



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (04): 940-954.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.107
袁亚平1( ), 刘向东2(
), 刘向东2( ), 张振凯2, 曾忠诚2, 何元方2
), 张振凯2, 曾忠诚2, 何元方2
收稿日期:2020-04-16
修回日期:2020-12-01
出版日期:2021-08-10
发布日期:2021-09-08
通讯作者:
刘向东
作者简介:刘向东,男,高级工程师,1985年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事区域地质调查及矿产勘查工作。Email: 283859688@qq.com。基金资助:
YUAN Yaping1( ), LIU Xiangdong2(
), LIU Xiangdong2( ), ZHANG Zhenkai2, ZENG Zhongcheng2, HE Yuanfang2
), ZHANG Zhenkai2, ZENG Zhongcheng2, HE Yuanfang2
Received:2020-04-16
Revised:2020-12-01
Online:2021-08-10
Published:2021-09-08
Contact:
LIU Xiangdong
摘要:
对阿尔金索尔库里地区二长花岗岩进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及全岩主量、微量和稀土元素测试,结果表明二长花岗岩结晶年龄为(377.5±1.6) Ma和(377.4±2.1) Ma;具有高硅(SiO2=72.55%~76.41%)和高碱(K2O+Na2O=7.32%~8.59%)、正常的铝含量(A/CNK=0.92~1.08)、高TFeO/MgO比值(2.57~6.47)的特征,为高钾钙碱性系列;富集轻稀土元素,具有明显Eu负异常;微量元素富集Rb、Th、Y、Zr和Hf等元素,亏损Ba、Sr、P和Ti等元素。上述特征表明索尔库里二长花岗岩为A型花岗岩,是幔源物质底侵作用引发的长英质地壳(变杂砂岩)部分熔融形成的母岩浆经过分离结晶而形成的,且具有A1型花岗岩特征。结合区域地质资料及同期岩浆岩活动历史,认为索尔库里地区二长花岗岩形成于板内伸展构造环境,为晚泥盆世南阿尔金构造带由后造山环境向板内构造体制转换的产物。
中图分类号:
袁亚平, 刘向东, 张振凯, 曾忠诚, 何元方. 南阿尔金晚泥盆世构造体制转换:来自索尔库里二长花岗岩年代学和地球化学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 940-954.
YUAN Yaping, LIU Xiangdong, ZHANG Zhenkai, ZENG Zhongcheng, HE Yuanfang. Late Devonian Tectonic Transition in South Altyn Tagh: Constraints from Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Suoerkuli Monzogranite[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 940-954.
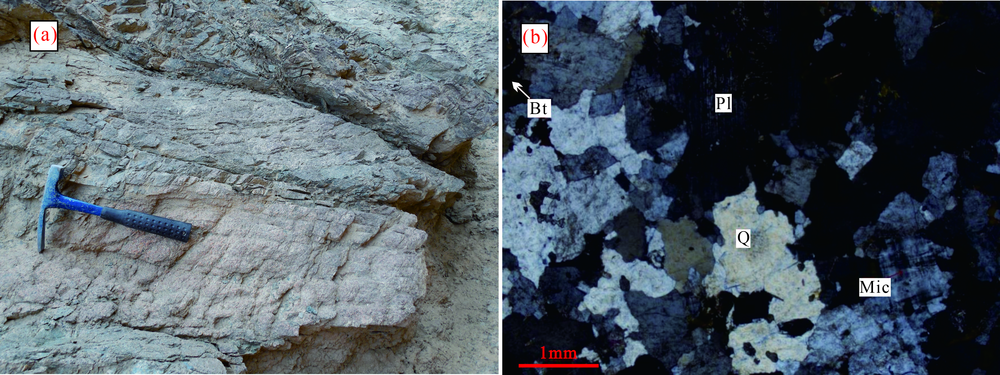
图2 二长花岗岩宏观(a)及镜下照片(b)(正交光下) Bt. 黑云母;Q. 石英;Pl. 斜长石;Mic. 微斜长石
Fig.2 Field photo (a) and microscopic thin-section photo (b) of the Suoerkuli monzogranite
| 测点号 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||
| D6533/1-1 | 0.055 50 | 0.001 61 | 0.461 45 | 0.012 52 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 48 | 0.018 28 | 0.000 27 | 432.2 | 63.13 | 385.3 | 8.70 | 377.4 | 2.91 | |||
| D6533/1-2 | 0.057 26 | 0.002 27 | 0.476 52 | 0.018 09 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 62 | 0.019 43 | 0.000 45 | 501.2 | 85.49 | 395.7 | 12.44 | 377.7 | 3.79 | |||
| D6533/1-3 | 0.115 44 | 0.005 22 | 0.822 90 | 0.035 06 | 0.051 69 | 0.000 82 | 0.025 35 | 0.000 73 | 1 886.8 | 79.18 | 609.7 | 19.53 | 324.9 | 5.03 | |||
| D6533/1-4 | 0.062 63 | 0.003 17 | 0.521 22 | 0.025 43 | 0.060 35 | 0.000 82 | 0.017 76 | 0.000 51 | 695.6 | 104.20 | 426.0 | 16.97 | 377.7 | 4.99 | |||
| D6533/1-5 | 0.053 27 | 0.002 34 | 0.443 07 | 0.018 74 | 0.060 32 | 0.000 65 | 0.017 91 | 0.000 37 | 340.1 | 96.15 | 372.4 | 13.19 | 377.5 | 3.95 | |||
| D6533/1-6 | 0.053 89 | 0.001 67 | 0.448 47 | 0.013 06 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 49 | 0.018 71 | 0.000 31 | 366.4 | 68.06 | 376.2 | 9.16 | 377.7 | 3.00 | |||
| D6533/1-7 | 0.053 25 | 0.002 59 | 0.443 44 | 0.020 84 | 0.060 39 | 0.000 74 | 0.017 85 | 0.000 45 | 339.5 | 106.21 | 372.7 | 14.66 | 378.0 | 4.51 | |||
| D6533/1-8 | 0.057 09 | 0.001 72 | 0.474 13 | 0.013 41 | 0.060 23 | 0.000 51 | 0.018 26 | 0.000 31 | 494.3 | 65.68 | 394.0 | 9.24 | 377.0 | 3.08 | |||
| D6533/1-9 | 0.052 81 | 0.002 10 | 0.439 41 | 0.016 80 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 60 | 0.018 30 | 0.000 36 | 320.5 | 88.04 | 369.8 | 11.85 | 377.7 | 3.67 | |||
| D6533/1-10 | 0.054 10 | 0.001 57 | 0.449 76 | 0.012 19 | 0.060 29 | 0.000 48 | 0.018 56 | 0.000 27 | 374.9 | 63.71 | 377.1 | 8.53 | 377.4 | 2.93 | |||
| D6533/1-11 | 0.054 53 | 0.001 84 | 0.453 32 | 0.014 54 | 0.060 29 | 0.000 54 | 0.018 82 | 0.000 34 | 392.8 | 73.32 | 379.6 | 10.16 | 377.4 | 3.28 | |||
| D6533/1-12 | 0.052 61 | 0.001 55 | 0.437 81 | 0.012 13 | 0.060 35 | 0.000 48 | 0.018 10 | 0.000 27 | 312.1 | 65.62 | 368.7 | 8.56 | 377.7 | 2.92 | |||
| D6533/1-13 | 0.050 25 | 0.001 79 | 0.417 44 | 0.014 22 | 0.060 25 | 0.000 55 | 0.018 15 | 0.000 39 | 206.4 | 80.72 | 354.2 | 10.19 | 377.1 | 3.34 | |||
| D6533/1-14 | 0.055 15 | 0.003 49 | 0.458 13 | 0.028 16 | 0.060 24 | 0.000 98 | 0.017 41 | 0.000 55 | 418.4 | 135.44 | 383.0 | 19.61 | 377.1 | 5.96 | |||
| D6533/1-15 | 0.051 78 | 0.002 43 | 0.431 06 | 0.019 57 | 0.060 38 | 0.000 69 | 0.017 86 | 0.000 43 | 275.6 | 103.88 | 363.9 | 13.89 | 377.9 | 4.19 | |||
| D6533/1-16 | 0.053 34 | 0.001 87 | 0.444 06 | 0.014 79 | 0.060 37 | 0.000 57 | 0.018 67 | 0.000 38 | 343.3 | 77.16 | 373.1 | 10.40 | 377.9 | 3.44 | |||
| D6533/1-17 | 0.067 61 | 0.002 15 | 0.461 14 | 0.013 80 | 0.049 46 | 0.000 46 | 0.017 66 | 0.000 31 | 856.7 | 64.67 | 385.0 | 9.59 | 311.2 | 2.82 | |||
