



现代地质 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (01): 85-97.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.01.09
收稿日期:2018-06-05
修回日期:2018-11-30
出版日期:2019-02-26
发布日期:2019-02-28
作者简介:袁晓博,男,博士研究生,1987年出生,海洋科学、海洋地质学专业,主要从事大地构造学研究。Email:xiaoboyuan@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
YUAN Xiaobo1( ), FANG Nianqiao1(
), FANG Nianqiao1( ), DONG Hailong2
), DONG Hailong2
Received:2018-06-05
Revised:2018-11-30
Online:2019-02-26
Published:2019-02-28
摘要:
海南岛南部地区遍布晚中生代花岗岩,高峰、保城岩体即为其中的典型代表。应用同位素地质年代学和岩石地球化学分析方法,测得两岩体的年龄分别为(105.4±3.7) Ma和(105.8±2.4) Ma,岩石硅、碱含量中等,铝饱和指数分别为0.95~1.03和1.05~1.30,轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损,轻重稀土分馏程度较高,高场强元素亏损,大离子亲石元素富集。斜长石含量>19%,角闪石含量>3%,石英含量﹤32%,P2O5与SiO2呈负相关,表明高峰、保城花岗岩体属于I型花岗岩。海南岛南部晚中生代花岗岩的大量形成并非孤立现象,该地区早白垩世安山岩-流纹岩组合和白垩纪沉积序列与花岗岩一起构建起较为完整的安第斯型大陆边缘弧体系,而且这一活动陆缘体系在岩石组合、展布和演化特征上与时代大体相当的浙闽地区活动陆缘体系存在明显区别,在区域构造意义的研究中值得给予特别关注。
中图分类号:
袁晓博, 方念乔, 董海龙. 海南岛高峰、保城地区花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 85-97.
YUAN Xiaobo, FANG Nianqiao, DONG Hailong. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Tectonic Significance of Gaofeng and Baocheng Granite Batholiths in Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(01): 85-97.

图1 区域地质简图(a)及高峰(b)、保城(c)岩体采样位置图(底图据文献[2]有修改) 1.早白垩世保亭单元;2.早白垩世抱跃单元;3.早白垩世廖次岭单元;4.早白垩世花岗斑岩;5.早白垩世六弓单元;6.早白垩世阜石斗单元;7.早白垩世加茂单元;8.早白垩世税町单元;9.中三叠世超盆单元;10.中三叠世布山村单元;11.中三叠世结尾单元;12.中二叠世通什单元;13.第四系八所组;14.海岸带;15.深大断裂带;16.正断层;17.采样点。红色曲线为高峰、保城岩体边界线
Fig.1 Regional geological sketch map(a) and samples’ location from Gaofeng(b) and Baocheng(c) batholiths (base map modified after reference [2])
| 测点号 | 元素含量/(μg/g) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 206Pb | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | ||||
| YL701-2 | 50.95 | 86.45 | 6.03 | 0.59 | 0.051 0±0.008 4 | 0.117 1±0.018 7 | 0.016 6±0.000 5 | 242.1±339.6 | 112.4±17.0 | 106.4±3.37 | ||
| YL701-4 | 1 072.10 | 1 393.70 | 96.12 | 0.77 | 0.055 8±0.002 6 | 0.127 3±0.004 8 | 0.016 5±0.000 3 | 445.1±101.3 | 121.7±4.3 | 105.7±1.72 | ||
| YL701-6 | 107.78 | 153.27 | 10.24 | 0.70 | 0.045 6±0.004 9 | 0.100 9±0.010 4 | 0.016 0±0.000 4 | 0.1±219.1 | 97.6±9.6 | 102.6±2.32 | ||
| YL701-7 | 117.51 | 129.00 | 8.90 | 0.91 | 0.050 8±0.005 7 | 0.116 0±0.012 5 | 0.016 6±0.000 4 | 230.1±240.8 | 111.5±11.4 | 106.0±2.59 | ||
| YL701-8 | 446.00 | 614.25 | 39.48 | 0.73 | 0.045 9±0.002 9 | 0.097 9±0.005 6 | 0.015 5±0.000 3 | 0.1±141.1 | 94.9±5.2 | 98.9±1.79 | ||
| YL701-9 | 174.51 | 298.16 | 20.54 | 0.59 | 0.049 3±0.003 5 | 0.112 7±0.007 3 | 0.016 6±0.000 3 | 159.6±157.9 | 108.4±6.6 | 106.1±2.01 | ||
| YL701-10 | 195.72 | 211.17 | 15.67 | 0.93 | 0.051 8±0.004 7 | 0.127 8±0.010 9 | 0.017 9±0.000 4 | 274.4±194.8 | 122.1±9.8 | 114.4±2.53 | ||
| YL701-15 | 270.54 | 333.97 | 23.33 | 0.81 | 0.047 5±0.003 2 | 0.110 9±0.006 7 | 0.016 9±0.000 3 | 74.5±153.5 | 106.8±6.2 | 108.2±2.00 | ||
| SHY401-3 | 257.50 | 397.83 | 27.57 | 0.65 | 0.047 3±0.002 5 | 0.109 4±0.005 0 | 0.016 8±0.000 3 | 62.4±123.6 | 105.4±4.6 | 107.3±1.68 | ||
| SHY401-4 | 250.51 | 397.51 | 27.14 | 0.63 | 0.046 3±0.002 6 | 0.105 7±0.005 2 | 0.016 5±0.000 3 | 15.5±131.7 | 102.0±4.8 | 105.7±1.68 | ||
| SHY401-6 | 246.88 | 380.59 | 26.40 | 0.65 | 0.048 7±0.002 9 | 0.112 7±0.005 9 | 0.016 8±0.000 3 | 133.6±134.6 | 108.4±5.4 | 107.2±1.80 | ||
