



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (01): 46-55.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.122
王亿1( ), 李立兴1(
), 李立兴1( ), 李厚民1, 李小赛1, 马兰晶2, 邢玉亮2, 孙欣宇3, 戴阳3, 王小慧1
), 李厚民1, 李小赛1, 马兰晶2, 邢玉亮2, 孙欣宇3, 戴阳3, 王小慧1
收稿日期:2023-06-10
修回日期:2023-11-11
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
李立兴,男,博士,研究员,1984年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事金属矿床成因与成矿规律研究。Email:作者简介:王 亿,男,硕士研究生,1997年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事金属矿床成因与成矿规律研究。Email:cagswangyi@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Yi1( ), LI Lixing1(
), LI Lixing1( ), LI Houmin1, LI Xiaosai1, MA Lanjing2, XING Yuliang2, SUN Xinyu3, DAI Yang3, WANG Xiaohui1
), LI Houmin1, LI Xiaosai1, MA Lanjing2, XING Yuliang2, SUN Xinyu3, DAI Yang3, WANG Xiaohui1
Received:2023-06-10
Revised:2023-11-11
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-03-20
摘要:
为探讨冀北—辽西地区太古宙变质岩系中铁磷矿床的成因问题,本研究选取招兵沟矿床开展了岩相学、年代学和地球化学研究。野外观察表明,前人描述的条带状铁磷矿石实际上大多为含铁磷矿脉的黑云角闪斜长片麻岩,可见铁磷矿脉切穿片麻理。含铁磷黑云角闪斜长片麻岩中的锆石与矿石矿物铁钛氧化物和磷灰石密切共生。阴极发光图像上显示基性岩浆锆石特征,无/弱环带或斑块状结构,LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年获得206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(282±3)Ma(MSWD=0.78),指示铁磷矿化时代为早二叠世,而非传统认为的新太古代。招兵沟含铁磷黑云角闪斜长片麻岩与区域辉石-角闪石岩侵入体形成时代接近,微量元素地球化学特征相似度高,说明成矿母岩为辉石-角闪石岩。招兵沟铁磷成矿与冀北地区沿红石砬—大庙断裂带发育的显生宙阿拉斯加型镁铁-超镁铁质岩浆活动密切相关。综合来看,招兵沟铁磷矿床可能是与基性岩浆活动有关的矿床,而非传统认为的变质型矿床,其他相似矿床的成因也需要进一步研究。
中图分类号:
王亿, 李立兴, 李厚民, 李小赛, 马兰晶, 邢玉亮, 孙欣宇, 戴阳, 王小慧. 冀北招兵沟铁磷矿床成矿时代及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 46-55.
WANG Yi, LI Lixing, LI Houmin, LI Xiaosai, MA Lanjing, XING Yuliang, SUN Xinyu, DAI Yang, WANG Xiaohui. Geochronology and Genesis of the Zhaobinggou Fe-P Deposit, Northern Hebei, China[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(01): 46-55.

图1 华北克拉通示意图(a)(据文献[24])和冀北招兵沟地区区域地质图(b)(改自文献[20])
Fig.1 Sketch map of the North China Craton (a) (modified after reference [24]) and simplified geologic map of the Zhaobinggou area (b) (modified after reference [20])

图3 招兵沟铁磷矿床岩(矿)石照片 (a)黑云角闪斜长片麻岩;(b)黑云斜长片麻岩;(c)苏长岩中有斜长角闪岩包体;(d)角闪石岩边部有铁磷矿石;(e)-(f)铁磷矿脉可见切穿黑云角闪斜长片麻岩的片麻理
Fig.3 Photographs of rocks and ores of the Zhaobinggou Fe-P deposit

图4 招兵沟铁磷矿床岩(矿)石镜下照片 (a)斜长角闪岩,单偏光;(b)黑云斜长片麻岩,单偏光;(c)苏长岩中斜方辉石边部被角闪石和黑云母交代,单偏光;(d)含磷灰石角闪石岩,单偏光;(e)—(f)黑云斜长角闪片麻岩中的条带状铁磷矿石,单偏光和正交偏光;(g)—(h)黑云斜长片麻岩中的条带状铁磷矿石,单偏光和正交偏光;(i)铁磷矿石中锆石产于钛铁矿内部或与其它矿物的间隙,背散射。Amp.角闪石;Ap.磷灰石;Bt.黑云母;Ilm.钛铁矿;Mag.磁铁矿;Plag.斜长石;Opx.斜方辉石;Zrn.锆石
Fig.4 Photomicrographs of rocks and ores from the Zhaobinggou Fe-P deposit
| 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Li | Be | Sc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZBG-2 | 25.44 | 6.50 | 10.18 | 29.32 | 0.22 | 4.11 | 12.43 | 1.59 | 1.30 | 6.38 | 1.91 | 99.38 | 6.26 | 0.16 | 26.00 | ||||||
| ZBG-3 | 14.15 | 10.74 | 5.53 | 38.71 | 0.35 | 3.57 | 13.34 | 0.32 | 1.84 | 8.21 | 2.65 | 99.41 | 12.00 | 0.16 | 19.90 | ||||||
| ZBG-5 | 15.56 | 10.36 | 4.93 | 47.41 | 0.26 | 5.10 | 9.40 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 5.56 | 0.18 | 99.49 | 5.00 | 0.14 | 26.40 | ||||||
| ZBG-11 | 29.00 | 7.52 | 5.95 | 32.75 | 0.25 | 7.75 | 11.03 | 0.86 | 0.26 | 3.99 | 0.13 | 99.49 | 3.40 | 0.22 | 48.70 | ||||||
| ZBG-12 | 25.88 | 8.24 | 7.18 | 39.10 | 0.27 | 6.44 | 7.17 | 1.07 | 0.95 | 3.04 | 0.17 | 99.50 | 7.17 | 0.25 | 27.40 | ||||||
| 样号 | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba | Hf | ||||||
| ZBG-2 | 1113.00 | 16.60 | 99.70 | 45.00 | 99.60 | 200.00 | 20.70 | 19.70 | 383.00 | 66.20 | 7.66 | 2.86 | 0.98 | 802.00 | 0.38 | ||||||
| ZBG-3 | 1716.00 | 26.20 | 126.00 | 66.10 | 297.00 | 201.00 | 21.40 | 28.30 | 410.00 | 80.00 | 7.68 | 6.02 | 2.81 | 924.00 | 0.47 | ||||||
| ZBG-5 | 2086.00 | 375.00 | 172.00 | 190.00 | 133.00 | 416.00 | 32.60 | 2.10 | 307.00 | 60.00 | 11.70 | 5.63 | 0.10 | 236.00 | 0.73 | ||||||
| ZBG-11 | 1251.00 | 192.00 | 128.00 | 117.00 | 96.60 | 288.00 | 22.30 | 1.42 | 328.00 | 54.50 | 25.80 | 5.56 | 0.07 | 152.00 | 1.25 | ||||||
| ZBG-12 | 1608.00 | 624.00 | 139.00 | 167.00 | 124.00 | 368.00 | 29.20 | 8.92 | 308.00 | 35.60 | 13.20 | 5.90 | 0.31 | 571.00 | 0.72 | ||||||
| 样号 | Ta | W | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | La | Ce | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | ||||||
