



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (05): 1254-1270.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.047
李庆1,2( ), 李江山1,2, 卢浩1,2, 齐奉强1,2, 何羽1,2, 安可钦1,2, 李隆禹1,2, 张厚民1,2, 伍岳3
), 李江山1,2, 卢浩1,2, 齐奉强1,2, 何羽1,2, 安可钦1,2, 李隆禹1,2, 张厚民1,2, 伍岳3
收稿日期:2022-02-28
修回日期:2022-06-29
出版日期:2022-10-10
发布日期:2022-11-03
作者简介:李 庆,男,副教授,博士生导师,1985年出生,地质资源与地质工程专业,主要从事沉积学及非常规油气地质学研究。Email: liqing@cup.edu.cn。
基金资助:
LI Qing1,2( ), LI Jiangshan1,2, LU Hao1,2, QI Fengqiang1,2, HE Yu1,2, AN Keqin1,2, LI Longyu1,2, ZHANG Houmin1,2, WU Yue3
), LI Jiangshan1,2, LU Hao1,2, QI Fengqiang1,2, HE Yu1,2, AN Keqin1,2, LI Longyu1,2, ZHANG Houmin1,2, WU Yue3
Received:2022-02-28
Revised:2022-06-29
Online:2022-10-10
Published:2022-11-03
摘要:
鄂尔多斯盆地长73亚段的页岩层系有机质含量、矿物含量变化大,发育凝灰岩夹层,具有较强的非均质性,不同岩相的孔隙结构差异及主控因素尚不明确。综合多种分析技术手段,对鄂尔多斯盆地南部长73页岩层系的岩相进行系统划分,对比不同岩相的孔隙结构及物性差异,探讨其有效孔隙网络及主控因素。根据粒度、TOC和矿物成分将长73细粒岩分为8种岩相类型,其中高有机质硅质页岩、凝灰岩及高有机质黏土质页岩三种岩相所占比例较高。长73页岩中有机质丰度高(平均20.04%),类型以Ⅰ型为主,处于低熟到成熟阶段。储集空间根据产状可分为基质孔隙(粒间孔、粒内孔、晶间孔、特大溶蚀孔)、有机质相关孔隙(有机质孔、有机质边缘孔隙)、裂缝(构造缝、成岩缝、晶面裂缝、粒边缝)。各岩相等温吸附曲线特征以IV型为主,迟滞回线以H3型为主。宏孔是储集游离油的有效孔隙,储集性能受岩相、有机质含量及矿物组成控制。凝灰岩孔隙度、渗透率及宏孔比孔容最高,其次为高有机质硅质页岩和高有机质黏土质页岩,而低有机质页岩宏孔比孔容最小,介孔比孔容大。页岩中有机质、黄铁矿含量与宏孔比孔容呈正相关,凝灰岩中石英含量与宏孔比孔容也呈正相关。研究成果可为长73亚段页岩油甜点评价及预测提供地质依据。
中图分类号:
李庆, 李江山, 卢浩, 齐奉强, 何羽, 安可钦, 李隆禹, 张厚民, 伍岳. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部长73页岩层系储层特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1254-1270.
LI Qing, LI Jiangshan, LU Hao, QI Fengqiang, HE Yu, AN Keqin, LI Longyu, ZHANG Houmin, WU Yue. Characteristics and Control Factors of the Chang 73 Shale Reservoirs in the Southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(05): 1254-1270.