| D6533/1-18 | 0.241 44 | 0.004 61 | 2.008 88 | 0.032 16 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 55 | 0.046 20 | 0.000 49 | 3 129.5 | 30.07 | 1 118.5 | 10.85 | 377.7 | 3.32 | |||
| D6533/1-19 | 0.103 45 | 0.002 79 | 0.766 22 | 0.018 96 | 0.053 71 | 0.000 50 | 0.024 25 | 0.000 40 | 1 687.0 | 48.91 | 577.6 | 10.90 | 337.3 | 3.07 | |||
| D6533/1-20 | 0.055 32 | 0.001 67 | 0.460 45 | 0.013 10 | 0.060 36 | 0.000 51 | 0.018 00 | 0.000 25 | 425.1 | 65.48 | 384.6 | 9.10 | 377.8 | 3.11 | |||
| D6533/1-21 | 0.058 50 | 0.002 58 | 0.486 00 | 0.020 64 | 0.060 24 | 0.000 72 | 0.021 50 | 0.000 54 | 548.7 | 93.52 | 402.2 | 14.10 | 377.1 | 4.39 | |||
| D6533/1-22 | 0.061 04 | 0.002 35 | 0.508 21 | 0.018 78 | 0.060 37 | 0.000 64 | 0.020 85 | 0.000 45 | 640.6 | 80.86 | 417.2 | 12.64 | 377.9 | 3.89 | |||
| D6533/1-23 | 0.057 73 | 0.002 12 | 0.479 92 | 0.016 87 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 61 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 34 | 519.2 | 79.00 | 398.0 | 11.58 | 377.4 | 3.72 | |||
| D6533/1-24 | 0.059 82 | 0.003 83 | 0.498 08 | 0.031 00 | 0.060 38 | 0.001 04 | 0.021 45 | 0.000 85 | 596.9 | 132.97 | 410.4 | 21.01 | 377.9 | 6.33 | |||
| PM034/3-1 | 0.065 37 | 0.002 84 | 0.543 27 | 0.022 62 | 0.060 24 | 0.000 74 | 0.022 65 | 0.000 51 | 786.4 | 88.65 | 440.6 | 14.88 | 377.1 | 4.49 | |||
| PM034/3-2 | 0.087 93 | 0.003 31 | 0.731 75 | 0.026 08 | 0.060 32 | 0.000 72 | 0.031 05 | 0.000 67 | 1 381.0 | 70.61 | 557.6 | 15.29 | 377.6 | 4.39 | |||
| PM034/3-3 | 0.061 14 | 0.003 91 | 0.508 28 | 0.031 54 | 0.060 27 | 0.001 03 | 0.021 88 | 0.000 81 | 644.1 | 131.65 | 417.3 | 21.23 | 377.3 | 6.24 | |||
| PM034/3-4 | 0.082 27 | 0.002 72 | 0.684 25 | 0.021 21 | 0.060 30 | 0.000 62 | 0.025 09 | 0.000 49 | 1 252.0 | 63.19 | 529.3 | 12.78 | 377.4 | 3.79 | |||
| PM034/3-5 | 0.066 97 | 0.002 94 | 0.557 81 | 0.023 47 | 0.060 39 | 0.000 74 | 0.022 04 | 0.000 52 | 836.9 | 88.81 | 450.1 | 15.30 | 378.0 | 4.51 | |||
| PM034/3-6 | 0.062 78 | 0.002 79 | 0.521 98 | 0.022 30 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 73 | 0.020 49 | 0.000 53 | 700.9 | 91.97 | 426.5 | 14.88 | 377.3 | 4.46 | |||
| PM034/3-7 | 0.056 44 | 0.002 59 | 0.468 97 | 0.020 71 | 0.060 25 | 0.000 73 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 48 | 468.9 | 99.18 | 390.5 | 14.31 | 377.2 | 4.46 | |||
| PM034/3-8 | 0.140 77 | 0.003 60 | 1.172 23 | 0.026 95 | 0.060 39 | 0.000 60 | 0.044 62 | 0.000 69 | 2 236.7 | 43.63 | 787.7 | 12.60 | 378.0 | 3.67 | |||
| PM034/3-9 | 0.076 19 | 0.002 80 | 0.633 54 | 0.022 04 | 0.060 30 | 0.000 65 | 0.025 12 | 0.000 53 | 1 100.1 | 71.71 | 498.3 | 13.70 | 377.4 | 3.95 | |||
| PM034/3-10 | 0.071 40 | 0.007 26 | 0.594 72 | 0.058 90 | 0.060 40 | 0.001 76 | 0.021 35 | 0.001 31 | 969.0 | 194.80 | 473.9 | 37.50 | 378.1 | 10.70 | |||
| PM034/3-11 | 0.069 00 | 0.001 90 | 0.573 59 | 0.014 63 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 49 | 0.020 44 | 0.000 29 | 898.9 | 55.83 | 460.3 | 9.44 | 377.3 | 3.00 | |||
| PM034/3-12 | 0.065 71 | 0.003 53 | 0.546 78 | 0.028 38 | 0.060 35 | 0.000 90 | 0.021 33 | 0.000 67 | 797.2 | 108.81 | 442.9 | 18.63 | 377.7 | 5.47 | |||
| PM034/3-13 | 0.054 58 | 0.004 20 | 0.453 47 | 0.034 10 | 0.060 26 | 0.001 13 | 0.017 14 | 0.000 75 | 395.1 | 163.95 | 379.7 | 23.82 | 377.2 | 6.89 | |||
| PM034/3-14 | 0.129 91 | 0.004 21 | 0.956 97 | 0.028 69 | 0.053 43 | 0.000 63 | 0.031 26 | 0.000 60 | 2 096.7 | 55.89 | 681.7 | 14.88 | 335.5 | 3.84 | |||
| PM034/3-15 | 0.069 31 | 0.002 14 | 0.575 93 | 0.016 70 | 0.060 26 | 0.000 55 | 0.021 86 | 0.000 38 | 908.1 | 62.47 | 461.8 | 10.76 | 377.2 | 3.33 | |||
| PM034/3-16 | 0.060 10 | 0.002 40 | 0.499 73 | 0.019 07 | 0.060 31 | 0.000 64 | 0.018 42 | 0.000 45 | 607.1 | 83.99 | 411.5 | 12.91 | 377.5 | 3.91 | |||
| PM034/3-17 | 0.055 68 | 0.002 67 | 0.462 57 | 0.021 42 | 0.060 25 | 0.000 72 | 0.018 86 | 0.000 52 | 439.4 | 103.51 | 386.0 | 14.87 | 377.1 | 4.38 | |||
| PM034/3-18 | 0.064 13 | 0.002 34 | 0.533 93 | 0.018 50 | 0.060 38 | 0.000 60 | 0.019 98 | 0.000 44 | 746.0 | 75.15 | 434.4 | 12.25 | 377.9 | 3.67 | |||
表1 索尔库里二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学测试结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Suoerkuli monzogranite
| 测点号 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||
| D6533/1-1 | 0.055 50 | 0.001 61 | 0.461 45 | 0.012 52 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 48 | 0.018 28 | 0.000 27 | 432.2 | 63.13 | 385.3 | 8.70 | 377.4 | 2.91 | |||
