



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (04): 1183-1192.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.04.20
• 地球化学与水资源 • 上一篇
姜哲1( ), 周训1,2(
), 周训1,2( ), 陈柄桦1,2, 陶广斌1, 李状1, 曹入文1, 隋丽嫒1
), 陈柄桦1,2, 陶广斌1, 李状1, 曹入文1, 隋丽嫒1
收稿日期:2021-09-02
修回日期:2022-01-10
出版日期:2022-08-10
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
周训
作者简介:周训,男,教授,博士生导师,1963年出生,水文地质专业,从事地下热水 (温泉)、海岸带地下水、地下卤水 (盐泉)、矿泉水、地下水循环及其模拟等的研究。Email: zhouxun@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
JIANG Zhe1( ), ZHOU Xun1,2(
), ZHOU Xun1,2( ), CHEN Binghua1,2, TAO Guangbin1, LI Zhuang1, CAO Ruwen1, SUI Liai1
), CHEN Binghua1,2, TAO Guangbin1, LI Zhuang1, CAO Ruwen1, SUI Liai1
Received:2021-09-02
Revised:2022-01-10
Online:2022-08-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
ZHOU Xun
摘要:
为研究四川省康定市二道桥地区地下热水稳定同位素特征和热储温度,对二道桥地区5个温泉(井)即二道桥温泉(SC107、SC107-2)、康巴人家温泉(SC107-3)、自流热水井(SC107-4)、自喷热水井(SC107-5)进行调查和分析。研究区温泉的分布及出露主要受雅拉沟断裂和雅拉河谷控制。温泉水温33.2~46 ℃,为中低温温泉,pH为6~6.5。水样的氢氧稳定同位素特征表明研究区地下热水的补给来源为大气降水。利用氢氧稳定同位素高程效应及温度效应估算区内地下热水补给区高程为3 000~4 500 m,补给区温度为-3.5~-0.3 ℃,表明地下热水有一部分补给源自附近山区的冰雪融水。Na-K-Mg三角图显示研究区热水均为未成熟水,不宜用阳离子地热温标计算热储温度。应用SiO2地热温标、多矿物饱和指数法以及用固定铝方法对部分温泉多矿物平衡图进行修正,得出研究区地下热水的热储温度为65~75 ℃。研究区温泉在东部跑马山以及西部农戈山附近接受大气降水补给,降水沿着大雪山—农戈山断裂和跑马山断裂下渗,地下水经历深循环,在此过程中获得大地热流加热,最终在雅拉河谷雅拉沟断裂附近出露成泉。
中图分类号:
姜哲, 周训, 陈柄桦, 陶广斌, 李状, 曹入文, 隋丽嫒. 四川康定市二道桥地区地下热水稳定同位素特征及热储温度计算[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1183-1192.
JIANG Zhe, ZHOU Xun, CHEN Binghua, TAO Guangbin, LI Zhuang, CAO Ruwen, SUI Liai. Stable Isotope Characteristics of Geothermal Water and Calculation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature in the Erdaoqiao Area of Kangding in Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 1183-1192.