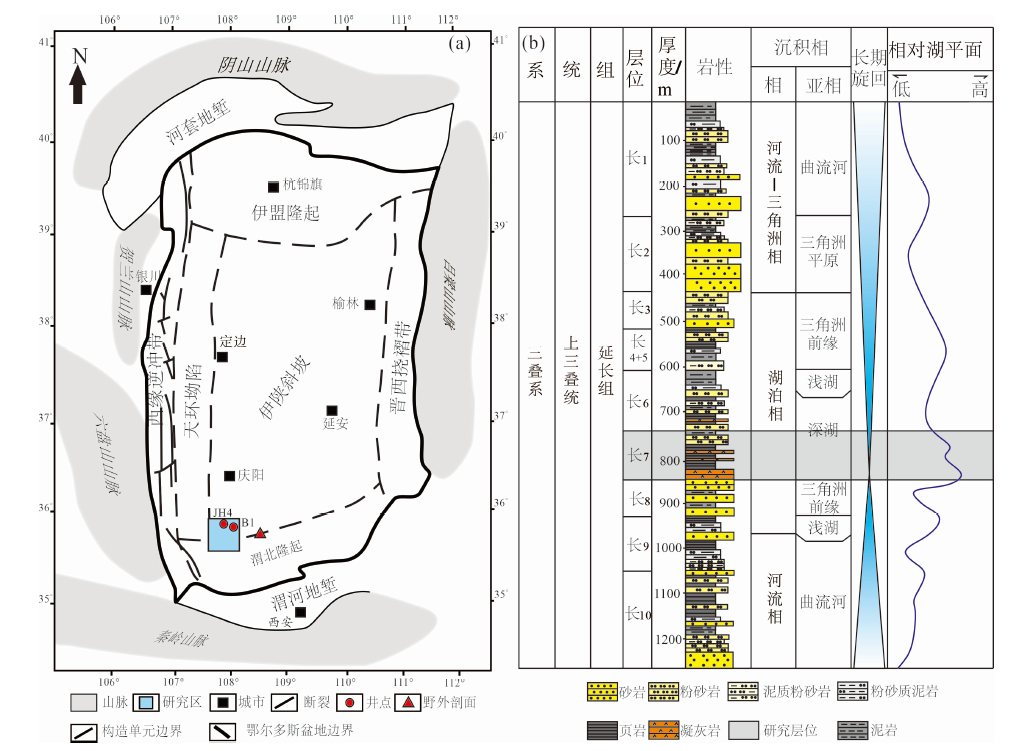
图1 鄂尔多斯盆地研究区位置及上三叠统延长组地层特征(据文献[25]修改) (a)鄂尔多斯盆地构造单元及研究区位置;(b)鄂尔多斯盆地延长组地层特征
Fig.1 Location of the study area and stratigraphy of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin (modified after reference[25])
| 岩石类别 | 粒度/mm | 岩性 | TOC含量/% | 玻屑/晶屑含量 | 硅质/黏土质比例 | 岩相 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常碎 屑岩 | <0.005 | 泥页岩 | >6 | - | R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)/(黏土矿物+云母)>1 | 高有机质硅质页岩 |
| R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)/(黏土矿物+云母)<1 | 高有机质黏土质页岩 | |||||
| 2~6 | - | R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)(黏土矿物+云母)>1 | 中有机质硅质页岩 | |||
| R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)/(黏土矿物+云母)<1 | 中有机质黏土质页岩 | |||||
| <2 | - | - | 低有机质页岩 | |||
| 0.005~0.01 | 粉砂岩 | - | - | - | 粉砂岩 | |
| 火山碎 屑岩 | <2 | 凝灰岩 | - | 玻屑>75% | - | 玻屑凝灰岩 |
| 50%<玻屑<75%, 晶屑>25% | - | 晶屑质玻屑凝灰岩 |
表1 岩相划分依据及方案
Table 1 Lithofacies division basis and scheme
| 岩石类别 | 粒度/mm | 岩性 | TOC含量/% | 玻屑/晶屑含量 | 硅质/黏土质比例 | 岩相 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常碎 屑岩 | <0.005 | 泥页岩 | >6 | - | R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)/(黏土矿物+云母)>1 | 高有机质硅质页岩 |
| R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)/(黏土矿物+云母)<1 | 高有机质黏土质页岩 | |||||
| 2~6 | - | R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)(黏土矿物+云母)>1 | 中有机质硅质页岩 | |||
| R(石英+长石+黄铁矿)/(黏土矿物+云母)<1 | 中有机质黏土质页岩 | |||||
| <2 | - | - | 低有机质页岩 | |||
| 0.005~0.01 | 粉砂岩 | - | - | - | 粉砂岩 | |
| 火山碎 屑岩 | <2 | 凝灰岩 | - | 玻屑>75% | - | 玻屑凝灰岩 |
| 50%<玻屑<75%, 晶屑>25% | - | 晶屑质玻屑凝灰岩 |

图4 研究区页岩层系不同岩相镜下特征 (a)高有机质硅质页岩,JH4井,1 453.62 m,(+);(b)高有机质黏土质页岩,JH4井,1 454.76 m,(-); (c)中有机质硅质页岩,LH2井,929.82 m,(-);(d)中有机质黏土质页岩,JH4井,1 434.59 m,(-); (e)低有机质页岩,JH4井,1 430.1 m,(+); (f)粉砂岩,JH4井,1 449.57 m,(-); (g)凝灰岩与页岩频繁互层,彬1井,1 442.46 m;(h)玻屑凝灰岩,彬1井,1 444.94 m,(-);(i)晶屑质玻屑凝灰岩,彬1井,1 442.46 m,(-)
Fig.4 Microscopic characteristics of different lithofacies of the shale reservoirs in the study area
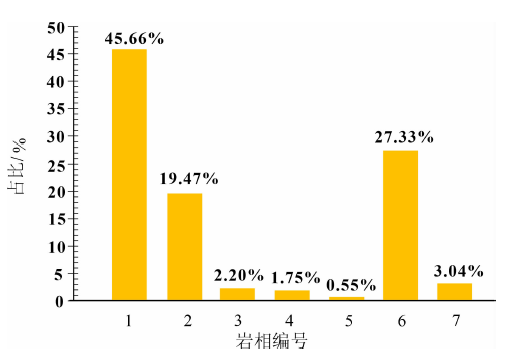
图5 研究区不同岩相比例 1.高有机质硅质页岩;2.高有机质黏土质页岩;3.中有机质硅质页岩;4.中有机质黏土质页岩;5.低有机质页岩;6.玻屑凝灰岩;7. 晶屑质玻屑凝灰岩
