



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (03): 728-751.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.112
吴晓贺1,2( ), 张聚全1,2,*(
), 张聚全1,2,*( ), 段站站1,2, 张乐民1,2, 温雨菁1,2, 郭子桤1,2, 李清1,2
), 段站站1,2, 张乐民1,2, 温雨菁1,2, 郭子桤1,2, 李清1,2
出版日期:2025-06-10
发布日期:2025-07-03
通信作者:
*张聚全,男,博士研究生,教授,1983年出生,主要从事成因矿物学、矿床学研究工作。Email:juquan1983@163.com。作者简介:吴晓贺,女,在读研究生,1998年出生,主要从事成因矿物学研究工作。Email:811209713@qq.com。
基金资助:
WU Xiaohe1,2( ), ZHANG Juquan1,2,*(
), ZHANG Juquan1,2,*( ), DUAN Zhanzhan1,2, ZHANG Lemin1,2, WEN Yujing1,2, GUO Ziqi1,2, LI Qing1,2
), DUAN Zhanzhan1,2, ZHANG Lemin1,2, WEN Yujing1,2, GUO Ziqi1,2, LI Qing1,2
Published:2025-06-10
Online:2025-07-03
摘要: 准确约束华北克拉通基底形成和变质变形年龄,是理解华北克拉通早期构造演化的关键。菅等岩体位于华北克拉通中部造山带的东南段赞皇杂岩中,为~2.5 Ga花岗岩,并经历多期变质和变形。本文对菅等岩体及侵入岩体内部的未变形伟晶岩、粗粒变形花岗岩脉、细粒变形花岗岩脉、花岗质岩株进行了系统的野外调查、岩相学、岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学研究。结果表明:菅等岩体主体岩性为正长花岗岩,未变形伟晶岩岩性为二长花岗伟晶岩,粗粒变形花岗岩脉、细粒变形花岗岩脉、花岗质岩株均为正长花岗岩;菅等岩体及其内部的侵入体具有高Si,富K,富碱,低Ti、Fe、Mg,贫Ca,富集大离子亲石元素Rb,亏损高场强元素Ti的特征,且Rb/Sr=0.75~1.56,显示出壳源特征;岩石具有的高Al低Ti特征,以及岩浆锆石高Pb低Th,均指示菅等岩体为过铝质S型花岗岩类型;对锆石进行LA-ICP-MS测定显示存在~2.5 Ga、~2.3 Ga两期的花岗岩侵入事件,岩体内部侵入活动分为三期,分别形成于~2.5 Ga、~2.3 Ga、~2.1 Ga,其中细粒变形花岗岩脉中保留了1897±17 Ma的变质事件的记录。华北克拉通的构造演化由多期次岩浆侵入与变质事件共同驱动。~2.5 Ga的菅等岩体形成标志克拉通形成统一基底,指示早期构造稳定化过程。古元古代两期花岗岩侵入(2.3 Ga和2.1 Ga)揭示克拉通内部发生裂解-伸展事件,~1.85 Ga的变质事件代表东部与西部陆块之间的俯冲碰撞过程。
中图分类号:
吴晓贺, 张聚全, 段站站, 张乐民, 温雨菁, 郭子桤, 李清. 华北克拉通中部菅等岩体的成因及构造意义: 锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 728-751.
WU Xiaohe, ZHANG Juquan, DUAN Zhanzhan, ZHANG Lemin, WEN Yujing, GUO Ziqi, LI Qing. The Genesis and Tectonic Significance of Jiandeng Intrusive Rock in the Central North China Craton: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Chronology and Petrogeochemistry[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(03): 728-751.
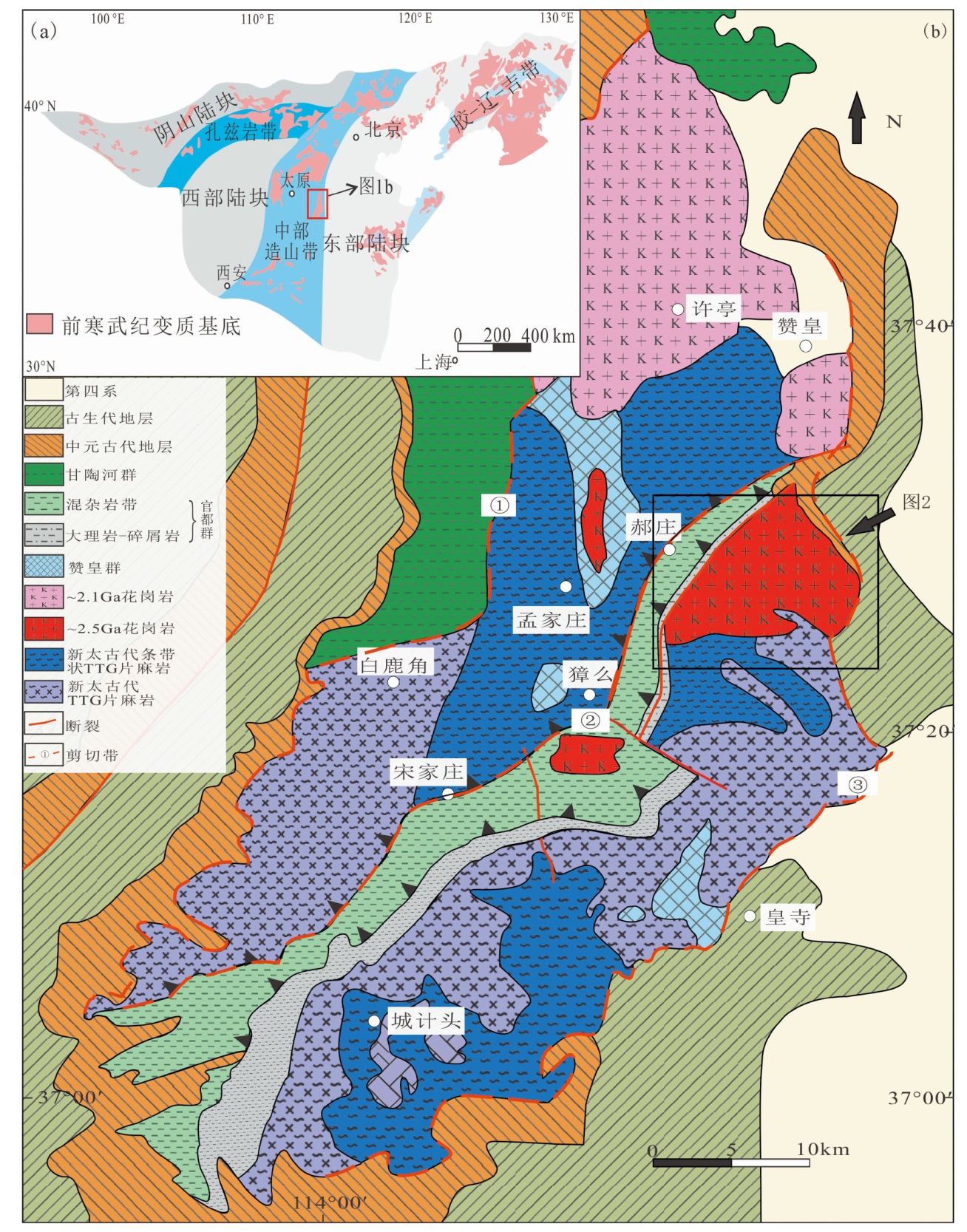
图1 华北克拉通构造单元图((a)据文献[1,41])及赞皇区域地质图((b)底图据文献[40,42-43] 修改) ①营房台—招也—障石岩—苍岩山剪切带;②邢台坡底—临城郝庄—官都剪切带;③赞皇榆底村—临城岗西—元氏黑水河剪切带
Fig.1 Diagram of the North China craton tectonic unit((a) from ref. [1,41])and geological map of the Zanhuang region((b) base map modified from ref. [40,42-43])

图3 菅等岩体野外地质特征及素描图 (a)ZH18-1、ZH18-2的野外特征素描图;(b)ZH18-1、ZH18-2野外采样位置及地质特征;(c)ZH18-3的野外特征素描图;(d)ZH18-3野外采样位置及地质特征;(e)ZH18-4的野外特征素描图;(d)ZH18-4野外采样位置及地质特征
Fig.3 Field geological characteristics and sketch map of Jiandeng intrusion

图5 岩相学特征(正交偏光) (a)ZH18-1;(b)ZH18-2;(c)、(d) ZH18-3;(e) ZH18-4;(f) ZH19-1-1b;(g)ZH19-1-2b;(h)ZH19-2b;(i)ZH19-3b Bt.黑云母;Mu.白云母;Q.石英;Mic.微斜长石;Pl.斜长石;Kfs.钾长石
Fig.5 Petrographic characteristics(cross-polarized light)
| 样品号 | 野外产出形态 | 岩性 | 矿物组合(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | P | A | |||
| ZH18-1 | 正长花岗岩 (菅等岩体) | 正长花岗岩 | 29 | 11 | 60 |
| ZH19-1-1b | 27 | 12 | 61 | ||
| ZH19-1-2b | 31 | 11 | 58 | ||
| ZH19-2b | 27 | 12 | 61 | ||
| ZH18-2 | 细粒变形花岗岩脉 | 正长花岗岩 | 29 | 15 | 56 |
| ZH18-3 | 未变形伟晶岩 | 二长花岗伟晶岩 | 31 | 37 | 32 |
| ZH18-4 | 粗粒变形花岗岩脉 | 正长花岗岩 | 30 | 10 | 60 |
| ZH19-3b | 花岗质岩株 | 正长花岗岩 | 30 | 10 | 60 |
表1 代表性样品的野外产出形态、岩性及QAP含量特征
Table 1 Morphology produced in the field, lithology and QAP assemblage characteristics of representativesamples
| 样品号 | 野外产出形态 | 岩性 | 矿物组合(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | P | A | |||
| ZH18-1 | 正长花岗岩 (菅等岩体) | 正长花岗岩 | 29 | 11 | 60 |
| ZH19-1-1b | 27 | 12 | 61 | ||
| ZH19-1-2b | 31 | 11 | 58 | ||
| ZH19-2b | 27 | 12 | 61 | ||
| ZH18-2 | 细粒变形花岗岩脉 | 正长花岗岩 | 29 | 15 | 56 |
| ZH18-3 | 未变形伟晶岩 | 二长花岗伟晶岩 | 31 | 37 | 32 |
| ZH18-4 | 粗粒变形花岗岩脉 | 正长花岗岩 | 30 | 10 | 60 |
| ZH19-3b | 花岗质岩株 | 正长花岗岩 | 30 | 10 | 60 |
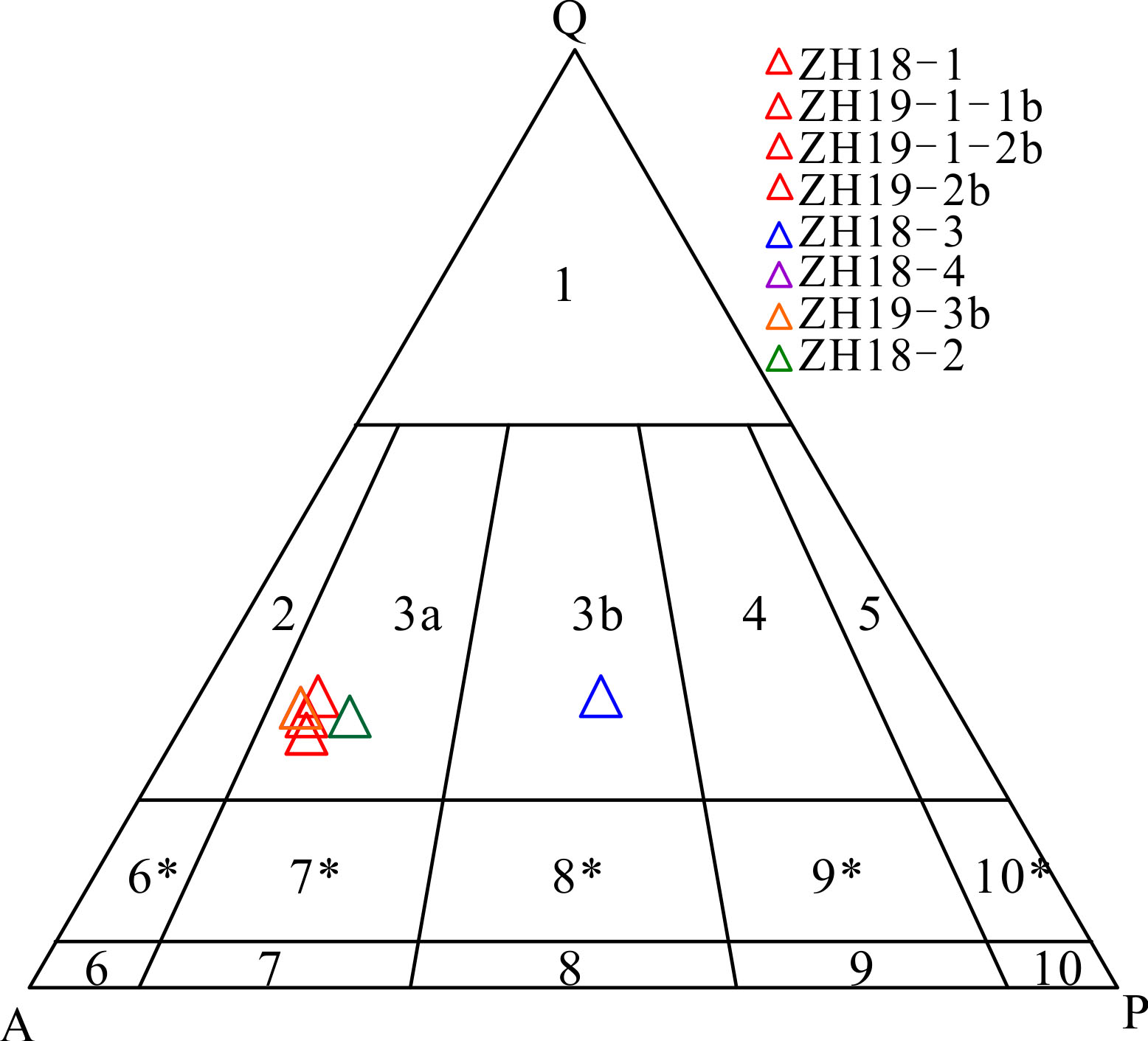
图6 菅等岩体QAP图解 1.富石英花岗岩;2.碱长花岗岩;3a.正长花岗岩;3b.二长花岗岩;4.花岗闪长岩;5.英云闪长岩:6*.石英碱长正长岩;7*.石英正长岩;8*.石英二长岩;9*.石英二长闪长岩/石英二长辉长岩;10*.闪长岩/辉长岩/斜长岩;6.碱长正长岩;7.正长岩;8.二长岩;9.二长闪长岩/二长辉长岩;10.闪长岩,辉长岩或斜长岩
Fig.6 QAP diagram of the Jiandeng intrusion
| ZH18-1 | ZH18-2 | ZH18-3 | ZH18-4 | ZH19-1-1b | ZH19-1-2b | ZH19-2b | ZH19-3b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 72.64 | 71.07 | 73.98 | 76.04 | 74.25 | 71.29 | 74.14 | 75.31 |
| TiO2 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.04 |
| Al2O3 | 14.27 | 15.17 | 14.77 | 13.43 | 13.72 | 15.36 | 13.77 | 14.10 |
| MnO | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| MgO | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.14 |
| CaO | 0.98 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 0.48 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 1.20 |
| Na2O | 3.49 | 4.09 | 4.32 | 3.44 | 3.04 | 3.22 | 3.02 | 4.36 |
| K2O | 5.57 | 4.78 | 5.02 | 5.44 | 5.48 | 6.51 | 5.51 | 3.77 |
| P2O5 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.94 | 1.06 | 1.20 | 0.40 |
| FeO | 0.61 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| 灼失量 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.46 |
