



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (01): 27-39.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.003
柳长峰1( ), 赵守恒2, 张浩然1, 郎海龙2, 张凤娟1, 刘文灿1
), 赵守恒2, 张浩然1, 郎海龙2, 张凤娟1, 刘文灿1
收稿日期:2019-09-30
修回日期:2019-10-28
出版日期:2020-03-05
发布日期:2020-03-07
作者简介:柳长峰,男,1982年出生,副研究员,古生物学与地层学专业,从事区域地质研究。Email: liuchangfeng@cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
LIU Changfeng1( ), ZHAO Shouheng2, ZHANG Haoran1, LANG Hailong2, ZHANG Fengjuan1, LIU Wencan1
), ZHAO Shouheng2, ZHANG Haoran1, LANG Hailong2, ZHANG Fengjuan1, LIU Wencan1
Received:2019-09-30
Revised:2019-10-28
Online:2020-03-05
Published:2020-03-07
摘要:
大西营子金矿区位于内蒙古赤峰地区,金矿赋存在玛尼吐组火山岩中。对大西营子金矿区赋矿围岩进行了岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究。矿区火山岩主要包括安山岩、粗安岩、粗面岩和火山碎屑岩。通过锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年,获得安山岩和粗安岩年龄分别为(157.8±6.2) Ma和(156.9±7.4) Ma,应代表其形成年龄。岩石地球化学数据显示该套火山岩具有相对富碱、富铝的特征,属于高钾钙碱性和碱性岩石系列。岩石富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素(Th、U、Zr、Hf),亏损重稀土元素和Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素。这些特征显示岩浆来自被俯冲流体交代富集的岩石圈地幔,且经历了以单斜辉石为主的结晶分异过程。结合区域地质资料,认为在大西营子金矿区火山岩形成于造山后伸展环境,与蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合作用有关。
中图分类号:
柳长峰, 赵守恒, 张浩然, 郎海龙, 张凤娟, 刘文灿. 内蒙古赤峰大西营子金矿区赋矿火山岩年代学与岩石地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 27-39.
LIU Changfeng, ZHAO Shouheng, ZHANG Haoran, LANG Hailong, ZHANG Fengjuan, LIU Wencan. Geochronology and Geochemistry Characteristics of Volcanic Rocks from the Daxiyingzi Gold Deposit in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(01): 27-39.

图1 研究区大地构造位置简图(a)、赤峰—朝阳区域地质简图(b)和大西营子金矿区地质简图(c) (底图引自文献[1,2,3,4]) 1.中新生代地层;2. 玛尼吐组火山岩;3. 古生代地层;4. 太古宙变质岩;5.中生代花岗岩;6.晚侏罗世花岗斑岩;7.古元古代闪长岩;8. 火山角砾岩;9. 含角砾凝灰岩;10. 含晶屑凝灰岩;11. 流纹质火山角砾岩;12. 粗安岩;13. 凝灰岩;14. 断层;15. 金矿床(点);16. 采样钻孔位置;17.区域深大断裂;18.国界
Fig.1 Tectonic skeleton map of study area (a), geological skeleton map of the Chifeng-Chaoyang region (b) and geological map of Daxiyingzi gold deposit map(c)(base map after refs.[1-4])

图2 大西营子金矿区岩心照片和显微照片 (a)火山角砾岩;(b)粗安岩;(c)安山岩;(d)地表出露的元古代弱片麻状二长花岗岩;(e)金多金属矿化脉;(f)金多金属矿化脉;(g)安山岩镜下特征;(h)粗安岩镜下特征;(i)粗面岩镜下特征; Pl.斜长石; Kfs.钾长石
Fig.2 Photos of cores from Daxiyingzi gold deposit
| 样品及测点 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | 谐和 度/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | |||||||||
| zk1603-tw1.1 | 515 | 254 | 2.03 | 0.049 64±0.002 64 | 0.181 04±0.008 84 | 0.026 48±0.000 79 | 178±119 | 169±8 | 169±5 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.2 | 18 | 16 | 1.13 | 0.105 42±0.005 10 | 4.335 93±0.197 70 | 0.298 61±0.011 33 | 1 722±86 | 1 700±38 | 1 684±56 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.3 | 28 | 30 | 0.95 | 0.067 14±0.010 46 | 0.186 27±0.025 96 | 0.020 14±0.001 51 | 842±295 | 173±22 | 129±10 | 74 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.4 | 35 | 36 | 0.97 | 0.032 16±0.005 96 | 0.114 04±0.020 05 | 0.025 74±0.001 66 | 0 | 110±18 | 164±10 | 149 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.5 | 185 | 125 | 1.48 | 0.095 01±0.005 87 | 0.352 17±0.018 72 | 0.026 91±0.001 05 | 1 528±112 | 306±14 | 171±7 | 56 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.6 | 51 | 175 | 0.29 | 0.153 75±0.003 48 | 8.915 08±0.200 99 | 0.420 90±0.009 20 | 2 388±38 | 2 329±21 | 2 265±42 | 97 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.7 | 31 | 41 | 0.75 | 0.103 42±0.003 62 | 4.218 92±0.140 77 | 0.296 10±0.008 54 | 1 686±63 | 1 678±27 | 1 672±42 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.8 | 105 | 147 | 0.72 | 0.165 40±0.003 78 | 11.334 63±0.259 62 | 0.497 39±0.011 07 | 2 512±38 | 2 551±21 | 2 603±48 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.9 | 76 | 116 | 0.65 | 0.158 05±0.003 72 | 10.023 76±0.235 02 | 0.460 29±0.010 44 | 2 435±39 | 2 437±22 | 2 441±46 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.10 | 117 | 106 | 1.10 | 0.041 32±0.003 90 | 0.141 99±0.012 54 | 0.024 94±0.001 01 | 0 | 135±11 | 159±6 | 118 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.11 | 28 | 38 | 0.74 | 0.045 43±0.007 09 | 0.153 40±0.022 13 | 0.024 51±0.001 61 | 0±308 | 145±19 | 156±10 | 108 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.12 | 24 | 33 | 0.71 | 0.057 54±0.008 02 | 0.192 85±0.024 16 | 0.024 32±0.001 63 | 512±281 | 179±21 | 155±10 | 86 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.13 | 263 | 259 | 1.01 | 0.162 45±0.003 58 | 9.824 02±0.215 26 | 0.438 81±0.009 33 | 2 481±37 | 2 418±20 | 2 345±42 | 97 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.14 | 10 | 287 | 0.03 | 0.113 46±0.002 63 | 4.211 51±0.095 72 | 0.269 33±0.005 79 | 1 856±41 | 1 676±19 | 1 537±29 | 92 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.15 | 85 | 84 | 1.02 | 0.044 75±0.004 83 | 0.146 97±0.014 76 | 0.023 83±0.001 09 | 0±175 | 139±13 | 152±7 | 109 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.16 | 41 | 37 | 1.10 | 0.101 76±0.003 72 | 4.122 40±0.143 43 | 0.293 95±0.008 70 | 1 656±66 | 1 659±28 | 1 661±43 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.17 | 65 | 49 | 1.33 | 0.102 66±0.003 39 | 4.238 