



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (01): 282-294.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.046
周桐1,2,3( ), 孙珍军1,2(
), 孙珍军1,2( ), 于赫楠1,2, 王承洋1,2, 刘广虎1,2
), 于赫楠1,2, 王承洋1,2, 刘广虎1,2
收稿日期:2020-11-20
修回日期:2021-11-10
出版日期:2022-02-10
发布日期:2022-03-08
通讯作者:
孙珍军
作者简介:孙珍军,男,副教授,1982年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床地质学、矿床地球化学研究。Email: 306292193@qq.com。基金资助:
ZHU Tong1,2,3( ), SUN Zhenjun1,2(
), SUN Zhenjun1,2( ), YU Henan1,2, WANG Chengyang1,2, LIU Guanghu1,2
), YU Henan1,2, WANG Chengyang1,2, LIU Guanghu1,2
Received:2020-11-20
Revised:2021-11-10
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2022-03-08
Contact:
SUN Zhenjun
摘要:
内蒙古赤峰浩布高铅锌矿床大地构造位置位于大兴安岭地区南段,属黄岗梁—甘珠尔庙褶皱成矿带。对浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体进行了详细的岩石学、年代学、岩石地球化学和Hf同位素研究。结果显示:小罕山岩体主要岩石类型为二长花岗岩,形成于(143.9±1.1) Ma,属于早白垩世;地球化学组成上表现出高硅(SiO2=66.96%~68.05%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=9.91%~10.09%)、弱铝(Al2O3=15.69%~16.49%)、低钙(CaO=1.22%~1.41%)及低TFe2O3/MgO值(平均值为8.29)的特征,属于准铝质到过铝质花岗岩;稀土元素配分曲线呈右倾轻稀土富集,δEu(0.33~0.41)表现为明显的负异常,总体表现出富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、K等元素)和不相容元素(Th、U等元素)、亏损高场强元素(Nb、P、Nb、Ta、Ti等元素)的特征,显示出A2型花岗岩属性。样品初始176Hf/177Hf值为0.282 829~0.282 936,平均值为0.282 888;εHf(t)范围在4.4~8.4之间,平均值为6.7,表明小罕山岩体主要源于中下地壳部分熔融,且有少量地幔物质加入。综合认为小罕山岩体的形成与早白垩世古太平洋板块俯冲大陆边缘的后碰撞伸展构造环境有关。
中图分类号:
周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294.
ZHU Tong, SUN Zhenjun, YU Henan, WANG Chengyang, LIU Guanghu. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Hf isotope and Whole-Rock Geochemical Characteristics of Xiaohanshan Pluton in Haobugao Pb-Zn Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(01): 282-294.
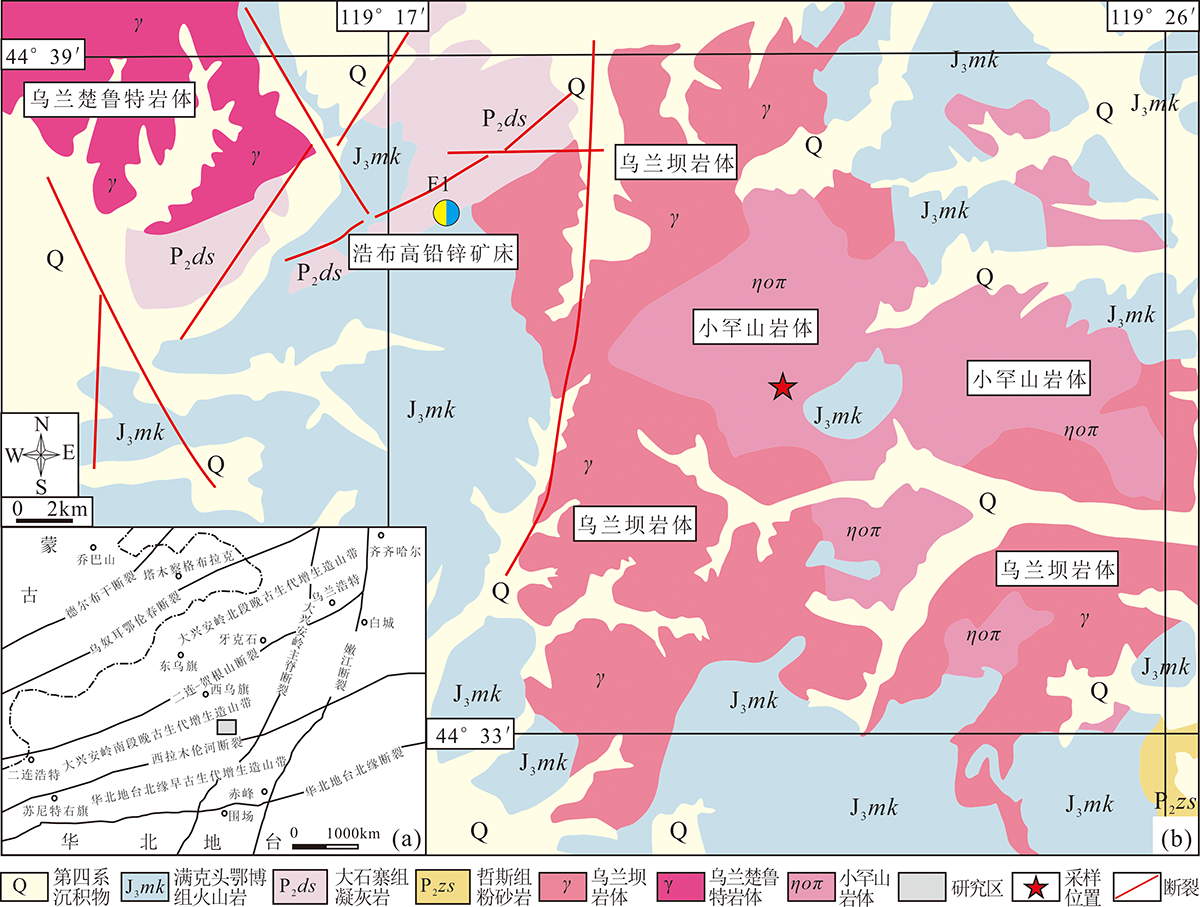
图1 研究区大地构造位置图(a)和浩布高铅锌矿地质简图(b) (分别据参考文献[12]和[28]修改)
Fig.1 Tectonic map of the study area (a) and geologic map of the Haobugao lead-zinc deposit (b) (modified after references [12] and [28], respectively)

图3 小罕山岩体手标本(a)及正交偏光镜下照片(b) Pl.斜长石;Qtz.石英;Kf.钾长石
Fig.3 Hand-specimen photo (a) and thin-section photomicrograph (crossed-polar)(b) of the Xiaohanshan pluton
| 分析点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||
| XHS-02-03 | 26 | 68 | 0.39 | 0.153 36 | 0.015 17 | 0.022 59 | 0.000 66 | 144.9 | 13.4 | 144.0 | 4.2 |
| XHS-02-04 | 989 | 1167 | 0.85 | 0.156 51 | 0.004 92 | 0.022 40 | 0.000 41 | 147.6 | 4.3 | 142.8 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-05 | 165 | 466 | 0.35 | 0.148 07 | 0.005 50 | 0.022 35 | 0.000 41 | 140.2 | 4.9 | 142.5 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-06 | 651 | 777 | 0.84 | 0.155 88 | 0.004 10 | 0.022 33 | 0.000 39 | 147.1 | 3.6 | 142.3 | 2.5 |
| XHS-02-07 | 117 | 324 | 0.36 | 0.156 13 | 0.004 63 | 0.022 56 | 0.000 36 | 147.3 | 4.1 | 143.8 | 2.3 |
| XHS-02-08 | 202 | 534 | 0.38 | 0.155 15 | 0.004 59 | 0.022 48 | 0.000 39 | 146.4 | 4.0 | 143.3 | 2.5 |
| XHS-02-09 | 719 | 650 | 1.11 | 0.156 90 | 0.005 63 | 0.022 79 | 0.000 41 | 148.0 | 4.9 | 145.2 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-10 | 154 | 450 | 0.34 | 0.151 25 | 0.004 65 | 0.022 48 | 0.000 41 | 143.0 | 4.1 | 143.3 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-11 | 212 | 297 | 0.71 | 0.148 68 | 0.007 04 | 0.022 47 | 0.000 44 | 140.7 | 6.2 | 143.2 | 2.7 |
| XHS-02-12 | 263 | 643 | 0.41 | 0.154 01 | 0.004 71 | 0.022 72 | 0.000 44 | 145.4 | 4.1 | 144.8 | 2.8 |
| XHS-02-13 | 189 | 426 | 0.44 | 0.153 81 | 0.005 38 | 0.022 72 | 0.000 40 | 145.3 | 4.7 | 144.8 | 2.5 |
| XHS-02-14 | 82 | 118 | 0.70 | 0.147 22 | 0.007 13 | 0.022 61 | 0.000 47 | 139.5 | 6.3 | 144.1 | 3.0 |
| XHS-02-15 | 164 | 506 | 0.32 | 0.151 08 | 0.005 37 | 0.022 64 | 0.000 35 | 142.9 | 4.7 | 144.3 | 2.2 |
