



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (05): 1194-1205.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.065
张志平1,2( ), 钟康惠1, 单树成1, 郑鑫1,3, 黄浩震1, 严钊1
), 钟康惠1, 单树成1, 郑鑫1,3, 黄浩震1, 严钊1
收稿日期:2020-02-24
修回日期:2021-02-15
出版日期:2021-10-10
发布日期:2021-11-04
作者简介:张志平,男,高级工程师,硕士研究生,1985年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事区域地质矿产调查工作。Email: zhangzhiping@stu.cdut.edu.cn。
基金资助:
ZHANG Zhiping1,2( ), ZHONG Kanghui1, SHAN Shucheng1, ZHENG Xin1,3, HUANG Haozhen1, YAN Zhao1
), ZHONG Kanghui1, SHAN Shucheng1, ZHENG Xin1,3, HUANG Haozhen1, YAN Zhao1
Received:2020-02-24
Revised:2021-02-15
Online:2021-10-10
Published:2021-11-04
摘要:
为加深对西藏泽当地区新特提斯洋演化的认识,对西藏泽当蛇绿混杂岩带内的共国日二长花岗岩进行了岩石学、岩石地球化学、同位素及年代学等研究,研究显示:共国日二长花岗岩岩体规模小、岩性稳定,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(90.40±0.68)Ma,属晚白垩世;岩石地球化学具高硅、富铝、富钾、低钛和准铝质钙碱性花岗岩特征;轻稀土富集、重稀土亏损,具明显的负Eu异常,微量元素表现为相对富集Rb、K、Ba、Th、U等大离子亲石元素,显著亏损Nb、P、Ti等高场强元素;(87Sr/86Sr)i=0.705 708~0.706 284,(143Nd/144Nd)i=0.512 689~0.512 716,εNd(t)=2.00~2.51。以上特征表明,位于泽当蛇绿混杂岩带内的共国日二长花岗岩属于I型花岗岩,由正常岛弧岩浆形成,应为晚白垩世新特提斯洋向北俯冲形成的岛弧环境下俯冲带上部地壳部分熔融的产物,其不属于泽当蛇绿岩的组成部分,表明在90 Ma前泽当洋内弧已经消失。
中图分类号:
张志平, 钟康惠, 单树成, 郑鑫, 黄浩震, 严钊. 新特提斯洋晚白垩世演化特点:来自泽当共国日二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1194-1205.
ZHANG Zhiping, ZHONG Kanghui, SHAN Shucheng, ZHENG Xin, HUANG Haozhen, YAN Zhao. Late Cretaceous Evolution of the Neo-Tethys:Evidence from Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Gongguori Monzogranite in Zedang[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1194-1205.

图1 西藏泽当共国日区域地质简图 1.第四系;2.中新统—渐新统大竹卡组;3.古新统典中组;4.上白垩统门中组;5.上白垩统比马组;6.白垩统麻木下组;7.上三叠统姐德秀岩组;8.上三叠统江雄岩组;9.岛弧型玄武岩岩块;10.洋壳型辉石橄榄岩岩块;11.岛弧型砂岩岩块;12.中新世石英闪长岩;13.渐新世二长花岗岩;14.始新世黑云母花岗闪长岩;15.始新世二长花岗岩;16.始新世石英二长岩;17.晚白垩世花岗闪长岩;18.晚白垩世二长花岗岩;19.晚白垩世角闪二长花岗岩;20.晚侏罗世奥长花岗岩;21.晚侏罗世英云闪长岩;22.研究区
Fig.1 Regional geological map of the Gongguori, Tibet
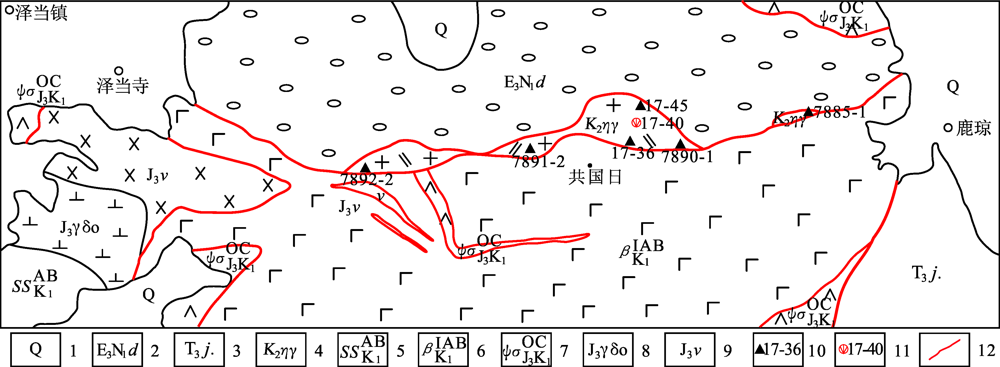
图2 共国日岩体地质图 1.第四系;2.大竹卡组;3.姐德秀岩组;4.二长花岗岩;5.砂岩岩块;6.玄武岩岩块;7.辉石橄榄岩岩块;8.英云闪长岩;9.辉长岩;10.采样位置及编号;11.同位素年龄样品及编号;12.断层
Fig.2 Geological map of the Gongguori monzogranite
| 分析 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th232 | U238 | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | |||
| 01 | 892 | 580 | 1.54 | 0.047 9(0.001 3) | 0.095 3(0.002 6) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 96(37) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 02 | 469 | 231 | 2.03 | 0.047 9(0.001 9) | 0.094 7(0.003 8) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 92(61) | 92(4) | 92(2) | |
| 04 | 291 | 169 | 1.72 | 0.048 0(0.002 6) | 0.096 2(0.005 1) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 98(85) | 93(5) | 93(2) | |
| 05 | 1 427 | 1 036 | 1.38 | 0.047 9(0.001 1) | 0.093 8(0.002 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 93(32) | 91(2) | 91(1) | |
| 07 | 2 140 | 1 240 | 1.73 | 0.047 9(0.001 5) | 0.090 2(0.002 8) | 0.013 7(0.000 2) | 92(45) | 88(3) | 88(1) | |
| 08 | 513 | 425 | 1.21 | 0.047 8(0.001 9) | 0.092 4(0.003 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(58) | 90(3) | 90(2) | |
| 09 | 986 | 549 | 1.80 | 0.046 1(0.006 8) | 0.091 4(0.013 5) | 0.014 4(0.000 3) | (270) | 89(13) | 92(2) | |
| 10 | 2 390 | 1 091 | 2.19 | 0.047 9(0.001 0) | 0.094 5(0.002 1) | 0.014 3(0.000 2) | 95(27) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 11 | 200 | 174 | 1.15 | 0.048 0(0.003 0) | 0.094 7(0.005 9) | 0.014 3(0.000 3) | 97(101) | 92(5) | 92(2) | |