25±0.133 78 | 0.299 55±0.008 21 | 1 673±60 | 1 682±26 | 1 689±41 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.18 | 261 | 227 | 1.15 | 0.045 86±0.002 73 | 0.158 06±0.008 66 | 0.025 01±0.000 78 | 0±128 | 149±8 | 159±5 | 107 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.19 | 38 | 208 | 0.18 | 0.175 62±0.003 93 | 11.01 27±0.244 55 | 0.454 93±0.009 80 | 2 612±37 | 2 524±21 | 2 417±43 | 96 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.20 | 71 | 101 | 0.70 | 0.050 05±0.004 44 | 0.155 97±0.012 60 | 0.022 61±0.000 98 | 198±194 | 147±11 | 144±6 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.21 | 10 890 | 2 866 | 3.80 | 0.333 23±0.015 40 | 1.490 70±0.050 33 | 0.032 45±0.001 27 | 3 632±69 | 927±21 | 206±8 | 22 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.22 | 12 | 217 | 0.06 | 0.111 92±0.002 62 | 4.789 90±0.109 72 | 0.310 46±0.006 69 | 1 831±42 | 1 783±19 | 1 743±33 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.23 | 25 | 28 | 0.90 | 0.048 27±0.007 79 | 0.174 44±0.025 73 | 0.026 22±0.001 88 | 112±342 | 163±22 | 167±12 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.24 | 41 | 42 | 0.99 | 0.055 66±0.007 05 | 0.186 39±0.021 42 | 0.024 29±0.001 44 | 438±260 | 174±18 | 155±9 | 89 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.1 | 93 | 1 072 | 0.09 | 0.108 98±0.002 28 | 4.623 14±0.102 13 | 0.307 71±0.006 66 | 1 782±38 | 1 754±18 | 1 729±33 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.2 | 349 | 265 | 1.32 | 0.049 53±0.004 63 | 0.179 08±0.015 31 | 0.026 22±0.001 20 | 173±205 | 167±13 | 167±8 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.3 | 342 | 507 | 0.67 | 0.164 94±0.003 58 | 10.629 31±0.243 47 | 0.467 46±0.010 53 | 2 507±36 | 2 491±21 | 2 472±46 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.4 | 55 | 33 | 1.66 | 0.100 24±0.003 93 | 4.071 06±0.153 83 | 0.294 60±0.009 41 | 1 629±71 | 1 649±31 | 1 665±47 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.5 | 178 | 541 | 0.33 | 0.115 92±0.002 57 | 5.157 78±0.119 28 | 0.322 74±0.007 23 | 1 894±39 | 1 846±20 | 1 803±35 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.6 | 269 | 589 | 0.46 | 0.161 41±0.003 40 | 10.246 43±0.228 61 | 0.460 48±0.010 12 | 2 470±35 | 2 457±21 | 2 442±45 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.7 | 31 | 33 | 0.95 | 0.049 25±0.007 50 | 0.164 16±0.022 98 | 0.024 18±0.001 61 | 160±321 | 154±20 | 154±10 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.8 | 40 | 44 | 0.90 | 0.049 78±0.010 76 | 0.182 67±0.035 59 | 0.026 62±0.002 68 | 185±438 | 170±31 | 169±17 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.9 | 233 | 331 | 0.70 | 0.156 52±0.003 35 | 10.181 00±0.230 22 | 0.471 83±0.010 48 | 2 418±36 | 2 451±21 | 2 492±46 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.10 | 6 | 101 | 0.06 | 0.110 55±0.003 03 | 4.920 49±0.135 46 | 0.322 84±0.008 21 | 1 809±49 | 1 806±23 | 1 804±40 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.11 | 262 | 843 | 0.31 | 0.159 83±0.003 31 | 10.081 77±0.22 18 | 0.457 55±0.009 92 | 2 454±35 | 2 442±20 | 2 429±44 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.12 | 23 | 22 | 1.02 | 0.048 20±0.043 65 | 0.148 86±0.127 59 | 0.022 40±0.006 77 | 109±1 355 | 141±113 | 143±43 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.13 | 64 | 123 | 0.52 | 0.155 23±0.003 75 | 9.858 69±0.246 95 | 0.460 69±0.011 21 | 2 404±40 | 2 422±23 | 2 443±49 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.14 | 37 | 35 | 1.06 | 0.050 51±0.019 51 | 0.169 90±0.059 86 | 0.024 40±0.004 07 | 219±710 | 159±52 | 155±26 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.15 | 121 | 93 | 1.30 | 0.049 52±0.007 57 | 0.162 39±0.022 57 | 0.023 79±0.001 67 | 173±322 | 153±20 | 152±11 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.16 | 106 | 69 | 1.54 | 0.105 38±0.003 21 | 4.372 58±0.131 72 | 0.300 98±0.008 14 | 1 721±55 | 1 707±25 | 1 696±40 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.17 | 160 | 205 | 0.78 | 0.051 23±0.002 55 | 0.279 31±0.012 94 | 0.039 54±0.001 18 | 251±110 | 250±10 | 250±7 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.18 | 133 | 133 | 1.00 | 0.157 22±0.003 71 | 10.175 71±0.249 98 | 0.469 50±0.011 24 | 2 426±39 | 2 451±23 | 2 481±49 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.19 | 143 | 250 | 0.57 | 0.160 64±0.003 53 | 10.045 36±0.232 03 | 0.453 59±0.010 27 | 2 462±37 | 2 439±21 | 2 411±46 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.20 | 85 | 124 | 0.69 | 0.166 49±0.003 89 | 10.716 87±0.261 22 | 0.466 92±0.011 13 | 2 523±39 | 2 499±23 | 2 470±49 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.21 | 94 | 93 | 1.01 | 0.048 10±0.009 59 | 0.147 04±0.027 34 | 0.022 17±0.001 74 | 104±414 | 139±24 | 141±11 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.22 | 194 | 250 | 0.77 | 0.155 10±0.004 07 | 9.523 82±0.256 36 | 0.445 41±0.011 57 | 2 403±44 | 2 390±25 | 2 375±52 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.23 | 492 | 317 | 1.55 | 0.048 36±0.004 26 | 0.163 93±0.013 21 | 0.024 59±0.001 08 | 117±196 | 154±12 | 157±7 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.24 | 214 | 380 | 0.56 | 0.051 19±0.002 00 | 0.280 20±0.010 40 | 0.039 71±0.001 05 | 249±88 | 251±8 | 251±6 | 100 | ||||