| D6533/1-2 | 0.057 26 | 0.002 27 | 0.476 52 | 0.018 09 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 62 | 0.019 43 | 0.000 45 | 501.2 | 85.49 | 395.7 | 12.44 | 377.7 | 3.79 | |||
| D6533/1-3 | 0.115 44 | 0.005 22 | 0.822 90 | 0.035 06 | 0.051 69 | 0.000 82 | 0.025 35 | 0.000 73 | 1 886.8 | 79.18 | 609.7 | 19.53 | 324.9 | 5.03 | |||
| D6533/1-4 | 0.062 63 | 0.003 17 | 0.521 22 | 0.025 43 | 0.060 35 | 0.000 82 | 0.017 76 | 0.000 51 | 695.6 | 104.20 | 426.0 | 16.97 | 377.7 | 4.99 | |||
| D6533/1-5 | 0.053 27 | 0.002 34 | 0.443 07 | 0.018 74 | 0.060 32 | 0.000 65 | 0.017 91 | 0.000 37 | 340.1 | 96.15 | 372.4 | 13.19 | 377.5 | 3.95 | |||
| D6533/1-6 | 0.053 89 | 0.001 67 | 0.448 47 | 0.013 06 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 49 | 0.018 71 | 0.000 31 | 366.4 | 68.06 | 376.2 | 9.16 | 377.7 | 3.00 | |||
| D6533/1-7 | 0.053 25 | 0.002 59 | 0.443 44 | 0.020 84 | 0.060 39 | 0.000 74 | 0.017 85 | 0.000 45 | 339.5 | 106.21 | 372.7 | 14.66 | 378.0 | 4.51 | |||
| D6533/1-8 | 0.057 09 | 0.001 72 | 0.474 13 | 0.013 41 | 0.060 23 | 0.000 51 | 0.018 26 | 0.000 31 | 494.3 | 65.68 | 394.0 | 9.24 | 377.0 | 3.08 | |||
| D6533/1-9 | 0.052 81 | 0.002 10 | 0.439 41 | 0.016 80 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 60 | 0.018 30 | 0.000 36 | 320.5 | 88.04 | 369.8 | 11.85 | 377.7 | 3.67 | |||
| D6533/1-10 | 0.054 10 | 0.001 57 | 0.449 76 | 0.012 19 | 0.060 29 | 0.000 48 | 0.018 56 | 0.000 27 | 374.9 | 63.71 | 377.1 | 8.53 | 377.4 | 2.93 | |||
| D6533/1-11 | 0.054 53 | 0.001 84 | 0.453 32 | 0.014 54 | 0.060 29 | 0.000 54 | 0.018 82 | 0.000 34 | 392.8 | 73.32 | 379.6 | 10.16 | 377.4 | 3.28 | |||
| D6533/1-12 | 0.052 61 | 0.001 55 | 0.437 81 | 0.012 13 | 0.060 35 | 0.000 48 | 0.018 10 | 0.000 27 | 312.1 | 65.62 | 368.7 | 8.56 | 377.7 | 2.92 | |||
| D6533/1-13 | 0.050 25 | 0.001 79 | 0.417 44 | 0.014 22 | 0.060 25 | 0.000 55 | 0.018 15 | 0.000 39 | 206.4 | 80.72 | 354.2 | 10.19 | 377.1 | 3.34 | |||
| D6533/1-14 | 0.055 15 | 0.003 49 | 0.458 13 | 0.028 16 | 0.060 24 | 0.000 98 | 0.017 41 | 0.000 55 | 418.4 | 135.44 | 383.0 | 19.61 | 377.1 | 5.96 | |||
| D6533/1-15 | 0.051 78 | 0.002 43 | 0.431 06 | 0.019 57 | 0.060 38 | 0.000 69 | 0.017 86 | 0.000 43 | 275.6 | 103.88 | 363.9 | 13.89 | 377.9 | 4.19 | |||
| D6533/1-16 | 0.053 34 | 0.001 87 | 0.444 06 | 0.014 79 | 0.060 37 | 0.000 57 | 0.018 67 | 0.000 38 | 343.3 | 77.16 | 373.1 | 10.40 | 377.9 | 3.44 | |||
| D6533/1-17 | 0.067 61 | 0.002 15 | 0.461 14 | 0.013 80 | 0.049 46 | 0.000 46 | 0.017 66 | 0.000 31 | 856.7 | 64.67 | 385.0 | 9.59 | 311.2 | 2.82 | |||
| D6533/1-18 | 0.241 44 | 0.004 61 | 2.008 88 | 0.032 16 | 0.060 34 | 0.000 55 | 0.046 20 | 0.000 49 | 3 129.5 | 30.07 | 1 118.5 | 10.85 | 377.7 | 3.32 | |||
| D6533/1-19 | 0.103 45 | 0.002 79 | 0.766 22 | 0.018 96 | 0.053 71 | 0.000 50 | 0.024 25 | 0.000 40 | 1 687.0 | 48.91 | 577.6 | 10.90 | 337.3 | 3.07 | |||
| D6533/1-20 | 0.055 32 | 0.001 67 | 0.460 45 | 0.013 10 | 0.060 36 | 0.000 51 | 0.018 00 | 0.000 25 | 425.1 | 65.48 | 384.6 | 9.10 | 377.8 | 3.11 | |||
| D6533/1-21 | 0.058 50 | 0.002 58 | 0.486 00 | 0.020 64 | 0.060 24 | 0.000 72 | 0.021 50 | 0.000 54 | 548.7 | 93.52 | 402.2 | 14.10 | 377.1 | 4.39 | |||
| D6533/1-22 | 0.061 04 | 0.002 35 | 0.508 21 | 0.018 78 | 0.060 37 | 0.000 64 | 0.020 85 | 0.000 45 | 640.6 | 80.86 | 417.2 | 12.64 | 377.9 | 3.89 | |||
| D6533/1-23 | 0.057 73 | 0.002 12 | 0.479 92 | 0.016 87 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 61 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 34 | 519.2 | 79.00 | 398.0 | 11.58 | 377.4 | 3.72 | |||
| D6533/1-24 | 0.059 82 | 0.003 83 | 0.498 08 | 0.031 00 | 0.060 38 | 0.001 04 | 0.021 45 | 0.000 85 | 596.9 | 132.97 | 410.4 | 21.01 | 377.9 | 6.33 | |||
| PM034/3-1 | 0.065 37 | 0.002 84 | 0.543 27 | 0.022 62 | 0.060 24 | 0.000 74 | 0.022 65 | 0.000 51 | 786.4 | 88.65 | 440.6 | 14.88 | 377.1 | 4.49 | |||
| PM034/3-2 | 0.087 93 | 0.003 31 | 0.731 75 | 0.026 08 | 0.060 32 | 0.000 72 | 0.031 05 | 0.000 67 | 1 381.0 | 70.61 | 557.6 | 15.29 | 377.6 | 4.39 | |||
| PM034/3-3 | 0.061 14 | 0.003 91 | 0.508 28 | 0.031 54 | 0.060 27 | 0.001 03 | 0.021 88 | 0.000 81 | 644.1 | 131.65 | 417.3 | 21.23 | 377.3 | 6.24 | |||
| PM034/3-4 | 0.082 27 | 0.002 72 | 0.684 25 | 0.021 21 | 0.060 30 | 0.000 62 | 0.025 09 | 0.000 49 | 1 252.0 | 63.19 | 529.3 | 12.78 | 377.4 | 3.79 | |||
| PM034/3-5 | 0.066 97 | 0.002 94 | 0.557 81 | 0.023 47 | 0.060 39 | 0.000 74 | 0.022 04 | 0.000 52 | 836.9 | 88.81 | 450.1 | 15.30 | 378.0 | 4.51 | |||
| PM034/3-6 | 0.062 78 | 0.002 79 | 0.521 98 | 0.022 30 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 73 | 0.020 49 | 0.000 53 | 700.9 | 91.97 | 426.5 | 14.88 | 377.3 | 4.46 | |||