| 12 | 809 | 499 | 1.62 | 0.061 9(0.002 8) | 0.121 5(0.005 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 3) | 671(61) | 116(5) | 91(2) | |
| 13 | 187 | 159 | 1.18 | 0.047 8(0.002 9) | 0.091 5(0.005 4) | 0.013 9(0.000 3) | 89(97) | 89(5) | 89(2) | |
| 14 | 369 | 306 | 1.20 | 0.046 1(0.004 8) | 0.089 6(0.009 3) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | (213) | 87(9) | 90(1) | |
| 15 | 444 | 393 | 1.13 | 0.054 1(0.003 3) | 0.104 3(0.006 2) | 0.014 0(0.000 3) | 376(91) | 101(6) | 89(2) | |
| 16 | 883 | 409 | 2.16 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 5(0.002 8) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 90(43) | 90(3) | 90(1) | |
| 18 | 904 | 604 | 1.50 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 6(0.002 7) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | 90(40) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 19 | 575 | 431 | 1.34 | 0.047 8(0.001 5) | 0.091 2(0.003 0) | 0.013 8(0.000 2) | 91(48) | 89(3) | 88(1) | |
| 20 | 1 575 | 733 | 2.15 | 0.047 8(0.001 3) | 0.092 6(0.002 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(38) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 21 | 447 | 286 | 1.56 | 0.048 3(0.002 8) | 0.097 2(0.005 5) | 0.014 6(0.000 3) | 115(90) | 94(5) | 93(2) | |
| 23 | 1 025 | 756 | 1.36 | 0.047 7(0.001 9) | 0.095 3(0.003 9) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 85(58) | 92(4) | 93(2) | |
| 24 | 1 977 | 1 220 | 1.62 | 0.060 0(0.001 8) | 0.117 7(0.003 6) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 604(37) | 113(3) | 91(2) | |
| 25 | 594 | 474 | 1.25 | 0.046 1(0.008 5) | 0.089 2(0.016 4) | 0.014 1(0.000 3) | (317) | 87(15) | 90(2) | |
表1 共国日二长花岗岩样品(17-40)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Gongguori monzogranite sample(17-40)
| 分析 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th232 | U238 | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | |||
| 01 | 892 | 580 | 1.54 | 0.047 9(0.001 3) | 0.095 3(0.002 6) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 96(37) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 02 | 469 | 231 | 2.03 | 0.047 9(0.001 9) | 0.094 7(0.003 8) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 92(61) | 92(4) | 92(2) | |
| 04 | 291 | 169 | 1.72 | 0.048 0(0.002 6) | 0.096 2(0.005 1) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 98(85) | 93(5) | 93(2) | |
| 05 | 1 427 | 1 036 | 1.38 | 0.047 9(0.001 1) | 0.093 8(0.002 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 93(32) | 91(2) | 91(1) | |
| 07 | 2 140 | 1 240 | 1.73 | 0.047 9(0.001 5) | 0.090 2(0.002 8) | 0.013 7(0.000 2) | 92(45) | 88(3) | 88(1) | |
| 08 | 513 | 425 | 1.21 | 0.047 8(0.001 9) | 0.092 4(0.003 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(58) | 90(3) | 90(2) | |
| 09 | 986 | 549 | 1.80 | 0.046 1(0.006 8) | 0.091 4(0.013 5) | 0.014 4(0.000 3) | (270) | 89(13) | 92(2) | |
| 10 | 2 390 | 1 091 | 2.19 | 0.047 9(0.001 0) | 0.094 5(0.002 1) | 0.014 3(0.000 2) | 95(27) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 11 | 200 | 174 | 1.15 | 0.048 0(0.003 0) | 0.094 7(0.005 9) | 0.014 3(0.000 3) | 97(101) | 92(5) | 92(2) | |
| 12 | 809 | 499 | 1.62 | 0.061 9(0.002 8) | 0.121 5(0.005 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 3) | 671(61) | 116(5) | 91(2) | |
