



现代地质 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (04): 703-714.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.04.02
收稿日期:2018-01-21
修回日期:2018-11-26
出版日期:2019-08-20
发布日期:2019-09-05
作者简介:黄泽森,男,工程师,硕士研究生,1988年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,从事区域地质矿产调查工作。Email: 289700742@qq.com。
基金资助:
HUANG Zesen1,2( ), JIANGBA Duoji3, DAWA Ciren3, TAER Jie3
), JIANGBA Duoji3, DAWA Ciren3, TAER Jie3
Received:2018-01-21
Revised:2018-11-26
Online:2019-08-20
Published:2019-09-05
摘要:
西藏谢通门县切穷地区发育面积较广的早白垩世花岗岩岩体。为了进一步查明花岗岩的特征、侵入时代及其形成环境,对其进行了地质学、岩石地球化学及年代学研究。岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果表明,研究区花岗岩岩体侵位年龄主要集中于(129.3±0.8)~(130.5±0.9) Ma,属早白垩世。从岩石地球化学特征来看,研究区花岗岩岩体具有高SiO2(73.19%~76.7%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O=7.81%~8.41%)特征,铝饱和指数(A/CNK)介于0.93~1.12之间,为强过铝质花岗岩;贫CaO(0.32%~7.31%)、MgO(0.01%~1.76%),显示明显的负铕(δEu=0.11~1.25)异常,富集Rb、Th、Nd元素,亏损Nb、Sr、P、Ti、K元素。从形成环境来看,研究区花岗岩具有明显的大陆碰撞环境的特征。研究认为,西藏切穷地区早白垩世花岗岩形成于同碰撞环境,但在后碰撞过程中地壳缩短增厚发生拆沉作用,玄武质岩浆岩底侵,经过中下地壳发生改造重熔形成的。
中图分类号:
黄泽森, 江巴多吉, 达瓦次仁, 塔尔杰. 西藏切穷地区早白垩世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 703-714.
HUANG Zesen, JIANGBA Duoji, DAWA Ciren, TAER Jie. Geochemistry and Geochronology of Early Cretaceous Granitic Intrusions and Tectonic Setting of Qieqiong Area in Tibet,China[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(04): 703-714.
| 测点 | 含量(10-6)及比值 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | U/Th | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | |||||||||
| 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | ||||||||||||||
| D0070TW-1 | 570.9 | 401.3 | 2.05 | 0.1319 | 0.003 2 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.048 3 | 0.001 2 | 126 | 1 | 126 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-2 | 319.5 | 247.4 | 1.42 | 0.133 5 | 0.004 1 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.048 6 | 0.001 6 | 129 | 1 | 127 | 4 | ||||
| D0070TW-3 | 632.9 | 423.8 | 1.29 | 0.137 8 | 0.003 0 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 7 | 0.001 1 | 129 | 1 | 131 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-4 | 518.7 | 338.2 | 1.49 | 0.139 9 | 0.003 4 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 5 | 0.001 3 | 129 | 1 | 133 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-5 | 688.0 | 488.6 | 1.53 | 0.134 2 | 0.003 0 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 9 | 0.001 0 | 129 | 1 | 128 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-6 | 318.9 | 759.1 | 1.41 | 0.139 5 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 5 | 0.001 6 | 132 | 1 | 133 | 4 | ||||
| D0070TW-7 | 697.4 | 526.1 | 0.42 | 0.147 7 | 0.003 0 | 0.021 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 0 | 134 | 1 | 140 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-8 | 362.4 | 376.5 | 0.62 | 0.137 0 | 0.003 8 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 7 | 0.001 4 | 128 | 1 | 130 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-9 | 280.6 | 371.6 | 0.96 | 0.134 2 | 0.004 3 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 1 | 0.001 7 | 126 | 1 | 128 | 4 | ||||
| D0070TW-10 | 266.3 | 258.2 | 0.76 | 0.129 5 | 0.005 0 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 5 | 0.001 9 | 128 | 2 | 124 | 1 | ||||
| D0070TW-11 | 469.9 | 754.9 | 1.32 | 0.134 9 | 0.003 8 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 5 | 0.001 4 | 126 | 1 | 129 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-1 | 118.7 | 123.4 | 1.42 | 0.171 2 | 0.008 4 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.062 5 | 0.003 3 | 132 | 2 | 160 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-2 | 538.8 | 448.9 | 1.29 | 0.150 7 | 0.004 0 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.052 7 | 0.001 4 | 132 | 1 | 143 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-3 | 741.3 | 714.5 | 1.49 | 0.147 1 | 0.002 7 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.052 8 | 0.001 0 | 129 | 1 | 139 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-4 | 74.9 | 82.5 | 1.53 | 0.139 2 | 0.011 0 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.053 2 | 0.004 5 | 129 | 3 | 132 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-5 | 326.6 | 345.9 | 1.41 | 0.147 3 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.051 7 | 0.001 6 | 133 | 1 | 140 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-6 | 979.6 | 847.0 | 0.42 | 0.136 9 | 0.002 5 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 1 | 0.048 6 | 0.000 9 | 131 | 1 | 130 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-7 | 479.4 | 415.2 | 0.96 | 0.134 4 | 0.003 5 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 9 | 0.001 2 | 130 | 1 | 128 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-8 | 423.5 | 523.5 | 0.76 | 0.142 5 | 0.004 1 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 5 | 130 | 1 | 135 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-9 | 549.5 | 346.8 | 1.03 | 0.132 4 | 0.003 1 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 4 | 0.001 2 | 130 | 1 | 126 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-10 | 452.8 | 480.1 | 0.62 | 0.140 4 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 9 | 0.001 6 | 131 | 1 | 133 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-11 | 174.1 | 497.5 | 0.96 | 0.154 1 | 0.008 6 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.054 2 | 0.003 1 | 132 | 2 | 146 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-12 | 170.0 | 572.5 | 1.2 | 0.140 8 | 0.006 4 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.051 8 | 0.002 5 | 128 | 2 | 134 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-13 | 253.6 | 317.3 | 1.24 | 0.147 8 | 0.006 4 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.052 9 | 0.002 4 | 132 | 2 | 140 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-14 | 255.3 | 599.7 | 0.91 | 0.134 1 | 0.004 3 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 7 | 127 | 1 | 128 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-15 | 455.7 | 751.5 | 0.94 | 0.146 3 | 0.003 8 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.052 5 | 0.001 4 | 129 | 1 | 139 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-16 | 252.7 | 537.0 | 1.16 | 0.141 4 | 0.004 9 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.052 3 | 0.001 9 | 127 | 1 | 134 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-17 | 488.9 | 947.6 | 1.15 | 0.137 0 | 0.005 7 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.050 1 | 0.002 2 | 128 | 2 | 130 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-18 | 315.5 | 485.3 | 0.81 | 0.141 3 | 0.004 5 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 7 | 0.001 7 | 130 | 1 | 134 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-19 | 393.6 | 663.2 | 1.58 | 0.140 2 | 0.004 0 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 5 | 129 | 1 | 133 | 4 | ||||
表1 花岗岩岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results for the Qieqiong granites
| 测点 | 含量(10-6)及比值 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | U/Th | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | |||||||||
| 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | ||||||||||||||
| D0070TW-1 | 570.9 | 401.3 | 2.05 | 0.1319 | 0.003 2 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.048 3 | 0.001 2 | 126 | 1 | 126 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-2 | 319.5 | 247.4 | 1.42 | 0.133 5 | 0.004 1 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.048 6 | 0.001 6 | 129 | 1 | 127 | 4 | ||||
| D0070TW-3 | 632.9 | 423.8 | 1.29 | 0.137 8 | 0.003 0 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 7 | 0.001 1 | 129 | 1 | 131 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-4 | 518.7 | 338.2 | 1.49 | 0.139 9 | 0.003 4 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 5 | 0.001 3 | 129 | 1 | 133 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-5 | 688.0 | 488.6 | 1.53 | 0.134 2 | 0.003 0 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 9 | 0.001 0 | 129 | 1 | 128 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-6 | 318.9 | 759.1 | 1.41 | 0.139 5 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 5 | 0.001 6 | 132 | 1 | 133 | 4 | ||||
| D0070TW-7 | 697.4 | 526.1 | 0.42 | 0.147 7 | 0.003 0 | 0.021 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 0 | 134 | 1 | 140 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-8 | 362.4 | 376.5 | 0.62 | 0.137 0 | 0.003 8 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 7 | 0.001 4 | 128 | 1 | 130 | 3 | ||||
| D0070TW-9 | 280.6 | 371.6 | 0.96 | 0.134 2 | 0.004 3 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 1 | 0.001 7 | 126 | 1 | 128 | 4 | ||||
| D0070TW-10 | 266.3 | 258.2 | 0.76 | 0.129 5 | 0.005 0 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 5 | 0.001 9 | 128 | 2 | 124 | 1 | ||||
| D0070TW-11 | 469.9 | 754.9 | 1.32 | 0.134 9 | 0.003 8 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 5 | 0.001 4 | 126 | 1 | 129 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-1 | 118.7 | 123.4 | 1.42 | 0.171 2 | 0.008 4 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.062 5 | 0.003 3 | 132 | 2 | 160 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-2 | 538.8 | 448.9 | 1.29 | 0.150 7 | 0.004 0 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.052 7 | 0.001 4 | 132 | 1 | 143 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-3 | 741.3 | 714.5 | 1.49 | 0.147 1 | 0.002 7 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.052 8 | 0.001 0 | 129 | 1 | 139 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-4 | 74.9 | 82.5 | 1.53 | 0.139 2 | 0.011 0 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.053 2 | 0.004 5 | 129 | 3 | 132 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-5 | 326.6 | 345.9 | 1.41 | 0.147 3 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.051 7 | 0.001 6 | 133 | 1 | 140 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-6 | 979.6 | 847.0 | 0.42 | 0.136 9 | 0.002 5 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 1 | 0.048 6 | 0.000 9 | 131 | 1 | 130 