



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (04): 968-980.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.076
刘洋1( ), 方念乔1(
), 方念乔1( ), 强萌麟2, 贾磊3, 宋超杰4
), 强萌麟2, 贾磊3, 宋超杰4
收稿日期:2020-04-29
修回日期:2020-09-10
出版日期:2021-08-10
发布日期:2021-09-08
通讯作者:
方念乔
作者简介:方念乔,男,教授,博士生导师,1949年出生,海洋地质专业,主要从事海洋地质、沉积地质和大地构造的科研与教学工作。Email: fangnq@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
LIU Yang1( ), FANG Nianqiao1(
), FANG Nianqiao1( ), QIANG Menglin2, JIA Lei3, SONG Chaojie4
), QIANG Menglin2, JIA Lei3, SONG Chaojie4
Received:2020-04-29
Revised:2020-09-10
Online:2021-08-10
Published:2021-09-08
Contact:
FANG Nianqiao
摘要:
华南沿海地区存在丰富的白垩纪岩浆活动记录。粤桂地区作为华南沿海的重要组成部分,其白垩纪安山岩的出露数量虽然有限,但对于揭示晚中生代大陆边缘的构造性质具有特殊意义。选取广西玉林、广东连平的安山岩作为研究对象,结合前人对广东仁化地区样品的研究成果,应用岩相学、同位素年代学、地球化学等多种分析方法,对上述岩石开展系统研究。结果显示:(1)安山岩具斑状结构,斑晶主要为角闪石、辉石和斜长石,基质主要为斜长石微晶;(2)玉林安山岩U-Pb谐和年龄为(93.38±0.83) Ma,略晚于仁化的105 Ma,白垩纪中期粤桂地区有众多安山岩形成;(3)安山岩高MgO含量和Mg#值, FeOT/MgO值较低,富集轻稀土元素和LILEs,但亏损HFSEs。研究区安山岩由俯冲沉积物部分熔融形成的硅质熔体与地幔橄榄岩平衡反应所形成。高镁安山岩与邻近区域的埃达克质岩石基本同时产出,显示与受太平洋域控制的浙闽地区在构造环境上存在明显差别。据此推测,南海北部陆缘在晚中生代时可能受到来自新特提斯域洋脊俯冲的影响。
中图分类号:
刘洋, 方念乔, 强萌麟, 贾磊, 宋超杰. 粤桂地区白垩纪中期安山岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 968-980.
LIU Yang, FANG Nianqiao, QIANG Menglin, JIA Lei, SONG Chaojie. Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Tectonic Significance of Mid-Cretaceous Andesites in Guangxi and Guangdong[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 968-980.

图1 区域地质简图(a)和玉林(b)、连平(c)安山岩采样地质简图(底图据文献[28,29]) $\rlap{-}C$.寒武系;O.奥陶系,S.志留系;D.泥盆系;C.石炭系;J.侏罗系;K.白垩系;E.古近系;N.新近系
Fig.1 Regional geologic sketch map (a), and andesite sampling location from Yulin (b) and Lianpin (c) (base map modified after references [28-29])

图2 玉林安山岩单偏光(a)、正交偏光(b)和连平安山岩单偏光(c)、正交偏光(d)镜下照片 Hb. 角闪石;Px. 辉石;Pl. 斜长石。样品均为安山结构,基质为斜长石微晶;玉林安山岩的斑晶为蚀变的角闪石和辉石,连平安山岩的斑晶主要为角闪石、斜长石和辉石
Fig.2 Thin-section photomicrographs of andesites in Yulin ((a) and (b)) and Lianping ((c) and (d))
| 点号 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/235U±1σ | 206Pb/238U±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/235U±1σ | 206Pb/238U±1σ | |||||||
| 4 | 778 | 660 | 1.18 | 0.052 943±0.002 028 | 0.105 863±0.004 260 | 0.014 550±0.000 162 | 327.84±87.03 | 102.17±3.91 | 93.12±1.03 | |||
| 8 | 215 | 319 | 0.67 | 0.055 402±0.005 689 | 0.106 484±0.009 310 | 0.014 642±0.000 365 | 427.83±226.82 | 102.74±8.54 | 93.71±2.32 | |||
| 10 | 785 | 647 | 1.21 | 0.048 431±0.002 114 | 0.095 819±0.004 078 | 0.014 437±0.000 160 | 120.46±103.69 | 92.91±3.78 | 92.40±1.02 | |||
| 12 | 662 | 887 | 0.75 | 0.052 819±0.002 251 | 0.105 023±0.004 352 | 0.014 548±0.000 155 | 320.43±98.14 | 101.40±4.00 | 93.11±0.98 | |||
| 13 | 52 | 563 | 0.09 | 0.047 487±0.004 553 | 0.095 395±0.009 201 | 0.014 721±0.000 308 | 72.32±214.79 | 92.52±8.53 | 94.21±1.95 | |||
| 17 | 807 | 1 007 | 0.80 | 0.048 714±0.001 889 | 0.097 236±0.003 751 | 0.014 577±0.000 148 | 200.08±97.21 | 94.22±3.47 | 93.29±0.94 | |||
| 18 | 288 | 1 658 | 0.17 | 0.048 054±0.001 621 | 0.097 694±0.003 339 | 0.014 783±0.000 153 | 101.94±84.25 | 94.65±3.09 | 94.60±0.97 | |||
| 1 | 370 | 1 097 | 0.34 | 0.069 394±0.000 946 | 1.479 264±0.022 043 | 0.154 699±0.001 383 | 910.19±27.78 | 921.93±9.03 | 927.25±7.72 | |||
| 2 | 352 | 814 | 0.43 | 0.073 216±0.001 017 | 1.542 407±0.023 326 | 0.152 604±0.001 137 | 1 020.37±28.55 | 947.47±9.32 | 915.54±6.36 | |||
| 3 | 6 | 722 | 0.01 | 0.151 631±0.001 552 | 8.842 395±0.097 376 | 0.422 511±0.002 668 | 2 364.51±18.36 | 2 321.88±10.05 | 2 271.87±12.09 | |||
| 5 | 360 | 1 971 | 0.18 | 0.060 137±0.000 686 | 0.842 628±0.010 756 | 0.101 390±0.000 711 | 609.28±24.07 | 620.59±5.93 | 622.55±4.16 | |||