| 13 | 187 | 159 | 1.18 | 0.047 8(0.002 9) | 0.091 5(0.005 4) | 0.013 9(0.000 3) | 89(97) | 89(5) | 89(2) | |
| 14 | 369 | 306 | 1.20 | 0.046 1(0.004 8) | 0.089 6(0.009 3) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | (213) | 87(9) | 90(1) | |
| 15 | 444 | 393 | 1.13 | 0.054 1(0.003 3) | 0.104 3(0.006 2) | 0.014 0(0.000 3) | 376(91) | 101(6) | 89(2) | |
| 16 | 883 | 409 | 2.16 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 5(0.002 8) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 90(43) | 90(3) | 90(1) | |
| 18 | 904 | 604 | 1.50 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 6(0.002 7) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | 90(40) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 19 | 575 | 431 | 1.34 | 0.047 8(0.001 5) | 0.091 2(0.003 0) | 0.013 8(0.000 2) | 91(48) | 89(3) | 88(1) | |
| 20 | 1 575 | 733 | 2.15 | 0.047 8(0.001 3) | 0.092 6(0.002 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(38) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 21 | 447 | 286 | 1.56 | 0.048 3(0.002 8) | 0.097 2(0.005 5) | 0.014 6(0.000 3) | 115(90) | 94(5) | 93(2) | |
| 23 | 1 025 | 756 | 1.36 | 0.047 7(0.001 9) | 0.095 3(0.003 9) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 85(58) | 92(4) | 93(2) | |
| 24 | 1 977 | 1 220 | 1.62 | 0.060 0(0.001 8) | 0.117 7(0.003 6) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 604(37) | 113(3) | 91(2) | |
| 25 | 594 | 474 | 1.25 | 0.046 1(0.008 5) | 0.089 2(0.016 4) | 0.014 1(0.000 3) | (317) | 87(15) | 90(2) | |
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 73.12 | 0.18 | 13.45 | 6.67 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 1.79 | 4.45 | 3.87 | 0.05 | 1.04 | 100.31 | 1.17 |
| 17-40 | 68.43 | 0.21 | 14.65 | 2.03 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 1.73 | 4.78 | 3.76 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 99.68 | 1.23 |
| 17-42 | 73.37 | 0.19 | 13.83 | 6.14 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 2.26 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 0.06 | 0.90 | 99.71 | 1.27 |
| 7885-1 | 73.21 | 0.14 | 14.23 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.05 | 5.42 | 3.98 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 100.15 | 1.08 |
| 7890-1 | 71.74 | 0.21 | 14.60 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 1.23 | 5.71 | 3.13 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 99.95 | 1.14 |
| 7891-2 | 71.46 | 0.23 | 14.77 | 0.56 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 6.21 | 2.84 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 100.15 | 1.11 |
| 7892-2 | 69.66 | 0.23 | 15.76 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 1.41 | 4.65 | 5.12 | 0.07 | 0.91 | 99.88 | 1.20 |
| 样品编号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | Mg# | K2O/Na2O | Rb | Sr | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr |
| 17-36 | 0.91 | 89.66 | 3.40 | 37.21 | 0.87 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 558.20 | 9.48 | 1.96 | 5.65 | 0.46 | 71.72 |
| 17-40 | 0.97 | 87.48 | 3.18 | 39.06 | 0.79 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 528.52 | 11.97 | 1.57 | 6.52 | 0.61 | 102.21 |
| 17-42 | 0.92 | 87.50 | 2.75 | 36.70 | 0.50 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 385.91 | 8.44 | 1.64 | 4.78 | 0.45 | 83.58 |