| XHS-02-16 | 176 | 490 | 0.36 | 0.153 86 | 0.007 54 | 0.022 71 | 0.000 52 | 145.3 | 6.6 | 144.7 | 3.3 |
| XHS-02-17 | 188 | 501 | 0.37 | 0.154 01 | 0.006 00 | 0.022 68 | 0.000 49 | 145.4 | 5.3 | 144.6 | 3.1 |
| XHS-02-18 | 108 | 341 | 0.32 | 0.153 60 | 0.007 03 | 0.022 78 | 0.000 41 | 145.1 | 6.2 | 145.2 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-20 | 421 | 798 | 0.53 | 0.155 54 | 0.003 54 | 0.022 58 | 0.000 36 | 146.8 | 3.1 | 144.0 | 2.3 |
| XHS-02-21 | 148 | 157 | 0.95 | 0.152 18 | 0.010 33 | 0.022 44 | 0.000 43 | 143.8 | 9.1 | 143.1 | 2.7 |
| XHS-02-22 | 148 | 436 | 0.34 | 0.155 08 | 0.006 60 | 0.022 64 | 0.000 45 | 146.4 | 5.8 | 144.3 | 2.8 |
| XHS-02-24 | 269 | 458 | 0.59 | 0.155 02 | 0.004 63 | 0.022 51 | 0.000 35 | 146.3 | 4.1 | 143.5 | 2.2 |
表1 小罕山岩体(样品XHS-02)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data for the Xiaohanshan pluton (Sample XHS-02)
| 分析点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||
| XHS-02-03 | 26 | 68 | 0.39 | 0.153 36 | 0.015 17 | 0.022 59 | 0.000 66 | 144.9 | 13.4 | 144.0 | 4.2 |
| XHS-02-04 | 989 | 1167 | 0.85 | 0.156 51 | 0.004 92 | 0.022 40 | 0.000 41 | 147.6 | 4.3 | 142.8 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-05 | 165 | 466 | 0.35 | 0.148 07 | 0.005 50 | 0.022 35 | 0.000 41 | 140.2 | 4.9 | 142.5 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-06 | 651 | 777 | 0.84 | 0.155 88 | 0.004 10 | 0.022 33 | 0.000 39 | 147.1 | 3.6 | 142.3 | 2.5 |
| XHS-02-07 | 117 | 324 | 0.36 | 0.156 13 | 0.004 63 | 0.022 56 | 0.000 36 | 147.3 | 4.1 | 143.8 | 2.3 |
| XHS-02-08 | 202 | 534 | 0.38 | 0.155 15 | 0.004 59 | 0.022 48 | 0.000 39 | 146.4 | 4.0 | 143.3 | 2.5 |
| XHS-02-09 | 719 | 650 | 1.11 | 0.156 90 | 0.005 63 | 0.022 79 | 0.000 41 | 148.0 | 4.9 | 145.2 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-10 | 154 | 450 | 0.34 | 0.151 25 | 0.004 65 | 0.022 48 | 0.000 41 | 143.0 | 4.1 | 143.3 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-11 | 212 | 297 | 0.71 | 0.148 68 | 0.007 04 | 0.022 47 | 0.000 44 | 140.7 | 6.2 | 143.2 | 2.7 |
| XHS-02-12 | 263 | 643 | 0.41 | 0.154 01 | 0.004 71 | 0.022 72 | 0.000 44 | 145.4 | 4.1 | 144.8 | 2.8 |
| XHS-02-13 | 189 | 426 | 0.44 | 0.153 81 | 0.005 38 | 0.022 72 | 0.000 40 | 145.3 | 4.7 | 144.8 | 2.5 |
| XHS-02-14 | 82 | 118 | 0.70 | 0.147 22 | 0.007 13 | 0.022 61 | 0.000 47 | 139.5 | 6.3 | 144.1 | 3.0 |
| XHS-02-15 | 164 | 506 | 0.32 | 0.151 08 | 0.005 37 | 0.022 64 | 0.000 35 | 142.9 | 4.7 | 144.3 | 2.2 |
| XHS-02-16 | 176 | 490 | 0.36 | 0.153 86 | 0.007 54 | 0.022 71 | 0.000 52 | 145.3 | 6.6 | 144.7 | 3.3 |
| XHS-02-17 | 188 | 501 | 0.37 | 0.154 01 | 0.006 00 | 0.022 68 | 0.000 49 | 145.4 | 5.3 | 144.6 | 3.1 |
| XHS-02-18 | 108 | 341 | 0.32 | 0.153 60 | 0.007 03 | 0.022 78 | 0.000 41 | 145.1 | 6.2 | 145.2 | 2.6 |
| XHS-02-20 | 421 | 798 | 0.53 | 0.155 54 | 0.003 54 | 0.022 58 | 0.000 36 | 146.8 | 3.1 | 144.0 | 2.3 |
| XHS-02-21 | 148 | 157 | 0.95 | 0.152 18 | 0.010 33 | 0.022 44 | 0.000 43 | 143.8 | 9.1 | 143.1 | 2.7 |
| XHS-02-22 | 148 | 436 | 0.34 | 0.155 08 | 0.006 60 | 0.022 64 | 0.000 45 | 146.4 | 5.8 | 144.3 | 2.8 |
| XHS-02-24 | 269 | 458 | 0.59 | 0.155 02 | 0.004 63 | 0.022 51 | 0.000 35 | 146.3 | 4.1 | 143.5 | 2.2 |
| 样品号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XHS-1 | 67.42 | 15.87 | 3.11 | 0.38 | 1.36 | 4.71 | 5.38 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 98.99 |
| XHS-2 | 67.12 | 15.69 | 3.31 | 0.41 | 1.22 | 4.64 | 5.30 | 0.08 | 0.38 | 0.10 | 0.95 | 98.78 |
| XHS-3 | 67.20 | 15.86 | 3.46 | 0.42 | 1.41 | 4.65 | 5.37 | 0.08 | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.63 | 99.16 |
| XHS-4 | 68.05 | 16.49 | 3.31 | 0.39 | 1.32 | 4.64 | 5.32 | 0.07 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 100.30 |
