



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (03): 599-612.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.041
收稿日期:2022-02-10
修回日期:2023-04-05
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-07-20
通讯作者:
席 振,男,博士,讲师,1986年出生,地球探测与信息技术专业,从事构造地质与遥感地质研究。Email: xizhen@hncu.edu.cn。
作者简介:马德成,男,高级工程师,1983年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,从事区域地质与矿产勘查研究。Email:hjnh-2004@qq.com。
基金资助:
MA Decheng1( ), XI Zhen2,3(
), XI Zhen2,3( ), GAO Guangming3, LI Huan3
), GAO Guangming3, LI Huan3
Received:2022-02-10
Revised:2023-04-05
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-07-20
摘要:
东昆仑祁漫塔格志留纪到泥盆纪岩浆活动强烈,其形成与大洋岩石圈俯冲造山、碰撞-后碰撞造山活动有关。本文对东昆仑祁漫塔格花土沟地区花岗闪长岩开展锆石U-Pb年代学、全岩地球化学研究,探讨岩石成岩过程及构造背景。花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果为(396.5±4.6) Ma,为早—中泥盆世岩浆活动产物。全岩SiO2含量为63.01%~74.70%,显示高K2O(1.53%~4.01%)、Na2O(2.16%~3.80%)和Al2O3(12.95%~14.48%)特征,Mg#为17.01~61.23,属钙碱性-高钾钙碱性系列岩石。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线呈中等倾斜的右倾平滑型曲线,具有负铕异常(δEu=0.48~0.72),微量元素蛛网图显示富集Rb、Th、La、Ce等大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ba等高场强元素,属I型花岗岩。结合岩体成岩年龄、地球化学特征与区域构造演化,认为花岗闪长岩为造山带地壳物质特别是增生地壳物质的部分熔融,有幔源物质的混入,演化过程中经历了长石等矿物的结晶分离作用,形成于大陆碰撞造山末期向后碰撞转化阶段下的挤压向伸展过渡的构造环境。
中图分类号:
马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612.
MA Decheng, XI Zhen, GAO Guangming, LI Huan. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Geological Significance of the Huatugou Intermediate-acid Intrusions at Qimantag, Xinjiang[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 599-612.

图1 花土沟地区大地构造位置图(a)和研究区地质简图(b)((a)底图据文献[6]) 1.第四系沉积物; 2.奥陶系祁漫塔格群碎屑岩; 3.花岗闪长岩; 4.英云闪长岩; 5.伟晶岩脉; 6.断层; 7.采样点
Fig.1 Tectonic location (a) and geological sketch map (b) of Huatugou area (basemap of (a) after ref.[6])

图2 花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩宏观及显微特征 (a)(b)花岗闪长岩及镜下照片;(c)(d)英云闪长岩及镜下照片。Q.石英;Pl.斜长石;Bt.黑云母
Fig.2 Macroscopic and microscopic photos of Huatugou intermediate-felsic intrusive rocks
| 测点 | Th (10-6) | U (10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb /206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb /235U(1σ) | 206Pb /238U(1σ) | 207Pb/206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/235U(1σ) | 206Pb/238U(1σ) | ||||
| 1 | 376 | 516 | 0.73 | 0.0553(0.0018) | 0.4732(0.0155) | 0.0617(0.0016) | 433(72) | 393(11) | 386(10) |
| 2 | 314 | 523 | 0.6 | 0.0552(0.0018) | 0.4703(0.0157) | 0.0614(0.0017) | 420(77) | 391(11) | 384(10) |
| 4 | 134 | 270 | 0.5 | 0.0563(0.0020) | 0.4897(0.0173) | 0.0629(0.0017) | 465(80) | 405(12) | 393(10) |
| 5 | 195 | 393 | 0.5 | 0.0581(0.0019) | 0.5049(0.0157) | 0.0630(0.0016) | 532(75) | 415(11) | 394(10) |
| 6 | 268 | 397 | 0.67 | 0.0538(0.0018) | 0.4689(0.0158) | 0.0628(0.0017) | 365(68) | 390(11) | 393(10) |
| 8 | 152 | 297 | 0.51 | 0.0555(0.0019) | 0.4790(0.0170) | 0.0624(0.0017) | 435(78) | 397(12) | 390(10) |
| 9 | 174 | 336 | 0.52 | 0.0539(0.0019) | 0.4732(0.0165) | 0.0637(0.0017) | 365(80) | 393(11) | 398(10) |
| 10 | 168 | 283 | 0.59 | 0.0531(0.0019) | 0.4617(0.0169) | 0.0630(0.0017) | 332(79) | 385(12) | 394(10) |
| 11 | 216 | 402 | 0.54 | 0.0564(0.0019) | 0.4710(0.0159) | 0.0605(0.0016) | 478(74) | 392(11) | 378(10) |