| 7885-1 | 0.94 | 94.23 | 4.19 | 30.11 | 0.73 | 86.45 | 113.25 | 481.03 | 8.21 | 1.55 | 6.09 | 0.48 | 70.09 |
| 7890-1 | 0.97 | 90.32 | 3.53 | 35.64 | 0.55 | 68.68 | 237.23 | 402.11 | 8.43 | 1.84 | 5.49 | 0.49 | 77.57 |
| 7891-2 | 0.95 | 91.08 | 3.60 | 34.77 | 0.46 | 58.79 | 257.73 | 347.18 | 9.06 | 1.36 | 5.55 | 0.46 | 71.28 |
| 7892-2 | 1.00 | 88.95 | 3.36 | 39.20 | 1.10 | 101.48 | 176.18 | 555.27 | 9.09 | 1.60 | 5.51 | 0.50 | 82.61 |
| 样品编号 | Hf | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Sc | Li | Cs | Be | Ga | Tl | Pb | As |
| 17-36 | 2.01 | 1.82 | 0.29 | 4.59 | 16.45 | 4.11 | 6.68 | 3.79 | 1.71 | 13.67 | 0.49 | 14.93 | 1.32 |
| 17-40 | 2.99 | 2.31 | 3.01 | 8.17 | 19.54 | 4.42 | 13.81 | 2.11 | 1.76 | 15.50 | 0.49 | 17.52 | 1.92 |
| 17-42 | 2.33 | 2.31 | 2.66 | 8.17 | 17.10 | 3.61 | 12.19 | 1.46 | 1.70 | 12.65 | 0.33 | 12.79 | 2.65 |
| 7885-1 | 2.26 | 0.27 | 0.77 | 2.78 | 7.85 | 6.35 | 3.95 | 1.86 | 1.73 | 12.86 | 0.46 | 19.44 | 3.69 |
| 7890-1 | 2.62 | 1.79 | 0.95 | 3.11 | 18.16 | 6.02 | 7.11 | 2.37 | 2.50 | 13.48 | 0.37 | 12.56 | 7.72 |
| 7891-2 | 2.23 | 1.78 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 23.55 | 5.38 | 3.61 | 1.58 | 0.93 | 12.99 | 0.29 | 16.98 | 6.65 |
| 7892-2 | 2.35 | 1.90 | 1.43 | 3.53 | 18.42 | 5.99 | 6.86 | 3.49 | 2.29 | 14.04 | 0.56 | 15.53 | 2.04 |
| 样品编号 | Bi | Ge | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er |
| 17-36 | 0.10 | 1.04 | 18.99 | 35.58 | 3.48 | 11.68 | 2.15 | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.29 | 0.87 |
| 17-40 | 0.04 | 1.17 | 23.11 | 44.67 | 4.26 | 15.22 | 2.64 | 0.54 | 2.04 | 0.32 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 1.10 |
| 17-42 | 0.04 | 1.09 | 18.02 | 34.24 | 3.49 | 11.95 | 2.18 | 0.43 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| 7885-1 | 0.02 | 1.20 | 17.01 | 35.46 | 3.16 | 11.13 | 2.15 | 0.40 | 1.61 | 0.26 | 1.51 | 0.35 | 0.94 |
| 7890-1 | 0.02 | 1.27 | 18.36 | 36.22 | 3.25 | 9.76 | 1.97 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 1.36 | 0.31 | 0.82 |
| 7891-2 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 20.48 | 40.00 | 3.69 | 11.86 | 2.17 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 1.46 | 0.32 | 0.88 |
| 7892-2 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 21.02 | 37.74 | 3.68 | 10.72 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 1.65 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 0.95 |
| 样品编号 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | La/Nb | Nb/Ta | Sm/Nd | REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | δEu | δCe |
| 17-36 | 0.14 | 0.93 | 0.16 | 9.39 | 3.36 | 12.16 | 0.18 | 78.11 | 12.48 | 13.44 | 5.37 | 0.69 | 1.02 |
| 17-40 | 0.18 | 1.29 | 0.22 | 12.21 | 3.55 | 10.67 | 0.17 | 97.76 | 12.34 | 11.80 | 5.34 | 0.71 | 1.05 |
| 17-42 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 9.97 | 3.77 | 10.65 | 0.18 | 76.17 | 11.99 | 11.71 | 5.03 | 0.70 | 1.01 |
| 7885-1 | 0.14 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 11.66 | 2.79 | 12.76 | 0.19 | 75.47 | 11.28 | 9.71 | 4.82 | 0.67 | 1.13 |
| 7890-1 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 10.86 | 3.34 | 11.31 | 0.20 | 75.48 | 12.67 | 12.91 | 5.69 | 0.70 | 1.10 |
| 7891-2 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 11.28 | 3.69 | 12.03 | 0.18 | 84.43 | 13.53 | 13.24 | 5.76 | 0.70 | 1.08 |