| XHS-5 | 66.97 | 15.71 | 3.31 | 0.39 | 1.39 | 4.72 | 5.20 | 0.08 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 1.07 | 98.93 |
| 样品号 | Sc | V | Co | Ni | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba |
| XHS-1 | 7.62 | 14.18 | 1.92 | 6.72 | 61.94 | 22.12 | 110.98 | 139.42 | 439.91 | 9.06 | 5.98 | 779.80 |
| XHS-2 | 8.13 | 16.43 | 3.22 | 37.37 | 111.11 | 23.41 | 121.61 | 139.72 | 452.24 | 10.26 | 6.91 | 733.44 |
| XHS-3 | 8.47 | 17.33 | 2.65 | 9.55 | 85.91 | 22.63 | 110.99 | 135.20 | 451.93 | 9.66 | 7.89 | 811.02 |
| XHS-4 | 7.99 | 16.24 | 2.78 | 12.97 | 94.63 | 23.84 | 110.94 | 152.48 | 468.80 | 9.80 | 6.01 | 810.71 |
| XHS-5 | 7.68 | 16.44 | 2.37 | 7.16 | 79.53 | 22.41 | 105.54 | 141.22 | 452.39 | 9.56 | 5.68 | 736.50 |
| 样品号 | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
| XHS-1 | 9.78 | 0.75 | 16.19 | 10.07 | 2.17 | 27.22 | 54.90 | 113.38 | 11.89 | 43.39 | 7.20 | 0.85 |
| XHS-2 | 10.03 | 0.83 | 21.86 | 10.99 | 2.79 | 29.92 | 58.34 | 122.85 | 12.85 | 46.04 | 7.55 | 0.80 |
| XHS-3 | 10.05 | 0.77 | 18.13 | 11.16 | 2.25 | 29.09 | 57.11 | 116.25 | 12.55 | 46.42 | 8.16 | 0.92 |
| XHS-4 | 10.18 | 0.78 | 19.71 | 9.69 | 2.38 | 28.64 | 48.84 | 100.66 | 11.23 | 41.11 | 7.25 | 0.93 |
| XHS-5 | 10.02 | 0.77 | 16.30 | 9.88 | 2.60 | 27.73 | 49.09 | 102.75 | 11.26 | 40.98 | 7.06 | 0.82 |
| 样品号 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (Ce/Yb)N |
| XHS-1 | 0.30 | 0.96 | 5.31 | 1.05 | 3.08 | 0.44 | 3.02 | 0.44 | 252.55 | 0.38 | 13.03 | 10.42 |
| XHS-2 | 0.60 | 1.05 | 5.72 | 1.15 | 3.40 | 0.47 | 3.20 | 0.48 | 271.00 | 0.33 | 13.08 | 10.66 |
| XHS-3 | 0.30 | 1.07 | 5.89 | 1.16 | 3.28 | 0.46 | 3.17 | 0.47 | 264.09 | 0.37 | 12.91 | 10.18 |
| XHS-4 | 0.30 | 1.01 | 5.52 | 1.13 | 3.23 | 0.45 | 3.10 | 0.46 | 231.45 | 0.41 | 11.32 | 9.03 |
| XHS-5 | 0.21 | 0.96 | 5.32 | 1.06 | 3.04 | 0.43 | 3.01 | 0.45 | 232.63 | 0.37 | 11.70 | 9.48 |
表2 小罕山岩体样品主量(%)、微量(10-6)及稀土元素分析数据
Table 2 Major(%), trace(10-6), and rare earth element(10-6) compositions of samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton
| 样品号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XHS-1 | 67.42 | 15.87 | 3.11 | 0.38 | 1.36 | 4.71 | 5.38 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 98.99 |
| XHS-2 | 67.12 | 15.69 | 3.31 | 0.41 | 1.22 | 4.64 | 5.30 | 0.08 | 0.38 | 0.10 | 0.95 | 98.78 |
| XHS-3 | 67.20 | 15.86 | 3.46 | 0.42 | 1.41 | 4.65 | 5.37 | 0.08 | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.63 | 99.16 |
| XHS-4 | 68.05 | 16.49 | 3.31 | 0.39 | 1.32 | 4.64 | 5.32 | 0.07 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 100.30 |
| XHS-5 | 66.97 | 15.71 | 3.31 | 0.39 | 1.39 | 4.72 | 5.20 | 0.08 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 1.07 | 98.93 |
| 样品号 | Sc | V | Co | Ni | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba |
| XHS-1 | 7.62 | 14.18 | 1.92 | 6.72 | 61.94 | 22.12 | 110.98 | 139.42 | 439.91 | 9.06 | 5.98 | 779.80 |
| XHS-2 | 8.13 | 16.43 | 3.22 | 37.37 | 111.11 | 23.41 | 121.61 | 139.72 | 452.24 | 10.26 | 6.91 | 733.44 |
| XHS-3 | 8.47 | 17.33 | 2.65 | 9.55 | 85.91 | 22.63 | 110.99 | 135.20 | 451.93 | 9.66 | 7.89 | 811.02 |
| XHS-4 | 7.99 | 16.24 | 2.78 | 12.97 | 94.63 | 23.84 | 110.94 | 152.48 | 468.80 | 9.80 | 6.01 | 810.71 |
| XHS-5 | 7.68 | 16.44 | 2.37 | 7.16 | 79.53 | 22.41 | 105.54 | 141.22 | 452.39 | 9.56 | 5.68 | 736.50 |
| 样品号 | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
| XHS-1 | 9.78 | 0.75 | 16.19 | 10.07 | 2.17 | 27.22 | 54.90 | 113.38 | 11.89 | 43.39 | 7.20 | 0.85 |
| XHS-2 | 10.03 | 0.83 | 21.86 | 10.99 | 2.79 | 29.92 | 58.34 | 122.85 | 12.85 | 46.04 | 7.55 | 0.80 |
| XHS-3 | 10.05 | 0.77 | 18.13 | 11.16 | 2.25 | 29.09 | 57.11 | 116.25 | 12.55 | 46.42 | 8.16 | 0.92 |
