



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (03): 438-452.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.03.03
王涛1,2( ), 张静1,2(
), 张静1,2( ), 佟子达1,2, 李腾建1,2
), 佟子达1,2, 李腾建1,2
收稿日期:2017-07-15
修回日期:2018-01-19
出版日期:2018-06-10
发布日期:2023-09-22
通讯作者:
张静
作者简介:张静,女,教授,博士生导师,1977年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学研究。Email:zhangjing@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
WANG Tao1,2( ), ZHANG Jing1,2(
), ZHANG Jing1,2( ), TONG Zida1,2, LI Tengjian1,2
), TONG Zida1,2, LI Tengjian1,2
Received:2017-07-15
Revised:2018-01-19
Online:2018-06-10
Published:2023-09-22
Contact:
ZHANG Jing
摘要:
莲花山富碱斑岩体位于兰坪盆地东缘,是滇西富碱斑岩带的重要组成部分。该岩体主要由石英二长斑岩和角闪石英二长斑岩组成,对不同岩性中的锆石进行了LA-ICP-MS U-Pb同位素测年,获得其形成年龄为(35.6±0.5)~(35.7±0.5) Ma,表明该岩体的形成时代为始新世。其K2O/Na2O比值为0.97~1.42、K2O+Na2O含量为8.86%~9.59%,显示高钾富碱的特征,属于钾玄岩系列岩石;岩体具有轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的特征,显示弱的Eu负异常。利用锆石Ti温度计,获得岩体中岩浆锆石样品的结晶温度较低,介于594~788 ℃,说明该岩体岩浆源区的形成与俯冲-碰撞作用有关。样品中存在有少量年龄为1 177~68 Ma的继承锆石,Nb/U比值为1.31~4.73,表明莲花山岩体的源区是由洋壳俯冲作用形成的交代富集地幔,在其上侵过程中受到壳源物质不同程度的混染;岩体侵位于印度板块—欧亚板块陆-陆碰撞的挤压环境向后碰撞伸展环境转换的构造背景下。
中图分类号:
王涛, 张静, 佟子达, 李腾建. 滇西莲花山富碱斑岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 438-452.
WANG Tao, ZHANG Jing, TONG Zida, LI Tengjian. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry Characteristics of the Lianhuashan Alkaline-rich Porphyry Intrusion in Western Yunnan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(03): 438-452.

图3 莲花山富碱斑岩体的岩石学和岩相学特征 A.石英二长斑岩与围岩接触;B.灰白色石英二长斑岩;C.石英二长斑岩显微照片,可见钾长石、斜长石斑晶和微粒石英、长石基质(+);D.石英二长斑岩与角闪石英二长斑岩接触;E.灰红色角闪石英二长斑岩;F.角闪石英二长斑岩显微照片,可见斜长石、钾长石和角闪石斑晶,基质为微粒状石英和钾长石(+)。Qz.石英;Pl.斜长石;Kfs.钾长石;Hb.角闪石;Bt.黑云母
Fig.3 Outcrops photos and photomicrographs of the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry
| 测点号 | 元素含量/10-6 | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U Th Pb | Pb | 1σ | 同位素 比值 | 1σ | 同位素 比值 | 1σ | 年龄/ Ma | 1σ | 年龄/ Ma | 1σ | 年龄/ Ma | 1σ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-2 | 1 426 | 1 174 | 10 | 0.82 | 0.047 1 | 0.004 2 | 0.035 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 200.0 | 35.6 | 2.6 | 36.2 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-3 | 1 271 | 476 | 8 | 0.37 | 0.047 9 | 0.003 8 | 0.034 9 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 100.1 | 233.3 | 34.8 | 2.2 | 34.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-4 | 1 301 | 989 | 9 | 0.76 | 0.047 8 | 0.003 6 | 0.034 9 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 87.1 | 170.3 | 34.8 | 2.2 | 34.2 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-5 | 702 | 411 | 5 | 0.59 | 0.049 8 | 0.005 3 | 0.038 8 | 0.003 1 | 0.006 0 | 0.000 1 | 187.1 | 229.6 | 38.6 | 3.0 | 38.4 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-6 | 1 060 | 726 | 7 | 0.69 | 0.054 0 | 0.007 3 | 0.038 8 | 0.004 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 2 | 372.3 | 307.4 | 38.6 | 4.2 | 35.4 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-7 | 377 | 252 | 3 | 0.67 | 0.046 8 | 0.006 1 | 0.038 4 | 0.004 0 | 0.006 0 | 0.000 2 | 39.0 | 285.1 | 38.2 | 3.9 | 38.5 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-8 | 1 240 | 951 | 9 | 0.77 | 0.048 2 | 0.004 3 | 0.037 2 | 0.003 0 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 109.4 | 196.3 | 37.1 | 2.9 | 36.8 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-9 | 735 | 370 | 5 | 0.50 | 0.049 6 | 0.004 4 | 0.040 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 189.0 | 183.3 | 39.8 | 3.1 | 37.7 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-10 | 1 184 | 602 | 7 | 0.51 | 0.046 7 | 0.004 7 | 0.034 4 | 0.003 6 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 31.60 | 225.9 | 34.4 | 3.5 | 34.1 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-11 | 212 | 127 | 52 | 0.60 | 0.079 6 | 0.002 6 | 2.204 6 | 0.072 6 | 0.200 2 | 0.002 6 | 1 187.0 | 64.80 | 1 182.5 | 23.0 | 1 176.6 | 13.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-12 | 1 249 | 900 | 9 | 0.72 | 0.047 3 | 0.004 5 | 0.035 6 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 64.9 | 211.1 | 35.5 | 2.8 | 35.6 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-14 | 671 | 401 | 4 | 0.60 | 0.048 9 | 0.005 4 | 0.033 3 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 1 | 0.000 1 | 142.7 | 246.3 | 33.3 | 2.5 | 33.1 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-16 | 1 094 | 462 | 7 | 0.42 | 0.049 8 | 0.004 8 | 0.034 5 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 187.1 | 211.1 | 34.4 | 2.8 | 34.4 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-17 | 931 | 683 | 6 | 0.73 | 0.048 4 | 0.005 0 | 0.036 0 | 0.003 4 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 116.8 | 225.9 | 35.9 | 3.3 | 36.1 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-18 | 1 959 | 701 | 12 | 0.36 | 0.045 9 | 0.004 1 | 0.033 3 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 33.3 | 2.5 | 34.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-19 | 1 116 | 400 | 7 | 0.36 | 0.052 2 | 0.005 0 | 0.038 1 | 0.003 2 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 2 | 294.5 | 218.5 | 38.0 | 3.1 | 34.8 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-20 | 809 | 628 | 11 | 0.78 | 0.048 8 | 0.004 1 | 0.071 4 | 0.005 2 | 0.010 5 | 0.000 3 | 200.1 | 124.1 | 70.0 | 5.0 | 67.6 | 1.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-21 | 1 332 | 622 | 8 | 0.47 | 0.045 2 | 0.003 6 | 0.035 3 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 35.2 | 2.7 | 35.4 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-22 | 1 354 | 1 009 | 9 | 0.75 | 0.048 1 | 0.004 1 | 0.037 1 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 105.6 | 192.6 | 37.0 | 2.8 | 36.7 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-23 | 1 320 | 1 155 | 10 | 0.87 | 0.048 5 | 0.003 8 | 0.037 4 | 0.002 4 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 124.2 | 174.1 | 37.3 | 2.3 | 36.2 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-24 | 369 | 268 | 3 | 0.73 | 0.054 0 | 0.009 7 | 0.037 5 | 0.005 3 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 2 | 372.3 | 360.8 | 37.3 | 5.2 | 35.9 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-25 | 727 | 482 | 12 | 0.66 | 0.046 7 | 0.004 9 | 0.078 1 | 0.007 7 | 0.011 3 | 0.000 8 | 31.6 | 301.8 | 76.3 | 7.2 | 72.1 | 5.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-26 | 3 044 | 807 | 19 | 0.27 | 0.045 6 | 0.002 9 | 0.034 8 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 34.8 | 2.0 | 35.6 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-1 | 1 814 | 748 | 12 | 0.41 | 0.047 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.036 0 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 77.9 | 133.3 | 35.9 | 1.9 | 35.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-2 | 1 597 | 778 | 10 | 0.49 | 0.045 8 | 0.003 3 | 0.035 0 | 0.002 4 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 34.9 | 2.3 | 35.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-3 | 1 240 | 465 | 8 | 0.37 | 0.051 4 | 0.005 1 | 0.037 1 | 0.003 1 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 257.5 | 231.5 | 37.0 | 3.0 | 35.6 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-4 | 1 910 | 771 | 12 | 0.40 | 0.048 6 | 0.003 5 | 0.034 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 131.6 | 168.5 | 34.5 | 2.0 | 34.3 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-5 | 1 758 | 683 | 11 | 0.39 | 0.046 4 | 0.003 3 | 0.034 4 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 16.8 | 172.2 | 34.3 | 2.2 | 34.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-6 | 1 467 | 773 | 10 | 0.53 | 0.046 9 | 0.003 6 | 0.035 0 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 42.7 | 177.8 | 34.9 | 2.2 | 35.3 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-7 | 1 907 | 1 452 | 13 | 0.76 | 0.045 4 | 0.003 2 | 0.032 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 2 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 32.0 | 2.0 | 33.3 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-8 | 1 575 | 1 069 | 11 | 0.68 | 0.047 7 | 0.002 6 | 0.038 5 | 0.0021 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 83.4 | 122.2 | 38.4 | 2.0 | 37.7 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-9 | 2 116 | 685 | 13 | 0.32 | 0.046 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.034 4 | 0.001 8 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 31.6 | 133.3 | 34.3 | 1.8 | 34.1 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-10 | 1 595 | 705 | 10 | 0.44 | 0.043 2 | 0.003 2 | 0.032 7 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 32.7 | 2.1 | 35.9 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-11 | 1 386 | 404 | 9 | 0.29 | 0.047 0 | 0.003 6 | 0.036 1 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 50.1 | 170.3 | 36.0 | 2.4 | 36.2 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-12 | 1 851 | 1 088 | 12 | 0.59 | 0.047 2 | 0.002 6 | 0.036 5 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 129.6 | 36.4 | 1.8 | 36.1 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-13 | 1 081 | 594 | 7 | 0.55 | 0.047 2 | 0.004 4 | 0.038 1 | 0.003 2 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 207.4 | 37.9 | 3.2 | 37.9 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-14 | 1 988 | 1 279 | 13 | 0.64 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 5 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 157.4 | 35.4 | 2.1 | 35.4 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-16 | 1 344 | 1 202 | 11 | 0.89 | 0.045 9 | 0.003 4 | 0.039 5 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 39.3 | 2.3 | 36.7 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-17 | 1 498 | 610 | 10 | 0.41 | 0.047 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.036 8 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 140.7 | 36.7 | 2.1 | 36.5 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-18 | 788 | 285 | 5 | 0.36 | 0.048 4 | 0.004 6 | 0.038 4 | 0.003 1 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 120.5 | 211.1 | 38.3 | 3.1 | 38.0 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-19 | 1 661 | 666 | 11 | 0.40 | 0.050 6 | 0.003 7 | 0.039 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 220.4 | 173.1 | 39.2 | 2.7 | 36.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-20 | 1 278 | 553 | 8 | 0.43 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 5 | 0.035 2 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 179.6 | 35.2 | 2.3 | 35.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-21 | 1 494 | 567 | 10 | 0.38 | 0.047 0 | 0.003 8 | 0.038 3 | 0.002 9 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 50.1 | 181.5 | 38.2 | 2.8 | 37.9 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-22 | 1 936 | 780 | 13 | 0.40 | 0.047 8 | 0.003 8 | 0.038 5 | 0.002 6 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 100.1 | 233.3 | 38.4 | 2.6 | 38.2 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-24 | 1 001 | 450 | 25 | 0.45 | 0.049 1 | 0.002 7 | 0.152 8 | 0.011 4 | 0.022 0 | 0.001 4 | 153.8 | 129.6 | 144.4 | 10.1 | 140.3 | 8.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-25 | 1 701 | 389 | 10 | 0.23 | 0.046 6 | 0.003 5 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 27.9 | 170.4 | 35.8 | 2.5 | 35.9 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-26 | 1 414 | 583 | 9 | 0.41 | 0.046 8 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 39.0 | 151.8 | 35.8 | 2.2 | 35.8 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-27 | 1 700 | 588 | 10 | 0.35 | 0.048 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 3 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 98.2 | 144.4 | 35.2 | 2.0 | 34.