



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (03): 722-732.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.040
收稿日期:2022-12-26
修回日期:2023-03-30
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-07-20
通讯作者:
张德贤,博士,副教授,1978年出生,地质学专业,主要从事矿物微量元素地球化学和矿床学研究。Email:dexian.zhang@csu.edu.cn。
作者简介:胡子奇,硕士,1998年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿物微量元素地球化学和U-Pb同位素定年研究。Email:ziqi.hu@csu.edu.cn。
基金资助:
HU Ziqi1,2( ), ZHANG Dexian1,2(
), ZHANG Dexian1,2( ), LIU Lei1,2
), LIU Lei1,2
Received:2022-12-26
Revised:2023-03-30
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-07-20
摘要:
激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)是锆石U-Pb定年常用的方法之一。应用LA-ICP-MS 进行锆石U-Pb定年的过程中,束斑直径的大小和能量密度的高低是影响定年准确度的两个关键因素。本文开展了应用LA-ICP-MS在不同束斑直径和能量密度条件下对锆石标样91500和GJ-1 U-Pb定年结果准确度的对比研究,旨在优化LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb定年的方法,提高分析准确度,也为其他实验室开展类似的研究工作提供一定的借鉴。实验结果表明:在剥蚀频率、扫描速度、载气流速保持不变的前提下,当能量密度固定,随着剥蚀束斑直径从25 μm增大至65 μm的过程中,锆石91500和GJ-1在互为标样和盲样的条件下实测年龄结果与推荐值之间的相对误差(RE)不断减小(RE分别为0.61%、0.41%、0.13%和0.08%),即增加束斑直径降低了相对误差,提高了定年准确度。而当束斑直径固定时,能量密度≤3.5 J/cm2时,随着能量密度不断增大,实测年龄结果与推荐值之间的相对误差逐渐减小(RE分别为8.69%、3.48%、3.95%、4.16%和0.41%),定年准确度逐渐增加;但是当能量密度大于3.5 J/cm2时,能量密度增大导致剥蚀速率显著增大,在深度方向上的分馏效应明显增加,对比3.5 J/cm2条件下,此时的实测年龄结果与推荐值之间的相对误差增大(RE分别为2.40%和0.83%),定年准确度降低。因此,在实际测试中,考虑到样品大小和尽可能少地对样品进行破坏,合理的能量密度和束斑大小可以有效提高定年的准确度。
