



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (06): 1608-1621.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.124
第鹏飞1( ), 汤庆艳2, 刘聪2, 宋宏2,3,4, 张家和2, 刘东晓5, 王玉玺6, 蒲万峰6
), 汤庆艳2, 刘聪2, 宋宏2,3,4, 张家和2, 刘东晓5, 王玉玺6, 蒲万峰6
收稿日期:2021-09-10
修回日期:2021-10-11
出版日期:2021-12-10
发布日期:2022-02-14
作者简介:第鹏飞,男,高级工程师,1985年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学,主要从事矿产资源储量评审和矿床学研究。Email: 236749076@qq.com。
基金资助:
DI Pengfei1( ), TANG Qingyan2, LIU Cong2, SONG Hong2,3,4, ZHANG Jiahe2, LIU Dongxiao5, WANG Yuxi6, PU Wanfeng6
), TANG Qingyan2, LIU Cong2, SONG Hong2,3,4, ZHANG Jiahe2, LIU Dongxiao5, WANG Yuxi6, PU Wanfeng6
Received:2021-09-10
Revised:2021-10-11
Online:2021-12-10
Published:2022-02-14
摘要:
西秦岭造山带发育有大量三叠纪的金矿床,早子沟和加甘滩金矿床是其中最典型的两个矿床,其金资源量分别为116 t和154 t,均为特大型金矿床。早子沟、加甘滩金矿床均位于夏河—合作区域性逆冲推覆断裂以南。早子沟赋矿地层为三叠统古浪堤组,赋矿岩石为泥质板岩、条带状硅质板岩及粉砂质板岩;加甘滩矿区出露地层为三叠统隆务河组,金矿体赋存于长石石英变砂岩夹粉砂质板岩岩性段内。加甘滩金矿床的研究程度相对较低,属中低温构造蚀变岩型金矿床;早子沟金矿床研究程度较高,但是对它的成因仍有不同的认识。石英的微量元素地球化学特征能够提供成矿流体来源与演化的信息,通过对早子沟和加甘滩金矿床开展石英的微量元素地球化学特征研究,探讨其成矿流体来源、成矿条件以及石英微量元素对金矿床形成的指示,为西秦岭造山带金矿床成因研究提供重要的信息。早子沟和加甘滩金矿床不同类型矿石中石英具有相似的稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线,总体表现出轻稀土元素相对富集、重稀土元素轻微亏损的特征,而且轻稀土元素与重稀土元素分馏程度高,重稀土元素内部分馏程度弱。 早子沟金矿床成矿期热液石英中Rb与Li呈负相关,Rb与Cs呈正相关,而加甘滩金矿床热液石英中Rb与Li、Cs相关性不明显,表明早子沟金矿床石英中Li含量随流体含量的增加而减少,而Cs含量随流体含量的增加而增加。大多数样品具有Eu负异常和弱的Ce正异常,表明早子沟和加甘滩金矿床形成于还原环境,成矿温度较低。样品的(La/Yb)N较大,反映成矿深度相对较浅。石英的Y/Ho值分别为25.14~30.14和23.40~28.94,指示成矿流体与地壳关系密切。大多数石英样品的Th/La和 Nb/La 值小于1,在大陆地壳标准化图解中具有明显的Sc负异常,Cr、W、Pb和U正异常,表明成矿流体富Cl-,相对富集Cr、W、Pb和U等元素。结合大地构造背景分析,早子沟和加甘滩金矿形成于大陆边缘环境。
中图分类号:
第鹏飞, 汤庆艳, 刘聪, 宋宏, 张家和, 刘东晓, 王玉玺, 蒲万峰. 西秦岭夏河—合作地区早子沟和加甘滩金矿床石英微量元素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1608-1621.
DI Pengfei, TANG Qingyan, LIU Cong, SONG Hong, ZHANG Jiahe, LIU Dongxiao, WANG Yuxi, PU Wanfeng. Trace Element Characteristics of Quartz from the Zaozigou and Jiagantan Gold Deposits in the Xiahe-Hezuo District, West Qinling[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1608-1621.