| 总和 | 99.86 | 99.86 | 99.95 | 99.89 | 99.88 | 99.85 | 99.90 | 99.93 |
表2 菅等岩体、二长花岗伟晶岩、粗粒变形花岗岩脉、花岗质岩株、细粒变形花岗岩脉的全岩主量元素(%)
Table 2 The main elements of Jiandeng intrusion, monzogranite pegmatites, coarse-grained deformed granite, granitic stock and fine-grained deformed granite
| ZH18-1 | ZH18-2 | ZH18-3 | ZH18-4 | ZH19-1-1b | ZH19-1-2b | ZH19-2b | ZH19-3b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 72.64 | 71.07 | 73.98 | 76.04 | 74.25 | 71.29 | 74.14 | 75.31 |
| TiO2 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.04 |
| Al2O3 | 14.27 | 15.17 | 14.77 | 13.43 | 13.72 | 15.36 | 13.77 | 14.10 |
| MnO | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| MgO | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.14 |
| CaO | 0.98 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 0.48 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 1.20 |
| Na2O | 3.49 | 4.09 | 4.32 | 3.44 | 3.04 | 3.22 | 3.02 | 4.36 |
| K2O | 5.57 | 4.78 | 5.02 | 5.44 | 5.48 | 6.51 | 5.51 | 3.77 |
| P2O5 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.94 | 1.06 | 1.20 | 0.40 |
| FeO | 0.61 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| 灼失量 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.46 |
| 总和 | 99.86 | 99.86 | 99.95 | 99.89 | 99.88 | 99.85 | 99.90 | 99.93 |
| 成分 | ZH18-1 | ZH18-2 | ZH18-3 | ZH18-4 | ZH19-1-1b | ZH19-1-2b | ZH19-2b | ZH19-3b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | 12.18 | 12.67 | 5.14 | 3.65 | 11.25 | 11.66 | 10.19 | 5.81 |
| Be | 1.27 | 1.76 | 1.09 | 1.05 | 1.50 | 1.36 | 1.50 | 2.09 |
| Sc | 1.60 | 2.53 | 0.78 | 0.33 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 1.71 | 0.64 |
| V | 14.75 | 15.28 | 4.38 | 6.83 | 11.48 | 10.40 | 11.73 | 4.92 |
| Cr | 2.54 | 2.97 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 3.50 | 2.99 | 4.28 | 2.94 |
| Co | 1.53 | 2.41 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 1.31 | 1.58 | 1.95 | 0.90 |
| Ni | 2.44 | 10.58 | 2.58 | 1.51 | 2.98 | 2.40 | 5.29 | 2.32 |
| Cu | 3.71 | 4.26 | 3.80 | 11.69 | 4.91 | 4.87 | 7.21 | 3.57 |
| Ga | 15.40 | 15.63 | 14.89 | 13.89 | 14.23 | 15.06 | 15.71 | 16.25 |
| Rb | 128.26 | 106.96 | 136.50 | 107.57 | 134.36 | 150.29 | 177.72 | 133.65 |
| Sr | 142.77 | 143.44 | 87.35 | 122.95 | 140.19 | 167.18 | 115.08 | 138.62 |
| Zr | 189.66 | 171.95 | 44.98 | 81.40 | 165.05 | 124.89 | 115.00 | 72.38 |
| Nb | 3.17 | 6.50 | 2.31 | 0.95 | 4.44 | 3.22 | 4.67 | 2.45 |
| Mo | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 0.12 | 0.21 |
| Cd | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| In | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Cs | 3.39 | 1.93 | 3.09 | 1.84 | 5.54 | 3.13 | 4.24 | 2.36 |
| Ba | 637.19 | 574.39 | 112.60 | 466.29 | 488.58 | 704.87 | 442.66 | 244.08 |
| Hf | 5.86 | 5.50 | 1.70 | 4.11 | 5.46 | 4.08 | 4.01 | 2.69 |
| Ta | 0.31 | 0.59 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.44 |
| W | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.27 |
| Tl | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.62 | 0.44 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.64 |
| Pb | 12.55 | 12.68 | 22.51 | 10.27 | 12.43 | 16.61 | 14.93 | 20.16 |
| Bi | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| Th | 12.82 | 14.96 | 0.38 | 3.85 | 16.57 | 14.98 | 11.82 | 19.54 |
| U | 0.98 | 1.10 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 1.08 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 1.43 |
| La | 38.34 | 30.43 | 1.61 | 4.92 | 27.46 | 22.57 | 16.52 | 2.05 |
| Ce | 72.49 | 56.47 | 2.65 | 9.68 | 48.75 | 45.58 | 33.68 | 3.51 |
| Pr | 8.41 | 6.55 | 0.37 | 1.15 | 5.80 | 5.23 | 3.50 | 0.49 |
| Nd | 28.44 | 21.76 | 1.43 | 3.95 | 19.68 | 17.12 | 11.69 | 1.85 |
| Sm | 4.29 | 3.50 | 0.38 | 0.66 | 3.01 | 2.57 | 1.84 | 0.50 |
| Eu | 0.86 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.47 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.51 | 0.33 |
| Gd | 3.61 | 3.02 | 0.33 | 0.54 | 2.70 | 2.32 | 1.60 | 0.43 |
| Tb | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.08 |
| Dy | 1.08 | 1.68 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.48 |
| Ho | 0.17 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| Er | 0.58 | 0.90 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.25 |
| Tm | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| Yb | 0.47 | 0.91 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.58 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.29 |
| Lu | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Y | 4.67 | 8.03 | 3.14 | 1.14 | 4.59 | 3.43 | 3.05 | 2.58 |
| ΣREE | 159.21 | 126.82 | 8.51 | 22.06 | 110.68 | 98.13 | 71.15 | 10.43 |
| LREE | 152.83 | 119.39 | 6.66 | 20.83 | 105.32 | 93.80 | 67.75 | 8.73 |
| HREE | 6.38 | 7.44 | 1.85 | 1.23 | 5.35 | 4.33 | 3.40 | 1.70 |
