



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (06): 1609-1623.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.010
席振1,2( ), 马德成2,3, 李欢2, 高光明2, 向夏楠1
), 马德成2,3, 李欢2, 高光明2, 向夏楠1
收稿日期:2022-06-01
修回日期:2023-03-03
出版日期:2023-12-10
发布日期:2024-01-24
作者简介:席振,男,讲师,1986年出生,地球探测与信息技术专业,主要从事构造地质研究。Email: xizhen@hncu.edu.cn。
基金资助:
XI Zhen1,2( ), MA Decheng2,3, LI Huan2, GAO Guangming2, XIANG Xianan1
), MA Decheng2,3, LI Huan2, GAO Guangming2, XIANG Xianan1
Received:2022-06-01
Revised:2023-03-03
Online:2023-12-10
Published:2024-01-24
摘要:
东昆仑造山带西段发育元古宙花岗质岩浆岩,其岩浆活动时限及构造环境仍存争议,制约了对东昆仑造山带元古代构造演化过程的深入认识。本文通过对东昆仑西段土窑洞花岗岩类进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学和全岩元素组成研究,探讨区域构造演化。土窑洞二长花岗岩和正长花岗岩具有片麻状构造,发育白云母等富铝矿物。岩石具有高SiO2(67.37%~ 76.35%)、Al2O3(12%~ 14.25%)和K2O(1.59%~ 6.01%),低TiO2(0.16%~ 0.56%)、Na2O(2.13%~ 3.86%)和CaO(0.9%~4.25%),A/CNK平均为1.02,A/NK平均为1.47。两类岩体球粒陨石标准化配分曲线和原始地幔标准化蛛网图较为一致,其轻稀土元素富集(La/Yb)N=5.04~ 16.76),有明显铕负异常(δEu平均0.47)。原始地幔标准化蛛网图显示岩石富集Rb、K和Th,亏损Nb、Ba、Sr、P和Ti,CaO/Na2O比值(0.35~ 1.41)较高。岩浆锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(932.7±2.4) Ma,表明岩体形成于新元古代早期。综合分析认为土窑洞正长花岗岩和二长花岗岩属于S型花岗岩,其岩浆源于陆壳上部含少量泥质成分的碎屑沉积物质,形成于同碰撞挤压背景,为东昆仑造山带响应Rodinia超大陆汇聚作用的物质记录。
中图分类号:
席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623.
XI Zhen, MA Decheng, LI Huan, GAO Guangming, XIANG Xianan. Geochronology,Geochemistry and Tectonic Implications of Early Neoproterozoic Tuyaodong Intrusive Rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen in Xinjiang[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623.

图1 东昆仑西段构造单元(a)(据文献[3]和[20]修改)及土窑洞地区地质简图(b)
Fig.1 Map showing the tectonic unit division of the western EKOB(a) (modified after refs.[3] and [20])and geological sketch map of the Tuyaodong area(b)
| 位置 | 岩性 | 测试方法 | 年龄(Ma) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 莫河下拉 | 花岗片麻岩 | 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb | 938±5 | [ |
| 莫河下拉 | 花岗片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 938±2 | [ |
| 夏日哈木 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 920±3 | [ |
| 夏日哈木 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 924±5 | [ |
| 夏日哈木 | 黑云斜长片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 915±2 | [ |
| 夏日哈木东 | 副片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 924±73 | [ |
| 夏日哈木东 | 副片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 909±120 | [ |
| 夏日哈木东 | 副片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1067±110 | [ |
| 博卡里克 | 片麻花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1006±20 | [ |
| 博卡里克 | 片麻花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1002±31 | [ |
| 博卡里克东 | 片麻状花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 941±13 | [ |
| 喀雅克登塔格 | 二长岩 | 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb | 1116 | [ |
| 喀雅克登塔格 | 黑云二长片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 824±3 | [ |
| 大灶火沟 | 变质碎屑岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 950 | [ |
| 那陵郭勒河 | 花岗闪长岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 840±2 | [ |
| 那陵郭勒河南 | 黑云母片岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 970±53 | [ |
| 阿确墩 | 片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 950 | [ |
| 水泉子沟 | 叠层石 | 全岩Sm-Nd | 815±26 | [ |
| 拉陵灶火 | 角闪岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 846±5 | [ |
| 卡尔却卡 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 910±3 | [ |
| 小南川 | 角闪岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1123±110 | [ |
表1 东昆仑西段中-新元古代岩石年代学统计
Table 1 Meso-Neoproterozoic age statistics in the western East Kunlun Orogen
| 位置 | 岩性 | 测试方法 | 年龄(Ma) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 莫河下拉 | 花岗片麻岩 | 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb | 938±5 | [ |
| 莫河下拉 | 花岗片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 938±2 | [ |
| 夏日哈木 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 920±3 | [ |
| 夏日哈木 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 924±5 | [ |
| 夏日哈木 | 黑云斜长片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 915±2 | [ |
| 夏日哈木东 | 副片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 924±73 | [ |
| 夏日哈木东 | 副片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 909±120 | [ |
| 夏日哈木东 | 副片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1067±110 | [ |
| 博卡里克 | 片麻花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1006±20 | [ |
| 博卡里克 | 片麻花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1002±31 | [ |
| 博卡里克东 | 片麻状花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 941±13 | [ |
| 喀雅克登塔格 | 二长岩 | 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb | 1116 | [ |
| 喀雅克登塔格 | 黑云二长片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 824±3 | [ |
