



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (06): 1702-1712.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.121
谢亘1,2( ), 喻光明2, 路英川2,3, 冯欣1,2, 田光昊1,2, 王然1,2, 王建4
), 喻光明2, 路英川2,3, 冯欣1,2, 田光昊1,2, 王然1,2, 王建4
收稿日期:2021-08-11
修回日期:2021-11-02
出版日期:2021-12-10
发布日期:2022-02-14
作者简介:谢 亘, 男, 工程师, 1987年出生, 矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事固体矿产勘查研究。Email: xiegen@mail.cgs.gov.cn。
基金资助:
XIE Gen1,2( ), YU Guangming2, LU Yingchuan2,3, FENG Xin1,2, TIAN Guanghao1,2, WANG Ran1,2, WANG Jian4
), YU Guangming2, LU Yingchuan2,3, FENG Xin1,2, TIAN Guanghao1,2, WANG Ran1,2, WANG Jian4
Received:2021-08-11
Revised:2021-11-02
Online:2021-12-10
Published:2022-02-14
摘要:
小秦岭地区位于华北中部造山带南段,是研究华北克拉通南缘演化的关键地区,对其研究不仅有助于深入了解华北克拉通古元古代构造演化特征,同时对于华北克拉通东西陆块碰撞时间的厘定也具有重要意义。通过对小秦岭北侧大湖金钼矿床围岩(花岗质片麻岩)的SIMS锆石U-Pb定年分析,获得其岩浆锆石谐和年龄为(2 455±59) Ma、变质锆石谐和年龄为(1 821±31) Ma。花岗质片麻岩具有高SiO2、富碱和低Al2O3、CaO、MgO、P2O5 的特征,同时富集LILEs(Rb、Th、K)、亏损 HFSEs(Nb)和Sr、P、Ti等元素。结合A/CNK-A/NK图解和Ga、Rb等微量元素特征分析,认为其原岩为A型花岗岩,具有非造山A1型花岗岩特征;大湖金钼矿床A型花岗岩在古元古代早期起源于基性岩浆(提供热源)底侵作用下的中—新太古代结晶基底物质的部分熔融,为陆内裂谷环境,并在古元古代晚期受到华北克拉通东部和西部陆块碰撞造山后伸展作用的影响。
中图分类号:
谢亘, 喻光明, 路英川, 冯欣, 田光昊, 王然, 王建. 华北克拉通南缘小秦岭地区花岗质片麻岩年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712.
XIE Gen, YU Guangming, LU Yingchuan, FENG Xin, TIAN Guanghao, WANG Ran, WANG Jian. Chronology and Geochemical Characteristics of Granitic Gneiss in Xiaoqinling District on the Southern Margin of North China Craton and Its Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712.

图1 华北克拉通划分模式图及研究区位置((a), 据文献[13]修改)、研究区在小秦岭金矿区位置示意图((b), 据文献[15]修改)及大湖金钼矿床地质简图((c), 据文献[16]修改)
Fig.1 Subdivisions of the North China Craton, showing the study area location ((a), modified from reference [13]), the study area location in the Xiaoqinling gold field ((b), modified from reference [15]), and simplified geological map of the Dahu Au-Mo deposit ((c), modified from reference [16])
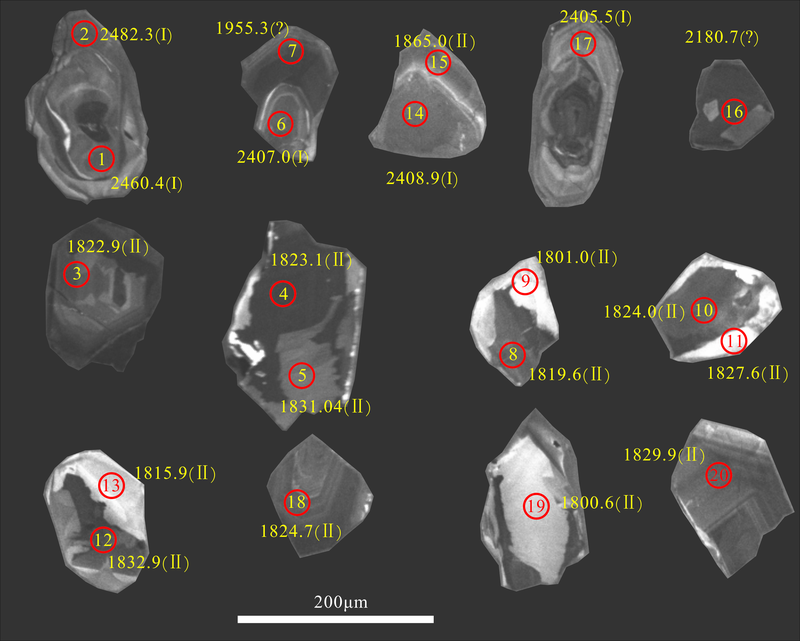
图3 大湖金钼矿床围岩锆石阴极发光图片和测点位号、分组及对应的年龄值(Ma)
Fig.3 Representative zircon CL images of wallrocks in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit, their analysis spot number, group type, and U-Pb ages (Ma)
| 测试 点号 | 分组 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 ±1σ | (年龄±1σ)/Ma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ||||
| 1 | Ⅰ | 250 | 106 | 0.42 | 0.160 5±0.5 | 10.404 9±1.6 | 0.470 3±1.6 | 2 460.4±8.2 | 2 471.5±15.2 | 2 484.9±32.2 | |
| 2 | Ⅰ | 323 | 100 | 0.31 | 0.162 5±0.4 | 10.281 9±1.5 | 0.458 8±1.5 | 2 482.3±6.2 | 2 460.5±14.4 | 2 434.1±30.5 | |
| 6 | Ⅰ | 409 | 140 | 0.34 | 0.155 5±0.4 | 9.555 9±1.6 | 0.445 8±1.5 | 2 407.0±7.3 | 2 392.9±14.5 | 2 376.4±29.9 | |