| PM034/3-7 | 0.056 44 | 0.002 59 | 0.468 97 | 0.020 71 | 0.060 25 | 0.000 73 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 48 | 468.9 | 99.18 | 390.5 | 14.31 | 377.2 | 4.46 | |||
| PM034/3-8 | 0.140 77 | 0.003 60 | 1.172 23 | 0.026 95 | 0.060 39 | 0.000 60 | 0.044 62 | 0.000 69 | 2 236.7 | 43.63 | 787.7 | 12.60 | 378.0 | 3.67 | |||
| PM034/3-9 | 0.076 19 | 0.002 80 | 0.633 54 | 0.022 04 | 0.060 30 | 0.000 65 | 0.025 12 | 0.000 53 | 1 100.1 | 71.71 | 498.3 | 13.70 | 377.4 | 3.95 | |||
| PM034/3-10 | 0.071 40 | 0.007 26 | 0.594 72 | 0.058 90 | 0.060 40 | 0.001 76 | 0.021 35 | 0.001 31 | 969.0 | 194.80 | 473.9 | 37.50 | 378.1 | 10.70 | |||
| PM034/3-11 | 0.069 00 | 0.001 90 | 0.573 59 | 0.014 63 | 0.060 28 | 0.000 49 | 0.020 44 | 0.000 29 | 898.9 | 55.83 | 460.3 | 9.44 | 377.3 | 3.00 | |||
| PM034/3-12 | 0.065 71 | 0.003 53 | 0.546 78 | 0.028 38 | 0.060 35 | 0.000 90 | 0.021 33 | 0.000 67 | 797.2 | 108.81 | 442.9 | 18.63 | 377.7 | 5.47 | |||
| PM034/3-13 | 0.054 58 | 0.004 20 | 0.453 47 | 0.034 10 | 0.060 26 | 0.001 13 | 0.017 14 | 0.000 75 | 395.1 | 163.95 | 379.7 | 23.82 | 377.2 | 6.89 | |||
| PM034/3-14 | 0.129 91 | 0.004 21 | 0.956 97 | 0.028 69 | 0.053 43 | 0.000 63 | 0.031 26 | 0.000 60 | 2 096.7 | 55.89 | 681.7 | 14.88 | 335.5 | 3.84 | |||
| PM034/3-15 | 0.069 31 | 0.002 14 | 0.575 93 | 0.016 70 | 0.060 26 | 0.000 55 | 0.021 86 | 0.000 38 | 908.1 | 62.47 | 461.8 | 10.76 | 377.2 | 3.33 | |||
| PM034/3-16 | 0.060 10 | 0.002 40 | 0.499 73 | 0.019 07 | 0.060 31 | 0.000 64 | 0.018 42 | 0.000 45 | 607.1 | 83.99 | 411.5 | 12.91 | 377.5 | 3.91 | |||
| PM034/3-17 | 0.055 68 | 0.002 67 | 0.462 57 | 0.021 42 | 0.060 25 | 0.000 72 | 0.018 86 | 0.000 52 | 439.4 | 103.51 | 386.0 | 14.87 | 377.1 | 4.38 | |||
| PM034/3-18 | 0.064 13 | 0.002 34 | 0.533 93 | 0.018 50 | 0.060 38 | 0.000 60 | 0.019 98 | 0.000 44 | 746.0 | 75.15 | 434.4 | 12.25 | 377.9 | 3.67 | |||
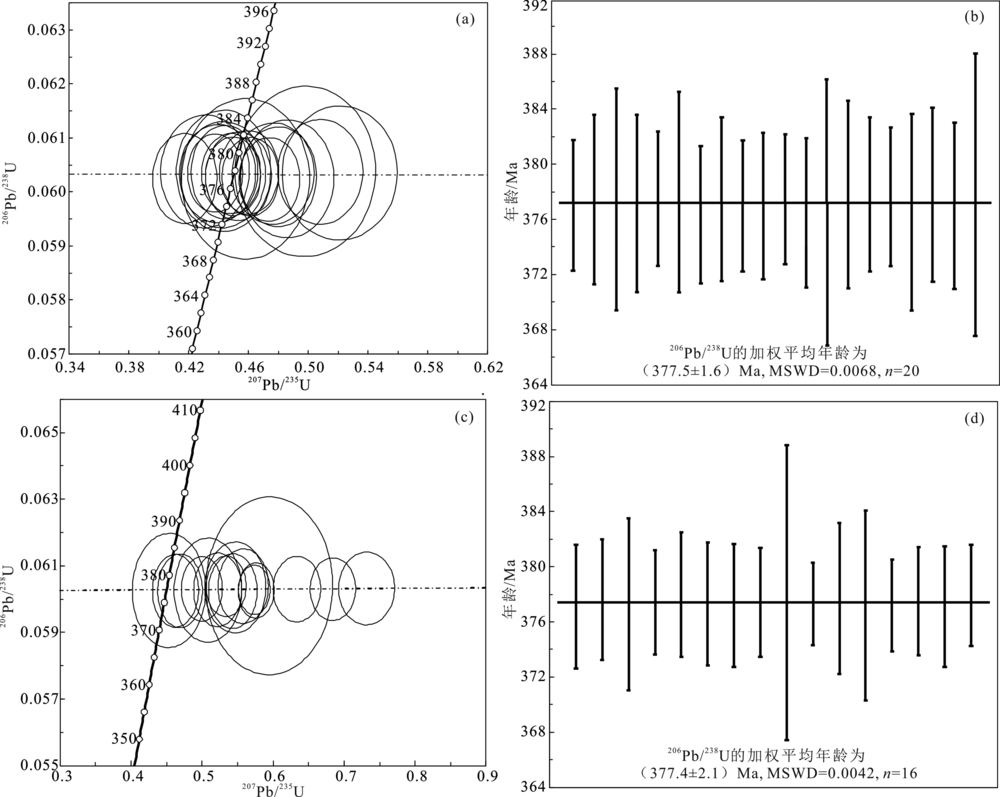
图4 索尔库里二长花岗岩样品D6533/1 ((a)和(b))、PM034/3 ((c)和(d)) U-Pb年龄谐和图及加权平均年龄图
Fig.4 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams and weighted average ages of samples D6533/1 ((a) and (b)), and PM034/3 ((c) and (d)) from the Suoerkuli monzogranite
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | TFeO | TFeO/ MgO | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM031/6 | 76.41 | 0.18 | 12.1 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.95 | 3.08 | 4.24 | 0.02 | 1.24 | 99.76 | 1.15 | 3.59 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 75.75 | 0.17 | 12.03 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.44 | 1.19 | 3.47 | 4.44 | 0.02 | 1.01 | 99.77 | 1.13 | 2.57 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 75.43 | 0.23 | 13.07 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 1.07 | 3.74 | 3.66 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 99.85 | 1.41 | 3.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 73.53 | 0.19 | 12.47 | 0.54 | 0.91 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 1.90 | 3.49 | 3.99 | 0.03 | 2.20 | 99.76 | 1.40 | 3.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 72.55 | 0.34 | 13.66 | 0.57 | 1.62 | 0.06 | 0.71 | 1.59 | 3.60 | 4.05 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 99.72 | 2.13 | 3.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 74.03 | 0.21 | 13.6 | 0.54 | 1.26 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.42 | 4.41 | 4.18 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 99.70 | 1.75 | 6.47 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | K2O/ Na2O | σ | SI | DI | A/CNK | A/NK | A/MF | C/MF | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/6 | 1.38 | 1.60 | 3.62 | 91.90 | 1.06 | 1.25 | 4.96 | 0.71 | 23.8 | 42.4 | 4.03 | 13.5 | 2.22 | 0.47 | 2.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 1.28 | 1.90 | 4.61 | 92.32 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 4.42 | 0.80 | 23.3 | 43.2 | 4.45 | 13.4 | 2.44 | 0.54 | 2.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 0.98 | 1.68 | 4.42 | 90.46 | 1.08 | 1.29 | 4.29 | 0.64 | 21.6 | 44.3 | 4.45 | 15.6 | 2.95 | 0.71 | 2.61 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 1.14 | 1.82 | 4.8 | 88.69 | 0.92 | 1.24 | 4.00 | 1.11 | 25.9 | 45.1 | 4.06 | 13.4 | 2.24 | 0.49 | 1.90 | |||||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 1.13 | 1.97 | 6.73 | 86.30 | 1.04 | 1.32 | 2.83 | 0.60 | 25.5 | 55.6 | 5.73 | 19.3 | 3.64 | 0.92 | 3.