| 6 | 375 | 1 076 | 0.35 | 0.089 175±0.000 967 | 2.883 195±0.032 698 | 0.234 226±0.001 542 | 1 409.26±20.83 | 1 377.53±8.55 | 1 356.61±8.05 | |||
| 7 | 214 | 722 | 0.30 | 0.070 226±0.001 039 | 1.500 139±0.025 399 | 0.154 576±0.001 463 | 1 000.00±29.63 | 930.44±10.32 | 926.56±8.17 | |||
| 9 | 570 | 871 | 0.65 | 0.072 671±0.001 129 | 1.533 127±0.027 094 | 0.152 402±0.001 352 | 1 005.56±31.48 | 943.75±10.86 | 914.41±7.57 | |||
| 11 | 614 | 896 | 0.69 | 0.097 284±0.001 131 | 3.598 950±0.046 454 | 0.267 513±0.002 156 | 1 572.53±21.76 | 1 549.30±10.26 | 1 528.17±10.96 | |||
| 14 | 2 119 | 662 | 3.20 | 0.064 143±0.001 041 | 0.993 233±0.015 529 | 0.112 186±0.000 638 | 746.30±33.33 | 700.37±7.91 | 685.43±3.70 | |||
| 15 | 536 | 507 | 1.06 | 0.059 697±0.001 110 | 0.838 994±0.016 053 | 0.101 737±0.000 750 | 592.31±40.73 | 618.59±8.86 | 624.58±4.39 | |||
| 16 | 432 | 551 | 0.78 | 0.064 711±0.001 099 | 1.103 915±0.019 405 | 0.123 530±0.000 941 | 764.82±236.11 | 755.24±9.37 | 750.85±5.40 | |||
表1 玉林安山岩(LC1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating results of the Yulin andesite sample (LC1-1)
| 点号 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/235U±1σ | 206Pb/238U±1σ | 207Pb/206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/235U±1σ | 206Pb/238U±1σ | |||||||
| 4 | 778 | 660 | 1.18 | 0.052 943±0.002 028 | 0.105 863±0.004 260 | 0.014 550±0.000 162 | 327.84±87.03 | 102.17±3.91 | 93.12±1.03 | |||
| 8 | 215 | 319 | 0.67 | 0.055 402±0.005 689 | 0.106 484±0.009 310 | 0.014 642±0.000 365 | 427.83±226.82 | 102.74±8.54 | 93.71±2.32 | |||
| 10 | 785 | 647 | 1.21 | 0.048 431±0.002 114 | 0.095 819±0.004 078 | 0.014 437±0.000 160 | 120.46±103.69 | 92.91±3.78 | 92.40±1.02 | |||
| 12 | 662 | 887 | 0.75 | 0.052 819±0.002 251 | 0.105 023±0.004 352 | 0.014 548±0.000 155 | 320.43±98.14 | 101.40±4.00 | 93.11±0.98 | |||
| 13 | 52 | 563 | 0.09 | 0.047 487±0.004 553 | 0.095 395±0.009 201 | 0.014 721±0.000 308 | 72.32±214.79 | 92.52±8.53 | 94.21±1.95 | |||
| 17 | 807 | 1 007 | 0.80 | 0.048 714±0.001 889 | 0.097 236±0.003 751 | 0.014 577±0.000 148 | 200.08±97.21 | 94.22±3.47 | 93.29±0.94 | |||
| 18 | 288 | 1 658 | 0.17 | 0.048 054±0.001 621 | 0.097 694±0.003 339 | 0.014 783±0.000 153 | 101.94±84.25 | 94.65±3.09 | 94.60±0.97 | |||
| 1 | 370 | 1 097 | 0.34 | 0.069 394±0.000 946 | 1.479 264±0.022 043 | 0.154 699±0.001 383 | 910.19±27.78 | 921.93±9.03 | 927.25±7.72 | |||
| 2 | 352 | 814 | 0.43 | 0.073 216±0.001 017 | 1.542 407±0.023 326 | 0.152 604±0.001 137 | 1 020.37±28.55 | 947.47±9.32 | 915.54±6.36 | |||
| 3 | 6 | 722 | 0.01 | 0.151 631±0.001 552 | 8.842 395±0.097 376 | 0.422 511±0.002 668 | 2 364.51±18.36 | 2 321.88±10.05 | 2 271.87±12.09 | |||
| 5 | 360 | 1 971 | 0.18 | 0.060 137±0.000 686 | 0.842 628±0.010 756 | 0.101 390±0.000 711 | 609.28±24.07 | 620.59±5.93 | 622.55±4.16 | |||
| 6 | 375 | 1 076 | 0.35 | 0.089 175±0.000 967 | 2.883 195±0.032 698 | 0.234 226±0.001 542 | 1 409.26±20.83 | 1 377.53±8.55 | 1 356.61±8.05 | |||
| 7 | 214 | 722 | 0.30 | 0.070 226±0.001 039 | 1.500 139±0.025 399 | 0.154 576±0.001 463 | 1 000.00±29.63 | 930.44±10.32 | 926.56±8.17 | |||
| 9 | 570 | 871 | 0.65 | 0.072 671±0.001 129 | 1.533 127±0.027 094 | 0.152 402±0.001 352 | 1 005.56±31.48 | 943.75±10.86 | 914.41±7.57 | |||
| 11 | 614 | 896 | 0.69 | 0.097 284±0.001 131 | 3.598 950±0.046 454 | 0.267 513±0.002 156 | 1 572.53±21.76 | 1 549.30±10.26 | 1 528.17±10.96 | |||
| 14 | 2 119 | 662 | 3.20 | 0.064 143±0.001 041 | 0.993 233±0.015 529 | 0.112 186±0.000 638 | 746.30±33.33 | 700.37±7.91 | 685.43±3.70 | |||