| 大灶火沟 | 变质碎屑岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 950 | [ |
| 那陵郭勒河 | 花岗闪长岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 840±2 | [ |
| 那陵郭勒河南 | 黑云母片岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 970±53 | [ |
| 阿确墩 | 片麻岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 950 | [ |
| 水泉子沟 | 叠层石 | 全岩Sm-Nd | 815±26 | [ |
| 拉陵灶火 | 角闪岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 846±5 | [ |
| 卡尔却卡 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 910±3 | [ |
| 小南川 | 角闪岩 | 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 1123±110 | [ |

图3 土窑洞地区侵入岩野外与显微照片 (a)二长花岗岩;(b)正长花岗岩;(c)(d)二长花岗岩显微照片;Bi.黑云母;hf.钾长岩;Pl.斜长石;Q.石英
Fig.3 Field photos and photomicrographs of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks
| 测点 | 含量(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | 谐和度 (%) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb / 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb / 235U | 1σ | 206Pb / 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||
| 1 | 253 | 463 | 1638 | 0.28 | 0.0714 | 0.0014 | 1.4298 | 0.0317 | 0.1452 | 0.0019 | 969 | 40.3 | 901 | 13.3 | 874 | 10.6 | 96 | |
| 2 | 583 | 1656 | 2342 | 0.71 | 0.1034 | 0.0025 | 2.1858 | 0.0666 | 0.1516 | 0.0020 | 1687 | 44.8 | 1177 | 21.2 | 910 | 11.4 | 74 | |
| 3 | 175 | 178 | 835 | 0.21 | 0.0975 | 0.0050 | 2.2061 | 0.1277 | 0.1598 | 0.0018 | 1577 | 95.2 | 1183 | 40.4 | 956 | 10.2 | 78 | |
| 4 | 197 | 275 | 1309 | 0.21 | 0.0718 | 0.0012 | 1.5598 | 0.0273 | 0.1575 | 0.0013 | 989 | 33.3 | 954 | 10.8 | 943 | 7.3 | 98 | |
| 5 | 220 | 325 | 1397 | 0.23 | 0.0749 | 0.0012 | 1.6053 | 0.0288 | 0.1550 | 0.0013 | 1133 | 31.9 | 972 | 11.3 | 929 | 7.1 | 95 | |
| 6 | 434 | 642 | 3944 | 0.16 | 0.0694 | 0.0010 | 1.2490 | 0.0343 | 0.1293 | 0.0026 | 922 | 31.5 | 823 | 15.5 | 784 | 15.1 | 95 | |
| 7 | 93 | 141 | 687 | 0.20 | 0.0729 | 0.0012 | 1.3434 | 0.0261 | 0.1331 | 0.0014 | 1011 | 33.3 | 865 | 11.3 | 806 | 8.1 | 95 | |
| 8 | 238 | 221 | 1201 | 0.18 | 0.1070 | 0.0027 | 2.1456 | 0.0576 | 0.1448 | 0.0015 | 1750 | 46.8 | 1164 | 18.6 | 872 | 8.7 | 71 | |
| 9 | 166 | 283 | 1064 | 0.27 | 0.0725 | 0.0019 | 1.5371 | 0.0343 | 0.1508 | 0.0015 | 1039 | 44.1 | 945 | 13.7 | 905 | 8.4 | 95 | |
| 10 | 162 | 70 | 1044 | 0.07 | 0.1517 | 0.0106 | 3.7773 | 0.4898 | 0.1459 | 0.0081 | 2365 | 120.0 | 1588 | 104.0 | 878 | 45.6 | 42 | |
| 11 | 143 | 307 | 804 | 0.38 | 0.0707 | 0.0013 | 1.5255 | 0.0308 | 0.1556 | 0.0015 | 950 | 38.9 | 941 | 12.4 | 932 | 8.5 | 99 | |
| 12 | 168 | 245 | 1173 | 0.21 | 0.0682 | 0.0011 | 1.4302 | 0.0240 | 0.1512 | 0.0012 | 876 | 33.3 | 902 | 10.1 | 908 | 6.7 | 99 | |
| 13 | 222 | 275 | 1182 | 0.23 | 0.0691 | 0.0014 | 1.5518 | 0.0227 | 0.1562 | 0.0017 | 949 | 32.8 | 951 | 9.0 | 952 | 9.5 | 97 | |
| 14 | 187 | 242 | 1190 | 0.20 | 0.0766 | 0.0014 | 1.6337 | 0.0320 | 0.1535 | 0.0012 | 1111 | 37.3 | 983 | 12.4 | 920 | 6.7 | 95 | |
| 15 | 156 | 216 | 1003 | 0.22 | 0.0688 | 0.0013 | 1.5024 | 0.0300 | 0.1572 | 0.0015 | 894 | 39.7 | 931 | 12.2 | 941 | 8.3 | 98 | |
| 16 | 80 | 135 | 486 | 0.28 | 0.0702 | 0.0016 | 1.5558 | 0.0366 | 0.1598 | 0.0016 | 933 | 52.0 | 953 | 14.6 | 956 | 9.2 | 99 | |
| 17 | 127 | 269 | 757 | 0.36 | 0.0695 | 0.0013 | 1.5084 | 0.0293 | 0.1566 | 0.0017 | 922 | 37.0 | 934 | 11.9 | 938 | 9.6 | 99 | |
| 18 | 272 | 219 | 1606 | 0.14 | 0.1008 | 0.0018 | 1.8289 | 0.0307 | 0.1316 | 0.0015 | 1639 | 33.3 | 1056 | 11.1 | 797 | 8.6 | 72 | |
| 19 | 122 | 162 | 805 | 0.20 | 0.0681 | 0.0012 | 1.5419 | 0.0291 | 0.1631 | 0.0015 | 870 | 35.2 | 947 | 11.7 | 974 | 8.2 | 97 | |
| 20 | 231 | 259 | 1925 | 0.13 | 0.0691 | 0.0013 | 1.3242 | 0.0283 | 0.1384 | 0.0020 | 902 | 37.5 | 856 | 12.4 | 835 | 11.6 | 97 | |
表2 土窑洞地区二长花岗岩(样号TW618)锆石U - Pb定年结果
Table 2 Zircon U-Pb dating results of the Tuyaodong monzogranite(sample No.TW618)
| 测点 | 含量(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | 谐和度 (%) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb / 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb / 235U | 1σ | 206Pb / 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||
| 1 | 253 | 463 | 1638 | 0.28 | 0.0714 | 0.0014 | 1.4298 | 0.0317 | 0.1452 | 0.0019 | 969 | 40.3 | 901 | 13.3 | 874 | 10.6 | 96 | |
| 2 | 583 | 1656 | 2342 | 0.71 | 0.1034 | 0.0025 | 2.1858 | 0.0666 | 0.1516 | 0.0020 | 1687 | 44.8 | 1177 | 21.2 | 910 | 11.4 | 74 | |
| 3 | 175 | 178 | 835 | 0.21 | 0.0975 | 0.0050 | 2.2061 | 0.1277 | 0.1598 | 0.0018 | 1577 | 95.2 | 1183 | 40.4 | 956 | 10.2 | 78 | |
| 4 | 197 | 275 | 1309 | 0.21 | 0.0718 | 0.0012 | 1.5598 | 0.0273 | 0.1575 | 0.0013 | 989 | 33.3 | 954 | 10.8 | 943 | 7.3 | 98 | |
| 5 | 220 | 325 | 1397 | 0.23 | 0.0749 | 0.0012 | 1.6053 | 0.0288 | 0.1550 | 0.0013 | 1133 | 31.9 | 972 | 11.3 | 929 | 7.1 | 95 | |