中图分类号:
胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732.
HU Ziqi, ZHANG Dexian, LIU Lei. Discussion on Spot Size and Energy Density Effects on Zircon U-Pb Dating Precision[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 722-732.
| 激光参数 | 设定值 | ICP-MS参数 | 设定值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 激光源 | TelydyneCetac HE Photon Machines Excimer | ICP-MS系统 | Analytik Jena Plasma Quant MS Elite |
| 波长 | 193 nm | 功率 | 1400 W |
| 脉冲宽度 | 20 ns | 等离子冷却气(Ar)流速 | 13.5 L/min |
| 激光束 | 均值化平顶光束 | 辅助气(He)流速 | 0.850 L/min |
| 脉冲能量 | 0.01~0.1 mJ | 样品传输气(He)流速 | 0.250 L/min |
| 能量密度 | 3.5 J/cm2(仪器配1~12 J/cm2) | 样品传输气(Ar)流速 | 0.90 L/min |
| 焦点 | 表面 | 扫描模式 | 峰跳跃模式,1点/峰 |
| 光栅扫描速度 | 5 Hz | 获取模式 | 时间分辨率分析 |
| 激光束直径 | 35 μm(仪器配置1~180 μm) | 分析持续时间 | 70 s(20 s背景,30 s 信号,20 s冲洗) |
表1 LA-ICP-MS仪器参数
Table 1 Operating parameters for LA-ICP-MS
| 激光参数 | 设定值 | ICP-MS参数 | 设定值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 激光源 | TelydyneCetac HE Photon Machines Excimer | ICP-MS系统 | Analytik Jena Plasma Quant MS Elite |
| 波长 | 193 nm | 功率 | 1400 W |
| 脉冲宽度 | 20 ns | 等离子冷却气(Ar)流速 | 13.5 L/min |