| 15 | 536 | 507 | 1.06 | 0.059 697±0.001 110 | 0.838 994±0.016 053 | 0.101 737±0.000 750 | 592.31±40.73 | 618.59±8.86 | 624.58±4.39 | |||
| 16 | 432 | 551 | 0.78 | 0.064 711±0.001 099 | 1.103 915±0.019 405 | 0.123 530±0.000 941 | 764.82±236.11 | 755.24±9.37 | 750.85±5.40 | |||
| 样品 | 编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeOT | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 54.67 | 0.81 | 15.72 | 7.09 | 0.13 | 7.61 | 7.83 | 2.8 | 2.06 | 0.17 | 1.24 | 100.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 54.07 | 0.80 | 15.16 | 7.67 | 0.12 | 8.28 | 7.54 | 2.88 | 2.02 | 0.17 | 1.47 | 100.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 54.39 | 0.80 | 15.48 | 7.67 | 0.13 | 7.84 | 7.35 | 2.83 | 2.05 | 0.17 | 1.37 | 100.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 54.31 | 0.80 | 15.46 | 7.74 | 0.12 | 7.85 | 7.32 | 2.88 | 2.09 | 0.17 | 1.33 | 100.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 60.55 | 0.73 | 16.86 | 5.65 | 0.11 | 3.05 | 5.93 | 3.20 | 2.19 | 0.40 | 0.99 | 99.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 60.28 | 0.71 | 17.00 | 5.59 | 0.11 | 3.23 | 5.92 | 3.30 | 2.17 | 0.39 | 0.96 | 99.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 60.52 | 0.65 | 17.17 | 5.47 | 0.13 | 3.14 | 5.96 | 3.10 | 2.11 | 0.40 | 0.96 | 99.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | 编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 28.7 | 51.8 | 6.44 | 24.5 | 4.41 | 1.11 | 3.51 | 0.62 | 3.19 | 0.63 | 1.73 | 0.31 | 1.80 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 24.3 | 40.6 | 5.25 | 19.5 | 3.51 | 0.87 | 2.89 | 0.49 | 2.50 | 0.50 | 1.35 | 0.25 | 1.52 | 0.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 27.0 | 49.9 | 6.13 | 24.0 | 4.38 | 1.23 | 3.77 | 0.58 | 3.25 | 0.62 | 1.76 | 0.28 | 1.81 | 0.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 26.7 | 50.7 | 6.12 | 23.4 | 4.39 | 1.25 | 3.82 | 0.60 | 3.27 | 0.62 | 1.77 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 35.4 | 65.4 | 7.65 | 29.0 | 5.07 | 1.65 | 4.36 | 0.62 | 3.26 | 0.63 | 1.83 | 0.28 | 1.77 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 35.6 | 65.5 | 7.62 | 28.8 | 5.05 | 1.62 | 4.33 | 0.61 | 3.24 | 0.62 | 1.81 | 0.27 | 1.76 | 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 36.8 | 67.6 | 7.91 | 29.7 | 5.26 | 1.72 | 4.50 | 0.64 | 3.40 | 0.65 | 1.87 | 0.29 | 1.84 | 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | 编号 | Y | Ba | Rb | Th | Nb | U | Ta | Sr | Zr | Hf | Pb | Sc | V | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 16.5 | 570 | 61.3 | 8.00 | 8.97 | 1.81 | 0.90 | 530 | 164 | 4.51 | 12.7 | 22.2 | 174 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 13.1 | 589 | 65.0 | 7.89 | 8.73 | 1.73 | 0.50 | 533 | 125 | 3.35 | 12.4 | 23.2 | 163 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 17.2 | 549 | 66.2 | 7.51 | 8.04 | 1.59 | 0.51 | 509 | 167 | 4.40 | 13.0 | 25.4 | 146 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 17.5 | 556 | 65.1 | 7.36 | 8.27 | 1.48 | 0.51 | 515 | 164 | 4.30 | 11.0 | 20.3 | 142 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 17.8 | 766 | 71.9 | 6.43 | 17.4 | 1.31 | 1.21 | 810 | 126 | 3.46 | 21.6 | 11.9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 17.8 | 757 | 71.8 | 6.44 | 17.5 | 1.33 | 1.15 | 810 | 128 | 3.49 | 20.8 | 11.7 | 098 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 18.5 | 910 | 70.7 | 6.70 | 17.7 | 1.37 | 1.17 | 818 | 130 | 3.56 | 21.5 | 12.5 | 105 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | 编号 | Cr | Co | Ni | (La/Yb)N | Eu/Eu* | Sr/Y | La/Yb | Nb/Yb | Th/Yb | Zr/Yb | Th/Nb | U/Th | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 369 | 33.1 | 147 | 11.42 | 0.84 | 32.09 | 15.92 | 4.98 | 4.44 | 91.34 | 0.89 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 353 | 34.3 | 148 | 11.47 | 0.81 | 40.82 | 15.99 | 5.75 | 5.19 | 82.04 | 0.90 | 0.