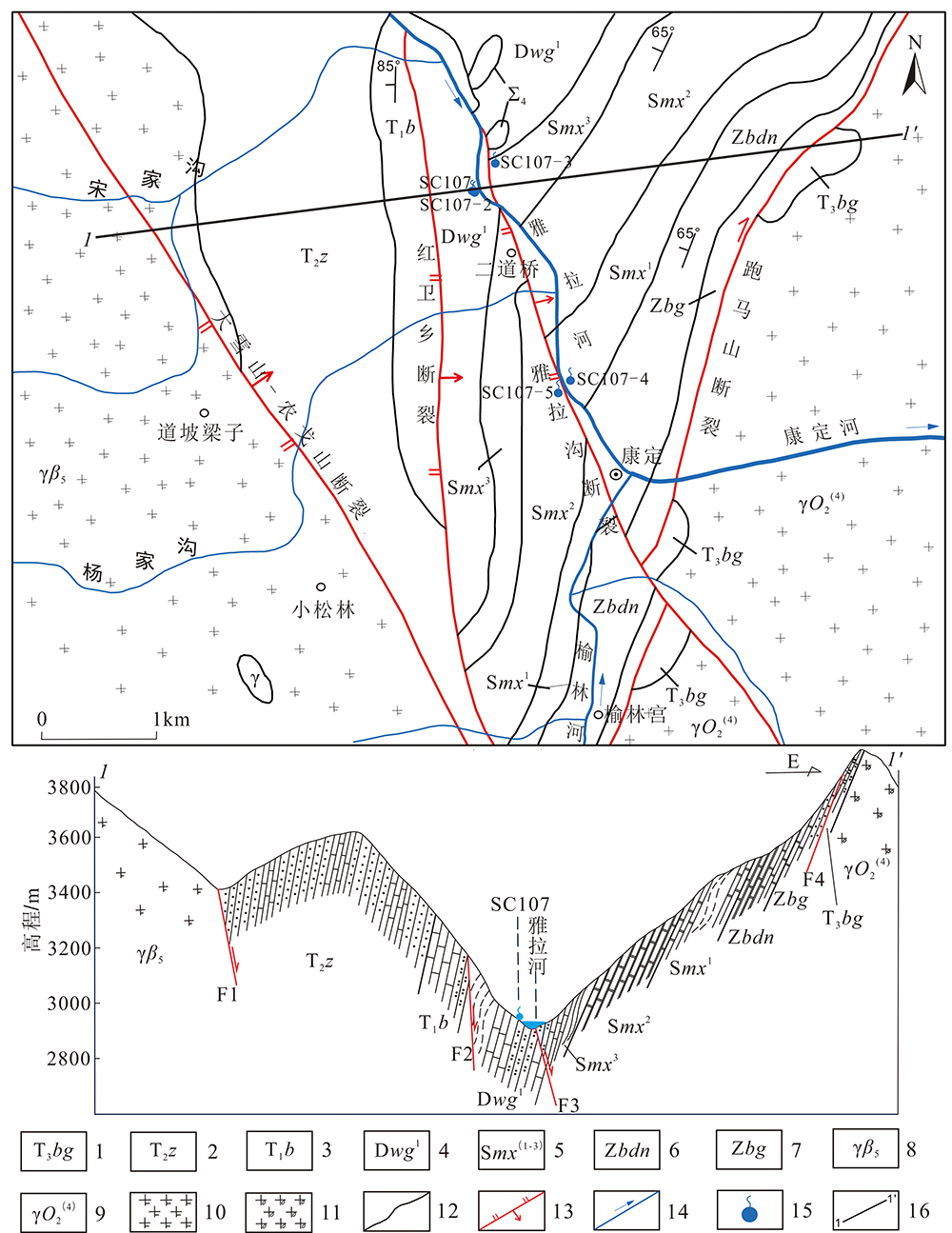
图1 康定二道桥地区地质简图 (据黄珣[17],2018,有改动) 1.三叠系上统白果湾组碳质粉砂岩、砾岩;2.三叠系中统杂谷脑组石英砂岩夹薄层灰岩;3.三叠系下统菠茨沟组板岩夹条带状粉砂岩、细晶灰岩;4.泥盆系危关群组碳硅质板岩夹千枚岩夹结晶灰岩、细晶灰岩及石英砂岩;5.志留系茂县群细晶灰岩、绿片岩、大理岩、千枚岩、白云岩;6.震旦系上统灯影组大理岩、白云岩夹千枚岩;7.震旦系上统观音崖组千枚岩夹白云岩、砂岩;8.燕山期黑云母花岗岩;9.晋宁期斜长花岗岩;10.黑云母花岗岩;11.斜长花岗岩;12.地层界线;13.断裂;14.河流及流向;15.泉眼(井);16.剖面线。
Fig.1 Simplified geologic map of the Erdaoqiao area in Kangding
| 名称 | 编号 | pH | C | M | Na+ | K+ | Cl- | TDS | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | Si | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二道桥“族”泉眼 | SC107 | 6.0 | 225 | 42.4 | 114 | 19.8 | 1 139 | 76.6 | 30.4 | 1 082 | -112.6 | -14.8 | 23.7 |
| 二道桥“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | 6.1 | 232 | 44.4 | 119 | 21.0 | 1 143 | 98.5 | 32.4 | 1 122 | -110.4 | -14.2 | 24.5 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | 6.5 | 152 | 47.5 | 199 | 27.2 | 1 120 | 68.9 | 56.8 | 1 116 | -95.8 | -12.9 | 24.0 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | 6.3 | 370 | 41.1 | 99.2 | 12.9 | 1 564 | 7.77 | 45.0 | 1 361 | -97.0 | -13.1 | 23.9 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | 6.4 | 368 | 48.5 | 100 | 13.1 | 1 571 | 9.86 | 46.2 | 1374 | -97.5 | -13.3 | 22.0 |
表1 康定二道桥地区温泉水样水化学数据(ρB/(mg/L))
Table 1 Hydrochemical data of the hot spring samples in the Erdaoqiao area in Kangding(ρB/(mg/L))
| 名称 | 编号 | pH | C | M | Na+ | K+ | Cl- | TDS | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | Si | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二道桥“族”泉眼 | SC107 | 6.0 | 225 | 42.4 | 114 | 19.8 | 1 139 | 76.6 | 30.4 | 1 082 | -112.6 | -14.8 | 23.7 |
| 二道桥“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | 6.1 | 232 | 44.4 | 119 | 21.0 | 1 143 | 98.5 | 32.4 | 1 122 | -110.4 | -14.2 | 24.5 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | 6.5 | 152 | 47.5 | 199 | 27.2 | 1 120 | 68.9 | 56.8 | 1 116 | -95.8 | -12.9 | 24.0 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | 6.3 | 370 | 41.1 | 99.2 | 12.9 | 1 564 | 7.77 | 45.0 | 1 361 | -97.0 | -13.1 | 23.9 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | 6.4 | 368 | 48.5 | 100 | 13.1 | 1 571 | 9.86 | 46.2 | 1374 | -97.5 | -13.3 | 22.0 |
| 温泉名称 | 水样编号 | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | 泉(井)口 标高/m | 补给高程/m | 补给高程/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 式(1) | 式(2) | |||||
| 二道桥温泉“族”泉眼 | SC107 | -112.6 | -14.8 | 2 550 | 4 280 | 4 411 |
| 二道桥温泉“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | -110.4 | -14.2 | 2 570 | 4 170 | 4 078 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | -95.8 | -12.9 | 2 560 | 3 440 | 3 356 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | -97 | -13.1 | 2 520 | 3 500 | 3 467 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | -97.5 | -13.3 | 2 500 | 3 525 | 3 578 |