| 14 | Ⅰ | 464 | 146 | 0.31 | 0.155 6±0.4 | 9.774 0±1.5 | 0.455 4±1.5 | 2 408.9±6.3 | 2 413.7±14.4 | 2 419.4±30.4 | |
| 17 | Ⅰ | 425 | 93 | 0.22 | 0.155 3±0.4 | 9.074 7±1.6 | 0.423 7±1.5 | 2 405.5±7.1 | 2 345.6±14.4 | 2 277.3±28.9 | |
| 7 | ? | 582 | 556 | 0.96 | 0.119 9±0.4 | 5.950 0±1.5 | 0.359 8±1.5 | 1 955.3±6.4 | 1 968.6±13.5 | 1 981.2±25.6 | |
| 16 | ? | 1 544 | 222 | 0.14 | 0.136 3±0.2 | 7.677 4±1.5 | 0.408 5±1.5 | 2 180.7±3.5 | 2 194.0±13.7 | 2 208.2±28.1 | |
| 15 | Ⅱ | 275 | 6 | 0.02 | 0.114 1±0.5 | 5.270 5±1.6 | 0.335 1±1.5 | 1 865.0±9.1 | 1 864.1±13.6 | 1 863.3±24.3 | |
| 3 | Ⅱ | 378 | 354 | 0.94 | 0.111 4±0.4 | 5.060 3±1.6 | 0.329 4±1.5 | 1 822.9±7.9 | 1 829.5±13.3 | 1 835.2±24.0 | |
| 4 | Ⅱ | 1 075 | 1 565 | 1.46 | 0.111 4±0.3 | 5.054 3±1.5 | 0.328 9±1.5 | 1 823.1±4.6 | 1 828.5±13.0 | 1 833.2±24.0 | |
| 5 | Ⅱ | 184 | 102 | 0.55 | 0.112 0±0.6 | 5.048 8±1.6 | 0.327 1±1.5 | 1 831.4±10.9 | 1 827.5±14.0 | 1 824.1±24.3 | |
| 8 | Ⅱ | 552 | 513 | 0.93 | 0.111 2±0.5 | 5.105 3±1.6 | 0.332 9±1.5 | 1 819.6±8.7 | 1 837.0±13.5 | 1 852.4±24.2 | |
| 9 | Ⅱ | 605 | 724 | 1.20 | 0.110 1±0.3 | 5.096 9±1.6 | 0.335 8±1.6 | 1 801.0±6.1 | 1 835.6±13.6 | 1 866.2±25.3 | |
| 10 | Ⅱ | 729 | 735 | 1.01 | 0.111 5±0.3 | 5.083 7±1.5 | 0.330 7±1.5 | 1 824.0±5.5 | 1 833.4±13.2 | 1 841.7±24.3 | |
| 11 | Ⅱ | 354 | 401 | 1.13 | 0.111 7±0.4 | 5.052 3±1.6 | 0.328 0±1.5 | 1 827.6±8.0 | 1 828.1±13.5 | 1 828.6±24.2 | |
| 12 | Ⅱ | 811 | 811 | 1.00 | 0.112 1±0.3 | 5.211 9±1.5 | 0.337 4±1.5 | 1 832.9±5.8 | 1 854.6±13.2 | 1 873.9±24.4 | |
| 13 | Ⅱ | 1 418 | 2 623 | 1.85 | 0.111 0±0.3 | 5.049 3±1.5 | 0.329 9±1.5 | 1 815.9±4.8 | 1 827.6±13.0 | 1 837.9±24.1 | |
| 18 | Ⅱ | 689 | 868 | 1.26 | 0.111 5±0.3 | 5.338 6±1.5 | 0.347 1±1.5 | 1 824.7±6.3 | 1 875.1±13.3 | 1 920.8±25.0 | |
| 19 | Ⅱ | 97 | 42 | 0.43 | 0.110 1±0.8 | 5.135 2±1.7 | 0.338 4±1.5 | 1 800.6±15.3 | 1 841.9±14.8 | 1 878.8±24.6 | |
| 20 | Ⅱ | 1 144 | 1 692 | 1.48 | 0.111 9±0.2 | 5.119 8±1.5 | 0.331 9±1.5 | 1 829.9±4.5 | 1 839.4±13.0 | 1 847.8±24.2 | |
表1 大湖金钼矿床围岩SIMS锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 Results of SIMS zircon U-Pb isotope data of the wallrocks in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit
| 测试 点号 | 分组 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 ±1σ | (年龄±1σ)/Ma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | ||||
| 1 | Ⅰ | 250 | 106 | 0.42 | 0.160 5±0.5 | 10.404 9±1.6 | 0.470 3±1.6 | 2 460.4±8.2 | 2 471.5±15.2 | 2 484.9±32.2 | |
| 2 | Ⅰ | 323 | 100 | 0.31 | 0.162 5±0.4 | 10.281 9±1.5 | 0.458 8±1.5 | 2 482.3±6.2 | 2 460.5±14.4 | 2 434.1±30.5 | |