图1 夏河—合作地区金矿床的分布图[41,42,43] 1.第四系;2.新近系;3.上三叠统;4.中—上三叠统;5.二叠系;6.石炭系;7.白垩纪玄武岩;8.三叠纪火山岩;9.印支期花岗岩;10.中酸性脉岩;11.断裂;12.角度不整合界线;13.金矿;14.铜矿;15.铅矿;16.锑矿;17.汞矿;18.铁矿;19.铁铜矿;20.铜钼矿;21.铜钨矿;22.多金属矿
Fig.1 Geologic map of the major gold deposits in the Xiahe-Hezuo region[41,42,43]
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 矿床 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cd | Rb | Sr | Y | Cs | W | Mo | Sb | Bi | Ba | Zr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZD① | 花岗斑岩 | 早子沟 | 2.57 | 0.062 | 0.042 | 0.433 | 4.370 | 0.103 | 0.871 | 1.570 | 16.60 | 7.96 | 0.015 | 2.830 | 3.30 | 0.200 | 0.320 | 0.396 | 1.770 | 10.5 | 0.042 | 11.40 | 8.3 | |
| ZH② | 花岗斑岩 | 3.15 | 0.119 | 0.265 | 1.120 | 1.250 | 0.337 | 1.010 | 4.450 | 22.40 | 3.77 | 0.017 | 6.370 | 13.70 | 0.908 | 0.605 | 0.883 | 0.393 | 17.0 | 0.473 | 17.10 | 16.0 | ||
| ZH③ | 板岩 | 26.80 | 0.195 | 0.047 | 0.762 | 9.860 | 0.071 | 0.872 | 1.090 | 5.08 | 20.10 | 0.049 | 1.440 | 8.85 | 0.262 | 0.261 | 0.635 | 0.300 | 23.5 | 0.020 | 5.97 | 0.8 | ||
| ZH④ | 石英脉 | 31.90 | 0.358 | 0.003 | 0.196 | 0.447 | 0.068 | 0.654 | 0.175 | 2.28 | 2.16 | n.d. | 0.893 | 2.43 | 0.090 | 0.337 | 0.102 | 0.078 | 124.0 | 0.010 | 5.18 | 0.7 | ||
| ZH⑤ | 石英脉 | 18.30 | 0.161 | 0.017 | 0.337 | 6.030 | 0.089 | 0.921 | 0.381 | 10.40 | 5.68 | 0.018 | 0.973 | 2.40 | 0.085 | 0.208 | 59.400 | 0.358 | 24.8 | 0.013 | 3.89 | 0.4 | ||
| ZH⑥ | 碳酸盐脉 | 14.10 | 0.176 | 0.079 | 1.310 | 2.220 | 0.218 | 7.310 | 3.310 | 16.90 | 4.05 | 0.009 | 3.320 | 5.98 | 0.176 | 0.337 | 1.600 | 0.069 | 274.0 | 0.112 | 9.04 | 1.6 | ||
| JH① | 蚀变细 粒长英 质砂岩 | 加甘滩 | 5.05 | 0.032 | 0.019 | 0.310 | 0.383 | 0.071 | 0.371 | 0.443 | 4.74 | 5.69 | n.d. | 0.801 | 1.32 | 0.109 | 0.129 | 0.200 | 0.038 | 20.90 | 10.100 | 5.08 | 4.8 | |
| JH② | 3.75 | 0.021 | 0.029 | 0.386 | 0.378 | 0.232 | 0.405 | 4.360 | 2.98 | 5.18 | n.d. | 0.847 | 1.64 | 0.117 | 0.124 | 0.226 | 0.043 | 28.60 | 9.810 | 5.99 | 1.0 | |||
| JH③ | 1.54 | 0.035 | n.d. | 0.307 | 0.459 | 0.097 | 0.445 | 2.470 | 2.26 | 10.60 | 0.007 | 0.457 | 9.38 | 0.040 | 0.131 | 0.837 | 4.290 | 214.00 | 2.230 | 6.49 | 0.4 | |||
| JH④ | 5.72 | 0.115 | 0.084 | 0.404 | 0.373 | 0.066 | 0.352 | 0.519 | 0.34 | 2.68 | n.d. | 0.654 | 23.40 | 0.463 | 0.129 | 0.415 | 0.048 | 8.06 | 0.021 | 3.13 | 0.2 | |||
| JH⑤ | 石英脉 | 6.54 | 0.053 | 0.051 | 0.476 | 0.426 | 0.237 | 0.747 | 2.180 | 7.18 | 34.40 | 0.065 | 0.710 | 12.60 | 0.286 | 0.156 | 0.206 | 0.042 | 13.10 | 0.033 | 7.77 | 0.5 | ||
| JH⑥ | 石英脉 | 4.42 | 0.050 | 0.004 | 0.571 | 0.487 | 0.152 | 1.400 | 0.835 | 1.03 | 5.40 | 0.005 | 0.779 | 5.02 | 0.101 | 0.145 | 0.283 | 0.199 | 14.70 | 0.036 | 6.23 | 0.8 | ||
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 矿床 | Nb | Ga | Tl | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Th | U | |
| ZD① | 花岗斑岩 | 早子沟 | 0.169 | 0.391 | 0.044 | 0.329 | 0.670 | 0.074 | 0.284 | 0.054 | 0.013 | 0.050 | 0.007 | 0.039 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.251 | 0.060 | 0.163 | 0.2 | |