| SHY401-9 | 188.96 | 302.21 | 19.85 | 0.63 | 0.050 1±0.003 6 | 0.109 5±0.007 2 | 0.015 9±0.000 3 | 199.0±159.5 | 105.5±6.6 | 101.4±1.90 | ||
| SHY401-10 | 230.68 | 432.05 | 30.52 | 0.53 | 0.046 3±0.002 6 | 0.108 9±0.005 4 | 0.017 0±0.000 3 | 14.6±131.5 | 104.9±4.9 | 108.9±1.80 | ||
| SHY401-11 | 167.08 | 288.97 | 19.88 | 0.58 | 0.045 0±0.002 7 | 0.102 9±0.005 4 | 0.016 6±0.000 3 | 0.1±81.5 | 99.4±5.0 | 106.1±1.76 | ||
| SHY401-15 | 104.77 | 144.68 | 10.42 | 0.72 | 0.046 3±0.003 9 | 0.110 5±0.008 7 | 0.017 3±0.000 3 | 12.2±189.2 | 106.4±7.9 | 110.6±2.08 | ||
| SHY401-21 | 115.88 | 187.81 | 12.40 | 0.62 | 0.053 2±0.003 7 | 0.116 1±0.007 4 | 0.015 8±0.000 3 | 338.8±149.2 | 111.6±6.7 | 101.2±1.87 | ||
| SHY401-22 | 132.51 | 147.57 | 9.96 | 0.90 | 0.049 3±0.004 1 | 0.109 9±0.008 6 | 0.016 2±0.000 3 | 162.1±184.5 | 105.8±7.9 | 103.4±2.01 | ||
表1 高峰(YL701)和保城(SHY401)岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS 分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Gaofeng and Baocheng batholiths
| 测点号 | 元素含量/(μg/g) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 206Pb | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | ||||
| YL701-2 | 50.95 | 86.45 | 6.03 | 0.59 | 0.051 0±0.008 4 | 0.117 1±0.018 7 | 0.016 6±0.000 5 | 242.1±339.6 | 112.4±17.0 | 106.4±3.37 | ||
| YL701-4 | 1 072.10 | 1 393.70 | 96.12 | 0.77 | 0.055 8±0.002 6 | 0.127 3±0.004 8 | 0.016 5±0.000 3 | 445.1±101.3 | 121.7±4.3 | 105.7±1.72 | ||
| YL701-6 | 107.78 | 153.27 | 10.24 | 0.70 | 0.045 6±0.004 9 | 0.100 9±0.010 4 | 0.016 0±0.000 4 | 0.1±219.1 | 97.6±9.6 | 102.6±2.32 | ||
| YL701-7 | 117.51 | 129.00 | 8.90 | 0.91 | 0.050 8±0.005 7 | 0.116 0±0.012 5 | 0.016 6±0.000 4 | 230.1±240.8 | 111.5±11.4 | 106.0±2.59 | ||
| YL701-8 | 446.00 | 614.25 | 39.48 | 0.73 | 0.045 9±0.002 9 | 0.097 9±0.005 6 | 0.015 5±0.000 3 | 0.1±141.1 | 94.9±5.2 | 98.9±1.79 | ||
| YL701-9 | 174.51 | 298.16 | 20.54 | 0.59 | 0.049 3±0.003 5 | 0.112 7±0.007 3 | 0.016 6±0.000 3 | 159.6±157.9 | 108.4±6.6 | 106.1±2.01 | ||
| YL701-10 | 195.72 | 211.17 | 15.67 | 0.93 | 0.051 8±0.004 7 | 0.127 8±0.010 9 | 0.017 9±0.000 4 | 274.4±194.8 | 122.1±9.8 | 114.4±2.53 | ||
| YL701-15 | 270.54 | 333.97 | 23.33 | 0.81 | 0.047 5±0.003 2 | 0.110 9±0.006 7 | 0.016 9±0.000 3 | 74.5±153.5 | 106.8±6.2 | 108.2±2.00 | ||
| SHY401-3 | 257.50 | 397.83 | 27.57 | 0.65 | 0.047 3±0.002 5 | 0.109 4±0.005 0 | 0.016 8±0.000 3 | 62.4±123.6 | 105.4±4.6 | 107.3±1.68 | ||
| SHY401-4 | 250.51 | 397.51 | 27.14 | 0.63 | 0.046 3±0.002 6 | 0.105 7±0.005 2 | 0.016 5±0.000 3 | 15.5±131.7 | 102.0±4.8 | 105.7±1.68 | ||
| SHY401-6 | 246.88 | 380.59 | 26.40 | 0.65 | 0.048 7±0.002 9 | 0.112 7±0.005 9 | 0.016 8±0.000 3 | 133.6±134.6 | 108.4±5.4 | 107.2±1.80 | ||
| SHY401-9 | 188.96 | 302.21 | 19.85 | 0.63 | 0.050 1±0.003 6 | 0.109 5±0.007 2 | 0.015 9±0.000 3 | 199.0±159.5 | 105.5±6.6 | 101.4±1.90 | ||
| SHY401-10 | 230.68 | 432.05 | 30.52 | 0.53 | 0.046 3±0.002 6 | 0.108 9±0.005 4 | 0.017 0±0.000 3 | 14.6±131.5 | 104.9±4.9 | 108.9±1.80 | ||
| SHY401-11 | 167.08 | 288.97 | 19.88 | 0.58 | 0.045 0±0.002 7 | 0.102 9±0.005 4 | 0.016 6±0.000 3 | 0.1±81.5 | 99.4±5.0 | 106.1±1.76 | ||
| SHY401-15 | 104.77 | 144.68 | 10.42 | 0.72 | 0.046 3±0.003 9 | 0.110 5±0.008 7 | 0.017 3±0.000 3 | 12.2±189.2 | 106.4±7.9 | 110.6±2.08 | ||
| SHY401-21 | 115.88 | 187.81 | 12.40 | 0.62 | 0.053 2±0.003 7 | 0.116 1±0.007 4 | 0.015 8±0.000 3 | 338.8±149.2 | 111.6±6.7 | 101.2±1.87 | ||
