



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (06): 1532-1544.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.091
包庆林1,2,3( ), 邓恩德2(
), 邓恩德2( ), 马子杰4, 姜秉仁4
), 马子杰4, 姜秉仁4
出版日期:2024-12-10
发布日期:2024-12-09
通信作者:
邓恩德,男,高级工程师,1990年出生,主要从事非常规天然气勘探开发、煤矿瓦斯防治等方面研究工作。Email: pjmdjtded@foxmail.com。作者简介:包庆林,男,高级工程师,1965年出生,主要从事煤炭开采、煤矿设计及煤层气勘探开发等方面研究工作。Email: 849902011@qq.com。
基金资助:
BAO Qinglin1,2,3( ), DENG Ende2(
), DENG Ende2( ), MA Zijie4, JIANG Bingren4
), MA Zijie4, JIANG Bingren4
Published:2024-12-10
Online:2024-12-09
摘要:
煤储层的微观孔隙是烃类气体赋存的主要位置,其微观孔隙结构特征对储气能力具有重要影响。研究煤储层孔隙及储气性对煤层气开采层段选取和瓦斯治理保护层选择具有基础性意义。黔西地区煤炭及煤层气资源丰富,但尚未见对煤储层孔隙结构特征及储气性研究。基于此,本文选取黔西织纳煤田戴家田矿D1井的二叠系龙潭组煤岩样品为研究对象,综合运用场发射扫描电镜、高压压汞、低温N2吸附及高温等温吸附等实验手段,对各煤层孔隙结构特征进行分析,并探讨煤储层孔隙结构特征对储气性的影响。结果表明研究区龙潭组煤储层微观孔隙类型多样,微孔、小孔、中孔和大孔均有发育,且不同煤样孔隙的种类、形态和成因类型存在差异,微孔的比表面积与CH4最大吸附气量和现场解吸气量均呈现一定的正相关性,对CH4吸附能力起到决定性作用。此次研究发现研究区14煤和27煤储气性较好,资源潜力较大,可考虑作为煤层气地面开采优质层段。
中图分类号:
包庆林, 邓恩德, 马子杰, 姜秉仁. 黔西煤储层孔隙结构特征与储气性研究:以戴家田煤矿D1井为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(06): 1532-1544.
BAO Qinglin, DENG Ende, MA Zijie, JIANG Bingren. Research on the Pore Structure Characteristics and Gas Storage Properties of Coal Reservoirs in Western Guizhou: A Case Study of Well D1 in Daijiatian Coal Mine[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(06): 1532-1544.

图1 黔西戴家田煤矿大地构造图(a)、地质背景图(b)及综合地层柱状剖面图(c)
Fig.1 Geological background map (a), construction map (b), and composite stratigraphic column (c) of the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 深度(m) | 水分(Mad)(%) | 灰分(Aad)(%) | 挥发分(Vdaf)(%) | 镜质组(%) | 惰质组(%) | 有机组分总量(%) | Ro(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6煤 | 425.00 | 2.56 | 27.57 | 10.22 | 55.8 | 21.7 | 77.5 | 2.85 |
| 14煤 | 475.71 | 2.48 | 17.24 | 9.12 | 64.3 | 24.7 | 89.0 | 3.09 |
| 16煤 | 506.13 | 1.69 | 18.99 | 15.57 | 56.2 | 20.7 | 76.9 | 3.06 |
| 27煤 | 580.00 | 2.80 | 22.49 | 7.32 | 71.2 | 22.3 | 93.5 | 3.15 |
| 32煤 | 612.80 | 2.80 | 38.32 | 11.11 | 58.4 | 21.5 | 79.9 | 3.17 |
表1 黔西戴家田煤矿煤样基础参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of coal samples from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 深度(m) | 水分(Mad)(%) | 灰分(Aad)(%) | 挥发分(Vdaf)(%) | 镜质组(%) | 惰质组(%) | 有机组分总量(%) | Ro(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6煤 | 425.00 | 2.56 | 27.57 | 10.22 | 55.8 | 21.7 | 77.5 | 2.85 |
| 14煤 | 475.71 | 2.48 | 17.24 | 9.12 | 64.3 | 24.7 | 89.0 | 3.09 |
| 16煤 | 506.13 | 1.69 | 18.99 | 15.57 | 56.2 | 20.7 | 76.9 | 3.06 |