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 0.95 | 2.37 | 2.53 | 93.38 | 1.08 | 1.15 | 4.30 | 0.24 | 21.0 | 48.2 | 4.45 | 15.6 | 2.73 | 0.50 | 2.46 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | REE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/6 | 0.31 | 1.48 | 0.42 | 1.10 | 0.20 | 1.52 | 0.23 | 10.7 | 93.74 | 86.42 | 7.32 | 11.81 | 11.23 | 0.67 | 1.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 0.35 | 2.01 | 0.43 | 1.34 | 0.20 | 1.55 | 0.27 | 10.6 | 95.68 | 87.33 | 8.35 | 10.46 | 10.78 | 0.71 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 0.47 | 2.04 | 0.54 | 1.57 | 0.28 | 2.01 | 0.35 | 14.7 | 99.48 | 89.61 | 9.87 | 9.08 | 7.71 | 0.78 | 1.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 0.33 | 1.48 | 0.39 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 1.54 | 0.27 | 11.3 | 98.48 | 91.19 | 7.29 | 12.51 | 12.06 | 0.73 | 1.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 0.54 | 2.80 | 0.64 | 1.70 | 0.30 | 1.99 | 0.30 | 15.9 | 122.16 | 110.69 | 11.47 | 9.65 | 9.19 | 0.82 | 1.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 0.45 | 2.22 | 0.58 | 1.61 | 0.29 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 14.1 | 102.51 | 92.48 | 10.03 | 9.22 | 7.17 | 0.59 | 1.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Ga | Sc | Sr | Ba | Rb | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | ||||||||||||||
| PM031/6 | 35.0 | 20.2 | 20.4 | 1.36 | 2.49 | 10.7 | 13.6 | 15.3 | 2.5 | 89.4 | 320 | 207 | 12.2 | 8.57 | 102.0 | 3.09 | 2.53 | 28.4 | ||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 14.0 | 19.5 | 13.3 | 2.06 | 3.03 | 5.0 | 10.5 | 13.0 | 2.0 | 126.0 | 336 | 137 | 13.3 | 5.23 | 74.1 | 2.96 | 2.71 | 41.8 | ||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 5.6 | 19.7 | 29.6 | 2.18 | 2.99 | 8.1 | 12.7 | 14.8 | 3.2 | 125.0 | 280 | 183 | 19.8 | 2.58 | 117.0 | 3.75 | 2.48 | 38.6 | ||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 6.8 | 14.8 | 24.2 | 2.08 | 3.78 | 6.2 | 14.0 | 14.7 | 5.6 | 105.0 | 212 | 189 | 11.1 | 5.59 | 89.8 | 3.41 | 2.68 | 31.0 | ||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 6.9 | 18.9 | 31.1 | 3.88 | 4.25 | 8.1 | 22.0 | 15.1 | 4.6 | 193.0 | 430 | 161 | 14.0 | 7.02 | 130.0 | 2.53 | 2.03 | 29.0 | ||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 9.8 | 17.3 | 32.1 | 2.00 | 3.22 | 4.8 | 10.2 | 16.8 | 2.9 | 96.3 | 589 | 175 | 15.3 | 2.04 | 195.0 | 4.79 | 2.41 | 33.6 | ||||||||||||||
表2 二长花岗岩样品主量(%)、微量(10-6)和稀土(10-6)元素分析结果
Table 2 Major (%), trace element (10-6) and REE (10-6) contents of the monzogranite samples
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | TFeO | TFeO/ MgO | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM031/6 | 76.41 | 0.18 | 12.1 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.95 | 3.08 | 4.24 | 0.02 | 1.24 | 99.76 | 1.15 | 3.59 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 75.75 | 0.17 | 12.03 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.44 | 1.19 | 3.47 | 4.44 | 0.02 | 1.01 | 99.77 | 1.13 | 2.57 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 75.43 | 0.23 | 13.07 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 1.07 | 3.74 | 3.66 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 99.85 | 1.41 | 3.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 73.53 | 0.19 | 12.47 | 0.54 | 0.91 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 1.90 | 3.49 | 3.99 | 0.03 | 2.20 | 99.76 | 1.40 | 3.10 | |||||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 72.55 | 0.34 | 13.66 | 0.57 | 1.62 | 0.06 | 0.71 | 1.59 | 3.60 | 4.05 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 99.72 | 2.13 | 3.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 74.03 | 0.21 | 13.6 | 0.54 | 1.26 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.42 | 4.41 | 4.18 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 99.70 | 1.75 | 6.47 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | K2O/ Na2O | σ | SI | DI | A/CNK | A/NK | A/MF | C/MF | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/6 | 1.38 | 1.60 | 3.62 | 91.90 | 1.06 | 1.25 | 4.96 | 0.71 | 23.8 | 42.4 | 4.03 | 13.5 | 2.22 | 0.47 | 2.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 1.28 | 1.90 | 4.61 | 92.32 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 4.42 | 0.80 | 23.3 | 43.2 | 4.45 | 13.4 | 2.44 | 0.54 | 2.