| SHY401-22 | 132.51 | 147.57 | 9.96 | 0.90 | 0.049 3±0.004 1 | 0.109 9±0.008 6 | 0.016 2±0.000 3 | 162.1±184.5 | 105.8±7.9 | 103.4±2.01 | ||
| 岩体 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | ALK | A/NKC | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高峰 | YL501 | 65.90 | 0.71 | 15.32 | 1.42 | 2.61 | 0.07 | 1.64 | 3.51 | 3.21 | 4.08 | 0.16 | 1.20 | 99.84 | 7.29 | 0.95 | 2.32 |
| YL601 | 71.45 | 0.27 | 14.32 | 1.42 | 1.00 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 1.71 | 3.44 | 4.69 | 0.08 | 0.88 | 99.86 | 8.13 | 1.03 | 2.32 | |
| YL701 | 69.05 | 0.52 | 14.67 | 1.24 | 1.84 | 0.06 | 1.20 | 2.52 | 3.08 | 4.59 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 99.89 | 7.67 | 1.00 | 2.26 | |
| YL703 | 69.74 | 0.45 | 14.51 | 0.82 | 1.89 | 0.05 | 1.10 | 2.54 | 3.01 | 4.83 | 0.10 | 0.85 | 99.89 | 7.84 | 0.98 | 2.30 | |
| 保城 | SHY101 | 72.42 | 0.25 | 14.63 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 1.58 | 3.19 | 4.27 | 0.06 | 1.32 | 99.9 | 7.47 | 1.15 | 1.89 |
| SHY201 | 71.76 | 0.32 | 14.57 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.81 | 2.14 | 3.63 | 3.74 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 99.87 | 7.37 | 1.05 | 1.89 | |
| SHY302 | 72.21 | 0.28 | 14.39 | 1.01 | 0.86 | 0.04 | 0.79 | 1.89 | 3.45 | 4.09 | 0.07 | 0.77 | 99.85 | 7.54 | 1.06 | 1.95 | |
| SHY401 | 69.37 | 0.34 | 15.80 | 1.14 | 0.98 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 1.70 | 2.99 | 3.81 | 0.08 | 2.70 | 99.85 | 6.80 | 1.30 | 1.75 |
表2 高峰和保城岩体主量元素含量(wB/%)
Table 2 Major element abundances of representative samples from the Gaofeng and Baocheng batholiths(%)
| 岩体 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | ALK | A/NKC | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高峰 | YL501 | 65.90 | 0.71 | 15.32 | 1.42 | 2.61 | 0.07 | 1.64 | 3.51 | 3.21 | 4.08 | 0.16 | 1.20 | 99.84 | 7.29 | 0.95 | 2.32 |
| YL601 | 71.45 | 0.27 | 14.32 | 1.42 | 1.00 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 1.71 | 3.44 | 4.69 | 0.08 | 0.88 | 99.86 | 8.13 | 1.03 | 2.32 | |
| YL701 | 69.05 | 0.52 | 14.67 | 1.24 | 1.84 | 0.06 | 1.20 | 2.52 | 3.08 | 4.59 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 99.89 | 7.67 | 1.00 | 2.26 | |
| YL703 | 69.74 | 0.45 | 14.51 | 0.82 | 1.89 | 0.05 | 1.10 | 2.54 | 3.01 | 4.83 | 0.10 | 0.85 | 99.89 | 7.84 | 0.98 | 2.30 | |
| 保城 | SHY101 | 72.42 | 0.25 | 14.63 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 1.58 | 3.19 | 4.27 | 0.06 | 1.32 | 99.9 | 7.47 | 1.15 | 1.89 |
| SHY201 | 71.76 | 0.32 | 14.57 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.81 | 2.14 | 3.63 | 3.74 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 99.87 | 7.37 | 1.05 | 1.89 | |
| SHY302 | 72.21 | 0.28 | 14.39 | 1.01 | 0.86 | 0.04 | 0.79 | 1.89 | 3.45 | 4.09 | 0.07 | 0.77 | 99.85 | 7.54 | 1.06 | 1.95 | |
| SHY401 | 69.37 | 0.34 | 15.80 | 1.14 | 0.98 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 1.70 | 2.99 | 3.81 | 0.08 | 2.70 | 99.85 | 6.80 | 1.30 | 1.75 |
| 岩体 | 样品号 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Y | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Th | U | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高峰 | YL501 | 159 | 356 | 724 | 23.5 | 16.3 | 1.35 | 274 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 4.1 | 50.4 | 96.9 | 11.0 | 39.0 | 6.68 | 1.37 | |||||||||