| 27煤 | 580.00 | 2.80 | 22.49 | 7.32 | 71.2 | 22.3 | 93.5 | 3.15 |
| 32煤 | 612.80 | 2.80 | 38.32 | 11.11 | 58.4 | 21.5 | 79.9 | 3.17 |
| 编号 | 孔隙类型 |
|---|---|
| 6煤 | 气孔、角砾孔、碎粒孔、摩擦孔 |
| 14煤 | 气孔、角砾孔、碎粒孔 |
| 16煤 | 胞间孔、屑间孔、气孔 |
| 27煤 | 气孔、角砾孔、碎粒孔、晶间孔 |
| 32煤 | 气孔、屑间孔、铸模孔 |
表2 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层孔隙类型
Table 2 Pore types in the coal reservoir of the Longtan Formation from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 孔隙类型 |
|---|---|
| 6煤 | 气孔、角砾孔、碎粒孔、摩擦孔 |
| 14煤 | 气孔、角砾孔、碎粒孔 |
| 16煤 | 胞间孔、屑间孔、气孔 |
| 27煤 | 气孔、角砾孔、碎粒孔、晶间孔 |
| 32煤 | 气孔、屑间孔、铸模孔 |

图2 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层孔隙镜下特征 (a)胞腔孔,16煤,506.13 m;(b)屑间孔,16煤,506.13 m;(c)气孔,6煤,425.00 m;(d)角砾孔,14煤,475.71 m;(e)碎粒孔,27煤,580.00 m;(f)摩擦孔,6煤,425.00 m; (g)(h)铸模孔,32煤,612.80 m,图(h)为图(g)局部放大;(i)晶间孔,32煤,612.80 m
Fig.2 Microscopic pore characteristics of coal reservoirs in the Longtan Formation from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou

图3 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层进汞退汞曲线(1 psi=6.895 kPa)
Fig.3 Diagrams of mercury intrusion and ejection in the Longtan Formation coal reservoir from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 总孔体积 (cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容(cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 0.0308 | 0.0069 | 0.0118 | 0.0075 | 0.0046 | 22.40 | 38.31 | 24.35 | 14.94 | |
| 14煤 | 0.0232 | 0.0080 | 0.0111 | 0.0024 | 0.0017 | 34.48 | 47.84 | 10.34 | 7.33 | |
| 16煤 | 0.0296 | 0.0070 | 0.0206 | 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 23.65 | 69.59 | 4.73 | 2.03 | |
| 27煤 | 0.0250 | 0.0084 | 0.0134 | 0.0016 | 0.0016 | 33.60 | 53.60 | 6.40 | 6.40 | |
| 32煤 | 0.0271 | 0.0073 | 0.0119 | 0.0027 | 0.0052 | 26.94 | 43.91 | 9.96 | 19.19 | |
表3 黔西戴家田煤矿基于压汞数据的龙潭组煤储层孔体积分布
Table 3 Pore volume distribution for the Longtan Formation coal reservoir, based on mercury injection data from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 总孔体积 (cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容(cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 0.0308 | 0.0069 | 0.0118 | 0.0075 | 0.0046 | 22.40 | 38.31 | 24.35 | 14.94 | |
| 14煤 | 0.0232 | 0.0080 | 0.0111 | 0.0024 | 0.0017 | 34.48 | 47.84 | 10.34 | 7.33 | |
| 16煤 | 0.0296 | 0.0070 | 0.0206 | 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 23.65 | 69.59 | 4.73 | 2.03 | |
| 27煤 | 0.0250 | 0.0084 | 0.0134 | 0.0016 | 0.0016 | 33.60 | 53.60 | 6.40 | 6.40 | |