表1 大西营子金矿区火山岩锆石U-Pb同位素测年分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS results for zircons U-Pb ages of volcanic rocks from the Daxiyingzi gold deposit
| 样品及测点 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 同位素年龄/Ma | 谐和 度/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U±1σ | |||||||||
| zk1603-tw1.1 | 515 | 254 | 2.03 | 0.049 64±0.002 64 | 0.181 04±0.008 84 | 0.026 48±0.000 79 | 178±119 | 169±8 | 169±5 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.2 | 18 | 16 | 1.13 | 0.105 42±0.005 10 | 4.335 93±0.197 70 | 0.298 61±0.011 33 | 1 722±86 | 1 700±38 | 1 684±56 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.3 | 28 | 30 | 0.95 | 0.067 14±0.010 46 | 0.186 27±0.025 96 | 0.020 14±0.001 51 | 842±295 | 173±22 | 129±10 | 74 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.4 | 35 | 36 | 0.97 | 0.032 16±0.005 96 | 0.114 04±0.020 05 | 0.025 74±0.001 66 | 0 | 110±18 | 164±10 | 149 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.5 | 185 | 125 | 1.48 | 0.095 01±0.005 87 | 0.352 17±0.018 72 | 0.026 91±0.001 05 | 1 528±112 | 306±14 | 171±7 | 56 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.6 | 51 | 175 | 0.29 | 0.153 75±0.003 48 | 8.915 08±0.200 99 | 0.420 90±0.009 20 | 2 388±38 | 2 329±21 | 2 265±42 | 97 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.7 | 31 | 41 | 0.75 | 0.103 42±0.003 62 | 4.218 92±0.140 77 | 0.296 10±0.008 54 | 1 686±63 | 1 678±27 | 1 672±42 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.8 | 105 | 147 | 0.72 | 0.165 40±0.003 78 | 11.334 63±0.259 62 | 0.497 39±0.011 07 | 2 512±38 | 2 551±21 | 2 603±48 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.9 | 76 | 116 | 0.65 | 0.158 05±0.003 72 | 10.023 76±0.235 02 | 0.460 29±0.010 44 | 2 435±39 | 2 437±22 | 2 441±46 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.10 | 117 | 106 | 1.10 | 0.041 32±0.003 90 | 0.141 99±0.012 54 | 0.024 94±0.001 01 | 0 | 135±11 | 159±6 | 118 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.11 | 28 | 38 | 0.74 | 0.045 43±0.007 09 | 0.153 40±0.022 13 | 0.024 51±0.001 61 | 0±308 | 145±19 | 156±10 | 108 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.12 | 24 | 33 | 0.71 | 0.057 54±0.008 02 | 0.192 85±0.024 16 | 0.024 32±0.001 63 | 512±281 | 179±21 | 155±10 | 86 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.13 | 263 | 259 | 1.01 | 0.162 45±0.003 58 | 9.824 02±0.215 26 | 0.438 81±0.009 33 | 2 481±37 | 2 418±20 | 2 345±42 | 97 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.14 | 10 | 287 | 0.03 | 0.113 46±0.002 63 | 4.211 51±0.095 72 | 0.269 33±0.005 79 | 1 856±41 | 1 676±19 | 1 537±29 | 92 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.15 | 85 | 84 | 1.02 | 0.044 75±0.004 83 | 0.146 97±0.014 76 | 0.023 83±0.001 09 | 0±175 | 139±13 | 152±7 | 109 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.16 | 41 | 37 | 1.10 | 0.101 76±0.003 72 | 4.122 40±0.143 43 | 0.293 95±0.008 70 | 1 656±66 | 1 659±28 | 1 661±43 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.17 | 65 | 49 | 1.33 | 0.102 66±0.003 39 | 4.238 25±0.133 78 | 0.299 55±0.008 21 | 1 673±60 | 1 682±26 | 1 689±41 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.18 | 261 | 227 | 1.15 | 0.045 86±0.002 73 | 0.158 06±0.008 66 | 0.025 01±0.000 78 | 0±128 | 149±8 | 159±5 | 107 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.19 | 38 | 208 | 0.18 | 0.175 62±0.003 93 | 11.01 27±0.244 55 | 0.454 93±0.009 80 | 2 612±37 | 2 524±21 | 2 417±43 | 96 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.20 | 71 | 101 | 0.70 | 0.050 05±0.004 44 | 0.155 97±0.012 60 | 0.022 61±0.000 98 | 198±194 | 147±11 | 144±6 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.21 | 10 890 | 2 866 | 3.80 | 0.333 23±0.015 40 | 1.490 70±0.050 33 | 0.032 45±0.001 27 | 3 632±69 | 927±21 | 206±8 | 22 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.22 | 12 | 217 | 0.06 | 0.111 92±0.002 62 | 4.789 90±0.109 72 | 0.310 46±0.006 69 | 1 831±42 | 1 783±19 | 1 743±33 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.23 | 25 | 28 | 0.90 | 0.048 27±0.007 79 | 0.174 44±0.025 73 | 0.026 22±0.001 88 | 112±342 | 163±22 | 167±12 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw1.24 | 41 | 42 | 0.99 | 0.055 66±0.007 05 | 0.186 39±0.021 42 | 0.024 29±0.001 44 | 438±260 | 174±18 | 155±9 | 89 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.1 | 93 | 1 072 | 0.09 | 0.108 98±0.002 28 | 4.623 14±0.102 13 | 0.307 71±0.006 66 | 1 782±38 | 1 754±18 | 1 729±33 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.2 | 349 | 265 | 1.32 | 0.049 53±0.004 63 | 0.179 08±0.015 31 | 0.026 22±0.001 20 | 173±205 | 167±13 | 167±8 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.3 | 342 | 507 | 0.67 | 0.164 94±0.003 58 | 10.629 31±0.243 47 | 0.467 46±0.010 53 | 2 507±36 | 2 491±21 | 2 472±46 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.4 | 55 | 33 | 1.66 | 0.100 