| 14 | 231 | 366 | 0.63 | 0.0558(0.0018) | 0.4692(0.0154) | 0.0610(0.0017) | 443(77) | 391(11) | 382(10) |
| 15 | 230 | 424 | 0.54 | 0.0543(0.0018) | 0.4759(0.0162) | 0.0635(0.0018) | 383(74) | 395(11) | 397(11) |
| 17 | 223 | 361 | 0.62 | 0.0544(0.0020) | 0.4949(0.0214) | 0.0665(0.0026) | 387(88) | 408(15) | 415(16) |
| 18 | 114 | 262 | 0.44 | 0.0531(0.0020) | 0.4696(0.0171) | 0.0650(0.0020) | 332(79) | 391(12) | 406(12) |
| 19 | 200 | 386 | 0.52 | 0.0540(0.0017) | 0.4785(0.0156) | 0.0642(0.0017) | 372(72) | 397(11) | 401(11) |
| 20 | 249 | 435 | 0.57 | 0.0534(0.0017) | 0.4717(0.0151) | 0.0642(0.0017) | 346(42) | 392(10) | 401(10) |
| 21 | 51 | 188 | 0.27 | 0.0569(0.0021) | 0.5257(0.0197) | 0.0669(0.0018) | 487(49) | 429(13) | 418(11) |
| 22 | 225 | 397 | 0.57 | 0.0549(0.0018) | 0.4922(0.0163) | 0.0650(0.0017) | 406(74) | 406(11) | 406(11) |
| 23 | 129 | 266 | 0.49 | 0.0565(0.0019) | 0.4944(0.0170) | 0.0633(0.0017) | 472(76) | 408(12) | 396(10) |
| 25 | 144 | 286 | 0.51 | 0.0584(0.0020) | 0.5322(0.0178) | 0.0662(0.0018) | 543(69) | 433(12) | 413(11) |
| 26 | 259 | 463 | 0.56 | 0.0531(0.0018) | 0.4786(0.0159) | 0.0651(0.0017) | 345(76) | 397(11) | 406(10) |
| 27 | 326 | 445 | 0.73 | 0.0541(0.0018) | 0.4757(0.016) | 0.0636(0.0017) | 376(76) | 395(11) | 397(10) |
表1 花土沟地区花岗闪长岩(H2-1)锆石U-Pb定年分析数据
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb data of the Huatugou granodiorite (H2-1)
| 测点 | Th (10-6) | U (10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb /206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb /235U(1σ) | 206Pb /238U(1σ) | 207Pb/206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/235U(1σ) | 206Pb/238U(1σ) | ||||
| 1 | 376 | 516 | 0.73 | 0.0553(0.0018) | 0.4732(0.0155) | 0.0617(0.0016) | 433(72) | 393(11) | 386(10) |
| 2 | 314 | 523 | 0.6 | 0.0552(0.0018) | 0.4703(0.0157) | 0.0614(0.0017) | 420(77) | 391(11) | 384(10) |
| 4 | 134 | 270 | 0.5 | 0.0563(0.0020) | 0.4897(0.0173) | 0.0629(0.0017) | 465(80) | 405(12) | 393(10) |
| 5 | 195 | 393 | 0.5 | 0.0581(0.0019) | 0.5049(0.0157) | 0.0630(0.0016) | 532(75) | 415(11) | 394(10) |
| 6 | 268 | 397 | 0.67 | 0.0538(0.0018) | 0.4689(0.0158) | 0.0628(0.0017) | 365(68) | 390(11) | 393(10) |
| 8 | 152 | 297 | 0.51 | 0.0555(0.0019) | 0.4790(0.0170) | 0.0624(0.0017) | 435(78) | 397(12) | 390(10) |
| 9 | 174 | 336 | 0.52 | 0.0539(0.0019) | 0.4732(0.0165) | 0.0637(0.0017) | 365(80) | 393(11) | 398(10) |
| 10 | 168 | 283 | 0.59 | 0.0531(0.0019) | 0.4617(0.0169) | 0.0630(0.0017) | 332(79) | 385(12) | 394(10) |
| 11 | 216 | 402 | 0.54 | 0.0564(0.0019) | 0.4710(0.0159) | 0.0605(0.0016) | 478(74) | 392(11) | 378(10) |
| 14 | 231 | 366 | 0.63 | 0.0558(0.0018) | 0.4692(0.0154) | 0.0610(0.0017) | 443(77) | 391(11) | 382(10) |
| 15 | 230 | 424 | 0.54 | 0.0543(0.0018) | 0.4759(0.0162) | 0.0635(0.0018) | 383(74) | 395(11) | 397(11) |
| 17 | 223 | 361 | 0.62 | 0.0544(0.0020) | 0.4949(0.0214) | 0.0665(0.0026) | 387(88) | 408(15) | 415(16) |
| 18 | 114 | 262 | 0.44 | 0.0531(0.0020) | 0.4696(0.0171) | 0.0650(0.0020) | 332(79) | 391(12) | 406(12) |
| 19 | 200 | 386 | 0.52 | 0.0540(0.0017) | 0.4785(0.0156) | 0.0642(0.0017) | 372(72) | 397(11) | 401(11) |