| 32煤 | 0.0271 | 0.0073 | 0.0119 | 0.0027 | 0.0052 | 26.94 | 43.91 | 9.96 | 19.19 | |
| 编号 | 比表面积 (m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积(m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 5.99800 | 3.45100 | 2.44350 | 0.09869 | 0.00481 | 57.54 | 40.74 | 1.65 | 0.08 | |
| 14煤 | 6.20400 | 3.86100 | 2.30767 | 0.03321 | 0.00212 | 62.23 | 37.20 | 0.54 | 0.03 | |
| 16煤 | 6.87400 | 2.93700 | 3.91553 | 0.02017 | 0.00130 | 42.73 | 56.96 | 0.29 | 0.02 | |
| 27煤 | 7.28500 | 4.44600 | 2.81339 | 0.02357 | 0.00204 | 61.03 | 38.62 | 0.32 | 0.03 | |
| 32煤 | 6.45000 | 3.91600 | 2.48750 | 0.04081 | 0.00569 | 60.71 | 38.57 | 0.63 | 0.09 | |
表4 黔西戴家田煤矿基于压汞数据的龙潭组煤储层比表面积分布
Table 4 Specific surface area distribution for the Longtan Formation coal reservoir, based on mercury injection data from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 比表面积 (m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积(m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 5.99800 | 3.45100 | 2.44350 | 0.09869 | 0.00481 | 57.54 | 40.74 | 1.65 | 0.08 | |
| 14煤 | 6.20400 | 3.86100 | 2.30767 | 0.03321 | 0.00212 | 62.23 | 37.20 | 0.54 | 0.03 | |
| 16煤 | 6.87400 | 2.93700 | 3.91553 | 0.02017 | 0.00130 | 42.73 | 56.96 | 0.29 | 0.02 | |
| 27煤 | 7.28500 | 4.44600 | 2.81339 | 0.02357 | 0.00204 | 61.03 | 38.62 | 0.32 | 0.03 | |
| 32煤 | 6.45000 | 3.91600 | 2.48750 | 0.04081 | 0.00569 | 60.71 | 38.57 | 0.63 | 0.09 | |

图4 黔西戴家田煤矿基于压汞数据的龙潭组煤储层孔径分布图
Fig.4 Pore size distribution map for the Longtan Formation coal reservoir, based on mercury injection data from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
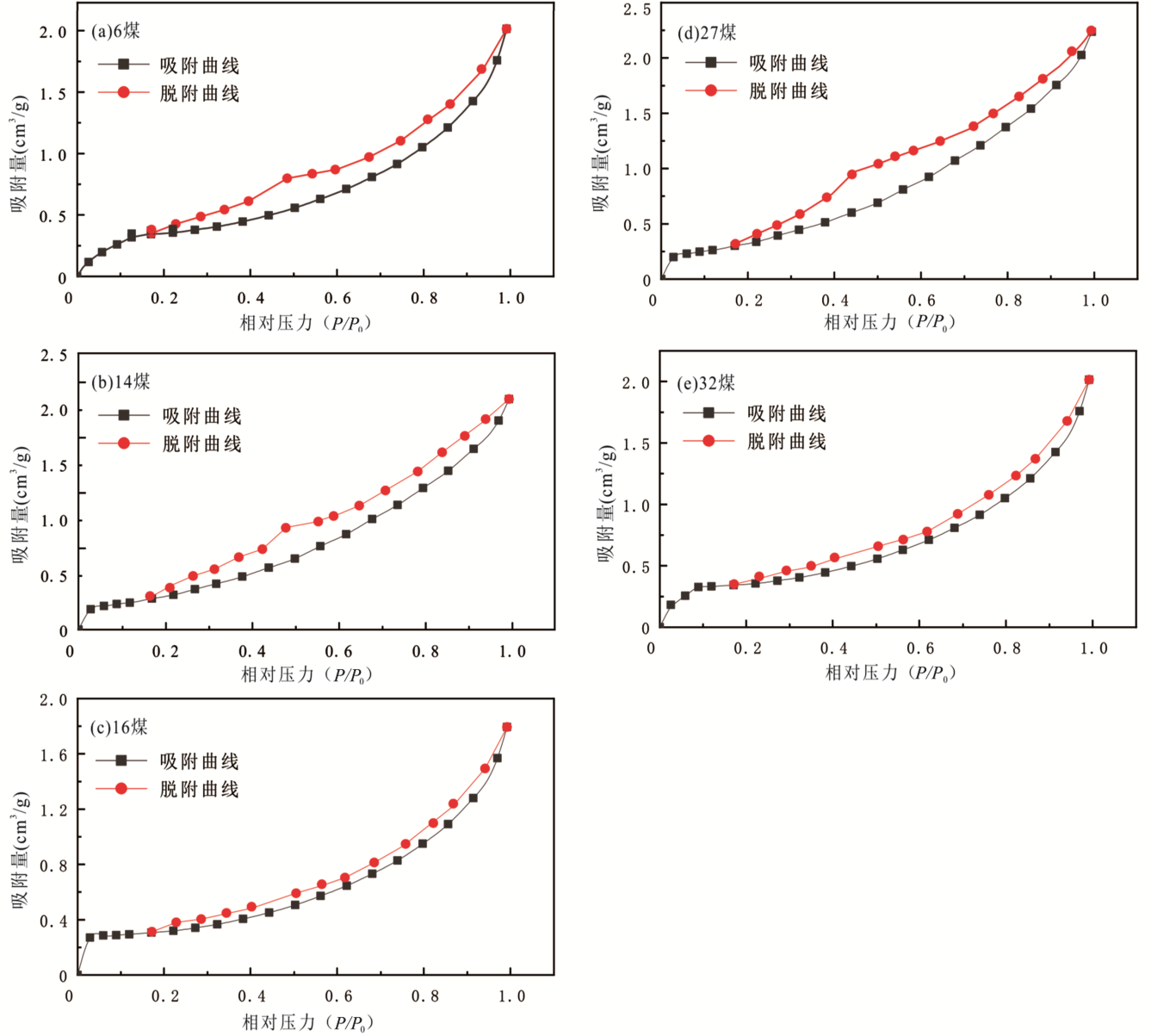
图5 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层低温氮气吸附-脱附曲线
Fig.5 Low-temperature nitrogen adsorption-desorption diagrams of the Longtan Formation coal reservoir from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 总孔体积 (cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容(cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 0.00323 | 0.00152 | 0.00130 | 0.00041 | 0 | 47.06 | 40.25 | 12.69 | 0 | |
| 14煤 | 0.00382 | 0.00238 | 0.00113 | 0.00031 | 0 | 62.30 | 29.58 | 8.12 | 0 | |
| 16煤 | 0.00290 | 0.00140 | 0.00114 | 0.00036 | 0 | 48.28 | 39.31 | 12.41 | 0 | |
| 27煤 | 0.00410 | 0.00258 | 0.00120 | 0.00032 | 0 | 62.93 | 29.27 | 7.80 | 0 | |
| 32煤 | 0.00349 | 0.00229 | 0.00108 | 0.00012 | 0 | 65.62 | 30.95 | 3.44 | 0 | |
表5 黔西戴家田煤矿基于氮气吸附数据的龙潭组煤储层孔体积分布