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-28 | 2 220 | 894 | 14 | 0.40 | 0.046 9 | 0.002 9 | 0.035 0 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 42.7 | 144.4 | 34.9 | 2.0 | 34.7 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-1 | 1 980 | 964 | 13 | 0.49 | 0.047 9 | 0.002 7 | 0.036 8 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 94.5 | 125.9 | 36.7 | 1.9 | 36.4 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-2 | 1 975 | 1 430 | 13 | 0.72 | 0.046 9 | 0.002 6 | 0.035 8 | 0.001 8 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 42.7 | 129.6 | 35.7 | 1.8 | 35.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-3 | 866 | 271 | 5 | 0.31 | 0.047 2 | 0.004 4 | 0.035 8 | 0.003 0 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 207.4 | 35.7 | 3.0 | 35.8 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-5 | 2 791 | 696 | 17 | 0.25 | 0.051 9 | 0.003 9 | 0.038 2 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 279.7 | 170.4 | 38.1 | 2.3 | 35.3 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-6 | 438 | 298 | 3 | 0.68 | 0.048 0 | 0.006 0 | 0.036 4 | 0.004 3 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 2 | 98.2 | 270.3 | 36.3 | 4.2 | 37.8 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-7 | 3 127 | 710 | 19 | 0.23 | 0.051 3 | 0.002 5 | 0.039 6 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 253.8 | 111.1 | 39.4 | 1.8 | 36.2 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-8 | 1 517 | 459 | 9 | 0.30 | 0.049 5 | 0.004 8 | 0.034 4 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 172.3 | 216.6 | 34.4 | 2.2 | 34.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-9 | 2 422 | 933 | 15 | 0.39 | 0.048 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.036 5 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 105.6 | 137.0 | 36.4 | 2.0 | 36.0 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-10 | 1 719 | 810 | 11 | 0.47 | 0.047 2 | 0.003 3 | 0.036 2 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 61.2 | 155.5 | 36.1 | 2.2 | 36.1 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-11 | 760 | 559 | 5 | 0.74 | 0.047 5 | 0.004 6 | 0.035 1 | 0.003 0 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 72.3 | 214.8 | 35.1 | 2.9 | 35.4 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-12 | 2 128 | 1 699 | 15 | 0.80 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 5 | 0.037 6 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 8 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 166.6 | 37.4 | 2.6 | 37.2 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-13 | 2 179 | 1 343 | 14 | 0.62 | 0.046 8 | 0.003 0 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 39.0 | 144.4 | 35.8 | 2.1 | 35.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-14 | 2 538 | 1 022 | 16 | 0.40 | 0.046 7 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 31.6 | 151.8 | 35.8 | 2.2 | 35.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-15 | 1 674 | 994 | 11 | 0.59 | 0.046 5 | 0.003 5 | 0.037 2 | 0.002 6 | 0.005 8 | 0.000 1 | 20.5 | 174.1 | 37.1 | 2.6 | 37.1 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-16 | 1 908 | 740 | 11 | 0.39 | 0.040 8 | 0.003 4 | 0.032 1 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 32.1 | 2.7 | 36.4 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-17 | 2 297 | 736 | 13 | 0.32 | 0.046 6 | 0.002 8 | 0.033 9 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 27.9 | 140.7 | 33.8 | 1.8 | 34.0 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-18 | 1 668 | 845 | 11 | 0.51 | 0.044 5 | 0.002 9 | 0.039 2 | 0.004 1 | 0.006 1 | 0.000 2 | — | — | 39.1 | 4.0 | 38.9 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-20 | 525 | 325 | 3 | 0.62 | 0.051 7 | 0.005 8 | 0.035 8 | 0.003 2 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 2 | 272.3 | 237.0 | 35.7 | 3.1 | 35.6 | 1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-21 | 2 156 | 656 | 13 | 0.30 | 0.046 2 | 0.002 8 | 0.034 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 9.4 | 140.7 | 34.0 | 1.9 | 34.3 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-22 | 1 843 | 815 | 12 | 0.44 | 0.047 4 | 0.003 3 | 0.036 7 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 77.9 | 155.5 | 36.6 | 2.2 | 36.7 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-23 | 1 437 | 368 | 9 | 0.26 | 0.046 2 | 0.003 1 | 0.037 0 | 0.002 4 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 9.4 | 155.5 | 36.9 | 2.4 | 36.8 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-24 | 1 257 | 686 | 8 | 0.55 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 7 | 0.036 2 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 50.1 | 181.5 | 36.1 | 2.6 | 35.8 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-25 | 892 | 325 | 6 | 0.36 | 0.049 0 | 0.006 1 | 0.036 0 | 0.003 7 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 150.1 | 266.6 | 35.9 | 3.6 | 35.2 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-26 | 1 050 | 380 | 7 | 0.36 | 0.050 4 | 0.006 2 | 0.039 0 | 0.004 0 | 0.005 8 | 0.000 2 | 213.0 | 262.9 | 38.9 | 3.9 | 37.2 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-27 | 2 892 | 885 | 17 | 0.31 | 0.045 8 | 0.002 6 | 0.033 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.005 2 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 33.2 | 1.8 | 33.5 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-28 | 760 | 214 | 5 | 0.28 | 0.050 8 | 0.006 0 | 0.037 9 | 0.004 0 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 231.6 | 251.8 | 37.7 | 3.9 | 35.3 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表1 莲花山富碱斑岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry
| 测点号 | 元素含量/10-6 | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U Th Pb | Pb | 1σ | 同位素 比值 | 1σ | 同位素 比值 | 1σ | 年龄/ Ma | 1σ | 年龄/ Ma | 1σ | 年龄/ Ma | 1σ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-2 | 1 426 | 1 174 | 10 | 0.82 | 0.047 1 | 0.004 2 | 0.035 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 200.0 | 35.6 | 2.6 | 36.2 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-3 | 1 271 | 476 | 8 | 0.37 | 0.047 9 | 0.003 8 | 0.034 9 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 100.1 | 233.3 | 34.8 | 2.2 | 34.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-4 | 1 301 | 989 | 9 | 0.76 | 0.047 8 | 0.003 6 | 0.034 9 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 87.1 | 170.3 | 34.8 | 2.2 | 34.2 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-5 | 702 | 411 | 5 | 0.59 | 0.049 8 | 0.005 3 | 0.038 8 | 0.003 1 | 0.006 0 | 0.000 1 | 187.1 | 229.6 | 38.6 | 3.0 | 38.4 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-6 | 1 060 | 726 | 7 | 0.69 | 0.054 0 | 0.007 3 | 0.038 8 | 0.004 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 2 | 372.3 | 307.4 | 38.6 | 4.2 | 35.4 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-7 | 377 | 252 | 3 | 0.67 | 0.046 8 | 0.006 1 | 0.038 4 | 0.004 0 | 0.006 0 | 0.000 2 | 39.0 | 285.1 | 38.2 | 3.9 | 38.5 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-8 | 1 240 | 951 | 9 | 0.77 | 0.048 2 | 0.004 3 | 0.037 2 | 0.003 0 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 109.4 | 196.3 | 37.1 | 2.9 | 36.8 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-9 | 735 | 370 | 5 | 0.50 | 0.049 6 | 0.004 4 | 0.040 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 189.0 | 183.3 | 39.8 | 3.1 | 37.7 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-10 | 1 184 | 602 | 7 | 0.51 | 0.046 7 | 0.004 7 | 0.034 4 | 0.003 6 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 31.60 | 225.9 | 34.4 | 3.5 | 34.1 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-11 | 212 | 127 | 52 | 0.60 | 0.079 6 | 0.002 6 | 2.204 6 | 0.072 6 | 0.200 2 | 0.002 6 | 1 187.0 | 64.80 | 1 182.5 | 23.0 | 1 176.6 | 13.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-12 | 1 249 | 900 | 9 | 0.72 | 0.047 3 | 0.004 5 | 0.035 6 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 64.9 | 211.1 | 35.5 | 2.8 | 35.6 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-14 | 671 | 401 | 4 | 0.60 | 0.048 9 | 0.005 4 | 0.033 3 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 1 | 0.000 1 | 142.7 | 246.3 | 33.3 | 2.5 | 33.1 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-16 | 1 094 | 462 | 7 | 0.42 | 0.049 8 | 0.004 8 | 0.034 5 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 187.1 | 211.1 | 34.4 | 2.8 | 34.4 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-17 | 931 | 683 | 6 | 0.73 | 0.048 4 | 0.005 0 | 0.036 0 | 0.003 4 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 116.8 | 225.9 | 35.9 | 3.3 | 36.1 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-18 | 1 959 | 701 | 12 | 0.36 | 0.045 9 | 0.004 1 | 0.033 3 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 33.3 | 2.5 | 34.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-19 | 1 116 | 400 | 7 | 0.36 | 0.052 2 | 0.005 0 | 0.038 1 | 0.003 2 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 2 | 294.5 | 218.5 | 38.0 | 3.1 | 34.8 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-20 | 809 | 628 | 11 | 0.78 | 0.048 8 | 0.004 1 | 0.071 4 | 0.005 2 | 0.010 5 | 0.000 3 | 200.1 | 124.1 | 70.0 | 5.0 | 67.6 | 1.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-21 | 1 332 | 622 | 8 | 0.47 | 0.045 2 | 0.003 6 | 0.035 3 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 35.2 | 2.7 | 35.4 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-22 | 1 354 | 1 009 | 9 | 0.75 | 0.048 1 | 0.004 1 | 0.037 1 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 105.6 | 192.6 | 37.0 | 2.8 | 36.7 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-23 | 1 320 | 1 155 | 10 | 0.87 | 0.048 5 | 0.003 8 | 0.037 4 | 0.002 4 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 124.2 | 174.1 | 37.3 | 2.3 | 36.2 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-24 | 369 | 268 | 3 | 0.73 | 0.054 0 | 0.009 7 | 0.037 5 | 0.005 3 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 2 | 372.3 | 360.8 | 37.3 | 5.2 | 35.9 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-25 | 727 | 482 | 12 | 0.66 | 0.046 7 | 0.004 9 | 0.078 1 | 0.007 7 | 0.011 3 | 0.000 8 | 31.6 | 301.8 | 76.3 | 7.2 | 72.1 | 5.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-26 | 3 044 | 807 | 19 | 0.27 | 0.045 6 | 0.002 9 | 0.034 8 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 34.8 | 2.0 | 35.6 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-1 | 1 814 | 748 | 12 | 0.41 | 0.047 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.036 0 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 77.9 | 133.3 | 35.9 | 1.9 | 35.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-2 | 1 597 | 778 | 10 | 0.49 | 0.045 8 | 0.003 3 | 0.035 0 | 0.002 4 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 34.9 | 2.3 | 35.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-3 | 1 240 | 465 | 8 | 0.37 | 0.051 4 | 0.005 1 | 0.037 1 | 0.003 1 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 257.5 | 231.5 | 37.0 | 3.0 | 35.6 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-4 | 1 910 | 771 | 12 | 0.40 | 0.048 6 | 0.003 5 | 0.034 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 131.6 | 168.5 | 34.5 | 2.0 | 34.3 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-5 | 1 758 | 683 | 11 | 0.39 | 0.046 4 | 0.003 3 | 0.034 4 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 16.8 | 172.2 | 34.3 | 2.2 | 34.