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 0.98 | 1.68 | 4.42 | 90.46 | 1.08 | 1.29 | 4.29 | 0.64 | 21.6 | 44.3 | 4.45 | 15.6 | 2.95 | 0.71 | 2.61 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 1.14 | 1.82 | 4.8 | 88.69 | 0.92 | 1.24 | 4.00 | 1.11 | 25.9 | 45.1 | 4.06 | 13.4 | 2.24 | 0.49 | 1.90 | |||||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 1.13 | 1.97 | 6.73 | 86.30 | 1.04 | 1.32 | 2.83 | 0.60 | 25.5 | 55.6 | 5.73 | 19.3 | 3.64 | 0.92 | 3.20 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 0.95 | 2.37 | 2.53 | 93.38 | 1.08 | 1.15 | 4.30 | 0.24 | 21.0 | 48.2 | 4.45 | 15.6 | 2.73 | 0.50 | 2.46 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | REE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/6 | 0.31 | 1.48 | 0.42 | 1.10 | 0.20 | 1.52 | 0.23 | 10.7 | 93.74 | 86.42 | 7.32 | 11.81 | 11.23 | 0.67 | 1.06 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 0.35 | 2.01 | 0.43 | 1.34 | 0.20 | 1.55 | 0.27 | 10.6 | 95.68 | 87.33 | 8.35 | 10.46 | 10.78 | 0.71 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 0.47 | 2.04 | 0.54 | 1.57 | 0.28 | 2.01 | 0.35 | 14.7 | 99.48 | 89.61 | 9.87 | 9.08 | 7.71 | 0.78 | 1.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 0.33 | 1.48 | 0.39 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 1.54 | 0.27 | 11.3 | 98.48 | 91.19 | 7.29 | 12.51 | 12.06 | 0.73 | 1.08 | |||||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 0.54 | 2.80 | 0.64 | 1.70 | 0.30 | 1.99 | 0.30 | 15.9 | 122.16 | 110.69 | 11.47 | 9.65 | 9.19 | 0.82 | 1.13 | |||||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 0.45 | 2.22 | 0.58 | 1.61 | 0.29 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 14.1 | 102.51 | 92.48 | 10.03 | 9.22 | 7.17 | 0.59 | 1.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Ga | Sc | Sr | Ba | Rb | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | ||||||||||||||
| PM031/6 | 35.0 | 20.2 | 20.4 | 1.36 | 2.49 | 10.7 | 13.6 | 15.3 | 2.5 | 89.4 | 320 | 207 | 12.2 | 8.57 | 102.0 | 3.09 | 2.53 | 28.4 | ||||||||||||||
| PM026/6 | 14.0 | 19.5 | 13.3 | 2.06 | 3.03 | 5.0 | 10.5 | 13.0 | 2.0 | 126.0 | 336 | 137 | 13.3 | 5.23 | 74.1 | 2.96 | 2.71 | 41.8 | ||||||||||||||
| PM031/10 | 5.6 | 19.7 | 29.6 | 2.18 | 2.99 | 8.1 | 12.7 | 14.8 | 3.2 | 125.0 | 280 | 183 | 19.8 | 2.58 | 117.0 | 3.75 | 2.48 | 38.6 | ||||||||||||||
| PM031/11 | 6.8 | 14.8 | 24.2 | 2.08 | 3.78 | 6.2 | 14.0 | 14.7 | 5.6 | 105.0 | 212 | 189 | 11.1 | 5.59 | 89.8 | 3.41 | 2.68 | 31.0 | ||||||||||||||
| D6533/1 | 6.9 | 18.9 | 31.1 | 3.88 | 4.25 | 8.1 | 22.0 | 15.1 | 4.6 | 193.0 | 430 | 161 | 14.0 | 7.02 | 130.0 | 2.53 | 2.03 | 29.0 | ||||||||||||||
| PM034/3 | 9.8 | 17.3 | 32.1 | 2.00 | 3.22 | 4.8 | 10.2 | 16.8 | 2.9 | 96.3 | 589 | 175 | 15.3 | 2.04 | 195.0 | 4.79 | 2.41 | 33.6 | ||||||||||||||

图6 二长花岗岩样品稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石和原始地幔数据据文献[24])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive-mantle-normalized spider diagram(b)for the monzogranite samples(normalized data after ref.[24])
| 样品号 | Al2O3/% | CaO/% | K2O/% | Na2O/% | SiO2/% | Zr/10-6 | lnDZr | M | tZr/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM031/6 | 12.10 | 0.95 | 4.24 | 3.08 | 76.41 | 102.00 | 8.49 | 0.75 | 797 |
| PM026/6 | 12.03 | 1.19 | 4.44 | 3.47 | 75.75 | 74.10 | 8.81 | 0.85 | 763 |
| PM031/10 | 13.07 | 1.07 | 3.66 | 3.74 | 75.43 | 117.00 | 8.35 | 0.74 | 810 |
| PM031/11 | 12.47 | 1.90 | 3.99 | 3.49 | 73.53 | 89.80 | 8.62 | 0.90 | 775 |
| D6533/1 | 13.66 | 1.59 | 4.05 | 3.60 | 72.55 | 130.00 | 8.25 | 0.81 | 815 |
| PM034/3 | 13.60 | 0.42 | 4.18 | 4.41 | 74.03 | 195.00 | 7.84 | 0.76 | 857 |
表3 二长花岗岩锆石饱和温度计算结果
Table 3 Results of zircon saturation temperature for the monzogranite samples
| 样品号 | Al2O3/% | CaO/% | K2O/% | Na2O/% | SiO2/% | Zr/10-6 | lnDZr | M | tZr/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM031/6 | 12.10 | 0.95 | 4.24 | 3.08 | 76.41 | 102.00 | 8.49 | 0.75 | 797 |
| PM026/6 | 12.03 | 1.19 | 4.44 | 3.47 | 75.75 | 74.10 | 8.81 | 0.85 | 763 |
| PM031/10 | 13.07 | 1.07 | 3.66 | 3.74 | 75.43 | 117.00 | 8.35 | 0.74 | 810 |
| PM031/11 | 12.47 | 1.90 | 3.99 | 3.49 | 73.53 | 89.80 | 8.62 | 0.90 | 775 |
| D6533/1 | 13.66 | 1.59 | 4.05 | 3.60 | 72.55 | 130.00 | 8.25 | 0.81 | 815 |
| PM034/3 | 13.60 | 0.42 | 4.18 | 4.41 | 74.03 | 195.00 | 7.84 | 0.76 | 857 |
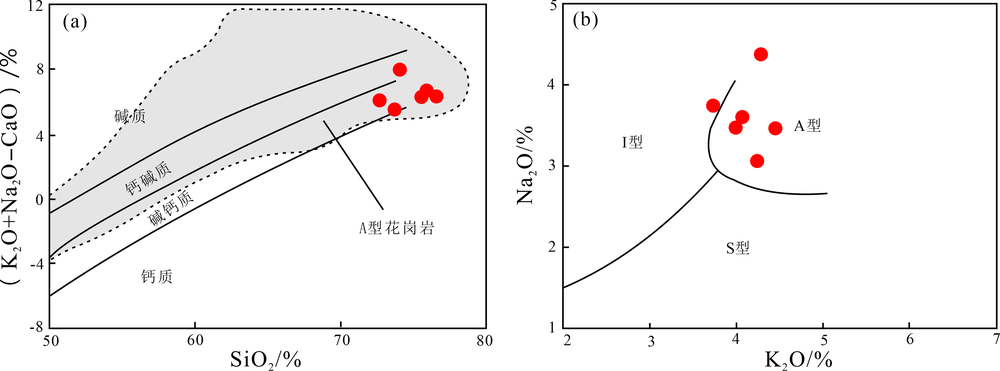
图7 二长花岗岩样品(K2O+Na2O-CaO)-SiO2图解(a)与Na2O-K2O图解(b)(底图分别据文献[38]和[37])
Fig.7 (K2O+Na2O-CaO) vs. SiO2 (a) and Na2O vs. K2O (b) diagrams of the monzogranite samples(base map after refs.[38] and [37], respectively)
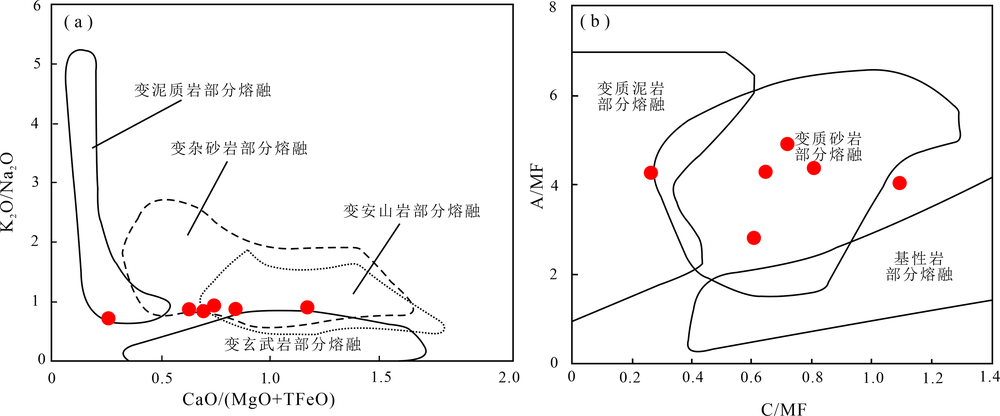
图8 二长花岗岩样品K2O/Na2O-CaO/(MgO+TFeO)图解((a),底图据文献[65])和A/MF-C/MF图解((b),底图据文献[66])