Table 5 Pore volume distribution of the Longtan Formation coal reservoir, based on N2 adsorption data from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 总孔体积 (cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容(cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 0.00323 | 0.00152 | 0.00130 | 0.00041 | 0 | 47.06 | 40.25 | 12.69 | 0 | |
| 14煤 | 0.00382 | 0.00238 | 0.00113 | 0.00031 | 0 | 62.30 | 29.58 | 8.12 | 0 | |
| 16煤 | 0.00290 | 0.00140 | 0.00114 | 0.00036 | 0 | 48.28 | 39.31 | 12.41 | 0 | |
| 27煤 | 0.00410 | 0.00258 | 0.00120 | 0.00032 | 0 | 62.93 | 29.27 | 7.80 | 0 | |
| 32煤 | 0.00349 | 0.00229 | 0.00108 | 0.00012 | 0 | 65.62 | 30.95 | 3.44 | 0 | |
| 编号 | 比表面积 (m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积(m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 1.46121 | 1.21187 | 0.23800 | 0.01134 | 0 | 82.94 | 16.29 | 0.78 | 0 | |
| 14煤 | 2.41003 | 2.16755 | 0.23657 | 0.00591 | 0 | 89.94 | 9.82 | 0.25 | 0 | |
| 16煤 | 1.34629 | 1.12677 | 0.20964 | 0.00988 | 0 | 83.69 | 15.57 | 0.73 | 0 | |
| 27煤 | 2.56813 | 2.32652 | 0.23526 | 0.00635 | 0 | 90.59 | 9.16 | 0.25 | 0 | |
| 32煤 | 2.08237 | 1.77562 | 0.29951 | 0.00724 | 0 | 85.27 | 14.38 | 0.35 | 0 | |
表6 黔西戴家田煤矿基于氮气吸附数据的龙潭组煤储层比表面积分布
Table 6 Specific surface area distribution of the Longtan Formation coal reservoir, based on N2 adsorption data from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 比表面积 (m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积(m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 1.46121 | 1.21187 | 0.23800 | 0.01134 | 0 | 82.94 | 16.29 | 0.78 | 0 | |
| 14煤 | 2.41003 | 2.16755 | 0.23657 | 0.00591 | 0 | 89.94 | 9.82 | 0.25 | 0 | |
| 16煤 | 1.34629 | 1.12677 | 0.20964 | 0.00988 | 0 | 83.69 | 15.57 | 0.73 | 0 | |
| 27煤 | 2.56813 | 2.32652 | 0.23526 | 0.00635 | 0 | 90.59 | 9.16 | 0.25 | 0 | |
| 32煤 | 2.08237 | 1.77562 | 0.29951 | 0.00724 | 0 | 85.27 | 14.38 | 0.35 | 0 | |

图6 黔西戴家田煤矿基于低温氮气吸附数据的龙潭组煤样孔径分布图
Fig.6 Pore size distribution map of the Longtan Formation coal reservoir, based on low-temperature N2 adsorption data from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in WesternGuizhou
| 编号 | 总孔体积 (cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容(cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 0.01612 | 0.00152 | 0.00250 | 0.0075 | 0.0046 | 9.43 | 15.51 | 46.53 | 28.54 | |
| 14煤 | 0.00851 | 0.00238 | 0.00203 | 0.0024 | 0.0017 | 27.97 | 23.85 | 28.20 | 19.98 | |
| 16煤 | 0.00544 | 0.00140 | 0.00204 | 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 25.74 | 37.50 | 25.74 | 11.03 | |