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-7 | 479.4 | 415.2 | 0.96 | 0.134 4 | 0.003 5 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 9 | 0.001 2 | 130 | 1 | 128 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-8 | 423.5 | 523.5 | 0.76 | 0.142 5 | 0.004 1 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 5 | 130 | 1 | 135 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-9 | 549.5 | 346.8 | 1.03 | 0.132 4 | 0.003 1 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.047 4 | 0.001 2 | 130 | 1 | 126 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-10 | 452.8 | 480.1 | 0.62 | 0.140 4 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 9 | 0.001 6 | 131 | 1 | 133 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-11 | 174.1 | 497.5 | 0.96 | 0.154 1 | 0.008 6 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.054 2 | 0.003 1 | 132 | 2 | 146 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-12 | 170.0 | 572.5 | 1.2 | 0.140 8 | 0.006 4 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.051 8 | 0.002 5 | 128 | 2 | 134 | 2 | ||||
| DPM07-13 | 253.6 | 317.3 | 1.24 | 0.147 8 | 0.006 4 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.052 9 | 0.002 4 | 132 | 2 | 140 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-14 | 255.3 | 599.7 | 0.91 | 0.134 1 | 0.004 3 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 7 | 127 | 1 | 128 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-15 | 455.7 | 751.5 | 0.94 | 0.146 3 | 0.003 8 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.052 5 | 0.001 4 | 129 | 1 | 139 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-16 | 252.7 | 537.0 | 1.16 | 0.141 4 | 0.004 9 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.052 3 | 0.001 9 | 127 | 1 | 134 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-17 | 488.9 | 947.6 | 1.15 | 0.137 0 | 0.005 7 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.050 1 | 0.002 2 | 128 | 2 | 130 | 3 | ||||
| DPM07-18 | 315.5 | 485.3 | 0.81 | 0.141 3 | 0.004 5 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 7 | 0.001 7 | 130 | 1 | 134 | 4 | ||||
| DPM07-19 | 393.6 | 663.2 | 1.58 | 0.140 2 | 0.004 0 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.050 8 | 0.001 5 | 129 | 1 | 133 | 4 | ||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | 含量/% | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | Fe2O3 | ||||||||||||
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.19 | 13.08 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 5.17 | 2.89 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1.34 | ||||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.81 | 13.13 | 0.33 | 1.38 | 0.15 | 5.49 | 2.67 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.93 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.82 | 12.76 | 0.10 | 1.47 | 0.16 | 5.04 | 3.37 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 1.59 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.86 | 12.79 | 0.55 | 1.49 | 0.19 | 5.21 | 3.01 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 1.11 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 74.02 | 12.49 | 0.31 | 1.51 | 0.20 | 5.41 | 2.79 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.93 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 74.82 | 12.88 | 0.89 | 1.56 | 0.22 | 4.76 | 3.11 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 1.08 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 74.84 | 13.36 | 0.76 | 1.64 | 0.26 | 5.01 | 3.16 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 1.14 | ||||||||||
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 75.08 | 12.51 | 0.46 | 1.69 | 0.43 | 5.15 | 2.89 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.88 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.01 | 12.16 | 0.56 | 2.16 | 0.45 | 5.11 | 3.06 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.74 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.29 | 11.89 | 0.58 | 3.45 | 0.49 | 5.27 | 2.69 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.46 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.57 | 12.33 | 0.17 | 3.47 | 1.58 | 5.10 | 3.06 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 1.21 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.77 | 12.7 | 1.02 | 7.31 | 1.76 | 4.74 | 3.07 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 1.43 | ||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | 相关参数 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| σ | AR | A/CNK | A/NK | R1 | R2 | DI | Q | An | Ab | Or | ||||||||||||