| 激光束 | 均值化平顶光束 | 辅助气(He)流速 | 0.850 L/min |
| 脉冲能量 | 0.01~0.1 mJ | 样品传输气(He)流速 | 0.250 L/min |
| 能量密度 | 3.5 J/cm2(仪器配1~12 J/cm2) | 样品传输气(Ar)流速 | 0.90 L/min |
| 焦点 | 表面 | 扫描模式 | 峰跳跃模式,1点/峰 |
| 光栅扫描速度 | 5 Hz | 获取模式 | 时间分辨率分析 |
| 激光束直径 | 35 μm(仪器配置1~180 μm) | 分析持续时间 | 70 s(20 s背景,30 s 信号,20 s冲洗) |
| 样品名称 | 束斑直径 (μm) | 能量密度 (J/cm2) | 标样为91500 | 标样为GJ-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb/238U 年龄(Ma) | 与推荐值相对 误差RE(%) | 206Pb/238U 年龄(Ma) | 与推荐值相对 误差RE(%) | ||||
| 91500 | 25 | 3.5 | 1062.6±4.5 | 0.01 | 1073.7±4.7 | 0.95 | |
| 35 | 3.5 | 1063.8±2.3 | 0.02 | 1071.0±3.4 | 0.70 | ||
| 50 | 3.5 | 1063.1±2.2 | 0.05 | 1064.5±2.3 | 0.09 | ||
| 65 | 3.5 | 1063.0±1.8 | 0.06 | 1059.9±2.0 | 0.35 | ||
| 35 | 1.5 | 1062.1±6.9 | 0.14 | 1176.5±1.8 | 10.61 | ||
| 35 | 2.0 | 1062.8±2.3 | 0.08 | 1079.8±4.2 | 1.49 | ||
| 35 | 2.5 | 1065.0±2.9 | 0.12 | 1094.7±5.0 | 2.93 | ||
| 35 | 3.0 | 1063.0±2.1 | 0.06 | 1096.7±3.9 | 3.11 | ||
| 35 | 3.5 | 1063.8±2.3 | 0.02 | 1071.0±3.4 | 0.70 | ||
| 35 | 4.0 | 1063.0±1.9 | 0.06 | 1088.9±3.5 | 2.38 | ||
| 35 | 4.5 | 1061.6±2.6 | 0.19 | 1078.4±2.6 | 1.40 | ||
| GJ-1 | 25 | 3.5 | 598.1±2.2 | 0.61 | 600.7±1.9 | 0.20 | |
| 35 | 3.5 | 599.4±1.5 | 0.41 | 600.6±1.5 | 0.21 | ||