| 6 | 434 | 642 | 3944 | 0.16 | 0.0694 | 0.0010 | 1.2490 | 0.0343 | 0.1293 | 0.0026 | 922 | 31.5 | 823 | 15.5 | 784 | 15.1 | 95 | |
| 7 | 93 | 141 | 687 | 0.20 | 0.0729 | 0.0012 | 1.3434 | 0.0261 | 0.1331 | 0.0014 | 1011 | 33.3 | 865 | 11.3 | 806 | 8.1 | 95 | |
| 8 | 238 | 221 | 1201 | 0.18 | 0.1070 | 0.0027 | 2.1456 | 0.0576 | 0.1448 | 0.0015 | 1750 | 46.8 | 1164 | 18.6 | 872 | 8.7 | 71 | |
| 9 | 166 | 283 | 1064 | 0.27 | 0.0725 | 0.0019 | 1.5371 | 0.0343 | 0.1508 | 0.0015 | 1039 | 44.1 | 945 | 13.7 | 905 | 8.4 | 95 | |
| 10 | 162 | 70 | 1044 | 0.07 | 0.1517 | 0.0106 | 3.7773 | 0.4898 | 0.1459 | 0.0081 | 2365 | 120.0 | 1588 | 104.0 | 878 | 45.6 | 42 | |
| 11 | 143 | 307 | 804 | 0.38 | 0.0707 | 0.0013 | 1.5255 | 0.0308 | 0.1556 | 0.0015 | 950 | 38.9 | 941 | 12.4 | 932 | 8.5 | 99 | |
| 12 | 168 | 245 | 1173 | 0.21 | 0.0682 | 0.0011 | 1.4302 | 0.0240 | 0.1512 | 0.0012 | 876 | 33.3 | 902 | 10.1 | 908 | 6.7 | 99 | |
| 13 | 222 | 275 | 1182 | 0.23 | 0.0691 | 0.0014 | 1.5518 | 0.0227 | 0.1562 | 0.0017 | 949 | 32.8 | 951 | 9.0 | 952 | 9.5 | 97 | |
| 14 | 187 | 242 | 1190 | 0.20 | 0.0766 | 0.0014 | 1.6337 | 0.0320 | 0.1535 | 0.0012 | 1111 | 37.3 | 983 | 12.4 | 920 | 6.7 | 95 | |
| 15 | 156 | 216 | 1003 | 0.22 | 0.0688 | 0.0013 | 1.5024 | 0.0300 | 0.1572 | 0.0015 | 894 | 39.7 | 931 | 12.2 | 941 | 8.3 | 98 | |
| 16 | 80 | 135 | 486 | 0.28 | 0.0702 | 0.0016 | 1.5558 | 0.0366 | 0.1598 | 0.0016 | 933 | 52.0 | 953 | 14.6 | 956 | 9.2 | 99 | |
| 17 | 127 | 269 | 757 | 0.36 | 0.0695 | 0.0013 | 1.5084 | 0.0293 | 0.1566 | 0.0017 | 922 | 37.0 | 934 | 11.9 | 938 | 9.6 | 99 | |
| 18 | 272 | 219 | 1606 | 0.14 | 0.1008 | 0.0018 | 1.8289 | 0.0307 | 0.1316 | 0.0015 | 1639 | 33.3 | 1056 | 11.1 | 797 | 8.6 | 72 | |
| 19 | 122 | 162 | 805 | 0.20 | 0.0681 | 0.0012 | 1.5419 | 0.0291 | 0.1631 | 0.0015 | 870 | 35.2 | 947 | 11.7 | 974 | 8.2 | 97 | |
| 20 | 231 | 259 | 1925 | 0.13 | 0.0691 | 0.0013 | 1.3242 | 0.0283 | 0.1384 | 0.0020 | 902 | 37.5 | 856 | 12.4 | 835 | 11.6 | 97 | |

图5 土窑洞地区二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)(b)与206Pb/238U加权平均年龄直方图(c)
Fig.5 Zircon U-Pb concordia(a)(b)and weighted mean ages(c)diagrams of monzogranite in Tuyaodong area
| 岩性 | 样品 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 67.37 | 1.38 | 4.09 | 14.25 | 4.25 | 2.45 | 1.59 | 3.86 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.18 | 1.04 | 101.10 | |||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 67.64 | 1.10 | 3.78 | 13.91 | 4.02 | 1.76 | 1.90 | 2.86 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.97 | 98.72 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 74.20 | 0.69 | 1.87 | 12.93 | 1.45 | 0.59 | 4.86 | 2.71 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.88 | 100.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 70.04 | 1.14 | 3.30 | 13.07 | 2.25 | 1.72 | 4.23 | 2.25 | 0.08 | 0.52 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 100.76 | ||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 76.35 | 0.15 | 1.59 | 12.08 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 6.10 | 2.18 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 100.54 | |||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 75.04 | 0.07 | 1.89 | 12.00 | 1.48 | 0.69 | 5.01 | 2.13 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 1.73 | 100.51 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 74.22 | 0.01 | 1.58 | 13.20 | 1.11 | 0.32 | 4.58 | 3.17 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 1.79 | 100.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 73.85 | 0.07 | 2.36 | 12.65 | 1.59 | 0.40 | 4.65 | 2.96 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 1.53 | 100.43 | ||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 74.61 | 0.21 | 1.96 | 12.35 | 1.29 | 0.51 | 3.67 | 2.98 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 2.60 | 100.51 | ||||||||||||||||
| 岩性 | 样品 | A/CNK | A/NK | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | |||||||||||||||
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 0.90 | 1.76 | 45.03 | 17.8 | 31.3 | 4.19 | 15.9 | 3.24 | 0.94 | 2.74 | 0.47 | 2.70 | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 0.99 | 2.06 | 39.68 | 24.1 | 43.2 | 6.14 | 23.6 | 5.45 | 0.89 | 4.89 | 0.96 | 5.55 | 1.13 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 1.05 | 1.33 | 29.69 | 62.4 | 114.5 | 14.30 | 49.4 | 9.24 | 1.41 | 6.77 | 1.10 | 5.62 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 1.05 | 1.58 | 41.48 | 45.5 | 87.0 | 10.90 | 40.8 | 8.22 | 1.03 | 6.63 | 1.12 | 5.94 | 1.11 | ||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 1.02 | 1.18 | 35.39 | 45.5 | 93.2 | 11.40 | 41.3 | 9.43 | 0.72 | 7.96 | 1.32 | 6.15 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 1.03 | 1.34 | 38.64 | 53.8 | 104.6 | 12.90 | 48.0 | 9.46 | 1.67 | 7.28 | 1.16 | 5.42 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 1.08 | 1.30 | 26.42 | 19.4 | 36.2 | 4.77 | 17.2 | 4.25 | 0.40 | 3.54 | 0.71 | 3.78 | 0.