赵越, 刘建民, 等. 华北地块北缘晚古生代—早中生代岩浆活动期次、特征及构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 824-842. |
| [2] |
LI J Y. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions; closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26(3/4): 207-224.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WILDE S A. Final amalgamation of the Central Asian orogenic belt in NE China: Paleo-Asian Ocean closure versus paleo-Pacific Plate subduction-a review of the evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 662: 345-362.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
JIAN P, LIU D, KRöNER A, et al. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China: Implications for continental growth[J]. Lithos, 2008, 101(3): 233-259.
DOI URL |
| [5] | XIAO W, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tecto-nics, 2003, 22(6): 1069. |
| [6] | 赵越, 翟明国, 陈虹, 等. 华北克拉通及相邻造山带古生代—侏罗纪早期大地构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(1): 44-60. |
| [7] | 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2): 15. |
| [8] | 朱日祥, 徐义刚. 西太平洋板块俯冲与华北克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2019, 49(9): 1346-1356. |
| [9] |
LIU J, CAI R, PEARSON D G, et al. Thinning and destruction of the lithospheric mantle root beneath the North China Craton: A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 196: 102873.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 赵越, 陈斌, 张拴宏, 等. 华北克拉通北缘及邻区前燕山期主要地质事件[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4): 900-915. |
| [11] |
WU F Y, YANG J H, XU Y G, et al. Destruction of the North China Craton in the Mesozoic[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2019, 47(1): 173-195.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史:东北亚陆缘中生代—古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2018, 48(5): 549-583. |
| [13] | 翟明国. 华北克拉通构造演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5): 24. |
| [14] | 朱日祥, 陈凌, 吴福元, 等. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2011, 41(5): 10. |
| [15] |
ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, DAVIS G A, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatism and deformation in the North China Craton: Implications for lithospheric thinning and decratoni-zation[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 131(131): 49-87.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 杨进辉, 许蕾, 孙金凤, 等. 华北克拉通破坏与岩浆—成矿的深部动力学过程[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51: 1401. |
| [17] | 甄世民, 王大钊, 白海军, 等. 华北克拉通北缘张家口-宣化地区古生代-中生代岩浆构造活动与成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(6): 1619-1652. |
| [18] | 巫建华, 郭国林, 郭佳磊, 等. 中国东部中生代岩浆岩的时空分布及其与热液型铀矿的关系[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5): 1591-1614. |
| [19] | 巫建华, 郭佳磊, 祝洪涛, 等. 内蒙古东南缘芝瑞盆地流纹斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(3): 383-396. |
| [20] | 蒋孝君, 彭云彪, 董晓杰, 等. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋的远程作用:来自内蒙古东南部羊盘沟地区流纹斑岩成因的证据[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(9): 3057-3073. |
| [21] | 林伟, 王军, 刘飞, 等. 华北克拉通及邻区晚中生代伸展构造及其动力学背景的讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5): 1791-1810. |
| [22] | 郑永飞, 徐峥, 赵子福, 等. 华北中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与克拉通减薄和破坏[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2018, 48(4): 379-414. |
| [23] | 张笑鸣. 华北克拉通东北缘中生代岩浆事件[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2021. |
| [24] | 高爽. 华北板块北缘中段内蒙古察右中旗地区中三叠世花岗岩成因研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2016. |
| [25] | 冯帆, 徐仲元, 董晓杰, 等. 内蒙古温都尔庙—集宁地区花岗斑岩年代学、地球化学、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(6): 1973-1992. |
| [26] | ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, SONG B, et al. Contrasting Late Carboniferous and Late Permian-Middle Triassic intrusive suites from the northern margin of the North China craton: Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic implications[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2009, 121(1/2): 181-200. |
| [27] | 廖祥东. 内蒙古赤峰南部地区晚古生代-中生代花岗岩类年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2019. |
| [28] | 吴福元, 杨进辉, 张艳斌, 等. 辽西东南部中生代花岗岩时代[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(2): 315-325. |
| [29] | 康月蓝, 石玉若. 北京云蒙山地区侵入岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(3): 379-394. |
| [30] | 梁键婷, 欧阳志侠, 张莹, 等. 医巫闾山变质核杂岩核部晚中生代花岗岩成因及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(4): 671-686. |
| [31] | 李春麟, 王宗秀, 陶涛. 华北板块北缘勃隆克A型花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(1): 40-50. |
| [32] | 解洪晶, 武广, 朱明田, 等. 内蒙古道郎呼都格地区A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 483-494. |
| [33] | 王春林. 内蒙古多伦地区早白垩世岩浆作用及其构造背景[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2021. |
| [34] | 雷光. 内蒙古正镶白旗中生代花岗岩类岩石学特征研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2019. |