| ZBG-2 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 2.35 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 59.80 | 140.00 | 2.51 | 12.10 | 2.22 | 5.54 | 0.76 | 4.02 | ||||||
| ZBG-3 | 0.28 | 4.12 | 0.23 | 1.99 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 1.10 | 75.00 | 183.00 | 3.28 | 15.30 | 2.76 | 6.73 | 0.90 | 4.59 | ||||||
| ZBG-5 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 1.34 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.79 | 53.40 | 126.00 | 2.36 | 11.40 | 2.04 | 5.01 | 0.68 | 3.73 | ||||||
| ZBG-11 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 2.31 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 1.53 | 41.70 | 100.00 | 2.19 | 10.60 | 1.97 | 4.82 | 0.68 | 3.69 | ||||||
| ZBG-12 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 2.73 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 1.55 | 31.40 | 73.50 | 1.38 | 6.69 | 1.23 | 3.11 | 0.44 | 2.46 | ||||||
| 样号 | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-2 | 0.55 | 391.23 | 346.52 | 44.71 | 7.75 | 10.67 | 0.89 | 0.98 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-3 | 0.61 | 510.44 | 435.47 | 56.97 | 7.96 | 11.72 | 0.80 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-5 | 0.50 | 357.46 | 315.84 | 41.62 | 7.59 | 10.27 | 0.80 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-11 | 0.51 | 294.09 | 255.33 | 38.76 | 6.59 | 8.11 | 0.84 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-12 | 0.33 | 209.33 | 184.16 | 25.17 | 7.32 | 9.16 | 0.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||
表1 招兵沟铁磷矿床铁磷矿石全岩主量(%)、微量元素(10-6)组成
Table 1 Major (%) and trace elements (10-6) of the Fe-P ores from the Zhaobinggou deposit
| 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Li | Be | Sc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZBG-2 | 25.44 | 6.50 | 10.18 | 29.32 | 0.22 | 4.11 | 12.43 | 1.59 | 1.30 | 6.38 | 1.91 | 99.38 | 6.26 | 0.16 | 26.00 | ||||||
| ZBG-3 | 14.15 | 10.74 | 5.53 | 38.71 | 0.35 | 3.57 | 13.34 | 0.32 | 1.84 | 8.21 | 2.65 | 99.41 | 12.00 | 0.16 | 19.90 | ||||||
| ZBG-5 | 15.56 | 10.36 | 4.93 | 47.41 | 0.26 | 5.10 | 9.40 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 5.56 | 0.18 | 99.49 | 5.00 | 0.14 | 26.40 | ||||||
| ZBG-11 | 29.00 | 7.52 | 5.95 | 32.75 | 0.25 | 7.75 | 11.03 | 0.86 | 0.26 | 3.99 | 0.13 | 99.49 | 3.40 | 0.22 | 48.70 | ||||||
| ZBG-12 | 25.88 | 8.24 | 7.18 | 39.10 | 0.27 | 6.44 | 7.17 | 1.07 | 0.95 | 3.04 | 0.17 | 99.50 | 7.17 | 0.25 | 27.40 | ||||||
| 样号 | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba | Hf | ||||||
| ZBG-2 | 1113.00 | 16.60 | 99.70 | 45.00 | 99.60 | 200.00 | 20.70 | 19.70 | 383.00 | 66.20 | 7.66 | 2.86 | 0.98 | 802.00 | 0.38 | ||||||
| ZBG-3 | 1716.00 | 26.20 | 126.00 | 66.10 | 297.00 | 201.00 | 21.40 | 28.30 | 410.00 | 80.00 | 7.68 | 6.02 | 2.81 | 924.00 | 0.47 | ||||||
| ZBG-5 | 2086.00 | 375.00 | 172.00 | 190.00 | 133.00 | 416.00 | 32.60 | 2.10 | 307.00 | 60.00 | 11.70 | 5.63 | 0.10 | 236.00 | 0.73 | ||||||
| ZBG-11 | 1251.00 | 192.00 | 128.00 | 117.00 | 96.60 | 288.00 | 22.30 | 1.42 | 328.00 | 54.50 | 25.80 | 5.56 | 0.07 | 152.00 | 1.25 | ||||||
| ZBG-12 | 1608.00 | 624.00 | 139.00 | 167.00 | 124.00 | 368.00 | 29.20 | 8.92 | 308.00 | 35.60 | 13.20 | 5.90 | 0.31 | 571.00 | 0.72 | ||||||
| 样号 | Ta | W | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U | La | Ce | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | ||||||
| ZBG-2 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 2.35 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 59.80 | 140.00 | 2.51 | 12.10 | 2.22 | 5.54 | 0.76 | 4.02 | ||||||
| ZBG-3 | 0.28 | 4.12 | 0.23 | 1.99 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 1.10 | 75.00 | 183.00 | 3.28 | 15.30 | 2.76 | 6.73 | 0.90 | 4.59 | ||||||
| ZBG-5 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 1.34 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.79 | 53.40 | 126.00 | 2.36 | 11.40 | 2.04 | 5.01 | 0.68 | 3.73 | ||||||
| ZBG-11 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 2.31 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 1.53 | 41.70 | 100.00 | 2.19 | 10.60 | 1.97 | 4.82 | 0.68 | 3.69 | ||||||