| 50 | 3.5 | 602.7±1.0 | 0.13 | 600.8±1.0 | 0.17 | ||
| 65 | 3.5 | 601.4±1.0 | 0.08 | 600.9±0.9 | 0.16 | ||
| 35 | 1.5 | 549.6±1.6 | 8.69 | 600.5±1.8 | 0.23 | ||
| 35 | 2.0 | 580.9±0.9 | 3.48 | 600.7±1.5 | 0.20 | ||
| 35 | 2.5 | 578.1±1.1 | 3.95 | 601.0±1.2 | 0.15 | ||
| 35 | 3.0 | 576.8±0.8 | 4.16 | 600.8±1.3 | 0.18 | ||
| 35 | 3.5 | 599.4±1.5 | 0.41 | 600.6±1.5 | 0.21 | ||
| 35 | 4.0 | 587.4±0.7 | 2.40 | 600.9±1.3 | 0.16 | ||
| 35 | 4.5 | 596.9±1.2 | 0.83 | 601.0±1.0 | 0.15 | ||
表2 锆石定年测量结果
Table 2 Zircon dating results
| 样品名称 | 束斑直径 (μm) | 能量密度 (J/cm2) | 标样为91500 | 标样为GJ-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb/238U 年龄(Ma) | 与推荐值相对 误差RE(%) | 206Pb/238U 年龄(Ma) | 与推荐值相对 误差RE(%) | ||||
| 91500 | 25 | 3.5 | 1062.6±4.5 | 0.01 | 1073.7±4.7 | 0.95 | |
| 35 | 3.5 | 1063.8±2.3 | 0.02 | 1071.0±3.4 | 0.70 | ||
| 50 | 3.5 | 1063.1±2.2 | 0.05 | 1064.5±2.3 | 0.09 | ||
| 65 | 3.5 | 1063.0±1.8 | 0.06 | 1059.9±2.0 | 0.35 | ||
| 35 | 1.5 | 1062.1±6.9 | 0.14 | 1176.5±1.8 | 10.61 | ||
| 35 | 2.0 | 1062.8±2.3 | 0.08 | 1079.8±4.2 | 1.49 | ||
| 35 | 2.5 | 1065.0±2.9 | 0.12 | 1094.7±5.0 | 2.93 | ||
| 35 | 3.0 | 1063.0±2.1 | 0.06 | 1096.7±3.9 | 3.11 | ||
| 35 | 3.5 | 1063.8±2.3 | 0.02 | 1071.0±3.4 | 0.70 | ||