| LREE/HREE | 23.97 | 16.05 | 3.60 | 16.94 | 19.67 | 21.68 | 19.90 | 5.14 |
| (La/Yb)N | 59.02 | 23.89 | 2.58 | 24.19 | 34.23 | 42.66 | 31.35 | 5.12 |
| δEu | 0.65 | 0.62 | 1.90 | 2.34 | 0.65 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 2.12 |
| δCe | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.83 |
| M | 2.59 | 2.32 | 1.41 | 1.44 | 1.29 | 1.36 | 1.28 | 1.36 |
| T(℃) | 717.75 | 727.93 | 685.51 | 727.71 | 796.66 | 767.56 | 766.47 | 724.18 |
表3 菅等岩体、二长花岗伟晶岩、粗粒变形花岗岩脉、花岗质岩株、细粒变形花岗岩脉的微量元素(10-6)
Table 3 Trace elements of Jiandeng intrusion, monzogranite pegmatites, coarse-grained deformed granite, granitic stock and fine-grained deformed granite (10-6)
| 成分 | ZH18-1 | ZH18-2 | ZH18-3 | ZH18-4 | ZH19-1-1b | ZH19-1-2b | ZH19-2b | ZH19-3b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | 12.18 | 12.67 | 5.14 | 3.65 | 11.25 | 11.66 | 10.19 | 5.81 |
| Be | 1.27 | 1.76 | 1.09 | 1.05 | 1.50 | 1.36 | 1.50 | 2.09 |
| Sc | 1.60 | 2.53 | 0.78 | 0.33 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 1.71 | 0.64 |
| V | 14.75 | 15.28 | 4.38 | 6.83 | 11.48 | 10.40 | 11.73 | 4.92 |
| Cr | 2.54 | 2.97 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 3.50 | 2.99 | 4.28 | 2.94 |
| Co | 1.53 | 2.41 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 1.31 | 1.58 | 1.95 | 0.90 |
| Ni | 2.44 | 10.58 | 2.58 | 1.51 | 2.98 | 2.40 | 5.29 | 2.32 |
| Cu | 3.71 | 4.26 | 3.80 | 11.69 | 4.91 | 4.87 | 7.21 | 3.57 |
| Ga | 15.40 | 15.63 | 14.89 | 13.89 | 14.23 | 15.06 | 15.71 | 16.25 |
| Rb | 128.26 | 106.96 | 136.50 | 107.57 | 134.36 | 150.29 | 177.72 | 133.65 |
| Sr | 142.77 | 143.44 | 87.35 | 122.95 | 140.19 | 167.18 | 115.08 | 138.62 |
| Zr | 189.66 | 171.95 | 44.98 | 81.40 | 165.05 | 124.89 | 115.00 | 72.38 |
| Nb | 3.17 | 6.50 | 2.31 | 0.95 | 4.44 | 3.22 | 4.67 | 2.45 |
| Mo | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 0.12 | 0.21 |
| Cd | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| In | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Cs | 3.39 | 1.93 | 3.09 | 1.84 | 5.54 | 3.13 | 4.24 | 2.36 |
| Ba | 637.19 | 574.39 | 112.60 | 466.29 | 488.58 | 704.87 | 442.66 | 244.08 |
| Hf | 5.86 | 5.50 | 1.70 | 4.11 | 5.46 | 4.08 | 4.01 | 2.69 |
| Ta | 0.31 | 0.59 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.44 |
| W | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.27 |
| Tl | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.62 | 0.44 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.64 |
| Pb | 12.55 | 12.68 | 22.51 | 10.27 | 12.43 | 16.61 | 14.93 | 20.16 |
| Bi | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| Th | 12.82 | 14.96 | 0.38 | 3.85 | 16.57 | 14.98 | 11.82 | 19.54 |
| U | 0.98 | 1.10 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 1.08 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 1.43 |
| La | 38.34 | 30.43 | 1.61 | 4.92 | 27.46 | 22.57 | 16.52 | 2.05 |
| Ce | 72.49 | 56.47 | 2.65 | 9.68 | 48.75 | 45.58 | 33.68 | 3.51 |
| Pr | 8.41 | 6.55 | 0.37 | 1.15 | 5.80 | 5.23 | 3.50 | 0.49 |
| Nd | 28.44 | 21.76 | 1.43 | 3.95 | 19.68 | 17.12 | 11.69 | 1.85 |
| Sm | 4.29 | 3.50 | 0.38 | 0.66 | 3.01 | 2.57 | 1.84 | 0.50 |
| Eu | 0.86 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.47 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.51 | 0.33 |
| Gd | 3.61 | 3.02 | 0.33 | 0.54 | 2.70 | 2.32 | 1.60 | 0.43 |
| Tb | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.08 |
| Dy | 1.08 | 1.68 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.48 |
| Ho | 0.17 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| Er | 0.58 | 0.90 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.25 |
| Tm | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| Yb | 0.47 | 0.91 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.58 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.29 |
| Lu | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Y | 4.67 | 8.03 | 3.14 | 1.14 | 4.59 | 3.43 | 3.05 | 2.58 |
| ΣREE | 159.21 | 126.82 | 8.51 | 22.06 | 110.68 | 98.13 | 71.15 | 10.43 |
| LREE | 152.83 | 119.39 | 6.66 | 20.83 | 105.32 | 93.80 | 67.75 | 8.73 |
| HREE | 6.38 | 7.44 | 1.85 | 1.23 | 5.35 | 4.33 | 3.40 | 1.70 |
| LREE/HREE | 23.97 | 16.05 | 3.60 | 16.94 | 19.67 | 21.68 | 19.90 | 5.14 |
| (La/Yb)N | 59.02 | 23.89 | 2.58 | 24.19 | 34.23 | 42.66 | 31.35 | 5.12 |
| δEu | 0.65 | 0.62 | 1.90 | 2.34 | 0.65 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 2.12 |
| δCe | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.83 |
| M | 2.59 | 2.32 | 1.41 | 1.44 | 1.29 | 1.36 | 1.28 | 1.36 |
| T(℃) | 717.75 | 727.93 | 685.51 | 727.71 | 796.66 | 767.56 | 766.47 | 724.18 |

图8 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分布型式图(a)及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)