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 424 | 34.6 | 134 | 10.70 | 0.90 | 29.53 | 14.91 | 4.43 | 4.14 | 92.35 | 0.93 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 415 | 33.8 | 128 | 10.54 | 0.91 | 29.34 | 14.70 | 4.55 | 4.04 | 90.27 | 0.89 | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 32.8 | 16.4 | 18.2 | 14.35 | 1.05 | 45.51 | 20.00 | 9.83 | 3.63 | 71.19 | 0.37 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 34.3 | 15.7 | 17.7 | 14.51 | 1.03 | 45.51 | 20.23 | 9.94 | 3.66 | 72.73 | 0.37 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 36.1 | 20.5 | 19.1 | 14.35 | 1.05 | 44.22 | 20.00 | 9.62 | 3.64 | 70.65 | 0.38 | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表2 玉林和连平安山岩主量元素(%)、稀土元素(10-6)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Analysis results of major elements (%), REE(10-6) and trace elements(10-6) of the Cretaceous andesites in Yulin and Lianping
| 样品 | 编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeOT | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 54.67 | 0.81 | 15.72 | 7.09 | 0.13 | 7.61 | 7.83 | 2.8 | 2.06 | 0.17 | 1.24 | 100.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 54.07 | 0.80 | 15.16 | 7.67 | 0.12 | 8.28 | 7.54 | 2.88 | 2.02 | 0.17 | 1.47 | 100.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 54.39 | 0.80 | 15.48 | 7.67 | 0.13 | 7.84 | 7.35 | 2.83 | 2.05 | 0.17 | 1.37 | 100.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 54.31 | 0.80 | 15.46 | 7.74 | 0.12 | 7.85 | 7.32 | 2.88 | 2.09 | 0.17 | 1.33 | 100.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 60.55 | 0.73 | 16.86 | 5.65 | 0.11 | 3.05 | 5.93 | 3.20 | 2.19 | 0.40 | 0.99 | 99.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 60.28 | 0.71 | 17.00 | 5.59 | 0.11 | 3.23 | 5.92 | 3.30 | 2.17 | 0.39 | 0.96 | 99.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 60.52 | 0.65 | 17.17 | 5.47 | 0.13 | 3.14 | 5.96 | 3.10 | 2.11 | 0.40 | 0.96 | 99.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | 编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 28.7 | 51.8 | 6.44 | 24.5 | 4.41 | 1.11 | 3.51 | 0.62 | 3.19 | 0.63 | 1.73 | 0.31 | 1.80 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 24.3 | 40.6 | 5.25 | 19.5 | 3.51 | 0.87 | 2.89 | 0.49 | 2.50 | 0.50 | 1.35 | 0.25 | 1.52 | 0.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 27.0 | 49.9 | 6.13 | 24.0 | 4.38 | 1.23 | 3.77 | 0.58 | 3.25 | 0.62 | 1.76 | 0.28 | 1.81 | 0.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 26.7 | 50.7 | 6.12 | 23.4 | 4.39 | 1.25 | 3.82 | 0.60 | 3.27 | 0.62 | 1.77 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 35.4 | 65.4 | 7.65 | 29.0 | 5.07 | 1.65 | 4.36 | 0.62 | 3.26 | 0.63 | 1.83 | 0.28 | 1.77 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 35.6 | 65.5 | 7.62 | 28.8 | 5.05 | 1.62 | 4.33 | 0.61 | 3.24 | 0.62 | 1.81 | 0.27 | 1.76 | 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 36.8 | 67.6 | 7.91 | 29.7 | 5.26 | 1.72 | 4.50 | 0.64 | 3.40 | 0.65 | 1.87 | 0.29 | 1.84 | 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | 编号 | Y | Ba | Rb | Th | Nb | U | Ta | Sr | Zr | Hf | Pb | Sc | V | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 16.5 | 570 | 61.3 | 8.00 | 8.97 | 1.81 | 0.90 | 530 | 164 | 4.51 | 12.7 | 22.2 | 174 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 13.1 | 589 | 65.0 | 7.89 | 8.73 | 1.73 | 0.50 | 533 | 125 | 