| ZH② | 花岗斑岩 | 0.430 | 0.848 | 0.041 | 3.970 | 7.560 | 0.800 | 2.860 | 0.492 | 0.070 | 0.440 | 0.050 | 0.219 | 0.035 | 0.095 | 0.011 | 0.067 | 0.010 | 0.474 | 0.105 | 1.600 | 0.4 | ||
| ZH③ | 板岩 | 0.119 | 0.173 | 0.016 | 1.100 | 2.150 | 0.236 | 0.835 | 0.152 | 0.030 | 0.120 | 0.013 | 0.055 | 0.010 | 0.027 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.029 | 0.020 | 0.375 | 0.1 | ||
| ZH④ | 石英脉 | 0.029 | 0.088 | 0.015 | 0.068 | 0.142 | 0.017 | 0.074 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0.009 | n.d. | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.027 | 0.1 | ||
| ZH⑤ | 石英脉 | 0.018 | 0.079 | 0.014 | 0.088 | 0.173 | 0.018 | 0.077 | 0.018 | 0.009 | 0.028 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.011 | n.d. | 0.007 | n.d. | 0.013 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.1 | ||
| ZH⑥ | 碳酸盐脉 | 0.180 | 0.513 | 0.039 | 0.682 | 1.230 | 0.123 | 0.415 | 0.054 | 0.012 | 0.056 | 0.005 | 0.032 | 0.007 | 0.022 | n.d. | 0.022 | 0.004 | 0.053 | 0.027 | 0.142 | 0.1 | ||
| JH① | 蚀变细 粒长英 质砂岩 | 加甘滩 | 0.049 | 0.098 | 0.011 | 0.086 | 0.170 | 0.019 | 0.070 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.003 | 0.140 | 0.016 | 0.104 | 1.8 | |
| JH② | 0.074 | 0.102 | 0.010 | 0.127 | 0.265 | 0.031 | 0.112 | 0.023 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.044 | 0.1 | |||
| JH③ | 0.035 | 0.056 | 0.011 | 0.158 | 0.294 | 0.032 | 0.111 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.017 | n.d. | 0.008 | n.d. | 0.005 | n.d. | 0.006 | n.d. | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.055 | 0 | |||
| JH④ | 0.023 | 0.044 | 0.011 | 0.033 | 0.089 | 0.036 | 0.101 | 0.037 | 0.013 | 0.074 | 0.013 | 0.082 | 0.016 | 0.040 | 0.006 | 0.032 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 0.197 | 0.1 | |||
| JH⑤ | 石英脉 | 0.040 | 0.076 | 0.018 | 0.387 | 0.811 | 0.094 | 0.347 | 0.062 | 0.017 | 0.069 | 0.010 | 0.057 | 0.010 | 0.030 | 0.004 | 0.025 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.157 | 6.0 | ||
| JH⑥ | 石英脉 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 0.014 | 0.645 | 1.300 | 0.148 | 0.524 | 0.063 | 0.009 | 0.042 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.003 | 0.023 | 0.014 | 0.176 | 0.4 | ||
表1 早子沟和加甘滩金矿床不同矿石中石英稀土和微量元素组成(10-6)
Table 1 REE and trace element concentrations of quartz for different ores from the Zaozigou and Jiagantan gold deposits(10-6)
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 矿床 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cd | Rb | Sr | Y | Cs | W | Mo | Sb | Bi | Ba | Zr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZD① | 花岗斑岩 | 早子沟 | 2.57 | 0.062 | 0.042 | 0.433 | 4.370 | 0.103 | 0.871 | 1.570 | 16.60 | 7.96 | 0.015 | 2.830 | 3.30 | 0.200 | 0.320 | 0.396 | 1.770 | 10.5 | 0.042 | 11.40 | 8.3 | |