| ZBG-12 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 2.73 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 1.55 | 31.40 | 73.50 | 1.38 | 6.69 | 1.23 | 3.11 | 0.44 | 2.46 | ||||||
| 样号 | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-2 | 0.55 | 391.23 | 346.52 | 44.71 | 7.75 | 10.67 | 0.89 | 0.98 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-3 | 0.61 | 510.44 | 435.47 | 56.97 | 7.96 | 11.72 | 0.80 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-5 | 0.50 | 357.46 | 315.84 | 41.62 | 7.59 | 10.27 | 0.80 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-11 | 0.51 | 294.09 | 255.33 | 38.76 | 6.59 | 8.11 | 0.84 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||
| ZBG-12 | 0.33 | 209.33 | 184.16 | 25.17 | 7.32 | 9.16 | 0.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||

图5 招兵沟铁磷矿石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化数值引自参考文献[32];数据取自参考文献[9,21])
Fig.5 Rare earth element chondrite-normalized diagram (a) and trace element primitive mantle-normalized diagram (b) of the Fe-P ore of the Zhaobinggou deposit (standardized values from reference [32],and data from references[9,21])
| 样品编号 | 元素含量(10-6) | 同位素比值 | U-Pb年龄(Ma) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/ 235U | 2σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 2σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 2σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 2σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 2σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 2σ | |||
| ZBG.12.01 | 43.3 | 35.7 | 170.0 | 0.21 | 0.2700 | 0.0680 | 0.0452 | 0.0022 | 0.0440 | 0.0110 | 220.0 | 53.0 | 285.0 | 14.0 | 290.0 | 350.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.02 | 43.5 | 49.6 | 233.3 | 0.21 | 0.2970 | 0.0670 | 0.0443 | 0.0021 | 0.0490 | 0.0110 | 238.0 | 51.0 | 279.0 | 13.0 | 150.0 | 340.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.03 | 96.2 | 119.3 | 460.5 | 0.26 | 0.3400 | 0.0560 | 0.0432 | 0.0017 | 0.0558 | 0.0094 | 279.0 | 42.0 | 273.0 | 10.0 | 260.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.04 | 13.5 | 2.2 | 71.4 | 0.03 | 0.3500 | 0.1300 | 0.0459 | 0.0038 | 0.0440 | 0.0190 | 206.0 | 77.0 | 288.0 | 24.0 | 810.0 | 380.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.05 | 201.5 | 202.7 | 1055.6 | 0.19 | 0.3600 | 0.0370 | 0.0451 | 0.0009 | 0.0583 | 0.0063 | 318.0 | 26.0 | 284.0 | 5.8 | 490.0 | 190.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.06 | 48.3 | 50.8 | 261.4 | 0.19 | 0.2830 | 0.0620 | 0.0434 | 0.0021 | 0.0480 | 0.0110 | 240.0 | 50.0 | 273.0 | 13.0 | 30.0 | 350.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.07 | 95.7 | 75.2 | 502.9 | 0.15 | 0.3430 | 0.0500 | 0.0452 | 0.0015 | 0.0537 | 0.0078 | 285.0 | 38.0 | 285.6 | 9.1 | 230.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.08 | 327.3 | 67.8 | 1759.1 | 0.04 | 0.3270 | 0.0250 | 0.0460 | 0.0009 | 0.0531 | 0.0040 | 285.0 | 19.0 | 289.6 | 5.5 | 280.0 | 150.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.09* | 1566.8 | 5120.8 | 1480.8 | 3.46 | 2.1110 | 0.0770 | 0.1812 | 0.0028 | 0.0845 | 0.0029 | 1150.0 | 25.0 | 1075.0 | 16.0 | 1299.0 | 69.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.10 | 78.6 | 66.7 | 423.9 | 0.16 | 0.3050 | 0.0440 | 0.0445 | 0.0016 | 0.0547 | 0.0078 | 267.0 | 36.0 | 280.7 | 9.7 | 210.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.11 | 102.1 | 98.5 | 547.7 | 0.18 | 0.3080 | 0.0480 | 0.0451 | 0.0014 | 0.0502 | 0.0077 | 264.0 | 38.0 | 285.1 | 8.9 | 170.0 | 270.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.12 | 88.4 | 76.7 | 467.7 | 0.16 | 0.3160 | 0.0460 | 0.0456 | 0.0018 | 0.0544 | 0.0080 | 272.0 | 37.0 | 287.0 | 11.0 | 240.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.13 | 102.4 | 132.7 | 566.0 | 0.23 | 0.3070 | 0.0440 | 0.0420 | 0.0014 | 0.0547 | 0.0080 | 257.0 | 34.0 | 264.8 | 8.8 | 210.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.14 | 144.4 | 181.5 | 788.9 | 0.23 | 0.2950 | 0.0380 | 0.0435 | 0.0011 | 0.0500 | 0.0067 | 258.0 | 31.0 | 275.3 | 6.8 | 180.0 | 230.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.15 | 65.2 | 83.9 | 345.2 | 0.24 | 0.3640 | 0.0610 | 0.0445 | 0.0019 | 0.0610 | 0.0100 | 295.0 | 45.0 | 281.0 | 12.0 | 350.