| 27煤 | 0.00778 | 0.00258 | 0.00200 | 0.0016 | 0.0016 | 33.16 | 25.71 | 20.57 | 20.57 | |
| 32煤 | 0.01192 | 0.00229 | 0.00173 | 0.0027 | 0.0034 | 19.21 | 14.51 | 22.65 | 28.52 | |
表7 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层不同孔径孔容分布
Table 7 Pore volume distribution of pore sizes in the Longtan Formation coal reservoir from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 总孔体积 (cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容(cm3·g-1) | 阶段孔容比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 0.01612 | 0.00152 | 0.00250 | 0.0075 | 0.0046 | 9.43 | 15.51 | 46.53 | 28.54 | |
| 14煤 | 0.00851 | 0.00238 | 0.00203 | 0.0024 | 0.0017 | 27.97 | 23.85 | 28.20 | 19.98 | |
| 16煤 | 0.00544 | 0.00140 | 0.00204 | 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 25.74 | 37.50 | 25.74 | 11.03 | |
| 27煤 | 0.00778 | 0.00258 | 0.00200 | 0.0016 | 0.0016 | 33.16 | 25.71 | 20.57 | 20.57 | |
| 32煤 | 0.01192 | 0.00229 | 0.00173 | 0.0027 | 0.0034 | 19.21 | 14.51 | 22.65 | 28.52 | |

图7 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层总孔体积和比表面积全孔径分布直方图 (a)—(e)总孔体积全孔径分布直方图;(f)—(j)比表面积全孔径分布直方图
Fig.7 Histograms of the full pore size distribution for the Longtan Formation coal reservoir from the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 比表面积 (m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积(m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 1.61047 | 1.21187 | 0.29510 | 0.09869 | 0.00481 | 75.25 | 18.32 | 6.13 | 0.30 | |
| 14煤 | 2.46641 | 2.16895 | 0.26213 | 0.03321 | 0.00212 | 87.94 | 10.63 | 1.35 | 0.09 | |
| 16煤 | 1.39939 | 1.12677 | 0.25115 | 0.02017 | 0.00130 | 80.52 | 17.95 | 1.44 | 0.09 | |
| 27煤 | 2.62820 | 2.32652 | 0.27607 | 0.02357 | 0.00204 | 88.52 | 10.50 | 0.90 | 0.08 | |
| 32煤 | 2.15487 | 1.77562 | 0.33275 | 0.04081 | 0.00569 | 82.40 | 15.44 | 1.89 | 0.26 | |
表8 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层不同孔径比表面积分布
Table 8 Specific surface area distribution of pore sizes in the Longtan Formation coal reservoir of the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| 编号 | 比表面积 (m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积(m2·g-1) | 阶段比表面积比例(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | 微孔 | 小孔 | 中孔 | 大孔 | |||
| 6煤 | 1.61047 | 1.21187 | 0.29510 | 0.09869 | 0.00481 | 75.25 | 18.32 | 6.13 | 0.30 | |
| 14煤 | 2.46641 | 2.16895 | 0.26213 | 0.03321 | 0.00212 | 87.94 | 10.63 | 1.35 | 0.09 | |