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 0.99 | 1.28 | 22.74 | 49.5 | 92.7 | 11.00 | 38.5 | 7.29 | 0.84 | 5.71 | 1.00 | 5.68 | 1.09 | ||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 1.10 | 1.39 | 29.73 | 12.7 | 23.7 | 3.35 | 12.5 | 3.32 | 0.33 | 3.07 | 0.66 | 3.52 | 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| 岩性 | 样品 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb | Ba | Th | K | Sr | P | Hf | Zr | |||||||||||||||
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 1.48 | 0.24 | 1.53 | 0.24 | 14.8 | 92.9 | 324.0 | 5.3 | 13481.9 | 313.6 | 755.1 | 4.7 | 163.6 | |||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 3.29 | 0.54 | 3.43 | 0.54 | 30.5 | 162.7 | 256.6 | 9.5 | 15433.1 | 245.4 | 576.3 | 5.1 | 156.7 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 2.56 | 0.41 | 2.67 | 0.41 | 25.5 | 193.8 | 796.6 | 19.3 | 39128.1 | 209.0 | 493.6 | 5.4 | 182.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 2.89 | 0.48 | 3.05 | 0.46 | 30.2 | 262.8 | 457.1 | 27.1 | 33230.8 | 149.5 | 442.0 | 6.1 | 169.7 | ||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 2.27 | 0.35 | 2.07 | 0.30 | 27.2 | 296.3 | 421.6 | 29.5 | 50132.8 | 140.9 | 352.8 | 5.1 | 132.6 | |||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 2.40 | 0.38 | 2.35 | 0.39 | 24.5 | 162.7 | 1036.0 | 18.1 | 40122.8 | 207.0 | 708.0 | 11.0 | 342.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 1.62 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 19.2 | 322.7 | 199.1 | 14.6 | 38238.4 | 71.1 | 364.6 | 3.0 | 70.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 3.04 | 0.53 | 3.35 | 0.53 | 31.7 | 287.7 | 576.3 | 25.5 | 34872.0 | 161.1 | 317.7 | 5.8 | 179.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 1.30 | 0.21 | 1.21 | 0.18 | 17.1 | 480.8 | 219.4 | 10.3 | 40053.4 | 52.9 | 788.9 | 3.0 | 75.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| 岩性 | 样品 | Ti | Nb | Sc | Cr | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | (La/Yb)N | (Ce/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||||||||
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 3555.3 | 6.6 | 11.20 | 8.7 | 83.31 | 73.37 | 9.94 | 8.35 | 5.68 | 0.94 | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 3585.2 | 12.0 | 12.50 | 23.20 | 123.71 | 103.38 | 20.33 | 5.04 | 3.50 | 0.52 | 0.85 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 1632.2 | 15.1 | 4.67 | 5.87 | 271.77 | 251.25 | 20.52 | 16.76 | 11.91 | 0.52 | 0.90 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 3055.6 | 20.0 | 9.29 | 4.90 | 215.13 | 193.45 | 21.68 | 10.70 | 7.92 | 0.41 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 965.7 | 19.6 | 3.18 | 8.24 | 222.93 | 201.55 | 21.38 | 15.77 | 12.51 | 0.25 | 0.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 1355.0 | 10.2 | 4.74 | 8.17 | 250.74 | 230.43 | 20.31 | 16.42 | 12.36 | 0.59 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 534.2 | 15.4 | 3.20 | 6.32 | 94.83 | 82.22 | 12.61 | 07.91 | 05.71 | 0.31 | 0.90 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 1233.9 | 19.0 | 3.55 | 7.47 | 220.76 | 199.83 | 20.93 | 10.60 | 07.69 | 0.38 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 622.2 | 20.6 | 2.97 | 6.83 | 66.61 | 55.90 | 10.71 | 07.53 | 05.44 | 0.31 | 0.87 | ||||||||||||||||||
表3 土窑洞地区侵入岩主量元素(%)、微量元素和稀土元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 3 Major elements(%),trace and REE elements(10-6) data of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks
| 岩性 | 样品 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 67.37 | 1.38 | 4.09 | 14.25 | 4.25 | 2.45 | 1.59 | 3.86 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.18 | 1.04 | 101.10 | |||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 67.64 | 1.10 | 3.78 | 13.91 | 4.02 | 1.76 | 1.90 | 2.86 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.97 | 98.72 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 74.20 | 0.69 | 1.87 | 12.93 | 1.45 | 0.59 | 4.86 | 2.71 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.88 | 100.