| [35] | 许文良, 孙晨阳, 唐杰, 等. 兴蒙造山带的基底属性与构造演化过程[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(5): 1620-1646. |
| [36] | 刘哲. 内蒙古正蓝旗地区中生代火山-侵入岩岩石学、地球化学特征及其成因意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2017. |
| [37] | 蒋孝君, 苗爱生, 李华明, 等. 内蒙古多伦山间盆地砂岩型铀矿新发现及找矿前景[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 88-96, 105. |
| [38] | 白志达, 顾德林, 徐德斌. 内蒙古多伦环形影像的成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2003, 30(3): 261-267. |
| [39] | 韩军, 薛伟, 宋庆年. 内蒙古多伦县核桃坝地区火山岩型铀成矿特征及找矿标志[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(3): 772-790. |
| [40] | 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(增): 600-601. |
| [41] |
LIU Y, HU Z, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1):34-43.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WU F Y, YANG Y H, XIE L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234(1): 105-126.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
CHU N C, TAYLOR R N, CHAVAGNAC V, et al. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: an evaluation of isobaric interference corrections[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2002, 17(12): 1567-1574.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
HOSKIN P W O, BLACK L P. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of metamorphic geology, 2000, 18(4): 423-439.
DOI URL |
| [45] | RUBATTO D, GEBAUER D, PAGEL M, et al. Use of cathodoluminescence for U-Pb zircon dating by ion microprobe: some examples from the Western Alps[M].Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences.Berlin: Springer, 2000: 373-400. |
| [46] |
赵志丹, 刘栋, 王青, 等. 锆石微量元素及其揭示的深部过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(6): 124-135.
DOI |
| [47] |
PETTKE T, AUDéTAT A, SCHALTEGGER U, et al. Magma-tic-to-hydrothermal crystallization in the W-Sn mineralized Mole Granite (NSW, Australia): Part II-Evolving zircon and thorite trace element chemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 220(3): 191-213.
DOI URL |
| [48] | BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements; meteorite studies[M]// HENDERSONP. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [49] |
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8(5): 523-548.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [52] | 秦亚, 梁一鸿, 邢济麟, 等. 内蒙古正镶白旗地区早白垩世A型花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS测年、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(增): 154-165. |
| [53] | 林智炜, 吴堑虹, 奚小双, 等. 华北板块北缘中段姚五沟岩体锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及其与区域构造演化的关系[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2019, 34(1): 104-116. |
| [54] | 姚国华, 胡乔青, 牛文林, 等. 内蒙古正镶白旗都比地区石英斑岩和花岗斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(3): 899-916. |
| [55] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts; implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641-644.
DOI URL |
| [57] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Earth Sciences, 1992, 79: 169-181. |
| [58] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 卢良兆, 许文良. 岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011. |
| [60] | 马鸿文. 花岗岩成因类型的判别分析[J]. 岩石学报, 1992, 8(4): 341. |
| [61] |
BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks: evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1/2):1-29.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2): 295-304.
DOI URL |
| [63] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [64] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. |
| [65] | 周振华, 武新丽, 欧阳荷根. 内蒙古莲花山铜银矿斜长花岗斑岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、Hf同位素研究及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6): 1472-1485. |
| [66] | 陈春良, 江思宏, 梁清玲, 等. 河北雾灵山杂岩体锆石Hf同位素特征及其区域对比研究[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 663-673. |
| [67] |
HOFMANN A W, JOCHUM K P, SEUFERT M, et al. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: new constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(1/2): 33-45.
DOI URL |
| [68] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M, ANONYMOU S. The composition and evolution of the continental crust: rare earth element evidence from sedimentary rocks[J]. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London (Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences) 1981, 301: 381-399. |
| [69] | 杨德彬, 许文良, 裴福萍, 等. 蚌埠隆起区古元古代钾长花岗岩的成因:岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素的制约[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(1): 148-164. |
| [70] | CLEMENS J D, HOLLOWAY J R, WHITE A. Origin of an A-type granite: experimental constraints[J]. American Minera-logist, 1986, 71(3): 317-324. |
| [71] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, LI H, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China: age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2): 143-173.