| 35 | 4.0 | 1063.0±1.9 | 0.06 | 1088.9±3.5 | 2.38 | ||
| 35 | 4.5 | 1061.6±2.6 | 0.19 | 1078.4±2.6 | 1.40 | ||
| GJ-1 | 25 | 3.5 | 598.1±2.2 | 0.61 | 600.7±1.9 | 0.20 | |
| 35 | 3.5 | 599.4±1.5 | 0.41 | 600.6±1.5 | 0.21 | ||
| 50 | 3.5 | 602.7±1.0 | 0.13 | 600.8±1.0 | 0.17 | ||
| 65 | 3.5 | 601.4±1.0 | 0.08 | 600.9±0.9 | 0.16 | ||
| 35 | 1.5 | 549.6±1.6 | 8.69 | 600.5±1.8 | 0.23 | ||
| 35 | 2.0 | 580.9±0.9 | 3.48 | 600.7±1.5 | 0.20 | ||
| 35 | 2.5 | 578.1±1.1 | 3.95 | 601.0±1.2 | 0.15 | ||
| 35 | 3.0 | 576.8±0.8 | 4.16 | 600.8±1.3 | 0.18 | ||
| 35 | 3.5 | 599.4±1.5 | 0.41 | 600.6±1.5 | 0.21 | ||
| 35 | 4.0 | 587.4±0.7 | 2.40 | 600.9±1.3 | 0.16 | ||
| 35 | 4.5 | 596.9±1.2 | 0.83 | 601.0±1.0 | 0.15 | ||

图1 不同束斑直径和能量密度条件下NIST SRM610(a)(b)和锆石GJ-1(c)(d)实际测量207Pb 信号强度
Fig.1 Measured 207Pb signal strength of NIST SRM610 (a) (b) and zircon GJ-1 (c)(d) under different beam spot sizes and energy densities
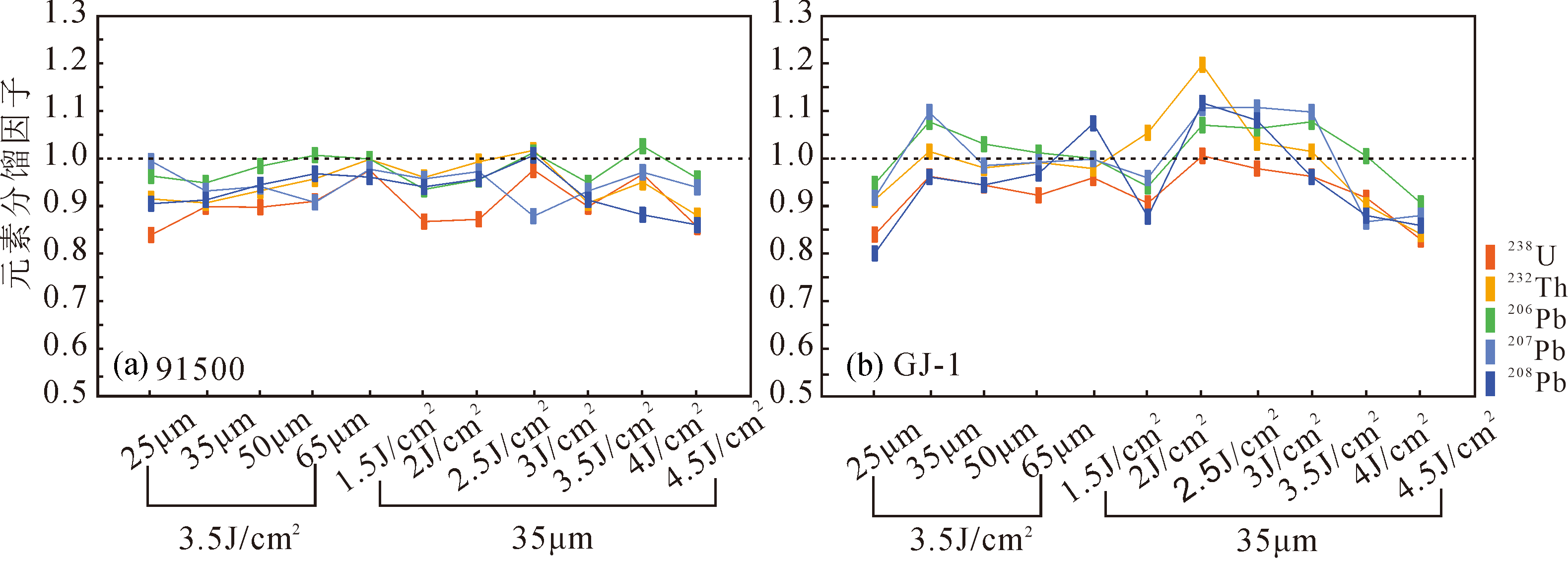
图3 不同能量密度和束斑条件下锆石91500(a)和GJ-1(b)的元素分馏因子变化
Fig.3 Variation of elemental fractionation factors of zircon 91500 (a) and GJ-1 (b) under different beam spot sizes and energy densities
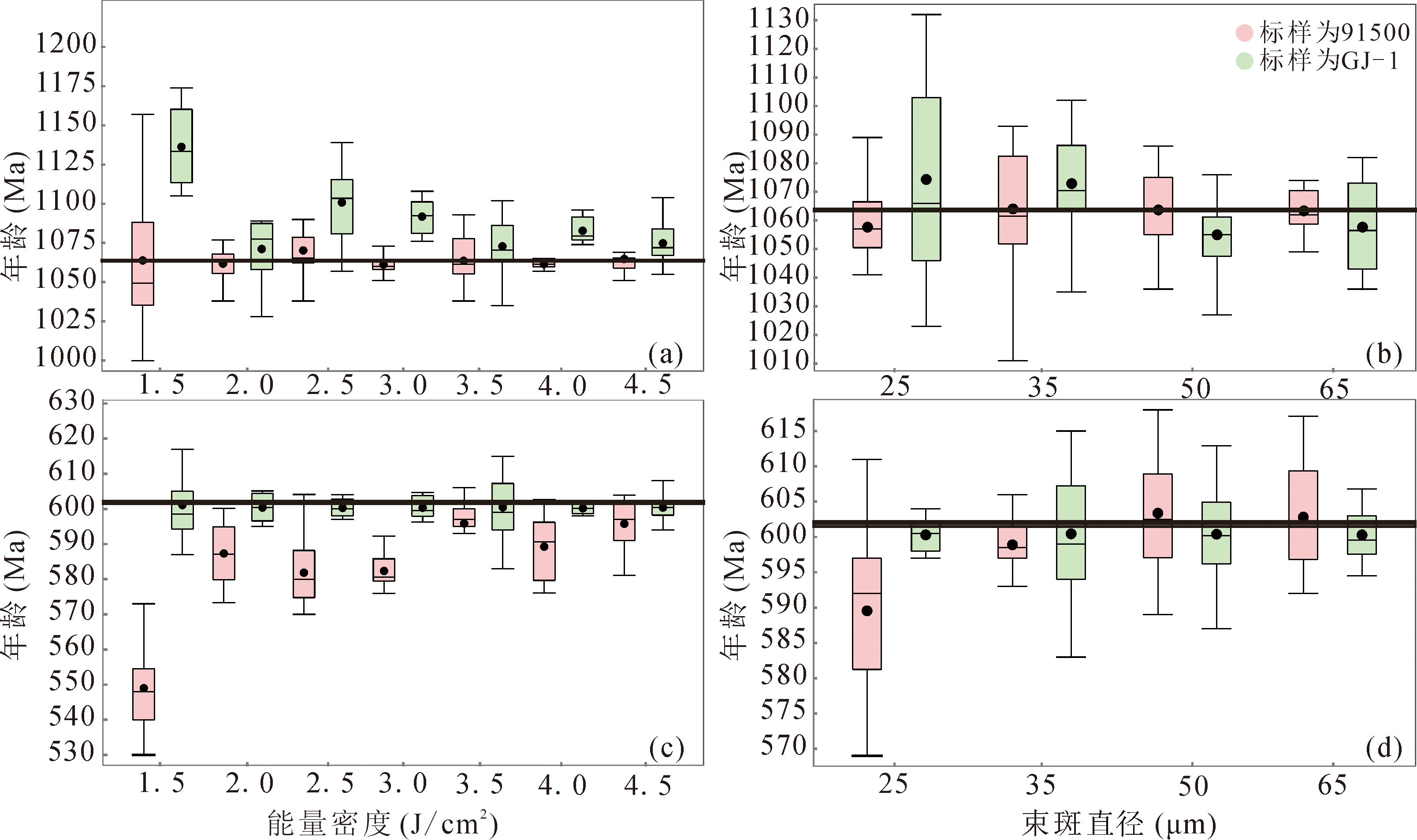
图4 不同能量密度和束斑直径条件下锆石91500(a)(b)与GJ-1(c)(d)的实测206Pb/238U年龄