| ZH② | 花岗斑岩 | 3.15 | 0.119 | 0.265 | 1.120 | 1.250 | 0.337 | 1.010 | 4.450 | 22.40 | 3.77 | 0.017 | 6.370 | 13.70 | 0.908 | 0.605 | 0.883 | 0.393 | 17.0 | 0.473 | 17.10 | 16.0 | ||
| ZH③ | 板岩 | 26.80 | 0.195 | 0.047 | 0.762 | 9.860 | 0.071 | 0.872 | 1.090 | 5.08 | 20.10 | 0.049 | 1.440 | 8.85 | 0.262 | 0.261 | 0.635 | 0.300 | 23.5 | 0.020 | 5.97 | 0.8 | ||
| ZH④ | 石英脉 | 31.90 | 0.358 | 0.003 | 0.196 | 0.447 | 0.068 | 0.654 | 0.175 | 2.28 | 2.16 | n.d. | 0.893 | 2.43 | 0.090 | 0.337 | 0.102 | 0.078 | 124.0 | 0.010 | 5.18 | 0.7 | ||
| ZH⑤ | 石英脉 | 18.30 | 0.161 | 0.017 | 0.337 | 6.030 | 0.089 | 0.921 | 0.381 | 10.40 | 5.68 | 0.018 | 0.973 | 2.40 | 0.085 | 0.208 | 59.400 | 0.358 | 24.8 | 0.013 | 3.89 | 0.4 | ||
| ZH⑥ | 碳酸盐脉 | 14.10 | 0.176 | 0.079 | 1.310 | 2.220 | 0.218 | 7.310 | 3.310 | 16.90 | 4.05 | 0.009 | 3.320 | 5.98 | 0.176 | 0.337 | 1.600 | 0.069 | 274.0 | 0.112 | 9.04 | 1.6 | ||
| JH① | 蚀变细 粒长英 质砂岩 | 加甘滩 | 5.05 | 0.032 | 0.019 | 0.310 | 0.383 | 0.071 | 0.371 | 0.443 | 4.74 | 5.69 | n.d. | 0.801 | 1.32 | 0.109 | 0.129 | 0.200 | 0.038 | 20.90 | 10.100 | 5.08 | 4.8 | |
| JH② | 3.75 | 0.021 | 0.029 | 0.386 | 0.378 | 0.232 | 0.405 | 4.360 | 2.98 | 5.18 | n.d. | 0.847 | 1.64 | 0.117 | 0.124 | 0.226 | 0.043 | 28.60 | 9.810 | 5.99 | 1.0 | |||
| JH③ | 1.54 | 0.035 | n.d. | 0.307 | 0.459 | 0.097 | 0.445 | 2.470 | 2.26 | 10.60 | 0.007 | 0.457 | 9.38 | 0.040 | 0.131 | 0.837 | 4.290 | 214.00 | 2.230 | 6.49 | 0.4 | |||
| JH④ | 5.72 | 0.115 | 0.084 | 0.404 | 0.373 | 0.066 | 0.352 | 0.519 | 0.34 | 2.68 | n.d. | 0.654 | 23.40 | 0.463 | 0.129 | 0.415 | 0.048 | 8.06 | 0.021 | 3.13 | 0.2 | |||
| JH⑤ | 石英脉 | 6.54 | 0.053 | 0.051 | 0.476 | 0.426 | 0.237 | 0.747 | 2.180 | 7.18 | 34.40 | 0.065 | 0.710 | 12.60 | 0.286 | 0.156 | 0.206 | 0.042 | 13.10 | 0.033 | 7.77 | 0.5 | ||
| JH⑥ | 石英脉 | 4.42 | 0.050 | 0.004 | 0.571 | 0.487 | 0.152 | 1.400 | 0.835 | 1.03 | 5.40 | 0.005 | 0.779 | 5.02 | 0.101 | 0.145 | 0.283 | 0.199 | 14.70 | 0.036 | 6.23 | 0.8 | ||
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 矿床 | Nb | Ga | Tl | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Th | U | |
| ZD① | 花岗斑岩 | 早子沟 | 0.169 | 0.391 | 0.044 | 0.329 | 0.670 | 0.074 | 0.284 | 0.054 | 0.013 | 0.050 | 0.007 | 0.039 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.251 | 0.060 | 0.163 | 0.2 | |
| ZH② | 花岗斑岩 | 0.430 | 0.848 | 0.041 | 3.970 | 7.560 | 0.800 | 2.860 | 0.492 | 0.070 | 0.440 | 0.050 | 0.219 | 0.035 | 0.095 | 0.011 | 0.067 | 0.010 | 0.474 | 0.105 | 1.600 | 0.4 | ||
| ZH③ | 板岩 | 0.119 | 0.173 | 0.016 | 1.100 | 2.150 | 0.236 | 0.835 | 0.152 | 0.030 | 0.120 | 0.013 | 0.055 | 0.010 | 0.027 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.029 | 0.020 | 0.375 | 0.1 | ||
| ZH④ | 石英脉 | 0.029 | 0.088 | 0.015 | 0.068 | 0.142 | 0.017 | 0.074 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0.009 | n.d. | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.027 | 0.1 | ||