| 16煤 | 1.39939 | 1.12677 | 0.25115 | 0.02017 | 0.00130 | 80.52 | 17.95 | 1.44 | 0.09 | |
| 27煤 | 2.62820 | 2.32652 | 0.27607 | 0.02357 | 0.00204 | 88.52 | 10.50 | 0.90 | 0.08 | |
| 32煤 | 2.15487 | 1.77562 | 0.33275 | 0.04081 | 0.00569 | 82.40 | 15.44 | 1.89 | 0.26 | |
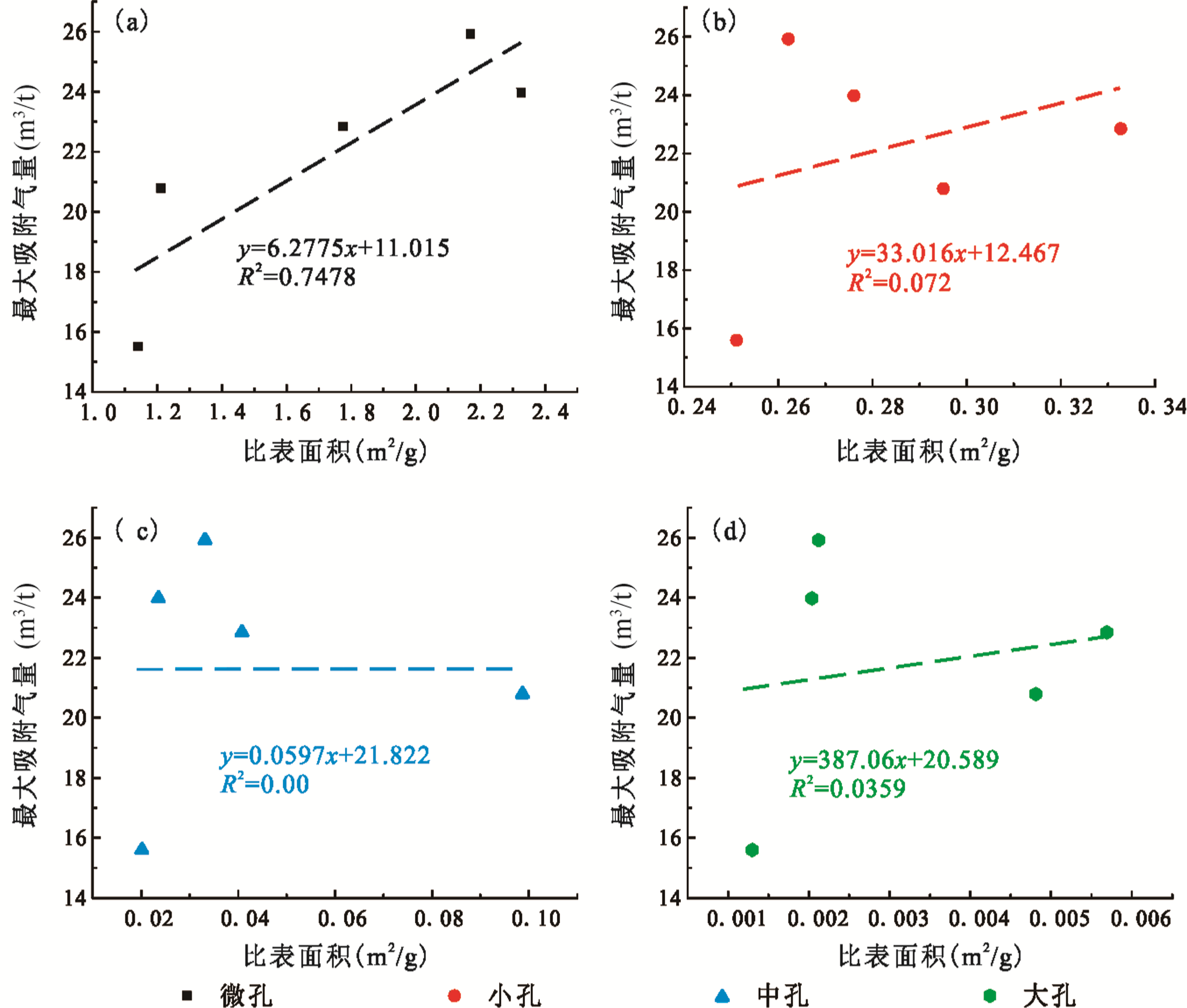
图9 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层孔隙比表面积与CH4最大吸附气量关系图 (a)微孔比表面积与最大吸附气量关系;(b)小孔比表面积与最大吸附气量关系;(c)中孔比表面积与最大吸附气量关系;(d)大孔比表面积与最大吸附气量关系
Fig.9 Relationship between pore surface area and maximum CH4 adsorption in the Longtan Formation coal reservoir of the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou

图10 黔西戴家田煤矿龙潭组煤储层孔隙比表面积与现场解吸气量关系图 (a)微孔比表面积与现场解吸气量关系;(b)小孔比表面积与现场解吸气量关系;(c)中孔比表面积与现场解吸气量关系;(d)大孔比表面积与现场解吸气量关系
Fig.10 Relationship between pore surface area and on-site desorption volume in the Longtan Formation coal reservoir of the Daijiatian Coal Mine in Western Guizhou
| [1] | 张玉贵, 焦银秋, 雷东记, 等. 煤体纳米级孔隙低温氮吸附特征及分形性研究[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 35(2): 141-148. |
| [2] | 刘娜, 康永尚, 李喆, 等. 煤岩孔隙度主控地质因素及其对煤层气开发的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(5): 963-974. |
| [3] | DENG E D, ZHANG Q, JIN Z J, et al. Non-overmature equivalents confirmed a high initial hydrocarbon generation potential of the Permian Longtan Shale in Southern China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2022, 259: 104043. |
| [4] | 王凯, 乔鹏, 王壮森, 等. 基于二氧化碳和液氮吸附、高压压汞和低场核磁共振的煤岩多尺度孔径表征[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(4): 146-152. |
| [5] | 付常青, 朱炎铭, 陈尚斌. 浙西荷塘组页岩孔隙结构及分形特征研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(1): 77-86. |
| [6] | LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian barnett shale[J]. Journal of Se-dimentary Research, 2009, 79(12): 848-861. |
| [7] | LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098. |
| [8] | 田华, 张水昌, 柳少波, 等. 压汞法和气体吸附法研究富有机质页岩孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 419-427. |
| [9] | 樊祺章, 蔡益栋, 贝金翰, 等. 煤岩演化程度对煤储层孔裂隙结构的控制作用[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(2): 273-280. |
| [10] | 邓恩德, 金军, 王冉, 等. 黔北地区龙潭组海陆过渡相页岩微观孔隙特征及其储气性[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(24): 190-195. |
| [11] | DANG W, NIE H K, ZHANG J C, et al. Pore-scale mechanisms and characterization of light oil storage in shale nanopores: New method and insights[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2022, 13(5): 50-58. |
| [12] | 邓恩德, 姜秉仁, 高为, 等. 黔西地区龙潭组煤系泥页岩孔隙结构及分形特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(8): 184-190. |