Fig.4 Measured 206Pb/238U age of zircon 91500 (a)(b) and GJ-1 (c)(d) with different laser energy density and different beam spot sizes
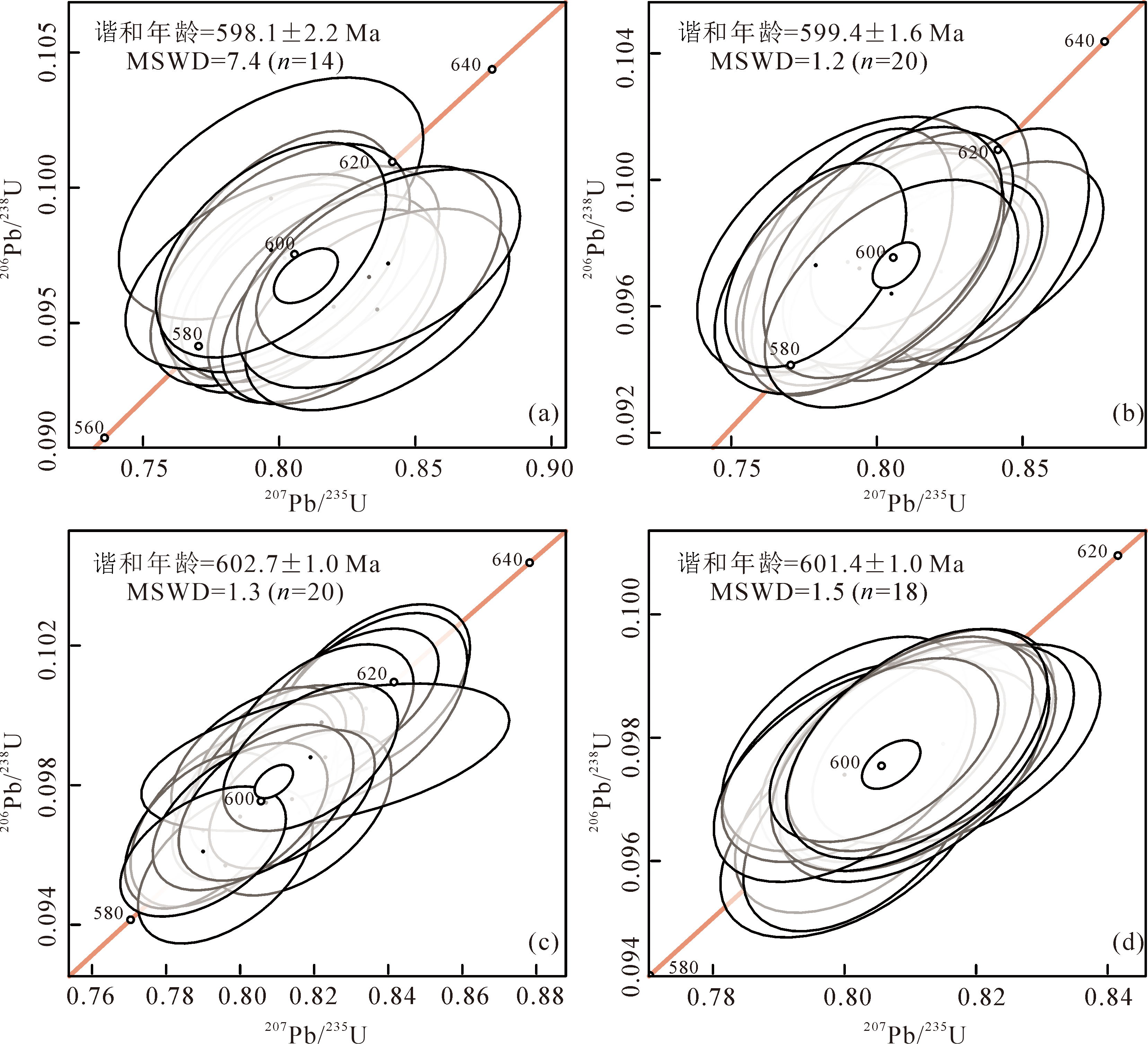
图5 3.5 J/cm2能量密度不同束斑条件下锆石GJ-1谐和年龄图(91500为标样) (a)束斑直径为25 μm;(b)束斑直径为35 μm;(c)束斑直径为50 μm;(d)束斑直径为65 μm
Fig.5 Concordia plots of zircon GJ-1 under 3.5 J/cm2 laser energy density and different beam spot sizes (using 91500 as standard)
| [1] | 第五春荣. 电感耦合等离子质谱仪在地质样品测试中的应用:小秦岭太华群灰色片麻岩地球化学及锆石年代学[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2005. |
| [2] |
ZONG K Q, LIU Y S, GAO C G, et al. In situ U-Pb dating and trace element analysis of zircons in thin sections of eclogite: Refining constraints on the ultra high-pressure metamorphism of the Sulu terrane, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 269(3/4): 237-251.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 陈文, 万渝生, 李华芹, 等. 同位素地质年龄测定技术及应用[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(11): 1917-1947. |
| [4] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. |
| [5] |
MARTINEZ M, BAUDELET M. Calibration strategies for elemental analysis of biological samples by LA-ICP-MS and LIBS-A review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 412(1): 27-36.