24±0.003 93 | 4.071 06±0.153 83 | 0.294 60±0.009 41 | 1 629±71 | 1 649±31 | 1 665±47 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.5 | 178 | 541 | 0.33 | 0.115 92±0.002 57 | 5.157 78±0.119 28 | 0.322 74±0.007 23 | 1 894±39 | 1 846±20 | 1 803±35 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.6 | 269 | 589 | 0.46 | 0.161 41±0.003 40 | 10.246 43±0.228 61 | 0.460 48±0.010 12 | 2 470±35 | 2 457±21 | 2 442±45 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.7 | 31 | 33 | 0.95 | 0.049 25±0.007 50 | 0.164 16±0.022 98 | 0.024 18±0.001 61 | 160±321 | 154±20 | 154±10 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.8 | 40 | 44 | 0.90 | 0.049 78±0.010 76 | 0.182 67±0.035 59 | 0.026 62±0.002 68 | 185±438 | 170±31 | 169±17 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.9 | 233 | 331 | 0.70 | 0.156 52±0.003 35 | 10.181 00±0.230 22 | 0.471 83±0.010 48 | 2 418±36 | 2 451±21 | 2 492±46 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.10 | 6 | 101 | 0.06 | 0.110 55±0.003 03 | 4.920 49±0.135 46 | 0.322 84±0.008 21 | 1 809±49 | 1 806±23 | 1 804±40 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.11 | 262 | 843 | 0.31 | 0.159 83±0.003 31 | 10.081 77±0.22 18 | 0.457 55±0.009 92 | 2 454±35 | 2 442±20 | 2 429±44 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.12 | 23 | 22 | 1.02 | 0.048 20±0.043 65 | 0.148 86±0.127 59 | 0.022 40±0.006 77 | 109±1 355 | 141±113 | 143±43 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.13 | 64 | 123 | 0.52 | 0.155 23±0.003 75 | 9.858 69±0.246 95 | 0.460 69±0.011 21 | 2 404±40 | 2 422±23 | 2 443±49 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.14 | 37 | 35 | 1.06 | 0.050 51±0.019 51 | 0.169 90±0.059 86 | 0.024 40±0.004 07 | 219±710 | 159±52 | 155±26 | 98 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.15 | 121 | 93 | 1.30 | 0.049 52±0.007 57 | 0.162 39±0.022 57 | 0.023 79±0.001 67 | 173±322 | 153±20 | 152±11 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.16 | 106 | 69 | 1.54 | 0.105 38±0.003 21 | 4.372 58±0.131 72 | 0.300 98±0.008 14 | 1 721±55 | 1 707±25 | 1 696±40 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.17 | 160 | 205 | 0.78 | 0.051 23±0.002 55 | 0.279 31±0.012 94 | 0.039 54±0.001 18 | 251±110 | 250±10 | 250±7 | 100 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.18 | 133 | 133 | 1.00 | 0.157 22±0.003 71 | 10.175 71±0.249 98 | 0.469 50±0.011 24 | 2 426±39 | 2 451±23 | 2 481±49 | 101 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.19 | 143 | 250 | 0.57 | 0.160 64±0.003 53 | 10.045 36±0.232 03 | 0.453 59±0.010 27 | 2 462±37 | 2 439±21 | 2 411±46 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.20 | 85 | 124 | 0.69 | 0.166 49±0.003 89 | 10.716 87±0.261 22 | 0.466 92±0.011 13 | 2 523±39 | 2 499±23 | 2 470±49 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.21 | 94 | 93 | 1.01 | 0.048 10±0.009 59 | 0.147 04±0.027 34 | 0.022 17±0.001 74 | 104±414 | 139±24 | 141±11 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.22 | 194 | 250 | 0.77 | 0.155 10±0.004 07 | 9.523 82±0.256 36 | 0.445 41±0.011 57 | 2 403±44 | 2 390±25 | 2 375±52 | 99 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.23 | 492 | 317 | 1.55 | 0.048 36±0.004 26 | 0.163 93±0.013 21 | 0.024 59±0.001 08 | 117±196 | 154±12 | 157±7 | 102 | ||||
| zk1603-tw2.24 | 214 | 380 | 0.56 | 0.051 19±0.002 00 | 0.280 20±0.010 40 | 0.039 71±0.001 05 | 249±88 | 251±8 | 251±6 | 100 | ||||
| 样品 | 岩性 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | LOI | A/ CNK | 里特曼 指数 | Y | La | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK1105-YQ1 | 粗安岩 | 58.63 | 16.96 | 0.88 | 3.34 | 2.93 | 4.78 | 1.89 | 3.30 | 4.70 | 0.07 | 0.42 | 1.82 | 0.85 | 3.95 | 20.16 | 34.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK801-YQ1 | 粗面岩 | 64.27 | 16.04 | 0.73 | 2.19 | 1.69 | 2.51 | 0.89 | 4.12 | 5.03 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 1.96 | 0.93 | 3.85 | 23.00 | 40.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK707-YQ2 | 粗面岩 | 64.69 | 14.62 | 0.64 | 2.75 | 2.61 | 1.17 | 0.56 | 3.82 | 5.74 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 2.90 | 0.93 | 4.10 | 34.02 | 30.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK804-YQ1 | 粗面岩 | 61.11 | 16.79 | 0.78 | 2.59 | 2.59 | 3.02 | 1.47 | 3.52 | 4.45 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 2.95 | 1.01 | 3.36 | 17.40 | 33.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1103-YQ1 | 粗安岩 | 57.91 | 16.93 | 1.07 | 4.14 | 3.13 | 5.20 | 2.44 | 2.62 | 3.88 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 1.95 | 0.91 | 2.72 | 20.37 | 33.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1603-YQ1 | 粗安岩 | 56.74 | 16.71 | 1.04 | 2.94 | 4.23 | 5.12 | 3.56 | 2.66 | 4.08 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 2.21 | 0.88 | 3.15 | 20.44 | 43.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1601-YQ1 | 粗面岩 | 63.91 | 16.49 | 0.60 | 2.86 | 1.46 | 2.47 | 1.36 | 3.66 | 4.40 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 2.25 | 1.05 | 3.03 | 17.89 | 39.