3.35 | 12.4 | 23.2 | 163 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 17.2 | 549 | 66.2 | 7.51 | 8.04 | 1.59 | 0.51 | 509 | 167 | 4.40 | 13.0 | 25.4 | 146 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 17.5 | 556 | 65.1 | 7.36 | 8.27 | 1.48 | 0.51 | 515 | 164 | 4.30 | 11.0 | 20.3 | 142 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 17.8 | 766 | 71.9 | 6.43 | 17.4 | 1.31 | 1.21 | 810 | 126 | 3.46 | 21.6 | 11.9 | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 17.8 | 757 | 71.8 | 6.44 | 17.5 | 1.33 | 1.15 | 810 | 128 | 3.49 | 20.8 | 11.7 | 098 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 18.5 | 910 | 70.7 | 6.70 | 17.7 | 1.37 | 1.17 | 818 | 130 | 3.56 | 21.5 | 12.5 | 105 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | 编号 | Cr | Co | Ni | (La/Yb)N | Eu/Eu* | Sr/Y | La/Yb | Nb/Yb | Th/Yb | Zr/Yb | Th/Nb | U/Th | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 玉林 | LC1-1 | 369 | 33.1 | 147 | 11.42 | 0.84 | 32.09 | 15.92 | 4.98 | 4.44 | 91.34 | 0.89 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC4-1 | 353 | 34.3 | 148 | 11.47 | 0.81 | 40.82 | 15.99 | 5.75 | 5.19 | 82.04 | 0.90 | 0.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-1 | 424 | 34.6 | 134 | 10.70 | 0.90 | 29.53 | 14.91 | 4.43 | 4.14 | 92.35 | 0.93 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LC2-2 | 415 | 33.8 | 128 | 10.54 | 0.91 | 29.34 | 14.70 | 4.55 | 4.04 | 90.27 | 0.89 | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 连平 | LP4-1 | 32.8 | 16.4 | 18.2 | 14.35 | 1.05 | 45.51 | 20.00 | 9.83 | 3.63 | 71.19 | 0.37 | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-1b | 34.3 | 15.7 | 17.7 | 14.51 | 1.03 | 45.51 | 20.23 | 9.94 | 3.66 | 72.73 | 0.37 | 0.21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LP4-2 | 36.1 | 20.5 | 19.1 | 14.35 | 1.05 | 44.22 | 20.00 | 9.62 | 3.64 | 70.65 | 0.38 | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
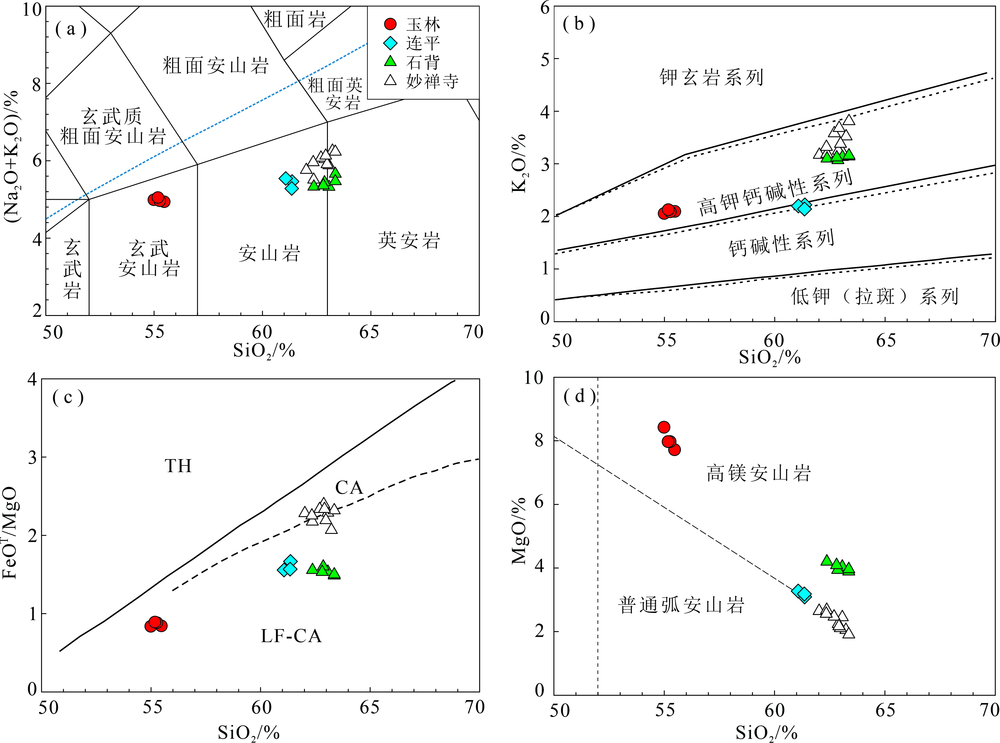
图4 白垩纪安山岩样品主量元素特征图解 (a)TAS图解,底图据文献[39],碱性-亚碱性系列界线据文献[40];(b)K2O-SiO2图解,底图据文献[41];(c)SiO2-FeOT/MgO图解,底图据文献[42];(d)SiO2-MgO图解,普通弧-高镁安山岩界线据文献[43]。石背和妙禅寺样品均为仁化地区的安山岩,数据来自文献[6]
Fig.4 Major element characteristics of Cretaceous andesite samples
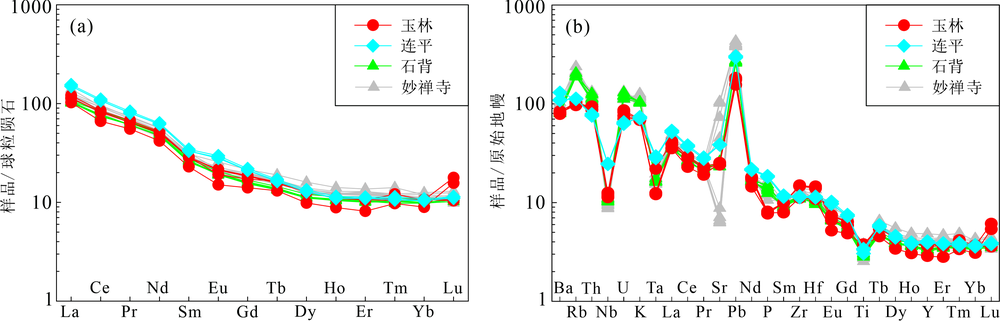
图5 安山岩样品稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b) 球粒陨石标准化值和原始地幔标准化值均据文献[44];石背和妙禅寺样品均为仁化地区的安山岩,数据来自文献[6]
Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram (b) of the andesite samples
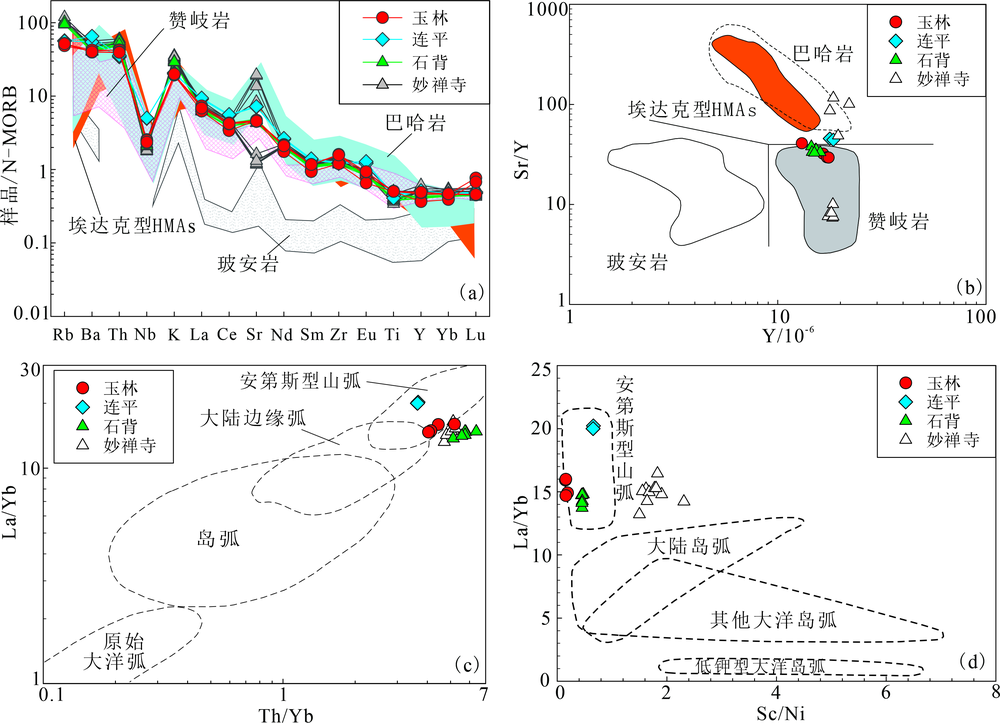
图6 高镁安山岩类型判别图和构造背景判别图 (a)安山岩微量元素N-MORB标准化蛛网图,N-MORB标准化值均据文献[54],底图据文献[55];(b)安山岩Sr/Y-Y判别图,修改自文献[36];(c)安山岩La/Yb-Th/Yb判别图解,底图据文献[56];(d)安山岩La/Yb-Sc/Ni判别图,底图据文献[57]。石背和妙禅寺样品均为仁化地区的安山岩,数据来自文献[6]
Fig.6 High-Mg andesite type and tectonic discrimination diagrams of the andesite samples
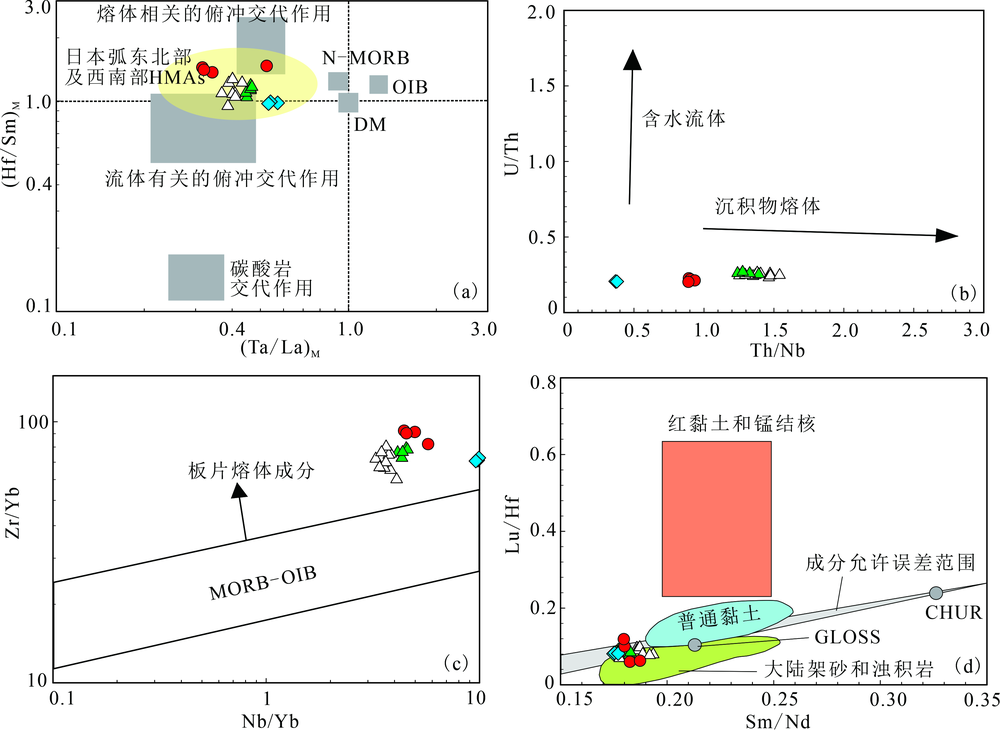
图7 安山岩样品源区性质判别图 (a) (Ta/La)M-(Hf/Sm)M 判别图,修改自文献[50],原始地幔标准化值均据文献[47],日本弧东北部和西南部HMAs数据据文献[36, 63-65];(b) U/Th-Th/Nb 判别图,修改自文献[52];(c) Zr/Yb-Nb/Yb判别图,修改自文献[53];(d) Lu/Hf-Sm/Nd判别图,修改自文献[66],GLOSS代表全球俯冲沉积物[67],CHUR代表球粒陨石储库,${{f}_{\text{Lu}}}_{/\text{Hf}}$/${{f}_{\text{Sm}}}_{/\text{Nd}}$范围为1.3~1.7[67]。石背和妙禅寺样品均为仁化地区的安山岩,数据来自文献[6]
Fig.7 Magmatic source discrimination diagrams of the andesite samples
| [1] |
LI J H, ZHANG Y Q, DONG S W, et al. Cretaceous tectonic evolution of South China: A preliminary synjournal[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 134:98-136.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LI Z, QIU J S, YANG X M. A review of the geochronology and geochemistry of Late Yanshanian (Cretaceous) plutons along the Fujian coastal area of southeastern China: Implications for magma evolution related to slab break-off and rollback in the Cretaceous[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 128:232-248.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 毛建仁, 高桥浩, 厉子龙, 等. 中国东南部与日本中—新生代构造-岩浆作用对比研究[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(7):844-856. |