表2 康定二道桥地区温泉的补给高程
Table 2 Estimated altitude of the recharge areas of the hot springs in the Erdaoqiao area in Kangding
| 温泉名称 | 水样编号 | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | 泉(井)口 标高/m | 补给高程/m | 补给高程/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 式(1) | 式(2) | |||||
| 二道桥温泉“族”泉眼 | SC107 | -112.6 | -14.8 | 2 550 | 4 280 | 4 411 |
| 二道桥温泉“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | -110.4 | -14.2 | 2 570 | 4 170 | 4 078 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | -95.8 | -12.9 | 2 560 | 3 440 | 3 356 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | -97 | -13.1 | 2 520 | 3 500 | 3 467 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | -97.5 | -13.3 | 2 500 | 3 525 | 3 578 |
| 温泉名称 | 水样编号 | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | 补给区温度/℃ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 式(3) | 式(4) | 式(5) | ||||
| 二道桥温泉“族”泉眼 | SC107 | -112.6 | -14.8 | -2.3 | -1.2 | -6.9 |
| 二道桥温泉“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | -110.4 | -14.2 | -1.9 | -0.6 | -6.1 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | -95.8 | -12.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | -1.3 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | -97 | -13.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | -1.7 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | -97.5 | -13.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | -1.8 |
表3 康定二道桥地区温泉的补给区温度
Table 3 Estimated temperature of the recharge areas of the hot springs in the Erdaoqiao area in Kangding
| 温泉名称 | 水样编号 | δ2H/‰ | δ18O/‰ | 补给区温度/℃ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 式(3) | 式(4) | 式(5) | ||||
| 二道桥温泉“族”泉眼 | SC107 | -112.6 | -14.8 | -2.3 | -1.2 | -6.9 |
| 二道桥温泉“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | -110.4 | -14.2 | -1.9 | -0.6 | -6.1 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | -95.8 | -12.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | -1.3 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | -97 | -13.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | -1.7 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | -97.5 | -13.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | -1.8 |
| 温泉名称 | 水样编号 | 水温/℃ | 热储温度/℃ | 估算热储温度/℃ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 式(6) | 式(7) | 式(8) | 式(9) | 式(10) | ||||
| 二道桥温泉“族”泉眼 | SC107 | 40.8 | 102.93 | 102.54 | 103.19 | 52.13 | 68.96 | 52~103 |