DOI |
| [6] | 唐燕文, 谢玉玲, 李应栩, 等. 浙江安吉多金属矿区石英二长斑岩岩石化学特征和锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 647-655. |
| [7] | 涂湘林, 张红, 邓文峰, 等. RESOlution激光剥蚀系统在微量元素原位微区分析中的应用[J]. 地球化学, 2011, 40(1):83-98. |
| [8] | 陈有炘, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑造山带东段元古界小庙岩组的锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(3): 510-521. |
| [9] | 李献华, 柳小明, 刘勇胜, 等. LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年的准确度:多实验室对比分析[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2015, 45(9): 1294-1303. |
| [10] | 罗涛. LA-ICP-MS分析过程中ICP引起的元素分馏效应研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2015. |
| [11] | 王家松, 许雅雯, 彭丽娜, 等. 应用激光拉曼光谱研究锆石LA-ICP-MSU-Pb定年中的α通量基体效应[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5): 458-467. |
| [12] | 周亮亮, 魏均启, 王芳, 等. LA-ICP-MS工作参数优化及在锆石U-Pb定年分析中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(4):350-359. |
| [13] | 侯振辉. 激光剥蚀束斑大小及深度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(6):1067-1076. |
| [14] |
WIEDENBECK M, HANCHAR J M, PECK W H, et al. Further characterisation of the 91500 zircon crystal[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(1): 9-39.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 王辉, 汪方跃, 关炳庭, 等. 激光能量密度对LA-ICP-MS分析数据质量的影响研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6):609-619. |
| [16] | 谭细娟, 郭超, 凤永刚, 等. 激光剥蚀系统气体流速变化对LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年精度的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(4):554-563. |
| [17] | 罗涛. LA-ICP-MS分析过程中元素分馏效应机理及其在副矿物U-Pb年代学中的应用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018. |
| [18] |
KOCH J, WÄLLE M, PISONERO J, et al. Performance characteristics of ultra-violet fem to second laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry at -265 and - 200 nm[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(9):932-940.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TIEPOLO M. In situ Pb geochronology of zircon with laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-sector field mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 199(1/2):159-177.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
钟玉芳, 马昌前. 含U副矿物的地质年代学研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(4):372-382.
DOI |
| [21] |
HORSTWOOD M S A, KOŠLER J, GEHRELS G, et al. Community-derived standards for LA-ICP-MS U-(Th-)Pb geochrono-logy—Uncertainty propagation, age interpretation and data reporting[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(3):311-332.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
JACKSON S E, PEARSON N J, GRIFFIN W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1/2):47-69.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GWOZDZ R, HANSEN H J, RASMUSSEN K L. Stevns Klint fish clay (FC-1): Preparation of, and preliminary results for a candidate reference material[J]. Geostandards Newsletter, 2001, 25(1):159-166.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SLÁMA J, KOŠLER J, CONDON D J, et al. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249(1/2):1-35.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
BLACK L P, KAMO S L, ALLEN C M, et al. TEMORA 1:A new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 200(1/2):155-170.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 李献华, 唐国强, 龚冰, 等. Qinghu(清湖)锆石:一个新的U-Pb年龄和O、Hf同位素微区分析工作标样[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(20):1954-1961. |
| [27] | 柳小明, 高山, 第五春荣, 等. 单颗粒锆石的20 μm小斑束原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄和微量元素的同时测定[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(2):228-235. |
| [28] | 吴石头, 杨岳衡, ROBERTS Nick M W, 等. 高灵敏度-单接收杯LA-SF-ICP-MS原位方解石U-Pb定年[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2022, 52(7):1375-1390. |
| [29] |
沈安江, 胡安平, 程婷, 等. 激光原位U-Pb同位素定年技术及其在碳酸盐岩成岩-孔隙演化中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6):1062-1074.