| [4] |
CHEN C H, LEE C Y, LU H Y, et al. Generation of Late Cretaceous silicic rocks in SE China: Age, major element and numerical simulation constraints[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 31(4/5/6):479-498.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 邱检生, 王德滋, 周金城. 福建永泰云山晚中生代双峰式火山岩的地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1999, 18(2):97-107. |
| [6] | 蒋英, 梁新权, 梁细荣, 等. 粤北仁化白垩纪安山玢岩锆石年代学、地球化学和岩石成因研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(3):481-496. |
| [7] | 耿红燕, 徐夕生, O’REILLY S Y, 等. 粤西白垩纪火山-侵入岩浆活动及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2006, 36(7):601-617. |
| [8] | 潘登, 吴仁贵, 邓伟强, 等. 水汶盆地碎斑熔岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 36(1):25-34. |
| [9] | 林义华, 吕昭英, 袁勤敏, 等. 琼北儋州市洛基地区早白垩世火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2019, 35(4):399-409. |
| [10] | 周云, 梁新权, 梁细荣, 等. 海南白垩纪六罗村组火山岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(5):903-918. |
| [11] |
ZHOU Y, LIANG X Q, KRÖNER A, et al. Late Cretaceous lithospheric extension in SE China: Constraints from volcanic rocks in Hainan Island[J]. Lithos, 2015, 232:100-110.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 方念乔. “海南陆缘弧”体系的构建与“特提斯南海”的识别: 一个关于“古南海”演化新模式的探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6):107-119. |
| [13] | 闵慧, 任建业, 高金耀, 等. 南海北部古俯冲带的位置及其对南海扩张的控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(4):599-605. |
| [14] | 张丽鹏. 特提斯闭合与白垩纪成矿: 以阳春盆地为例[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2017. |
| [15] | 强萌麟. 南海北部陆缘白垩纪安山岩基本特征及其与东南沿海安山岩对比[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [16] | 韩琦. 南海北部陆缘中、新生代流纹岩基本特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. |
| [17] | 梁飞刚. 琼南晚燕山期花岗岩研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [18] | 董海龙. 琼南—越南白垩纪花岗岩岩石地球化学特征与古南海构造演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [19] | 袁晓博, 方念乔, 董海龙. 海南岛高峰、保城地区花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1):85-97. |
| [20] | 汤稚音. 南海北缘陆相盆地白垩系沉积学与地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [21] | 梁霄. 茂名盆地晚中生代沉积记录与古南海演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [22] | 贾磊. 三水盆地与茂名盆地白垩系构造沉积特征及其对古南海俯冲的响应[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [23] |
YU J H, O’REILLY Y S, WANG L J, et al. Finding of ancient materials in Cathaysia and implication for the formation of Precambrian crust[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(1):13-22.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YU J H, WANG L J, O’REILLY S Y, et al. A Paleoproterozoic orogeny recorded in a long-lived cratonic remnant (Wuyishan terrane), eastern Cathaysia Block, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 174(3/4):347-363.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YU J H, O’REILLY S Y, WANG L J, et al. Components and episodic growth of Precambrian crust in the Cathaysia Block, South China: Evidence from U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of zircons in Neoproterozoic sediments[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 181(1/2/3/4):97-114.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LIU X, GAO S, DIWU C, et al. Precambrian crustal growth of Yangtze Craton as revealed by detrital zircon studies[J]. American Journal of Science, 2008, 308(4):421-468.