| 7892-2 | 0.14 | 1.05 | 0.16 | 10.77 | 3.81 | 10.94 | 0.20 | 81.76 | 12.67 | 13.23 | 6.03 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
表2 共国日二长花岗岩样品主量元素、稀土元素和微量元素分析结果
Table 2 Analysis results of major elements, REE and trace elements of the monzogranite samples
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 73.12 | 0.18 | 13.45 | 6.67 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 1.79 | 4.45 | 3.87 | 0.05 | 1.04 | 100.31 | 1.17 |
| 17-40 | 68.43 | 0.21 | 14.65 | 2.03 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 1.73 | 4.78 | 3.76 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 99.68 | 1.23 |
| 17-42 | 73.37 | 0.19 | 13.83 | 6.14 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 2.26 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 0.06 | 0.90 | 99.71 | 1.27 |
| 7885-1 | 73.21 | 0.14 | 14.23 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.05 | 5.42 | 3.98 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 100.15 | 1.08 |
| 7890-1 | 71.74 | 0.21 | 14.60 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 1.23 | 5.71 | 3.13 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 99.95 | 1.14 |
| 7891-2 | 71.46 | 0.23 | 14.77 | 0.56 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 6.21 | 2.84 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 100.15 | 1.11 |
| 7892-2 | 69.66 | 0.23 | 15.76 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 1.41 | 4.65 | 5.12 | 0.07 | 0.91 | 99.88 | 1.20 |
| 样品编号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | Mg# | K2O/Na2O | Rb | Sr | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr |
| 17-36 | 0.91 | 89.66 | 3.40 | 37.21 | 0.87 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 558.20 | 9.48 | 1.96 | 5.65 | 0.46 | 71.72 |
| 17-40 | 0.97 | 87.48 | 3.18 | 39.06 | 0.79 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 528.52 | 11.97 | 1.57 | 6.52 | 0.61 | 102.21 |
| 17-42 | 0.92 | 87.50 | 2.75 | 36.70 | 0.50 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 385.91 | 8.44 | 1.64 | 4.78 | 0.45 | 83.58 |
| 7885-1 | 0.94 | 94.23 | 4.19 | 30.11 | 0.73 | 86.45 | 113.25 | 481.03 | 8.21 | 1.55 | 6.09 | 0.48 | 70.09 |
| 7890-1 | 0.97 | 90.32 | 3.53 | 35.64 | 0.55 | 68.68 | 237.23 | 402.11 | 8.43 | 1.84 | 5.49 | 0.49 | 77.57 |
| 7891-2 | 0.95 | 91.08 | 3.60 | 34.77 | 0.46 | 58.79 | 257.73 | 347.18 | 9.06 | 1.36 | 5.55 | 0.46 | 71.28 |
| 7892-2 | 1.00 | 88.95 | 3.36 | 39.20 | 1.10 | 101.48 | 176.18 | 555.27 | 9.09 | 1.60 | 5.51 | 0.50 | 82.61 |
| 样品编号 | Hf | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Sc | Li | Cs | Be | Ga | Tl | Pb | As |
| 17-36 | 2.01 | 1.82 | 0.29 | 4.59 | 16.45 | 4.11 | 6.68 | 3.79 | 1.71 | 13.67 | 0.49 | 14.93 | 1.32 |
| 17-40 | 2.99 | 2.31 | 3.01 | 8.17 | 19.54 | 4.42 | 13.81 | 2.11 | 1.76 | 15.50 | 0.49 | 17.52 | 1.92 |
| 17-42 | 2.33 | 2.31 | 2.66 | 8.17 | 17.10 | 3.61 | 12.19 | 1.46 | 1.70 | 12.65 | 0.33 | 12.79 | 2.65 |
| 7885-1 | 2.26 | 0.27 | 0.77 | 2.78 | 7.85 | 6.35 | 3.95 | 1.86 | 1.73 | 12.86 | 0.46 | 19.44 | 3.69 |
| 7890-1 | 2.62 | 1.79 | 0.95 | 3.11 | 18.16 | 6.02 | 7.11 | 2.37 | 2.50 | 13.48 | 0.37 | 12.56 | 7.72 |
| 7891-2 | 2.23 | 1.78 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 23.55 | 5.38 | 3.61 | 1.58 | 0.93 | 12.99 | 0.29 | 16.98 | 6.65 |
| 7892-2 | 2.35 | 1.90 | 1.43 | 3.53 | 18.42 | 5.99 | 6.86 | 3.49 | 2.29 | 14.04 | 0.56 | 15.53 | 2.04 |