| ZH⑤ | 石英脉 | 0.018 | 0.079 | 0.014 | 0.088 | 0.173 | 0.018 | 0.077 | 0.018 | 0.009 | 0.028 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.011 | n.d. | 0.007 | n.d. | 0.013 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.1 | ||
| ZH⑥ | 碳酸盐脉 | 0.180 | 0.513 | 0.039 | 0.682 | 1.230 | 0.123 | 0.415 | 0.054 | 0.012 | 0.056 | 0.005 | 0.032 | 0.007 | 0.022 | n.d. | 0.022 | 0.004 | 0.053 | 0.027 | 0.142 | 0.1 | ||
| JH① | 蚀变细 粒长英 质砂岩 | 加甘滩 | 0.049 | 0.098 | 0.011 | 0.086 | 0.170 | 0.019 | 0.070 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.003 | 0.140 | 0.016 | 0.104 | 1.8 | |
| JH② | 0.074 | 0.102 | 0.010 | 0.127 | 0.265 | 0.031 | 0.112 | 0.023 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.044 | 0.1 | |||
| JH③ | 0.035 | 0.056 | 0.011 | 0.158 | 0.294 | 0.032 | 0.111 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.017 | n.d. | 0.008 | n.d. | 0.005 | n.d. | 0.006 | n.d. | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.055 | 0 | |||
| JH④ | 0.023 | 0.044 | 0.011 | 0.033 | 0.089 | 0.036 | 0.101 | 0.037 | 0.013 | 0.074 | 0.013 | 0.082 | 0.016 | 0.040 | 0.006 | 0.032 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 0.197 | 0.1 | |||
| JH⑤ | 石英脉 | 0.040 | 0.076 | 0.018 | 0.387 | 0.811 | 0.094 | 0.347 | 0.062 | 0.017 | 0.069 | 0.010 | 0.057 | 0.010 | 0.030 | 0.004 | 0.025 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.157 | 6.0 | ||
| JH⑥ | 石英脉 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 0.014 | 0.645 | 1.300 | 0.148 | 0.524 | 0.063 | 0.009 | 0.042 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.003 | 0.023 | 0.014 | 0.176 | 0.4 | ||
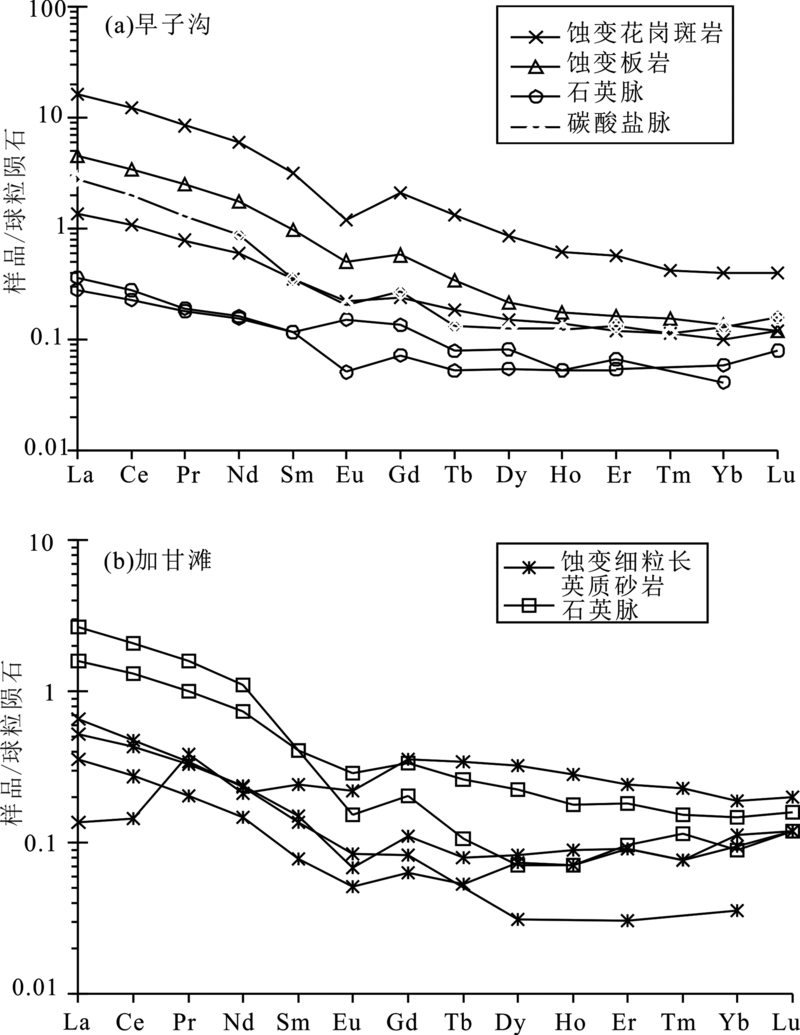
图4 早子沟(a)和加甘滩(b)金矿床不同矿石中石英微量元素原始地幔标准化配分曲线(球粒陨石数据引自Palme 和 O’Neill[48])
Fig.4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the quartz for different ores from the Zaozigou(a) and Jiagantan(b) gold deposits (chondrite-normalized data after ref. [48])

图5 早子沟(a)和加甘滩(b)金矿床石英微量元素大陆地壳标准化曲线(大陆地壳数据引自文献[49])
Fig.5 Continental crust-normalized trace element patterns for the quartz from the Zaozigou (a) and Jiagantan (b) gold deposits (continental data after ref.[49])
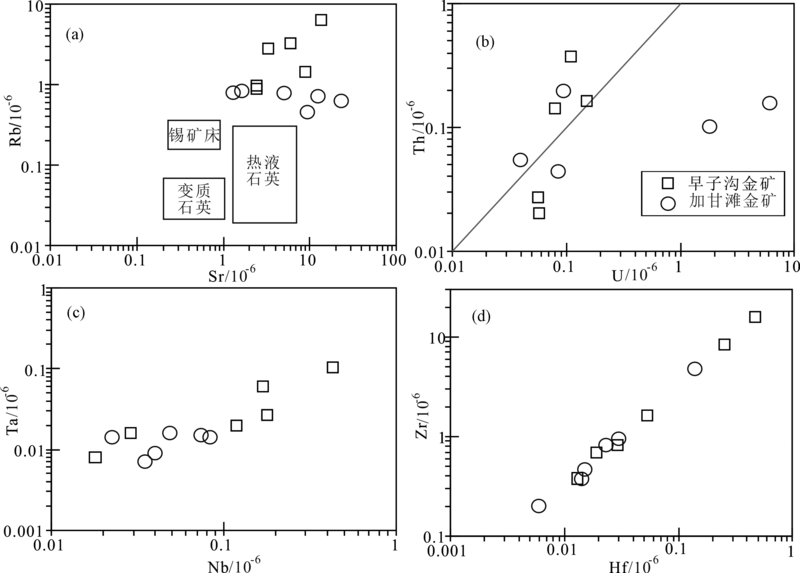
图7 早子沟和加甘滩金矿床石英Sr与Rb(a)、U与Th(b)、Nb与Ta (c)、Hf与Zr(d)含量的相关性图解(锡矿床、变质石英和热液石英的范围来自Monecke et al. [57] )
Fig.7 Plots of Sr vs. Rb(a), U vs.Th (b), Nb vs. Ta (c), and Hf vs. Zr (d) of quartz from the Zaozigou and Jiagantan gold deposits (other data from ref. [57])
| [1] |
WATT G R, WRIGHT P, GALLOWAY S, et al. Cathodoluminescence and trace element zoning in quartz phenocrysts and xenocrysts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(20):4337-4348.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GÖTZE J, PLÖTZE M, HABERMANN D. Origin, spectral characteristics and practical applications of the cathodoluminescence (CL) of quartz—a review[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2001, 71(3/4):225-250.