Fig.5 Proportions of the different lithofacies in the study area
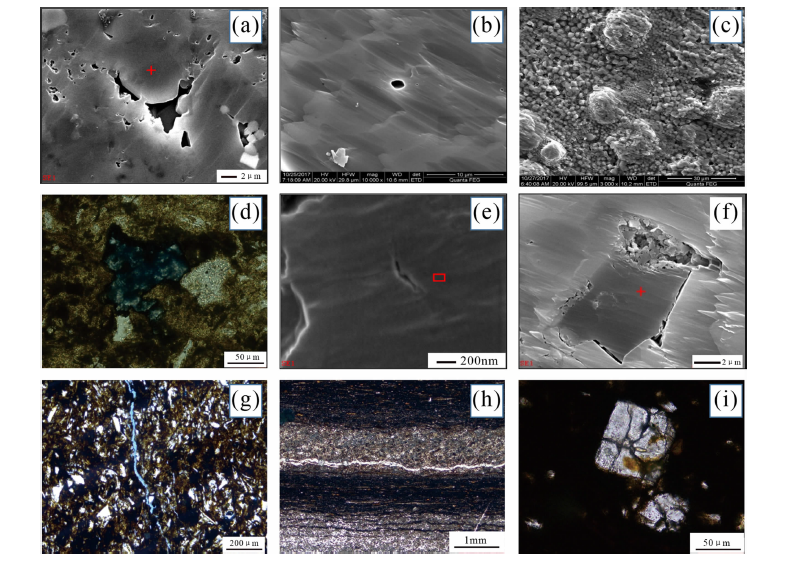
图6 不同孔隙类型微观特征 (a)粒间孔,扫描电镜,彬1井,1 436.74 m; (b)粒内孔,扫描电镜,JH4井,1 452.5 m; (c)晶间孔,扫描电镜,LH2井,970.99 m; (d)特大溶孔,彬1井, 1 433.76 m, (-);(e)有机质孔,扫描电镜,JH4井,1 454.76 m;(f)有机质边缘孔,扫描电镜,JH4井,1 452.5 m; (g)构造缝,JH4, 1 454.19 m, (-);(h)成岩缝,彬1井,1 433.85 m,(-); (i)晶面裂缝,彬1井,1 437.96 m,(+)
Fig.6 Microscopic characteristics of the different reservoir space types
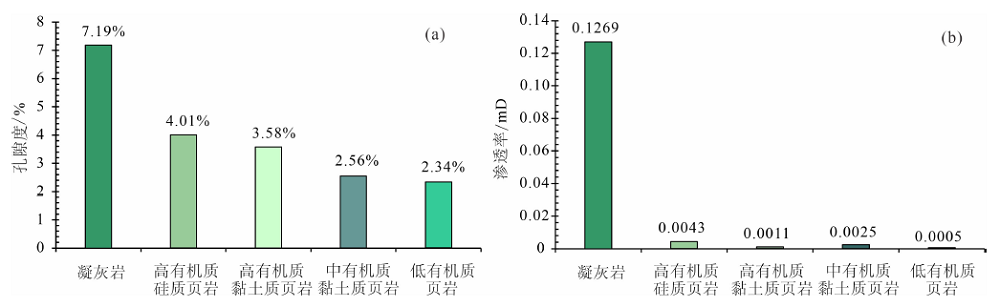
图11 页岩层系不同岩相孔隙度及渗透率特征(1 mD=10-3 μm2)
Fig.11 Porosity and permeability characteristics for the different lithofacies in the shale reservoirs (1 mD=10-3 μm2)
| [1] | 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. |
| [2] | 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2): 129-136. |
| [3] | 邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等. 中国油气储层中纳米孔首次发现及其科学价值[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(6): 1857-1864. |
| [4] |
LI Y F, SCHIEBER J, FAN T L, et al. Pore characterization and shale facies analysis of the Ordovician-Silurian transition of northern Guizhou, South China: The controls of shale facies on pore distribution[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 697-718.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
姜在兴, 张文昭, 梁超, 等. 页岩油储层基本特征及评价要素[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(1): 184-196.
DOI |
| [6] |
姜在兴, 梁超, 吴靖, 等. 含油气细粒沉积岩研究的几个问题[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(6): 1031-1038.
DOI |
| [7] | 刘树根, 马文辛, 黄文明, 等. 四川盆地东部地区下志留统龙马溪组页岩储层特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(8): 2239-2252. |
| [8] | 梁超, 姜在兴, 杨镱婷, 等. 四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组页岩岩相及储集空间特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6): 691-698. |
| [9] | 王永诗, 李政, 巩建强, 等. 济阳坳陷页岩油气评价方法--以沾化凹陷罗家地区为例[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1): 83-91. |
| [10] | 刘传联, 舒小辛, 刘志伟. 济阳坳陷下第三系湖相生油岩的微观特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(2): 293-298. |
| [11] | 姜秀芳. 济阳坳陷湖相碳酸盐岩沉积主控因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(6): 23-27,112. |
| [12] |