| YL601 | 153 | 191 | 719 | 23.2 | 12.4 | 1.23 | 160 | 7.6 | 14 | 2.3 | 57.1 | 103.0 | 11.5 | 39.6 | 6.41 | 1.14 | ||||||||||
| YL701 | 207 | 270 | 755 | 27.9 | 18.1 | 1.70 | 256 | 14.2 | 25.3 | 5.7 | 42.2 | 85.3 | 10.4 | 38.4 | 7.09 | 1.22 | ||||||||||
| YL703 | 222 | 292 | 720 | 24.1 | 16.5 | 1.83 | 220 | 13.0 | 25.4 | 5.1 | 46.7 | 92.2 | 10.7 | 38.2 | 6.70 | 1.07 | ||||||||||
| 保城 | SHY101 | 173 | 327 | 705 | 6.4 | 8.5 | 0.71 | 125 | 5.88 | 61.0 | 7.8 | 24.9 | 40.9 | 4.71 | 15.4 | 2.39 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| SHY201 | 162 | 412 | 778 | 17.5 | 11.0 | 1.12 | 152 | 8.79 | 17.6 | 6.8 | 57.3 | 69.7 | 10.40 | 34.1 | 5.66 | 1.35 | ||||||||||
| SHY302 | 174 | 413 | 825 | 8.5 | 9.6 | 0.90 | 141 | 7.37 | 12.7 | 5.3 | 23.1 | 46.7 | 5.26 | 18.0 | 2.82 | 0.75 | ||||||||||
| SHY401 | 137 | 431 | 858 | 5.6 | 9.2 | 0.73 | 169 | 8.96 | 24.2 | 3.9 | 33.8 | 57.0 | 6.21 | 19.2 | 2.78 | 0.69 | ||||||||||
| 岩体 | 样品号 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | Lan/Ybn | |||||||||||||||
| 高峰 | YL501 | 5.80 | 0.85 | 4.65 | 0.89 | 2.42 | 0.41 | 2.35 | 0.34 | 222.97 | 15.38 | |||||||||||||||
| YL601 | 5.53 | 0.81 | 4.59 | 0.86 | 2.44 | 0.42 | 2.58 | 0.42 | 236.48 | 15.89 | ||||||||||||||||
| YL701 | 5.92 | 0.93 | 5.36 | 1.01 | 2.75 | 0.49 | 2.93 | 0.44 | 204.45 | 10.32 | ||||||||||||||||
| YL703 | 5.61 | 0.87 | 4.88 | 0.89 | 2.37 | 0.42 | 2.41 | 0.35 | 213.37 | 13.89 | ||||||||||||||||
| 保城 | SHY101 | 1.95 | 0.26 | 1.28 | 0.24 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.13 | 94.35 | 23.83 | |||||||||||||||
| SHY201 | 4.84 | 0.71 | 3.62 | 0.64 | 1.66 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 0.26 | 192.30 | 23.46 | ||||||||||||||||
| SHY302 | 2.37 | 0.31 | 1.60 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.16 | 103.25 | 17.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| SHY401 | 2.29 | 0.28 | 1.38 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 125.46 | 31.13 | ||||||||||||||||
表3 高峰和保城岩体微量、稀土元素含量(wB/10-6)
Table 3 Trace element and REE abundances of representative samples from the Gaofeng and Baocheng batholiths(10-6)
| 岩体 | 样品号 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Y | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Th | U | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高峰 | YL501 | 159 | 356 | 724 | 23.5 | 16.3 | 1.35 | 274 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 4.1 | 50.4 | 96.9 | 11.0 | 39.0 | 6.68 | 1.37 | |||||||||
| YL601 | 153 | 191 | 719 | 23.2 | 12.4 | 1.23 | 160 | 7.6 | 14 | 2.3 | 57.1 | 103.0 | 11.5 | 39.6 | 6.41 | 1.14 | ||||||||||
| YL701 | 207 | 270 | 755 | 27.9 | 18.1 | 1.70 | 256 | 14.2 | 25.3 | 5.7 | 42.2 | 85.3 | 10.4 | 38.4 | 7.09 | 1.22 | ||||||||||
| YL703 | 222 | 292 | 720 | 24.1 | 16.5 | 1.83 | 220 | 13.0 | 25.4 | 5.1 | 46.7 | 92.2 | 10.7 | 38.2 | 6.70 | 1.07 | ||||||||||
| 保城 | SHY101 | 173 | 327 | 705 | 6.4 | 8.5 | 0.71 | 125 | 5.88 | 61.0 | 7.8 | 24.9 | 40.9 | 4.71 | 15.4 | 2.39 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| SHY201 | 162 | 412 | 778 | 17.5 | 11.0 | 1.12 | 152 | 8.79 | 17.6 | 6.8 | 57.3 | 69.7 | 10.40 | 34.1 | 5.66 | 1.35 | ||||||||||
| SHY302 | 174 | 413 | 825 | 8.5 | 9.6 | 0.90 | 141 | 7.37 | 12.7 | 5.3 | 23.1 | 46.7 | 5.26 | 18.0 | 2.82 | 0.75 | ||||||||||
| SHY401 | 137 | 431 | 858 | 5.6 | 9.2 | 0.73 | 169 | 8.96 | 24.2 | 3.9 | 33.8 | 57.0 | 6.21 | 19.2 | 2.78 | 0.69 | ||||||||||