| 20 | 249 | 435 | 0.57 | 0.0534(0.0017) | 0.4717(0.0151) | 0.0642(0.0017) | 346(42) | 392(10) | 401(10) |
| 21 | 51 | 188 | 0.27 | 0.0569(0.0021) | 0.5257(0.0197) | 0.0669(0.0018) | 487(49) | 429(13) | 418(11) |
| 22 | 225 | 397 | 0.57 | 0.0549(0.0018) | 0.4922(0.0163) | 0.0650(0.0017) | 406(74) | 406(11) | 406(11) |
| 23 | 129 | 266 | 0.49 | 0.0565(0.0019) | 0.4944(0.0170) | 0.0633(0.0017) | 472(76) | 408(12) | 396(10) |
| 25 | 144 | 286 | 0.51 | 0.0584(0.0020) | 0.5322(0.0178) | 0.0662(0.0018) | 543(69) | 433(12) | 413(11) |
| 26 | 259 | 463 | 0.56 | 0.0531(0.0018) | 0.4786(0.0159) | 0.0651(0.0017) | 345(76) | 397(11) | 406(10) |
| 27 | 326 | 445 | 0.73 | 0.0541(0.0018) | 0.4757(0.016) | 0.0636(0.0017) | 376(76) | 395(11) | 397(10) |
| 样品 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2-10 | 74.7 | 0.31 | 1.80 | 13.45 | 1.01 | 0.24 | 3.67 | 3.80 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 100.13 |
| H4-4 | 63.01 | 1.11 | 4.24 | 14.48 | 4.05 | 2.04 | 4.01 | 2.16 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.19 | 3.85 | 99.75 |
| H4-6 | 65.47 | 0.68 | 3.35 | 12.95 | 3.59 | 3.51 | 2.53 | 2.98 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 3.88 | 99.87 |
| H2-1 | 65.10 | 0.04 | 5.01 | 15.27 | 4.39 | 2.33 | 0.98 | 3.07 | 0.09 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 2.90 | 99.78 |
| H2-2 | 67.32 | 0.90 | 5.19 | 13.86 | 2.78 | 2.49 | 1.53 | 3.62 | 0.11 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 2.09 | 100.65 |
| 样品 | Na2O+K2O | A/CNK | A/NK | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy |
| H2-10 | 7.47 | 1.11 | 1.31 | 17.01 | 10.7 | 18.7 | 2.35 | 8.1 | 1.79 | 0.38 | 1.59 | 0.33 | 2.22 |
| H4-4 | 6.17 | 0.95 | 1.83 | 40.97 | 35.3 | 58.4 | 7.13 | 25.4 | 4.07 | 0.91 | 3.53 | 0.58 | 3.28 |
| H4-6 | 5.51 | 0.91 | 1.69 | 61.23 | 35.8 | 65.7 | 9.18 | 36.8 | 7.34 | 1.56 | 6.38 | 1.16 | 6.67 |
| H2-1 | 6.05 | 0.92 | 1.60 | 46.10 | 15.0 | 31.0 | 4.81 | 21.5 | 5.23 | 0.84 | 5.46 | 1.14 | 7.55 |
| H2-2 | 5.15 | 1.09 | 1.82 | 42.52 | 41.7 | 73.8 | 9.56 | 37.2 | 6.78 | 1.37 | 6.17 | 1.09 | 6.32 |
| 样品 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb | Ba | Th | K | Sr | P | Hf |
| H2-10 | 0.49 | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.68 | 0.26 | 17.3 | 109.8 | 533.6 | 5.0 | 30135.8 | 74.34 | 200 | 3.28 |
| H4-4 | 0.63 | 1.79 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 33.3 | 59.0 | 1026.5 | 19.6 | 32764.6 | 350.20 | 810 | 2.43 |
| H4-6 | 1.34 | 5.62 | 0.62 | 3.88 | 0.59 | 43.3 | 125.6 | 1224.2 | 14.4 | 32457.2 | 373.70 | 1180 | 3.88 |
| H2-1 | 1.60 | 4.73 | 0.72 | 4.25 | 0.61 | 48.9 | 21.5 | 274.6 | 4.5 | 9176.4 | 308.20 | 500 | 0.86 |
| H2-2 | 1.27 | 4.66 | 0.59 | 3.73 | 0.56 | 26.8 | 121.1 | 478.5 | 6.4 | 12963.8 | 285.30 | 540 | 8.69 |
| 样品 | Zr | Ti | Nb | Ta | Sc | Cr | ΣREE | (La/Yb)N | (Ce/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | ||
| H2-10 | 75.9 | 400.7 | 6.4 | 0.62 | 1.51 | 10.5 | 50.25 | 4.31 | 2.89 | 0.67 | 0.87 | ||
| H4-4 | 182.8 | 3439.0 | 14.8 | 0.89 | 5.72 | 44.2 | 143.33 | 13.57 | 8.61 | 0.72 | 0.85 | ||
| H4-6 | 162.3 | 4478.0 | 25.8 | 1.61 | 17.62 | 290.0 | 182.64 | 6.24 | 4.39 | 0.68 | 0.87 | ||