| [13] |
党伟, 张金川, 聂海宽, 等. 页岩油微观赋存特征及其主控因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延安地区延长组7段3亚段陆相页岩为例[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 507-523.
DOI |
| [14] | 李松, 汤达祯, 许浩, 等. 贵州省织金、纳雍地区煤储层物性特征研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2012, 41(6): 951-958. |
| [15] | ZHANG S, WANG Z M, ZHANG X D, et al. Construction of molecular structure model of Tunlan coal and its microscopic physicochemical mechanism[J]. Fuel, 2022, 308: 121936. |
| [16] | 兰海平, 包庆林, 邓恩德. 贵州织金地区八步向斜煤层气储层特征及有利勘探层段研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2023, 42(6): 100-103. |
| [17] | 牛新生, 冯常茂, 刘进. 黔中隆起的形成时间及形成机制探讨[J]. 海相油气地质, 2007, 12(2): 46-50. |
| [18] | 曹文杰, 何金先, 杨甜甜, 等. 贵州织金地区龙潭组沉积环境及其对页岩发育的控制[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2021, 33(5): 25-31, 37. |
| [19] | 张金川, 金之钧, 袁明生. 页岩气成藏机理和分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, 24(7): 15-18, 131-132. |
| [20] | GAN H, NANDI S P, WALKER P L. Nature of porosity in American coals[J]. Fuel, 1972, 51(4):272-277. |
| [21] | 郝琦. 煤的显微孔隙形态特征及其成因探讨[J]. 煤炭学报, 1987, (4): 51-56+97-101. |
| [22] | 张慧. 煤孔隙的成因类型及其研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2001, 26(1): 40-44. |
| [23] | XIE J N, XIE J, NI G H, et al. Effects of pulse wave on the variation of coal pore structure in pulsating hydraulic fracturing process of coal seam[J]. Fuel, 2020, 264: 116906. |
| [24] |
许耀波, 朱玉双. 高阶煤的孔隙结构特征及其对煤层气解吸的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(1): 84-92.
DOI |
| [25] |
朱炎铭, 王阳, 陈尚斌, 等. 页岩储层孔隙结构多尺度定性-定量综合表征: 以上扬子海相龙马溪组为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 154-163.
DOI |
| [26] |
刘世明, 唐书恒, 霍婷, 等. 柴达木盆地东缘上石炭统泥页岩孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(8): 1069-1081.
DOI |
| [27] | LUO N, SUO Y C, FAN X R, et al. Research on confining pressure effect of pore structure of coal-rich in coalbed methane under cyclic impact[J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8: 7336-7348. |
| [28] | 李振, 邵龙义, 侯海海, 等. 高煤阶煤孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(3): 595-605. |
| [29] | GREGG S J, SING K S W. Adsorption, Surface Area, and Porosity[M]. 2nd ed. London: Academic Press, 1982. |
| [30] | 李阳, 张玉贵, 张浪, 等. 基于压汞、低温N2吸附和CO2吸附的构造煤孔隙结构表征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(4): 1188-1196. |
| [31] |
符宏斌, 苑坤, 卢树藩, 等. 黔西上二叠统龙潭组高煤级煤微观孔隙结构特征及其对含气性的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(12): 1814-1825.