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 70.04 | 1.14 | 3.30 | 13.07 | 2.25 | 1.72 | 4.23 | 2.25 | 0.08 | 0.52 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 100.76 | ||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 76.35 | 0.15 | 1.59 | 12.08 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 6.10 | 2.18 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 100.54 | |||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 75.04 | 0.07 | 1.89 | 12.00 | 1.48 | 0.69 | 5.01 | 2.13 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 1.73 | 100.51 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 74.22 | 0.01 | 1.58 | 13.20 | 1.11 | 0.32 | 4.58 | 3.17 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 1.79 | 100.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 73.85 | 0.07 | 2.36 | 12.65 | 1.59 | 0.40 | 4.65 | 2.96 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 1.53 | 100.43 | ||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 74.61 | 0.21 | 1.96 | 12.35 | 1.29 | 0.51 | 3.67 | 2.98 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 2.60 | 100.51 | ||||||||||||||||
| 岩性 | 样品 | A/CNK | A/NK | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | |||||||||||||||
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 0.90 | 1.76 | 45.03 | 17.8 | 31.3 | 4.19 | 15.9 | 3.24 | 0.94 | 2.74 | 0.47 | 2.70 | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 0.99 | 2.06 | 39.68 | 24.1 | 43.2 | 6.14 | 23.6 | 5.45 | 0.89 | 4.89 | 0.96 | 5.55 | 1.13 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 1.05 | 1.33 | 29.69 | 62.4 | 114.5 | 14.30 | 49.4 | 9.24 | 1.41 | 6.77 | 1.10 | 5.62 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 1.05 | 1.58 | 41.48 | 45.5 | 87.0 | 10.90 | 40.8 | 8.22 | 1.03 | 6.63 | 1.12 | 5.94 | 1.11 | ||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 1.02 | 1.18 | 35.39 | 45.5 | 93.2 | 11.40 | 41.3 | 9.43 | 0.72 | 7.96 | 1.32 | 6.15 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 1.03 | 1.34 | 38.64 | 53.8 | 104.6 | 12.90 | 48.0 | 9.46 | 1.67 | 7.28 | 1.16 | 5.42 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 1.08 | 1.30 | 26.42 | 19.4 | 36.2 | 4.77 | 17.2 | 4.25 | 0.40 | 3.54 | 0.71 | 3.78 | 0.65 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 0.99 | 1.28 | 22.74 | 49.5 | 92.7 | 11.00 | 38.5 | 7.29 | 0.84 | 5.71 | 1.00 | 5.68 | 1.09 | ||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 1.10 | 1.39 | 29.73 | 12.7 | 23.7 | 3.35 | 12.5 | 3.32 | 0.33 | 3.07 | 0.66 | 3.52 | 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| 岩性 | 样品 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb | Ba | Th | K | Sr | P | Hf | Zr | |||||||||||||||
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 1.48 | 0.24 | 1.53 | 0.24 | 14.8 | 92.9 | 324.0 | 5.3 | 13481.9 | 313.6 | 755.1 | 4.7 | 163.6 | |||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 3.29 | 0.54 | 3.43 | 0.54 | 30.5 | 162.7 | 256.6 | 9.5 | 15433.1 | 245.4 | 576.3 | 5.1 | 156.7 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 2.56 | 0.41 | 2.67 | 0.41 | 25.5 | 193.8 | 796.6 | 19.3 | 39128.1 | 209.0 | 493.6 | 5.4 | 182.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 2.89 | 0.48 | 3.05 | 0.46 | 30.2 | 262.8 | 457.1 | 27.1 | 33230.8 | 149.5 | 442.0 | 6.1 | 169.7 | ||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 2.27 | 0.35 | 2.07 | 0.30 | 27.2 | 296.3 | 421.6 | 29.5 | 50132.8 | 140.9 | 352.8 | 5.1 | 132.6 | |||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 2.40 | 0.38 | 2.35 | 0.39 | 24.5 | 162.7 | 1036.0 | 18.1 | 40122.8 | 207.0 | 708.0 | 11.0 | 342.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 1.62 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 19.2 | 322.7 | 199.1 | 14.6 | 38238.4 | 71.1 | 364.6 | 3.0 | 70.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 3.04 | 0.53 | 3.35 | 0.53 | 31.7 | 287.7 | 576.3 | 25.5 | 34872.0 | 161.1 | 317.7 | 5.8 | 179.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 1.30 | 0.21 | 1.21 | 0.18 | 17.1 | 480.8 | 219.4 | 10.3 | 40053.4 | 52.9 | 788.9 | 3.0 | 75.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| 岩性 | 样品 | Ti | Nb | Sc | Cr | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | (La/Yb)N | (Ce/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||||||||
| 正长 花岗岩 | TW516 | 3555.3 | 6.6 | 11.20 | 8.7 | 83.31 | 73.37 | 9.94 | 8.35 | 5.68 | 0.94 | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||
| TW518 | 3585.2 | 12.0 | 12.50 | 23.20 | 123.71 | 103.38 | 20.33 | 5.04 | 3.50 | 0.52 | 0.85 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW508 | 1632.2 | 15.1 | 4.67 | 5.87 | 271.77 | 251.25 | 20.52 | 16.76 | 11.91 | 0.52 | 0.90 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW509 | 3055.6 | 20.0 | 9.29 | 4.90 | 215.13 | 193.45 | 21.68 | 10.70 | 7.92 | 0.41 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 二长 花岗岩 | TW317 | 965.7 | 19.6 | 3.18 | 8.24 | 222.93 | 201.55 | 21.38 | 15.77 | 12.51 | 0.25 | 0.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| TW501 | 1355.0 | 10.2 | 4.74 | 8.17 | 250.74 | 230.43 | 20.31 | 16.42 | 12.36 | 0.59 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW519 | 534.2 | 15.4 | 3.20 | 6.32 | 94.83 | 82.22 | 12.61 | 07.91 | 05.71 | 0.31 | 0.90 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TW618 | 1233.9 | 19.0 | 3.55 | 7.47 | 220.76 | 199.83 | 20.93 | 10.60 | 07.69 | 0.38 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||||
