



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 947-963.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2025.023
王鼎( ), 陈玉明, 谭明赈, 胡治鑫, 李振生*(
), 陈玉明, 谭明赈, 胡治鑫, 李振生*( ), 李全忠
), 李全忠
出版日期:2025-08-10
发布日期:2025-08-27
通信作者:
*李振生,男,博士,副教授,1976年出生,主要从事沉积岩石学和基础油气地质学研究工作。Email:lizhensh@163.com。作者简介:王鼎,男,硕士研究生,1998年出生,主要从事沉积岩石学和地球化学研究工作。Email:2022110681@mail.hfut.edu.cn。
基金资助:
WANG Ding( ), CHEN Yuming, TAN Mingzhen, HU Zhixin, LI Zhensheng*(
), CHEN Yuming, TAN Mingzhen, HU Zhixin, LI Zhensheng*( ), LI Quanzhong
), LI Quanzhong
Published:2025-08-10
Online:2025-08-27
摘要:
与相邻的长江中下游成矿带和郯庐断裂带强烈的晚中生代岩浆活动相比,巢湖北部(巢北)地区侵入岩分布和发育有限。本文运用锆石LA-ICP-MS定年结果和全岩元素地球化学分析确定巢北地区花岗斑岩的形成时代及成因,为晚中生代区域构造演化提供新的制约。巢北花岗斑岩属于强过铝质高钾钙碱性花岗岩,由15%~30%斑晶(细粒长石、少量石英和黑云母)和70%~85%基质(微粒长石和石英或黑云母)组成。本次获得的巢北花岗斑岩三个结晶年龄为(106.0±3.7) Ma、(103.9±4.4) Ma和(97.1±4.6) Ma,属于早白垩世阿尔布期—晚白垩世塞诺曼期,与郯庐断裂带108~103 Ma高分异A型花岗岩和宁镇地区109~100 Ma埃达克岩同期或稍晚。巢北花岗斑岩为较低分异的S型花岗岩,是加厚的扬子下地壳在相对高温条件下发生部分熔融的产物,形成于古太平洋板块正向俯冲背景下的远场弧后弱拉张环境。巢北花岗斑岩Sr/Y 比值的降低以及宁镇地区埃达克岩约束下扬板块存在阿尔布期岩石圈减薄;同时,郯庐断裂带A型花岗岩及双峰式火山岩表明其是岩石圈减薄中的强减薄带。
中图分类号:
王鼎, 陈玉明, 谭明赈, 胡治鑫, 李振生, 李全忠. 巢湖北部地区晚中生代花岗斑岩锆石 U-Pb年龄与成因探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 947-963.
WANG Ding, CHEN Yuming, TAN Mingzhen, HU Zhixin, LI Zhensheng, LI Quanzhong. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic Granitic Porphyries in the Northern Chaohu Area[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(04): 947-963.

图1 长江中下游和大别造山带构造框架及晚中生代岩浆岩分布图(a)和巢北地区地质图(b)
Fig.1 Tectonic framework of the Dabie Orogen and the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt with distributions of Late Mesozoic magmatic rocks (a) and geological map of the northern Chaohu area (b)
| 采样位置 | 样号 | 岩性 | 岩性特征 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 马脊山 | MJS1 MJS3 | 青灰色弱风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占30%,粒径0.5~1.5 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石斑晶部分粘土化;基质约占70%,粒径~0.06 mm左右,主要是长石和石英。 |
| 马脊山 | MJS2 | 灰白色强风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占15%,粒径~0.5 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石斑晶全部粘土化和碳酸盐岩化;基质约占85%,粒径~0.04 mm左右,主要是长石和黑云母。 |
| 向核山 南坡 | XHS2 | 灰色半风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占25%,粒径0.5~2 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石斑晶全部碳酸盐岩化及粘土化;基质约占75%,粒径~0.03 mm左右,主要是粘土化长石和石英。 |
| 向核山 南坡 | XHS3 | 灰色半风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占35%,粒径~1 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石环带和双晶清晰;基质约占85%,粒径~0.07mm左右,主要是长石和黑云母。 |