| 6 | Ⅰ | 409 | 140 | 0.34 | 0.155 5±0.4 | 9.555 9±1.6 | 0.445 8±1.5 | 2 407.0±7.3 | 2 392.9±14.5 | 2 376.4±29.9 | |
| 14 | Ⅰ | 464 | 146 | 0.31 | 0.155 6±0.4 | 9.774 0±1.5 | 0.455 4±1.5 | 2 408.9±6.3 | 2 413.7±14.4 | 2 419.4±30.4 | |
| 17 | Ⅰ | 425 | 93 | 0.22 | 0.155 3±0.4 | 9.074 7±1.6 | 0.423 7±1.5 | 2 405.5±7.1 | 2 345.6±14.4 | 2 277.3±28.9 | |
| 7 | ? | 582 | 556 | 0.96 | 0.119 9±0.4 | 5.950 0±1.5 | 0.359 8±1.5 | 1 955.3±6.4 | 1 968.6±13.5 | 1 981.2±25.6 | |
| 16 | ? | 1 544 | 222 | 0.14 | 0.136 3±0.2 | 7.677 4±1.5 | 0.408 5±1.5 | 2 180.7±3.5 | 2 194.0±13.7 | 2 208.2±28.1 | |
| 15 | Ⅱ | 275 | 6 | 0.02 | 0.114 1±0.5 | 5.270 5±1.6 | 0.335 1±1.5 | 1 865.0±9.1 | 1 864.1±13.6 | 1 863.3±24.3 | |
| 3 | Ⅱ | 378 | 354 | 0.94 | 0.111 4±0.4 | 5.060 3±1.6 | 0.329 4±1.5 | 1 822.9±7.9 | 1 829.5±13.3 | 1 835.2±24.0 | |
| 4 | Ⅱ | 1 075 | 1 565 | 1.46 | 0.111 4±0.3 | 5.054 3±1.5 | 0.328 9±1.5 | 1 823.1±4.6 | 1 828.5±13.0 | 1 833.2±24.0 | |
| 5 | Ⅱ | 184 | 102 | 0.55 | 0.112 0±0.6 | 5.048 8±1.6 | 0.327 1±1.5 | 1 831.4±10.9 | 1 827.5±14.0 | 1 824.1±24.3 | |
| 8 | Ⅱ | 552 | 513 | 0.93 | 0.111 2±0.5 | 5.105 3±1.6 | 0.332 9±1.5 | 1 819.6±8.7 | 1 837.0±13.5 | 1 852.4±24.2 | |
| 9 | Ⅱ | 605 | 724 | 1.20 | 0.110 1±0.3 | 5.096 9±1.6 | 0.335 8±1.6 | 1 801.0±6.1 | 1 835.6±13.6 | 1 866.2±25.3 | |
| 10 | Ⅱ | 729 | 735 | 1.01 | 0.111 5±0.3 | 5.083 7±1.5 | 0.330 7±1.5 | 1 824.0±5.5 | 1 833.4±13.2 | 1 841.7±24.3 | |
| 11 | Ⅱ | 354 | 401 | 1.13 | 0.111 7±0.4 | 5.052 3±1.6 | 0.328 0±1.5 | 1 827.6±8.0 | 1 828.1±13.5 | 1 828.6±24.2 | |
| 12 | Ⅱ | 811 | 811 | 1.00 | 0.112 1±0.3 | 5.211 9±1.5 | 0.337 4±1.5 | 1 832.9±5.8 | 1 854.6±13.2 | 1 873.9±24.4 | |
| 13 | Ⅱ | 1 418 | 2 623 | 1.85 | 0.111 0±0.3 | 5.049 3±1.5 | 0.329 9±1.5 | 1 815.9±4.8 | 1 827.6±13.0 | 1 837.9±24.1 | |
| 18 | Ⅱ | 689 | 868 | 1.26 | 0.111 5±0.3 | 5.338 6±1.5 | 0.347 1±1.5 | 1 824.7±6.3 | 1 875.1±13.3 | 1 920.8±25.0 | |
| 19 | Ⅱ | 97 | 42 | 0.43 | 0.110 1±0.8 | 5.135 2±1.7 | 0.338 4±1.5 | 1 800.6±15.3 | 1 841.9±14.8 | 1 878.8±24.6 | |
| 20 | Ⅱ | 1 144 | 1 692 | 1.48 | 0.111 9±0.2 | 5.119 8±1.5 | 0.331 9±1.5 | 1 829.9±4.5 | 1 839.4±13.0 | 1 847.8±24.2 | |
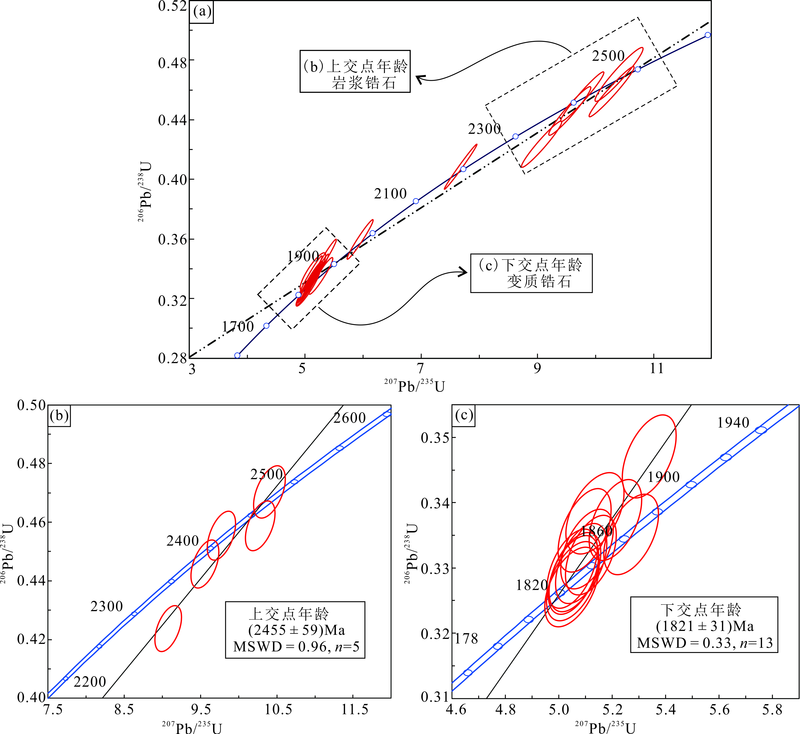
图4 大湖金钼矿床围岩综合锆石U-Pb一致曲线图(a)和SIMS U-Pb谐和年龄图(b)(c)
Fig.4 Zircon U-Pb age plots (a) and SIMS zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams (b)(c) of wallrocks in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit
| 样品 编号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | MnO | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O+ Na2O | K2O/ Na2O | A/CNK | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F7-017 | 56.23 | 16.44 | 2.42 | 5.77 | 6.33 | 3.61 | 1.99 | 3.81 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 99.37 | 5.80 | 0.52 | 0.97 | 1.94 |