| H2-1 | 142.4 | 3913.0 | 8.5 | 0.47 | 10.52 | 30.7 | 104.44 | 2.39 | 1.89 | 0.48 | 0.89 | ||
| H2-2 | 143.5 | 4283.0 | 20.5 | 1.54 | 12.79 | 22.9 | 194.80 | 7.54 | 5.12 | 0.64 | 0.87 | ||
表2 花土沟地区花岗闪长岩主量元素(%)、微量和稀土元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major elements (%), trace and REE elements (10-6) data of the Huatugou granodiorite
| 样品 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2-10 | 74.7 | 0.31 | 1.80 | 13.45 | 1.01 | 0.24 | 3.67 | 3.80 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 100.13 |
| H4-4 | 63.01 | 1.11 | 4.24 | 14.48 | 4.05 | 2.04 | 4.01 | 2.16 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.19 | 3.85 | 99.75 |
| H4-6 | 65.47 | 0.68 | 3.35 | 12.95 | 3.59 | 3.51 | 2.53 | 2.98 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 3.88 | 99.87 |
| H2-1 | 65.10 | 0.04 | 5.01 | 15.27 | 4.39 | 2.33 | 0.98 | 3.07 | 0.09 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 2.90 | 99.78 |
| H2-2 | 67.32 | 0.90 | 5.19 | 13.86 | 2.78 | 2.49 | 1.53 | 3.62 | 0.11 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 2.09 | 100.65 |
| 样品 | Na2O+K2O | A/CNK | A/NK | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy |
| H2-10 | 7.47 | 1.11 | 1.31 | 17.01 | 10.7 | 18.7 | 2.35 | 8.1 | 1.79 | 0.38 | 1.59 | 0.33 | 2.22 |
| H4-4 | 6.17 | 0.95 | 1.83 | 40.97 | 35.3 | 58.4 | 7.13 | 25.4 | 4.07 | 0.91 | 3.53 | 0.58 | 3.28 |
| H4-6 | 5.51 | 0.91 | 1.69 | 61.23 | 35.8 | 65.7 | 9.18 | 36.8 | 7.34 | 1.56 | 6.38 | 1.16 | 6.67 |
| H2-1 | 6.05 | 0.92 | 1.60 | 46.10 | 15.0 | 31.0 | 4.81 | 21.5 | 5.23 | 0.84 | 5.46 | 1.14 | 7.55 |
| H2-2 | 5.15 | 1.09 | 1.82 | 42.52 | 41.7 | 73.8 | 9.56 | 37.2 | 6.78 | 1.37 | 6.17 | 1.09 | 6.32 |
| 样品 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb | Ba | Th | K | Sr | P | Hf |
| H2-10 | 0.49 | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.68 | 0.26 | 17.3 | 109.8 | 533.6 | 5.0 | 30135.8 | 74.34 | 200 | 3.28 |
| H4-4 | 0.63 | 1.79 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 33.3 | 59.0 | 1026.5 | 19.6 | 32764.6 | 350.20 | 810 | 2.43 |
| H4-6 | 1.34 | 5.62 | 0.62 | 3.88 | 0.59 | 43.3 | 125.6 | 1224.2 | 14.4 | 32457.2 | 373.70 | 1180 | 3.88 |
| H2-1 | 1.60 | 4.73 | 0.72 | 4.25 | 0.61 | 48.9 | 21.5 | 274.6 | 4.5 | 9176.4 | 308.20 | 500 | 0.86 |
| H2-2 | 1.27 | 4.66 | 0.59 | 3.73 | 0.56 | 26.8 | 121.1 | 478.5 | 6.4 | 12963.8 | 285.30 | 540 | 8.69 |
| 样品 | Zr | Ti | Nb | Ta | Sc | Cr | ΣREE | (La/Yb)N | (Ce/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | ||
| H2-10 | 75.9 | 400.7 | 6.4 | 0.62 | 1.51 | 10.5 | 50.25 | 4.31 | 2.89 | 0.67 | 0.87 | ||
| H4-4 | 182.8 | 3439.0 | 14.8 | 0.89 | 5.72 | 44.2 | 143.33 | 13.57 | 8.61 | 0.72 | 0.85 | ||
| H4-6 | 162.3 | 4478.0 | 25.8 | 1.61 | 17.62 | 290.0 | 182.64 | 6.24 | 4.39 | 0.68 | 0.87 | ||
| H2-1 | 142.4 | 3913.0 | 8.5 | 0.47 | 10.52 | 30.7 | 104.44 | 2.39 | 1.89 | 0.48 | 0.89 | ||
| H2-2 | 143.5 | 4283.0 | 20.5 | 1.54 | 12.79 | 22.9 | 194.80 | 7.54 | 5.12 | 0.64 | 0.87 | ||
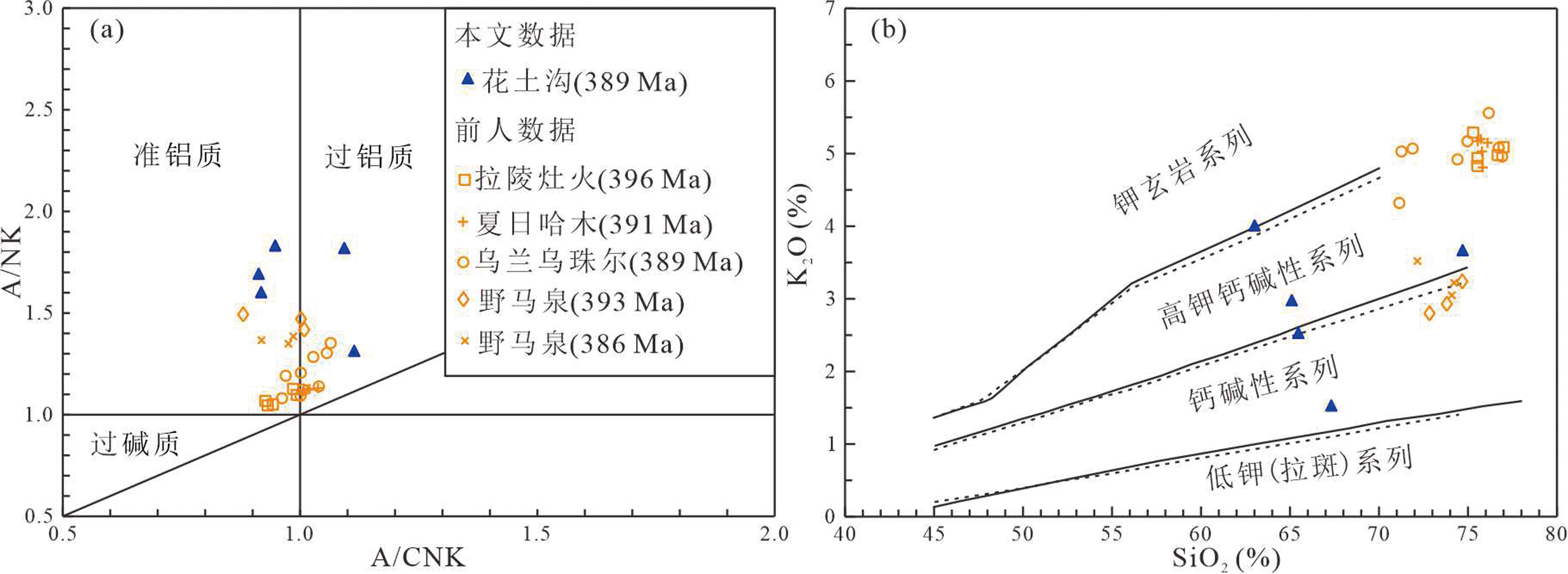
图5 花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩A/CNK-A/NK(a)、 SiO2-K2O (b)图解(底图分别据文献[18]和[19];拉陵灶火数据据文献[20],夏日哈木据文献[21],乌兰乌珠尔据文献[22],野马泉据文献[23];图例下同)