YANG H, NIU X B, XU L M, et al. Exploration potential of shale oil in Chang 7 Member, Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 560-569.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 96(6): 1071-1098.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 于炳松. 页岩气储层孔隙分类与表征[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 211-220. |
| [15] | 杨峰, 宁正福, 王庆, 等. 页岩纳米孔隙分形特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(4): 146-151. |
| [16] | 陈燕燕, 邹才能, MARIA M, 等. 页岩微观孔隙演化及分形特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(9): 1646-1656. |
| [17] |
LU H, XIA D L, LI Q, et al. Quantitative characterization and differences of the pore structure in lacustrine siliceous shale and argillaceous shale: a case study of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation shales in the Southern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Energy and Fuel, 2021, 35: 15525-15544.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LAZAR O R, BOHACS K M, MACQUAKER J, et al. Capturing key attributes of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in outcrops, cores, and thin sections: nomenclature and description guidelines[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2015, 85: 230-246.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHU J, LEI C, YUE W, et al. Hybrid plays of Upper Triassic Chang 7 lacustrine source rock interval of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 159: 182-196.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LI Q, YOU X L, JIANG Z X, et al. A type of continuous petroleum accumulation system in the Shulu sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(11): 1791-1811.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 马文忠, 王永宏, 张三, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陕北地区长7段页岩油储层微观特征及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1810-1821. |
| [22] | 付金华, 李士祥, 牛小兵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(5): 870-883. |
| [23] |
付金华, 牛小兵, 淡卫东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组长7段页岩油地质特征及勘探开发进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 601-614.