表1 巢北花岗斑岩的岩性特征
Table 1 Lithological characteristics of the Chaobei granitic porphyries
| 采样位置 | 样号 | 岩性 | 岩性特征 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 马脊山 | MJS1 MJS3 | 青灰色弱风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占30%,粒径0.5~1.5 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石斑晶部分粘土化;基质约占70%,粒径~0.06 mm左右,主要是长石和石英。 |
| 马脊山 | MJS2 | 灰白色强风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占15%,粒径~0.5 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石斑晶全部粘土化和碳酸盐岩化;基质约占85%,粒径~0.04 mm左右,主要是长石和黑云母。 |
| 向核山 南坡 | XHS2 | 灰色半风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占25%,粒径0.5~2 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石斑晶全部碳酸盐岩化及粘土化;基质约占75%,粒径~0.03 mm左右,主要是粘土化长石和石英。 |
| 向核山 南坡 | XHS3 | 灰色半风化花岗斑岩 | 斑晶约占35%,粒径~1 mm,主要是长石、石英和黑云母,长石环带和双晶清晰;基质约占85%,粒径~0.07mm左右,主要是长石和黑云母。 |
| 项目 | 单位 | MJS1(%) | MJS3(%) | XHS3(%) | 项目 | 单位 | MJS1(μg/g) | MJS3(μg/g) | XHS3(μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | % | 69.51 | 70.26 | 69.76 | Cs | μg/g | 1.50 | 2.81 | 1.56 |
| TiO2 | % | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.31 | Rb | μg/g | 102.5 | 94.4 | 57.3 |
| Al2O3 | % | 14.10 | 14.34 | 15.42 | Ba | μg/g | 1610 | 1545 | 1775 |
| Fe2O3 | % | 2.19 | 2.44 | 2.05 | Th | μg/g | 6.67 | 6.62 | 6.88 |
| MnO | % | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | U | μg/g | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.86 |
| MgO | % | 1.82 | 1.49 | 0.73 | Nb | μg/g | 12.4 | 12.2 | 12.6 |
| CaO | % | 1.58 | 1.62 | 1.94 | Ta | μg/g | 0.78 | 0.79 | 1.19 |
| Na2O | % | 1.82 | 2.13 | 3.28 | K | % | 3.58 | 3.45 | 3.30 |
| K2O | % | 4.62 | 4.45 | 4.17 | Pb | μg/g | 17.8 | 17.4 | 20.0 |
| P2O5 | % | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11 | Sr | μg/g | 130.0 | 188.0 | 492 |
| LOI | % | 3.62 | 2.99 | 1.88 | P | μg/g | 510 | 510 | 570 |
| La | μg/g | 45.3 | 45.8 | 55.9 | Zr | μg/g | 221 | 229 | 235 |
| Ce | μg/g | 78.9 | 79.5 | 93.5 | Hf | μg/g | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.3 |
| Pr | μg/g | 8.05 | 7.92 | 9.39 | Ti | % | 0.162 | 0.166 | 0.182 |
| Nd | μg/g | 25.5 | 26.0 | 30.0 | Y | μg/g | 8.4 | 7.9 | 8.9 |
| Sm | μg/g | 3.60 | 3.64 | 4.11 | Ga | μg/g | 18.05 | 17.40 | 18.75 |
| Eu | μg/g | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.89 | R1 | 2957 | 2896 | 2502 | |
| Gd | μg/g | 2.47 | 2.32 | 2.53 | R2 | 558 | 544 | 559 | |