Fig.5 A/CNK vs. A/NK(a),SiO2 vs. K2O(b) plots of the Huatugou intermediate-acid intrusive rocks(basemap after refs.[18] and [19], respectively)

图7 花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)及微量元素地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据文献[31], 上、下地壳值据文献[32], 古老地壳和新生地壳值据文献[33])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spidergram for the Huatugou intermediate-acid intrusive rocks(normalizing data after ref.[31], upper and lower crust data after ref.[32], ancient crust and juvenile crust after ref. [33])

图8 花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩成因判别图解((a)、 (b)底图据文献[36]) (a) (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO图; (b) (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-FeOT/MgO图; (c) Rb-Th图; (d) SiO2-P2O5图
Fig.8 Diagram for genetic discrimination of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in Huatugou area (basemaps of (a) and (b) after ref.[36])

图9 花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩SiO2-Mg#(a)、CaO/(MgO+FeOT)-Al2O3/( FeOT+MgO)(b)、(Al2O3+MgO+FeOT+TiO2)-Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT+TiO2)(c)和Rb/Sr-Y/Sr(d)图解((a)底图据文献[40]; (b)(c)底图据文献[41])
Fig.9 SiO2-Mg#(a), CaO/(MgO+FeOT)-Al2O3/(FeOT+MgO) (b), (Al2O3+MgO+FeOT+TiO2)- Al2O3/(MgO+FeOT+TiO2) (c) and Rb/Sr-Y/Sr (d) diagrams for the Huatugou intermediate-acid intrusive rocks(basemap of (a) after ref.[40], (b) and (c) after ref.[41])
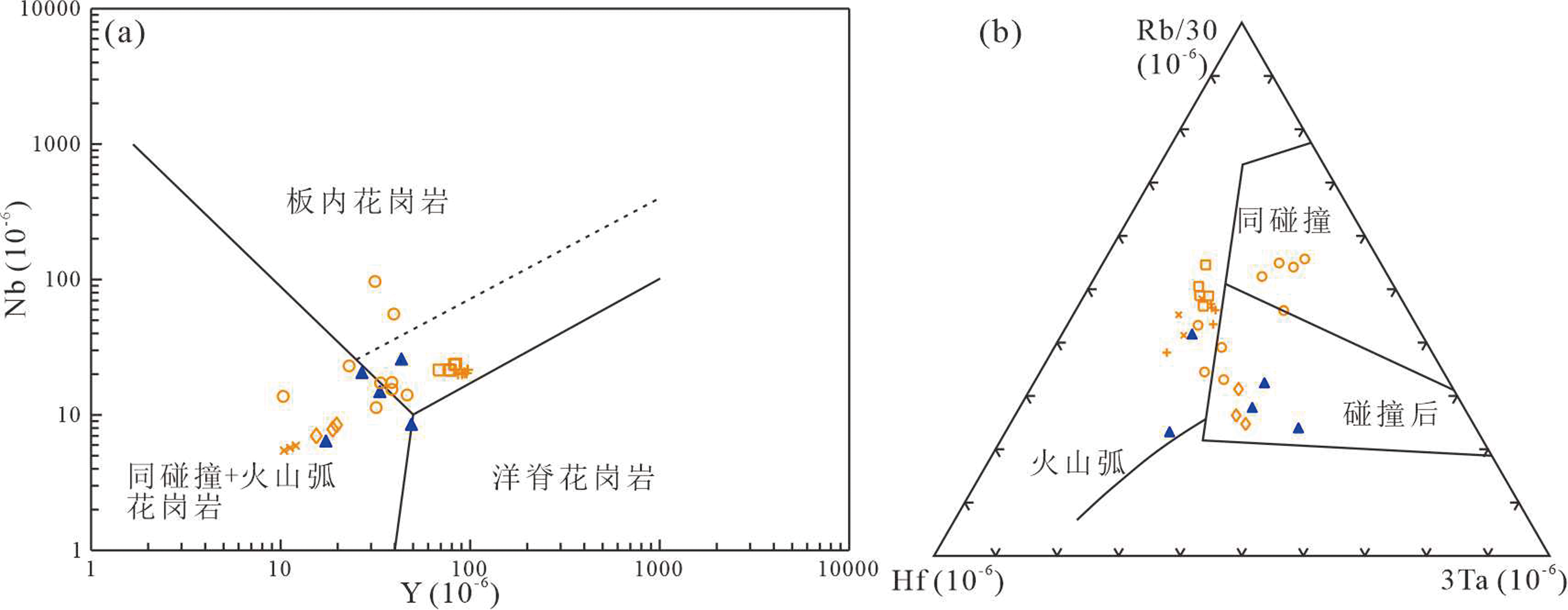
图10 花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩Y-Nb (a)和Rb/30-Hf-3Ta(b)图解(底图分别据文献[55]和[56])
Fig.10 Y vs.Nb (a) and Rb/30-Hf-3Ta (b) diagrams for the Huatugou intermediate-acid intrusive rocks(basemap after refs.[55] and [56], respectively)
| [1] | 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 403-414. |
| [2] | 钱兵, 高永宝, 李侃, 等. 新疆东昆仑于沟子地区与铁-稀有多金属成矿有关的碱性花岗岩地球化学、年代学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(9): 2508-2520. |
| [3] | 王松, 丰成友, 李世金, 等. 青海祁漫塔格卡尔却卡铜多金属矿区花岗闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1): 74-84. |
| [4] | 姚磊. 青海祁漫塔格地区三叠纪成岩成矿作用及地球动力学背景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [5] |
YAO L, LÜ Z C, ZHAO C S, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological, trace element, and Hf isotopic constraints on the genesis of the Fe and Cu skarn deposits in the Qiman Tagh area, Qinghai Province, Eastern Kunlun Orogen, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 91: 387-403.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG Y P, HE D F, SUN S S, et al. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 231-261.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
YU M, DICK J M, FENG C Y, et al. The tectonic evolution of the East Kunlun Orogen, northern Tibetan Plateau:A critical review with an integrated geodynamic model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 191: 104168.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 于淼, 丰成友, 何书跃, 等. 祁漫塔格造山带: 青藏高原北部地壳演化窥探[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(4): 703-723. |
| [9] |