DOI URL |
| [3] | LEHMANN G. On the colour centres of iron in amethyst and synthetic quartz: A discussion[J]. American Mineralogist, 1975, 60:335-337. |
| [4] |
WEIL J A. A review of electron spin spectroscopy and its application to the study of paramagnetic defects in crystalline quartz[J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 1984, 10(4):149-165.
DOI URL |
| [5] | PAGEL M, BARBIN V, BLANC P, et al. Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2000: 1-21. |
| [6] |
GÖTZE J. Chemistry, textures and physical properties of quartz—geological interpretation and technical application[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2009, 73(4):645-671.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 郭林楠, 黄春梅, 张良, 等. 胶东罗山金矿床成矿流体来源: 蚀变岩型和石英脉型矿石载金黄铁矿稀土与微量元素特征约束[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1):121-136. |
| [8] |
RUSK B G. Intensity of quartz cathodoluminescence and trace-element content in quartz from the porphyry copper deposit at Butte, Montana[J]. American Mineralogist, 2006, 91(8/9):1300-1312.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 陈小丹, 陈振宇, 程彦博, 等. 热液石英中微量元素特征及应用: 认识与进展[J]. 地质论评, 2011, 57(5):707-717. |
| [10] | 申俊峰, 李胜荣, 黄绍锋, 等. 成因矿物学与找矿矿物学研究进展(2010—2020)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(3):610-623,777. |
| [11] |
CAO Y, LI S R, YAO M J, et al. Significance of quartz REE geochemistry, Shihu gold deposit, western Hebei Province, North China, using LA-ICP-MS[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 2010, 4(3):337-344.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
BREITER K, BADANINA E, URIŠOVÁ J, et al. Chemistry of quartz-A new insight into the origin of the Orlovka Ta-Li deposit, Eastern Transbaikalia, Russia[J]. Lithos, 2019, 348/349:105206.
DOI URL |
| [13] | ZHAO X F, LI Y Y. The significance and application of researching trace element in quartz[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(suppl.):295. |
| [14] | 李学刚, 杨坤光, 王军. 东秦岭—大别造山带南、北缘晚白垩世以来构造演化的石英ESR年代学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2):308-316. |
| [15] | 何忠庠, 陈友良, 常丹, 等. 若尔盖510-1铀矿床方解石、石英微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 黑龙江冶金, 2015, 35(4):12-17. |
| [16] | 陈衍景. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4):854-865. |
| [17] |
LI N, DENG J, YANG L Q, et al. Paragenesis and geochemistry of ore minerals in the epizonal gold deposits of the Yangshan gold belt, West Qinling, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2014, 49(4):427-449.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 李楠, 杨立强, 张闯, 等. 西秦岭阳山金矿带硫同位素特征: 成矿环境与物质来源约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):1577-1587. |
| [19] |
HAN J S, YAO J M, CHEN Y J. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Dashui adakitic granitoids in the western Qinling Orogen, central China: Implications for Triassic tectonic setting[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49(4/5):383-401.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
PENG X H, YANG H, ZHANG J S. Geology, geochemistry, and genesis of the Dashui Carlin-type gold deposit in the West Qinling orogenic belt, Gansu Province, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53(3):835-856.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 蒲万峰, 李鸿睿, 袁臻, 等. 甘肃省玛曲县大水金矿“三位一体”找矿预测地质模型[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(8):1163-1172. |
| [22] | 李林积, 李堂积, 王丹. 西秦岭大水金矿床方解石Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(3):469-475. |
| [23] | 赵彦庆, 叶得金, 李永琴, 等. 西秦岭大水金矿的花岗岩成矿作用特征[J]. 现代地质, 2003, 17(2):151-156. |
| [24] |
LIU J J, DAI H Z, ZHAI D G, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the Zhaishang Carlin-like type gold deposit, western Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 64:273-298.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 赵福德, 黄菲, 高尚, 等. 甘肃寨上金矿黄铁矿特征与成因[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(6):637-648. |
| [26] |
SUI J X, LI J W, JIN X Y, et al. 40Ar/39Ar and U-Pb constraints on the age of the Zaozigou gold deposit, Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China: Relation to Early Triassic reduced intrusions emplaced during slab rollback[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101:885-899.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
TANG Q Y, DI P F, YU M, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of pyrite and arsenopyrite from the zaozigou gold deposit in west Qinling orogenic belt, central China: Implications for ore genesis[J]. Resource Geology, 2019, 69(3):314-332.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