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.16 | 121.0 | 127.9 | 630.5 | 0.20 | 0.4010 | 0.0510 | 0.0453 | 0.0014 | 0.0627 | 0.0080 | 326.0 | 37.0 | 285.3 | 8.8 | 510.0 | 250.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.17 | 73.5 | 75.6 | 394.7 | 0.19 | 0.3290 | 0.0470 | 0.0438 | 0.0018 | 0.0556 | 0.0078 | 280.0 | 37.0 | 276.0 | 11.0 | 310.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.18 | 111.1 | 108.7 | 600.4 | 0.18 | 0.3250 | 0.0400 | 0.0438 | 0.0014 | 0.0555 | 0.0073 | 277.0 | 32.0 | 276.0 | 8.8 | 310.0 | 240.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.19 | 183.6 | 41.0 | 984.1 | 0.04 | 0.3120 | 0.0360 | 0.0455 | 0.0014 | 0.0494 | 0.0057 | 265.0 | 29.0 | 286.5 | 8.7 | 130.0 | 210.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.20 | 32.6 | 32.5 | 163.4 | 0.20 | 0.3700 | 0.1000 | 0.0463 | 0.0031 | 0.0710 | 0.0200 | 266.0 | 69.0 | 291.0 | 19.0 | 0.0 | 410.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.21 | 73.4 | 71.9 | 383.8 | 0.19 | 0.2970 | 0.0500 | 0.0451 | 0.0017 | 0.0485 | 0.0079 | 249.0 | 39.0 | 284.0 | 11.0 | 40.0 | 270.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.22 | 131.1 | 135.7 | 716.2 | 0.19 | 0.3040 | 0.0380 | 0.0431 | 0.0012 | 0.0513 | 0.0063 | 262.0 | 30.0 | 271.8 | 7.2 | 140.0 | 210.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.23 | 432.8 | 132.2 | 2267.3 | 0.06 | 0.3430 | 0.0250 | 0.0447 | 0.0008 | 0.0546 | 0.0039 | 295.0 | 19.0 | 281.8 | 4.9 | 360.0 | 140.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.24 | 81.5 | 98.0 | 433.8 | 0.23 | 0.3050 | 0.0510 | 0.0436 | 0.0015 | 0.0531 | 0.0091 | 256.0 | 40.0 | 275.0 | 9.4 | 160.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.25 | 79.2 | 81.9 | 408.7 | 0.20 | 0.3480 | 0.0550 | 0.0455 | 0.0016 | 0.0559 | 0.0092 | 290.0 | 42.0 | 287.0 | 9.7 | 240.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.26 | 69.8 | 94.7 | 375.8 | 0.25 | 0.2930 | 0.0560 | 0.0431 | 0.0018 | 0.0474 | 0.0092 | 248.0 | 44.0 | 272.0 | 11.0 | 40.0 | 310.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.27 | 293.0 | 415.9 | 1450.4 | 0.29 | 0.3610 | 0.0300 | 0.0463 | 0.0010 | 0.0578 | 0.0049 | 306.0 | 22.0 | 291.4 | 6.3 | 390.0 | 170.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.28 | 89.4 | 77.9 | 380.4 | 0.20 | 0.3700 | 0.0530 | 0.0442 | 0.0017 | 0.0651 | 0.0099 | 304.0 | 41.0 | 278.0 | 11.0 | 470.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.29 | 71.4 | 102.2 | 373.0 | 0.27 | 0.2890 | 0.0490 | 0.0445 | 0.0018 | 0.0457 | 0.0081 | 239.0 | 39.0 | 281.0 | 11.0 | 30.0 | 280.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.30 | 90.1 | 65.6 | 367.8 | 0.18 | 0.3800 | 0.0630 | 0.0458 | 0.0018 | 0.0566 | 0.0094 | 310.0 | 46.0 | 288.0 | 11.0 | 330.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.31 | 340.8 | 89.9 | 1752.6 | 0.05 | 0.3480 | 0.0300 | 0.0465 | 0.0009 | 0.0536 | 0.0046 | 296.0 | 23.0 | 292.7 | 5.6 | 290.0 | 160.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.32* | 17.9 | 26.8 | 39.1 | 0.68 | 0.7800 | 0.2700 | 0.0979 | 0.0091 | 0.0520 | 0.0190 | 360.0 | 120.0 | 597.0 | 53.0 | 670.0 | 390.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.33 | 322.5 | 64.1 | 1688.8 | 0.04 | 0.3500 | 0.0280 | 0.0461 | 0.0009 | 0.0534 | 0.0043 | 301.0 | 21.0 | 290.2 | 5.6 | 360.0 | 160.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.34 | 72.0 | 58.6 | 383.0 | 0.15 | 0.3230 | 0.0570 | 0.0448 | 0.0019 | 0.0550 | 0.0098 | 261.0 | 43.0 | 282.0 | 12.0 | 110.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.35 | 148.1 | 130.7 | 778.3 | 0.17 | 0.3060 | 0.0370 | 0.0448 | 0.0013 | 0.0491 | 0.0060 | 260.0 | 29.0 | 282.6 | 7.8 | 80.0 | 210.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.36 | 69.4 | 107.8 | 362.0 | 0.30 | 0.2760 | 0.0570 | 0.0443 | 0.0020 | 0.0446 | 0.0097 | 223.0 | 44.0 | 279.0 | 12.0 | 130.0 | 310.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.37 | 146.2 | 260.4 | 715.6 | 0.36 | 0.3570 | 0.0480 | 0.0461 | 0.0014 | 0.0560 | 0.0075 | 301.0 | 36.0 | 290.6 | 8.9 | 280.0 | 240.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.38 | 48.7 | 31.8 | 258.5 | 0.12 | 0.2900 | 0.0700 | 0.0440 | 0.0025 | 0.0510 | 0.0120 | 234.0 | 53.0 | 277.0 | 16.0 | 80.0 | 360.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.39 | 128.9 | 135.1 | 708.0 | 0.19 | 0.3460 | 0.0490 | 0.0427 | 0.0013 | 0.0568 | 0.0079 | 285.0 | 36.0 | 269.7 | 8.0 | 300.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.40 | 91.4 | 97.0 | 507.9 | 0.19 | 0.2930 | 0.0450 | 0.0422 | 0.0014 | 0.0515 | 0.0079 | 249.0 | 36.0 | 266.5 | 8.6 | 240.0 | 270.0 | ||