WANG Q, ZHAO J, ZHANG C L, et al. Paleozoic post-collisional magmatism and high-temperature granulite-facies metamorphism coupling with lithospheric delamination of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2022, 13(1): 101271.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DAI J G, WANG C S, HOURIGAN J, et al. Multi-stage tectono-magmatic events of the Eastern Kunlun Range, northern Tibet: Insights from U-Pb geochronology and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 599: 97-106.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI R B, PEI X Z, LI Z C, et al. Late Silurian to Early Devonian volcanics in the East Kunlun orogen, northern Tibetan Plateau: Record of postcollisional magmatism related to the evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2020, 140: 101780.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XIONG F H, MA C Q, JIANG H A, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Middle Devonian mafic dykes in the East Kunlun orogenic belt, northern Tibet Plateau: Implications for the transition from Prototethys to Paleotethys orogeny[J]. Geochemistry, 2014, 74(2): 225-235.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DONG J L, SONG S G, SU L, et al. Early Devonian mafic ig-neous rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, NW China: Implications for the transition from the Proto- to Paleo-Tethys oceans[J]. Lithos, 2020, 376/377: 105771.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
QIN Y, FENG Q, CHEN G, et al. Devonian post-orogenic extension-related volcano-sedimentary rocks in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, NW China: Implications for the Paleozoic tectonic transition in the North Qaidam Orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 156: 145-166.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 王秉璋, 罗照华, 李怀毅, 等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格走廊域晚古生代—早中生代侵入岩岩石组合及时空格架[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(4): 769-782. |
| [16] | 郝娜娜, 袁万明, 张爱奎, 等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格晚志留世—早泥盆世花岗岩: 年代学、地球化学及形成环境[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(1): 201-215. |
| [17] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4):247-263.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58: 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 陈静, 谢智勇, 李彬, 等. 东昆仑拉陵灶火地区泥盆纪侵入岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2013, 33(2): 26-34. |
| [21] | 王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等. 东昆仑夏日哈木矿区早泥盆世正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其动力学意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(4): 685-697. |
| [22] | 郭通珍, 刘荣, 陈发彬, 等. 青海祁漫塔格山乌兰乌珠尔斑状正长花岗岩LA-MC-ICP MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(8): 1203-1211. |
| [23] | 高永宝, 李文渊, 钱兵, 等. 东昆仑野马泉铁矿相关花岗质岩体年代学、地球化学及Hf同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(6): 1647-1665. |
| [24] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WHALEN J B. Geochemistry of an Island-Arc Plutonic Suite: the Uasilau-Yau Yau intrusive complex, New Britain, P.N.G[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1985, 26(3): 603-632.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and pre-servation inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6): 529-532.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 王川, 彭建堂, 徐接标, 等. 湘中白马山复式岩体成因及其成矿效应[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(3): 805-829. |