| Tb | μg/g | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.34 | A/CNK(ASI) | 1.30 | 1.27 | 1.15 | |
| Dy | μg/g | 1.59 | 1.47 | 1.68 | A/NK | 1.76 | 1.72 | 1.56 | |
| Ho | μg/g | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.31 | M | 1.13 | 1.15 | 1.30 | |
| Er | μg/g | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.83 | TZr | ℃ | 837 | 838 | 828 |
| Tm | μg/g | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.11 | Ce* | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.98 | |
| Yb | μg/g | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.71 | Eu* | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.84 | |
| Lu | μg/g | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 10000Ga/Al | 2.63 | 2.48 | 2.46 |
表2 巢北花岗斑岩的主量和微量-稀土元素含量分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace, and rare earth element contents of the Chaobei granitic porphyries
| 项目 | 单位 | MJS1(%) | MJS3(%) | XHS3(%) | 项目 | 单位 | MJS1(μg/g) | MJS3(μg/g) | XHS3(μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | % | 69.51 | 70.26 | 69.76 | Cs | μg/g | 1.50 | 2.81 | 1.56 |
| TiO2 | % | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.31 | Rb | μg/g | 102.5 | 94.4 | 57.3 |
| Al2O3 | % | 14.10 | 14.34 | 15.42 | Ba | μg/g | 1610 | 1545 | 1775 |
| Fe2O3 | % | 2.19 | 2.44 | 2.05 | Th | μg/g | 6.67 | 6.62 | 6.88 |
| MnO | % | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | U | μg/g | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.86 |
| MgO | % | 1.82 | 1.49 | 0.73 | Nb | μg/g | 12.4 | 12.2 | 12.6 |
| CaO | % | 1.58 | 1.62 | 1.94 | Ta | μg/g | 0.78 | 0.79 | 1.19 |
| Na2O | % | 1.82 | 2.13 | 3.28 | K | % | 3.58 | 3.45 | 3.30 |
| K2O | % | 4.62 | 4.45 | 4.17 | Pb | μg/g | 17.8 | 17.4 | 20.0 |
| P2O5 | % | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11 | Sr | μg/g | 130.0 | 188.0 | 492 |
| LOI | % | 3.62 | 2.99 | 1.88 | P | μg/g | 510 | 510 | 570 |
| La | μg/g | 45.3 | 45.8 | 55.9 | Zr | μg/g | 221 | 229 | 235 |
| Ce | μg/g | 78.9 | 79.5 | 93.5 | Hf | μg/g | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.3 |
| Pr | μg/g | 8.05 | 7.92 | 9.39 | Ti | % | 0.162 | 0.166 | 0.182 |
| Nd | μg/g | 25.5 | 26.0 | 30.0 | Y | μg/g | 8.4 | 7.9 | 8.9 |
| Sm | μg/g | 3.60 | 3.64 | 4.11 | Ga | μg/g | 18.05 | 17.40 | 18.75 |
| Eu | μg/g | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.89 | R1 | 2957 | 2896 | 2502 | |
| Gd | μg/g | 2.47 | 2.32 | 2.53 | R2 | 558 | 544 | 559 | |