| F7-037 | 75.99 | 12.91 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 1.28 | 0.20 | 3.57 | 4.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 99.32 | 7.59 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.15 |
| F7-039 | 73.14 | 13.81 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.30 | 7.29 | 1.82 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 1.46 | 99.34 | 9.11 | 4.01 | 0.93 | 0.99 |
| F7-040 | 71.53 | 13.20 | 1.76 | 0.25 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 8.29 | 1.24 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.90 | 99.37 | 9.53 | 6.69 | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| 样品 编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | LREE/ HREE | REE | δEu |
| F7-017 | 25.49 | 65.06 | 9.26 | 38.43 | 8.04 | 1.55 | 7.35 | 1.26 | 7.93 | 1.65 | 4.74 | 0.74 | 4.99 | 0.78 | 5.02 | 177.27 | 0.62 |
| F7-037 | 63.55 | 100.07 | 9.70 | 27.38 | 3.65 | 0.23 | 3.58 | 0.49 | 3.02 | 0.68 | 2.16 | 0.38 | 2.80 | 0.50 | 15.03 | 218.19 | 0.19 |
| F7-039 | 65.90 | 127.69 | 13.11 | 37.69 | 4.43 | 0.80 | 3.09 | 0.30 | 0.93 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 49.75 | 254.63 | 0.66 |
| F7-040 | 77.62 | 142.28 | 14.29 | 40.26 | 5.12 | 0.86 | 3.59 | 0.34 | 1.19 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 43.48 | 286.87 | 0.61 |
| 样品 编号 | Y | Zr | Hf | Rb | Sr | Nb | Ba | Ta | Th | Li | Be | Sc | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga |
| F7-017 | 42.04 | 133.31 | 4.06 | 97.98 | 217.41 | 11.14 | 267.83 | 0.83 | 7.69 | 31.08 | 2.04 | 22.65 | 20.35 | 8.79 | 6.76 | 104.14 | 20.06 |
| F7-037 | 20.65 | 123.93 | 4.70 | 226.86 | 61.49 | 8.11 | 33.20 | 1.74 | 136.53 | 7.13 | 3.57 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.57 | 1.96 | 20.83 | 15.23 |
| F7-039 | 3.67 | 115.17 | 3.78 | 138.84 | 261.11 | 4.13 | 1 248.52 | 0.19 | 18.82 | 3.48 | 0.96 | 1.67 | 2.22 | 1.33 | 5.58 | 10.45 | 16.48 |
| F7-040 | 5.59 | 35.87 | 1.38 | 190.48 | 284.57 | 32.41 | 2 308.30 | 0.30 | 14.61 | 1.19 | 1.04 | 0.90 | 5.47 | 1.36 | 7.89 | 7.36 | 18.19 |
| 样品 编号 | Cs | Pb | U | Bi | V | Cr | Tl | ||||||||||
| F7-017 | 4.17 | 12.43 | 1.19 | 0.09 | 165.20 | 17.30 | 0.63 | ||||||||||
| F7-037 | 11.74 | 30.06 | 17.89 | 6.45 | 8.95 | 1.76 | 0.66 | ||||||||||
| F7-039 | 1.44 | 17.10 | 1.12 | 1.06 | 15.63 | 4.16 | 0.62 | ||||||||||
| F7-040 | 1.27 | 15.42 | 0.91 | 3.77 | 11.03 | 1.87 | 0.72 |
表2 大湖金钼矿床矿石和围岩全岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)含量