| D90 | 622.2 | 20.6 | 2.97 | 6.83 | 66.61 | 55.90 | 10.71 | 07.53 | 05.44 | 0.31 | 0.87 | ||||||||||||||||||
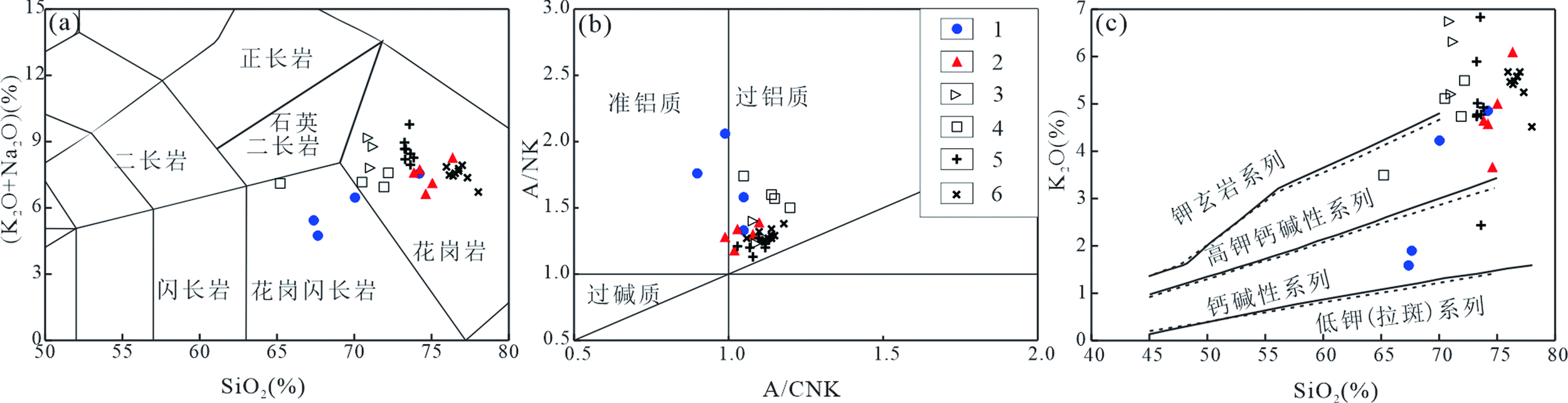
图6 土窑洞地区侵入岩(K2O+Na2O)-SiO2(a),A/NK-A/CNK(b)和K2O-SiO2(c)图解(底图据文献[33?-35]) 1.土窑洞正长花岗岩;2.土窑洞二长花岗岩;3.喀雅克登塔格黑云母二长片麻岩(824 ± 3 Ma)[12];4.那陵郭勒河花岗闪长岩(840 ± 2 Ma)[18];5.夏日哈木二长花岗岩(920 ± 3 Ma和924 ± 5 Ma)[22];6.博卡里克片麻花岗岩(1006 ± 20 Ma)[25];投点图例下同
Fig.6 (K2O+Na2O)- SiO2(a),A/NK-A/CNK(b) and K2O-SiO2(c) petrogenetic discrimination plots of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks(basemap after refs.[33?-35],respectively)
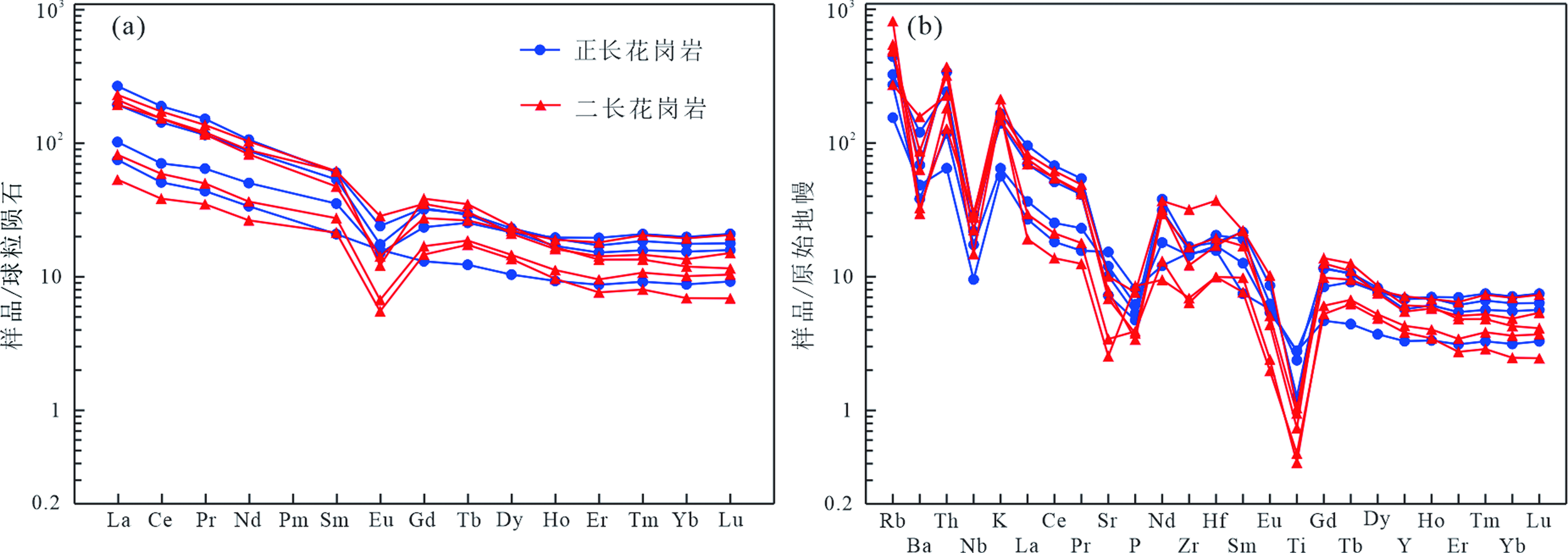
图7 土窑洞地区侵入岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)(标准化值据文献[36])及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据文献[37])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)(normalizing data from ref.[36]) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram (b)(normalizing data from reference [37]) of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks

图8 土窑洞地区侵入岩(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)、(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-FeOT/MgO(b)、SiO2- P2O5(c)和Rb-Y(d)图解((a)(b)底图据文献[39]);投点图例同图6)
Fig.8 (Na2O+K2O)/CaO -(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)(a),FeOT/MgO -(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)(b),SiO2-P2O5(c)and Rb - Y (d) granite petrogenetic diagrams of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks(basemap of (a) and (b) after refs.[39])

图9 土窑洞地区侵入岩Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT+TiO2)-(Al2O3+MgO+FeOT+TiO2)(a)(据文献[47])和Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr(b)(据文献[46])图解(投点图例同图6)
Fig.9 Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT+TiO2)-(Al2O3+MgO+FeOT+TiO2)(a)(basemap after ref.[47]) and Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr(b)(basemap after ref.[46]) petrogenetic discrimination diagrams of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks

图10 土窑洞地区侵入岩R2-R1(a)(底图据文献[66])和Rb-(Y+Nb)(b)(底图据文献[56])图解(投点图例同图6)
Fig.10 R2-R1(a)(basemap after ref.[66]) and Rb vs.(Y+Nb)(b)(basemap after ref.[56]) granite discrimination diagrams of the Tuyaodong intrusive rocks
| [1] | MCMENAMIN M A S, MCMENAMIN D L. The Emergence of Animals the Cambrian Breakthrough[M]. New York: Columbia University Press, 1990: 1-13. |
| [2] | 雷会敏. 塔里木北缘Rodinia超大陆聚合时间:来自新元古代早期花岗岩成因的证据[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2020. |
| [3] |
WU D Q, SUN F Y, PAN Z C, et al. Neoproterozoic magmatic and metamorphic imprints in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt,North Tibetan Plateau,NW China: Implications for the assembly and initial breakup of the Rodinia supercontinent[J]. Precambrian Research, 2021, 354: 106076.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WANG C, LIU L, YANG W Q, et al. Provenance and ages of the Altyn Complex in Altyn Tagh: Implications for the Early Neoproterozoic evolution of northwestern China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 230: 193-208.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
YU S Y, LI S Z, ZHANG J X, et al. Grenvillian orogeny in the Oulongbuluke block,NW China: Constraints from an 1.1 Ga andean-type arc magmatism and metamorphism[J]. Precambrian Research, 2019, 320: 424-437.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HAO J B, WANG C, ZHANG J H, et al. Episodic Neoproterozoic extension-related magmatism in the Altyn Tagh,NW China: Implications for extension and breakup processes of Rodinia supercontinent[J]. International Geology Review, 2022, 64(10): 1474-1489.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHENG F, JOLIVET M, HALLOT E, et al. Tectono-magma-tic rejuvenation of the Qaidam craton,northern Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 49: 248-263.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 陈能松, 李晓彦, 王新宇, 等. 柴达木地块南缘昆北单元变质新元古代花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(11): 1311-1314. |
| [9] | 郝江波. 中—南阿尔金地区中—新元古代物质组成、年代学及构造演化[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2021. |
| [10] | 王国灿, 王青海, 简平, 等. 东昆仑前寒武纪基底变质岩系的锆石SHRIMP年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4): 481-490. |
| [11] | 张金明, 王钦元, 许海全, 等. 喀雅克登塔格地区古元古代金水口变质侵入岩(体)的发现及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2012, 45(3): 13-19. |