| 样品编号 | Bi | Ge | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er |
| 17-36 | 0.10 | 1.04 | 18.99 | 35.58 | 3.48 | 11.68 | 2.15 | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.29 | 0.87 |
| 17-40 | 0.04 | 1.17 | 23.11 | 44.67 | 4.26 | 15.22 | 2.64 | 0.54 | 2.04 | 0.32 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 1.10 |
| 17-42 | 0.04 | 1.09 | 18.02 | 34.24 | 3.49 | 11.95 | 2.18 | 0.43 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| 7885-1 | 0.02 | 1.20 | 17.01 | 35.46 | 3.16 | 11.13 | 2.15 | 0.40 | 1.61 | 0.26 | 1.51 | 0.35 | 0.94 |
| 7890-1 | 0.02 | 1.27 | 18.36 | 36.22 | 3.25 | 9.76 | 1.97 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 1.36 | 0.31 | 0.82 |
| 7891-2 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 20.48 | 40.00 | 3.69 | 11.86 | 2.17 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 1.46 | 0.32 | 0.88 |
| 7892-2 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 21.02 | 37.74 | 3.68 | 10.72 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 1.65 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 0.95 |
| 样品编号 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | La/Nb | Nb/Ta | Sm/Nd | REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | δEu | δCe |
| 17-36 | 0.14 | 0.93 | 0.16 | 9.39 | 3.36 | 12.16 | 0.18 | 78.11 | 12.48 | 13.44 | 5.37 | 0.69 | 1.02 |
| 17-40 | 0.18 | 1.29 | 0.22 | 12.21 | 3.55 | 10.67 | 0.17 | 97.76 | 12.34 | 11.80 | 5.34 | 0.71 | 1.05 |
| 17-42 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 9.97 | 3.77 | 10.65 | 0.18 | 76.17 | 11.99 | 11.71 | 5.03 | 0.70 | 1.01 |
| 7885-1 | 0.14 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 11.66 | 2.79 | 12.76 | 0.19 | 75.47 | 11.28 | 9.71 | 4.82 | 0.67 | 1.13 |
| 7890-1 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 10.86 | 3.34 | 11.31 | 0.20 | 75.48 | 12.67 | 12.91 | 5.69 | 0.70 | 1.10 |
| 7891-2 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 11.28 | 3.69 | 12.03 | 0.18 | 84.43 | 13.53 | 13.24 | 5.76 | 0.70 | 1.08 |
| 7892-2 | 0.14 | 1.05 | 0.16 | 10.77 | 3.81 | 10.94 | 0.20 | 81.76 | 12.67 | 13.23 | 6.03 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
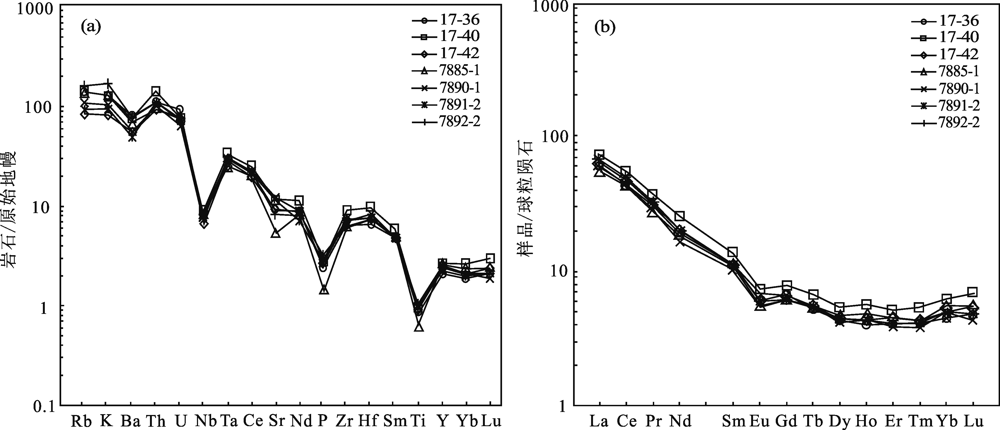
图10 共国日二长花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(a)和稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分布模式图(b) (底图分别据文献[19]和[20])
Fig.10 Primitive-mantle-normalized trace element patterns (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Gongguori monzogranite (b) (base map after refs.[19] and [20],respectively)
| 样号 编号 | t/Ma | Rb | Sr | Sm | Nd | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd | εNd(t) | TDM/Ma | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr | ISr | INd | εSr(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 90.67 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 2.15 | 11.68 | 0.111 5 | 0.512 716 | 2.51 | 650 | 1.315 2 | 0.706 284 | 0.704 59 | 0.512 650 | 2.8 |
| 17-40 | 90.67 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 2.64 | 15.22 | 0.104 9 | 0.512 708 | 2.43 | 621 | 1.085 1 | 0.706 084 | 0.704 69 | 0.512 646 | 4.2 |
| 17-42 | 90.67 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 2.18 | 11.95 | 0.110 5 | 0.512 689 | 2.00 | 684 | 0.830 2 | 0.705 708 | 0.704 64 | 0.512 624 | 3.5 |
表3 共国日二长花岗岩样品Sr-Nd同位素参数汇总表