| Tb | μg/g | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.34 | A/CNK(ASI) | 1.30 | 1.27 | 1.15 | |
| Dy | μg/g | 1.59 | 1.47 | 1.68 | A/NK | 1.76 | 1.72 | 1.56 | |
| Ho | μg/g | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.31 | M | 1.13 | 1.15 | 1.30 | |
| Er | μg/g | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.83 | TZr | ℃ | 837 | 838 | 828 |
| Tm | μg/g | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.11 | Ce* | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.98 | |
| Yb | μg/g | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.71 | Eu* | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.84 | |
| Lu | μg/g | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 10000Ga/Al | 2.63 | 2.48 | 2.46 |
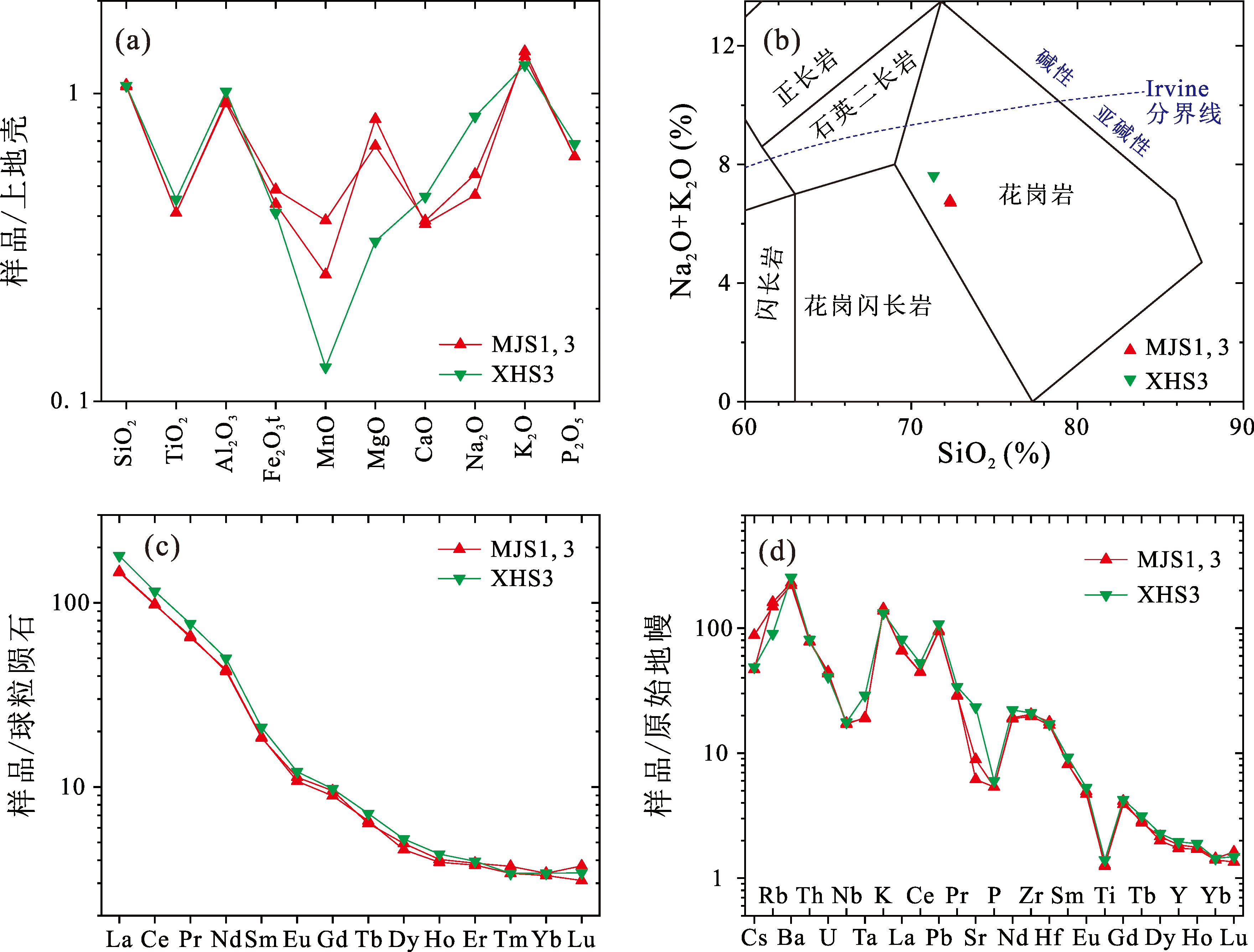
图4 巢北花岗斑岩的上地壳标准化[13]的主量元素型式(a)、TAS图[14](b)、球粒陨石标准化[15]的稀土元素型式(c)和原始地幔标准化[16]的微量元素型式(d)
Fig.4 Major element patterns normalized to upper continental crust[13] (a), TAS diagram[14] (b), rare earth element patterns normalized to chondrites[15] (c), and trace element patterns normalized to primitive mantle[16](d) for the Chaobei granitic porphyries
| 点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | rho | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 谐和度 (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/g | μg/g | 比例 | 1σ | 比例 | 1σ | 年龄 (Ma) | 1σ | 年龄 (Ma) | 1σ | ||||||
| MJS1 (马脊山, GPS: 31°38'21.51″; E117°52'13.30″) | |||||||||||||||
| MJS1-01 | 39.9 | 129 | 0.31 | 0.1641 | 0.0245 | 0.0141 | 0.0008 | 0.3510 | 154 | 21 | 90 | 5 | 47 | ||
| MJS1-02 | 212 | 122 | 1.74 | 0.1345 | 0.0144 | 0.0161 | 0.0008 | 0.4450 | 128 | 13 | 103 | 5 | 78 | ||
| MJS1-03 | 118 | 74.9 | 1.57 | 0.2030 | 0.0310 | 0.0133 | 0.0011 | 0.5350 | 188 | 26 | 85 | 7 | 24 | ||
| MJS1-04 | 113 | 62.6 | 1.80 | 0.3676 | 0.0503 | 0.0165 | 0.0010 | 0.4350 | 318 | 37 | 105 | 6 | -1 | ||
| MJS1-05 | 116 | 62.8 | 1.84 | 0.5571 | 0.0656 | 0.0202 | 0.0011 | 0.4610 | 450 | 43 | 129 | 7 | -11 | ||
| MJS1-06 | 194 | 91.9 | 2.11 | 0.6845 | 0.0832 | 0.0183 | 0.0011 | 0.4851 | 529 | 50 | 117 | 7 | -28 | ||
| MJS1-07 | 1.40 | 308 | 0.00 | 0.1629 | 0.0104 | 0.0156 | 0.0005 | 0.5326 | 153 | 9 | 100 | 3 | 57 | ||
| MJS1-08 | 64.4 | 67.1 | 0.96 | 0.1083 | 0.0172 | 0.0146 | 0.0007 | 0.2866 | 104 | 16 | 93 | 4 | 88 | ||
| MJS1-09 | 65.1 | 73.6 | 0.88 | 0.4006 | 0.0599 | 0.0174 | 0.0010 | 0.3797 | 342 | 43 | 111 | 6 | -2 | ||