| [12] | 魏小林, 张得鑫, 甘承萍, 等. 卡而却卡地区新元古代变质侵入岩体的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2016, 31(2): 236-244. |
| [13] | 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 403-414. |
| [14] | 陈有炘. 东昆仑东段中元古代—早古生代变质岩系地质特征及其构造属性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012. |
| [15] |
DONG Y P, HE D F, SUN S S, et al. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen,western segment of the Central China Orogenic System[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 231-261.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YU M, DICK J M, FENG C Y, et al. The tectonic evolution of the East Kunlun Orogen,northern Tibetan Plateau: A critical review with an integrated geodynamic model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 191: 104168.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 孟繁聪, 崔美慧, 吴祥珂, 等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格花岗片麻岩记录的岩浆和变质事件[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(6): 2107-2122. |
| [18] | 严玉峰, 杨波, 李焕学, 等. 东昆仑那陵格勒河地区新元古代变质侵入体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及意义[J]. 西北地质, 2017, 50(4): 33-40. |
| [19] | 陈有炘, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑东段巴隆花岗质片麻岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(8): 2230-2244. |
| [20] | 姜春发, 王宗起, 李锦轶. 中央造山带开合构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000. |
| [21] | 于淼, 丰成友, 何书跃, 等. 祁漫塔格造山带: 青藏高原北部地壳演化窥探[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(4): 703-723. |
| [22] | 王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等. 东昆仑夏日哈木矿区新元古代早期二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(6): 1247-1260. |
| [23] | 甘彩红. 青海东昆仑造山带火成岩岩石学、地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [24] |
HE D F, DONG Y P, LIU X M, et al. Tectono-thermal events in East Kunlun,northern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 30: 179-190.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HE D F, DONG Y P, ZHANG F F, et al. The 1.0 Ga S-type granite in the East Kunlun Orogen,Northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the Meso- to Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 130: 46-59.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
HE D F, DONG Y P, LIU X M, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotope of granitoids in East Kunlun: Implications for the neoproterozoic magmatism of Qaidam block,northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Precambrian Research, 2018, 314: 377-393.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 谌宏伟, 罗照华, 莫宣学, 等. 东昆仑喀雅克登塔格杂岩体的SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(1): 25-32. |
| [28] | 靳立杰, 周汉文, 朱云海, 等. 东昆仑地区赛什腾组碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学: 对其物质来源及地层时代的约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(4): 691-703. |
| [29] | 李猛, 查显锋, 胡朝斌, 等. 东昆仑西段阿确墩地区白沙河岩组锆石U-Pb年龄: 对前寒武纪基底演化的约束[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 41-57. |
| [30] | 修群业, 颜妍, 刘正荣, 等. 新疆祁曼塔格地区发现新元古代叠层石[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2022, 41(3): 643-650. |
| [31] | 张海迪, 李荣社, 计文化, 等. 青海省格尔木市小南川地区昆南构造混杂岩带的物质组成、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(1): 38-49. |
| [32] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area,Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [36] | BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[M]//Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [37] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 舒徐洁. 华南南岭地区中生代花岗岩成因与地壳演化[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. |
| [39] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics,discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [41] |
MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and pre-servation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6): 529-532.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
GAO P, ZHENG Y F, ZHAO Z F. Distinction between S-type and peraluminous I-type granites: Zircon versus whole-rock geochemistry[J]. Lithos, 2016, 258/259: 77-91.
DOI URL |
| [44] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974, 8: 173-174. |
| [45] |
CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 535-551.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/2/3/4): 29-44.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
PATIÑO DOUCE A E. What do experiments tell us about the rela-tive contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas?[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 1999, 168(1): 55-75.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
PATIÑO DOUCE A E. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8): 743.