| 岩体 | 样品号 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | Lan/Ybn | |||||||||||||||
| 高峰 | YL501 | 5.80 | 0.85 | 4.65 | 0.89 | 2.42 | 0.41 | 2.35 | 0.34 | 222.97 | 15.38 | |||||||||||||||
| YL601 | 5.53 | 0.81 | 4.59 | 0.86 | 2.44 | 0.42 | 2.58 | 0.42 | 236.48 | 15.89 | ||||||||||||||||
| YL701 | 5.92 | 0.93 | 5.36 | 1.01 | 2.75 | 0.49 | 2.93 | 0.44 | 204.45 | 10.32 | ||||||||||||||||
| YL703 | 5.61 | 0.87 | 4.88 | 0.89 | 2.37 | 0.42 | 2.41 | 0.35 | 213.37 | 13.89 | ||||||||||||||||
| 保城 | SHY101 | 1.95 | 0.26 | 1.28 | 0.24 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.13 | 94.35 | 23.83 | |||||||||||||||
| SHY201 | 4.84 | 0.71 | 3.62 | 0.64 | 1.66 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 0.26 | 192.30 | 23.46 | ||||||||||||||||
| SHY302 | 2.37 | 0.31 | 1.60 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.16 | 103.25 | 17.56 | ||||||||||||||||
| SHY401 | 2.29 | 0.28 | 1.38 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 125.46 | 31.13 | ||||||||||||||||
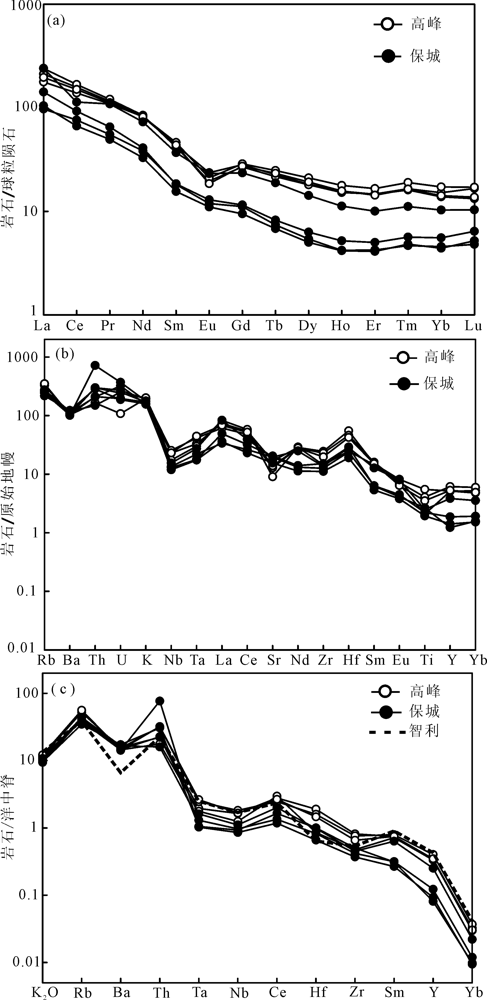
图6 高峰和保城岩体稀土元素球粒陨石配分曲线(a)、 微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)及洋脊花岗岩标准化微量元素蛛网图(c)(底图及智利花岗岩数据据文献[26])
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a), primitive-mantle normalized incompatible element spidergrams(b) and ORG-granite normalized patterns(c) for the Gaofeng and Baocheng batholiths

图7 高峰和保城花岗岩成因类型判别图 (a)w(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-w(K2O+Na2O)/w(CaO)图解(底图据文献[31], A代表A型花岗岩区,OGT代表未分异的I、S、M型花岗岩区,FG代表分异的I型花岗岩区);(b)w(SiO2)-w(P2O5)图解(底图据文献[33])
Fig.7 Genetic type discrimination diagram for the Gaofeng and Baocheng granites

图8 高峰和保城岩体R1-R2判别图解(底图据文献[41])和Rb/30-Hf-3Ta判别图解(底图据文献[42])
Fig.8 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of R1 vs. R2((a),base map after reference [41]) and Rb/30-Hf-3Ta((b), base map after reference [42]) for the Gaofeng and Baocheng batholiths
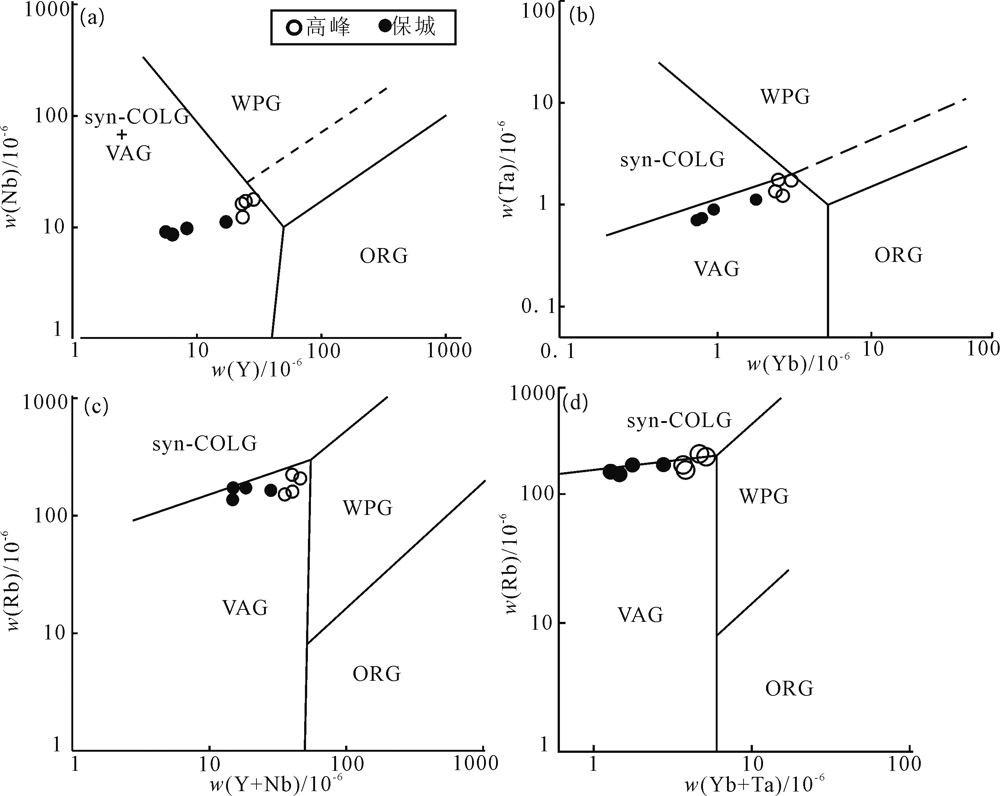
图9 高峰和保成岩体花岗岩构造环境判别图(底图据文献[26];ORG,洋脊花岗岩;WPG,板内花岗岩;VAG,火山弧花岗岩;Syn-COLG,同碰撞花岗岩)
Fig.9 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for granites(base map after reference [26])

图10 海南岛与闽浙地区晚中生代花岗岩地球化学特征对比图 (a)A/NK-A/CNK图(底图据文献[24]);(b)Sr-Yb花岗岩类型判别图(底图据文献[54,55]); (c)R1-R2图解(底图据文献[39]);R1=4Si-11(Na+K)-2(Fe+Ti), R2=6Ca+2Mg+Al);(d)Ta-Rb-Hf图解(底图据文献[40]);数据来自本文及文献[8-9,48,50,56-63]);灰色区域为闽浙花岗岩大致分布区,黄色区域为海南岛花岗岩大致分布区
Fig.10 Geochemical diagrams comparing the Late Mesozoic granites from Hainan and Zhejiang-Fujian
| [1] | 地质部广东省地质局. 中华人民共和国地质部区域地质测量报告书(1∶20万)[R]. 广州:地质部广东省地质局, 1964. |
| [2] | 海南省地质调查院. 中华人民共和国地质部区域地质调查报告,乐东县幅、陵水县幅,比例尺1∶25万.[M]. 海口:海南省地质调查院, 2004. |
| [3] | 汪啸风, 马大铨, 蒋大海. 海南岛地质( 二):火成岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 1-10. |
| [4] | 李孙雄, 云平, 范渊, 等. 海南岛琼中地区琼中岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2005,29(2):227-233. |
| [5] | 龙文国, 谢盛周. 海南岛屯昌地区发现印支期爆破角砾岩筒[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2000(3):42-45. |
| [6] | 莫宴情, 施央申. 海南岛地体及其毗邻陆缘晚中生代—新生代古地磁研究和构造演化[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 1987,23(3):521-532. |
| [7] | 云平, 吴育波, 谢盛周. 海南岛燕山晚期典型侵入岩成因矿物学研究及其地质意义[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2004(4):1-8. |
| [8] | 云平, 谢盛周. 海南岛晚中生代屯昌岩体的成因类型及其构造意义[J]. 广东地质, 2003,18(4):9-14. |
| [9] | 贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建, 等. 海南屯昌早白垩世晚期埃达克质侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学与岩石成因[J]. 地球化学, 2010,39(6):497-519. |