| XHS-4 | 10.18 | 0.78 | 19.71 | 9.69 | 2.38 | 28.64 | 48.84 | 100.66 | 11.23 | 41.11 | 7.25 | 0.93 |
| XHS-5 | 10.02 | 0.77 | 16.30 | 9.88 | 2.60 | 27.73 | 49.09 | 102.75 | 11.26 | 40.98 | 7.06 | 0.82 |
| 样品号 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (Ce/Yb)N |
| XHS-1 | 0.30 | 0.96 | 5.31 | 1.05 | 3.08 | 0.44 | 3.02 | 0.44 | 252.55 | 0.38 | 13.03 | 10.42 |
| XHS-2 | 0.60 | 1.05 | 5.72 | 1.15 | 3.40 | 0.47 | 3.20 | 0.48 | 271.00 | 0.33 | 13.08 | 10.66 |
| XHS-3 | 0.30 | 1.07 | 5.89 | 1.16 | 3.28 | 0.46 | 3.17 | 0.47 | 264.09 | 0.37 | 12.91 | 10.18 |
| XHS-4 | 0.30 | 1.01 | 5.52 | 1.13 | 3.23 | 0.45 | 3.10 | 0.46 | 231.45 | 0.41 | 11.32 | 9.03 |
| XHS-5 | 0.21 | 0.96 | 5.32 | 1.06 | 3.04 | 0.43 | 3.01 | 0.45 | 232.63 | 0.37 | 11.70 | 9.48 |
| 点号 | t/Ma | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | 1σ | εHf(t) | TDM1/Ma | TDM2/Ma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XHS-02-03 | 144.0 | 0.001 562 | 0.060 470 | 0.282 897 | 0.000 019 | 7.02 | 510.45 | 723.57 |
| XHS-02-04 | 142.8 | 0.002 278 | 0.090 737 | 0.282 882 | 0.000 016 | 6.40 | 542.38 | 762.29 |
| XHS-02-05 | 142.5 | 0.001 236 | 0.047 621 | 0.282 894 | 0.000 017 | 6.90 | 510.89 | 730.21 |
| XHS-02-06 | 142.3 | 0.001 776 | 0.067 297 | 0.282 829 | 0.000 019 | 4.54 | 612.77 | 881.02 |
| XHS-02-07 | 143.8 | 0.002 251 | 0.088 018 | 0.282 861 | 0.000 021 | 5.68 | 572.94 | 809.34 |
| XHS-02-08 | 143.3 | 0.002 070 | 0.085 905 | 0.282 923 | 0.000 021 | 7.88 | 479.62 | 668.22 |
| XHS-02-10 | 143.3 | 0.001 053 | 0.040 029 | 0.282 870 | 0.000 017 | 6.09 | 542.17 | 782.46 |
| XHS-02-11 | 143.2 | 0.002 322 | 0.089 539 | 0.282 889 | 0.000 021 | 6.63 | 533.63 | 747.85 |
| XHS-02-14 | 144.1 | 0.000 649 | 0.023 870 | 0.282 884 | 0.000 017 | 6.63 | 517.26 | 748.71 |
| XHS-02-15 | 144.3 | 0.000 978 | 0.034 827 | 0.282 916 | 0.000 020 | 7.76 | 475.49 | 676.66 |
| XHS-02-17 | 144.6 | 0.000 989 | 0.039 083 | 0.282 874 | 0.000 015 | 6.28 | 534.95 | 771.27 |
| XHS-02-20 | 144 | 0.001 411 | 0.055 054 | 0.282 870 | 0.000 017 | 6.09 | 546.86 | 783.39 |
| XHS-02-21 | 143.1 | 0.001 360 | 0.052 966 | 0.282 936 | 0.000 019 | 8.40 | 451.72 | 634.36 |
| XHS-02-22 | 144.3 | 0.002 057 | 0.083 746 | 0.282 892 | 0.000 018 | 6.80 | 524.89 | 738.10 |
| XHS-02-24 | 143.5 | 0.001 578 | 0.060 935 | 0.282 914 | 0.000 016 | 7.58 | 487.24 | 687.12 |
表3 小罕山岩体(样品XHS-02)锆石Hf同位素数据
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic data of the Xiaohanshan pluton (sample XHS-02)
| 点号 | t/Ma | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | 1σ | εHf(t) | TDM1/Ma | TDM2/Ma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XHS-02-03 | 144.0 | 0.001 562 | 0.060 470 | 0.282 897 | 0.000 019 | 7.02 | 510.45 | 723.57 |
| XHS-02-04 | 142.8 | 0.002 278 | 0.090 737 | 0.282 882 | 0.000 016 | 6.40 | 542.38 | 762.29 |
| XHS-02-05 | 142.5 | 0.001 236 | 0.047 621 | 0.282 894 | 0.000 017 | 6.90 | 510.89 | 730.21 |
| XHS-02-06 | 142.3 | 0.001 776 | 0.067 297 | 0.282 829 | 0.000 019 | 4.54 | 612.77 | 881.02 |
| XHS-02-07 | 143.8 | 0.002 251 | 0.088 018 | 0.282 861 | 0.000 021 | 5.68 | 572.94 | 809.34 |
| XHS-02-08 | 143.3 | 0.002 070 | 0.085 905 | 0.282 923 | 0.000 021 | 7.88 | 479.62 | 668.22 |
| XHS-02-10 | 143.3 | 0.001 053 | 0.040 029 | 0.282 870 | 0.000 017 | 6.09 | 542.17 | 782.46 |
| XHS-02-11 | 143.2 | 0.002 322 | 0.089 539 | 0.282 889 | 0.000 021 | 6.63 | 533.63 | 747.85 |
| XHS-02-14 | 144.1 | 0.000 649 | 0.023 870 | 0.282 884 | 0.000 017 | 6.63 | 517.26 | 748.71 |
| XHS-02-15 | 144.3 | 0.000 978 | 0.034 827 | 0.282 916 | 0.000 020 | 7.76 | 475.49 | 676.66 |
| XHS-02-17 | 144.6 | 0.000 989 | 0.039 083 | 0.282 874 | 0.000 015 | 6.28 | 534.95 | 771.27 |