| 二道桥温泉“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | 33.2 | 104.48 | 104.10 | 104.53 | 53.66 | 72.66 | 53~104 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | 46 | 103.52 | 103.13 | 103.70 | 52.71 | 74.34 | 52~103 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | 36.7 | 103.33 | 102.93 | 103.53 | 52.52 | 73.30 | 52~103 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | 36 | 99.52 | 99.09 | 100.20 | 48.75 | 68.96 | 48~100 |
表4 康定二道桥地区温泉热储温度估算结果
Table 4 Estimated temperature of the geothermal reservoirs of the hot springs in the Erdaoqiao area in Kangding
| 温泉名称 | 水样编号 | 水温/℃ | 热储温度/℃ | 估算热储温度/℃ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 式(6) | 式(7) | 式(8) | 式(9) | 式(10) | ||||
| 二道桥温泉“族”泉眼 | SC107 | 40.8 | 102.93 | 102.54 | 103.19 | 52.13 | 68.96 | 52~103 |
| 二道桥温泉“卫”泉眼 | SC107-2 | 33.2 | 104.48 | 104.10 | 104.53 | 53.66 | 72.66 | 53~104 |
| 康巴人家温泉 | SC107-3 | 46 | 103.52 | 103.13 | 103.70 | 52.71 | 74.34 | 52~103 |
| 自流热水井 | SC107-4 | 36.7 | 103.33 | 102.93 | 103.53 | 52.52 | 73.30 | 52~103 |
| 自喷热水井 | SC107-5 | 36 | 99.52 | 99.09 | 100.20 | 48.75 | 68.96 | 48~100 |
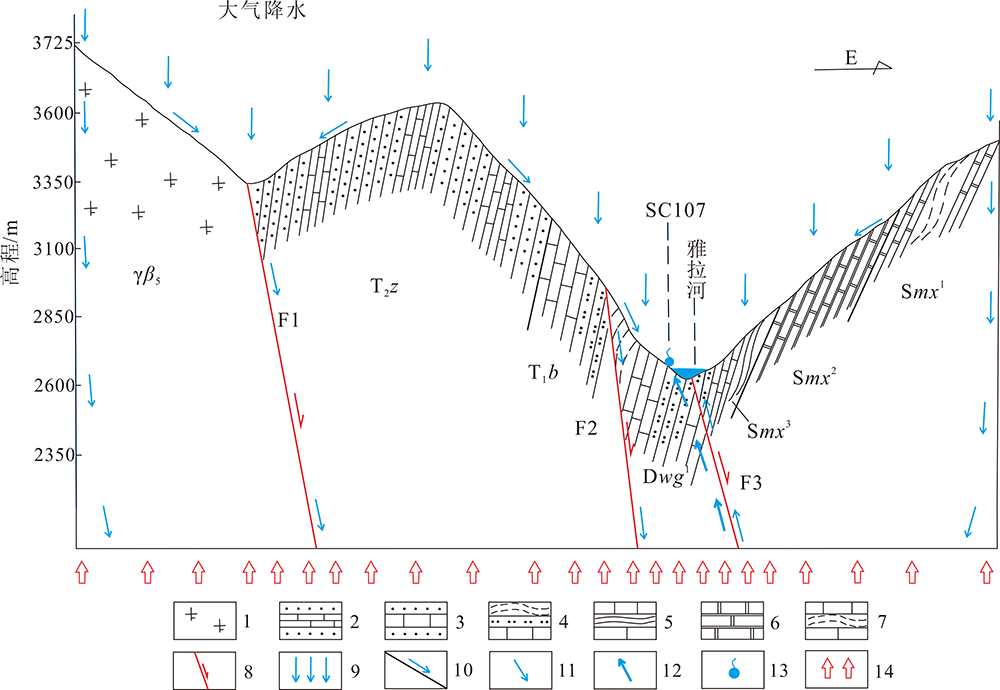
图7 康定二道桥地区温泉成因模式示意剖面图 1.斜长花岗岩;2.石英砂岩夹薄层灰岩;3.石英砂岩、灰岩;4.千枚岩夹粉砂岩;5.灰岩、片岩;6.大理岩;7.灰岩夹千枚岩;8.断层(F1为大雪山—农戈山断裂,F2为红卫乡断裂,F3为雅拉沟断裂);9.大气降水;10.地表径流;11.地下径流;12.汇集于断层带的地下水径流方向;13.温泉(SC107);14.大地热流;γβ5.燕山期花岗岩;T1b.三叠系上统白果湾组;T2z.三叠系中统杂谷脑组;Dwg1.泥盆系危关群;Smx(1-3).志留系茂县群。
Fig.7 Schematic profiles showing the formation of the hot springs in the Erdaoqiao area in Kangding
| [1] | 汪集旸, 熊亮萍, 庞忠和. 中低温对流型地热系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 1-240. |
| [2] | RYBACH L, MUFFLER L J P. Gerthermal Systems: Principles and Case Histories[M]. New York: Wiley, 1981: 1-371. |
| [3] | 韩建光, 蒋宗霖, 田颖, 等. 中国地热资源及开发利用[J]. 消费导刊, 2008, 48(23): 39-40. |
| [4] | 陈墨香, 汪集旸. 中国地热研究的回顾和展望[J]. 地球物理学报, 1994, 35(A1): 320-338. |
| [5] | 廖志杰, 赵平. 滇藏地热带--地热资源和典型地热系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 1-153. |
| [6] | 陈墨香, 汪集旸, 邓孝, 等. 中国地热资源--形成特点和潜力评估[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 1-39. |
| [7] | 王建国, 宁丽荣, 李广之, 等. 沉积盆地型与隆起山地型地热系统地表地球化学异常模式差异性分析[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(1): 117-128. |
| [8] | 谭肖波, 薄本玉, 姜佃卿, 等. 山东高青县沉积盆地型地热流体地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 92(A1): 168-177. |
| [9] | 温煜华, 王乃昂, 朱锡芬, 等. 甘肃武山地热田水化学与地热水起源[J]. 自然资源学报, 2010, 25(7): 1186-1193. |
| [10] | 拓明明, 周训, 郭娟, 等. 重庆温泉及地下热水的分布及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2018, 45(1): 165-172. |
| [11] | 卢丽, 陈余道, 代俊鸽, 等. 四川昭觉竹核温泉水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(3): 703-710. |