| [10] | WANG Q, LI X H, JIA X H, et al. Late Early Cretaceous adakitic granitoids and associated magnesian and potassium-rich mafic enclaves and dikes in the Tunchang-Fengmu area, Hainan Province (South China): Partial melting of lower crust and mantle, and magma hybridization[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012,328(11):222-243. |
| [11] | 梁飞刚. 琼南晚燕山期花岗岩研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [12] | 陈沐龙, 李孙雄, 曾雁玲, 等. 海南岛白垩纪千家岩体岩石地球化学特征及其成矿作用分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2008,22(1):36-42. |
| [13] | 陈沐龙. 海南岛千家复式岩体的成因及相关的钼多金属成矿研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [14] | JIANG X Y, LI X H. In situ zircon U-Pb and Hf-O isotopic results for ca. 73 Ma granite in Hainan Island: Implications for the termination of an Andean-type active continental margin in southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014,82(3):32-46. |
| [15] | 方念乔. “海南陆缘弧”体系的构建与“特提斯南海”的识别:一个关于“古南海”演化新模式的探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2016,23(6):107-119. |
| [16] | 王大英. 琼南崖城—高峰地区花岗岩的成因类型及定位机制初探[J]. 广东地质, 1998(4):13-17. |
| [17] | ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemica Geology, 2002,192:59-79. |
| [18] | LUDWIG K R. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003: 1-5. |
| [19] | BELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W, O’REILLT S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2002,143(5):602-622. |
| [20] | 曾庆銮. 海南岛三亚地区基础地质研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992: 1-20. |
| [21] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224. |
| [22] | IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971,8(5):523-548. |
| [23] | PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1976,58(1):63-81. |
| [24] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLO P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [25] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [26] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25(4):956-983. |
| [27] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974,8:173-174. |
| [28] | ISHIHARA S. The magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitic rocks[J]. Mining Geology, 1977,27:293-305. |
| [29] | COLLINS J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1982,80(2):189-200. |
| [30] | PITCHER W S. Granite type and tectonic environment[M] //HSUK D. Mountain Building Processes. London: Academic Press, 1983: 1-10. |
| [31] | JOSEPH B W, KENNETH L C, BRUCE W C. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1987,95(4):407-419. |
| [32] | 刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 等. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003,9(4):573-591. |
| [33] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Earth Sciences, 1992,83(1/2):1-26. |
| [34] | 徐夕生, 邱检生. 火成岩岩石学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. |
| [35] | LI X H, LI Z X, LI W X, et al. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I-and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab?[J]. Lithos, 2007,96(1/2):186-204. |
| [36] | 邓晋福. 岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 1-50. |
| [37] | WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (II): isotopic geochemistry and implications for crustal growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Lithos, 2003,67(3):191-204. |