DOI |
| [32] | 林海飞, 卜婧婷, 严敏, 等. 中低阶煤孔隙结构特征的氮吸附法和压汞法联合分析[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2019, 39(1): 1-8. |
| [33] | FU H J, YAN D T, YANG S G, et al. A study of the gas-water characteristics and their implications for the coalbed methane accumulation modes in the Southern Junggar Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2021, 105(1): 189-221. |
| [34] | 许启鲁, 黄文辉, 唐书恒, 等. 深部中-高煤级煤储层孔隙结构与吸附性[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2): 413-419. |
| [35] | WANG X L, CHENG Y P, ZHANG D M, et al. Influence of tectonic evolution on pore structure and fractal characteristics of coal by low pressure gas adsorption[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 87: 103788. |
| [36] | 降文萍, 崔永君, 张群, 等. 不同变质程度煤表面与甲烷相互作用的量子化学研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2007, 32(3): 292-295. |
| [37] | 王可新, 潘树仁, 傅雪海. 低煤级煤的孔、裂隙特征研究[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(增): 67-68. |
| [1] | 闫涛滔, 邓志宇, 吴鹏, 高国森, 常锁亮, 付鑫宇, 孟艳军, 刘彦飞. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴东区杨家坡区块煤层气井产能特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(06): 1545-1556. |
| [2] | 李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 刘若冰, 蔡益栋, 李刚, 周秦, 肖贤明. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1293-1305. |
| [3] | 张金晴, 李贤庆, 张博翔, 张学庆, 杨经纬, 于振锋. 沁水盆地武乡区块上古生界煤系页岩气储层孔隙特征和孔隙结构[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1551-1562. |
| [4] | 李庆, 李江山, 卢浩, 齐奉强, 何羽, 安可钦, 李隆禹, 张厚民, 伍岳. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部长73页岩层系储层特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1254-1270. |
| [5] | 漆洋, 吕春研, 王宇慧, 唐书恒, 郗兆栋. 生物地层格架下湘西北地区五峰组—龙马溪组孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1292-1303. |
| [6] | 魏永恒, 葛燕燕, 王刚, 王文峰, 田继军, 李鑫, 吴斌, 张晓. 新疆库拜煤田铁列克矿区地应力分布及其对煤层气开发的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1324-1332. |
| [7] | 翟佳宇, 张松航, 唐书恒, 郭慧秋, 刘冰, 纪朝琪. 云南老厂雨汪煤层气区块气水成因及产能响应[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1341-1350. |
| [8] | 李金龙, 李倩, 蔡益栋, 陈伟, 陈志柱, 王坚, 薛晓辉. 云南老厂矿区煤层气储层地质条件及其资源潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1351-1359. |
| [9] | 闫涛滔, 郭怡琳, 孟艳军, 常锁亮, 金尚文, 康丽芳, 付鑫宇, 王青青, 赵媛, 张宇. 基于煤层气井生产数据的储层含气量校正新方法[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1360-1370. |
| [10] | 姜秉仁, 邓恩德, 韩明辉, 马子杰. 黔西北地区石炭系祥摆组页岩微观孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1065-1073. |
| [11] | 崔维平, 杨玉卿, 刘建新. 基于岩性相单元和孔隙结构的低孔低渗储层有效性测井识别方法:以西湖凹陷NB1构造为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 140-148. |
| [12] | 杨毅, 张恒荣, 袁伟, 杨冬, 胡德胜. 常规砂岩与砂砾岩分形特征对比及成因分析:以乌石凹陷X构造流沙港组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 149-158. |
| [13] | 刘文锋, 张小栓, 刘谨铭, 艾力曼·道尔吉, 杨远峰, 张曦文, 祁利祺, 于景维. AH5井区八道湾组砂质和砾质储层孔隙结构特征及评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1844-1853. |
| [14] | 李阳阳, 李贤庆, 张学庆, 杨经纬, 张博翔, 肖贤明, 于振锋. 沁水盆地阳泉区块太原组煤系页岩孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1033-1042. |
| [15] | 于景维, 牛志杰, 祁利祺, 孙新铭, 柳妮, 张进, 曹嵩. 准噶尔盆地阜北地区头屯河组非均质性综合研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 819-831. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||