Fig.8 K2O/Na2O vs. CaO/(MgO+TFeO) (a) and A/MF vs. C/MF (b) diagrams for the monzogranite samples(base map after refs.[65] and [66], respectively)
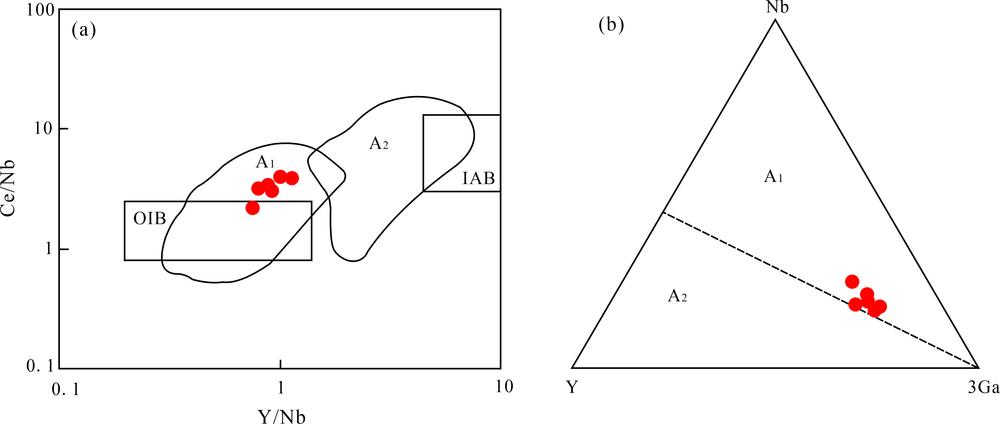
图9 索尔库里二长花岗岩Ce/Nb-Y/Nb图解(a)和Nb-Y-3Ga三角图解(b)(底图据文献[71])
Fig.9 Ce/Nb-Y/Nb (a) and ternary Nb-Y-3Ga (b) diagrams for the monzogranite samples (base map after reference[71])
| [1] | 曹玉亭, 刘良, 王超, 等. 阿尔金南缘塔特勒克布拉克花岗岩的地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb定年及Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(11):3259-3271. |
| [2] | 孙吉明, 马中平, 唐卓, 等. 阿尔金南缘鱼目泉岩浆混合花岗岩LA-ICP-MS测年与构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(2):247-257. |
| [3] | 赵子贤, 柳长峰, 赫英福, 等. 新疆南阿尔金木纳布拉克构造混杂岩带物质组成及变形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1):25-35. |
| [4] | 康磊, 刘良, 曹玉亭, 等. 阿尔金南缘塔特勒克布拉克复式花岗质岩体东段片麻状花岗岩的地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(9):3039-3048. |
| [5] | 吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静. A型花岗岩研究现状及其述评[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):57-66. |
| [6] | 葛肖虹, 张梅生, 刘永江, 等. 阿尔金断裂研究的科学问题与研究思路[J]. 现代地质, 1998, 12(3):295-301. |
| [7] | 吴才来, 郜源红, 雷敏, 等. 南阿尔金茫崖地区花岗岩类锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年、Lu-Hf同位素特征及岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(8):2297-2323. |
| [8] | KANG L, LIU L, WANG C, et al. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating of Changshagou Adakite from the south Altyn UHPM Terrane: Evidence of the partial melting of the lower crust[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(5):1454-1465. |
| [9] |
KANG L, XIAO P, GAO X, et al. Age, petrogenesis and tecto-nic implications of Early Devonian bimodal volcanic rocks in the South Altyn, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 111:733-750.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 刘良, 车自成, 罗金海, 等. 阿尔金山西段榴辉岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 1996, 41(16):1485-1488. |
| [11] | 刘良, 车自成, 王焰, 等. 阿尔金高压变质岩带的特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1999, 44(1):58-65. |
| [12] | 车自成, 刘良, 刘洪福, 等. 阿尔金山地区高压变质泥质岩石的发现及其产出环境[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(14):1298-1300. |
| [13] | 崔军文, 张晓卫, 李朋武. 阿尔金断裂: 几何学、性质和生长方式[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(6):509-516. |
| [14] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 等. 阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制[J]. 地质学报, 1999, 73(3):193-205. |
| [15] | 周勇, 潘裕生. 阿尔金断裂早期走滑运动方向及其活动时间探讨[J]. 地质论评, 1999, 45(1):1-9. |
| [16] | 刘良, 孙勇, 车自成, 等. 阿尔金发现超高压(>3.8GPa)石榴二辉橄榄岩[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(9):657-662. |
| [17] | 胡云绪, 校培喜, 高晓峰, 等. 东昆仑西段-阿尔金地区区域地层划分及地层时空格架建立[J]. 西北地质, 2010, 43(4):152-158. |
| [18] |
YUAN H, GAO S, LIU X, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2010, 28(3):353-370.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 柳小明, 高山, 袁洪林, 等. 193nm LA-ICPMS对国际地质标准参考物质中42种主量和微量元素的分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2002, 18(3):408-418. |
| [20] | 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(14):1511-1520. |
| [21] |
WRIGHT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to ques tions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969, 106(4):370~384.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 邓晋福. 中国大陆根-柱构造——大陆动力学钥匙[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-110. |
| [23] | 谢建成, 陈思, 荣伟, 等. 安徽牯牛降A型花岗岩的年代学、地球化学和构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(12):4007-4020. |
| [24] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 秦江锋, 赖绍聪, 李永飞, 等. 扬子板块北缘阳坝岩体锆石饱和温度的计算及其意义[J]. 西北地质, 2005, 38(3):1-5. |
| [26] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. |
| [27] |
MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granite implications for zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6):529-532.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
KING P L, WHITE A J R, CHAPPELL B W. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
HARRISON T M, WATSON E B, AIKMAN A B. Temperature spectra of zircon crystallization in plutonic rocks[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(7):635-638.
DOI URL |
| [31] | CHAPPELL B W. Two contrasting granite type[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974, 8:173-174. |
| [32] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, ChAPPELL B W. A-type gra-nites: Geochemical characteristics, discriminations and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407-419.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problem and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1/2):1-29.