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1207-YQ2 | 安山岩 | 52.39 | 15.83 | 0.97 | 3.02 | 4.76 | 5.48 | 2.66 | 2.97 | 2.24 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 9.04 | 0.94 | 2.23 | 17.50 | 30.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Zn | Ga | Cs | Rb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1105-YQ1 | 72.80 | 8.59 | 34.22 | 6.06 | 1.84 | 5.24 | 0.77 | 3.87 | 0.75 | 2.16 | 0.31 | 2.04 | 0.34 | 51.88 | 18.37 | 1.57 | 67.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK801-YQ1 | 95.30 | 11.80 | 46.20 | 7.61 | 1.86 | 7.52 | 1.00 | 4.55 | 0.82 | 2.51 | 0.35 | 2.01 | 0.32 | 52.30 | 18.70 | 1.33 | 56.40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK707-YQ2 | 95.66 | 14.10 | 59.71 | 12.02 | 2.53 | 9.35 | 1.47 | 7.68 | 1.47 | 3.97 | 0.61 | 3.92 | 0.64 | 60.31 | 19.26 | 0.75 | 57.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK804-YQ1 | 78.40 | 10.30 | 40.80 | 6.97 | 1.89 | 6.72 | 0.87 | 3.91 | 0.69 | 2.16 | 0.28 | 1.63 | 0.31 | 75.30 | 17.10 | 3.40 | 54.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1103-YQ1 | 70.04 | 8.52 | 33.40 | 6.29 | 1.86 | 5.06 | 0.84 | 4.08 | 0.76 | 2.12 | 0.30 | 1.89 | 0.35 | 137.10 | 19.26 | 3.13 | 65.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1603-YQ1 | 88.61 | 10.23 | 38.97 | 6.55 | 1.81 | 5.37 | 0.80 | 4.11 | 0.76 | 2.16 | 0.33 | 2.11 | 0.56 | 88.49 | 19.99 | 1.37 | 58.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1601-YQ1 | 81.31 | 9.38 | 34.53 | 5.67 | 1.61 | 4.73 | 0.70 | 3.47 | 0.65 | 1.97 | 0.28 | 1.84 | 0.31 | 68.35 | 19.62 | 2.11 | 88.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1207-YQ2 | 62.22 | 7.63 | 29.78 | 5.51 | 1.69 | 4.58 | 0.74 | 3.79 | 0.70 | 1.82 | 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.30 | 121.10 | 19.17 | 8.38 | 127.57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Sr | Ba | Zr | Nb | Ta | Hf | Th | U | Pb | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | (La/ Yb)N | Eu* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1105-YQ1 | 597.35 | 1 514.0 | 232.91 | 9.52 | 0.62 | 7.19 | 3.85 | 0.58 | 23.46 | 78.98 | 12.16 | 9.93 | 2.24 | 8.84 | 11.54 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK801-YQ1 | 285.00 | 1 269.0 | 266.00 | 14.00 | 0.73 | 7.70 | 3.99 | 0.39 | 24.70 | 45.80 | 10.70 | 3.90 | 2.30 | 7.40 | 13.45 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK707-YQ2 | 208.74 | 1 278.0 | 364.45 | 16.66 | 0.82 | 8.96 | 5.69 | 0.62 | 39.21 | 22.58 | 11.06 | 6.83 | 12.92 | 13.28 | 5.28 | 0.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK804-YQ1 | 385.00 | 1 053.0 | 318.00 | 10.00 | 0.53 | 6.82 | 3.20 | 0.52 | 26.50 | 40.00 | 7.80 | 6.37 | 2.21 | 5.12 | 13.89 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1103-YQ1 | 623.60 | 1 322.0 | 207.75 | 10.04 | 0.59 | 5.96 | 3.60 | 0.50 | 29.43 | 121.80 | 12.12 | 16.99 | 3.25 | 21.16 | 11.95 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1603-YQ1 | 659.61 | 1 201.0 | 238.98 | 12.38 | 0.74 | 5.65 | 7.11 | 1.21 | 16.80 | 146.04 | 28.41 | 22.53 | 19.18 | 27.27 | 13.99 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1601-YQ1 | 425.57 | 1 406.0 | 383.59 | 12.59 | 0.69 | 11.16 | 4.78 | 0.73 | 25.27 | 55.10 | 14.97 | 7.48 | 4.79 | 9.61 | 14.62 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1207-YQ2 | 448.04 | 720.3 | 172.28 | 4.56 | 0.32 | 4.43 | 2.41 | 0.32 | 13.43 | 142.80 | 17.20 | 19.41 | 6.54 | 11.72 | 13.48 | 1.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表2 大西营子金矿区火山岩主量元素(%)及微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major(%) and trace (10-6) elements composition of the volcanic rocks from the Daxiyingzi gold deposit
| 样品 | 岩性 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | LOI | A/ CNK | 里特曼 指数 | Y | La | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK1105-YQ1 | 粗安岩 | 58.63 | 16.96 | 0.88 | 3.34 | 2.93 | 4.78 | 1.89 | 3.30 | 4.70 | 0.07 | 0.42 | 1.82 | 0.85 | 3.95 | 20.16 | 34.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK801-YQ1 | 粗面岩 | 64.27 | 16.04 | 0.73 | 2.19 | 1.69 | 2.51 | 0.89 | 4.12 | 5.03 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 1.96 | 0.93 | 3.85 | 23.00 | 40.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK707-YQ2 | 粗面岩 | 64.69 | 14.62 | 0.64 | 2.75 | 2.61 | 1.17 | 0.56 | 3.82 | 5.74 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 2.90 | 0.93 | 4.10 | 34.02 | 30.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK804-YQ1 | 粗面岩 | 61.11 | 16.79 | 0.78 | 2.59 | 2.59 | 3.02 | 1.47 | 3.52 | 4.45 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 2.95 | 1.01 | 3.36 | 17.40 | 33.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1103-YQ1 | 粗安岩 | 57.91 | 16.93 | 1.07 | 4.14 | 3.13 | 5.20 | 2.44 | 2.62 | 3.88 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 1.95 | 0.91 | 2.72 | 20.37 | 33.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1603-YQ1 | 粗安岩 | 56.74 | 16.71 | 1.04 | 2.94 | 4.23 | 5.12 | 3.56 | 2.66 | 4.08 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 2.21 | 0.88 | 3.15 | 20.44 | 43.