DOI URL |
| [27] | WANG Y J, ZHANG F F, FAN W M, et al. Tectonic setting of the South China Block in the Early Paleozoic: Resolving intracontinental and ocean closure models from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2010, 29(6): TC6020. |
| [28] | 广西壮族自治区地质矿产局. 广西壮族自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 351-355. |
| [29] | 广东省地质矿产局. 广东省区域地质志 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 320-322. |
| [30] | 巫建华, 周维勋, 章邦桐. 江西及广东北部中生代晚期地层层序和时代: 兼论《江西省岩石地层》中存在的问题[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(1):44-53. |
| [31] |
LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-north China orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2):537-571.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4):481-492. |
| [33] |
BELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 巫建华, 徐勋胜, 刘帅. 赣南-粤北地区晚白垩世早期长英质火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(8):1296-1305. |
| [35] | 劳玉军, 巫建华, 徐勋胜. 粤北长塘盆地晚白垩世早期流纹岩的成因: 地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O同位素制约[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5):558-567. |
| [36] |
TATSUMI Y. High-Mg andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, Southwestern Japan: analogy to Archean magmatism and continental crust formation?[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2006, 34(1):467-499.
DOI URL |
| [37] | CRAWFORD A J, FALLOON T J, GREEN D H. Classification petrogenesis and tectonic setting of boninites[M]//CRAWFORD A J.Boninites [M]. London: Academic Division of Unwin Hyaman, Ltd, 1989: 1-49. |
| [38] |
SAUNDERS A D, ROGERS G, MARRINER G F, et al. Geochemistry of Cenezoic volcanic rocks, Baja California, Mexico: Implications for the petrogenesis of post-subduction magmas[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1987, 32(1/2/3):223-245.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8(5):523-548.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等. 高镁安山岩/闪长岩类(HMA)和镁安山岩/闪长岩类(MA): 与洋俯冲作用相关的两类典型的火成岩类[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4):1112-1118. |
| [43] |
MCCARRON J J, SMELLIE J L. Tectonic implications of fore-arc magmatism and generation of high-magnesian andesites: Alexander Island, Antarctica[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1998, 155(2):269-280.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347:662-665.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
SHIMODA G, TATSUMI Y, NOHDA S, et al. Setouchi high-Mg andesites revisited: Geochemical evidence for melting of subducting sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 160(3/4):479-492.
DOI URL |
| [47] | TATSUMI Y, EGGINS S. Subduction Zone Magmatism[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1995: 211. |
| [48] | KELEMEN P B, HANGHØJ K, GREENE A R. One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[M]// Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007: 1-70. |
| [49] |
MCCULLOCH M T, GAMBLE J A. Geochemical and geodynamical constraints on subduction zone magmatism[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 102(3/4):358-374.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
LA FLÈCHE M R, CAMIRÉ G, JENNER G A. Geochemistry of post-Acadian, Carboniferous continental intraplate basalts from the Maritimes Basin, Magdalen Islands, Québec, Canada[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 148(3/4):115-136.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TURNER S, CAULFIELD J, TURNER M, et al. Recent contribution of sediments and fluids to the mantle’s volatile budget[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(1):50-54.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
KOHUT E J, STERN R J, KENT A J R, et al. Evidence for adiabatic decompression melting in the Southern Mariana Arc from high-Mg lavas and melt inclusions[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 152(2):201-221.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
PEARCE J A, PEATE D W. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic ARC Magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1995, 23(1):251-285.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
HOFMANN A W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: the relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3):297-314.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
KAMEI A, OWADA M, NAGAO T, et al. High-Mg diorites derived from sanukitic HMA magmas, Kyushu Island, southwest Japan arc: evidence from clinopyroxene and whole rock compositions[J]. Lithos, 2004, 75(3/4):359-371.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
CONDIE K C. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of early Proterozoic supracrustal rocks in the southwestern United States[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1986, 94(6):845-864.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
BAILEY J C. Geochemical criteria for a refined tectonic discrimination of orogenic andesites[J]. Chemical Geology, 1981, 32(1/2/3/4):139-154.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 326(3/4):269-287.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
ZHOU X M, SUN T, SHEN W Z, et al. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 2006, 29(1):26-33.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
WONG J, SUN M, XING G F, et al. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of the Baijuhuajian metaluminous A-type granite: Extension at 125-100 Ma and its tectonic significance for South China[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4):289-305.
DOI URL |
| [61] | 张倩, 吴湘滨, 杨牧, 等. 福建紫金山矿集区浸铜湖花岗斑岩的成因及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5):1025-1035. |
| [62] | 陈卫锋, 陈培荣, 徐夕生, 等. 华南白垩纪玄武质岩石的地球化学特征及其对太平洋板块俯冲作用的制约[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2005, 35(11):1007-1018. |
| [63] |
SHINJO R. Geochemistry of high Mg andesites and the tectonic evolution of the Okinawa Trough-Ryukyu arc system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 157(1/2):69-88.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
TSUCHIYA N, SUZUKI S, KIMURA J I, et al. Evidence for slab melt/mantle reaction: Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous and Eocene high-Mg andesites from the Kitakami Mountains, Japan[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(1/2):179-206.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
SATO M, SHUTO K, NOHARA-IMANAKA R, et al. Repeated magmatism at 34 Ma and 23-20 Ma producing high magnesian adakitic andesites and transitional basalts on southern Okushiri Island, NE Japan arc[J]. Lithos, 2014, 205:60-83.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
PLANK T, LANGMUIR C H. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 145(3/4):325-394.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
PATCHETT P J, WHITE W M, FELDMANN H, et al. Hafnium/rare earth element fractionation in the sedimentary system and crustal recycling into the Earth’s mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 69(2):365-378.