表2 招兵沟铁磷矿床铁磷矿石LA-ICP-MS锆石同位素比值
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon isotopic ratios of the Fe-P ores from the Zhaobinggou deposit
| 样品编号 | 元素含量(10-6) | 同位素比值 | U-Pb年龄(Ma) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/ 235U | 2σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 2σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 2σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 2σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 2σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 2σ | |||
| ZBG.12.01 | 43.3 | 35.7 | 170.0 | 0.21 | 0.2700 | 0.0680 | 0.0452 | 0.0022 | 0.0440 | 0.0110 | 220.0 | 53.0 | 285.0 | 14.0 | 290.0 | 350.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.02 | 43.5 | 49.6 | 233.3 | 0.21 | 0.2970 | 0.0670 | 0.0443 | 0.0021 | 0.0490 | 0.0110 | 238.0 | 51.0 | 279.0 | 13.0 | 150.0 | 340.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.03 | 96.2 | 119.3 | 460.5 | 0.26 | 0.3400 | 0.0560 | 0.0432 | 0.0017 | 0.0558 | 0.0094 | 279.0 | 42.0 | 273.0 | 10.0 | 260.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.04 | 13.5 | 2.2 | 71.4 | 0.03 | 0.3500 | 0.1300 | 0.0459 | 0.0038 | 0.0440 | 0.0190 | 206.0 | 77.0 | 288.0 | 24.0 | 810.0 | 380.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.05 | 201.5 | 202.7 | 1055.6 | 0.19 | 0.3600 | 0.0370 | 0.0451 | 0.0009 | 0.0583 | 0.0063 | 318.0 | 26.0 | 284.0 | 5.8 | 490.0 | 190.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.06 | 48.3 | 50.8 | 261.4 | 0.19 | 0.2830 | 0.0620 | 0.0434 | 0.0021 | 0.0480 | 0.0110 | 240.0 | 50.0 | 273.0 | 13.0 | 30.0 | 350.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.07 | 95.7 | 75.2 | 502.9 | 0.15 | 0.3430 | 0.0500 | 0.0452 | 0.0015 | 0.0537 | 0.0078 | 285.0 | 38.0 | 285.6 | 9.1 | 230.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.08 | 327.3 | 67.8 | 1759.1 | 0.04 | 0.3270 | 0.0250 | 0.0460 | 0.0009 | 0.0531 | 0.0040 | 285.0 | 19.0 | 289.6 | 5.5 | 280.0 | 150.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.09* | 1566.8 | 5120.8 | 1480.8 | 3.46 | 2.1110 | 0.0770 | 0.1812 | 0.0028 | 0.0845 | 0.0029 | 1150.0 | 25.0 | 1075.0 | 16.0 | 1299.0 | 69.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.10 | 78.6 | 66.7 | 423.9 | 0.16 | 0.3050 | 0.0440 | 0.0445 | 0.0016 | 0.0547 | 0.0078 | 267.0 | 36.0 | 280.7 | 9.7 | 210.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.11 | 102.1 | 98.5 | 547.7 | 0.18 | 0.3080 | 0.0480 | 0.0451 | 0.0014 | 0.0502 | 0.0077 | 264.0 | 38.0 | 285.1 | 8.9 | 170.0 | 270.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.12 | 88.4 | 76.7 | 467.7 | 0.16 | 0.3160 | 0.0460 | 0.0456 | 0.0018 | 0.0544 | 0.0080 | 272.0 | 37.0 | 287.0 | 11.0 | 240.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.13 | 102.4 | 132.7 | 566.0 | 0.23 | 0.3070 | 0.0440 | 0.0420 | 0.0014 | 0.0547 | 0.0080 | 257.0 | 34.0 | 264.8 | 8.8 | 210.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.14 | 144.4 | 181.5 | 788.9 | 0.23 | 0.2950 | 0.0380 | 0.0435 | 0.0011 | 0.0500 | 0.0067 | 258.0 | 31.0 | 275.3 | 6.8 | 180.0 | 230.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.15 | 65.2 | 83.9 | 345.2 | 0.24 | 0.3640 | 0.0610 | 0.0445 | 0.0019 | 0.0610 | 0.0100 | 295.0 | 45.0 | 281.0 | 12.0 | 350.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.16 | 121.0 | 127.9 | 630.5 | 0.20 | 0.4010 | 0.0510 | 0.0453 | 0.0014 | 0.0627 | 0.0080 | 326.0 | 37.0 | 285.3 | 8.8 | 510.0 | 250.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.17 | 73.5 | 75.6 | 394.7 | 0.19 | 0.3290 | 0.0470 | 0.0438 | 0.0018 | 0.0556 | 0.0078 | 280.0 | 37.0 | 276.0 | 11.0 | 310.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.18 | 111.1 | 108.7 | 600.4 | 0.18 | 0.3250 | 0.0400 | 0.0438 | 0.0014 | 0.0555 | 0.0073 | 277.0 | 32.0 | 276.0 | 8.8 | 310.0 | 240.