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-6 | 1 467 | 773 | 10 | 0.53 | 0.046 9 | 0.003 6 | 0.035 0 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 42.7 | 177.8 | 34.9 | 2.2 | 35.3 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-7 | 1 907 | 1 452 | 13 | 0.76 | 0.045 4 | 0.003 2 | 0.032 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 2 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 32.0 | 2.0 | 33.3 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-8 | 1 575 | 1 069 | 11 | 0.68 | 0.047 7 | 0.002 6 | 0.038 5 | 0.0021 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 83.4 | 122.2 | 38.4 | 2.0 | 37.7 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-9 | 2 116 | 685 | 13 | 0.32 | 0.046 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.034 4 | 0.001 8 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 31.6 | 133.3 | 34.3 | 1.8 | 34.1 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-10 | 1 595 | 705 | 10 | 0.44 | 0.043 2 | 0.003 2 | 0.032 7 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 32.7 | 2.1 | 35.9 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-11 | 1 386 | 404 | 9 | 0.29 | 0.047 0 | 0.003 6 | 0.036 1 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 50.1 | 170.3 | 36.0 | 2.4 | 36.2 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-12 | 1 851 | 1 088 | 12 | 0.59 | 0.047 2 | 0.002 6 | 0.036 5 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 129.6 | 36.4 | 1.8 | 36.1 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-13 | 1 081 | 594 | 7 | 0.55 | 0.047 2 | 0.004 4 | 0.038 1 | 0.003 2 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 207.4 | 37.9 | 3.2 | 37.9 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-14 | 1 988 | 1 279 | 13 | 0.64 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 5 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 157.4 | 35.4 | 2.1 | 35.4 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-16 | 1 344 | 1 202 | 11 | 0.89 | 0.045 9 | 0.003 4 | 0.039 5 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 39.3 | 2.3 | 36.7 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-17 | 1 498 | 610 | 10 | 0.41 | 0.047 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.036 8 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 140.7 | 36.7 | 2.1 | 36.5 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-18 | 788 | 285 | 5 | 0.36 | 0.048 4 | 0.004 6 | 0.038 4 | 0.003 1 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 120.5 | 211.1 | 38.3 | 3.1 | 38.0 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-19 | 1 661 | 666 | 11 | 0.40 | 0.050 6 | 0.003 7 | 0.039 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 220.4 | 173.1 | 39.2 | 2.7 | 36.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-20 | 1 278 | 553 | 8 | 0.43 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 5 | 0.035 2 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 179.6 | 35.2 | 2.3 | 35.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-21 | 1 494 | 567 | 10 | 0.38 | 0.047 0 | 0.003 8 | 0.038 3 | 0.002 9 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 50.1 | 181.5 | 38.2 | 2.8 | 37.9 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-22 | 1 936 | 780 | 13 | 0.40 | 0.047 8 | 0.003 8 | 0.038 5 | 0.002 6 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 1 | 100.1 | 233.3 | 38.4 | 2.6 | 38.2 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-24 | 1 001 | 450 | 25 | 0.45 | 0.049 1 | 0.002 7 | 0.152 8 | 0.011 4 | 0.022 0 | 0.001 4 | 153.8 | 129.6 | 144.4 | 10.1 | 140.3 | 8.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-25 | 1 701 | 389 | 10 | 0.23 | 0.046 6 | 0.003 5 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 5 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 27.9 | 170.4 | 35.8 | 2.5 | 35.9 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-26 | 1 414 | 583 | 9 | 0.41 | 0.046 8 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 39.0 | 151.8 | 35.8 | 2.2 | 35.8 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-27 | 1 700 | 588 | 10 | 0.35 | 0.048 0 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 3 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 98.2 | 144.4 | 35.2 | 2.0 | 34.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-28 | 2 220 | 894 | 14 | 0.40 | 0.046 9 | 0.002 9 | 0.035 0 | 0.002 1 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 42.7 | 144.4 | 34.9 | 2.0 | 34.7 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-1 | 1 980 | 964 | 13 | 0.49 | 0.047 9 | 0.002 7 | 0.036 8 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 94.5 | 125.9 | 36.7 | 1.9 | 36.4 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-2 | 1 975 | 1 430 | 13 | 0.72 | 0.046 9 | 0.002 6 | 0.035 8 | 0.001 8 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 42.7 | 129.6 | 35.7 | 1.8 | 35.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-3 | 866 | 271 | 5 | 0.31 | 0.047 2 | 0.004 4 | 0.035 8 | 0.003 0 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 57.5 | 207.4 | 35.7 | 3.0 | 35.8 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-5 | 2 791 | 696 | 17 | 0.25 | 0.051 9 | 0.003 9 | 0.038 2 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 279.7 | 170.4 | 38.1 | 2.3 | 35.3 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-6 | 438 | 298 | 3 | 0.68 | 0.048 0 | 0.006 0 | 0.036 4 | 0.004 3 | 0.005 9 | 0.000 2 | 98.2 | 270.3 | 36.3 | 4.2 | 37.8 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-7 | 3 127 | 710 | 19 | 0.23 | 0.051 3 | 0.002 5 | 0.039 6 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 253.8 | 111.1 | 39.4 | 1.8 | 36.2 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-8 | 1 517 | 459 | 9 | 0.30 | 0.049 5 | 0.004 8 | 0.034 4 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 4 | 0.000 1 | 172.3 | 216.6 | 34.4 | 2.2 | 34.6 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-9 | 2 422 | 933 | 15 | 0.39 | 0.048 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.036 5 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 105.6 | 137.0 | 36.4 | 2.0 | 36.0 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-10 | 1 719 | 810 | 11 | 0.47 | 0.047 2 | 0.003 3 | 0.036 2 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 61.2 | 155.5 | 36.1 | 2.2 | 36.1 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-11 | 760 | 559 | 5 | 0.74 | 0.047 5 | 0.004 6 | 0.035 1 | 0.003 0 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 72.3 | 214.8 | 35.1 | 2.9 | 35.4 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-12 | 2 128 | 1 699 | 15 | 0.80 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 5 | 0.037 6 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 8 | 0.000 1 | 53.8 | 166.6 | 37.4 | 2.6 | 37.2 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-13 | 2 179 | 1 343 | 14 | 0.62 | 0.046 8 | 0.003 0 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 2 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 39.0 | 144.4 | 35.8 | 2.1 | 35.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-14 | 2 538 | 1 022 | 16 | 0.40 | 0.046 7 | 0.003 1 | 0.035 9 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 31.6 | 151.8 | 35.8 | 2.2 | 35.7 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-15 | 1 674 | 994 | 11 | 0.59 | 0.046 5 | 0.003 5 | 0.037 2 | 0.002 6 | 0.005 8 | 0.000 1 | 20.5 | 174.1 | 37.1 | 2.6 | 37.1 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-16 | 1 908 | 740 | 11 | 0.39 | 0.040 8 | 0.003 4 | 0.032 1 | 0.002 8 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 32.1 | 2.7 | 36.4 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-17 | 2 297 | 736 | 13 | 0.32 | 0.046 6 | 0.002 8 | 0.033 9 | 0.001 9 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 27.9 | 140.7 | 33.8 | 1.8 | 34.0 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-18 | 1 668 | 845 | 11 | 0.51 | 0.044 5 | 0.002 9 | 0.039 2 | 0.004 1 | 0.006 1 | 0.000 2 | — | — | 39.1 | 4.0 | 38.9 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-20 | 525 | 325 | 3 | 0.62 | 0.051 7 | 0.005 8 | 0.035 8 | 0.003 2 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 2 | 272.3 | 237.0 | 35.7 | 3.1 | 35.6 | 1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-21 | 2 156 | 656 | 13 | 0.30 | 0.046 2 | 0.002 8 | 0.034 0 | 0.002 0 | 0.005 3 | 0.000 1 | 9.4 | 140.7 | 34.0 | 1.9 | 34.3 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-22 | 1 843 | 815 | 12 | 0.44 | 0.047 4 | 0.003 3 | 0.036 7 | 0.002 3 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 77.9 | 155.5 | 36.6 | 2.2 | 36.7 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-23 | 1 437 | 368 | 9 | 0.26 | 0.046 2 | 0.003 1 | 0.037 0 | 0.002 4 | 0.005 7 | 0.000 1 | 9.4 | 155.5 | 36.9 | 2.4 | 36.8 | 0.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-24 | 1 257 | 686 | 8 | 0.55 | 0.047 1 | 0.003 7 | 0.036 2 | 0.002 7 | 0.005 6 | 0.000 1 | 50.1 | 181.5 | 36.1 | 2.6 | 35.8 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-25 | 892 | 325 | 6 | 0.36 | 0.049 0 | 0.006 1 | 0.036 0 | 0.003 7 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 150.1 | 266.6 | 35.9 | 3.6 | 35.2 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-26 | 1 050 | 380 | 7 | 0.36 | 0.050 4 | 0.006 2 | 0.039 0 | 0.004 0 | 0.005 8 | 0.000 2 | 213.0 | 262.9 | 38.9 | 3.9 | 37.2 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-27 | 2 892 | 885 | 17 | 0.31 | 0.045 8 | 0.002 6 | 0.033 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.005 2 | 0.000 1 | — | — | 33.2 | 1.8 | 33.5 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-28 | 760 | 214 | 5 | 0.28 | 0.050 8 | 0.006 0 | 0.037 9 | 0.004 0 | 0.005 5 | 0.000 1 | 231.6 | 251.8 | 37.7 | 3.9 | 35.3 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | σ | 资料来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 66.40 | 0.39 | 15.42 | 5.71 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 3.68 | 5.24 | 0.18 | 1.90 | 99.49 | 8.92 | 1.42 | 3.40 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 69.17 | 0.33 | 16.00 | 2.16 | - | 0.40 | 0.43 | 4.86 | 4.73 | 0.15 | 1.09 | 99.32 | 9.59 | 0.97 | 3.51 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 67.11 | 0.34 | 15.52 | 2.63 | 0.02 | 1.48 | 1.63 | 4.79 | 4.69 | 0.16 | 0.71 | 99.08 | 9.48 | 0.98 | 3.73 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 68.30 | 0.27 | 17.71 | 2.46 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 2.20 | 4.18 | 5.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 101.75 | 9.21 | 1.20 | 3.35 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.80 | 0.31 | 15.82 | 2.67 | 0.02 | 1.19 | 2.32 | 4.27 | 4.82 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 99.89 | 9.09 | 1.13 | 3.33 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.88 | 0.30 | 15.98 | 2.36 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 2.39 | 4.38 | 4.79 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 99.75 | 9.17 | 1.09 | 3.38 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.43 | 0.38 | 15.81 | 2.70 | 0.03 | 1.29 | 2.53 | 4.06 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 99.71 | 8.86 | 1.18 | 3.21 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.89 | 0.31 | 15.64 | 2.67 | 0.03 | 1.13 | 2.58 | 4.44 | 4.48 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 99.74 | 8.92 | 1.01 | 3.20 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 68.30 | 0.27 | 15.71 | 2.46 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 2.20 | 4.18 | 5.