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic parameters of the Gongguori monzogranite samples
| 样号 编号 | t/Ma | Rb | Sr | Sm | Nd | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd | εNd(t) | TDM/Ma | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr | ISr | INd | εSr(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 90.67 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 2.15 | 11.68 | 0.111 5 | 0.512 716 | 2.51 | 650 | 1.315 2 | 0.706 284 | 0.704 59 | 0.512 650 | 2.8 |
| 17-40 | 90.67 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 2.64 | 15.22 | 0.104 9 | 0.512 708 | 2.43 | 621 | 1.085 1 | 0.706 084 | 0.704 69 | 0.512 646 | 4.2 |
| 17-42 | 90.67 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 2.18 | 11.95 | 0.110 5 | 0.512 689 | 2.00 | 684 | 0.830 2 | 0.705 708 | 0.704 64 | 0.512 624 | 3.5 |
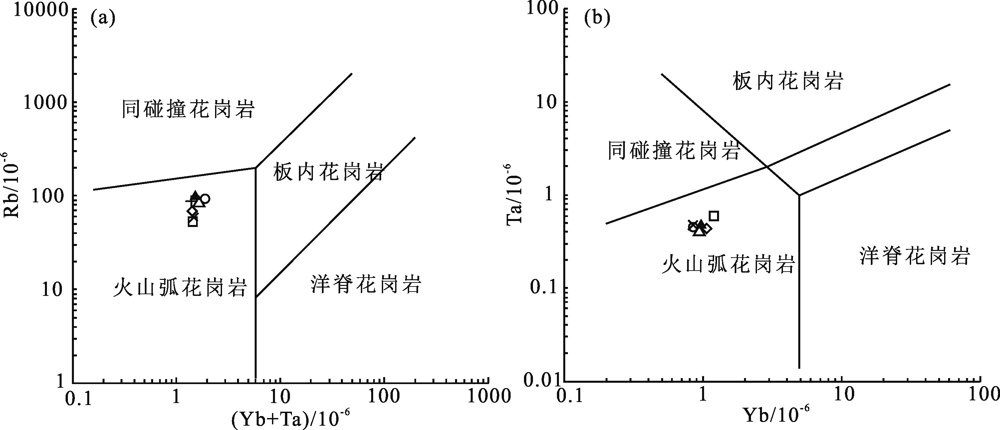
图14 共国日二长花岗岩Rb-(Yb+Ta)(a)和Ta-Yb(b)构造环境判别图(底图据文献[19])
Fig.14 Rb-(Yb+Ta)(a) and Ta-Yb (b) tectonic discrimination plots for the Gongguori monzogranite(base map after ref. [19])
| [1] | 吴福元, 刘传周, 张亮亮, 等. 雅鲁藏布蛇绿岩——事实与臆想[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2):293-325. |
| [2] | 张进, 邓晋福, 肖庆辉, 等. 蛇绿岩研究的最新进展[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(1):1-12. |
| [3] | 鲍佩声, 苏犁, 王军, 等. 雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015:1-74. |
| [4] | 王成善, 李亚林, 刘志飞, 等. 雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩再研究:从地质调查到矿物记录[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(3):323-330. |
| [5] | 梁凤华, 许志琴, 巴登珠, 等. 西藏罗布莎—泽当蛇绿岩体的构造产出与侵位机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11):3255-3268. |
| [6] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 等. 西藏日喀则地区雅鲁藏布蛇绿岩地球化学特征及其源区性质[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):294-302. |
| [7] |
COLEMAN R G, PETERMAN Z E. Oceanic plagiogranite[J]. Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(8):1099-1108.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 韦栋梁, 夏斌, 周国庆, 等. 西藏泽当英云闪长岩的地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素特征:特提斯洋内俯冲的新证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2007, 42(5):1515-1534. |
| [9] | 赵珍, 吴珍汉, 胡道功, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯带南缘泽当多金属矿田多期岩浆活动及年代意义[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(6):703-712. |
| [10] | LUDWIG K R. ISOPLOT3.0:A Geochronological Tool Kit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 39. |
| [11] |
STEIGER R H, JAGER E. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geochronology and cosmochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36:359-362.
DOI URL |
| [12] | WILLIARNS I S. Some observations on the use of zircon U-Pb geochronology in the study of granitic rocks[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Edinburgh-Earth Sciences, 1992, 83:447-458. |
| [13] | HU D G, WW Z H, JIANG W. et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ale and Nd isotopic study on the Nyainqentanghab Group[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2005, 48(9):1377-1386. |
| [14] |
BELOUSOVA E A, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37:215-224.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PECCERILLO J, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58:63-81.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101:635-643.