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.19 | 183.6 | 41.0 | 984.1 | 0.04 | 0.3120 | 0.0360 | 0.0455 | 0.0014 | 0.0494 | 0.0057 | 265.0 | 29.0 | 286.5 | 8.7 | 130.0 | 210.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.20 | 32.6 | 32.5 | 163.4 | 0.20 | 0.3700 | 0.1000 | 0.0463 | 0.0031 | 0.0710 | 0.0200 | 266.0 | 69.0 | 291.0 | 19.0 | 0.0 | 410.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.21 | 73.4 | 71.9 | 383.8 | 0.19 | 0.2970 | 0.0500 | 0.0451 | 0.0017 | 0.0485 | 0.0079 | 249.0 | 39.0 | 284.0 | 11.0 | 40.0 | 270.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.22 | 131.1 | 135.7 | 716.2 | 0.19 | 0.3040 | 0.0380 | 0.0431 | 0.0012 | 0.0513 | 0.0063 | 262.0 | 30.0 | 271.8 | 7.2 | 140.0 | 210.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.23 | 432.8 | 132.2 | 2267.3 | 0.06 | 0.3430 | 0.0250 | 0.0447 | 0.0008 | 0.0546 | 0.0039 | 295.0 | 19.0 | 281.8 | 4.9 | 360.0 | 140.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.24 | 81.5 | 98.0 | 433.8 | 0.23 | 0.3050 | 0.0510 | 0.0436 | 0.0015 | 0.0531 | 0.0091 | 256.0 | 40.0 | 275.0 | 9.4 | 160.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.25 | 79.2 | 81.9 | 408.7 | 0.20 | 0.3480 | 0.0550 | 0.0455 | 0.0016 | 0.0559 | 0.0092 | 290.0 | 42.0 | 287.0 | 9.7 | 240.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.26 | 69.8 | 94.7 | 375.8 | 0.25 | 0.2930 | 0.0560 | 0.0431 | 0.0018 | 0.0474 | 0.0092 | 248.0 | 44.0 | 272.0 | 11.0 | 40.0 | 310.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.27 | 293.0 | 415.9 | 1450.4 | 0.29 | 0.3610 | 0.0300 | 0.0463 | 0.0010 | 0.0578 | 0.0049 | 306.0 | 22.0 | 291.4 | 6.3 | 390.0 | 170.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.28 | 89.4 | 77.9 | 380.4 | 0.20 | 0.3700 | 0.0530 | 0.0442 | 0.0017 | 0.0651 | 0.0099 | 304.0 | 41.0 | 278.0 | 11.0 | 470.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.29 | 71.4 | 102.2 | 373.0 | 0.27 | 0.2890 | 0.0490 | 0.0445 | 0.0018 | 0.0457 | 0.0081 | 239.0 | 39.0 | 281.0 | 11.0 | 30.0 | 280.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.30 | 90.1 | 65.6 | 367.8 | 0.18 | 0.3800 | 0.0630 | 0.0458 | 0.0018 | 0.0566 | 0.0094 | 310.0 | 46.0 | 288.0 | 11.0 | 330.0 | 290.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.31 | 340.8 | 89.9 | 1752.6 | 0.05 | 0.3480 | 0.0300 | 0.0465 | 0.0009 | 0.0536 | 0.0046 | 296.0 | 23.0 | 292.7 | 5.6 | 290.0 | 160.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.32* | 17.9 | 26.8 | 39.1 | 0.68 | 0.7800 | 0.2700 | 0.0979 | 0.0091 | 0.0520 | 0.0190 | 360.0 | 120.0 | 597.0 | 53.0 | 670.0 | 390.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.33 | 322.5 | 64.1 | 1688.8 | 0.04 | 0.3500 | 0.0280 | 0.0461 | 0.0009 | 0.0534 | 0.0043 | 301.0 | 21.0 | 290.2 | 5.6 | 360.0 | 160.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.34 | 72.0 | 58.6 | 383.0 | 0.15 | 0.3230 | 0.0570 | 0.0448 | 0.0019 | 0.0550 | 0.0098 | 261.0 | 43.0 | 282.0 | 12.0 | 110.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.35 | 148.1 | 130.7 | 778.3 | 0.17 | 0.3060 | 0.0370 | 0.0448 | 0.0013 | 0.0491 | 0.0060 | 260.0 | 29.0 | 282.6 | 7.8 | 80.0 | 210.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.36 | 69.4 | 107.8 | 362.0 | 0.30 | 0.2760 | 0.0570 | 0.0443 | 0.0020 | 0.0446 | 0.0097 | 223.0 | 44.0 | 279.0 | 12.0 | 130.0 | 310.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.37 | 146.2 | 260.4 | 715.6 | 0.36 | 0.3570 | 0.0480 | 0.0461 | 0.0014 | 0.0560 | 0.0075 | 301.0 | 36.0 | 290.6 | 8.9 | 280.0 | 240.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.38 | 48.7 | 31.8 | 258.5 | 0.12 | 0.2900 | 0.0700 | 0.0440 | 0.0025 | 0.0510 | 0.0120 | 234.0 | 53.0 | 277.0 | 16.0 | 80.0 | 360.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.39 | 128.9 | 135.1 | 708.0 | 0.19 | 0.3460 | 0.0490 | 0.0427 | 0.0013 | 0.0568 | 0.0079 | 285.0 | 36.0 | 269.7 | 8.0 | 300.0 | 260.0 | ||
| ZBG.12.40 | 91.4 | 97.0 | 507.9 | 0.19 | 0.2930 | 0.0450 | 0.0422 | 0.0014 | 0.0515 | 0.0079 | 249.0 | 36.0 | 266.5 | 8.6 | 240.0 | 270.0 | ||
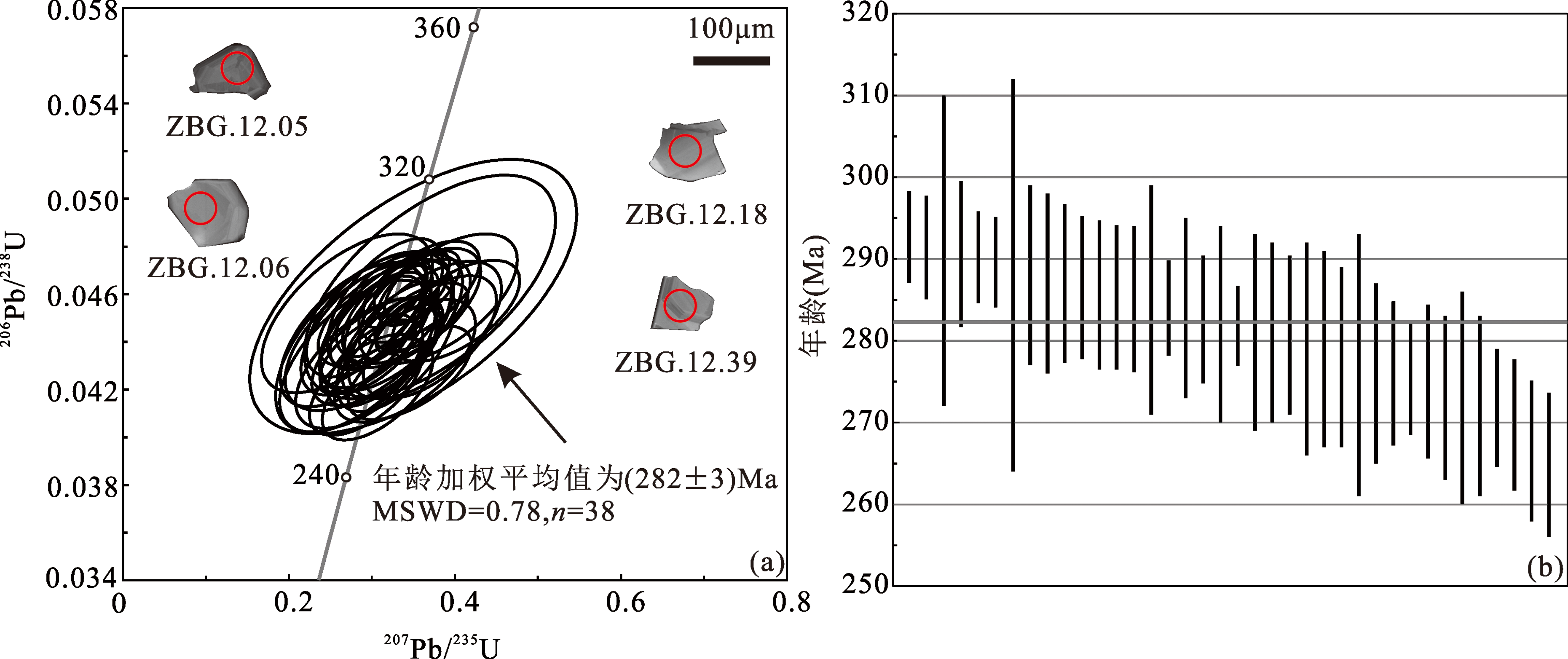
图6 招兵沟矿床铁磷矿石中锆石U-Pb谐和图(a)及加权平均年龄图(b)
Fig.6 Concordia diagram of the U-Pb data (a) and weighted diagram average ages (b) of zircon from the Fe-P ore of the Zhaobinggou deposit