| [28] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641-644.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
GAO P, ZHENG Y F, ZHAO Z F. Distinction between S-type and peraluminous I-type granites: Zircon versus whole-rock geochemistry[J]. Lithos, 2016, 258/259: 77-91.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 国显正, 栗亚芝, 贾群子, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟金多金属矿集区晚二叠世—三叠纪岩浆岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(8): 2359-2379. |
| [31] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [32] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[M]// Treatise on Geochemistry. Amesterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 1-51. |
| [33] |
ZHOU H Z, ZHANG D H, WEI J H, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic mafic enclaves and host granodiorite in the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, China: Implications for the reworking of juve-nile crust by delamination-induced asthenosphere upwelling[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 84: 52-70.
DOI URL |
| [34] | CHAPPELL B W. Origin of infracrustal (I-type) granite magmas[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (Earth Sciences), 1988, 79:71-86. |
| [35] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. |
| [36] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type gra-nites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等. 关于火成岩常用图解的正确使用: 讨论与建议[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(4): 717-734. |
| [38] |
WEAVER B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions: Trace element and isotopic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104(2/3/4): 381-397.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
GAO P, ZHENG Y F, ZHAO Z F. Experimental melts from crustal rocks: A lithochemical constraint on granite petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2016, 266/267: 133-157.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ALTHERR R, SIEBEL W. I-type plutonism in a continental back-arc setting: Miocene granitoids and monzonites from the central Aegean Sea, Greece[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(4): 397-415.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
PATIÑO DOUCE A E. What do experiments tell us about the re-lative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas?[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1999, 168: 55-75.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 高永宝. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区中酸性侵入岩浆活动与成矿作用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013. |
| [43] | 王盘喜, 郭峰, 王振宁. 东昆仑祁漫塔格鸭子沟地区花岗岩类岩石年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5): 987-1000. |
| [44] |
LI J Y, QIAN Y, LI H R, et al. The Late Ordovician granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northwestern China: Petroge-nesis and constraints for tectonic evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2020, 109(4): 1439-1461.