| [38] | ROBERTS M P, CLEMENS J D. Origin of high-potassium, talc-alkaline, I-type granitoids[J]. Geology, 1993,21(9):825. |
| [39] | PITCHER W S. Granites and yet more granites forty years on[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1987,76:51-79. |
| [40] | BARBARIN B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999,46(3):605-626. |
| [41] | BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985,48(1):43-55. |
| [42] | HARRIS N B W, PEARCE J A, TINDLE A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Collision Tectonics, 1986,19(5):67-81. |
| [43] | 强萌麟. 南海北部陆缘白垩纪安山岩基本特征及其与东南沿海安山岩对比[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [44] | 韩琦. 南海北部陆缘中、新生代流纹岩基本特征研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2017. |
| [45] | 汤稚音. 南海北缘陆相盆地白垩系沉积学与地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [46] | 葛小月, 李献华, 周汉文. 琼南晚白垩世基性岩墙群的年代学、元素地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素研究[J]. 地球化学, 2003,32(1):11-20. |
| [47] | 唐立梅, 陈汉林, 董传万. 海南岛晚中生代花岗闪长岩及其包体的锆石U-Pb定年及构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 2014,49(1):259-274. |
| [48] | ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,326(3):269-287. |
| [49] | 毛建仁, 叶海敏, 厉子龙, 等. 钦杭结合带(东段)晚中生代挤压-伸展构造的岩浆活动与成矿记录[J]. 矿物学报, 2013,52(增刊):30-31. |
| [50] | 李良林, 周汉文, 陈植华, 等. 福建沿海晚中生代花岗质岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2013,32(7):1047-1062. |
| [51] | 赵希林, 毛建仁, 陈荣, 等. 闽西南地区才溪岩体锆石SHRIMP定年及其地球化学特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007,26(3):223-231. |
| [52] | 邱检生, 李真, 刘亮, 等. 福建漳浦复式花岗岩体的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、元素地球化学及Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 地质学报, 2012,86(4):561-576. |
| [53] | 魏昌欣. 海南保亭地区早白垩世保城复式岩体的岩石成因及地质意义[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [54] | 张旗. 广西型花岗岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014,33(1):199-210. |
| [55] | 张旗, 李承东, 王焰, 等. 中国东部中生代高Sr低Yb和低Sr高Yb型花岗岩:对比及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(6):1527-1537. |
| [56] | CHEN J Y, YANG J H, ZHANG J H, et al. Geochemical transition shown by Cretaceous granitoids in southeastern China: Implications for continental crustal reworking and growth[J]. Lithos, 2014,196/197:115-130. |
| [57] | CHEN J Y, YANG J H, ZHANG J H, et al. Petrogenesis of the Cretaceous Zhangzhou batholith in southeastern China: Zircon U-Pb age and Sr-Nd-Hf-O isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2013,162/163(2):140-156. |
| [58] | 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等. 福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008,24(11):2468-2484. |
| [59] | 邱检生, 李真, 刘亮, 等. 福建漳浦复式花岗岩体的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、元素地球化学及Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 地质学报, 2012,86(4):561-576. |
| [60] | 赵姣龙, 邱检生, 李真, 等. 福建太武山花岗岩体成因:锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(12):3938-3950. |
| [61] | THUY N T B, SATIR M, SIEBEL W, et al. Geochemical and isotopic constraints on the petrogenesis of granitoids from the Dalat zone, southern Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004,23(4):467-482. |
| [62] | NGUYEN T T B, SATIR M, SIEBEL W, et al. Granitoids in the Dalat zone, southern Vietnam: age constraints on magmatism and regional geological implications[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2004,93(3):329-340. |