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1601-YQ1 | 粗面岩 | 63.91 | 16.49 | 0.60 | 2.86 | 1.46 | 2.47 | 1.36 | 3.66 | 4.40 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 2.25 | 1.05 | 3.03 | 17.89 | 39.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1207-YQ2 | 安山岩 | 52.39 | 15.83 | 0.97 | 3.02 | 4.76 | 5.48 | 2.66 | 2.97 | 2.24 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 9.04 | 0.94 | 2.23 | 17.50 | 30.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Zn | Ga | Cs | Rb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1105-YQ1 | 72.80 | 8.59 | 34.22 | 6.06 | 1.84 | 5.24 | 0.77 | 3.87 | 0.75 | 2.16 | 0.31 | 2.04 | 0.34 | 51.88 | 18.37 | 1.57 | 67.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK801-YQ1 | 95.30 | 11.80 | 46.20 | 7.61 | 1.86 | 7.52 | 1.00 | 4.55 | 0.82 | 2.51 | 0.35 | 2.01 | 0.32 | 52.30 | 18.70 | 1.33 | 56.40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK707-YQ2 | 95.66 | 14.10 | 59.71 | 12.02 | 2.53 | 9.35 | 1.47 | 7.68 | 1.47 | 3.97 | 0.61 | 3.92 | 0.64 | 60.31 | 19.26 | 0.75 | 57.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK804-YQ1 | 78.40 | 10.30 | 40.80 | 6.97 | 1.89 | 6.72 | 0.87 | 3.91 | 0.69 | 2.16 | 0.28 | 1.63 | 0.31 | 75.30 | 17.10 | 3.40 | 54.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1103-YQ1 | 70.04 | 8.52 | 33.40 | 6.29 | 1.86 | 5.06 | 0.84 | 4.08 | 0.76 | 2.12 | 0.30 | 1.89 | 0.35 | 137.10 | 19.26 | 3.13 | 65.35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1603-YQ1 | 88.61 | 10.23 | 38.97 | 6.55 | 1.81 | 5.37 | 0.80 | 4.11 | 0.76 | 2.16 | 0.33 | 2.11 | 0.56 | 88.49 | 19.99 | 1.37 | 58.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1601-YQ1 | 81.31 | 9.38 | 34.53 | 5.67 | 1.61 | 4.73 | 0.70 | 3.47 | 0.65 | 1.97 | 0.28 | 1.84 | 0.31 | 68.35 | 19.62 | 2.11 | 88.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1207-YQ2 | 62.22 | 7.63 | 29.78 | 5.51 | 1.69 | 4.58 | 0.74 | 3.79 | 0.70 | 1.82 | 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.30 | 121.10 | 19.17 | 8.38 | 127.57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品 | Sr | Ba | Zr | Nb | Ta | Hf | Th | U | Pb | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | (La/ Yb)N | Eu* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1105-YQ1 | 597.35 | 1 514.0 | 232.91 | 9.52 | 0.62 | 7.19 | 3.85 | 0.58 | 23.46 | 78.98 | 12.16 | 9.93 | 2.24 | 8.84 | 11.54 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK801-YQ1 | 285.00 | 1 269.0 | 266.00 | 14.00 | 0.73 | 7.70 | 3.99 | 0.39 | 24.70 | 45.80 | 10.70 | 3.90 | 2.30 | 7.40 | 13.45 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK707-YQ2 | 208.74 | 1 278.0 | 364.45 | 16.66 | 0.82 | 8.96 | 5.69 | 0.62 | 39.21 | 22.58 | 11.06 | 6.83 | 12.92 | 13.28 | 5.28 | 0.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK804-YQ1 | 385.00 | 1 053.0 | 318.00 | 10.00 | 0.53 | 6.82 | 3.20 | 0.52 | 26.50 | 40.00 | 7.80 | 6.37 | 2.21 | 5.12 | 13.89 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1103-YQ1 | 623.60 | 1 322.0 | 207.75 | 10.04 | 0.59 | 5.96 | 3.60 | 0.50 | 29.43 | 121.80 | 12.12 | 16.99 | 3.25 | 21.16 | 11.95 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1603-YQ1 | 659.61 | 1 201.0 | 238.98 | 12.38 | 0.74 | 5.65 | 7.11 | 1.21 | 16.80 | 146.04 | 28.41 | 22.53 | 19.18 | 27.27 | 13.99 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1601-YQ1 | 425.57 | 1 406.0 | 383.59 | 12.59 | 0.69 | 11.16 | 4.78 | 0.73 | 25.27 | 55.10 | 14.97 | 7.48 | 4.79 | 9.61 | 14.62 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZK1207-YQ2 | 448.04 | 720.3 | 172.28 | 4.56 | 0.32 | 4.43 | 2.41 | 0.32 | 13.43 | 142.80 | 17.20 | 19.41 | 6.54 | 11.72 | 13.48 | 1.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

图4 大西营子金矿区火山岩TAS图解(a) 、SiO2-K2O图解(b) 和AFM图解(c) (底图引自文献[21,22,23,24])
Fig.4 Classification diagram of TAS (a),K2O versus SiO2 (b) and AFM (c) for volcanic rocks from Daxiyingzi gold deposit(base map after refs.[21-24])

图5 大西营子金矿区火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b) (球粒陨石和原始地幔数值引自文献[25,26])
Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (b) of volcanic rocks from Daxiyingzi gold deposit(base map after refs.[25-26])
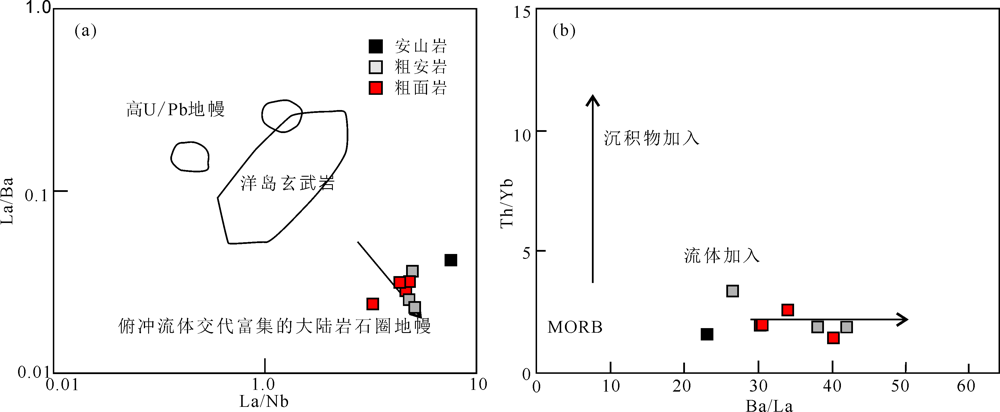
图6 大西营子金矿区火山岩La/Nb-La/Ba (a)和Ba/La-Th/Yb图解(b) (底图引自文献[38,39,40])
Fig.6 Plots of La/Nb versus La/Ba (a) and Ba/La versus Th/Yb(b) (base map after refs.[38-40])

图7 大西营子金矿区火山岩双变量图解 (a)SiO2-Al2O3图解;(b)SiO2-TiO2图解;(c)SiO2-MgO图解;(d)SiO2-CaO图解;(e)SiO2-TFe2O3图解;(f)SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)图解;(g)SiO2-Eu*图解;(h)CaO-CaO/Al2O3图解
Fig.7 Bivariate diagrams for the volcanic rocks from Daxiyingzi gold deposit

图8 大西营子金矿区火山岩构造环境判别图解(底图据文献[46,47,48,49]) (a)Hf-Nb-Th图解;(b)Nb-Y-Zr图解;(c)Ti-Y-Zr图解;(d)Zr-Zr/Y图解;N-MORB. 亏损地幔;E-MORB. 富集地幔; MORB. 大洋中脊玄武岩;OIB. 洋岛玄武岩;ARC. 弧;PM.原始地幔;AV. 弧岩浆岩;WPB. 板内玄武岩;CA. 大陆弧;IAT. 岛弧拉斑玄武岩;WPAB. 板内碱性玄武岩; WPT. 板内拉斑玄武岩
Fig.8 Discrimination diagrams for tectonic settings of the volcanic rocks from Daxiyingzi gold deposit (base map after refs.[46-49])
| [1] | 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(1) : 169-188. |