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.99 | 3.19 | 0.93 | 1.17 | 2648.40 | 438.52 | 87.57 | 33.82 | 7.5 | 24.81 | 30.96 | ||||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.00 | 3.44 | 0.96 | 1.20 | 2731.90 | 412.12 | 89.58 | 35.41 | 6.68 | 22.79 | 32.71 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.02 | 3.55 | 0.99 | 1.21 | 2494.22 | 407.82 | 89.68 | 32.48 | 4.89 | 29.05 | 30.29 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.08 | 3.57 | 0.99 | 1.21 | 2585.21 | 421.91 | 90.62 | 33.45 | 6.13 | 25.88 | 31.29 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.08 | 3.62 | 0.99 | 1.25 | 2695.23 | 409.04 | 90.91 | 35.28 | 5.7 | 23.97 | 32.46 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.1 | 3.7 | 0.99 | 1.26 | 2647.17 | 506.45 | 91.03 | 32.84 | 7.19 | 26.46 | 28.27 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.11 | 3.83 | 1.02 | 1.26 | 2528.33 | 452.91 | 91.71 | 31.69 | 7.24 | 27.03 | 29.93 | ||||||||||
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.12 | 3.89 | 1.04 | 1.26 | 2792.51 | 297.01 | 91.82 | 38.76 | 2.12 | 24.83 | 30.85 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.19 | 4.27 | 1.05 | 1.27 | 2760.37 | 313.24 | 94.29 | 37.59 | 2.98 | 26.16 | 30.54 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.21 | 4.54 | 1.07 | 1.5 | 2894.44 | 298.45 | 94.44 | 40.04 | 2.53 | 23.05 | 31.61 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.26 | 4.56 | 1.11 | 1.66 | 2780.13 | 282.55 | 94.70 | 38.63 | 1.23 | 26.14 | 30.39 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.3 | 4.63 | 1.12 | 1.68 | 2602.24 | 384.94 | 95.16 | 34.62 | 4.95 | 26.51 | 28.55 | ||||||||||
表2 花岗岩岩体岩石化学成分及岩石地球化学参数
Table 2 Geochemical compositions and parameters of the Qieqiong granites
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | 含量/% | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | Fe2O3 | ||||||||||||
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.19 | 13.08 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 5.17 | 2.89 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1.34 | ||||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.81 | 13.13 | 0.33 | 1.38 | 0.15 | 5.49 | 2.67 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.93 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.82 | 12.76 | 0.10 | 1.47 | 0.16 | 5.04 | 3.37 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 1.59 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.86 | 12.79 | 0.55 | 1.49 | 0.19 | 5.21 | 3.01 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 1.11 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 74.02 | 12.49 | 0.31 | 1.51 | 0.20 | 5.41 | 2.79 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.93 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 74.82 | 12.88 | 0.89 | 1.56 | 0.22 | 4.76 | 3.11 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 1.08 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 74.84 | 13.36 | 0.76 | 1.64 | 0.26 | 5.01 | 3.16 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 1.14 | ||||||||||
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 75.08 | 12.51 | 0.46 | 1.69 | 0.43 | 5.15 | 2.89 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.88 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.01 | 12.16 | 0.56 | 2.16 | 0.45 | 5.11 | 3.06 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.74 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.29 | 11.89 | 0.58 | 3.45 | 0.49 | 5.27 | 2.69 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.46 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.57 | 12.33 | 0.17 | 3.47 | 1.58 | 5.10 | 3.06 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 1.21 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 76.77 | 12.7 | 1.02 | 7.31 | 1.76 | 4.74 | 3.07 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 1.43 | ||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | 相关参数 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| σ | AR | A/CNK | A/NK | R1 | R2 | DI | Q | An | Ab | Or | ||||||||||||
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.99 | 3.19 | 0.93 | 1.17 | 2648.40 | 438.52 | 87.57 | 33.82 | 7.5 | 24.81 | 30.96 | ||||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.00 | 3.44 | 0.96 | 1.20 | 2731.90 | 412.12 | 89.58 | 35.41 | 6.68 | 22.79 | 32.71 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.02 | 3.55 | 0.99 | 1.21 | 2494.22 | 407.82 | 89.68 | 32.48 | 4.89 | 29.05 | 30.29 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.08 | 3.57 | 0.99 | 1.21 | 2585.21 | 421.91 | 90.62 | 33.45 | 6.13 | 25.88 | 31.29 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.08 | 3.62 | 0.99 | 1.25 | 2695.23 | 409.04 | 90.91 | 35.28 | 5.7 | 23.97 | 32.46 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.1 | 3.7 | 0.99 | 1.26 | 2647.17 | 506.45 | 91.03 | 32.84 | 7.19 | 26.46 | 28.27 | ||||||||||
| YPM1GS090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.11 | 3.83 | 1.02 | 1.26 | 2528.33 | 452.91 | 91.71 | 31.69 | 7.24 | 27.03 | 29.93 | ||||||||||
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.12 | 3.89 | 1.04 | 1.26 | 2792.51 | 297.01 | 91.82 | 38.76 | 2.12 | 24.83 | 30.85 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.19 | 4.27 | 1.05 | 1.27 | 2760.37 | 313.24 | 94.29 | 37.59 | 2.98 | 26.16 | 30.54 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.21 | 4.54 | 1.07 | 1.5 | 2894.44 | 298.45 | 94.44 | 40.04 | 2.53 | 23.05 | 31.61 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.26 | 4.56 | 1.11 | 1.66 | 2780.13 | 282.55 | 94.70 | 38.63 | 1.23 | 26.14 | 30.39 | ||||||||||