DOI URL |
| [49] | 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2249-2269. |
| [50] | WATSON E B, WARK D A, THOMAS J B. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile[J]. Contributions to Minera-logy and Petrology, 2006, 151(4): 413-433. |
| [51] |
CHAPPELL B W, BRYANT C J, WYBORN D, et al. High- and low-temperature I-type granites[J]. Resource Geology, 1998, 48(4): 225-235.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R, WILLIAMS I S, et al. Low- and high-temperature granites[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 2004, 95(1/2): 125-140.
DOI URL |
| [53] | 徐倩, 曾令森, 高家昊, 等. 藏南冈底斯岩基东段中新世中酸性高Sr/Y比岩浆岩的地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(6): 1627-1646. |
| [54] |
HU F Y, DUCEA M N, LIU S W, et al. Quantifying crustal thickness in continental collisional belts: Global perspective and a geologic application[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 7058.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 等. 岩浆弧火成岩构造组合与洋陆转换[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(3): 473-484. |
| [56] |
BARBARIN B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types,their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 605-626.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
COLLINS W J, RICHARDS S W. Geodynamic significance of S-type granites in circum-Pacific orogens[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(7): 559.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 吴泰然. 花岗岩及其形成的大地构造环境[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1995, 31(3): 358-365. |
| [60] | 王国灿, 魏启荣, 贾春兴, 等. 关于东昆仑地区前寒武纪地质的几点认识[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(8): 929-937. |
| [61] | 孟繁聪, 贾丽辉, 任玉峰, 等. 东昆仑东段温泉地区片麻岩记录的岩浆和变质事件: 锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(12): 3691-3709. |
| [62] | 祁生胜. 青海省东昆仑造山带火成岩岩石构造组合与构造演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [63] |
WU C, ZUZA A V, CHEN X H, et al. Tectonics of the eastern Kunlun range: Cenozoic reactivation of Apaleozoic-Early Me-sozoic orogen[J]. Tectonics, 2019, 38(5): 1609-1650.
DOI URL |
| [64] | 周文孝, 赵晓成, 吕新彪. 东昆仑诺木洪地区白沙河岩组岩石学、地球化学及年代学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(12): 4370-4388. |
| [65] | 孟繁聪, 崔美慧, 贾丽辉, 等. 东昆仑造山带早古生代的大陆碰撞: 来自榴辉岩原岩性质的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(12): 3581-3594. |
| [66] | BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multi-cationic parameters[J]. Che-mical Geology, 1985, 48(1/2/3/4): 43-55. |
| [67] |
LU S N, LI H K, ZHANG C L, et al. Geological and geochronological evidence for the Precambrian evolution of the Tarim Craton and surrounding continental fragments[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 160(1/2): 94-107.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
SHU L S, DENG X L, ZHU W B, et al. Precambrian tectonic evolution of the Tarim Block,NW China: New geochronological insights from the Quruqtagh domain[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(5): 774-790.
DOI URL |
| [69] | 张建新, 李怀坤, 孟繁聪, 等. 塔里木盆地东南缘(阿尔金山)“变质基底”记录的多期构造热事件: 锆石U-Pb年代学的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 23-46. |
| [70] |
SONG S G, SU L, LI X H, et al. Grenville-age orogenesis in the Qaidam-Qilian block: The link between South China and Ta-rim[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 220/221: 9-22.
DOI URL |
| [71] | 夏林圻, 李向民, 余吉远, 等. 祁连山新元古代中—晚期至早古生代火山作用与构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4): 1087-1138. |
| [72] |
JIAN X, WEISKLOGEL A, PULLEN A, et al. Formation and evolution of the Eastern Kunlun Range,northern Tibet: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 83:63-79.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [2] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [3] | 晁海德, 陈建洲, 王瑾, 李吉庆, 王国仓, 赵洪岳, 蔡廷俊, 刘立波, 李生福, 任文恺, 邱亮. 青藏高原北部东昆仑地区三叠系页岩成岩作用及其对储层的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1052-1064. |
| [4] | 李王鹏, 王毅, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 刘少峰, 杨伟利, 蔡习尧, 聂海宽, 钱涛, 李晓剑. 塔里木地块西北缘阿克苏地区新元古代冰碛岩年代与冰期事件[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 27-47. |
| [5] | 陈邦学, 徐胜利, 周能武, 白权金, 李超, 张洪深. 塔里木北缘库鲁克塔格地区新元古代花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 477-491. |
| [6] | 宋志冬, 颜丹平. 扬子地块东缘新元古代造山后构造转化:瓮安穹隆构造岩石与年代学限定[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 937-956. |
| [7] | 张斌, 杨涛, 杨生飞, 李金超, 孔会磊. 东昆仑哈日扎铅锌多金属矿床金属矿物与S-Pb同位素特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 646-654. |
| [8] | 胡桥, 陈建平, 田业. 三维成矿预测与预测评价——以东昆仑成矿带红旗沟—深水潭金矿为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 335-343. |
| [9] | 蒋幸福, 彭松柏, KUSKY Timothy, 王璐, 邓浩, 王军鹏. 江南造山带东段赣东北蛇绿岩的形成时代:来自辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 697-704. |
| [10] | 武若晨, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 何格, 康继祖, 余福承, 冯李强, 徐劲驰. 东昆仑造山带早古生代—早中生代构造演化的沉积地球化学记录[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 716-733. |
| [11] | 郑勇 ,杨有生 ,陈邦学 ,朱彦菲. 东昆仑西段巴什康阔勒辉长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1004-1013. |
| [12] | 李琦,曾忠诚,陈宁,赵江林,张若愚,易鹏飞,高海峰,毕政家. 阿尔金南缘新元古代盖里克片麻岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(6): 1271-1283. |
| [13] | 宋忠宝,张雨莲,贾群子,陈向阳,江磊,李东生,何书跃,李金超,杨涛,全守村,栗亚芝,张晓飞. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区野马泉深部的华力西期花岗闪长岩U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1161-1169. |
| [14] | 陈有炘,裴先治,李瑞保,李佐臣,裴磊,刘成军,杨杰. 东昆仑东段纳赤台岩群变沉积岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 489-500. |
| [15] | 焦建刚,鲁浩,孙亚莉,黄喜峰,段俊. 青海德尔尼铜(锌钴)矿床Re-Os年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 577-584. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||