Fig.8 Diagram of the standardized distribution pattern of rare earth element chondrite meteorite (a) and the normalized spider web of trace element primitive mantle (b)
| 样品号 | 含量(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | rho | 同位素年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-1 | Min | 28 | 62 | 0.15 | 0.1280 | 0.0025 | 2.3781 | 0.0436 | 0.1345 | 0.0020 | 0.6950 | 2072 | 12 | 1236 | 12 | 813 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 1729 | 1884 | 1.15 | 0.1663 | 0.0013 | 11.1929 | 0.3867 | 0.4947 | 0.0152 | 0.9586 | 2522 | 32 | 2539 | 44 | 2591 | 72 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 213 | 425 | 0.56 | 0.1562 | 0.0018 | 8.2923 | 0.1807 | 0.3767 | 0.0070 | 0.8413 | 2410 | 20 | 2197 | 19 | 2037 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH19- 1-1b | Min | 75 | 140 | 0.21 | 0.1401 | 0.0017 | 5.4676 | 0.1036 | 0.2819 | 0.0032 | 0.5330 | 2229 | 16 | 1896 | 15 | 1601 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 871 | 633 | 5.37 | 0.1643 | 0.0023 | 10.6698 | 0.2516 | 0.4723 | 0.0108 | 0.9725 | 2502 | 27 | 2495 | 38 | 2494 | 53 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 237 | 245 | 1.20 | 0.1534 | 0.0020 | 8.2413 | 0.1748 | 0.3862 | 0.0068 | 0.8044 | 2383 | 22 | 2242 | 20 | 2099 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH19- 1-2b | Min | 59 | 112 | 0.20 | 0.1272 | 0.0018 | 3.4471 | 0.0867 | 0.1953 | 0.0034 | 0.6727 | 2059 | 16 | 1515 | 15 | 1150 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 833 | 452 | 2.32 | 0.1643 | 0.0023 | 11.0064 | 0.2889 | 0.4856 | 0.0132 | 0.9952 | 2502 | 28 | 2524 | 29 | 2552 | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 218 | 267 | 0.76 | 0.1525 | 0.0021 | 8.0571 | 0.1841 | 0.3779 | 0.0073 | 0.8262 | 2375 | 23 | 2207 | 21 | 2056 | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-3 | Min | 252 | 73 | 0.15 | 0.1261 | 0.0014 | 2.3652 | 0.0292 | 0.1358 | 0.0013 | 0.7068 | 2044 | 14 | 1232 | 9 | 821 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 1538 | 2296 | 1.15 | 0.1652 | 0.0026 | 11.1065 | 0.4401 | 0.5008 | 0.0173 | 0.9573 | 2510 | 27 | 2532 | 45 | 2617 | 80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 378 | 835 | 0.52 | 0.1503 | 0.0018 | 5.8881 | 0.1528 | 0.2769 | 0.0061 | 0.8408 | 2343 | 20 | 1894 | 21 | 1556 | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-4 | Min | 20 | 150 | 0.03 | 0.1188 | 0.0013 | 1.5191 | 0.0361 | 0.0922 | 0.0015 | 0.6525 | 1939 | 11 | 938 | 10 | 569 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 2161 | 2455 | 1.07 | 0.1657 | 0.0025 | 10.2253 | 0.3616 | 0.5330 | 0.0190 | 0.9814 | 2515 | 31 | 2455 | 56 | 2754 | 80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 385 | 1357 | 0.25 | 0.1467 | 0.0017 | 5.7666 | 0.1423 | 0.2794 | 0.0061 | 0.8596 | 2302 | 20 | 1856 | 22 | 1561 | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH19-3b | Min | 64 | 117 | 0.13 | 0.1172 | 0.0017 | 1.8639 | 0.0470 | 0.1145 | 0.0022 | 0.6134 | 1914 | 22 | 1068 | 14 | 699 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 1029 | 1618 | 1.68 | 0.1598 | 0.0030 | 10.7330 | 0.2912 | 0.5214 | 0.0105 | 0.9197 | 2453 | 37 | 2500 | 48 | 2705 | 51 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 277 | 610 | 0.53 | 0.1423 | 0.0021 | 6.5445 | 0.1730 | 0.3240 | 0.0067 | 0.7679 | 2248 | 26 | 1981 | 24 | 1785 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-2 | Min | 2 | 54 | 0.03 | 0.1106 | 0.0015 | 2.6552 | 0.0795 | 0.1735 | 0.0037 | 0.6925 | 1810 | 12 | 1316 | 12 | 1032 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 969 | 1346 | 2.96 | 0.1670 | 0.0024 | 11.7878 | 0.3210 | 0.5220 | 0.0131 | 0.9595 | 2528 | 36 | 2588 | 46 | 2708 | 66 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 277 | 294 | 1.01 | 0.1506 | 0.0019 | 8.3723 | 0.1753 | 0.3944 | 0.0069 | 0.8225 | 2335 | 21 | 2227 | 19 | 2131 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
表4 锆石LA-ICP-MS测定结果数据简表
Table 4 Summary data of LA-ICP-MS zircon determination
| 样品号 | 含量(10-6) | Th/U | 同位素比值 | rho | 同位素年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-1 | Min | 28 | 62 | 0.15 | 0.1280 | 0.0025 | 2.3781 | 0.0436 | 0.1345 | 0.0020 | 0.6950 | 2072 | 12 | 1236 | 12 | 813 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 1729 | 1884 | 1.15 | 0.1663 | 0.0013 | 11.1929 | 0.3867 | 0.4947 | 0.0152 | 0.9586 | 2522 | 32 | 2539 | 44 | 2591 | 72 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 213 | 425 | 0.56 | 0.1562 | 0.0018 | 8.2923 | 0.1807 | 0.3767 | 0.0070 | 0.8413 | 2410 | 20 | 2197 | 19 | 2037 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH19- 1-1b | Min | 75 | 140 | 0.21 | 0.1401 | 0.0017 | 5.4676 | 0.1036 | 0.2819 | 0.0032 | 0.5330 | 2229 | 16 | 1896 | 15 | 1601 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 