Table 2 Whole-rock major (%) and trace element (10-6) contents for the ores and wallrocks in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit
| 样品 编号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | MnO | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O+ Na2O | K2O/ Na2O | A/CNK | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F7-017 | 56.23 | 16.44 | 2.42 | 5.77 | 6.33 | 3.61 | 1.99 | 3.81 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 99.37 | 5.80 | 0.52 | 0.97 | 1.94 |
| F7-037 | 75.99 | 12.91 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 1.28 | 0.20 | 3.57 | 4.02 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 99.32 | 7.59 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.15 |
| F7-039 | 73.14 | 13.81 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.30 | 7.29 | 1.82 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 1.46 | 99.34 | 9.11 | 4.01 | 0.93 | 0.99 |
| F7-040 | 71.53 | 13.20 | 1.76 | 0.25 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 8.29 | 1.24 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.90 | 99.37 | 9.53 | 6.69 | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| 样品 编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | LREE/ HREE | REE | δEu |
| F7-017 | 25.49 | 65.06 | 9.26 | 38.43 | 8.04 | 1.55 | 7.35 | 1.26 | 7.93 | 1.65 | 4.74 | 0.74 | 4.99 | 0.78 | 5.02 | 177.27 | 0.62 |
| F7-037 | 63.55 | 100.07 | 9.70 | 27.38 | 3.65 | 0.23 | 3.58 | 0.49 | 3.02 | 0.68 | 2.16 | 0.38 | 2.80 | 0.50 | 15.03 | 218.19 | 0.19 |
| F7-039 | 65.90 | 127.69 | 13.11 | 37.69 | 4.43 | 0.80 | 3.09 | 0.30 | 0.93 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 49.75 | 254.63 | 0.66 |
| F7-040 | 77.62 | 142.28 | 14.29 | 40.26 | 5.12 | 0.86 | 3.59 | 0.34 | 1.19 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 43.48 | 286.87 | 0.61 |
| 样品 编号 | Y | Zr | Hf | Rb | Sr | Nb | Ba | Ta | Th | Li | Be | Sc | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga |
| F7-017 | 42.04 | 133.31 | 4.06 | 97.98 | 217.41 | 11.14 | 267.83 | 0.83 | 7.69 | 31.08 | 2.04 | 22.65 | 20.35 | 8.79 | 6.76 | 104.14 | 20.06 |
| F7-037 | 20.65 | 123.93 | 4.70 | 226.86 | 61.49 | 8.11 | 33.20 | 1.74 | 136.53 | 7.13 | 3.57 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.57 | 1.96 | 20.83 | 15.23 |
| F7-039 | 3.67 | 115.17 | 3.78 | 138.84 | 261.11 | 4.13 | 1 248.52 | 0.19 | 18.82 | 3.48 | 0.96 | 1.67 | 2.22 | 1.33 | 5.58 | 10.45 | 16.48 |
| F7-040 | 5.59 | 35.87 | 1.38 | 190.48 | 284.57 | 32.41 | 2 308.30 | 0.30 | 14.61 | 1.19 | 1.04 | 0.90 | 5.47 | 1.36 | 7.89 | 7.36 | 18.19 |
| 样品 编号 | Cs | Pb | U | Bi | V | Cr | Tl | ||||||||||
| F7-017 | 4.17 | 12.43 | 1.19 | 0.09 | 165.20 | 17.30 | 0.63 | ||||||||||