| [1] | 孙小虹, 陈春琳, 王高尚, 等. 中国磷矿资源需求预测[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(2): 213-219. |
| [2] | 吴发富, 王建雄, 刘江涛, 等. 磷矿的分布、特征与开发现状[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(1): 82-101. |
| [3] | 张招崇, 李厚民, 李建威, 等. 我国铁矿成矿背景与富铁矿成矿机制[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(6):827-852. |
| [4] | 焦森, 郑厚义, 任永健, 等. 中国主要农用矿产资源安全保障战略研究[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(2): 279-285. |
| [5] | 李厚民, 王瑞江, 肖克炎, 等. 我国铁矿找矿潜力分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(增): 537-538. |
| [6] | 熊先孝, 李博昀, 姚超美, 等. 中国北方磷矿成矿预测[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2007, 29(3): 150-158. |
| [7] | 丁晓姜, 吴艳妮. 北方低品位磷铁矿综合回收研究[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2021, 43(2): 165-169. |
| [8] | 唐文龙, 李俊建, 侯占国, 等. 华北地区磷矿资源特征及潜力分析[J]. 华北地质, 2021, 44(3): 33-40. |
| [9] |
ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, LIU X C, et al. Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic mafic-ultramafic complexes from the northern North China Block: Constraints on the composition and evolution of the lithospheric mantle[J]. Lithos, 2009, 110(1/2/3/4): 229-246.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 李立兴, 李厚民, 王德忠, 等. 河北承德铁马哈叭沁超贫铁矿床的成因与成矿时代[J]. 岩矿测试, 2012, 31(5): 898-905. |
| [11] | 李立兴, 李厚民, 陈振宇, 等. 冀北与角闪石岩相关铁钛磷灰岩的特征及成因: 磷灰石矿物化学的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(3): 380-388. |
| [12] |
HOU T, ZHANG Z C, KEIDING J K, et al. Petrogenesis of the ultrapotassic Fanshan intrusion in the North China Craton: Implications for lithospheric mantle metasomatism and the origin of apatite ores[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2015, 56(5): 893-918.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
PAN R H, HOU T, ZHANG Z C. Mineralogical and geochemical study on the Yaojiazhuang ultrapotassic complex, North China Craton: Constraints on the magmatic differentiation processes and genesis of apatite ores[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2020, 8: 357.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 熊先孝, 李博昀, 姚超美, 等. 中国北方磷矿矿床类型及成矿规律[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2007, 29(3): 159-168. |
| [15] | 夏学惠, 连卫. 中国北方内生磷矿资源分布特征及潜力[J]. 武汉工程大学学报, 2011, 33(3): 81-86. |
| [16] | 夏学惠, 郝尔宏. 中国磷矿床成因分类[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2012, 34(1): 1-14. |
| [17] | 东野脉兴. 中国北方早、中前寒武纪磷矿[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1989, 19(2): 181-186. |
| [18] | 薛珂, 张润宇. 中国磷矿资源分布及其成矿特征研究进展[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(1): 7-14. |
| [19] | 张连昌, 翟明国, 万渝生, 等. 华北克拉通前寒武纪BIF铁矿研究: 进展与问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(11): 3431-3445. |
| [20] |
SUN G Z, LIU S W, LÜ Y J, et al. Chronological framework of Precambrian Dantazi Complex: Implications for the formation and evolution of the northern North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2022, 379: 106819.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
GE S S, ZHAI M G, LI T S, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of low-grade metamorphosed volcanic rocks from the Dantazi Complex: Implications for the evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 111: 948-965.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 相鹏, 崔敏利, 吴华英, 等. 河北滦平周台子条带状铁矿地质特征、围岩时代及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(11): 3655-3669. |
| [23] | 孙会一, 董春艳, 颉颃强, 等. 冀东青龙地区新太古代朱杖子群和单塔子群形成时代: 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(6): 888-898. |
| [24] |
ZHAO G C, SUN M, WILDE S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136(2): 177-202.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAO T P, CHEN W, ZHOU M F. Geochemical and Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of the -1.74 Ga Damiao anorthosite complex, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4): 673-690.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LI L X, LI H M, ZI J W, et al. Role of fluids in Fe-Ti-P mineralization of the Proterozoic Damiao anorthosite complex, China: Insights from baddeleyite-zircon relationships in ore and altered anorthosite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 115: 103186.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI L, ZI J, LI H, et al. Characterizing a new type of nelsonite recognized in the Damiao anorthosite complex, North China Craton, with implications for the genesis of giant magmatic Fe-Ti oxide deposits[J]. American Mineralogist, 2023, 109(1):184-197.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 张拴宏, 赵越, 刘建民, 等. 华北地块北缘晚古生代: 早中生代岩浆活动期次、特征及构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 824-842. |