| YPM2\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 2.3 | 4.63 | 1.12 | 1.68 | 2602.24 | 384.94 | 95.16 | 34.62 | 4.95 | 26.51 | 28.55 | ||||||||||
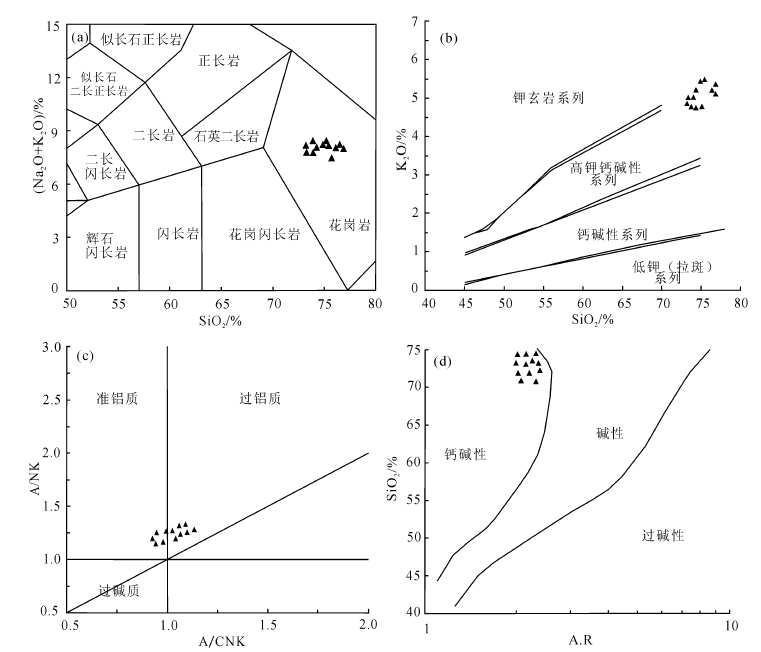
图5 花岗岩岩类硅-全碱TAS图解底图据Middlemoste[14]SiO2-K2O图解((b)底图据Middlemoste[15]、A/CNK-A/NK图解((c)底图据Maniar等[16]和SiO2-AR图解((d)底图据Wright[17]
Fig.5 Total alkali-silica TAS of granite((a)base map after Middlemoste[14],SiO2-K2O((b)base map after Middlemoste[15], A/CNK-A/NKbase map after Maniar et al.[16]and SiO2-AR((d)base map after Wright[17]
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Rb | K | Th | U | Nb | La | Ce | Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 248.33 | 42 954.25 | 39.29 | 5.61 | 14.62 | 43.68 | 62.89 | 43.14 |
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 308.31 | 45 598.21 | 40.26 | 6.23 | 15.25 | 73.79 | 114.25 | 49.22 |
| YPM1WL005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 311.34 | 41 816.14 | 41.52 | 6.43 | 15.51 | 24.08 | 93.62 | 57.21 |
| YPM1WL037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 328.56 | 43 221.55 | 46.17 | 7.05 | 16.43 | 39.77 | 72.4 | 59.14 |
| YPM1WL069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 337.48 | 44 864.38 | 50.83 | 7.06 | 17.68 | 67.78 | 109.76 | 67.15 |
| YPM1WL084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 352.43 | 39 480.15 | 55.87 | 7.15 | 18.14 | 10.47 | 72.32 | 69.22 |
| YPM1WL090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 359.64 | 41 579.55 | 57.72 | 10.73 | 18.8 | 30.22 | 78.31 | 82.50 |
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 368.13 | 42 718.49 | 59.02 | 12.49 | 21.92 | 15.66 | 19.38 | 114.20 |
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 370.52 | 42 423.79 | 62.47 | 16.89 | 23.82 | 65.65 | 96.74 | 121.40 |
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 408.83 | 43 764.45 | 65.48 | 18.13 | 28.46 | 51.83 | 89.73 | 124.44 |
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 415.82 | 42 311.73 | 73.83 | 19.84 | 33.30 | 35.95 | 62.52 | 377.10 |
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 471.62 | 39 339.86 | 78.99 | 22.85 | 41.30 | 146.51 | 175.91 | 392.30 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Nd | P | Hf | Sm | Ti | Y | Yb | Lu |
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 30.61 | 313.53 | 4.38 | 5.82 | 532.09 | 29.67 | 3.30 | 0.51 |
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32.29 | 154.52 | 4.74 | 6.05 | 444.69 | 46.46 | 6.69 | 0.94 |
| YPM1WL005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 17.22 | 222.12 | 4.98 | 2.36 | 533.75 | 23.64 | 3.17 | 0.47 |
| YPM1WL037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 25.64 | 300.73 | 5.04 | 5.20 | 556.68 | 63.67 | 7.81 | 1.13 |
| YPM1WL069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 35.34 | 161.82 | 5.28 | 6.13 | 351.31 | 34.71 | 4.05 | 0.62 |
| YPM1WL084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 15.25 | 370.24 | 5.32 | 1.77 | 647.96 | 16.11 | 3.95 | 0.47 |
| YPM1WL090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32.57 | 375.84 | 5.32 | 6.66 | 660.65 | 36.24 | 2.39 | 0.36 |
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 9.5 | 94.28 | 5.42 | 1.50 | 898.65 | 14.16 | 1.22 | 0.18 |
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 39.03 | 99.95 | 5.52 | 5.50 | 1 003.56 | 24.14 | 2.74 | 0.46 |
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 41.18 | 126.14 | 6.34 | 6.89 | 918.43 | 30.88 | 3.11 | 0.47 |
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 29.06 | 249.22 | 6.36 | 5.87 | 1 113.87 | 35.19 | 3.29 | 0.49 |
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 80.18 | 302.47 | 6.6 | 11.37 | 1 019.15 | 38.92 | 2.72 | 0.38 |
表3 花岗岩岩体微量元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 3 Trace element compositions of the Qieqiong granites(10-6)
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Rb | K | Th | U | Nb | La | Ce | Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 248.33 | 42 954.25 | 39.29 | 5.61 | 14.62 | 43.68 | 62.89 | 43.14 |
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 308.31 | 45 598.21 | 40.26 | 6.23 | 15.25 | 73.79 | 114.25 | 49.22 |
| YPM1WL005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 311.34 | 41 816.14 | 41.52 | 6.43 | 15.51 | 24.08 | 93.62 | 57.21 |
| YPM1WL037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 328.56 | 43 221.55 | 46.17 | 7.05 | 16.43 | 39.77 | 72.4 | 59.14 |
| YPM1WL069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 337.48 | 44 864.38 | 50.83 | 7.06 | 17.68 | 67.78 | 109.76 | 67.15 |
| YPM1WL084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 352.43 | 39 480.15 | 55.87 | 7.15 | 18.14 | 10.47 | 72.32 | 69.22 |
| YPM1WL090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 359.64 | 41 579.55 | 57.72 | 10.73 | 18.8 | 30.22 | 78.31 | 82.50 |
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 368.13 | 42 718.49 | 59.02 | 12.49 | 21.92 | 15.66 | 19.38 | 114.20 |