DOI URL |
| [68] | 夏戡原, 黄慈流. 南海中生代特提斯期沉积盆地的发现与找寻中生代含油气盆地的前景[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(3):227-238. |
| [69] | 颜佳新, 周蒂. 南海北部陆缘区中特提斯构造演化研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(4):49-54. |
| [70] | 邵磊, 尤洪庆, 郝沪军, 等. 南海东北部中生界岩石学特征及沉积环境[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(2):164-169. |
| [71] | 肖昌浩, 申玉科, 韦昌山, 等. 广西右江褶皱带东南缘西大明山矿集区燕山期酸性岩浆锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素和Ce(Ⅳ)/Ce(Ⅲ)特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(2):289-304. |
| [72] | 朱伟林, 解习农, 王振峰, 等. 南海西沙隆起基底成因新认识[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(12):1460-1468. |
| [73] |
ZHANG L P, HU Y B, LIANG J L, et al. Adakitic rocks associated with the Shilu copper-molybdenum deposit in the Yangchun Basin, South China, and their tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2017, 36(2):132-150.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
SUN S J, ZHANG L P, ZHANG R Q, et al. Mid-Late Cretaceous igneous activity in South China: The Qianjia example, Hainan island[J]. International Geology Review, 2018, 60(11/12/13/14):1665-1683.
DOI URL |
| [75] | 唐功建, 王强. 高镁安山岩及其地球动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(8):2495-2512. |
| [76] |
KELEMEN P B. Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 120(1):1-19.
DOI URL |
| [77] | TATSUMI Y, HANYU T. Geochemical modeling of dehydration and partial melting of subducting lithosphere: Toward a comprehensive understanding of high-Mg andesite formation in the Setouchi volcanic belt, SW Japan[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(9):1081. |
| [78] |
ROGERS G, SAUNDERS A D, TERRELL D J, et al. Geochemistry of Holocene volcanic rocks associated with ridge subduction in Baja California, Mexico[J]. Nature, 1985, 315:389-392.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
GUIVEL C, LAGABRIELLE Y, BOURGOIS J, et al. New geochemical constraints for the origin of ridge-subduction-related plutonic and volcanic suites from the Chile Triple Junction (Taitao Peninsula and Site 862, LEG ODP141 on the Taitao Ridge)[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 311(1/2/3/4):83-111.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
MICHAUD F, ROYER J Y, BOURGOIS J, et al. Oceanic-ridge subduction vs. slab break off: Plate tectonic evolution along the Baja California Sur continental margin since 15 Ma[J]. Geology, 2006, 34(1):13.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
WANG Q, LI X H, JIA X H, et al. Late Early Cretaceous adakitic granitoids and associated magnesian and potassium-rich mafic enclaves and dikes in the Tunchang-Fengmu area, Hainan Province (South China): Partial melting of lower crust and mantle, and magma hybridization[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328:222-243.
DOI URL |
| [82] | 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 等. 冈底斯岩浆弧的形成与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(2):275-294. |
| [83] |
JIANG Z Q, WANG Q, LI Z X, et al. Late Cretaceous (ca. 90 Ma) adakitic intrusive rocks in the Kelu area, Gangdese Belt (southern Tibet): Slab melting and implications for Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53:67-81.
DOI URL |
| [84] | 徐倩, 曾令森, 高家昊, 等. 西藏南部冈底斯南缘松卡晚白垩世埃达克质高镁闪长岩地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(2):455-471. |
| [85] |
ZHANG L L, ZHU D C, WANG Q, et al. Late Cretaceous volcanic rocks in the Sangri area, southern Lhasa Terrane, Tibet: Evidence for oceanic ridge subduction[J]. Lithos, 2019, 326/327:144-157.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 刘光祥. 峨眉山地幔柱主要研究进展及四川盆地二叠纪成盆动力学机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1089-1099. |
| [2] | 刘冬梅, 康志强, 杨锋, 李岱鲜. 桂西南早中生代流纹岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 981-996. |
| [3] | 张宇, 唐名鹰, 崔霄峰, 何玉良, 董卫东. 西昆仑东段苏巴什洋向北俯冲:来自早—中二叠世火山岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 763-775. |
| [4] | 郭硕, 何鹏, 刘洋, 滕飞, 胡晓佳, 王文龙, 杨泽黎. 内蒙古别鲁乌图铜多金属矿床锆石U-Pb年龄和S、Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 40-50. |
| [5] | 柴云, 赵娟, 李德彪, 马正婷, 安朝, 魏有宁, 王成勇. 南祁连擦勒特地区志留纪巴龙贡嘎尔组火山岩地球化学特征及其地质意义(撤回)[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 64-73. |
| [6] | 周能武, 陈邦学, 邓中飞, 桑明帅, 白权金. 喀拉昆仑火烧云一带早侏罗世双峰式火山岩的发现及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 990-1002. |
| [7] | 赵亚云, 杨春四, 吕金梁, 刘晓峰, 刘波, 郑常云, 刘远超, 李莉, 付海龙. 西藏罗布真矿区林子宗群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 73-84. |
| [8] | 张耀玲, 倪晋宇, 沈燕绪, 王超群, 高万里, 胡道功. 柴北缘牦牛山组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 329-334. |
| [9] | 司志发, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 刘军港, 王健, 田明明. 江西相山铀矿田河元背地区流纹斑岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf-Sr-Nd同位素特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(01): 45-55. |
| [10] | 葛玉魁,王成善,戴紧根,李亚林. 西藏仲巴县特提斯喜马拉雅早白垩世日朗组玄武岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 69-77. |
| [11] | 崔玉良,王根厚,李典. 西藏改则热那错地区下—中侏罗统色哇组玄武岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 78-86. |
| [12] | 权瑞,董国臣,李玉成,刘昕曜,杨洋,任龙. 太行山南段洪山火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及Hf同位素组成[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(6): 1284-1295. |
| [13] | 于淼,苏新,陶春辉,武光海,李怀明,娄汉林. 西南印度洋中脊49.6°E和50.5°E区玄武岩岩石学及元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 497-508. |
| [14] | 程天赦,杨文静,王登红. 内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场大石寨组细碧-角斑岩系地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 525-536. |
| [15] | 崔晓庄,江新胜,王剑,卓皆文,熊国庆,陆俊泽. 滇中新元古代澄江组层型剖面锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 547-556. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||