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 99.76 | 9.21 | 1.20 | 3.35 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.80 | 0.31 | 15.82 | 2.67 | 0.03 | 1.19 | 2.32 | 4.27 | 4.82 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 99.90 | 9.09 | 1.13 | 3.33 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.88 | 0.30 | 15.98 | 2.36 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 2.39 | 4.38 | 4.79 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 99.75 | 9.17 | 1.09 | 3.38 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.43 | 0.38 | 15.81 | 2.70 | 0.03 | 1.29 | 2.53 | 4.06 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 99.71 | 8.86 | 1.18 | 3.21 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.89 | 0.31 | 15.64 | 2.67 | 0.03 | 1.13 | 2.58 | 4.44 | 4.48 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 99.74 | 8.92 | 1.01 | 3.20 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | Ba | Cu | Hf | Nb | Pb | Rb | Sr | Ta | Th | U | Zn | Zr | Cs | Cr | Ni | 资料来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 610 | 175 | 6.3 | 10.1 | 33 | 191 | 877 | 0.9 | 19.3 | 5.91 | 35 | 196 | 6.31 | 38 | 21 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 280 | 33 | 6.1 | 9.9 | 27 | 173 | 960 | 0.9 | 18.6 | 4.76 | 11 | 199 | 7.01 | 24 | 14 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 1 320 | 41 | 6.1 | 9.6 | 23 | 161 | 1 180 | 0.9 | 19.5 | 4.99 | 15 | 187 | 6.26 | 29 | 16 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 380 | 11 | 7.4 | 11.4 | 55 | 148 | 1 163 | 0.9 | 17.1 | 8.70 | 34 | 152 | 3.17 | 27 | 12 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 434 | 24 | 7.7 | 11.2 | 37 | 144 | 1 254 | 0.9 | 15.6 | 4.86 | 31 | 167 | 3.44 | 37 | 13 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 367 | 14 | 7.1 | 12.5 | 30 | 123 | 1 190 | 1.0 | 16.8 | 5.00 | 28 | 154 | 2.83 | 34 | 14 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 611 | 9 | 7.7 | 12.2 | 36 | 94 | 1 237 | 0.9 | 17.2 | 2.59 | 42 | 151 | 2.19 | 40 | 15 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 206 | 14 | 8.1 | 12.1 | 31 | 134 | 1 252 | 1.0 | 17.3 | 4.60 | 31 | 174 | 3.61 | 32 | 14 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 380 | 11 | 7.4 | 11.4 | 55 | 148 | 1 163 | 0.9 | 17.1 | 8.70 | 34 | 152 | 3.17 | 27 | 12 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 434 | 24 | 7.7 | 11.2 | 37 | 144 | 1 254 | 0.9 | 15.6 | 4.86 | 31 | 167 | 3.44 | 37 | 13 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 367 | 14 | 7.1 | 12.5 | 30 | 123 | 1 190 | 1.0 | 16.8 | 5.00 | 28 | 154 | 2.83 | 34 | 14 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 611 | 9 | 7.7 | 12.2 | 36 | 94 | 1 237 | 0.9 | 17.2 | 2.59 | 42 | 151 | 2.19 | 40 | 15 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 206 | 14 | 8.1 | 12.1 | 31 | 134 | 1 252 | 1.0 | 17.3 | 4.60 | 31 | 174 | 3.61 | 32 | 14 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | Co | V | Sc | Ga | Zn | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | 资料来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 11 | 53 | 6 | 19.8 | 35 | 44.9 | 82.0 | 8.60 | 31.80 | 5.50 | 1.23 | 3.86 | 0.51 | 3.04 | 0.56 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 9 | 37 | 4 | 19.2 | 11 | 24.7 | 52.5 | 5.14 | 19.30 | 3.49 | 1.09 | 3.14 | 0.46 | 2.43 | 0.51 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 38 | 4 | 18.8 | 15 | 45.4 | 84.4 | 8.78 | 32.90 | 5.55 | 1.54 | 4.04 | 0.53 | 2.79 | 0.59 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 32 | 4 | 18.2 | 34 | 41.9 | 78.8 | 8.30 | 30.20 | 4.90 | 1.20 | 3.96 | 0.53 | 2.57 | 0.45 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 39 | 5 | 18.1 | 31 | 42.1 | 80.3 | 8.90 | 32.20 | 5.30 | 1.30 | 4.23 | 0.57 | 2.86 | 0.51 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 41 | 5 | 19.9 | 28 | 41.3 | 81.5 | 8.90 | 32.80 | 5.40 | 1.40 | 4.34 | 0.59 | 2.92 | 0.51 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 46 | 6 | 19.8 | 42 | 47.6 | 99.1 | 11.50 | 42.40 | 6.50 | 1.60 | 5.01 | 0.64 | 3.01 | 0.53 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 35 | 5 | 19.3 | 31 | 41.3 | 79.3 | 8.80 | 32.50 | 5.30 | 1.30 | 4.21 | 0.57 | 2.84 | 0.51 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 32 | 4 | 18.2 | 34 | 41.9 | 78.8 | 8.33 | 30.21 | 4.94 | 1.20 | 3.96 | 0.53 | 2.57 | 0.45 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 39 | 5 | 18.1 | 31 | 42.1 | 80.3 | 8.88 | 32.17 | 5.32 | 1.31 | 4.23 | 0.57 | 2.86 | 0.51 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 41 | 5 | 19.9 | 28 | 41.3 | 81.5 | 8.95 | 32.80 | 5.37 | 1.35 | 4.34 | 0.59 | 2.92 | 0.51 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 46 | 6 | 19.8 | 42 | 47.6 | 99.1 | 11.52 | 42.40 | 6.54 | 1.55 | 5.01 | 0.64 | 3.01 | 0.53 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 35 | 5 | 19.3 | 31 | 41.3 | 79.3 | 8.80 | 32.50 | 5.34 | 1.30 | 4.21 | 0.57 | 2.84 | 0.51 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | Nb /U | 资料来源 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.71 | 0.25 | 1.62 | 0.23 | 15.20 | 186 | 174 | 12 | 14.77 | 19.9 | 0.77 | 1.71 | 本文 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.36 | 0.19 | 1.28 | 0.19 | 14.20 | 116 | 106 | 10 | 11.11 | 13.8 | 0.99 | 2.08 | 本文 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.36 | 0.22 | 14.70 | 190 | 178 | 11 | 15.87 | 24.0 | 0.95 | 1.92 | 本文 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 0.16 | 13.44 | 176 | 165 | 10 | 15.97 | 23.8 | 0.80 | 1.31 | 刘金宇等,2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 1.33 | 0.17 | 14.80 | 181 | 170 | 11 | 15.08 | 22.6 | 0.82 | 2.29 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.21 | 1.37 | 0.18 | 15.00 | 183 | 171 | 12 | 14.88 | 21.6 | 0.83 | 2.49 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 1.41 | 0.18 | 15.00 | 221 | 209 | 12 | 16.79 | 24.3 | 0.80 | 4.73 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.36 | 0.21 | 1.38 | 0.18 | 14.80 | 180 | 169 | 11 | 14.96 | 21.5 | 0.81 | 2.64 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 0.16 | 13.44 | 176 | 165 | 10 | 15.98 | 23.8 | 0.80 | 1.31 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 1.33 | 0.17 | 14.77 | 181 | 170 | 11 | 15.08 | 22.6 | 0.82 | 2.29 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.21 | 1.37 | 0.18 | 14.98 | 183 | 171 | 12 | 14.88 | 21.6 | 0.83 | 2.49 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 1.41 | 0.18 | 14.99 | 221 | 209 | 12 | 16.79 | 24.3 | 0.80 | 4.73 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.36 | 0.21 | 1.38 | 0.18 | 14.80 | 180 | 169 | 11 | 14.97 | 21.5 | 0.81 | 2.64 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表2 莲花山富碱斑岩体全岩主量元素(wB/%)、微量元素和稀土元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major(%) and trace element and REEs (10-6) composition of the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry
| 样号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | σ | 资料来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 66.40 | 0.39 | 15.42 | 5.71 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 3.68 | 5.24 | 0.18 | 1.90 | 99.49 | 8.92 | 1.42 | 3.40 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 69.17 | 0.33 | 16.00 | 2.16 | - | 0.40 | 0.43 | 4.86 | 4.73 | 0.15 | 1.09 | 99.32 | 9.59 | 0.97 | 3.51 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 67.11 | 0.34 | 15.52 | 2.63 | 0.02 | 1.48 | 1.63 | 4.79 | 4.69 | 0.16 | 0.71 | 99.08 | 9.48 | 0.98 | 3.73 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 68.30 | 0.27 | 17.71 | 2.46 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 2.20 | 4.18 | 5.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 101.75 | 9.21 | 1.20 | 3.35 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.80 | 0.31 | 15.82 | 2.67 | 0.02 | 1.19 | 2.32 | 4.27 | 4.82 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 99.89 | 9.09 | 1.13 | 3.33 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.88 | 0.30 | 15.98 | 2.36 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 2.39 | 4.38 | 4.79 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 99.75 | 9.17 | 1.09 | 3.38 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.43 | 0.38 | 15.81 | 2.70 | 0.03 | 1.29 | 2.53 | 4.06 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 99.71 | 8.86 | 1.18 | 3.21 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.89 | 0.31 | 15.64 | 2.67 | 0.03 | 1.13 | 2.58 | 4.44 | 4.48 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 99.74 | 8.92 | 1.01 | 3.20 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 68.30 | 0.27 | 15.71 | 2.46 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 2.20 | 4.18 | 5.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 99.76 | 9.21 | 1.20 | 3.35 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.80 | 0.31 | 15.82 | 2.67 | 0.03 | 1.19 | 2.32 | 4.27 | 4.82 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 99.90 | 9.09 | 1.13 | 3.33 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.88 | 0.30 | 15.98 | 2.36 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 2.39 | 4.38 | 4.79 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 99.75 | 9.17 | 1.09 | 3.38 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.43 | 0.38 | 15.81 | 2.70 | 0.03 | 1.29 | 2.53 | 4.06 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 99.71 | 8.86 | 1.18 | 3.21 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 67.89 | 0.31 | 15.64 | 2.67 | 0.03 | 1.13 | 2.58 | 4.44 | 4.48 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 99.74 | 8.92 | 1.01 | 3.20 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | Ba | Cu | Hf | Nb | Pb | Rb | Sr | Ta | Th | U | Zn | Zr | Cs | Cr | Ni | 资料来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 610 | 175 | 6.3 | 10.1 | 33 | 191 | 877 | 0.9 | 19.3 | 5.91 | 35 | 196 | 6.31 | 38 | 21 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 280 | 33 | 6.1 | 9.9 | 27 | 173 | 960 | 0.9 | 18.6 | 4.76 | 11 | 199 | 7.01 | 24 | 14 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 1 320 | 41 | 6.1 | 9.6 | 23 | 161 | 1 180 | 0.9 | 19.5 | 4.99 | 15 | 187 | 6.26 | 29 | 16 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 380 | 11 | 7.4 | 11.4 | 55 | 148 | 1 163 | 0.9 | 17.1 | 8.70 | 34 | 152 | 3.17 | 27 | 12 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 434 | 24 | 7.7 | 11.2 | 37 | 144 | 1 254 | 0.9 | 15.6 | 4.86 | 31 | 167 | 3.44 | 37 | 13 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 367 | 14 | 7.1 | 12.5 | 30 | 123 | 1 190 | 1.0 | 16.8 | 5.00 | 28 | 154 | 2.83 | 34 | 14 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 611 | 9 | 7.7 | 12.2 | 36 | 94 | 1 237 | 0.9 | 17.2 | 2.59 | 42 | 151 | 2.19 | 40 | 15 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 206 | 14 | 8.1 | 12.1 | 31 | 134 | 1 252 | 1.0 | 17.3 | 4.60 | 31 | 174 | 3.61 | 32 | 14 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 380 | 11 | 7.4 | 11.4 | 55 | 148 | 1 163 | 0.9 | 17.1 | 8.70 | 34 | 152 | 3.17 | 27 | 12 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 434 | 24 | 7.7 | 11.2 | 37 | 144 | 1 254 | 0.9 | 15.6 | 4.86 | 31 | 167 | 3.44 | 37 | 13 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 367 | 14 | 7.1 | 12.5 | 30 | 123 | 1 190 | 1.0 | 16.8 | 5.00 | 28 | 154 | 2.83 | 34 | 14 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 611 | 9 | 7.7 | 12.2 | 36 | 94 | 1 237 | 0.9 | 17.2 | 2.59 | 42 | 151 | 2.19 | 40 | 15 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1 206 | 14 | 8.1 | 12.1 | 31 | 134 | 1 252 | 1.0 | 17.3 | 4.60 | 31 | 174 | 3.61 | 32 | 14 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | Co | V | Sc | Ga | Zn | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | 资料来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 11 | 53 | 6 | 19.8 | 35 | 44.9 | 82.0 | 8.60 | 31.80 | 5.50 | 1.23 | 3.86 | 0.51 | 3.04 | 0.56 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 9 | 37 | 4 | 19.2 | 11 | 24.7 | 52.5 | 5.14 | 19.30 | 3.49 | 1.09 | 3.14 | 0.46 | 2.43 | 0.51 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 38 | 4 | 18.8 | 15 | 45.4 | 84.4 | 8.78 | 32.90 | 5.55 | 1.54 | 4.04 | 0.53 | 2.79 | 0.59 | 本文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 32 | 4 | 18.2 | 34 | 41.9 | 78.8 | 8.30 | 30.20 | 4.90 | 1.20 | 3.96 | 0.53 | 2.57 | 0.45 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 39 | 5 | 18.1 | 31 | 42.1 | 80.3 | 8.90 | 32.20 | 5.30 | 1.30 | 4.23 | 0.57 | 2.86 | 0.51 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 41 | 5 | 19.9 | 28 | 41.3 | 81.5 | 8.90 | 32.80 | 5.40 | 1.40 | 4.34 | 0.59 | 2.92 | 0.51 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 46 | 6 | 19.8 | 42 | 47.6 | 99.1 | 11.50 | 42.40 | 6.50 | 1.60 | 5.01 | 0.64 | 3.01 | 0.53 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 35 | 5 | 19.3 | 31 | 41.3 | 79.3 | 8.80 | 32.50 | 5.30 | 1.30 | 4.21 | 0.57 | 2.84 | 0.51 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 32 | 4 | 18.2 | 34 | 41.9 | 78.8 | 8.33 | 30.21 | 4.94 | 1.20 | 3.96 | 0.53 | 2.57 | 0.45 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 39 | 5 | 18.1 | 31 | 42.1 | 80.3 | 8.88 | 32.17 | 5.32 | 1.31 | 4.23 | 0.57 | 2.86 | 0.51 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 41 | 5 | 19.9 | 28 | 41.3 | 81.5 | 8.95 | 32.80 | 5.37 | 1.35 | 4.34 | 0.59 | 2.92 | 0.51 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 5 | 46 | 6 | 19.8 | 42 | 47.6 | 99.1 | 11.52 | 42.40 | 6.54 | 1.55 | 5.01 | 0.64 | 3.01 | 0.53 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 4 | 35 | 5 | 19.3 | 31 | 41.3 | 79.3 | 8.80 | 32.50 | 5.34 | 1.30 | 4.21 | 0.57 | 2.84 | 0.51 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | 岩性 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | Nb /U | 资料来源 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.71 | 0.25 | 1.62 | 0.23 | 15.20 | 186 | 174 | 12 | 14.77 | 19.9 | 0.77 | 1.71 | 本文 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.36 | 0.19 | 1.28 | 0.19 | 14.20 | 116 | 106 | 10 | 11.11 | 13.8 | 0.99 | 2.08 | 本文 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11 | 角闪石英二长斑岩 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.36 | 0.22 | 14.70 | 190 | 178 | 11 | 15.87 | 24.0 | 0.95 | 1.92 | 本文 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 0.16 | 13.44 | 176 | 165 | 10 | 15.97 | 23.8 | 0.80 | 1.31 | 刘金宇等,2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 1.33 | 0.17 | 14.80 | 181 | 170 | 11 | 15.08 | 22.6 | 0.82 | 2.29 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.21 | 1.37 | 0.18 | 15.00 | 183 | 171 | 12 | 14.88 | 21.6 | 0.83 | 2.49 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 1.41 | 0.18 | 15.00 | 221 | 209 | 12 | 16.79 | 24.3 | 0.80 | 4.73 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.36 | 0.21 | 1.38 | 0.18 | 14.80 | 180 | 169 | 11 | 14.96 | 21.5 | 0.81 | 2.64 | 刘金宇等, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-01 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.22 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 0.16 | 13.44 | 176 | 165 | 10 | 15.98 | 23.8 | 0.80 | 1.31 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-02 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 1.33 | 0.17 | 14.77 | 181 | 170 | 11 | 15.08 | 22.6 | 0.82 | 2.29 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-03 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.39 | 0.21 | 1.37 | 0.18 | 14.98 | 183 | 171 | 12 | 14.88 | 21.6 | 0.83 | 2.49 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-04 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 1.41 | 0.18 | 14.99 | 221 | 209 | 12 | 16.79 | 24.3 | 0.80 | 4.73 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-05 | 石英二长斑岩 | 1.36 | 0.21 | 1.38 | 0.18 | 14.80 | 180 | 169 | 11 | 14.97 | 21.5 | 0.81 | 2.64 | 肖昌浩, 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
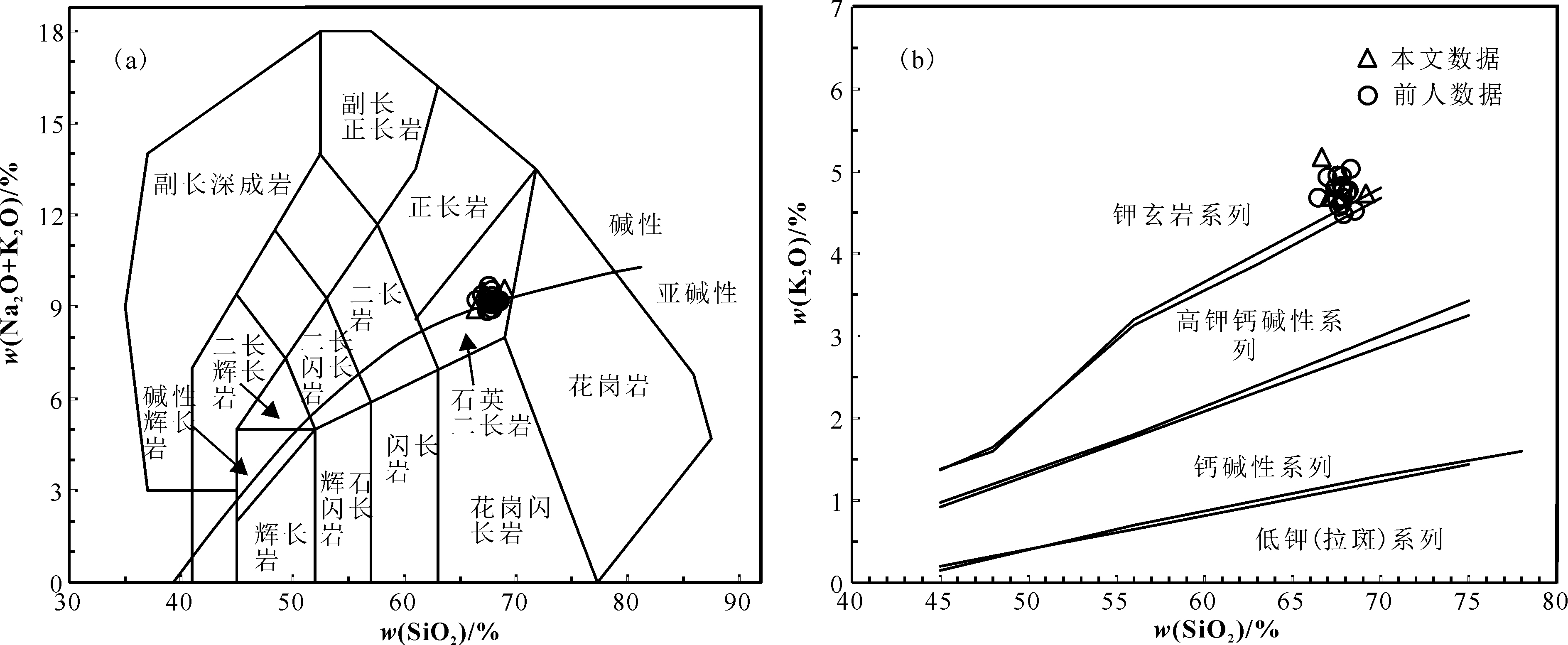
图6 莲花山富碱斑岩体SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)判别图(a. 底图据Middlemost[36], 1994) 和SiO2-K2O判别图(b. 底图据Peccerillo和Taylor[37], 1976) 前人数据来源于肖昌浩[20]、刘金宇[21] 和李学仁等[35]
Fig.6 Discrimination diagrams of SiO2 vs. Na2O+K2O (a.Base map after Middlemost[36], 1994) and SiO2 vs. K2O (b.Base map after Peccerillo and Taylor[37], 1976) of the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry

图7 莲花山富碱斑岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图(a)及微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b) 标准化值据McDonought 和Sun[39];平均地壳数据来自黎彤[40]; 前人数据来源于肖昌浩[20]和刘金宇等[21]
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (b) for the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry

图8 莲花山岩体锆石稀土元素配分曲线图(球粒陨石标准化值据Sun和McDonough[38])
Fig.8 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of zircons from the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry (normalizing values from after Sun and McDonough[38])
| 测点号 | Ti | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | δCe | δEu | LREE/ HREE | ΣREE | t/℃ | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS-3-2 | 6.22 | 0.15 | 79.10 | 0.16 | 2.52 | 6.29 | 2.98 | 37 | 11 | 129 | 50 | 222 | 48 | 476 | 87 | 114.1 | 0.46 | 0.09 | 1 152 | 703 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-3 | 2.83 | 0.10 | 31.31 | 0.17 | 1.40 | 2.47 | 1.41 | 15 | 5 | 65 | 28 | 147 | 38 | 420 | 88 | 47.7 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 842 | 639 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-4 | 6.76 | 0.02 | 73.22 | 0.16 | 2.37 | 5.77 | 2.89 | 34 | 11 | 122 | 45 | 198 | 45 | 440 | 84 | 137.0 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 1 065 | 710 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-5 | 5.73 | 0.15 | 49.10 | 0.14 | 1.78 | 4.72 | 1.90 | 31 | 10 | 122 | 46 | 207 | 45 | 422 | 79 | 76.3 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 1 019 | 696 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-6 | 5.41 | 0.30 | 48.12 | 0.27 | 2.85 | 6.11 | 2.80 | 31 | 10 | 121 | 47 | 209 | 47 | 457 | 90 | 38.2 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 1 071 | 691 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-7 | 3.56 | 0.01 | 35.02 | 0.14 | 1.84 | 4.21 | 2.09 | 24 | 8 | 95 | 36 | 165 | 36 | 344 | 66 | 74.7 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 819 | 657 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-9 | 7.58 | 0.12 | 42.11 | 0.11 | 1.81 | 5.31 | 2.18 | 28 | 10 | 116 | 45 | 205 | 46 | 446 | 87 | 80.7 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 1 034 | 720 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-10 | 5.23 | 0.03 | 50.27 | 0.15 | 2.01 | 4.89 | 2.53 | 29 | 10 | 114 | 46 | 207 | 48 | 476 | 95 | 96.4 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 1 084 | 688 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-11 | 12.65 | 0.03 | 22.27 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 2.62 | 0.48 | 15 | 4 | 49 | 18 | 84 | 18 | 181 | 36 | 83.6 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 430 | 768 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-12 | 7.56 | 0.11 | 79.71 | 0.20 | 3.83 | 6.84 | 3.45 | 38 | 12 | 140 | 54 | 247 | 55 | 542 | 106 | 101.8 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 1 289 | 720 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-13 | 9.14 | 0.00 | 30.07 | 0.23 | 4.40 | 6.77 | 2.84 | 31 | 9 | 113 | 41 | 184 | 41 | 386 | 74 | 40.0 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 923 | 737 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-14 | 2.78 | 0.00 | 58.05 | 0.13 | 1.76 | 4.51 | 2.20 | 29 | 10 | 129 | 51 | 231 | 53 | 513 | 97 | 142.5 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 1 180 | 638 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-16 | 8.64 | 0.00 | 37.86 | 0.14 | 2.70 | 5.39 | 2.63 | 29 | 9 | 105 | 41 | 180 | 41 | 403 | 79 | 84.2 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 937 | 732 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-18 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 31.58 | 0.08 | 1.06 | 3.77 | 1.52 | 17 | 5 | 68 | 28 | 146 | 35 | 384 | 84 | 77.5 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 806 | 606 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-19 | 12.19 | 0.48 | 26.91 | 0.10 | 2.15 | 3.28 | 2.38 | 21 | 7 | 87 | 34 | 166 | 40 | 424 | 92 | 29.1 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 906 | 765 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-20 | 5.13 | 0.17 | 54.41 | 0.19 | 2.56 | 5.91 | 2.45 | 35 | 11 | 120 | 45 | 194 | 40 | 387 | 71 | 64.4 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 968 | 687 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-21 | 6.20 | 0.07 | 41.74 | 0.05 | 1.46 | 3.66 | 1.89 | 22 | 7 | 86 | 34 | 158 | 37 | 380 | 79 | 159.7 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 852 | 703 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-22 | 4.38 | 0.03 | 75.19 | 0.07 | 3.40 | 6.32 | 3.28 | 34 | 11 | 131 | 50 | 236 | 53 | 508 | 101 | 263.1 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 1 211 | 674 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-23 | 6.43 | 0.03 | 79.87 | 0.10 | 2.75 | 7.53 | 3.09 | 42 | 13 | 154 | 57 | 246 | 53 | 505 | 97 | 216.7 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 1 261 | 706 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-24 | 10.69 | 0.00 | 35.59 | 0.07 | 1.55 | 3.02 | 1.91 | 18 | 5 | 65 | 25 | 113 | 25 | 247 | 48 | 154.8 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 587 | 752 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-25 | 3.35 | 0.49 | 44.75 | 0.24 | 3.29 | 3.38 | 2.12 | 26 | 9 | 96 | 38 | 176 | 40 | 387 | 78 | 31.8 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 903 | 652 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-26 | 7.73 | 0.06 | 29.19 | 0.05 | 1.16 | 2.95 | 1.56 | 15 | 6 | 69 | 30 | 147 | 36 | 381 | 82 | 127.3 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 802 | 722 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-1 | 9.29 | 0.01 | 47.76 | 0.08 | 1.59 | 4.15 | 2.36 | 24 | 8 | 94 | 38 | 185 | 45 | 467 | 90 | 168.4 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 1 007 | 739 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-3 | 5.55 | 0.03 | 45.24 | 0.06 | 1.28 | 3.14 | 1.94 | 21 | 8 | 100 | 41 | 202 | 49 | 537 | 102 | 189.5 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 1 112 | 693 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-4 | 2.96 | 0.01 | 32.80 | 0.05 | 0.84 | 2.46 | 1.53 | 16 | 5 | 62 | 25 | 125 | 31 | 336 | 67 | 192.8 | 0.56 | 0.06 | 705 | 643 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-5 | 6.21 | 0.02 | 41.18 | 0.10 | 1.57 | 3.55 | 2.10 | 19 | 7 | 81 | 33 | 159 | 39 | 410 | 81 | 114.6 | 0.62 | 0.06 | 877 | 703 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-6 | 3.66 | 0.00 | 45.75 | 0.04 | 1.20 | 3.67 | 2.17 | 18 | 6 | 68 | 26 | 125 | 31 | 316 | 61 | 331.9 | 0.67 | 0.08 | 704 | 659 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-7 | 8.07 | 0.02 | 80.49 | 0.12 | 3.22 | 6.21 | 3.44 | 30 | 9 | 111 | 41 | 185 | 43 | 436 | 81 | 202.5 | 0.63 | 0.10 | 1 030 | 726 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-8 | 5.39 | 0.04 | 61.81 | 0.14 | 2.59 | 4.95 | 2.56 | 26 | 8 | 99 | 38 | 174 | 41 | 416 | 78 | 125.0 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 953 | 691 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-10 | 1.91 | 0.00 | 38.97 | 0.04 | 1.20 | 2.73 | 1.46 | 16 | 5 | 68 | 28 | 139 | 35 | 381 | 73 | 280.0 | 0.53 | 0.06 | 790 | 611 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-11 | 5.13 | 0.02 | 26.67 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 2.44 | 1.34 | 14 | 5 | 69 | 29 | 151 | 39 | 422 | 86 | 61.0 | 0.53 | 0.04 | 847 | 687 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-12 | 8.38 | 0.26 | 57.93 | 0.19 | 2.22 | 4.67 | 2.48 | 24 | 8 | 87 | 33 | 150 | 36 | 370 | 70 | 61.7 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 845 | 729 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-13 | 6.97 | 0.02 | 47.15 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 3.96 | 1.99 | 19 | 7 | 75 | 28 | 130 | 31 | 310 | 59 | 126.7 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 713 | 713 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-14 | 5.37 | 0.14 | 74.01 | 0.16 | 2.71 | 5.82 | 3.29 | 29 | 10 | 115 | 43 | 201 | 46 | 458 | 87 | 107.1 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 1 076 | 690 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-15 | 4.83 | 0.20 | 53.98 | 0.13 | 2.10 | 4.91 | 2.48 | 23 | 8 | 92 | 35 | 161 | 39 | 387 | 71 | 78.5 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 880 | 682 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-17 | 3.48 | 0.00 | 43.45 | 0.06 | 1.41 | 3.73 | 2.10 | 22 | 8 | 92 | 37 | 175 | 43 | 439 | 87 | 218.2 | 0.55 | 0.06 | 953 | 655 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-18 | 7.54 | 0.09 | 28.20 | 0.11 | 0.88 | 2.57 | 1.80 | 19 | 6 | 83 | 33 | 168 | 42 | 437 | 85 | 59.4 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 907 | 720 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-20 | 7.24 | 0.01 | 54.47 | 0.12 | 1.76 | 5.73 | 2.64 | 29 | 10 | 127 | 50 | 233 | 56 | 563 | 103 | 141.5 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 1 235 | 716 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-21 | 5.81 | 0.08 | 28.62 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 1.81 | 1.18 | 13 | 4 | 54 | 22 | 115 | 30 | 334 | 69 | 109.9 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 673 | 697 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-25 | 2.01 | 0.00 | 28.21 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 2.48 | 1.77 | 18 | 6 | 73 | 29 | 143 | 35 | 371 | 76 | 160.1 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 784 | 615 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-26 | 1.50 | 0.01 | 46.04 | 0.10 | 1.36 | 3.48 | 2.10 | 21 | 7 | 83 | 34 | 160 | 40 | 415 | 84 | 138.7 | 0.57 | 0.06 | 898 | 594 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-27 | 3.25 | 0.10 | 31.08 | 0.04 | 1.41 | 3.10 | 1.49 | 17 | 6 | 74 | 31 | 152 | 38 | 408 | 84 | 122.1 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 847 | 650 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-28 | 3.10 | 0.01 | 36.07 | 0.06 | 1.20 | 3.51 | 1.88 | 17 | 6 | 70 | 29 | 144 | 35 | 369 | 77 | 164.7 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 790 | 647 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-1 | 4.10 | 0.13 | 45.86 | 0.08 | 1.67 | 3.03 | 1.98 | 18 | 6 | 78 | 31 | 153 | 38 | 400 | 83 | 109.3 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 860 | 668 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-2 | 7.69 | 0.36 | 95.92 | 0.30 | 5.11 | 8.62 | 4.35 | 43 | 14 | 157 | 60 | 271 | 61 | 585 | 112 | 66.6 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 1 417 | 722 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-4 | 15.43 | 2.28 | 28.22 | 0.63 | 4.96 | 6.13 | 2.64 | 30 | 10 | 101 | 35 | 152 | 34 | 326 | 63 | 5.7 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 796 | 788 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-5 | 5.54 | 0.04 | 32.26 | 0.06 | 1.26 | 3.03 | 1.88 | 22 | 7 | 92 | 37 | 185 | 47 | 486 | 102 | 128.4 | 0.52 | 0.04 | 1 015 | 693 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-6 | 3.00 | 0.01 | 24.27 | 0.06 | 0.83 | 2.91 | 1.70 | 16 | 5 | 58 | 22 | 100 | 22 | 214 | 41 | 126.9 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 508 | 644 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-8 | 5.98 | 0.05 | 32.63 | 0.06 | 1.02 | 2.67 | 1.79 | 19 | 7 | 86 | 37 | 193 | 48 | 508 | 105 | 122.3 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 1 042 | 700 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-9 | 8.91 | 0.01 | 40.90 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 3.26 | 2.06 | 20 | 7 | 82 | 34 | 166 | 41 | 430 | 87 | 118.1 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 914 | 735 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-10 | 3.13 | 0.04 | 51.08 | 0.08 | 2.64 | 4.57 | 2.74 | 24 | 8 | 92 | 36 | 165 | 38 | 380 | 78 | 167.3 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 882 | 647 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-11 | 5.55 | 0.04 | 48.00 | 0.12 | 2.32 | 4.93 | 2.78 | 26 | 8 | 98 | 37 | 174 | 39 | 381 | 73 | 112.9 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 894 | 693 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-12 | 2.84 | 0.07 | 68.84 | 0.16 | 2.43 | 5.17 | 2.96 | 25 | 7 | 88 | 33 | 158 | 38 | 380 | 78 | 111.7 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 886 | 640 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-13 | 5.38 | 0.03 | 61.96 | 0.10 | 1.89 | 4.88 | 2.40 | 25 | 8 | 97 | 39 | 186 | 43 | 437 | 85 | 173.6 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 991 | 691 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-14 | 8.59 | 0.00 | 42.13 | 0.09 | 1.59 | 3.69 | 2.57 | 25 | 9 | 104 | 44 | 223 | 55 | 578 | 123 | 150.7 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 1 210 | 732 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-15 | 8.75 | 0.02 | 72.29 | 0.14 | 2.83 | 5.36 | 3.06 | 31 | 10 | 118 | 46 | 215 | 48 | 481 | 93 | 146.6 | 0.57 | 0.08 | 1 126 | 733 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-16 | 3.81 | 0.00 | 45.14 | 0.09 | 1.44 | 4.28 | 2.36 | 23 | 8 | 104 | 43 | 217 | 55 | 559 | 115 | 156.6 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 1 176 | 663 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-17 | 1.78 | 0.08 | 36.05 | 0.09 | 1.31 | 3.58 | 2.01 | 22 | 7 | 87 | 36 | 183 | 45 | 464 | 97 | 90.6 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 984 | 606 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-18 | 4.77 | 0.03 | 53.97 | 0.04 | 1.98 | 3.69 | 2.45 | 24 | 8 | 90 | 34 | 165 | 38 | 394 | 79 | 337.7 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 893 | 681 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-19 | 4.00 | 0.04 | 47.24 | 0.09 | 2.10 | 4.12 | 2.72 | 23 | 8 | 94 | 38 | 187 | 45 | 476 | 101 | 137.0 | 0.66 | 0.06 | 1 030 | 666 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-20 | 4.54 | 0.02 | 44.22 | 0.17 | 2.82 | 5.07 | 2.95 | 32 | 10 | 111 | 41 | 176 | 36 | 328 | 60 | 77.1 | 0.54 | 0.07 | 849 | 677 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-21 | 5.87 | 0.02 | 27.95 | 0.06 | 0.98 | 2.39 | 1.64 | 18 | 6 | 83 | 36 | 188 | 47 | 510 | 106 | 133.5 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 1 027 | 698 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-22 | 7.00 | 0.02 | 43.88 | 0.06 | 1.32 | 3.48 | 1.84 | 20 | 6 | 79 | 32 | 159 | 37 | 398 | 86 | 192.1 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 868 | 713 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-25 | 3.22 | 0.84 | 29.81 | 0.37 | 2.80 | 3.41 | 1.75 | 18 | 6 | 78 | 33 | 169 | 41 | 429 | 89 | 13.1 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 903 | 649 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-26 | 10.89 | 0.16 | 25.91 | 0.10 | 1.21 | 2.01 | 1.65 | 16 | 6 | 70 | 29 | 144 | 33 | 359 | 77 | 48.2 | 0.62 | 0.04 | 765 | 754 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-27 | 3.57 | 0.11 | 39.83 | 0.10 | 1.82 | 3.58 | 2.28 | 22 | 7 | 88 | 36 | 181 | 42 | 448 | 94 | 88.8 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 965 | 657 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-28 | 4.14 | 0.06 | 20.84 | 0.03 | 0.86 | 2.02 | 1.17 | 12 | 4 | 53 | 22 | 117 | 28 | 307 | 67 | 118.3 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 635 | 669 | |||||||||||||||||||||
表3 莲花山富碱斑岩体中锆石的微量元素测试结果(wB/10-6)
Table 3 Zircon trace element data of the Lianhuashan alkalic porphyry(10-6)
| 测点号 | Ti | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | δCe | δEu | LREE/ HREE | ΣREE | t/℃ | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS-3-2 | 6.22 | 0.15 | 79.10 | 0.16 | 2.52 | 6.29 | 2.98 | 37 | 11 | 129 | 50 | 222 | 48 | 476 | 87 | 114.1 | 0.46 | 0.09 | 1 152 | 703 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-3 | 2.83 | 0.10 | 31.31 | 0.17 | 1.40 | 2.47 | 1.41 | 15 | 5 | 65 | 28 | 147 | 38 | 420 | 88 | 47.7 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 842 | 639 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-4 | 6.76 | 0.02 | 73.22 | 0.16 | 2.37 | 5.77 | 2.89 | 34 | 11 | 122 | 45 | 198 | 45 | 440 | 84 | 137.0 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 1 065 | 710 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-5 | 5.73 | 0.15 | 49.10 | 0.14 | 1.78 | 4.72 | 1.90 | 31 | 10 | 122 | 46 | 207 | 45 | 422 | 79 | 76.3 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 1 019 | 696 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-6 | 5.41 | 0.30 | 48.12 | 0.27 | 2.85 | 6.11 | 2.80 | 31 | 10 | 121 | 47 | 209 | 47 | 457 | 90 | 38.2 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 1 071 | 691 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-7 | 3.56 | 0.01 | 35.02 | 0.14 | 1.84 | 4.21 | 2.09 | 24 | 8 | 95 | 36 | 165 | 36 | 344 | 66 | 74.7 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 819 | 657 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-9 | 7.58 | 0.12 | 42.11 | 0.11 | 1.81 | 5.31 | 2.18 | 28 | 10 | 116 | 45 | 205 | 46 | 446 | 87 | 80.7 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 1 034 | 720 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-10 | 5.23 | 0.03 | 50.27 | 0.15 | 2.01 | 4.89 | 2.53 | 29 | 10 | 114 | 46 | 207 | 48 | 476 | 95 | 96.4 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 1 084 | 688 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-11 | 12.65 | 0.03 | 22.27 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 2.62 | 0.48 | 15 | 4 | 49 | 18 | 84 | 18 | 181 | 36 | 83.6 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 430 | 768 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-12 | 7.56 | 0.11 | 79.71 | 0.20 | 3.83 | 6.84 | 3.45 | 38 | 12 | 140 | 54 | 247 | 55 | 542 | 106 | 101.8 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 1 289 | 720 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-13 | 9.14 | 0.00 | 30.07 | 0.23 | 4.40 | 6.77 | 2.84 | 31 | 9 | 113 | 41 | 184 | 41 | 386 | 74 | 40.0 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 923 | 737 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-14 | 2.78 | 0.00 | 58.05 | 0.13 | 1.76 | 4.51 | 2.20 | 29 | 10 | 129 | 51 | 231 | 53 | 513 | 97 | 142.5 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 1 180 | 638 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-16 | 8.64 | 0.00 | 37.86 | 0.14 | 2.70 | 5.39 | 2.63 | 29 | 9 | 105 | 41 | 180 | 41 | 403 | 79 | 84.2 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 937 | 732 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-18 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 31.58 | 0.08 | 1.06 | 3.77 | 1.52 | 17 | 5 | 68 | 28 | 146 | 35 | 384 | 84 | 77.5 