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 370.52 | 42 423.79 | 62.47 | 16.89 | 23.82 | 65.65 | 96.74 | 121.40 |
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 408.83 | 43 764.45 | 65.48 | 18.13 | 28.46 | 51.83 | 89.73 | 124.44 |
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 415.82 | 42 311.73 | 73.83 | 19.84 | 33.30 | 35.95 | 62.52 | 377.10 |
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 471.62 | 39 339.86 | 78.99 | 22.85 | 41.30 | 146.51 | 175.91 | 392.30 |
| 样品号 | 岩性 | Nd | P | Hf | Sm | Ti | Y | Yb | Lu |
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 30.61 | 313.53 | 4.38 | 5.82 | 532.09 | 29.67 | 3.30 | 0.51 |
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32.29 | 154.52 | 4.74 | 6.05 | 444.69 | 46.46 | 6.69 | 0.94 |
| YPM1WL005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 17.22 | 222.12 | 4.98 | 2.36 | 533.75 | 23.64 | 3.17 | 0.47 |
| YPM1WL037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 25.64 | 300.73 | 5.04 | 5.20 | 556.68 | 63.67 | 7.81 | 1.13 |
| YPM1WL069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 35.34 | 161.82 | 5.28 | 6.13 | 351.31 | 34.71 | 4.05 | 0.62 |
| YPM1WL084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 15.25 | 370.24 | 5.32 | 1.77 | 647.96 | 16.11 | 3.95 | 0.47 |
| YPM1WL090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32.57 | 375.84 | 5.32 | 6.66 | 660.65 | 36.24 | 2.39 | 0.36 |
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 9.5 | 94.28 | 5.42 | 1.50 | 898.65 | 14.16 | 1.22 | 0.18 |
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 39.03 | 99.95 | 5.52 | 5.50 | 1 003.56 | 24.14 | 2.74 | 0.46 |
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 41.18 | 126.14 | 6.34 | 6.89 | 918.43 | 30.88 | 3.11 | 0.47 |
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 29.06 | 249.22 | 6.36 | 5.87 | 1 113.87 | 35.19 | 3.29 | 0.49 |
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 80.18 | 302.47 | 6.6 | 11.37 | 1 019.15 | 38.92 | 2.72 | 0.38 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 43.68 | 62.89 | 8.21 | 30.61 | 5.82 | 1.44 | 4.81 | 1.21 | 5.16 | 1.15 | 3.27 | ||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.79 | 114.25 | 9.46 | 32.29 | 6.05 | 0.54 | 5.44 | 1.20 | 8.43 | 2.3 | 6.78 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 24.08 | 93.62 | 4.93 | 17.22 | 2.36 | 0.47 | 2.84 | 0.57 | 3.91 | 0.91 | 2.71 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 39.77 | 72.41 | 7.61 | 25.64 | 5.21 | 0.20 | 4.97 | 1.26 | 8.27 | 2.34 | 9.80 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 67.78 | 109.76 | 10.19 | 35.34 | 6.13 | 0.97 | 5.54 | 1.03 | 5.33 | 1.29 | 3.70 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 10.47 | 72.32 | 4.15 | 15.25 | 1.77 | 0.54 | 2.51 | 0.43 | 3.12 | 1.02 | 2.01 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 30.22 | 78.31 | 7.23 | 32.57 | 6.66 | 0.36 | 5.87 | 0.91 | 4.87 | 1.12 | 2.69 | ||||||||
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 15.66 | 19.38 | 2.33 | 9.51 | 1.51 | 0.61 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 1.53 | 0.35 | 1.12 | ||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 65.65 | 96.74 | 10.73 | 39.03 | 5.50 | 0.65 | 5.04 | 0.62 | 3.32 | 0.73 | 2.31 | ||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 51.83 | 89.73 | 10.04 | 41.18 | 6.89 | 0.69 | 5.79 | 0.84 | 4.39 | 0.93 | 2.80 | ||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 35.95 | 62.52 | 6.91 | 29.06 | 5.87 | 0.79 | 5.51 | 0.91 | 5.19 | 1.09 | 3.23 | ||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 146.51 | 175.91 | 20.95 | 80.18 | 11.37 | 1.36 | 9.87 | 1.23 | 6.14 | 1.21 | 3.34 | ||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | LaN/YbN | |||||||||
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.55 | 3.30 | 0.51 | 29.67 | 161.29 | 152.64 | 19.76 | 7.46 | 0.28 | 6.47 | |||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.80 | 6.69 | 0.94 | 46.46 | 173.81 | 236.37 | 32.58 | 7.73 | 0.33 | 7.92 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.66 | 3.17 | 0.47 | 23.64 | 187.00 | 142.70 | 15.25 | 7.78 | 0.37 | 9.07 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.16 | 7.81 | 1.13 | 63.67 | 187.55 | 150.82 | 36.73 | 8.07 | 0.38 | 9.23 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.63 | 4.05 | 0.62 | 34.71 | 199.62 | 230.17 | 22.19 | 8.42 | 0.42 | 9.50 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.47 | 3.95 | 0.47 | 16.11 | 215.24 | 104.51 | 13.97 | 9.36 | 0.46 | 10.29 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.37 | 2.39 | 0.36 | 36.24 | 219.13 | 155.35 | 18.46 | 10.37 | 0.5 | 11.94 | |||||||||
| PM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.18 | 1.22 | 0.18 | 14.16 | 233.89 | 48.97 | 6.30 | 10.57 | 0.56 | 12.00 | |||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.38 | 2.74 | 0.46 | 24.14 | 244.73 | 218.30 | 15.59 | 10.67 | 0.74 | 15.22 | |||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.45 | 3.11 | 0.47 | 30.88 | 252.37 | 200.36 | 18.77 | 11.85 | 0.78 | 16.26 | |||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.5 | 3.29 | 0.49 | 35.19 | 268.95 | 141.08 | 20.21 | 14.00 | 0.81 | 17.18 | |||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.44 | 2.72 | 0.38 | 38.92 | 461.63 | 436.30 | 25.33 | 17.22 | 1.25 | 38.66 | |||||||||