| F7-037 | 11.74 | 30.06 | 17.89 | 6.45 | 8.95 | 1.76 | 0.66 | ||||||||||
| F7-039 | 1.44 | 17.10 | 1.12 | 1.06 | 15.63 | 4.16 | 0.62 | ||||||||||
| F7-040 | 1.27 | 15.42 | 0.91 | 3.77 | 11.03 | 1.87 | 0.72 |
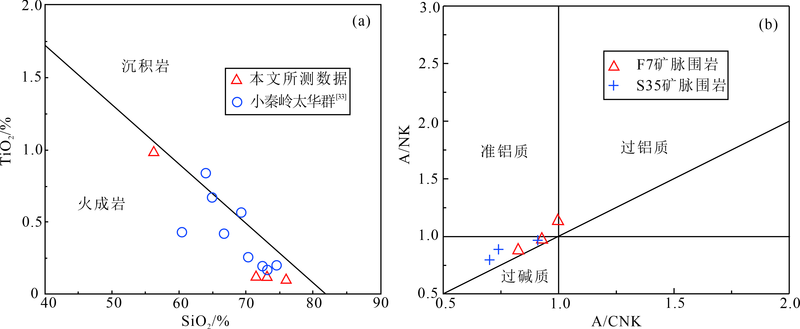
图5 F7矿脉围岩原岩恢复图解((a), 底图据文献[31])和A/CNK-A/NK图解((b), 底图据文献[32])(S35矿脉围岩结果来自笔者未刊数据)
Fig.5 Discrimination diagrams of SiO2-TiO2 ((a), from reference [31]) and A/CNK versus A/NK ((b), from reference [32]) for wallrocks of the F7 vein (wallrock data of the S35 vein from authors’ unpubl. data)
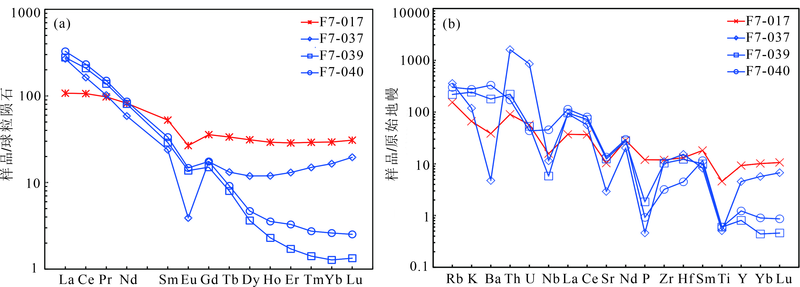
图6 大湖金钼矿床围岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图 ((a), 标准化值据文献[34])和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图((b), 标准化值据文献[34])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE diagram (a) and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element diagram (b) for wallrocks in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit (Normalizing values from reference[34])
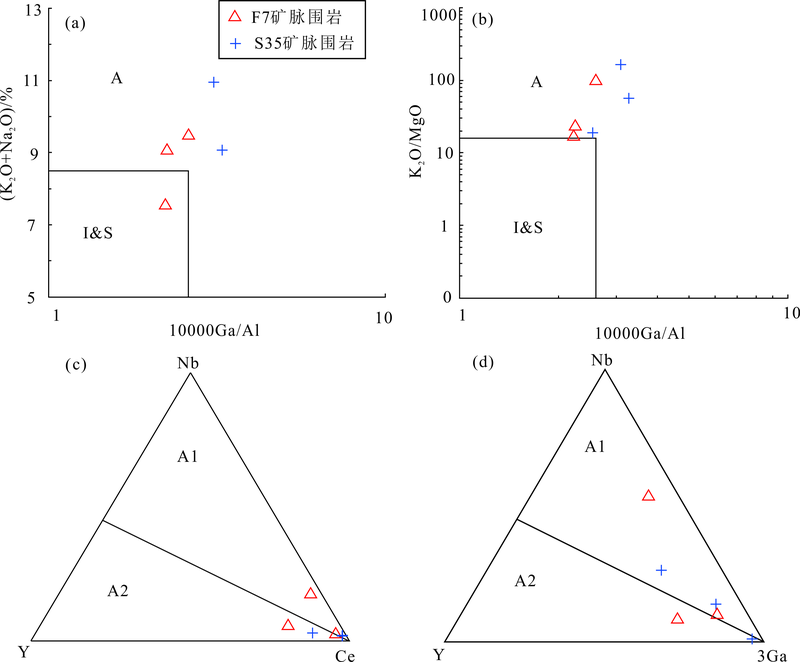
图7 大湖金钼矿床围岩10000Ga/Al对(K2O+Na2O)、K2O/MgO图解((a)(b),底图据文献[7])以及Nb-Y-Ce和Nb-Y-3Ga图解((c)(d),底图据文献[3])(S35矿脉围岩结果来自笔者未刊数据) A.A型花岗岩; I.I型花岗岩;S.S型花岗岩;A1.非造山型花岗岩;A2.后造山型花岗岩。图(a)中,另有一个S35矿脉围岩样品投于A型花岗岩区域,因其K2O+Na2O>13,未显示
Fig.7 Granite discrimination plots of 10000Ga/Al vs.(K2O+Na2O) and K2O/MgO ((a)(b), from reference [7]), ternary Nb-Y-Ce and Nb-Y-3Ga ((c)(d), from reference [3])from wallrocks in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit (wallrock data of the S35 vein from authors’ unpubl. data)
| [1] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 1979, 11(7):468. |
| [2] |
EBY G N. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26(1/2):115-134.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7):641-644.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, CHUNG S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, northeast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1-2):89-106.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SHELLNUTT J G, WANG C Y, ZHOU M F, et al. Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of metaluminous and peralkaline A-type granitic plutons of the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China): Constraints on the mantle source[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35(1):45-55.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HUANG H Q, LI X H, LI W X, et al. Formation of high δ18O fayalite-bearing A-type granite by high-temperature melting of granulitic metasedimentary rocks, southern China[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(10):903-906.