871 | 633 | 5.37 | 0.1643 | 0.0023 | 10.6698 | 0.2516 | 0.4723 | 0.0108 | 0.9725 | 2502 | 27 | 2495 | 38 | 2494 | 53 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 237 | 245 | 1.20 | 0.1534 | 0.0020 | 8.2413 | 0.1748 | 0.3862 | 0.0068 | 0.8044 | 2383 | 22 | 2242 | 20 | 2099 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH19- 1-2b | Min | 59 | 112 | 0.20 | 0.1272 | 0.0018 | 3.4471 | 0.0867 | 0.1953 | 0.0034 | 0.6727 | 2059 | 16 | 1515 | 15 | 1150 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 833 | 452 | 2.32 | 0.1643 | 0.0023 | 11.0064 | 0.2889 | 0.4856 | 0.0132 | 0.9952 | 2502 | 28 | 2524 | 29 | 2552 | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 218 | 267 | 0.76 | 0.1525 | 0.0021 | 8.0571 | 0.1841 | 0.3779 | 0.0073 | 0.8262 | 2375 | 23 | 2207 | 21 | 2056 | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-3 | Min | 252 | 73 | 0.15 | 0.1261 | 0.0014 | 2.3652 | 0.0292 | 0.1358 | 0.0013 | 0.7068 | 2044 | 14 | 1232 | 9 | 821 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 1538 | 2296 | 1.15 | 0.1652 | 0.0026 | 11.1065 | 0.4401 | 0.5008 | 0.0173 | 0.9573 | 2510 | 27 | 2532 | 45 | 2617 | 80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 378 | 835 | 0.52 | 0.1503 | 0.0018 | 5.8881 | 0.1528 | 0.2769 | 0.0061 | 0.8408 | 2343 | 20 | 1894 | 21 | 1556 | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-4 | Min | 20 | 150 | 0.03 | 0.1188 | 0.0013 | 1.5191 | 0.0361 | 0.0922 | 0.0015 | 0.6525 | 1939 | 11 | 938 | 10 | 569 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 2161 | 2455 | 1.07 | 0.1657 | 0.0025 | 10.2253 | 0.3616 | 0.5330 | 0.0190 | 0.9814 | 2515 | 31 | 2455 | 56 | 2754 | 80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 385 | 1357 | 0.25 | 0.1467 | 0.0017 | 5.7666 | 0.1423 | 0.2794 | 0.0061 | 0.8596 | 2302 | 20 | 1856 | 22 | 1561 | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH19-3b | Min | 64 | 117 | 0.13 | 0.1172 | 0.0017 | 1.8639 | 0.0470 | 0.1145 | 0.0022 | 0.6134 | 1914 | 22 | 1068 | 14 | 699 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 1029 | 1618 | 1.68 | 0.1598 | 0.0030 | 10.7330 | 0.2912 | 0.5214 | 0.0105 | 0.9197 | 2453 | 37 | 2500 | 48 | 2705 | 51 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 277 | 610 | 0.53 | 0.1423 | 0.0021 | 6.5445 | 0.1730 | 0.3240 | 0.0067 | 0.7679 | 2248 | 26 | 1981 | 24 | 1785 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ZH18-2 | Min | 2 | 54 | 0.03 | 0.1106 | 0.0015 | 2.6552 | 0.0795 | 0.1735 | 0.0037 | 0.6925 | 1810 | 12 | 1316 | 12 | 1032 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Max | 969 | 1346 | 2.96 | 0.1670 | 0.0024 | 11.7878 | 0.3210 | 0.5220 | 0.0131 | 0.9595 | 2528 | 36 | 2588 | 46 | 2708 | 66 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Avg | 277 | 294 | 1.01 | 0.1506 | 0.0019 | 8.3723 | 0.1753 | 0.3944 | 0.0069 | 0.8225 | 2335 | 21 | 2227 | 19 | 2131 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||

图12 全岩10000Ga/Al与Zr、Y、FeOT/MgO关系图((a)、 (c)、 (e)文献据[71])、Zr+Nb+Ce+Y与FeOT/MgO、10000Ga/Al关系图((b)、 (d)据文献[71])和锆石Pb-Th图((f)据文献[70]) FG.分异花岗岩;OGT.未分异的I型、S型花岗岩
Fig.12 Relationships between 10000Ga/Al and Zr, Y, FeOT/MgO in whole rock ((a), (c), (e) from ref.[71]), Zr+Nb+Ce+Y with FeOT/MgO, 10000Ga/A ((b), (d) from ref.[71]) and zircon Pb-Th map((f) from ref.[70])
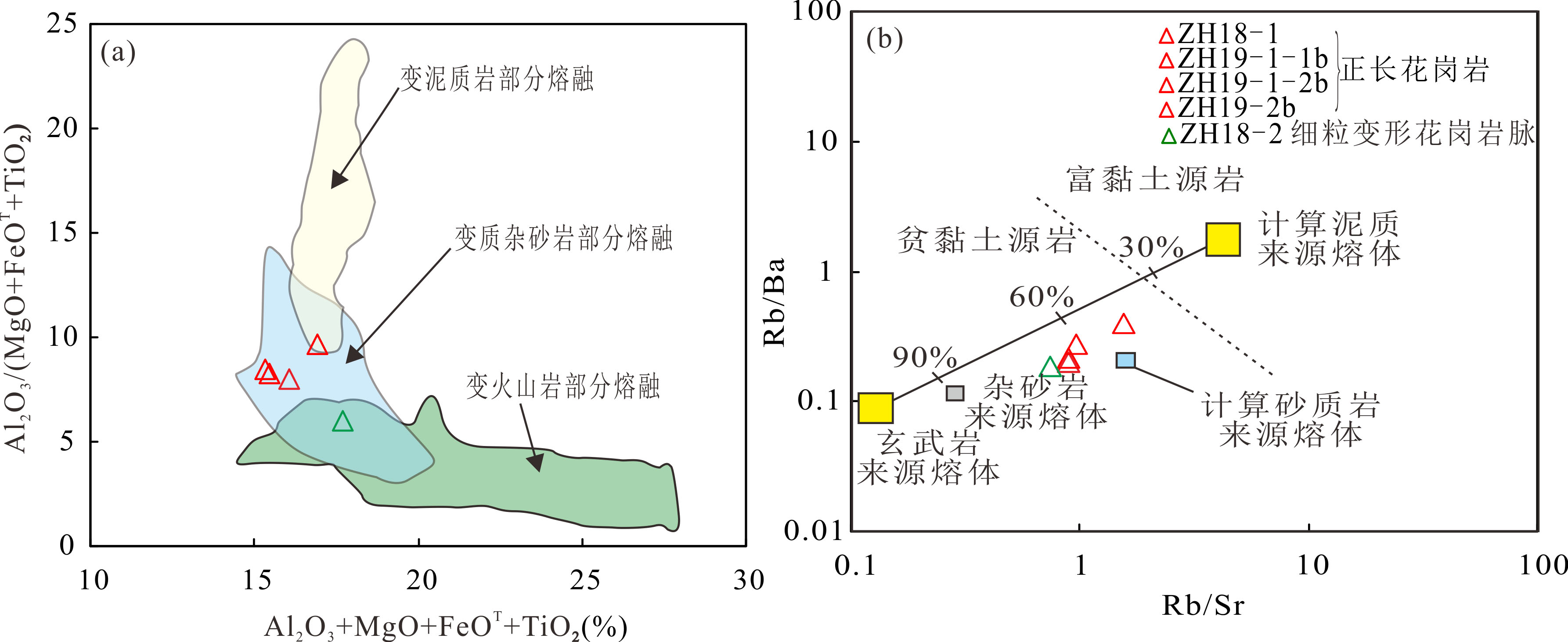
图13 Al2O3/(MgO+TiO2+FeOT-Al2O3+MgO+TiO2+FeOT图((a)据文献[78])及Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba图((b)据文献[73])
Fig.13 Diagram of Al2O3/(MgO+TiO2+FeOT-Al2O3+MgO+TiO2+FeOT ((a) from ref.[78]) and Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba((b) from ref.[73])

图14 花岗质岩石三角分类图((a)底图据文献[82])、花岗质岩石可能源区图((b)底图据文献[82])和花岗质岩石等温等压图((c)据文献[84])
Fig.14 Triangular classification map of granitic rocks ((a) base map ref. [82]), granitic rock energy zone ((b) base map ref. [82]) and granitic rock isothermal isobaric map((c) based on ref. [84]) FMSB=(FeOT+MgO)wt%*(Ba+Sr)wt%
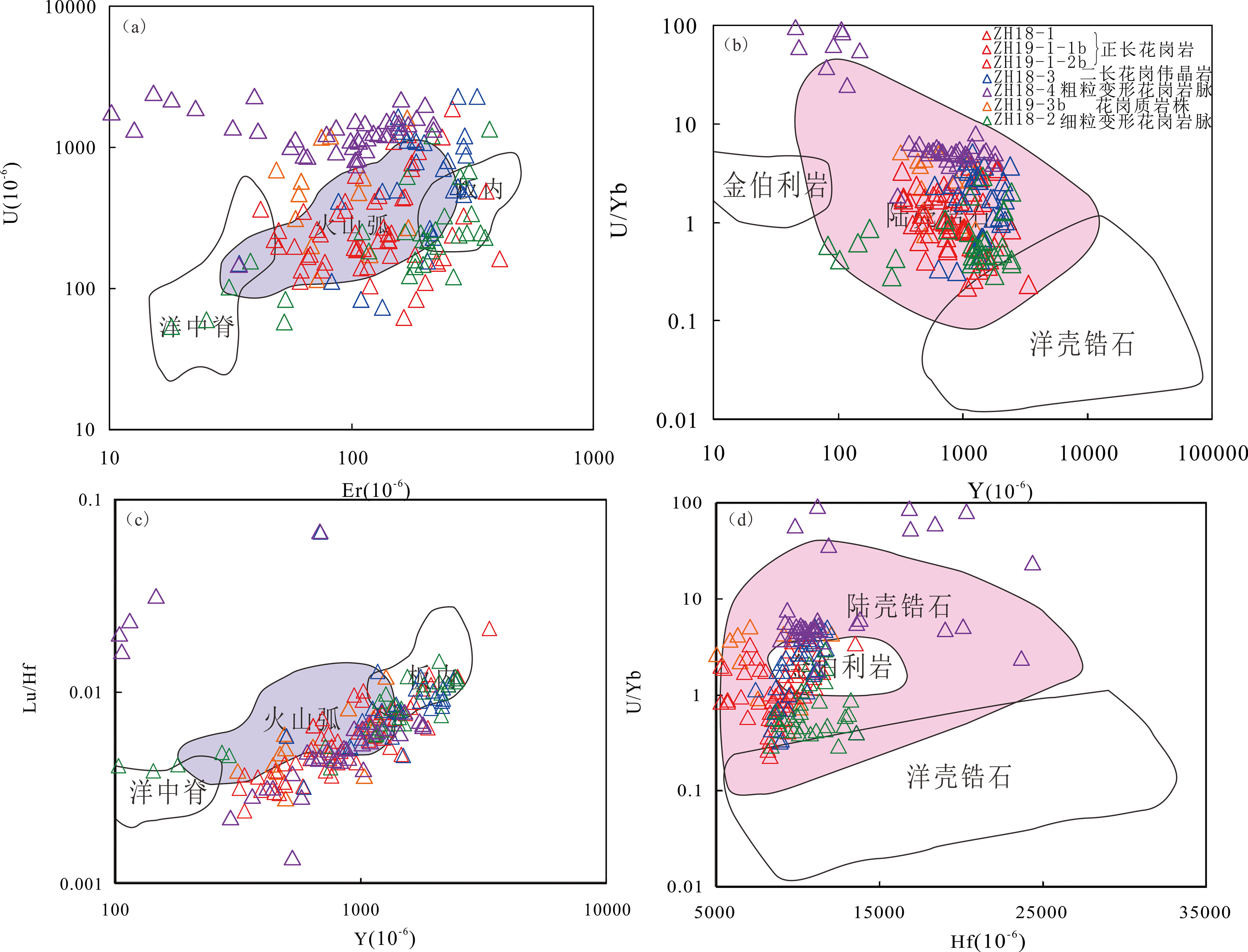
图15 锆石U-Er图((a)据文献[92])、 U/Yb-Y图((b)据文献[91])、 Lu/Hf图((c)据文献[92])、 U/Yb-Hf图((d)据文献[91])
Fig.15 Zircon diagram of U-Er((a) from ref.[92]), U/Yb-Y ((b) from ref.[91]), Lu/Hf((c) from ref.[92]), U/Yb-Hf((d) from ref.[91])
| 样品号 | U | Pb | Hf | Er | Lu | Y | Lu/Hf | U/Yb | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH18 -1 | Min | 62 | 71 | 8144 | 50 | 28 | 337 | 0.002 | 0.225 | |||||||
| Max | 1884 | 847 | 13481 | 359 | 119 | 2477 | 0.012 | 3.723 | ||||||||
| Avg | 425 | 250 | 9673 | 165 | 61 | 1144 | 0.006 | 1.388 | ||||||||
| ZH19- 1-1b | Min | 140 | 245 | 4320 | 48 | 32 | 382 | 0.004 | 0.234 | |||||||
| Max | 633 | 931 | 9384 | 412 | 92 | 3351 | 0.021 | 2.409 | ||||||||
| Avg | 245 | 608 | 7255 | 132 | 46 | 993 | 0.007 | 1.041 | ||||||||