| [2] | HART C J, GOLDFARB R J, QIU Y M, et al. Gold deposits of the northern margin of the North China Craton: Multiple Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic mineralizing events[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002,37(3/4):326-351. |
| [3] | KUSKY T M, LI J. Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003,22:383-397. |
| [4] | YANG J H, WU F Y, WILDE S A. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: an association with lithospheric thinning[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2003,23:125-152. |
| [5] | 孙珍军. 华北克拉通北缘赤峰—朝阳地区金矿成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013: 1-194. |
| [6] | 徐贵忠, 佘宏全, 杨忆, 等. 赤峰西部地区金矿床成矿时代及其成矿机制的新认识[J]. 矿床地质, 2001,20(2):99-106. |
| [7] | 苗来成, 范蔚茗, 翟明国, 等. 金厂沟梁—二道沟金矿田内花岗岩类侵入体锆石的离子探针U-Pb年代学及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2003,19(1):71-80. |
| [8] | 李永刚, 翟明国, 杨进辉, 等. 内蒙古赤峰安家营子金矿成矿时代以及对华北中生代爆发成矿的意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2003,33(10):960-966. |
| [9] | 姜能, 张文淮. 内蒙古赤峰莲花山金矿床成矿物理化学条件及成矿机理[J]. 地球化学, 1996,25(1):73-83. |
| [10] | 李延河, 丁悌平. 内蒙古赤峰红花沟金矿稳定同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1990,9(3):257-269. |
| [11] | 邱玉民, 谢锡才. 内蒙古红花沟金矿床同位素地质特征及矿床成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 1992,15(4):311-314. |
| [12] | FU L B, WEI J H, CHEN H Y, et al. The relationship between gold mineralization, exhumation of metamorphic core complex and magma cooling: Formation of the Anjiayingzi Au deposit, northern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016,73(2):222-240. |
| [13] | 罗镇宽, 苗来成. 中国绿岩型金矿床——认识、问题与展望[J]. 黄金科学技术, 1994,2(3):1-9. |
| [14] | 陈伟军, 刘红涛. 赤峰—朝阳金矿化集中区主要金矿类型及其地质特征研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2006,14(5):1-7. |
| [15] | 李永刚, 翟明国, 苗来成, 等. 内蒙古赤峰地区安家营子金矿成矿流体研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2004,20(4):961-968. |
| [16] | 张长春, 王时麒, 张韬. 内蒙古金厂沟梁金矿床稳定同位素组成和矿床成因讨论[J]. 地质力学学报, 2002,8(2):156-164. |
| [17] | 程裕棋. 中国区域地质概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994: 1-152. |
| [18] | 柳小明, 高山, 第五春荣, 等. 单颗粒锆石的20μm小斑束原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄和微量元素的同时测定[J]. 科学通报, 2007,52(2):228-235. |
| [19] | PUPIN J P. Zircon and granite petrology[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1980,3(8):207-220. |
| [20] | KOSCHEK G. Origin and significance of the SEM cathodoluminescence from zircon[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2011,171(3):223-232. |
| [21] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224. |
| [22] | LE MAITRE R W. A proposal by the IUGS subcommission on the systematics of igneous rocks for a chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali silica (TAS) diagram[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1984,31(2):243-255. |
| [23] | RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989,22(4):247-263. |
| [24] | IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W P A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971,8(5):523-548. |
| [25] | BOYNTON W V. Geochemistry of the earth elements: Meteorite studies[M] //HENDERSON R. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry: Developments in Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 89-92. |
| [26] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M] //SAUNDERS A D, NORRY M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basalts. London:Geological Society of London, 1989: 313-345. |
| [27] | 付乐兵. 华北克拉通北缘赤峰—朝阳地区中生代构造岩浆演化与金成矿 [D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2012: 1-175. |
| [28] | 段培新, 李长民, 刘翠, 等. 内蒙古赤峰金厂沟梁金矿区花岗岩类年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(11):3189-3202. |
| [29] | 侯万荣. 内蒙古哈达门沟金矿床与金厂沟梁金矿床对比研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2011: 1-180. |
| [30] | 宋维民, 邢德和, 郭胜哲, 等. 内蒙古金厂沟梁西对面沟岩体岩石地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2009,18(2):134-139. |
| [31] | 陈井胜, 彭艳东, 刘淼, 等. 辽西建平烧锅营子金矿花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2016,43(1):395-409. |
| [32] | 李洪奎, 时文革, 李逸凡, 等. 山东胶东地区金矿成矿时代研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2013,21(3):1-9. |
| [33] | 林博磊, 李碧乐. 胶东玲珑花岗岩的地球化学、U-Pb 年代学、Lu-Hf 同位素及地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,40(2):147-160. |
| [34] | 韩世炯, 孙景贵, 邢树文, 等. 中国东北部陆缘内生金矿床成因类型、成矿时代及地球动力学背景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013,43(3):716-733. |
| [35] | GREEN T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995,120(3):347-359. |
| [36] | TISCHENDORF G, PAELCHEN W. Classification of granitoids[J]. Zeitschrift Fuer Geologische Wissenschaften, 1985,13(5):615-627. |
| [37] | WILSON M. Igneous Petrogenesis [M]. London: Unwin Hyman Press, 1989: 295-323. |
| [38] | SAUNDERS A D, STOREY M, KENT R W, et al. Consequences of plume-lithosphere interactions, magmatism and the cause of continental breakup[J]. Geological Society, 1992,68(1):41-60. |
| [39] | MCKENZIE D, O’NIONS R K. Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1991,32(5):1021-1091. |
| [40] | WOODHEAD J D, HERGT J M, DAVIDSON J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for‘conservative’ element mobility during subduction zone processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001,192(3):331-346. |