QIU K F, YU H C, DENG J, et al. The giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China: Magmatic-or metamorphic-hydrothermal origin?[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 55(2):345-362.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 曹晓峰, MOHAMED L S S, 吕新彪, 等. 甘肃枣子沟金矿床成矿过程分析: 来自矿床地质特征、金的赋存状态及稳定同位素证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(4):1039-1054. |
| [30] | 陈瑞莉, 陈正乐, 伍俊杰, 等. 甘肃合作早子沟金矿床流体包裹体及硫铅同位素特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(1):87-104. |
| [31] | 刘东晓, 第鹏飞, 张鑫, 等. 甘肃早子沟金矿矿床成因: 来自流体包裹体及H-O-S同位素的证据[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(2):168-175. |
| [32] | 代文军, 史文全, 李鸿睿, 等. 加甘滩金矿床地质特征及矿床成因初探[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(1):18-22. |
| [33] | 田向盛, 第鹏飞, 刘东晓, 等. 甘肃加甘滩金矿床金的赋存状态研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2016, 24(3):40-51. |
| [34] | 罗高培. 加甘滩金矿床成矿过程分析:来自岩石地球化学及金赋存状态的证据[J]. 甘肃科技, 2016, 32(13):17-22. |
| [35] | 白云, 李鸿睿, 史文全, 等. 甘肃加甘滩超大型金矿床矿化富集规律及控矿因素[J]. 金属矿山, 2017(6):117-124. |
| [36] | 李俊. 西秦岭造山带加甘滩金矿床变质砂岩特征及其物源区判别[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [37] |
DU B S, SHEN J F, SANTOSH M, et al. Textural, compositional and isotopic characteristics of pyrite from the Zaozigou gold deposit in West Qinling, China: Implications for gold metallogeny[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 130:103917.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 代文军, 陈耀宇. 甘肃枣子沟金矿区中性岩脉与成矿关系[J]. 黄金, 2012, 33(1):19-24. |
| [39] | 刘勇, 刘云华, 董福辰, 等. 甘肃枣子沟金矿床成矿时代精确测定及其地质意义[J]. 黄金, 2012, 33(11):10-17. |
| [40] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化、构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1):1-10. |
| [41] |
MENG Q R, ZHANG G W. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 323(3/4):183-196.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1):1-28. |
| [43] | 李康宁, 李鸿睿, 贾儒雅, 等. 甘肃早子沟金矿“三位一体”找矿预测地质模型的构建[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(6):1397-1408. |
| [44] | 姚书振, 丁振举, 周宗桂, 等. 秦岭造山带金属成矿系统[J]. 地球科学, 2002, 27(5):599-604. |
| [45] |
ZHANG G W. Mianlüe tectonic zone and Mianlüe suture zone on southern margin of Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2004, 47(4):300.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 梁志录, 李鸿睿, 姜桂鹏, 等. 甘肃省合作市早子沟金矿资源储量核实(接替资源勘查)报告[R]. 兰州:甘肃省地质矿产勘查开发局第三地质矿产勘查院, 2017. |
| [47] | 田向盛, 李鸿睿, 史文全, 等. 夏河县加甘滩金矿资源储量核实暨扩大区勘探报告[R]. 兰州:甘肃省地质矿产勘查开发局第三地质矿产勘查院, 2016. |
| [48] | PALME H, O'NEILL H S C. Cosmochemical estimates of mantle composition[M]//RICHARD W C. Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 1-38. |
| [49] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[M]//RICHARD W C.Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 1-51. |
| [50] | 张德贤, 戴塔根, RUSK B G. 石英研究进展[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(2):333-341. |
| [51] | 陈剑锋, 张辉. 石英晶格中微量元素组成对成岩成矿作用的示踪意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2011, 17(1):125-135. |
| [52] |
GÖTZE J, PLÖTZE M, GRAUPNER T, et al. Trace element incorporation into quartz: A combined study by ICP-MS, electron spin resonance, cathodoluminescence, capillary ion analysis, and gas chromatography[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(18):3741-3759.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
GÖTTE T, PETTKE T, RAMSEYER K, et al. Cathodoluminescence properties and trace element signature of hydrothermal quartz: A fingerprint of growth dynamics[J]. American Mineralogist, 2011, 96(5/6):802-813.
DOI URL |
| [54] | 赵振华. 微量元素地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. |
| [55] | GERLER J, SCHNIER C. Neutron activation analysis of liquid inclusions exemplified by a quartz sample from the Ramsbeck Mine[J]. Nuclear Geophysics, 1989, 3 :41-48. |
| [56] |
ROSSMAN G R, WEIS D, WASSERBURG G J. Rb, Sr, Nd and Sm concentrations in quartz[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(9):2325-2329.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
MONECKE T, KEMPE U, GÖTZE J. Genetic significance of the trace element content in metamorphic and hydrothermal quartz: A reconnaissance study[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 202(3/4):709-724.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
RUSK B G, LOWERS H A, REED M H. Trace elements in hydrothermal quartz: Relationships to cathodoluminescent textures and insights into vein formation[J]. Geology, 2008, 36:547.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 徐莉, 孙晓明, 汤倩, 等. CCSD HP-UHP变质岩中石英脉微量元素和稀土元素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(12):3287-3294. |
| [60] | 唐宏, 张辉. 可可托海3号伟晶岩脉石英中微量元素组成特征与岩浆-热液演化[J]. 矿物学报, 2018, 38(1):15-24. |
| [61] |
MURRAY R W, TENBRINK M R B, GERLACH D C, et al. Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environments in chert and shale[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(3):268.