| [29] | 夏学惠, 魏祥松. 河北丰宁招兵沟铁磷矿床地质及综合利用前景[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2005, 27(1): 1-5. |
| [30] | 应思淮, 俞理宝, 杨主恩, 等. 丰宁变质磷矿深成变质作用及其成矿问题[J]. 岩石学报, 1991, 7(3): 45-55. |
| [31] | 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. |
| [32] | SUNSS M W F. Chemical and Isotopic systematics of ocean basalts: Implications for mantle composition and process[M]// SAUNDERSA D, NORRYM J. Magmatism in Ocean Basins. London: Special Publlication, 1989: 345. |
| [33] | 雷玮琰, 施光海, 刘迎新. 不同成因锆石的微量元素特征研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 273-284. |
| [34] | 吴元保, 陈道公, 夏群科, 等. 大别山黄镇榴辉岩锆石的微区微量元素分析: 榴辉岩相变质锆石的微量元素特征[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(11): 859-863. |
| [35] | 李长民. 锆石成因矿物学与锆石微区定年综述[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2009, 32(3): 161-174. |
| [36] |
CORFU F. Atlas of zircon textures[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 469-500.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 周剑雄, 陈振宇. 电子探针下锆石阴极发光的研究[M]. 成都: 电子科技大学出版社, 2007. |
| [38] | 马旭, 陈斌, 陈家富, 等. 华北克拉通北缘晚古生代岩体的成因和意义: 岩石学、锆石U-Pb年龄、Nd-Sr同位素及锆石原位Hf同位素证据[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2012, 42(12): 1830-1850. |
| [39] | TAYLOR Jr H P. The Zoned Ultramafic Complexes of South-eastern Alaska[M]. New York: Wiley Press, 1967: 97-121. |
| [40] | HIMMELBERG G R, LONEY R A. Characteristics and Petrogenesis of Alaskan-type Ultramafic-mafic Intrusions, Southeastern Alaska[M]. Washington: USGPO, 1995. |
| [41] | 李立兴, 朱明玉, 方同明, 等. 应用电子探针技术研究北京密云放马峪铬铁矿床成因: 来自含铬尖晶石矿物化学的证据[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5): 600-608. |
| [42] | 崔梦萌, 白洋, 罗扬, 等. 阿拉斯加型岩体的基本特征、成岩过程及成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(3): 397-418. |
| [43] | 李立兴, 李厚民, 王德忠, 等. 冀北哈叭沁超镁铁岩锆石年代学及Hf同位素: 对区域岩浆活动期次及源区的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(5): 1472-1484. |
| [1] | 张保涛, 梅贞华, 李秀章, 姜晓平, 胡兆国, 王小玉, 赵晓博, 胡加斌, 柳森. 华北克拉通矽卡岩型富铁矿成矿关键控制因素:来自地层学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 98-116. |
| [2] | 胡生平, 韩善楚, 张洪求, 张勇, 潘家永, 钟福军, 卢建研, 李惟鑫. 庐枞盆地西湾铅锌矿床黄铁矿微量元素组成特征及成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 183-197. |
| [3] | 刘金波, 张德贤, 胡子奇, 陈绍炜, 谢小雨. 豫西熊耳山蒿坪沟Ag-Au-Pb-Zn多金属矿床闪锌矿矿物学和微量元素组成特征及其成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 198-213. |
| [4] | 苏惠, 曾认宇, 甘德斌, 严杰. 阿拉善北大山地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1580-1596. |
| [5] | 贾冰玲, 张碧云, 汤彬, 郑德顺. 豫西寒武系辛集组含磷层沉积环境及磷酸盐富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 858-869. |
| [6] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [7] | 杨帆, 陈岳龙, 于洋. 鲁西地区新太古代晚期正长-二长花岗岩成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1155-1172. |
| [8] | 高银虎, 尹刚, 龚泽强, 郭明春. 甘肃两当湘潭子金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| [9] | 汪超, 王瑞廷, 刘云华, 薛玉山, 胡西顺, 牛亮. 陕西商南三官庙金矿床流体包裹体及C-H-O-S稳定同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1551-1564. |
| [10] | 刘天航, 高永宝, 魏立勇, 张振, 唐卫东, 贾彬. 陕西旬阳泗人沟铅锌矿床地质及S、Pb同位素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1597-1607. |
| [11] | 丁坤, 王瑞廷, 刘凯, 王智慧, 申喜茂. 南秦岭柞水—山阳矿集区夏家店金矿床黄铁矿微量元素和氢、氧、硫同位素对矿床成因的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1622-1632. |
| [12] | 阎昆, 杨延伟, 王丽伟, 朱荣彬, 卢允申, 赵辉. 北秦岭西峡龙王庙石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 589-598. |
| [13] | 叶枫, 董国臣, 任建勋, 龚杰立, 李猛兴, 王权, 张兆琪, 赵三波. 山西黄榆沟岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 787-797. |
| [14] | 何泽宇, 申俊峰, 张善明, 刘俊, 杜佰松. 内蒙古乌海桌子山花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 523-534. |
| [15] | 吴天昊, 徐丽娟, 肖益林, 刘盛遨. 华北陆块东南缘蚌埠地区侏罗纪花岗岩中多种类型白云母的识别及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 532-544. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||