| XHS-02-20 | 144 | 0.001 411 | 0.055 054 | 0.282 870 | 0.000 017 | 6.09 | 546.86 | 783.39 |
| XHS-02-21 | 143.1 | 0.001 360 | 0.052 966 | 0.282 936 | 0.000 019 | 8.40 | 451.72 | 634.36 |
| XHS-02-22 | 144.3 | 0.002 057 | 0.083 746 | 0.282 892 | 0.000 018 | 6.80 | 524.89 | 738.10 |
| XHS-02-24 | 143.5 | 0.001 578 | 0.060 935 | 0.282 914 | 0.000 016 | 7.58 | 487.24 | 687.12 |
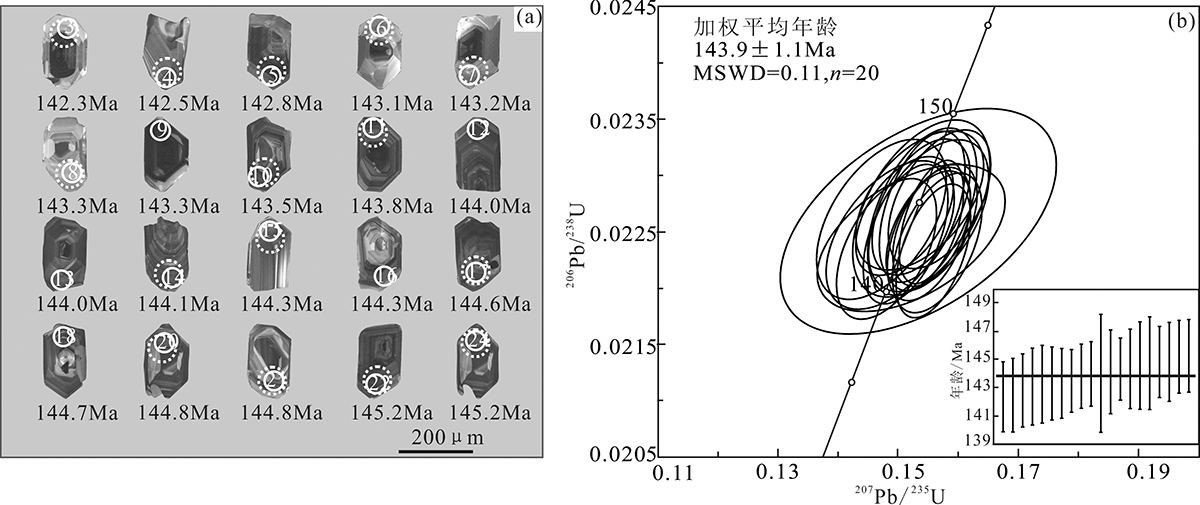
图4 小罕山岩体(样品XHS-02)锆石阴极发光(CL)图像(a)及年龄谐和图(b) (图4(a)中实线为U-Pb同位素测试点,虚线为Hf同位素测试点)
Fig.4 Zircon CL image (a) and concordia diagram (b) for the Xiaohanshan pluton (sample XHS-02)
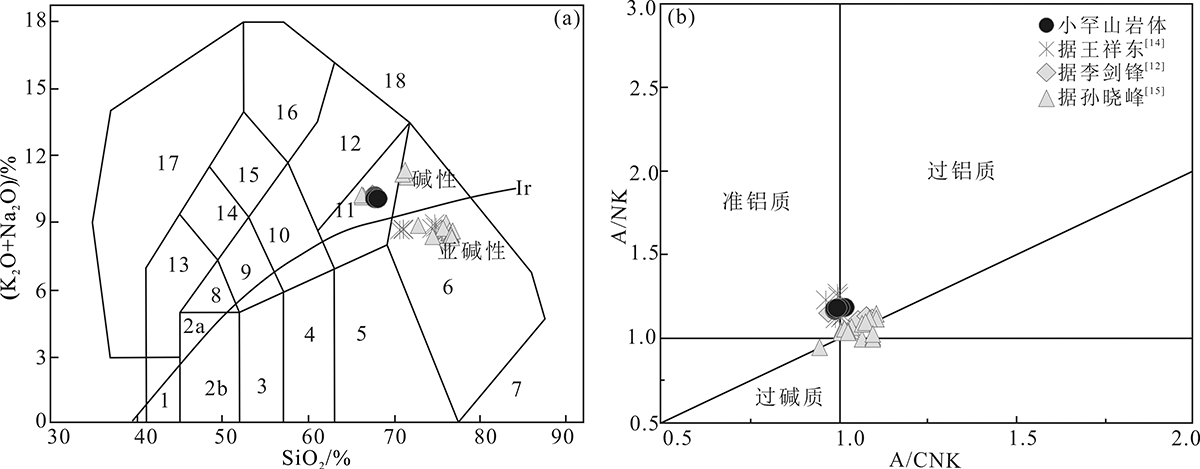
图5 小罕山岩体样品TAS图解(a)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(b) (底图分别据文献[41]和[42]) 1.橄榄辉长岩;2a.碱性辉长岩;2b.亚碱性辉长岩;3.辉长闪长岩;4.闪长岩;5.花岗闪长岩;6.花岗岩;7.硅英岩;8.二长辉长岩;9.二长闪长岩;10.二长岩;11.石英二长岩;12.正长岩;13.副长石辉长岩;14.副长石二长闪长岩;15.副长石二长正长岩;16.副长正长岩;17.副长深成岩;18.霓方钠岩/磷霞岩/粗白榴岩
Fig. 5 TAS (a) and A/CNK-A/NK (b) diagrams of samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton (Base map after references [41] and [42], respectively)
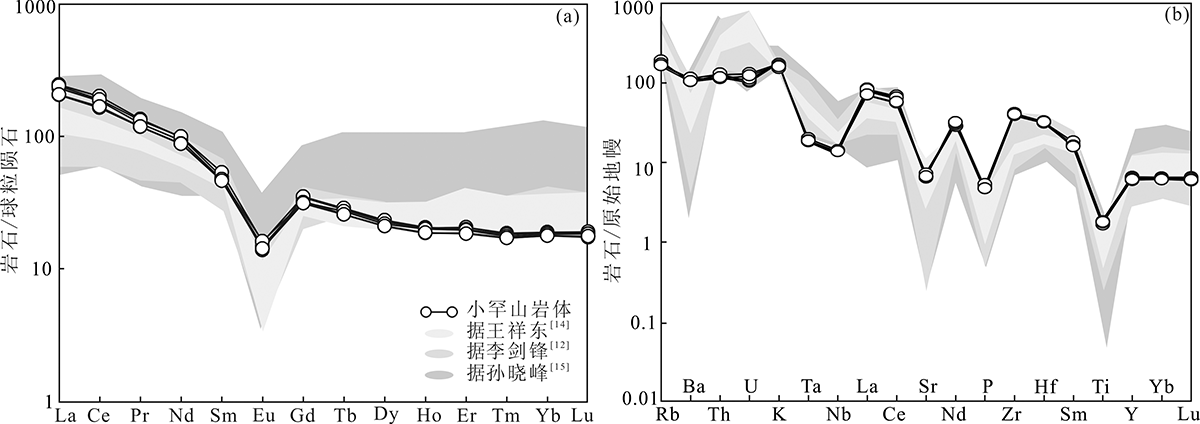
图6 小罕山岩体样品稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化数据据文献[44])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE (a) and primitive-mantle normalized trace element spider diagrams (b) for samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton (Normalized data after reference [44])

图7 小罕山岩体样品εHf(t)-t和176Hf/177Hf-t图解(底图据文献[46]) εHf(t)-t和176Hf/177Hf-t (b) diagrams of samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton (base map after reference [46])
Fig.7
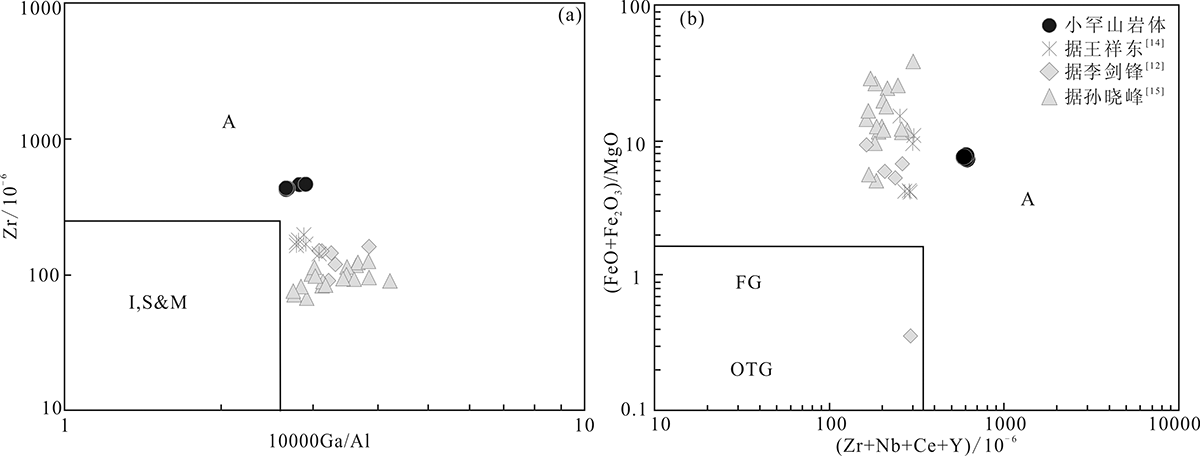
图8 小罕山岩体样品10000Ga/Al - Zr(a)和(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(FeO+Fe2O3)/MgO图解(底图分别据文献[54]和[60]) FG.长英质花岗岩;OGT.末分馏的M型、I型和S型花岗岩
Fig.8 10000Ga/Al (a) -Zr and (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) -(FeO+Fe2O3)/MgO(b) diagrams of samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton (base map after references [54] and [60], respectively)

图9 小罕山岩体样品δEu-(La/Yb)N (a) 和MgO-TFeO (b)图解(底图分别据文献[62]和[63])
Fig.9 δEu-(La/Yb)N (a) and MgO-TFeO (b) diagrams of samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton (base map after references [62] and [63], respectively)
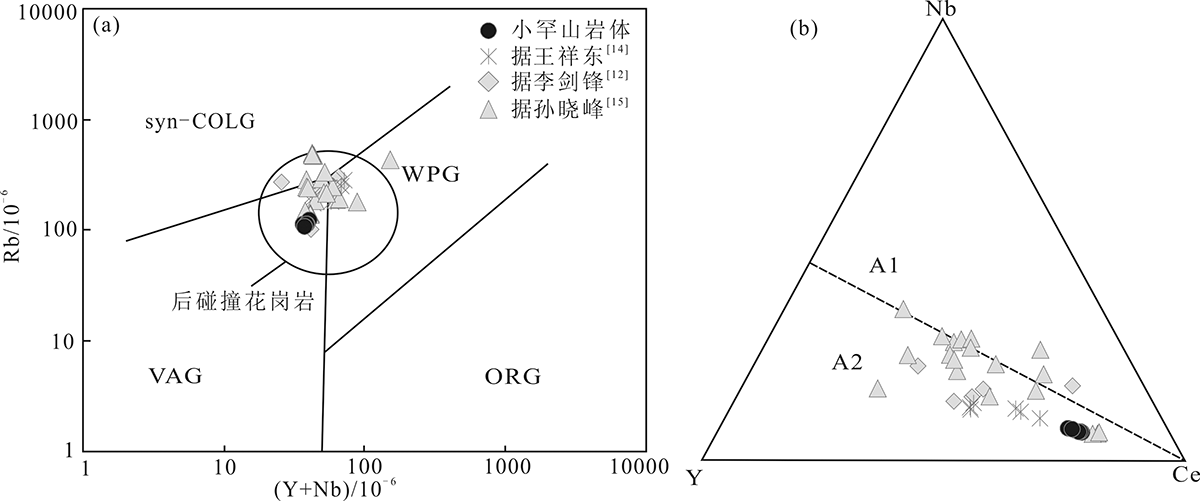
图10 小罕山岩体样品Rb-(Y+Nb) (a)和Nb-Y-Ce (b)图解(底图分别据文献[53]和[60]) syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;VAG.火山弧花岗岩;WPG.板内花岗岩;ORG.洋中脊花岗岩;A1.非造山A型花岗岩;A2.造山后A型花岗岩
Fig. 10 Rb-(Y+Nb) (a) and Nb-Y-Ce (b) diagrams of samples from the Xiaohanshan pluton (base map after references [53] and [60], respectively)
| [1] | 芮宗瑶, 王龙生. 中国铜矿床分类新方案[J]. 有色金属矿产与勘查, 1994(2):96-97. |
| [2] | 刘建明, 张锐, 张庆洲. 大兴安岭地区的区域成矿特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1):269-277. |
| [3] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, LI H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China: Ages and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2): 143-173.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FAN W, GUO F, WANG Y, et al. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2003, 121(1): 115-135.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MENG Q. What drove late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract?[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 369(3): 155-174.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG F, ZHOU X, ZHANG L, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China): Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 251(1): 179-198.
DOI URL |
| [7] | WU F Y, ZHAO G C, SUN D Y, et al. The Hulan Group: Its role in the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth ences, 2007, 30(3/4): 542-556. |