DOI |
| [24] |
LI Q, LU H, LI J, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the tight tuff reservoirs of the Upper Triassic Chang 7 member in the southern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 139: 105625.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LU H, LI Q, Yue D L, et al. Study on optimal selection of porosity logging interpretation methods for Chang 73 segment of the Yanchang Formation in the southwestern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 198: 108153.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 邓秀芹, 付金华, 姚泾利, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中及上三叠统延长组沉积相与油气勘探的突破[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(4): 443-455. |
| [27] | 李德生. 重新认识鄂尔多斯盆地油气地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(6): 1-7. |
| [28] | 田媛, 钟建华, 王书宝, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地富县探区三叠系延长组震积岩及其地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(4): 541-552. |
| [29] | 周利明. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部长7沉积环境对细粒沉积物的影响[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2016: 1-64. |
| [30] | 王芮. 鄂尔多斯盆地志丹-甘泉地区延长组长7段页岩油及页岩气成藏条件研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2015: 8-11. |
| [31] | 付金华, 罗顺社, 牛小兵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7段沟道型重力流沉积特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1): 29-37. |
| [32] | 杨仁超, 何治亮, 邱桂强, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部晚三叠世重力流沉积体系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(6): 661-670. |
| [33] |
LI Q, WU S H, XIA D L, et al. Major and trace element geochemistry of the lacustrine organic-rich shales from the Upper Triassic Chang 7 Member in the southwestern Ordos Basin, China: Implications for paleoenvironment and organic matter accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 111: 852-867.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHAO X Z, LI Q, JIANG Z X, et al. Organic geochemistry and reservoir characterization of the organic matter-rich calcilutite in the Shulu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, North China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 51: 239-255.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 于炳松. 页岩气储层的特殊性及其评价思路和内容[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(3): 252-258. |
| [36] | 陈平, 张敏强, 许永哲, 等. 下扬子巢湖-泾县地区上二叠统大隆组泥页岩储层特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8): 2925-2935. |
| [37] | 赵海玲, 黄微, 王成, 等. 火山岩中脱玻化孔及其对储层的贡献[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(1): 47-52. |
| [38] | 李庆. 冀中坳陷束鹿凹陷中南部沙三下亚段砾岩及泥灰岩致密储层评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015: 1-165. |
| [39] | CURTIS M E, SONDERGELD C H, RAI C S, et al. Relationship between organic shale microstructure and hydrocarbon generation[M]//SPE.Unconventional Resources Conference. Washington:SPE, 2013: 164540. |
| [40] | 陈世悦, 龚文磊, 张顺, 等. 黄骅坳陷沧东凹陷孔二段泥页岩裂缝发育特征及主控因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 144-154. |
| [41] | 袁玉松, 周雁, 邱登峰, 等. 泥页岩非构造裂缝形成机制及特征[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 155-162. |
| [42] |
马剑, 黄志龙, 刘再振, 等. 三塘湖盆地条湖组含沉积有机质凝灰岩致密储层特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(6): 185-196.