| ZH19- 1-2b | Min | 112 | 265 | 4879 | 42 | 18 | 324 | 0.003 | 0.363 | |||||||
| Max | 452 | 1877 | 9960 | 227 | 68 | 1597 | 0.010 | 3.281 | ||||||||
| Avg | 267 | 632 | 7523 | 96 | 35 | 730 | 0.005 | 1.537 | ||||||||
| ZH18-3 | Min | 73 | 80 | 7387 | 88 | 36 | 591 | 0.003 | 0.318 | |||||||
| Max | 2296 | 1151 | 11770 | 330 | 119 | 2384 | 0.013 | 5.016 | ||||||||
| Avg | 835 | 415 | 9932 | 220 | 80 | 1553 | 0.008 | 2.105 | ||||||||
| ZH18-4 | Min | 150 | 41 | 664 | 10 | 25 | 45 | 0.001 | 1.819 | |||||||
| Max | 2455 | 1584 | 45044 | 219 | 569 | 1809 | 0.068 | 126.210 | ||||||||
| Avg | 1357 | 587 | 13407 | 102 | 119 | 734 | 0.010 | 19.023 | ||||||||
| ZH19 -3b | Min | 117 | 336 | 4406 | 49 | 22 | 316 | 0.003 | 0.735 | |||||||
| Max | 1618 | 3774 | 12065 | 172 | 66 | 1266 | 0.012 | 5.142 | ||||||||
| Avg | 610 | 1414 | 7260 | 93 | 38 | 708 | 0.006 | 2.927 | ||||||||
| ZH18-2 | Min | 54 | 23 | 8365 | 18 | 28 | 84 | 0.002 | 0.287 | |||||||
| Max | 1346 | 1621 | 13557 | 371 | 128 | 2485 | 0.014 | 2.932 | ||||||||
| Avg | 294 | 278 | 10772 | 192 | 79 | 1278 | 0.008 | 0.754 | ||||||||
表5 锆石的微量元素简表(10-6)
Table 5 Brief table of trace elements in some zircons(10-6)
| 样品号 | U | Pb | Hf | Er | Lu | Y | Lu/Hf | U/Yb | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH18 -1 | Min | 62 | 71 | 8144 | 50 | 28 | 337 | 0.002 | 0.225 | |||||||
| Max | 1884 | 847 | 13481 | 359 | 119 | 2477 | 0.012 | 3.723 | ||||||||
| Avg | 425 | 250 | 9673 | 165 | 61 | 1144 | 0.006 | 1.388 | ||||||||
| ZH19- 1-1b | Min | 140 | 245 | 4320 | 48 | 32 | 382 | 0.004 | 0.234 | |||||||
| Max | 633 | 931 | 9384 | 412 | 92 | 3351 | 0.021 | 2.409 | ||||||||
| Avg | 245 | 608 | 7255 | 132 | 46 | 993 | 0.007 | 1.041 | ||||||||
| ZH19- 1-2b | Min | 112 | 265 | 4879 | 42 | 18 | 324 | 0.003 | 0.363 | |||||||
| Max | 452 | 1877 | 9960 | 227 | 68 | 1597 | 0.010 | 3.281 | ||||||||
| Avg | 267 | 632 | 7523 | 96 | 35 | 730 | 0.005 | 1.537 | ||||||||
| ZH18-3 | Min | 73 | 80 | 7387 | 88 | 36 | 591 | 0.003 | 0.318 | |||||||
| Max | 2296 | 1151 | 11770 | 330 | 119 | 2384 | 0.013 | 5.016 | ||||||||
| Avg | 835 | 415 | 9932 | 220 | 80 | 1553 | 0.008 | 2.105 | ||||||||
| ZH18-4 | Min | 150 | 41 | 664 | 10 | 25 | 45 | 0.001 | 1.819 | |||||||
| Max | 2455 | 1584 | 45044 | 219 | 569 | 1809 | 0.068 | 126.210 | ||||||||
| Avg | 1357 | 587 | 13407 | 102 | 119 | 734 | 0.010 | 19.023 | ||||||||
| ZH19 -3b | Min | 117 | 336 | 4406 | 49 | 22 | 316 | 0.003 | 0.735 | |||||||
| Max | 1618 | 3774 | 12065 | 172 | 66 | 1266 | 0.012 | 5.142 | ||||||||
| Avg | 610 | 1414 | 7260 | 93 | 38 | 708 | 0.006 | 2.927 | ||||||||
| ZH18-2 | Min | 54 | 23 | 8365 | 18 | 28 | 84 | 0.002 | 0.287 | |||||||
| Max | 1346 | 1621 | 13557 | 371 | 128 | 2485 | 0.014 | 2.932 | ||||||||
| Avg | 294 | 278 | 10772 | 192 | 79 | 1278 | 0.008 | 0.754 | ||||||||

图16 Rb-Nb+Y、R1-R2、Rb/10-Hf-3Ta、Rb/30-Hf-3Ta图(据文献[63]) WPG.板内花岗岩;VAG.火山弧花岗岩;Syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;ORG.洋脊花岗岩;①地幔斜长花岗岩;②破坏性活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④晚造期花岗岩;⑤非造山区A型花岗岩;⑥同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦造山期后A型花岗岩
Fig.16 Diagram of Rb-Nb+Y、R1-R2、Rb/10-Hf-3Ta、Rb/30-Hf-3Ta(from ref.[63])
| [1] | ZHAO G C, SUN M, WILDE S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136(2): 177-202. |
| [2] | ZHAO G C, ZHAI M G. Lithotectonic elements of Precambrian basement in the North China Craton: Review and tectonic implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1207-1240. |
| [3] | ROGERS J J W, SANTOSH M. Supercontinents in earth history[J]. Gondwana Research, 2003, 6(3): 357-368. |
| [4] | WAN Y S, LIU D Y, SONG B, et al. Geochemical and Nd isotopic compositions of 3.8 Ga meta-quartz dioritic and trondhjemitic rocks from the Anshan area and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24(5): 563-575. |
| [5] | WAN Y S, LIU D Y, NUTMAN A, et al. Multiple 3.8-3.1Ga tectono-magmatic events in a newly discovered area of ancient rocks (the Shengousi Complex),Anshan, North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 54/55: 18-30. |
| [6] | 翟明国. 华北克拉通的形成演化与成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1): 24-36. |
| [7] | 万渝生, 董春艳, 任鹏, 等. 华北克拉通太古宙TTG岩石的时空分布、组成特征及形成演化: 综述[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5): 1405-1419. |
| [8] | 万渝生, 董春艳, 颉颃强, 等. 华北克拉通太古宙研究若干进展[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(6): 685-700. |
| [9] | 马杏垣, 吴正文, 谭应佳, 等. 华北地台基底构造[J]. 地质学报, 1979(4): 293-304. |
| [10] | 唐先梅, 刘树文. 太行山北段晚太古宙变质杂岩伸展变形带的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, (4): 41-49. |
| [11] | 肖玲玲, 刘福来. 华北克拉通中部造山带早前寒武纪变质演化历史评述[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 3012-3044. |
| [12] |
李三忠, 李玺瑶, 戴黎明, 等. 前寒武纪地球动力学(Ⅵ): 华北克拉通形成[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(6): 77-96.