| [8] |
WU F, HAN R H, YANG J, et al. Initial constraints on the timing of granitic magmatism in North Korea using U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 238(3): 232-248.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WU F Y, ZHAO G C, SUN DY, et al. The Hulan Group: Its role in the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 30(3/4): 542-556.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 邵济安, 牟保磊, 朱慧忠, 等. 大兴安岭中南段中生代成矿物质的深部来源与背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(3):649-656. |
| [11] | 王承洋. 内蒙古黄岗梁-甘珠尔庙成矿带铅锌多金属成矿系列与找矿方向[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015. |
| [12] | 李剑锋. 内蒙古赤峰红岭铅锌多金属矿床成矿作用及外围成矿预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015. |
| [13] | 王继春, 王银宏, 张梅, 等. 内蒙古高尔旗银铅锌矿区花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5):961-980. |
| [14] | 王祥东. 内蒙古林东地区银铅锌多金属矿床成岩成矿作用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2017. |
| [15] | 孙晓峰. 内蒙古乌兰坝和小罕山岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [16] | 张德全. 大兴安岭及邻区铜多金属矿床论文集[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1993. |
| [17] | 白大明, 刘光海. 浩布高铅锌铜锡矿床地物化综合找矿模式探讨[J]. 矿产勘查, 1996(6):361-367. |
| [18] | 蔡剑辉. 太行山-大兴安岭构造岩浆带中生代侵入岩岩石地球化学特征及成因探讨[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2003. |
| [19] | 王莉娟, 王京彬, 王玉往, 等. 内蒙古东部与夕卡岩型矿床有关的花岗岩氧同位素特征--以浩布高矿床为例[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(5):513-560. |
| [20] | 王殿良, 吕古贤, 任宏, 等. 赤峰市巴林左旗浩布高矽卡岩型铅锌多金属矿床地质特征的初步研究[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2010, 32(增1):185-186. |
| [21] | 盛继福, 傅先政, 李鹤年. 大兴安岭中段成矿环境与铜多金属矿床地质特征[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999. |
| [22] | XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et a1. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6): 1069. |
| [23] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1):1-30.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YING J F, ZHOU X H, ZHANG L C, et a1. Geochronological framework of mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, NE China, and their geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 39(6S1): 786-793.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
JUNG S, MEZGER K, HOERNES S. Petrology and geochemistry of syn-and post-collisional metaluminous A-type granites: a major and trace element and Nd-Sr-Pb-O-isotope study from the Proterozoic Damara Belt, Namibia[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45: 147-176.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHANG J H, GAO S, GE W C, et a1. Geochronology of the Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, Northeastern China: Implications for Subduction-Induced Delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3/4): 144-165.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHENG J, O“REILLY S Y, GRIFFIN W L, et al. Nature and Evolution of Cenozoic Lithospheric Mantle beneath Shandong Peninsula, Sino-Korean Craton, Eastern China[J]. International Geology Review, 1998, 40(6): 471-499.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 中国地质调查局发展研究中心. 内蒙古浩布高矿集区1:5万找矿预测地质填图[R]. 北京: 中国地质调查局发展研究中心, 2017. |
| [29] | 张健. 内蒙古东部大石寨组火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学及其地球化学研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012. |
| [30] | 张吉衡. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩年代学及地球化学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009. |
| [31] | 杨扬, 高福红, 陈井胜, 等. 赤峰地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(增):257-268. |
| [32] |