| [12] |
FOURNIER R O, ROWE J J. Estimation of underground tempe-ratures from the silica content of water from hot springs and wet-steam wells[J]. American Journal of Science, 1966, 264(9): 685-697.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
REED M, SPYCHER N. Calculation of pH and mineral equilibria in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983, 48(7): 1479-1492.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
GIGGENBACH W F. Geothermal solute equilibria.Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(12): 2749-2765.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PANG Z H, REED M. Theoretical chemical thermometry on geothermal waters: problems and methods[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(6): 1083-1091.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MOHAMMADI Z, BAGHERI R, JAHANSHAHI R. Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of Changal thermal springs, Zagros region, Iran[J]. Geothermics, 2010, 39(3): 242-249.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 黄珣, 李晓, 余中友, 等. 康定中谷地区热储特征及温度计算[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2018, 29(4): 96-104. |
| [18] | 刘再华, 袁道先, 何师意, 等. 地热CO2-水-碳酸盐岩系统的地球化学特征及其CO2来源--以四川黄龙沟、康定和云南中甸下给为例[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000, 30(2): 209-214. |
| [19] | 卞跃跃, 赵丹. 四川康定地热田地下热水成因研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(4): 491-497. |
| [20] | 李玥樾, 李晓. 康定二道桥-榆林宫地区地下热水出露特征[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2019, 30(1): 106-112. |
| [21] | 郭琦. 川西高原康定高温地热系统流体地球化学成因[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017: 1-158. |
| [22] | GUO Q, PANG Z H, WANG Y C, et al. Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry applications of the Kangding high-temperature geothermal system in eastern Himalayas[J]. Applied Geochemi-stry, 2017, 81: 63-75. |
| [23] | 陈柄桦. 四川康定市榆林宫地区温泉水化学特征及成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021: 1-70. |
| [24] |
CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science, 1961, 133(3465): 1702-1703.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 周训, 金晓媚, 梁四海, 等. 地下水科学专论(第二版·彩色版)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 75-76. |
| [26] |
DANSGAARD W. Stable isotopes in precipitation[J]. Tellus, 1964, 16(4): 436-468.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 郑淑蕙, 侯发高, 倪葆龄. 我国大气降水的氢氧稳定同位素研究[J]. 科学通报, 1983, 28(13): 801-806. |
| [28] | 朱磊, 范弢, 郭欢. 西南地区大气降水中氢氧稳定同位素特征与水汽来源[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2014, 26(5): 61-67. |
| [29] |