DOI |
| [13] | 朱日祥, 郑天愉. 华北克拉通破坏机制与古元古代板块构造体系[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(14): 1950-1961. |
| [14] | LI S S, SANTOSH M, TENG X M, et al. Paleoproterozoic arc-continent collision in the North China Craton: Evidence from the Zanhuang Complex[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 286: 281-305. |
| [15] | ZHAI M G, SANTOSH M. The early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton: A synoptic overview[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 20(1): 6-25. |
| [16] | LIU D Y, NUTMAN A P, COMPSTON W, et al. Remnants of ≥3800 Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(4): 339. |
| [17] | 吕畅, 王浩, 杨进辉, 等. 华北克拉通始太古代演化——来自冀东38亿年片麻岩锆石Hf-O同位素的记录[J]. 岩石学报, 2024, 40(03): 689-701. |
| [18] | KUSKY T M, LI J H. Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003, 22(4): 383-397. |
| [19] | KUSKY T, LI J H, SANTOSH M. The Paleoproterozoic North Hebei Orogen: North China Craton’s collisional suture with the Columbia supercontinent[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 12(1/2): 4-28. |
| [20] | 李江海. 华北中北部晚太古代高压麻粒岩的地质产状及其出露的区域构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 1998, 14(2): 176-189. |
| [21] | 李江海, 钱祥麟, 黄雄南, 等. 华北陆块基底构造格局及早期大陆克拉通化过程[J]. 岩石学报, 2000, 16(1): 1-10. |
| [22] | 李江海, 侯贵廷, 黄雄南, 等. 华北克拉通对前寒武纪超大陆旋回的基本制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(2): 177-186. |
| [23] |
李江海, 侯贵廷, 刘守偈. 早期碰撞造山过程与板块构造: 前寒武纪地质研究的机遇和挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(8): 843-848.
DOI |
| [24] | WANG J P, KUSKY T, POLAT A, et al. A late Archean tectonic mélange in the Central Orogenic Belt, North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 608: 929-946. |
| [25] | WANG J P, KUSKY T, WANG L, et al. A Neoarchean subduction polarity reversal event in the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2015, 220/221/222/223: 133-146. |
| [26] | WANG J P, KUSKY T, WANG L, et al. Petrogenesis and geochemistry ofcirca 2.5 Ga granitoids in the Zanhuang Massif: Implications for magmatic source and Neoarchean metamorphism of the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2017, 268/269/270/271: 149-162. |
| [27] | KUSKY T M, POLAT A, WINDLEY B F, et al. Insights into the tectonic evolution of the North China Craton through comparative tectonic analysis: A record of outward growth of Precambrian continents[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 162: 387-432. |
| [28] | DENG H, KUSKY T, POLAT A, et al. Geochemistry of Neoarchean mafic volcanic rocks and late mafic dikes in the Zanhuang Complex, Central Orogenic Belt, North China Craton: Implications for geodynamic setting[J]. Lithos, 2013, 175/176: 193-212. |
| [29] | DENG H, KUSKY T, POLAT A, et al. Geochronology, mantle source composition and geodynamic constraints on the origin of Neoarchean mafic dikes in the Zanhuang Complex, Central Orogenic Belt, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2014, 205: 359-378. |
| [30] | DU L L, YANG C H, WYMAN D A, et al. 2090—2070 Ma A-type granitoids in Zanhuang Complex: Further evidence on a Paleoproterozoic Rift-related tectonic regime in the Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Lithos, 2016, 254/255: 18-35. |
| [31] | DU L L, YANG C H, WYMAN D A, et al. Age and depositional setting of the Paleoproterozoic Gantaohe Group in Zanhuang Complex: Constraints from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of sandstones and dacite[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 286: 59-100. |
| [32] | XIE H Q, LIU D Y, YIN X Y, et al. Formation age and tectonic environment of the Gantaohe Group, North China Craton: Geology, geochemistry, SHRIMP zircon geochronology and Hf-Nd isotopic systematics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(36): 4735-4745. |
| [33] | ZHAO G C, CAWOOD P A, WILDE S A, et al. High-pressure granulites (retrograded eclogites) from the Hengshan complex, North China Craton: Petrology and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(6): 1141-1170. |
| [34] | ZHAO G C, GUO J H. Precambrian geology of China: Preface[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222/223: 1-12. |
| [35] | 翟明国, 卞爱国. 华北克拉通新太古代末超大陆拼合及古元古代末—中元古代裂解[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2000, 30(增): 129-137. |
| [36] |
万渝生, 董春艳, 颉颃强, 等. 华北克拉通新太古代晚期岩浆作用: 对构造体制和克拉通化的启示[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(1): 77-94.
DOI |
| [37] | 伍家善, 耿元生, 沈其韩, 等. 中朝古大陆太古宙地质特征及构造演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998. |
| [38] |
郭晓伟, 杨延伟, 张宇. 华北克拉通南缘箕山地区新太古代末期地壳演化——来自叶寨花岗岩年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 83-95.