LIU Y, GAO S, Hu Z, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-Peridotite interactions in the trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf Isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ANDERSON T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [34] | LUDWING K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. California: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003:1-70. |
| [35] |
YUAN H, GAO S, LIU X, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3): 353-370.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG X L, ZHOU J C, QIU J S, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China: Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 145(1/2): 111-130.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 刘颖, 刘海臣. 用ICP-MS准确测定岩石样品中的40余种微量元素[J]. 地球化学, 1996, 25(6):552-558. |
| [38] | 吴才来, 郜源红, 雷敏, 等. 南阿尔金茫崖地区花岗岩类锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年,Lu-Hf同位素特征及岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(8):2297-2323. |
| [39] | GENG J Z, QIU K F, GOU Z Y, et al. Tectonic regime switchover of Triassic Western Qinling Orogen: Constraints from LAICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope of Dangchuan intrusive complex in Gansu, China[J]. Chemie der Erde-Geochemistry, 2017, 77(4): 673-651. |
| [40] |
HOSKIN P W O, BLACK L P. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010, 18(4): 423-439.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 赵凯, 姚华舟, 王建雄, 等. 厄立特里亚Koka花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学,地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1): 156-167. |
| [44] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42 (1) :313-345. |
| [45] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. |
| [46] |
VERVOORT J D, PACHELT P J, GEHRELS G E, et al. Constraintsοn Early Earth Differentiation From Hafnium and Neodymium Isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996, 379:624-627.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 万多, 李剑锋, 工一存, 等. 内蒙古红岭铅锌多金属矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2014, 39 (6):687-695. |
| [48] |
YANG L Q, GAO X, SHU Q H. Multiple Mesozoic porphyry-skarn Cu (Mo-W) systems in Yidun Terrane, East Tethys: constraints from zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90: 813-826.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
DENG J, WANG C M, BAGAS L, et al. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 182: 251-272.
DOI URL |
| [50] | QIU K F, YU H C, DENG J, et al. The giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China: magmatic-or metamorphic-hydrothermal origin?[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 18: 1-18. |
| [51] | 张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 等. 造山前、造山和造山后花岗岩的识别[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(1):1-18. |
| [52] | 杨立强, 高雪, 文言. 义敦岛弧晚白垩世斑岩成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(11):3155-3170. |
| [53] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Traceelement discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25: 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
QIU J, WANG D, MCINNES B I, et al. Two subgroups of A-type granites in the coastal area of Zhejiang and Fujian Provinces, SE China: age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh-earth Sciences, 2004, 95(1/2): 227-236.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
KING P L, WHITE A, CHAPPELL B W, et al. Characterization and Origin of Aluminous A-type Granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3): 371-391.
DOI URL |
| [57] | 李昌年. 火成岩微量元素岩石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992. |
| [58] | 曹国雄, 高太忠, 吴有民. 堡子湾金矿同位素及稀土元素地球化学研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2000, 28(1):10-14. |