DOI |
| [43] | 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等. 页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 301-311. |
| [44] |
BRUNAUER S, EMMET P H, TELLER E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1938, 60(2): 309-319.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
THIERFELDER C, WITTE M S, BLANKENBURG S, et al. Methane adsorption on graphene from first principles including dispersion interaction[J]. Surface Science, 2011, 605(7/8): 746-749.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等. 高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. |
| [47] |
KUILA U, PRASAD M. Surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2013, 61(2): 341-362.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
BOLTON A J, MALTMAN A J, FISHER Q. Anisotropic permeability and bimodal pore-size distributions of fine-grained marine sediments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(6): 657-672.
DOI URL |
| [49] | 田华, 张水昌, 柳少波, 等. 压汞法和气体吸附法研究富有机质页岩孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 419-427. |
| [50] | 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等. 高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. |
| [51] | JARVIE D M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: Part 2-Shale-oil resource systems[M]//BREYER J A. Shale Reservoirs-Giant Resources for the 21st Century. Washington: AAPG Memoir, 2012: 89-119. |
| [1] | 刘旺威, 李一凡, 高志前, 樊太亮, 张坦, 匡明志. 塔里木盆地东北缘下寒武统页岩岩相特征与沉积模式[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1155-1168. |
| [2] | 李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 刘若冰, 蔡益栋, 李刚, 周秦, 肖贤明. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1293-1305. |
| [3] | 张卓, 陈社明, 柳富田, 高志鹏, 牛笑童. 滨海平原区深层高氟地下水富集机理:以滦河三角洲为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 925-932. |
| [4] | 张金晴, 李贤庆, 张博翔, 张学庆, 杨经纬, 于振锋. 沁水盆地武乡区块上古生界煤系页岩气储层孔隙特征和孔隙结构[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1551-1562. |
| [5] | 漆洋, 吕春研, 王宇慧, 唐书恒, 郗兆栋. 生物地层格架下湘西北地区五峰组—龙马溪组孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1292-1303. |
| [6] | 刘倩, 樊太亮, 高志前, 张同辉, 马晓萱, 卫端, 鲁新便. 新疆塔北隆起桥古地区前中生界碳酸盐岩潜山储层特征与发育模式[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1391-1402. |
| [7] | 姜秉仁, 邓恩德, 韩明辉, 马子杰. 黔西北地区石炭系祥摆组页岩微观孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1065-1073. |
| [8] | 郑庆华, 刘行军, 张小龙, 王洪君, 廖永乐, 安二亮, 刘涛, 张建娜, 左琴. 再论鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长73砂层组与烃源岩相关的高伽马砂岩[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1087-1094. |
| [9] | 于景维, 罗刚, 李斌, 潘拓, 余海涛, 况昊, 褚旭, 张晓童. 沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储层成岩作用及成岩相分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1095-1104. |
| [10] | 刘茂涵, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 王振, 吴通航, 王玉罡. 鄱阳湖流域赣江北支水体和沉积物中稀土元素的含量和分异特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 389-405. |
| [11] | 唐相路, 姜振学, 邵泽宇, 龙国徽, 贺世杰, 刘晓雪, 王昱超. 第四系泥岩型生物气储层特征及动态成藏过程[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 682-694. |
| [12] | 崔维平, 杨玉卿, 刘建新. 基于岩性相单元和孔隙结构的低孔低渗储层有效性测井识别方法:以西湖凹陷NB1构造为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 140-148. |
| [13] | 杨毅, 张恒荣, 袁伟, 杨冬, 胡德胜. 常规砂岩与砂砾岩分形特征对比及成因分析:以乌石凹陷X构造流沙港组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 149-158. |
| [14] | 刘文锋, 张小栓, 刘谨铭, 艾力曼·道尔吉, 杨远峰, 张曦文, 祁利祺, 于景维. AH5井区八道湾组砂质和砾质储层孔隙结构特征及评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1844-1853. |
| [15] | 吕承训, 霍庆龙, 唐占信, 范潇, 汤磊, 许亚青, 袁月蕾. 胶西北断裂构造蚀变分带及其铲式分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1274-1281. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||