DOI |
| [39] | YANG C H, DU L L, REN L D, et al. Delineation of the Ca. 2.7 Ga TTG gneisses in the Zanhuang Complex, North China Craton and its geological implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 72: 178-189. |
| [40] | 杨崇辉, 杜利林, 任留东, 等. 赞皇杂岩中太古宙末期菅等钾质花岗岩的成因及动力学背景[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(2): 62-78. |
| [41] | ZHAO G, YIN C, GUO J, et al. Metamorphism of the Luliang amphibolite: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(10): 1480-1502. |
| [42] | TRAP P, FAURE M, LIN W, et al. The Zanhuang Massif, the second and eastern suture zone of the Paleoproterozoic Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 172(1/2): 80-98. |
| [43] | 河北省地质矿产局. 河北北京天津区域志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989. |
| [44] | 杨崇辉, 杜利林, 任留东, 等. 河北赞皇地区许亭花岗岩的时代及成因: 对华北克拉通中部带构造演化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(4): 1003-1016. |
| [45] | 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 郭锋, 等. 赞皇变质穹隆黑云母40Ar/39Ar年代学研究及其对构造热事件的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(1): 131-140. |
| [46] | 牛树银. 太行山阜平、赞皇隆起是中新生代变质核杂岩[J]. 地质科技情报, 1994(2): 15-16. |
| [47] | 牛树银, 许传诗, 国连杰, 等. 太行山变质核杂岩的特征及成因探讨[J]. 河北地质学院学报, 1994(1): 43-53. |
| [48] | TRAP P, FAURE M, LIN W, et al. The Lüliang Massif: A key area for the understanding of the Palaeoproterozoic Trans-North China Belt, North China Craton[J]. Geological Society,London, Special Publications, 2009, 323(1): 99-125. |
| [49] | COLLINS W J, RICHARDS S W. Geodynamic significance of S-type granites in circum-Pacific orogens[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(7): 559. |
| [50] | 河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所. 中国区域地质志·河北志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017. |
| [51] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. |
| [52] | LEE J K W, WILLIAMS I S, ELLIS D J. Pb, U and Th diffusion in natural zircon[J]. Nature, 1997, 390: 159-162. |
| [53] | 高少华, 赵红格, 鱼磊, 等. 锆石U-Pb同位素定年的原理、方法及应用[J]. 江西科学, 2013, 31(3): 363-368, 408. |
| [54] | CHERNIAK D J, WATSON E B. Pb diffusion in zircon[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 172(1/2): 5-24. |
| [55] | BELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622. |
| [56] | RUBATTO D, GEBAUER D. Use of cathodoluminescence for U-Pb zircon dating by ion microprobe: Some examples from the westernAlps[M]// PAGEL M, BARBIN V, BLANC P, et al. Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2000: 373-400. |
| [57] | MÖLLER A, O’BRIEN P J, KENNEDY A, et al. Linking growth episodes of zircon and metamorphic textures to zircon chemistry: An example from the ultrahigh-temperature granulites of Rogaland (SW Norway)[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2003, 220(1): 65-81. |
| [58] | 王立峰. 临城岐山湖矿产勘查实习教程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018. |
| [59] | 肖玲玲, 蒋宗胜, 王国栋, 等. 赞皇前寒武纪变质杂岩区变质反应结构与变质作用P-T-t轨迹[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(04): 980-1002. |
| [60] | XIAO L L, WANG G D, WANG H, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Zanhuang metamorphic complex: Reappraisal of the Palaeoproterozoic amalgamation of the Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Geological Magazine, 2013, 150(4): 756-764. |
| [61] | 河北省地质矿产局第十一地质大队. 1:5万将军墓幅、西丘村幅、西黄村幅、邢台市幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 1996. |
| [62] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [63] | PEARCE J A, NORRY M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1979, 69(1): 33-47. |
| [64] | COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200. |
| [65] | WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2): 295-304. |
| [66] | MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6): 529. |
| [67] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan fold belt[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1992, 83(1/2): 1-26. |
| [68] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2001, 48(4): 489-499. |
| [69] | 徐克勤, 孙鼐, 王德滋, 等. 华南两类不同成因花岗岩岩石学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 1982, 1(2): 1-12. |
| [70] | WANG Q, ZHU D C, ZHAO Z D, et al. Magmatic zircons from I-, S- and A-type granitoids in Tibet: Trace element characteristics and their application to detrital zircon provenance study[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 59-66. |
| [71] | WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. |
| [72] | WAIGHT T E, MAAS R, NICHOLLS I A. Geochemical investigations of microgranitoid enclaves in the S-type Cowra Granodiorite, Lachlan Fold Belt, SE Australia[J]. Lithos, 2001, 56(2/3): 165-186. |
| [73] | SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/2/3/4): 29-44. |
| [74] | 史少飞, 袁浩为, 肖渊甫, 等. 西藏青龙乡地区早白垩世侵入岩年代学和地球化学: 对班公湖—怒江洋盆闭合时限的制约[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(5): 998-1011. |
| [75] | 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002. |
| [76] | 张泽明, 康东艳, 丁慧霞, 等. 喜马拉雅造山带的部分熔融与淡色花岗岩成因机制. 地球科学, 2018, 43(1): 82-98. |
| [77] | 于胜尧, 张建新, 宫江华, 等. 高压麻粒岩相变质作用及深熔作用: 以柴北缘都兰地区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(6): 2061-2072. |
| [78] | ALTHERR R, SIEBEL W. I-type plutonism in a continental back-arc setting: Miocene granitoids and monzonites from the central Aegean Sea, Greece[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(4): 397-415. |
| [79] | 郑方顺, 宋国学. 铕异常在地质学中的应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2023, 39(9): 2832-2856. |
| [80] | 李伦, 杨永强, 杨崇辉, 等. 赞皇地区-2.5 Ga A型花岗岩的成因及构造背景: 以黄岔岩体为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(9): 2850-2866. |
| [81] | 李伦. 华北克拉通赞皇地区-2.5 Ga A型花岗岩的成因及构造意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. |
| [82] | LAURENT A, JANOUŠEK V, MAGNA T, et al. Petrogenesis and geochronology of a post-orogenic calc-alkaline magmatic association: The Žulová Pluton, Bohemian Massif[J]. Journal of Geosciences, 2014: 415-440. |
| [83] | 张帆. 华北克拉通中部带赞皇杂岩新太古代—古元古代地质演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2019. |
| [84] | HUANG W L, WYLLIE P J. Melting reactions in the system NaAlSi3O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2 to 35 kilobars, dry and with excess water[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1975, 83(6): 737-748. |
| [85] |
席振, 马德成, 李欢, 等. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623.
DOI |
| [86] | GAO P, ZHENG Y F, MAYNE M J, et al. Miocene high-temperature leucogranite magmatism in the Himalayan Orogen[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2021, 133(3/4): 679-690. |
| [87] | ZHENG Y F, GAO P. The production of granitic magmas through crustal anatexis at convergent plate boundaries[J]. Lithos, 2021, 402/403: 106232. |
| [88] | XU J, XIA X P, WANG Q, et al. Pure sediment-derived granites in a subduction zone[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2022, 134(3/4): 599-615. |
| [89] | CAI K D, SUN M, YUAN C, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of peraluminous granites from the Chinese Altai, NW China[J]. Lithos, 2011, 127(1/2): 261-281. |
| [90] | LYTWYN J, LOCKHART S, CASEY J, et al. Geochemistry of near-trench intrusives associated with ridge subduction, Seldova Quadrangle, southem Alaska[J]. Joumal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2000, 105: 27957-27978. |
| [91] | GRIMES C B, JOHN B E, KELEMEN P B, et al. Trace element chemistry of zircons from oceanic crust: A method for distinguishing detrital zircon provenance[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(7): 643. |
| [92] | SCHULZ B, KLEMD R, BRÄTZ H. Host rock compositional controls on zircon trace element signatures in metabasites from the Austroalpine basement[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(3): 697-710. |
| [93] | GRIMES C B, WOODEN J L, CHEADLE M J, et al. “Fingerprinting” tectono-magmatic provenance using trace elements in igneous zircon[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 170(5): 46. |
| [94] | BARTH A P, WOODEN J L, JACOBSON C E, et al. Detrital zircon as a proxy for tracking the magmatic arc system: The California arc example[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(2): 223-226. |
| [95] | 张鑫, 谢晖. 贺兰山滚钟口花岗岩岩石成因和构造背景[J]. 矿物学报, 2024, 44(2): 188-199. |
| [96] | 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等. 再论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类: 标志[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(4): 985-1015. |
| [97] | GAO L E, ZENG L S, ASIMOW P D. Contrasting geochemical signatures of fluid-absent versus fluid-fluxed melting of muscovite in metasedimentary sources: The Himalayan leucogranites[J]. Geology, 2017, 45(1): 39-42. |
| [1] | 孙玉洁, 李晓彦, 张超. 基于机器学习的黑云母成分判别花岗岩成因类型方法研究[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 523-540. |
| [2] | 杨宇婷, 白峰, 温宇航, 张启东, 张道元, 王雯. 吉林“磐龙玉”的地球化学特征及颜色成因探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 167-182. |
| [3] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 王翠彭, 史宏江, 鞠楠, 何云龙. 大兴安岭北段呼玛地区晚石炭世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征:对古亚洲洋构造演化的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 62-82. |
| [4] | 郭晓伟, 杨延伟, 张宇. 华北克拉通南缘箕山地区新太古代末期地壳演化——来自叶寨花岗岩年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 83-95. |
| [5] | 王亿, 李立兴, 李厚民, 李小赛, 马兰晶, 邢玉亮, 孙欣宇, 戴阳, 王小慧. 冀北招兵沟铁磷矿床成矿时代及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 46-55. |
| [6] | 张保涛, 梅贞华, 李秀章, 姜晓平, 胡兆国, 王小玉, 赵晓博, 胡加斌, 柳森. 华北克拉通矽卡岩型富铁矿成矿关键控制因素:来自地层学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 98-116. |
| [7] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [8] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [9] | 苏惠, 曾认宇, 甘德斌, 严杰. 阿拉善北大山地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1580-1596. |
| [10] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [11] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623. |
| [12] | 贾冰玲, 张碧云, 汤彬, 郑德顺. 豫西寒武系辛集组含磷层沉积环境及磷酸盐富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 858-869. |
| [13] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [14] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [15] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||