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407-419.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SHI G H, MIAO L C, ZHANG F Q, et al. Emplacement age and tectonic implications of the Xilinhot A-type granite in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(7):723-729.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 邱啸飞, 杨红梅, 卢山松, 等. 扬子陆核古元古代A型花岗岩的年代学与地球化学研究及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(4):884-895. |
| [10] | 王建, 谢亘, 施光海, 等. 北祁连川刺沟A型花岗岩的年代学及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(6):1657-1668. |
| [11] |
ZHAI M G, SANTOSH M, ZHANG L C. Precambrian geology and tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 20(1):1-5.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 翟明国, 胡波, 彭澎, 等. 华北中—新元古代的岩浆作用与多期裂谷事件[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(1):100-119. |
| [13] |
ZHAO G C, CAWOOD P A, WILDE S A, et al. Review of global 2.1-1.8 Ga orogens: Implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2002, 59:125-162.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 沈其韩, 耿元生, 宋彪, 等. 华北和扬子陆块及秦岭—大别造山带地表和深部太古宙基底的新信息[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(5):616-627. |
| [15] | 陈衍景. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1181-1196. |
| [16] |
MAO J W, GOLDFARB R J, ZHANG Z W, et al. Gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling Xiong'ershan region, Central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37:306-325.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 冯建之, 张灯堂, 张为民, 等. 河南小秦岭金矿稀土元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6):1151-1160. |
| [18] | 王振强, 徐建昌, 冯建之, 等. 华北陆块南缘燕山期花岗岩带岩浆演化:以小秦岭—外方山地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(6):1032-1046. |
| [19] | 周汉文, 钟国楼, 钟增球, 等. 豫西小秦岭地区太华杂岩中花岗质片麻岩的元素地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 1998, 23(6):553-556. |
| [20] |
DIWU C R, WANG T Y, ZHAO J. Persistence of partial melting in the southern North China Craton: Evidence from Paleoproterozoic migmatites of the Taihua Complex[J]. Precambrian Research, 2020, 348:105872.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 黎世美, 瞿伦全, 苏振邦. 小秦岭金矿地质和成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996. |
| [22] | 王亨治. 小秦岭金矿田地质特征及矿床成因[J]. 矿床地质, 1987, 6(1):57-67. |
| [23] | LI X H, LIU Y, LI Q L, et al. Precise determination of Phanerozoic zircon Pb/Pb age by multicollector SIMS without external standardization[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2009, 10:Q04010. |
| [24] |
SLÁMA J, KOŠLER J, CONDON D J, et al. Plešovice zircon-a new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249:1-35.