| [41] | ALBAREDE F, LUAIS B, FITTON G, et al. The geochemical regimes of Piton de la Fournaise volcano(Reunion) during the last 530000 years[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997,38(2):171-201. |
| [42] | GEIST D, NAUMANN T, LARSON P. Evolution of Galapagos magmas: mantle and crustal fractionation without assimilation[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998,39(5):953-971. |
| [43] | ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,326(3/4):269-287. |
| [44] | 杨扬, 高福红, 陈井胜, 等. 赤峰地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012,42(增):256-268. |
| [45] | XU W L, PEI F P, WANG F, et al. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2013,74(18):167-193. |
| [46] | WOOD D A. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonic magmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980,50(1):11-30. |
| [47] | MESCHEDE M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986,56(3/4):207-218. |
| [48] | PEARCE J A, CANN J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic-rocks determined using trace-element analyses[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1973,19(2):290-300. |
| [49] | PEARCE J A, NORRY M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1979,69(1):33-47. |
| [50] | 陈志广, 张连昌, 周新华, 等. 满洲里新右旗火山岩剖面年代学和地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(12):2971-2986. |
| [51] | 张玉涛, 张连昌, 英基丰, 等. 大兴安岭北段塔河地区早白垩世火山岩地球化学及源区特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(11) : 2811-2822. |
| [52] | LIU C F, ZHOU Z G, WANG G S, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Late Jurassic bimodal volcanic rocks from Hailisen area, central-southern Great Xing’an Range, Northeast China[J]. Geological Journal, 2018,53(5):2099-2117. |
| [53] | 赵越, 徐刚, 张拴宏, 等. 燕山运动与东亚构造体制的转变[J]. 地学前缘, 2004,11(3):319-328. |
| [54] | 于海飞, 张志诚, 帅歌伟, 等. 北京十三陵—西山髫髻山组火山岩年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2016,62(4):807-826. |
| [55] | YANG W, LI S G. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Western Liaoning:Implications for lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2008,102(1):88-117. |
| [56] | MA Q, ZHENG J P, XU Y G, et al. Are continental “adakites” derived from thickened or foundered lower crust?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015,419:125-133. |
| [57] | LI S Z, ZHAO G C, SUN M, et al. Mesozoic, not Paleoproterozoic SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of two Liaoji granites, eastern block, North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review, 2004,46(2):162-176. |
| [58] | WU F Y, YANG J H, WILDE S A, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Jurassic granites in the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005,221(1/2):127-156. |
| [59] | YANG K F, FAN H R, SANTOSH M, et al.Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012,146/147(8):112-127. |
| [60] | MA L, JIANG S Y, DAI B Z, et al.Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China: Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence [J]. Lithos, 2013,162/163(3):251-263. |
| [61] | 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(2):339-353. |
| [62] | 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史:东北亚陆缘中生代—古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2018,48(5):549-583. |
| [63] | HILDE T W C, UYEDA S, KROENKE L. Evolution of the western Pacific and its margin[J]. Tectonophysics, 1977,38(1/2):145-165. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [3] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [4] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [5] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [6] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [7] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [8] | 欧伟程, 李承东, 张永清, 赵利刚, 许腾, 许雅雯, 孙烜烨. 北秦岭二郎坪群抱树坪组碎屑锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及物源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 347-361. |
| [9] | 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 郑艳荣, 李晓东, 武海文, 张龙. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1633-1650. |
| [10] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [11] | 陈欢, 康志强, 吴佳昌, 李岱鲜, 曹延, 韦天伟, 韦乃韶, 刘迪, 周桐, 刘冬梅, 蓝海洋. 广西大瑶山朴全岩体形成时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1277-1290. |
| [12] | 杨元江, 李成禄, 邓昌州, 李文龙, 张立, 赵忠海, 赵寒冬. 大兴安岭大洋山钼矿成矿岩体地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及构造背景[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1092-1102. |
| [13] | 欧阳鑫, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 刘丽, 刘涛, 王文东. 内蒙古撰山子金矿床成岩成矿年代学与地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 635-652. |
| [14] | 鞠鹏程, 王训练, 王振涛, 刘喜方, 仲佳爱, 张在明. 渝北温泉镇地区三叠系“绿豆岩”特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 431-449. |
| [15] | 李琦, 王疆涛, 曾忠诚, 石卫, 李惠, 郭倩怡. 阿尔金造山带南缘蛇绿构造混杂岩带中晚奥陶世—早志留世二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 51-63. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||