表4 花岗岩岩体稀土元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 4 REE results of the Qieqiong granites(10-6)
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 43.68 | 62.89 | 8.21 | 30.61 | 5.82 | 1.44 | 4.81 | 1.21 | 5.16 | 1.15 | 3.27 | ||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 73.79 | 114.25 | 9.46 | 32.29 | 6.05 | 0.54 | 5.44 | 1.20 | 8.43 | 2.3 | 6.78 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 24.08 | 93.62 | 4.93 | 17.22 | 2.36 | 0.47 | 2.84 | 0.57 | 3.91 | 0.91 | 2.71 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 39.77 | 72.41 | 7.61 | 25.64 | 5.21 | 0.20 | 4.97 | 1.26 | 8.27 | 2.34 | 9.80 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 67.78 | 109.76 | 10.19 | 35.34 | 6.13 | 0.97 | 5.54 | 1.03 | 5.33 | 1.29 | 3.70 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 10.47 | 72.32 | 4.15 | 15.25 | 1.77 | 0.54 | 2.51 | 0.43 | 3.12 | 1.02 | 2.01 | ||||||||
| YPM1XT090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 30.22 | 78.31 | 7.23 | 32.57 | 6.66 | 0.36 | 5.87 | 0.91 | 4.87 | 1.12 | 2.69 | ||||||||
| YPM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 15.66 | 19.38 | 2.33 | 9.51 | 1.51 | 0.61 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 1.53 | 0.35 | 1.12 | ||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 65.65 | 96.74 | 10.73 | 39.03 | 5.50 | 0.65 | 5.04 | 0.62 | 3.32 | 0.73 | 2.31 | ||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 51.83 | 89.73 | 10.04 | 41.18 | 6.89 | 0.69 | 5.79 | 0.84 | 4.39 | 0.93 | 2.80 | ||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 35.95 | 62.52 | 6.91 | 29.06 | 5.87 | 0.79 | 5.51 | 0.91 | 5.19 | 1.09 | 3.23 | ||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 146.51 | 175.91 | 20.95 | 80.18 | 11.37 | 1.36 | 9.87 | 1.23 | 6.14 | 1.21 | 3.34 | ||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | LaN/YbN | |||||||||
| GS2008 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.55 | 3.30 | 0.51 | 29.67 | 161.29 | 152.64 | 19.76 | 7.46 | 0.28 | 6.47 | |||||||||
| GS3070 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.80 | 6.69 | 0.94 | 46.46 | 173.81 | 236.37 | 32.58 | 7.73 | 0.33 | 7.92 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT005 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.66 | 3.17 | 0.47 | 23.64 | 187.00 | 142.70 | 15.25 | 7.78 | 0.37 | 9.07 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT037 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.16 | 7.81 | 1.13 | 63.67 | 187.55 | 150.82 | 36.73 | 8.07 | 0.38 | 9.23 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT069 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.63 | 4.05 | 0.62 | 34.71 | 199.62 | 230.17 | 22.19 | 8.42 | 0.42 | 9.50 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT084 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.47 | 3.95 | 0.47 | 16.11 | 215.24 | 104.51 | 13.97 | 9.36 | 0.46 | 10.29 | |||||||||
| YPM1XT090 | 似斑状粗粒二长花岗岩 | 0.37 | 2.39 | 0.36 | 36.24 | 219.13 | 155.35 | 18.46 | 10.37 | 0.5 | 11.94 | |||||||||
| PM2-1\GS2 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.18 | 1.22 | 0.18 | 14.16 | 233.89 | 48.97 | 6.30 | 10.57 | 0.56 | 12.00 | |||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS22-1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.38 | 2.74 | 0.46 | 24.14 | 244.73 | 218.30 | 15.59 | 10.67 | 0.74 | 15.22 | |||||||||
| YPM2-2\GS24 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.45 | 3.11 | 0.47 | 30.88 | 252.37 | 200.36 | 18.77 | 11.85 | 0.78 | 16.26 | |||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS1 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.5 | 3.29 | 0.49 | 35.19 | 268.95 | 141.08 | 20.21 | 14.00 | 0.81 | 17.18 | |||||||||
| YPM2-3\GS3 | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 0.44 | 2.72 | 0.38 | 38.92 | 461.63 | 436.30 | 25.33 | 17.22 | 1.25 | 38.66 | |||||||||

图6 原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网((a)原始地幔数据据Sun等[18])和球粒陨石标准化REE配分图((b)球粒陨石数据据Taylor等[19])
Fig.6 Primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram((a) normalizing values after Sun et al.[18])and chondrite-normalized REE pattern((b) normalizing values after Taylor et al.[19]) of the Qieqiong granites
| 类型 | SiO2/% | 钙碱指数 | A/CNK | A/NK | Na2O/CaO | Na2O/K2O | MgO/TFeO | MgO/MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAG | 60~68 | 钙质-钙碱性主要为偏铝质 | <1 | >1.40 | 1 | 0.40~3.00 | 0.30~0.85 | 12~28 |
| CAG | 62~76 | 钙碱性偏铝质,过铝质 | 0.10~1.15 | >1.10 | 4 | 0.40~2.00 | 0.10~0.50 | 2~38 |
| CCG | 70~76 | 钙碱-碱钙性过铝质 | >1 | >1.10 | 2~10 | 0.40~1.50 | 0.05~0.60 | 2~45 |
| POG | 70~78 | 碱性-钙质过铝,偏铝,过碱 | 0.85~1.25 | 0.90~1.40 | 2~18 | 0.60~1.20 | 0.02~0.30 | 2~18 |
| 研究区 岩体 | 65.3~76.7 | 钙碱性-碱性准-过铝质 | 0.63~1.12 | 1.17~1.68 | 0.41~4.58 | 0.48~0.66 | 0.98~4.16 | 1.44~35.2 |