DOI |
| [30] | 刘勇胜, 胡兆初, 李明, 等. LA-ICP-MS在地质样品元素分析中的应用[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(36):3753-3769. |
| [31] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, LI M, et al. Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(32):3863-3878.
DOI URL |
| [32] | FRYER B, JACKSON S, LONGERICH H. The design, operation and role of the laser-ablation microprobe coupled with an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (LAM-ICP-MS) in the earth sciences[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1995, 33(2): 303-312. |
| [33] | JACKSON S E. Correction of fractionation in LA-ICP-MS elemental and U-Pb analysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(13): A579. |
| [34] |
POPOV D V, SPIKINGS R A, SCAILLET S. Diffusion and fluid interaction in Itrongay pegmatite (Madagascar): Evidence from in situ 40Ar/39Ar dating of gem-quality alkali feldspar and U-Pb dating of protogenetic apatite inclusions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 556:119841.
DOI URL |
| [35] | GEHRELS G E, VALENCIA V A, RUIZ J. Enhanced precision, accuracy, efficiency, and spatial resolution of U-Pb ages by laser ablation-multicollector-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(3): Q03017. |
| [36] |
GABOARDI M, HUMAYUN M. Elemental fractionation during LA-ICP-MS analysis of silicate glasses: Implications for matrix-independent standardization[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2009, 24(9):1188-1197.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
GERDES A, ZEH A. Combined U-Pb and Hf isotope LA-(MC-)ICP-MS analyses of detrital zircons: Comparison with SHRIMP and new constraints for the provenance and age of an Armorican metasediment in Central Germany[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 249(1/2):47-61.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
HIRATA T. Chemically assisted laser ablation ICP mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 75(2): 228-233.
PMID |
| [39] |
JOCHUM K P, STOLL B, HERWIG K, et al. Validation of LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of geological glasses using a new solid-state 193 nm Nd: YAG laser and matrix-matched calibration[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22(2):112-121.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
JOCHUM K P, WEIS U, STOLL B, et al. Determination of re-ference values for NIST SRM 610-617 glasses following ISO guidelines[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2011, 35(4): 397-429.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
GÜNTHER D, HATTENDORF B. Solid sample analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 24(3): 255-265.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [3] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [4] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [5] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [6] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [7] | 欧伟程, 李承东, 张永清, 赵利刚, 许腾, 许雅雯, 孙烜烨. 北秦岭二郎坪群抱树坪组碎屑锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及物源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 347-361. |
| [8] | 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 郑艳荣, 李晓东, 武海文, 张龙. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1633-1650. |
| [9] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [10] | 陈欢, 康志强, 吴佳昌, 李岱鲜, 曹延, 韦天伟, 韦乃韶, 刘迪, 周桐, 刘冬梅, 蓝海洋. 广西大瑶山朴全岩体形成时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1277-1290. |
| [11] | 欧阳鑫, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 刘丽, 刘涛, 王文东. 内蒙古撰山子金矿床成岩成矿年代学与地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 635-652. |
| [12] | 鞠鹏程, 王训练, 王振涛, 刘喜方, 仲佳爱, 张在明. 渝北温泉镇地区三叠系“绿豆岩”特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 431-449. |
| [13] | 柳长峰, 赵守恒, 张浩然, 郎海龙, 张凤娟, 刘文灿. 内蒙古赤峰大西营子金矿区赋矿火山岩年代学与岩石地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 27-39. |
| [14] | 李琦, 王疆涛, 曾忠诚, 石卫, 李惠, 郭倩怡. 阿尔金造山带南缘蛇绿构造混杂岩带中晚奥陶世—早志留世二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 51-63. |
| [15] | 黄泽森, 江巴多吉, 达瓦次仁, 塔尔杰. 西藏切穷地区早白垩世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 703-714. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||