| [59] | GREEN T H, PEARSON N J. An experimental study of Nb and Ta partitioning between Ti-rich minerals and silicate liquids at high pressure and temperature[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(1): 5-62. |
| [60] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641-644.
DOI URL |
| [61] | 许保良, 阎国翰, 张臣, 等. A型花岗岩的岩石学亚类及其物质来源[J]. 地学前缘, 1998, 5(3):113-124. |
| [62] | 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989:222-246 |
| [63] |
SCHIANO P, MONZIER M, EISSEN J P, et al. Simple mixing as the major control of the evolution of volcanic suites in the Ecuadorian Andes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 160(2):297-312.
DOI URL |
| [64] | 林强, 葛文春, 曹林, 等. 大兴安岭中生代双峰式火山岩的地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(3):208-222. |
| [65] | 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(3):403-412. |
| [66] | 林强, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等. 中国东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 1998, 33(2):3-13. |
| [67] | 王喜龙, 刘家军, 翟德高, 等. 内蒙古边家大院矿区石英斑岩U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(5):654-665. |
| [68] | 杨增海, 王建平, 刘家军, 等. 内蒙古乌日尼图花岗岩的年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3):528-540. |
| [69] | 董树文, 吴锡浩, 吴珍汉, 等. 论东亚大陆的构造翘变-燕山运动的全球意义[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(1):8-13. |
| [70] |
ZHANG F Q, CHEN H L, YU X, et al. Early Cretaceous volcanism in the northern Songliao Basin, NE China, and its geodynamic implication[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19:163-176.
DOI URL |
| [71] | 梅微. 内蒙古赤峰北部地区中生代岩浆作用与成矿研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014. |
| [72] |
VAN DER VOO R, SPAKMAN W, BIJWAARD H. Tethyan subducted slabs under India[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 171(1): 7-20.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
MARUYAMA S. Pacific-type orogeny revisited: Miyashiro-type orogeny proposed[J]. Island Arc, 2010, 6(1): 91-120.
DOI URL |
| [74] | 赵越. 东亚大地构造发展的重要转折[J]. 地质科学, 1994, 29(2):105-119. |
| [75] | 赵越, 徐刚, 张拴宏, 等. 燕山运动与东亚构造体制的转变[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):319-328. |
| [76] | 毛景文, 张作衡, 余金杰, 等. 华北及邻区中生代大规模成矿的地球动力学--背景:从金属矿床年龄精测得到启示[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2003, 33(4):289-299. |
| [77] | 代军治, 毛景文, 杨富全, 等. 华北地台北缘燕辽钼(铜)成矿带矿床地质特征及动力学背景[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(5):598-612. |
| [78] | 廖震, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等. 内蒙古大井锡多金属矿床岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(7):2292-2306. |
| [79] | 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊. 大兴安岭中南段中生代的构造热演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 1998, 28(3):193-200. |
| [80] | 邵济安, 张履桥, 肖庆辉, 等. 中生代大兴安岭的隆起--一种可能的陆内造山机制[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):789-794. |
| [81] | 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):339-353. |
| [82] | 华北, 高雪, 胡兆国, 等. 兴蒙造山带西段乌珠新乌苏花岗岩岩石成因和构造背景:地球化学、U-Pb年代学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5):1426-1444. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [4] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [5] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [6] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [7] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [8] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [9] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [10] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [11] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [12] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [13] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [14] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [15] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||