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 806 | 606 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-19 | 12.19 | 0.48 | 26.91 | 0.10 | 2.15 | 3.28 | 2.38 | 21 | 7 | 87 | 34 | 166 | 40 | 424 | 92 | 29.1 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 906 | 765 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-20 | 5.13 | 0.17 | 54.41 | 0.19 | 2.56 | 5.91 | 2.45 | 35 | 11 | 120 | 45 | 194 | 40 | 387 | 71 | 64.4 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 968 | 687 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-21 | 6.20 | 0.07 | 41.74 | 0.05 | 1.46 | 3.66 | 1.89 | 22 | 7 | 86 | 34 | 158 | 37 | 380 | 79 | 159.7 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 852 | 703 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-22 | 4.38 | 0.03 | 75.19 | 0.07 | 3.40 | 6.32 | 3.28 | 34 | 11 | 131 | 50 | 236 | 53 | 508 | 101 | 263.1 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 1 211 | 674 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-23 | 6.43 | 0.03 | 79.87 | 0.10 | 2.75 | 7.53 | 3.09 | 42 | 13 | 154 | 57 | 246 | 53 | 505 | 97 | 216.7 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 1 261 | 706 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-24 | 10.69 | 0.00 | 35.59 | 0.07 | 1.55 | 3.02 | 1.91 | 18 | 5 | 65 | 25 | 113 | 25 | 247 | 48 | 154.8 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 587 | 752 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-25 | 3.35 | 0.49 | 44.75 | 0.24 | 3.29 | 3.38 | 2.12 | 26 | 9 | 96 | 38 | 176 | 40 | 387 | 78 | 31.8 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 903 | 652 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-3-26 | 7.73 | 0.06 | 29.19 | 0.05 | 1.16 | 2.95 | 1.56 | 15 | 6 | 69 | 30 | 147 | 36 | 381 | 82 | 127.3 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 802 | 722 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-1 | 9.29 | 0.01 | 47.76 | 0.08 | 1.59 | 4.15 | 2.36 | 24 | 8 | 94 | 38 | 185 | 45 | 467 | 90 | 168.4 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 1 007 | 739 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-3 | 5.55 | 0.03 | 45.24 | 0.06 | 1.28 | 3.14 | 1.94 | 21 | 8 | 100 | 41 | 202 | 49 | 537 | 102 | 189.5 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 1 112 | 693 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-4 | 2.96 | 0.01 | 32.80 | 0.05 | 0.84 | 2.46 | 1.53 | 16 | 5 | 62 | 25 | 125 | 31 | 336 | 67 | 192.8 | 0.56 | 0.06 | 705 | 643 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-5 | 6.21 | 0.02 | 41.18 | 0.10 | 1.57 | 3.55 | 2.10 | 19 | 7 | 81 | 33 | 159 | 39 | 410 | 81 | 114.6 | 0.62 | 0.06 | 877 | 703 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-6 | 3.66 | 0.00 | 45.75 | 0.04 | 1.20 | 3.67 | 2.17 | 18 | 6 | 68 | 26 | 125 | 31 | 316 | 61 | 331.9 | 0.67 | 0.08 | 704 | 659 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-7 | 8.07 | 0.02 | 80.49 | 0.12 | 3.22 | 6.21 | 3.44 | 30 | 9 | 111 | 41 | 185 | 43 | 436 | 81 | 202.5 | 0.63 | 0.10 | 1 030 | 726 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-8 | 5.39 | 0.04 | 61.81 | 0.14 | 2.59 | 4.95 | 2.56 | 26 | 8 | 99 | 38 | 174 | 41 | 416 | 78 | 125.0 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 953 | 691 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-10 | 1.91 | 0.00 | 38.97 | 0.04 | 1.20 | 2.73 | 1.46 | 16 | 5 | 68 | 28 | 139 | 35 | 381 | 73 | 280.0 | 0.53 | 0.06 | 790 | 611 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-11 | 5.13 | 0.02 | 26.67 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 2.44 | 1.34 | 14 | 5 | 69 | 29 | 151 | 39 | 422 | 86 | 61.0 | 0.53 | 0.04 | 847 | 687 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-12 | 8.38 | 0.26 | 57.93 | 0.19 | 2.22 | 4.67 | 2.48 | 24 | 8 | 87 | 33 | 150 | 36 | 370 | 70 | 61.7 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 845 | 729 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-13 | 6.97 | 0.02 | 47.15 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 3.96 | 1.99 | 19 | 7 | 75 | 28 | 130 | 31 | 310 | 59 | 126.7 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 713 | 713 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-14 | 5.37 | 0.14 | 74.01 | 0.16 | 2.71 | 5.82 | 3.29 | 29 | 10 | 115 | 43 | 201 | 46 | 458 | 87 | 107.1 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 1 076 | 690 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-15 | 4.83 | 0.20 | 53.98 | 0.13 | 2.10 | 4.91 | 2.48 | 23 | 8 | 92 | 35 | 161 | 39 | 387 | 71 | 78.5 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 880 | 682 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-17 | 3.48 | 0.00 | 43.45 | 0.06 | 1.41 | 3.73 | 2.10 | 22 | 8 | 92 | 37 | 175 | 43 | 439 | 87 | 218.2 | 0.55 | 0.06 | 953 | 655 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-18 | 7.54 | 0.09 | 28.20 | 0.11 | 0.88 | 2.57 | 1.80 | 19 | 6 | 83 | 33 | 168 | 42 | 437 | 85 | 59.4 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 907 | 720 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-20 | 7.24 | 0.01 | 54.47 | 0.12 | 1.76 | 5.73 | 2.64 | 29 | 10 | 127 | 50 | 233 | 56 | 563 | 103 | 141.5 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 1 235 | 716 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-21 | 5.81 | 0.08 | 28.62 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 1.81 | 1.18 | 13 | 4 | 54 | 22 | 115 | 30 | 334 | 69 | 109.9 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 673 | 697 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-25 | 2.01 | 0.00 | 28.21 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 2.48 | 1.77 | 18 | 6 | 73 | 29 | 143 | 35 | 371 | 76 | 160.1 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 784 | 615 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-26 | 1.50 | 0.01 | 46.04 | 0.10 | 1.36 | 3.48 | 2.10 | 21 | 7 | 83 | 34 | 160 | 40 | 415 | 84 | 138.7 | 0.57 | 0.06 | 898 | 594 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-27 | 3.25 | 0.10 | 31.08 | 0.04 | 1.41 | 3.10 | 1.49 | 17 | 6 | 74 | 31 | 152 | 38 | 408 | 84 | 122.1 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 847 | 650 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-5-28 | 3.10 | 0.01 | 36.07 | 0.06 | 1.20 | 3.51 | 1.88 | 17 | 6 | 70 | 29 | 144 | 35 | 369 | 77 | 164.7 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 790 | 647 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-1 | 4.10 | 0.13 | 45.86 | 0.08 | 1.67 | 3.03 | 1.98 | 18 | 6 | 78 | 31 | 153 | 38 | 400 | 83 | 109.3 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 860 | 668 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-2 | 7.69 | 0.36 | 95.92 | 0.30 | 5.11 | 8.62 | 4.35 | 43 | 14 | 157 | 60 | 271 | 61 | 585 | 112 | 66.6 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 1 417 | 722 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-4 | 15.43 | 2.28 | 28.22 | 0.63 | 4.96 | 6.13 | 2.64 | 30 | 10 | 101 | 35 | 152 | 34 | 326 | 63 | 5.7 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 796 | 788 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-5 | 5.54 | 0.04 | 32.26 | 0.06 | 1.26 | 3.03 | 1.88 | 22 | 7 | 92 | 37 | 185 | 47 | 486 | 102 | 128.4 | 0.52 | 0.04 | 1 015 | 693 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-6 | 3.00 | 0.01 | 24.27 | 0.06 | 0.83 | 2.91 | 1.70 | 16 | 5 | 58 | 22 | 100 | 22 | 214 | 41 | 126.9 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 508 | 644 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-8 | 5.98 | 0.05 | 32.63 | 0.06 | 1.02 | 2.67 | 1.79 | 19 | 7 | 86 | 37 | 193 | 48 | 508 | 105 | 122.3 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 1 042 | 700 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-9 | 8.91 | 0.01 | 40.90 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 3.26 | 2.06 | 20 | 7 | 82 | 34 | 166 | 41 | 430 | 87 | 118.1 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 914 | 735 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-10 | 3.13 | 0.04 | 51.08 | 0.08 | 2.64 | 4.57 | 2.74 | 24 | 8 | 92 | 36 | 165 | 38 | 380 | 78 | 167.3 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 882 | 647 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-11 | 5.55 | 0.04 | 48.00 | 0.12 | 2.32 | 4.93 | 2.78 | 26 | 8 | 98 | 37 | 174 | 39 | 381 | 73 | 112.9 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 894 | 693 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-12 | 2.84 | 0.07 | 68.84 | 0.16 | 2.43 | 5.17 | 2.96 | 25 | 7 | 88 | 33 | 158 | 38 | 380 | 78 | 111.7 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 886 | 640 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-13 | 5.38 | 0.03 | 61.96 | 0.10 | 1.89 | 4.88 | 2.40 | 25 | 8 | 97 | 39 | 186 | 43 | 437 | 85 | 173.6 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 991 | 691 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-14 | 8.59 | 0.00 | 42.13 | 0.09 | 1.59 | 3.69 | 2.57 | 25 | 9 | 104 | 44 | 223 | 55 | 578 | 123 | 150.7 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 1 210 | 732 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-15 | 8.75 | 0.02 | 72.29 | 0.14 | 2.83 | 5.36 | 3.06 | 31 | 10 | 118 | 46 | 215 | 48 | 481 | 93 | 146.6 | 0.57 | 0.08 | 1 126 | 733 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-16 | 3.81 | 0.00 | 45.14 | 0.09 | 1.44 | 4.28 | 2.36 | 23 | 8 | 104 | 43 | 217 | 55 | 559 | 115 | 156.6 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 1 176 | 663 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-17 | 1.78 | 0.08 | 36.05 | 0.09 | 1.31 | 3.58 | 2.01 | 22 | 7 | 87 | 36 | 183 | 45 | 464 | 97 | 90.6 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 984 | 606 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-18 | 4.77 | 0.03 | 53.97 | 0.04 | 1.98 | 3.69 | 2.45 | 24 | 8 | 90 | 34 | 165 | 38 | 394 | 79 | 337.7 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 893 | 681 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-19 | 4.00 | 0.04 | 47.24 | 0.09 | 2.10 | 4.12 | 2.72 | 23 | 8 | 94 | 38 | 187 | 45 | 476 | 101 | 137.0 | 0.66 | 0.06 | 1 030 | 666 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-20 | 4.54 | 0.02 | 44.22 | 0.17 | 2.82 | 5.07 | 2.95 | 32 | 10 | 111 | 41 | 176 | 36 | 328 | 60 | 77.1 | 0.54 | 0.07 | 849 | 677 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-21 | 5.87 | 0.02 | 27.95 | 0.06 | 0.98 | 2.39 | 1.64 | 18 | 6 | 83 | 36 | 188 | 47 | 510 | 106 | 133.5 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 1 027 | 698 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-22 | 7.00 | 0.02 | 43.88 | 0.06 | 1.32 | 3.48 | 1.84 | 20 | 6 | 79 | 32 | 159 | 37 | 398 | 86 | 192.1 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 868 | 713 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-25 | 3.22 | 0.84 | 29.81 | 0.37 | 2.80 | 3.41 | 1.75 | 18 | 6 | 78 | 33 | 169 | 41 | 429 | 89 | 13.1 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 903 | 649 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-26 | 10.89 | 0.16 | 25.91 | 0.10 | 1.21 | 2.01 | 1.65 | 16 | 6 | 70 | 29 | 144 | 33 | 359 | 77 | 48.2 | 0.62 | 0.04 | 765 | 754 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-27 | 3.57 | 0.11 | 39.83 | 0.10 | 1.82 | 3.58 | 2.28 | 22 | 7 | 88 | 36 | 181 | 42 | 448 | 94 | 88.8 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 965 | 657 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| LHS-11-28 | 4.14 | 0.06 | 20.84 | 0.03 | 0.86 | 2.02 | 1.17 | 12 | 4 | 53 | 22 | 117 | 28 | 307 | 67 | 118.3 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 635 | 669 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| [1] | 邓军, 杨立强, 葛良胜, 等. 滇西富碱斑岩型金成矿系统特征与变化保存[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(6): 1633-1645. |