DOI URL |
| [25] | WIEDENBECK M, ALLÉ P, CORFU F, et al. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace-element and REE analyses[J]. Geostandards Newsletter, 1995, 19:1-23. |
| [26] |
LI Q L, LI X H, LIU Y, et al. Precise U-Pb and Pb-Pb dating of Phanerozoic baddeleyite by SIMS with oxygen flooding technique[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2010, 25:1107-1113.
DOI URL |
| [27] | LUDWIG K R. Users manual for Isoplot/Ex rev. 2.49[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Centre, 2001: 1-56. |
| [28] |
SHI G H, CUI W Y, CAO S M, et al. Ion microprobe zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of the Myanmar jadeitite[J]. Journal of Geological Society, London, 2008, 165:221-234.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. |
| [30] | 郭云成. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床包裹体特征与成矿物质来源研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2018: 1-60. |
| [31] | TARNEY J. Geochemistry of Archaean high-grade gneisses, with implications as to the origin and evolution of the Precambrian crust[M]//WINDLEY B F. The Early History Earth. London: Wiley, 1976: 405-417. |
| [32] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 赵东杰. 豫西小秦岭太华群变质岩蚀变与金成矿[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2017, 1-83. |
| [34] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]//SAUNDERS A D, NORRY M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society, London, 1989:313-345. |
| [35] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-30. |
| [36] | 贾晓亮. 小秦岭和鲁山地区太华杂岩的研究: 对华北南缘基底演化的意义[D]. 西安:西北大学, 2016: 1-190. |
| [37] |
HUANG X L, WILDE S A, ZHONG J W. Episodic crustal growth in the southern segment of the Trans-North China Orogen across the Archean-Proterozoic boundary[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 233:337-357.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
DIWU C R, SUN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Early Paleoproterozoic (2.45~2.20 Ga ) magmatic activity during the period of global magmatic shutdown: Implications for the crustal evolution of the southern North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 255:627-640.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WANG G D, WANG H Y C, CHEN H X, et al. Metamorphic P-T-t paths of pelitic granulites of the Taihua metamorphic complex in the Mts. Huashan area and tectonothermal implications for the Palaeoproterozoic Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 290:147-162.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 张瑞英, 张成立, 孙勇. 华北克拉通~2.5 Ga地壳再造事件:来自中条山TTG质片麻岩的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(7):2265-2280. |
| [41] |
CONDIE K C. A Planet in Transition: The onset of plate tectonics on Earth between 3 and 2 Ga?[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2018, 9(1):51-60.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 林慈銮, 等. 豫西宜阳地区TTG质片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素地质学[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):253-262. |
| [43] |
KING P L, WHITE A J R, CHAPPELL B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [3] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [4] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [5] | 朱德全, 唐名鹰, 丁正江, 朱海波, 王炜晓, 张宇, 何宗围, 吴洪彬. 柴北缘赛坝沟金矿床花岗斑岩脉的成因及动力学背景: 来自年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 898-910. |
| [6] | 吴小雷, 常晋阳, 曾南石, 徐文杰, 陶明荣, 赵刚, 韩建. 辽宁红透山铜锌矿床含矿岩系地球化学特征及找矿指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 362-377. |
| [7] | 郭云成, 刘家军, 尹超, 郭梦需. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床地质特征及成矿流体[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1536-1550. |
| [8] | 孙晓东, 陈海云, 于光宁. 内蒙古海拉斯图乌拉A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1218-1230. |
| [9] | 袁亚平, 刘向东, 张振凯, 曾忠诚, 何元方. 南阿尔金晚泥盆世构造体制转换:来自索尔库里二长花岗岩年代学和地球化学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 940-954. |
| [10] | 寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260. |
| [11] | 任永健, 程烁, 张明明, 曹光远, 于汪, 赵寒, 梁恒, 王富强, 祁才吉. 黑龙江张家湾地区中侏罗世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076. |
| [12] | 滕超, 张晓飞, 周毅, 冯俊岭, 李树才. 内蒙古锡林浩特小乌兰沟早白垩世二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1003-1014. |
| [13] | 黄泽森, 江巴多吉, 达瓦次仁, 塔尔杰. 西藏切穷地区早白垩世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 703-714. |
| [14] | 毛艳丽, 王滔, 李鸿睿, 潘中奎. 甘肃省文县刘家坪蓟县系变基性火山岩地球化学特征及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1254-1262. |
| [15] | 杨瀚文, 申俊峰, 魏立勇, 张振, 刘满年, 冯博鑫, 张洛宁. 西秦岭西段共和盆地周缘西功卡花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 316-328. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||