PANICHI C, GONFIANTINI R. Environmental isotopes in geothermal studies[J]. Geothermics, 1977, 6(3/4): 143-161.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 王东升. 中国大气降水氢氧稳定同位素浓度场的时间-空间展布及其环境效应[M]// 王东升, 徐乃安. 第二届全国同位素水文地质方法讨论会论文选--中国同位素水文地质学之进展. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 1993: 5-11. |
| [31] | 张洪平, 刘恩凯, 王东升, 等. 中国大气降水稳定同位素组成及影响因素[M]//汪蕴璞.中国地质科学院水文地质工程地质研究所文集(7). 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 101-110. |
| [32] | FOURNIER R O, POTTER R W Ⅱ. A revised and expanded silica (quartz) geothermometer[J]. Geothermal Resources Council Bulletin, 1982, 11(10): 3-12. |
| [33] |
FOURNIER R O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics, 1977, 5(1/4): 41-50.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
GIGGENBACH W F, GLOVER R B. Tectonic regime and major processe governing the chemistry of water and gas discharges from the Rotorua geothermal field, New Zealand[J]. Geothermics, 1992, 21(1/2): 121-140.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
GIGGENBACH W F. Geochemical structure and position of the Waiotapu geothermal field, New Zealand[J]. Geothermics, 1994, 23(5/6): 599-644.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 霍冬雪, 周训, 刘海生, 等. 云南祥云县王家庄碱性温泉水化学特征与成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(3): 680-690. |
| [37] | PARKHURST D L, APPELO C A J. User’s guide to PHREEQC a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations[J]. Water-Resources Investigation Report, 1999: 99. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [5] | 张一范, 高远, 陈积权, 黄帅, 海伦, 毋正轩, 杨柳, 董甜. 松辽盆地晚白垩世湖相白云岩碳氧同位素特征及其古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1243-1253. |
| [6] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [7] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [8] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [9] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [10] | 张红雨, 杨立明, 苏犁, 宋述光, 王大川. LA-ICP-MS独居石的U(Th)-Pb年龄精确测定方法及地质意义探究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 443-462. |
| [11] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [12] | 唐名鹰, 华磊, 丁正江, 董振昆, 王炜晓, 翟孝志, 王汝杰, 郑成龙. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区乌腊德石墨矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1475-1485. |
| [13] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| [14] | 刘思逸, 高平, 肖贤明, 刘若冰, 秦婧, 袁桃, 王旭. 四川盆地五峰—龙马溪组黑色页岩有机岩石学特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1281-1291. |
| [15] | 李二庭, 马万云, 李际, 马新星, 潘长春, 曾立飞, 王明. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系煤生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1313-1323. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||