| [63] | SHELLNUTT J G, LAN C Y, LONG T V, et al. Formation of Cretaceous Cordilleran and post-orogenic granites and their microgranular enclaves from the Dalat zone, southern Vietnam: Tectonic implications for the evolution of Southeast Asia[J]. Lithos, 2013,182(12):229-241. |
| [64] | 李平鲁, 梁慧娴, 戴一丁. 珠江口盆地基岩油气藏远景探讨[J]. 中国海上油气, 1998(6):361-369. |
| [65] | 李平鲁, 梁慧娴. 珠江口盆地燕山期岩浆岩的成因及构造环境[J]. 广东地质, 1999(1):1-8. |
| [66] | 刘安, 吴世敏. 珠江口盆地花岗岩成因探讨及其对油气资源指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2011,18(1):141-148. |
| [67] | 陈卫锋, 陈培荣, 徐夕生, 等. 华南白垩纪玄武质岩石的地球化学特征及其对太平洋板块俯冲作用的制约[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2005,35(11):1007-1018. |
| [68] | 朱炳泉, 王慧芬, 陈毓蔚, 等. 新生代华夏岩石圈减薄与东亚边缘海盆构造演化的年代学与地球化学制约研究[J]. 地球化学, 2002,31(3):213-221. |
| [69] | ZHU B Q, WANG H F, CHEN Y W, et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraint on the Cenozoic extension of Cathaysian lithosphere and tectonic evolution of the border sea basins in East Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004,24(2):163-175. |
| [70] | 颜佳新, 周蒂. 南海北部陆缘区中特提斯构造演化研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001,21(4):49-54. |
| [71] | 颜佳新, 周蒂. 南海及周边部分地区特提斯构造遗迹:问题与思考[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2002,21(2):43-49. |
| [72] | 颜佳新. 加里曼丹岛和马来半岛中生代岩相古地理特征及其构造意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005,24(2):26-32. |
| [73] | 刘海龄, 阎贫, 张伯友, 等. 南海前新生代基底与东特提斯构造域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004,24(1):15-28. |
| [74] | 夏戡原, 黄慈流. 南海中生代特提斯期沉积盆地的发现与找寻中生代含油气盆地的前景[J]. 地学前缘, 2000,7(3):227-238. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 滕超, 张学斌, 杨欣杰, 来林, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古西乌旗早泥盆世I型石英闪长岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1624-1633. |
| [3] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [4] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [5] | 王玉平, 吴文彬, 刘永俊, 李海洋, 王晓亮, 李超. 辽东岫岩地区晚侏罗世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 955-967. |
| [6] | 刘洋, 方念乔, 强萌麟, 贾磊, 宋超杰. 粤桂地区白垩纪中期安山岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 968-980. |
| [7] | 李盛, 倪金龙, 张尚坤, 申颖. 晚中生代沂沭断裂带左旋韧性剪切与岩浆迁移规律[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 776-786. |
| [8] | 张宪依, 庞成宝, 王安婷, 袁国礼, 桑学镇, 李元仲, 杨毅. 海南岛表层及深层土壤重金属分布特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 970-978. |
| [9] | 蔺新望, 王星, 陈光庭, 赵端昌, 赵江林. 新疆北部阿尔泰山东段泥盆纪岩浆活动及侵位方式的探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 514-531. |
| [10] | 吴天昊, 徐丽娟, 肖益林, 刘盛遨. 华北陆块东南缘蚌埠地区侏罗纪花岗岩中多种类型白云母的识别及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 532-544. |
| [11] | 蒋德鑫, 姜鹍鹏, 张贺, 姜正龙. 西北太平洋边缘海热流特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 117-129. |
| [12] | 高健翁, 林逸, 张长厚, 丁照月, 侯丽玉, 黄滢竹. 基于断层滑动数据反演的燕山中西段晚中生代古构造应力场:对华北克拉通破坏峰期应力状态的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 919-936. |
| [13] | 罗晓华, 杨明慧, 贾春阳, 李占元, 雷志斌, 张少华. 晋北地区口泉断裂带晚中生代分段构造特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 551-560. |
| [14] | 杨鑫朋, 张振利, 张泽国, 王金贵, 邓科, 侯德华. 西藏冈底斯南缘中侏罗世辉长闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年和Lu-Hf同位素组成及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 63-72. |
| [15] | 刘伯崇, 李康宁, 史海龙, 蒲万峰, 汪宏涛, 王舒恒. 西秦岭甘青交界一带晚三叠世火山岩岩石成因及构造指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 704-717. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||