DOI URL |
| [34] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1979, 11(7):468. |
| [35] | 袁忠信. 关于A型花岗岩命名问题的讨论[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2001, 20(3):293-296. |
| [36] | 廖忠礼, 莫宣学, 潘桂棠, 等. 西藏过铝花岗岩锆石群型的成因信息[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(1):63-71. |
| [37] |
COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2):189-200.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
FROST B R, BARNES C G, COLLINS W J. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(11):2033-2048.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 刘彬, 马昌前, 郭盼, 等. 东昆仑中泥盆世A型花岗岩的确定及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(5):947-962. |
| [40] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Earth Sciences, 1992, 83(1/2):1-26. |
| [41] | 王强, 赵振华. 桐柏-大别造山带燕山期A型花岗岩的厘定[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2000, 19(4):297-306,315. |
| [42] | 贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建. A型花岗岩的研究进展及意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(3):465-480. |
| [43] |
FROST C D, FROST B R. On Ferroan (A-type) granitoids: their compositional variability and modes of origin[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2011, 52(1):39-53.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
MUSHKIN A, NAVON O, HALICZ L, et al. The petrogenesis of A-type magmas from the Amram Massif, Southern Israel[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(5):815-832.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
KERR A, FRYER B J. Nd isotope evidence for crust-mantle interaction in the generation of A-type granitoid suites in Labrador, Canada[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 104(1/4):39-60.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
YANG J H, CHUNG S L, WILDE S A, et al. A hybrid origin from the Qianshan A-type granite, Northeast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1/2):89-106.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
WONG J, SUN M, XING G F, et al. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of the Baijuhuajian metaluminous A-type granite: Extension at 125~100Ma and its tectonic significance for South China[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4):289-305.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
CREASE R A, PRICE R C, WORMALD R J. A-type granites revisited: Assessment of a residual-source modal[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(2):163-166.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
DOUCE A E P. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):743-746.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
WANG Q, WYMAN D A, LI Z X, et al. Petrology, geochronology and geochemistry of ca. 780Ma A-type granites in South China: Petrogenesis and implications for crustal growth during the breakup of supercontinent Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 178(1/4):185-208.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
HUANG H Q, LI X H, LI W X, et al. Formation of high δ18O fayalite-bearing A-type by high-temperature melting of granulitic metasedimentary rocks, southern China[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(10):903-906.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
SUN Y, MA C Q, LIU Y Y, et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Late Triassic aluminous A-type granites in southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(6):1117-1131.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
TURNER S P, FODEN J D, MORRISON R S. Derivation of some A-type magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma: An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia[J]. Lithos, 1992, 28(2):151-179.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
KEMP A, HAWKESWORTH C J, FOSTER G L, et al. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon[J]. Science, 2007, 315:980-983.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
HOFMANN A W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: the relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3):297-314.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
GREEN T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical process in the Crust-Mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4):347-359.
DOI URL |
| [57] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985:1-132. |
| [58] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347:662-665.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
HE Y S, LI S G, HOEFS J, et al. Post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie orogen: New evidence for partial melting of a thickened continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(13):3815-3838.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
PATINO DOUCE A E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1999, 168(1):55-75.
DOI URL |
| [61] | 赵永久, 袁超, 周美夫, 等. 川西老君沟和孟通沟花岗岩的地球化学特征、成因机制及对松潘—甘孜地体基底性质的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(5):995-1006. |
| [62] |
PATINO DOUCE A E, BEARD J. Dehydration-melting of biotite gneiss and quartz amphibolite from 3 to 15 kbar[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36:707-738.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
GARDIEN V, THOMPSON A B, GRUJIC D, et al. Experimental melting of biotite+plagioclase+quartz±muscovite assemblages and implications of crustal melting[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100:15581-15591.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
PATINO DOUCE A E, BEARD J. Effects of P, f(O2) and Mg/Fe ratio on dehydration-melting model metagreywackes[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(5):999-1024.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
KAYGUSUZ A, SIEBEL W, ŞEN C, et al. Petrochemistry and petrology of I-type granitoids in an arc setting: the composite Torul Pluton, Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2008, 97(4):739-764.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
ALTHERR R, HOLL A, HENGNER E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European variscides: Northern Vosges (France) and Northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(1):51-73.
DOI URL |
| [67] | 邱检生, 胡建, 王孝磊, 等. 广东河源白石冈岩体:一个高分异的Ⅰ型花岗岩[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(4):503-514. |
| [68] |
RYERSON F J, WATSON E B. Rutile saturation in magmas: implications for Ti, Nb, Ta depletion in island-arc basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1987, 86(2/4):225-239.
DOI URL |
| [69] | 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 王立全, 等. 西藏冈底斯东部察隅高分异I型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素约束[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2009, 39(7):833-848. |
| [70] | 吴锁平, 吴才来, 陈其龙. 阿尔金断裂南侧吐拉铝质A型花岗岩的特征及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(10):1385-1392. |
| [71] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenesis and implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7):641-644.
DOI URL |
| [72] | 李小伟, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 关于A型花岗岩判别过程中若干问题的讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(增):278-285. |
| [73] | 康磊. 南阿尔金高压-超高压变质带早古生代多期花岗质岩浆作用及其地质意义[D]. 西安:西北大学, 2014. |
| [74] |
WANG C, LIU L, XIAO P X, et al. Geochemical and geochronologic constraints for Paleozoic magmatism related to the orogenic collapse in the Qimantagh-South Altyn region, northwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2014, 202/203:1-20.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
BONIN B. Do coeval mafic and felsic magmas in post-collisional to within-plate regimes necessarily imply two contrasting, mantle and crustal, sources A review[J]. Lithos, 2004, 78(1):1-24.
DOI URL |
| [76] | 梁培, 陈华勇, 韩金生, 等. 东准噶尔北缘早石炭世构造体制转变:来自碱性花岗岩年代学和地球化学制约[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(1):202-221. |
| [77] | 韩宝福. 后碰撞花岗岩类的多样性及其构造环境判别的复杂性[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(3):64-72. |
| [78] | LIEGEOIS J P. Some words on the post-collisional magmatism[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45:15-17. |
| [79] | 康磊, 校培喜, 高晓峰, 等. 茫崖二长花岗岩、石英闪长岩的年代学、地球化学及岩石成因:对阿尔金南缘早古生代构造-岩浆演化的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(6):1731-1748. |
| [1] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [2] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [3] | 路芳, 高明星, 周书贤, 王顺. 阿尔金东段断裂带流域地貌特征及其构造活动[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1100-1109. |
| [4] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [5] | 谢亘, 喻光明, 路英川, 冯欣, 田光昊, 王然, 王建. 华北克拉通南缘小秦岭地区花岗质片麻岩年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712. |
| [6] | 孙晓东, 陈海云, 于光宁. 内蒙古海拉斯图乌拉A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1218-1230. |
| [7] | 任永健, 程烁, 张明明, 曹光远, 于汪, 赵寒, 梁恒, 王富强, 祁才吉. 黑龙江张家湾地区中侏罗世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076. |
| [8] | 王迪, 赵国春, 苏尚国, 李宏星. 大兴安岭南段晚中生代侵入岩时空分布及主脊与东坡岩体特征对比[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 466-482. |
| [9] | 张云, 孙立新, 张天福, 孙义伟, 张祺, 李艳锋, 杨泽黎, 刘文刚. 内蒙古狼山地区乌花辉长岩的年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成:对地幔源区特征和岩石成因的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 450-465. |
| [10] | 滕超, 张晓飞, 周毅, 冯俊岭, 李树才. 内蒙古锡林浩特小乌兰沟早白垩世二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1003-1014. |
| [11] | 赵子贤, 柳长峰, 赫英福, 叶宝莹, 许鑫, 霍东亮. 新疆南阿尔金木纳布拉克构造混杂岩带物质组成及变形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 25-35. |
| [12] | 王训练, 周洪瑞, 王振涛, 高正升, 杨利超, 张海军, 于子栋, 鞠鹏程. 阿尔金断裂东段红柳峡早白垩世晚期岩浆事件及其区域构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(01): 1-15. |
| [13] | 袁建国, 任永健, 姜振宁, 屈云燕, 魏浩. 内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场早石炭世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1131-1146. |
| [14] | 余超, 柳振江, 宓奎峰, 王常波, 张杰, 王建平, 刘家军, 张梅. 内蒙古巴彦都兰铜矿地质特征及矿床成因——岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1095-1113. |
| [15] | 袁建国, 顾玉超, 肖荣阁, 屈云燕, 段凯波, 韩玥. 内蒙古锡林浩特东部地区早白垩世花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 20-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||