DOI URL |
| [72] | FROST C D, RÄMÖ O T, DALL'AGNOL R. IGCP Project 510 — A-type granites and related rocks through time[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1): vii-xiii. |
| [73] | AZER M K. The petrogenesis of Late Precambrian felsic alkaline magmatism in south Sinai, Egypt[J]. Acta Geologica Polonica, 2006, 56(4): 463-484. |
| [74] | 刘哲, 薛怀民, 曹光跃. 内蒙古正蓝旗地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄与板内伸展环境成因讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(1): 151-176. |
| [75] | 林少泽, 王飞, 谢成龙, 等. 华北克拉通北缘喀喇沁变质核杂岩早白垩世构造演化过程与形成模式[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(1): 1-16. |
| [76] | 陈印, 朱光, 刘文刚, 等. 北京云蒙山地区中生代岩浆活动及构造演化[J]. 地质论评, 2018, 64(4): 843-868. |
| [77] |
BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1/4): 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [78] | ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, SONG B, et al. Petrogenesis of the Middle Devonian Gushan diorite pluton on the northern margin of the North China block and its tectonic implications[J]. Geolo-gical Magazine, 2007, 144(3): 553-568. |
| [79] | 翟明国, 樊祺诚, 张宏福, 等. 华北东部岩石圈减薄中的下地壳过程:岩浆底侵、置换与拆沉作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(6): 1509-1526. |
| [80] | 刘红涛, 翟明国, 刘建明, 等. 华北克拉通北缘中生代花岗岩:从碰撞后到非造山[J]. 岩石学报, 2002, 18(4): 433-448. |
| [81] | 柳永清, 刘燕学, 姬书安, 等. 内蒙古宁城和辽西凌源热水汤地区道虎沟生物群与相关地层SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及有关问题的讨论[J]. 科学通报, 2006(19): 2273-2282. |
| [82] | 王春林, 孟明亮, 鲁孝军, 等. 内蒙古多伦晚中生代中酸性火山岩岩石地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(5): 988-1000. |
| [83] | 李宇. 兴安地块中生代火成岩的年代学与地球化学:对蒙古—鄂霍次克构造体系演化的制约[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018. |
| [84] |
COGNé J P, KRAVCHINSKY V A, HALIM N, et al. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean demonstrated by new Mesozoic palaeomagnetic results from the Trans-Baïkal area (SE Siberia)[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 163(2): 813-832.
DOI URL |
| [85] | 车亚文. 大兴安岭南段早白垩世岩浆活动及其构造背景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021. |
| [86] |
王涛, 张建军, 李舢, 等. 东北亚晚古生代—中生代岩浆时空演化:多重板块构造体制范围及叠合的鉴别证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(2): 28-44.
DOI |
| [87] | 许文良, 王旖旎, 王枫, 等. 西太平洋俯冲带的演变: 来自东北亚陆缘增生杂岩的制约[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(1): 1-17. |
| [88] |
WU F Y, LIN J Q, WILDE S A, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1): 103-119.
DOI URL |
| [89] | 蒋孝君, 彭云彪, 薛伟, 等. 内蒙古正蓝旗丹金地区赋矿火山岩年代学、地球化学特征及铀成矿时代[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(4): 893-907. |
| [1] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [2] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [3] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [4] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [5] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [6] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [7] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [8] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [9] | 杨文鹏, 李成禄, 杨元江, 符安宗, 郑博, 周腾飞, 赵瑞君. 黑龙江塔溪地区中侏罗世侵入岩地球化学特征、成因及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 390-403. |
| [10] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [11] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [12] | 王战永, 隆兆笃, 解波, 孙悦, 李巨初, 向杰, 范永宏. 四川冕西岩体岩石地球化学特征及铀成矿条件分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1465-1474. |
| [13] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [14] | 杨瀚文, 王建中, 赵军, 段俊, 王荣敏, 高文彬, 魏文昊, 郑延河. 新疆温泉地区晚石炭世古老地壳重熔: 花岗斑岩脉侵位年龄及其Sr、Nd同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 824-835. |
| [15] | 吕云鹤, 董国臣, 赵丽玮, 苏麟, 殷国栋, 汤家辉. 内蒙古沙章土矿区闪长玢岩成岩时代及岩浆源区探讨:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 836-847. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||