DOI URL |
| [62] | 王京彬, 李朝阳. 金顶超大型铅锌矿床REE地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 1991, 20(4):359-365. |
| [63] | 宋国瑞, 赵振华. 河北省东坪碱性杂岩金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1996. |
| [64] | 吕俊男, 李峰, 张志发, 等. 云南易门铜厂矿床脉石矿物稀土元素研究[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 2017, 29(1):81-86. |
| [65] |
HAAS J R, SHOCK E L, SASSANI D C. Rare earth elements in hydrothermal systems: Estimates of standard partial molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous complexes of the rare earth elements at high pressures and temperatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(21):4329-4350.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
ORESKES N, EINAUDI M T. Origin of rare earth element-enriched hematite breccias at the Olympic Dam Cu-U-Au-Ag deposit, Roxby Downs, South Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 1990, 85(1):1-28.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
KEPPLER H. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction-zone fluids[J]. Nature, 1996, 380:237-240.
DOI URL |
| [68] | 王可新, 王建平, 曾祥涛, 等. 陕西双王金矿床成矿流体的性质:来自黄铁矿微量元素的证据[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 31(增):510-511. |
| [69] | SHANNON R D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section A, 1976, A32:751-767. |
| [70] |
POKROVSKI G S, TAGIROV B R, SCHOTT J, et al. An in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of gold-chloride complexing in hydrothermal fluids[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 259(1/2):17-29.
DOI URL |
| [71] | 刘家军, 刘冲昊, 王建平, 等. 西秦岭地区金矿类型及其成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5):1-16. |
| [72] | 第鹏飞. 西秦岭夏河—合作早子沟金矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018. |
| [1] | 胡生平, 韩善楚, 张洪求, 张勇, 潘家永, 钟福军, 卢建研, 李惟鑫. 庐枞盆地西湾铅锌矿床黄铁矿微量元素组成特征及成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 183-197. |
| [2] | 刘金波, 张德贤, 胡子奇, 陈绍炜, 谢小雨. 豫西熊耳山蒿坪沟Ag-Au-Pb-Zn多金属矿床闪锌矿矿物学和微量元素组成特征及其成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 198-213. |
| [3] | 张靓, 陈奇, 高添, 李雯, 钱金龙, 刘俐君, 王长明. 三江特提斯马厂箐斑岩铜钼矿床成矿时间尺度探讨:来自石英中Ti-Al扩散年代学的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1509-1523. |
| [4] | 师良, 范柏江, 王霞, 李亚婷, 黄飞飞, 戴欣洋. 鄂尔多斯盆地长9页岩烃源岩的元素组成及其古沉积环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1254-1263. |
| [5] | 陈全红, 阳怀忠, 赵红岩, 张科, 黄海滨, 郭家铭, 刘新颖, 袁野. 加蓬盆地盐下裂谷期碎屑岩储层地球化学特征及物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1385-1397. |
| [6] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [7] | 李慧, 温汉辉, 蔡立梅, 徐耀辉, 罗杰, 梅敬娴, 徐述邦. 广东省揭阳市揭东区微量元素分布特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(01): 208-216. |
| [8] | 翟佳宇, 张松航, 唐书恒, 郭慧秋, 刘冰, 纪朝琪. 云南老厂雨汪煤层气区块气水成因及产能响应[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1341-1350. |
| [9] | 付嵩, 李社宏, 马文恩, 蒋超, 谢卓麟, 吴金铭, 胡煦阚, 张紫桐. 广西龙围地区石英脉型铜矿中硫化物Re-Os测年及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1146-1154. |
| [10] | 杨培奇, 刘敬党, 刘淑梅, 杨飞, 杨孝伟. 内蒙古乌拉特中旗大乌淀石墨矿床石英片岩地球化学特征与SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 672-681. |
| [11] | 丁坤, 王瑞廷, 刘凯, 王智慧, 申喜茂. 南秦岭柞水—山阳矿集区夏家店金矿床黄铁矿微量元素和氢、氧、硫同位素对矿床成因的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1622-1632. |
| [12] | 陈海云, 孙晓东, 张志. 西昆仑上其木干花岗岩锆石饱和温度和Ti温度的地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1206-1217. |
| [13] | 逯永卓, 韩杰, 王明, 余福承, 王泰山, 袁博武. 柴达木盆地北缘三角顶金矿床成矿特征及其找矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1363-1370. |
| [14] | 叶枫, 董国臣, 任建勋, 龚杰立, 李猛兴, 王权, 张兆琪, 赵三波. 山西黄榆沟岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 787-797. |
| [15] | 柯昌炜, 李素梅, 张洪安, 徐田武, 张云献, 曾凡纲, 张树海, 张韩静. 东濮凹陷盐湖相烃源岩有机硫同位素分布特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 301-314. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||