表5 花岗岩类岩石化学成分对比
Table 5 Comparison of geochemical ratios of granitic rocks
| 类型 | SiO2/% | 钙碱指数 | A/CNK | A/NK | Na2O/CaO | Na2O/K2O | MgO/TFeO | MgO/MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAG | 60~68 | 钙质-钙碱性主要为偏铝质 | <1 | >1.40 | 1 | 0.40~3.00 | 0.30~0.85 | 12~28 |
| CAG | 62~76 | 钙碱性偏铝质,过铝质 | 0.10~1.15 | >1.10 | 4 | 0.40~2.00 | 0.10~0.50 | 2~38 |
| CCG | 70~76 | 钙碱-碱钙性过铝质 | >1 | >1.10 | 2~10 | 0.40~1.50 | 0.05~0.60 | 2~45 |
| POG | 70~78 | 碱性-钙质过铝,偏铝,过碱 | 0.85~1.25 | 0.90~1.40 | 2~18 | 0.60~1.20 | 0.02~0.30 | 2~18 |
| 研究区 岩体 | 65.3~76.7 | 钙碱性-碱性准-过铝质 | 0.63~1.12 | 1.17~1.68 | 0.41~4.58 | 0.48~0.66 | 0.98~4.16 | 1.44~35.2 |

图9 Y-Nb(a)和(Y+Nb)-Rb(b)构造环境判别 syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;WPG.板内花岗岩;ORG.洋脊花岗岩;VAG.岛弧花岗岩
Fig.9 Y-Nb(a)and (Y+Nb)-Rb (b) tectonic discrimination diagrams of the Qieqiong granites
| [1] | 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(3):521-533. |
| [2] | 黄圭成, 李志昌, 邱瑞照, 等. 西藏冈底斯西段狮多地区火山岩的地质地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2004,18(4):511-517. |
| [3] | 王立全, 李定谋, 潘桂棠, 等. 青藏高原矿产及成矿背景图及说明书[M]. 成都: 成都地图出版社, 2014: 94-96. |
| [4] | 王程, 魏启荣, 刘小念, 等. 冈底斯印支晚期后碰撞花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石地球化学证据[J]. 地球科学, 2014,39(9):1278-1300. |
| [5] | 李才, 王天武, 李惠民, 等. 冈底斯地区发现印支期巨斑花岗闪长岩——古冈底斯造山的存在证据[J]. 地质通报, 2003,22(5):364-366. |
| [6] | 和钟铧, 杨德明, 郑常青, 等. 冈底斯带门巴花岗岩同位素测年及其对新特提斯俯冲时代的约束[J]. 地质论评, 2006,52(1):100-106. |
| [7] | 王立全, 朱弟成, 潘桂棠. 青藏高原1∶25万区域地质调查主要成果和进展综述(南区)[J]. 地质通报, 2004,23(5):414-420. |
| [8] | 潘桂棠, 王立全, 张万平, 等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013: 98-99. |
| [9] | 吴新国, 贾建称, 崔邢涛. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带开合演化模式的探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2005,19(4):489-484. |
| [10] | 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 喻学惠, 等. 青藏高原新生代碰撞-后碰撞火成岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 1-5. |
| [11] |
ANDERSON T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204 Pb [J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,192:59-79.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004,49(16):1589-1602. |
| [13] |
RUTATTO D. Zircon trace element geochemistry :Partitioningwithgarnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism[J]. Chemical Geology , 2002,184:123-138.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MIDDLEMOSTE A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science-Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224.
DOI URL |
| [15] | MIDDLEMOSTE A K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks[M]. London: Longman, 1985: 1-266. |
| [16] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WRIGHT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969,106(4):370-384.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989,42(2):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [19] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENANN S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. London: Oxford Press, 1985: 1-312. |
| [20] |
MANIAP D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邢作云, 等. 花岗岩成因研究前沿的认识[J]. 地质论评, 2007,53(增刊):18-27. |
| [22] |
BHATIA M R. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks provinces and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1985,45(3):97-113.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 41-55. |
| [24] | 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩构造环境问题:关于花岗岩研究的思考之三[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(11):2683-2698. |
| [25] | BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series usingmulticationicparameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985,11:43-45. |
| [26] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25(4):956-983.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LIEGEOIS J P, NAVES J, HERTOGEN J, et al. Contrasting origin of post-collisional high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic versus alkaline and peralkaline granitoids[J]. Lithos, 1998,45:1-28.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 翟庆国, 李才, 李惠民, 等. 西藏冈底斯中部淡色花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2005,24(4):350-353. |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [3] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [6] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623. |
| [7] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 滕超, 张学斌, 杨欣杰, 来林, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古西乌旗早泥盆世I型石英闪长岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1624-1633. |
| [8] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [9] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [10] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| [11] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [12] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [13] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [14] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [15] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||