DOI URL |
| [18] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Magas and Magmatic Rocks[M]. London: Longman, 1985:1-266. |
| [19] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25:656-682. |
| [20] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:528-548. |
| [21] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985:1-312. |
| [22] | 韩吟文, 马振东. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003. |
| [23] | 王中刚. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992. |
| [24] |
JIANG Ziqi, WANG Qiang, WYMAN DEREK A, et al. Transition from oceanic to continental lithosphere subduction in southern Tibet: Evidence from the Late Cretaceous-Early Oligocene (~91-30 Ma) intrusive rocks in the Chanang-Zedong area, southern Gangdese[J]. Lithos, 2014, 196/197:213-231.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 张丽莹, 黄丰, 许继峰, 等. 西藏山南地区花岗质岩石成因及其对地壳结构变化的记录[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 44(6):1822-1833. |
| [26] | 纪伟强, 吴福元, 锺孙霖, 等. 西藏南部冈底斯岩基花岗岩时代与岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 2009, 39(7):849-871. |
| [27] | SETSUYA Nakada, MASAKI Takahashi. Regional variation in chemistry of the Miocene intermediate to felsic magmas in the Outer Zone and the Setouchi Province of Southwest Japan[J]. The Geological Society of Japan, 1979, 85(9):571-582. |
| [28] |
COLLINS W, BEAMS S, WHITE A, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2):189-200.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邢作云, 等. 花岗岩成因研究前沿的认识[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(增):18-27. |
| [30] | 李昌年. 火成岩微量元素岩石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992. |
| [31] |
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2):241-265.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PFANDER J A, MUINKER C, STRACKE A, et al. Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf in ocean island basalts-Implications for crust-mantle differentiation and the fate of Niobium[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 254(1):158-172.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 陈德潜, 陈刚. 实用稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1990. |
| [34] |
MCKENZIE D, BICKLE M J. The volume and composition of melt generated by extension of the lithosphere[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1988, 29:625-679.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
FOLEY S, TIEPOLO M, VANNUCCI R. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones[J]. Nature, 2002, 417:837-840.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 黄泽森, 江巴多吉, 达瓦次仁, 等. 西藏切穷地区早白垩世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4):703-714. |
| [37] |
PATIÑO DOUCE A E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas?[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1999, 168:55-75.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 许庆林, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等. 东昆仑莫河下拉银多金属矿床花岗斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(2):421-433. |
| [39] | FAURE G. Principle of Isotope Geology[M]. New York:Wiley, 1987:117-247. |
| [40] | 邱瑞照, 肖润, 周肃, 等. 藏北班公湖—怒江带中段舍玛拉沟蛇绿岩中辉长岩Sm-Nd同位素年龄和Sr、Nd同位素特征[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(增):64-68. |
| [41] | 邱瑞照, 邓晋福, 周肃, 等. 青藏高原中新生代花岗岩Sr、Nd同位素研究[J]. 地球科学, 2003, 24(6):611-617. |
| [42] | 洪大卫, 王式光, 谢锡林, 等. 兴蒙造山带正εNd(t)值花岗岩的成因和大陆地壳生长[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(2):441-456. |
| [43] |
HARRIS N B W, PEARCE J A, TINDLE A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1986, 19:67-81.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoid[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [45] | 梁华英, 魏启荣, 许继峰, 等. 西藏冈底斯矿带南缘矽卡岩型铜矿床含矿岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(6):1692-1698. |
| [46] | 董瀚, 张志平, 魏学平, 等. 西藏泽当蛇绿岩物质组成、年代格架及地质意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(6):1265-1273. |
| [47] | 杨鑫朋, 张振利, 张泽国, 等. 西藏冈底斯南缘中侏罗世辉长闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年和Lu-Hf位素组成及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1):63-72. |
| [48] | 代作文, 李光明, 丁俊, 等. 西藏努日晚白垩世埃达克岩:洋脊俯冲的产物[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8):2727-2741. |
| [49] | 岳相元, 杨波, 周雄, 等. 川西地区热达门石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征:岩石成因与构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5):1015-1024. |
| [1] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [2] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [5] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [6] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [7] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [8] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [9] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [10] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [11] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [12] | 杨文鹏, 李成禄, 杨元江, 符安宗, 郑博, 周腾飞, 赵瑞君. 黑龙江塔溪地区中侏罗世侵入岩地球化学特征、成因及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 390-403. |
| [13] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [14] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [15] | 王战永, 隆兆笃, 解波, 孙悦, 李巨初, 向杰, 范永宏. 四川冕西岩体岩石地球化学特征及铀成矿条件分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1465-1474. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||