DOI |
| [45] |
HUANG H, NIU Y L, NOWELL G, et al. Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic belt, northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for continental crust growth through syn-collisional felsic magmatism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 370: 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
CHEN J J, FU L B, WEI J H, et al. Proto-Tethys magmatic evolution along northern Gondwana: Insights from Late Silurian-Middle Devonian A-type magmatism, East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Lithos, 2020, 356/357: 105304.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
LI W, NEUBAUER F, LIU Y J, et al. Paleozoic evolution of the Qimantagh magmatic arcs, Eastern Kunlun Mountains: Constraints from zircon dating of granitoids and modern river sands[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 77: 183-202.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
ZHOU B, DONG Y P, ZHANG F F, et al. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetan Plateau: Origin and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 130: 265-281.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHEN J, WANG B Z, LU H F, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Devonian intrusions in the Qimantagh area, Northwest China: Evidence for post-collisional slab break-off[J]. International Geology Review, 2018, 60(4): 479-495.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
SONG S G, BI H Z, QI S S, et al. HP-UHP metamorphic belt in the East Kunlun orogen: Final closure of the Proto-Tethys Ocean and formation of the Pan-North-China Continent[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2018, 59(11): 2043-2060.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 国显正, 贾群子, 李金超, 等. 东昆仑高压变质带榴辉岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(12): 4300-4318. |
| [52] | 孟繁聪, 崔美慧, 贾丽辉, 等. 东昆仑造山带早古生代的大陆碰撞: 来自榴辉岩原岩性质的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(12): 3581-3594. |
| [53] | 刘彬, 马昌前, 蒋红安, 等. 东昆仑早古生代洋壳俯冲与碰撞造山作用的转换:来自胡晓钦镁铁质岩石的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(6): 2093-2106. |
| [54] | 谌宏伟, 罗照华, 莫宣学, 等. 东昆仑喀雅克登塔格杂岩体的SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(1): 25-32. |
| [55] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [56] | HARRIS N B W, PEARCE J A, TINDLE A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological So-ciety, London, Special Publications, 1986, 19(1): 67-81. |
| [57] |
BARBARIN B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 605-626.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 吴泰然. 花岗岩及其形成的大地构造环境[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1995, 31(3): 358-365. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 王建华, 朱幼安, 李强. 藏南亚东帕里地区早泥盆世沉积及古生物特征[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 224-229. |
| [3] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 滕超, 张学斌, 杨欣杰, 来林, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古西乌旗早泥盆世I型石英闪长岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1624-1633. |
| [4] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [5] | 唐名鹰, 华磊, 丁正江, 董振昆, 王炜晓, 翟孝志, 王汝杰, 郑成龙. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区乌腊德石墨矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1475-1485. |
| [6] | 王玉平, 吴文彬, 刘永俊, 李海洋, 王晓亮, 李超. 辽东岫岩地区晚侏罗世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 955-967. |
| [7] | 杨硕, 刘阁, 靳刘圆, 郑海峰. 东准噶尔卡拉麦里松喀尔苏岩体花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 492-503. |
| [8] | 王盘喜, 郭峰, 王振宁. 东昆仑祁漫塔格鸭子沟地区花岗岩类岩石年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 987-1000. |
| [9] | 李阅薇, 王成善, 李国彪, 徐星, 马文恩, 李兴鹏, 吕昶良, 吕贝贝, 张文苑, 韩丹丹. 广西龙江泥盆纪苔藓虫的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 745-756. |
| [10] | 袁晓博, 方念乔, 董海龙. 海南岛高峰、保城地区花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 85-97. |
| [11] | 张耀玲, 倪晋宇, 沈燕绪, 王超群, 高万里, 胡道功. 柴北缘牦牛山组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 329-334. |
| [12] | 武若晨, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 何格, 康继祖, 余福承, 冯李强, 徐劲驰. 东昆仑造山带早古生代—早中生代构造演化的沉积地球化学记录[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 716-733. |
| [13] | 鲁艳明, 专少鹏, 所承逊, 殷敏. 内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁地区晚侏罗世侵入岩年代学、地球化学特征及成矿潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 981-993. |
| [14] | 王永文,颜丹平,刘红旭,潘澄雨,陈峰,孟云飞,丁波,刘涛. 西天山伊犁地块北缘桦木沟高分异I型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(3): 529-541. |
| [15] | 宋忠宝,张雨莲,贾群子,陈向阳,江磊,李东生,何书跃,李金超,杨涛,全守村,栗亚芝,张晓飞. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区野马泉深部的华力西期花岗闪长岩U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1161-1169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||