| [2] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 侯增谦, 等. 青藏高原大陆动力学研究若干进展[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(1): 1-42. |
| [3] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LI G J, et al. Geology and genesis of the giant Beiya porphyry-skarn gold deposit, northwestern Yangtze Block, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 70: 457-485.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LI G J, et al. Structural control and genesis of the Oligocene Zhenyuan orogenic gold deposit, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 42-54.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 张道红, 张学书, 杨艳, 等. 扬子地台西缘富碱斑岩的岩石地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 地球学报, 2013, 34(1) : 168-176. |
| [6] |
ZHANG J, WANG H, LI S H, et al. Paleogene magmatism and gold metallogeny of the Jinping terrane in the Ailaoshan ore belt, Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen (SW China): Geology, deposit type and tectonic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 91:620-637.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HOU Z Q, ZAWB K, PANC G, et al. Sanjiang Tethyan metallogenesis in S.W. China: Tectonic setting, metallogenic epochs and deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2004, 31(1): 48-87.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 张玉泉, 谢应雯, 涂光炽. 哀牢山—金沙江富碱侵入岩及其与裂谷构造关系初步研究[J]. 岩石学报, 1987, 3(1): 17-26. |
| [9] | 张玉泉, 谢应雯, 李献华, 等. 青藏高原东部钾玄岩系岩浆岩同位素特征: 岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑):地球科学, 2000, 30(5): 493-498. |
| [10] | 邓万明, 黄萱, 钟大赉. 滇西新生代富碱斑岩的岩石特征与成因[J]. 地质科学, 1998, 33(4): 31-44. |
| [11] | 侯增谦, 钟大赉, 邓万明. 青藏高原东缘斑岩铜钼金成矿带的构造模式[J]. 中国地质, 2004, 31(1): 1-14. |
| [12] | 曾普胜, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 滇西北中甸地区中-酸性斑岩及其含矿性初步研究[J]. 地球学报, 1999, 20(增刊): 359-367. |
| [13] |
TAPPONNIER P, XU Z, ROGER F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294:1671-1678.
PMID |
| [14] | 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 喻学惠, 等. 青藏高原新生代碰撞-后碰撞火成岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 1-396. |
| [15] | 许志琴, 王勤, 李忠海, 等. 印度-亚洲碰撞: 从挤压到走滑的构造转换[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(1): 1-23. |
| [16] |
LU Y J, KERRICH R, CAWOOD P A, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of potassic felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China: Constraints on the relationship of magmatism to the Jinsha suture[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(2): 737-747.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LU Y J, KERRICH R, KEMP A I S, et al. Intracontinental Eocene-Oligocene porphyry Cu mineral systems of Yunnan, western Yangtze Craton, China: Compositional characteristics, sources, and implications for continental collision metallogeny[J]. Economic Geology, 2013, 108(7) : 1541-1576.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LI G J, et al. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(2): 419-437.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 董方浏, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 云南兰坪盆地喜马拉雅期碱性岩40Ar/39Ar年龄及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2005, 24(2): 103-109. |
| [20] | 肖昌浩. 三江中南段低温热液矿床成矿系列研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013: 1-153. |
| [21] | 刘金宇, 邓军, 李龚健, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地莲花山岩体成因与构造意义: 岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(7): 2115-2128. |
| [22] | 和文言, 喻学惠, 莫宣学, 等. 滇西北衙多金属矿田矿床成因类型及其与富碱斑岩关系初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5): 1401-1412. |
| [23] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LI G J, et al. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 138: 268-299.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG C M, DENG J, LU Y J, et al. Age, nature, and origin of Ordovician Zhibenshan granite from the Baoshan terrane in the Sanjiang region and its significance for understanding Proto-Tethys evolution[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(15): 1922-1939.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 王长明, 陈晶源, 杨立飞, 等. 三江特提斯兰坪盆地构造-流体-成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(7):1957-1977. |
| [26] | 李龚健, 王庆飞, 禹丽, 等. 哀牢山古特提斯洋缝合时限: 晚二叠世花岗岩类锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 3883-3900. |
| [27] |
WANG C M, DENG J, CARRANZA E J M, et al. Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain: Nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26: 576-593.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG C M, DENG J, SANTOSH M, et al. Age and origin of the Bulangshan and Mengsong granitoids and their significance for post-collisional tectonics in the Changning-Menglian Paleo-Tethys Orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 656-676.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 陈喜峰, 曾普胜, 张雪亭, 等. 云南永平卓潘碱性杂岩体岩石学和地球化学特征及成因研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(9): 2597-2608. |
| [30] | 李腾建, 张静, 佟子达, 等. 云南省卓潘碱性杂岩体矿物学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(3): 474-485. |
| [31] |
QI L, HU J, CONARD D G, et al. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2016, 51(3): 507-513.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
YUAN H L, GAO S, LIU X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3): 353-370.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
HOSKIN P W O, BLACK L P. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18(4): 423-439.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. |
| [35] | 李学仁. 滇西巍山大莲花山富碱斑岩岩石特征及含矿性[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014: 1-70. |
| [36] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224
DOI URL |
| [37] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
MCDONOUGH W F, SUN S S. Composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3): 223-253.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 黎彤. 地壳元素丰度的若干统计特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 1992, 28(10): 3-9. |
| [41] | 胥磊落, 毕献武, 苏文超, 等. 云南金平铜厂斑岩Cu(Mo-Au)矿床含矿石英正长斑岩地球化学特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(10): 3109-3122. |
| [42] | 郭晓东, 葛良胜, 王梁, 等. 云南马厂箐岩体中深源包体特征及其锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):1413-1424. |
| [43] |
HOSKIN P W O, SCHALTEGGER U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 27-62.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
WATSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth[J]. Science, 2005, 308: 841-844.
PMID |
| [45] |
WATSON E B, WARK D A, THOMAS J B. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 151(4): 413-433.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
FERRY J M, WATSON E B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 154(4): 429-437.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6): 529-532.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [49] |
LIU H Q, XU Y G, HE B. Implications from zircon-saturation temperatures and lithological assemblages for Early Permian thermal anomaly in Northwest China[J]. Lithos, 2013, 182/183: 125-133.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
AYERS J. Trace element modeling of aqueous fluid-peridotite interaction in the mantle wedge of subduction zones[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 132(4): 390-404.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
PLANK T, LANGMUIR C H. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 145(3/4): 325-394.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
ZI J W, CAWOOD P A, FAN W M, et al. Generation of Early Indosinian enriched mantle-derived granitoid pluton in the Sanjiang orogen (SW China) in response to closure of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2012, 140/141: 166-182.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
FAN W M, WANG Y J, ZHANG A M, et al. Permian arc-back-arc basin development along the Ailaoshan tectonic zone: Geochemical, isotopic and geochronological evidence from the Mojiang volcanic rocks, Southwest China[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(3/4): 553-568.
DOI URL |
| [54] | 涂光炽. 近年来地球化学领域中的重大进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通讯, 1982(2): 1-4. |
| [55] |
TURNER S, ARNAUD N O, LIU J. Post-collision, shoshonitie volcanism on the Tibet plateau: Implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and source of ocean island basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37: 45-71.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DING L, KAPP P, ZHONG D, et al. Cenozoic volcanism in Tibet: Evidence for a transition from oceanic to continental subduction[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(10): 1833-1865.
DOI URL |
| [57] | MULLER D, ROCK N M S, GROVES D I. Geochemical discrimination between shoshonitic and potassic volcanic rocks in different tectonic settings[J]. A Pilot Study of University of Western Australia, 1992, 46(4): 259-289. |
| [58] | RATSCHBACHEER L, FRISH W, CHEN C, et al. Cenozoic deformation, rotation, and stress patterns in eastern Tibet and western Sichuan, China[M]//YIN A, HARRISON T M. The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1996: 227-249. |
| [59] | HOLT W E, NI J F, WALLACE T C, et al. The active tectonics of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and surrounding regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1991, 96(B9):14595-14632. |
| [60] |
DONG G C, MO XX, ZHAO Z D, et al. Geochronologic constraints on the magmatic underplating of the Gangdise belt in the India-Eurasia collision: evidence of SHRIMP II zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(6): 787-794.
DOI URL |
| [61] | DING L, KAPP P, WAN X. Paleocene-Eocene record of ophiolite obduction and initial India-Asia collision, south central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2005, 24(3): 1-18. |
| [62] | 李勇, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 金沙江—哀牢山断裂带几个富碱斑岩体的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(2): 189-200. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [3] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [4] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [5] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [6] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [7] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [8] | 欧伟程, 李承东, 张永清, 赵利刚, 许腾, 许雅雯, 孙烜烨. 北秦岭二郎坪群抱树坪组碎屑锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及物源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 347-361. |
| [9] | 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 郑艳荣, 李晓东, 武海文, 张龙. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1633-1650. |
| [10] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [11] | 陈欢, 康志强, 吴佳昌, 李岱鲜, 曹延, 韦天伟, 韦乃韶, 刘迪, 周桐, 刘冬梅, 蓝海洋. 广西大瑶山朴全岩体形成时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1277-1290. |
| [12] | 欧阳鑫, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 刘丽, 刘涛, 王文东. 内蒙古撰山子金矿床成岩成矿年代学与地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 635-652. |
| [13] | 鞠鹏程, 王训练, 王振涛, 刘喜方, 仲佳爱, 张在明. 渝北温泉镇地区三叠系“绿豆岩”特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 431-449. |
| [14] | 柳长峰, 赵守恒, 张浩然, 郎海龙, 张凤娟, 刘文灿. 内蒙古赤峰大西营子金矿区赋矿火山岩年代学与岩石地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 27-39. |
| [15] | 李琦, 王疆涛, 曾忠诚, 石卫, 李惠, 郭倩怡. 阿尔金造山带南缘蛇绿构造混杂岩带中晚奥陶世—早志留世二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 51-63. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||