| MJS1-10 | 377 | 234 | 1.61 | 0.7722 | 0.0995 | 0.0222 | 0.0013 | 0.4393 | 581 | 57 | 141 | 8 | -22 | ||
| MJS1-11 | 97.4 | 225 | 0.43 | 1.3330 | 0.0894 | 0.1368 | 0.0070 | 0.7665 | 860 | 39 | 826 | 40 | 95 | ||
| MJS1-12 | 118 | 250 | 0.47 | 1.1838 | 0.0835 | 0.1316 | 0.0058 | 0.6237 | 793 | 39 | 797 | 33 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-13 | 55.8 | 153 | 0.37 | 3.2401 | 0.3032 | 0.2534 | 0.0141 | 0.5947 | 1467 | 73 | 1456 | 73 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-14 | 158 | 188 | 0.84 | 0.3927 | 0.0722 | 0.0185 | 0.0029 | 0.8407 | 336 | 53 | 118 | 18 | 4 | ||
| MJS1-16 | 232 | 708 | 0.33 | 1.2143 | 0.1007 | 0.1080 | 0.0045 | 0.4997 | 807 | 46 | 661 | 26 | 80 | ||
| MJS1-17 | 174 | 114 | 1.53 | 0.3505 | 0.0682 | 0.0236 | 0.0017 | 0.3656 | 305 | 51 | 150 | 11 | 31 | ||
| MJS1-18 | 69.9 | 60.4 | 1.16 | 0.1899 | 0.0414 | 0.0169 | 0.0015 | 0.4204 | 177 | 35 | 108 | 10 | 51 | ||
| MJS1-19 | 180 | 264 | 0.68 | 1.3451 | 0.0574 | 0.1434 | 0.0043 | 0.6966 | 865 | 25 | 864 | 24 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-20 | 80.5 | 99.6 | 0.81 | 0.3028 | 0.0463 | 0.0190 | 0.0013 | 0.4359 | 269 | 36 | 121 | 8 | 24 | ||
| MJS1-21 | 276 | 111 | 2.50 | 0.1011 | 0.0125 | 0.0161 | 0.0008 | 0.4233 | 98 | 12 | 103 | 5 | 95 | ||
| MJS1-22 | 140 | 88.6 | 1.58 | 1.7836 | 0.2747 | 0.0296 | 0.0034 | 0.7414 | 1040 | 100 | 188 | 21 | -39 | ||
| MJS1-23 | 159 | 80.0 | 1.99 | 0.1082 | 0.0136 | 0.0164 | 0.0009 | 0.4173 | 104 | 13 | 105 | 5 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-24 | 249 | 372 | 0.67 | 1.4254 | 0.0696 | 0.1546 | 0.0050 | 0.6590 | 900 | 29 | 927 | 28 | 97 | ||
| MJS1-25 | 328 | 155 | 2.11 | 0.1606 | 0.0144 | 0.0166 | 0.0008 | 0.5104 | 151 | 13 | 106 | 5 | 64 | ||
| MJS1-26 | 186 | 102 | 1.83 | 0.5000 | 0.0768 | 0.0184 | 0.0012 | 0.4334 | 412 | 52 | 117 | 8 | -12 | ||
| MJS1-27 | 216 | 104 | 2.07 | 0.3448 | 0.0629 | 0.0170 | 0.0010 | 0.3174 | 301 | 47 | 109 | 6 | 6 | ||
| MJS1-28 | 341 | 533 | 0.64 | 10.0890 | 0.3445 | 0.4625 | 0.0130 | 0.8254 | 2443 | 32 | 2451 | 57 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-29 | 111 | 198 | 0.56 | 1.2507 | 0.0517 | 0.1416 | 0.0041 | 0.7004 | 824 | 23 | 854 | 23 | 96 | ||
| MJS1-30 | 41.3 | 29.5 | 1.40 | 0.2502 | 0.0375 | 0.0206 | 0.0014 | 0.4542 | 227 | 30 | 131 | 9 | 46 | ||
| MJS1-31 | 99.9 | 134 | 0.74 | 1.5599 | 0.0745 | 0.1562 | 0.0047 | 0.6289 | 954 | 30 | 936 | 26 | 98 | ||
| MJS1-32 | 421 | 198 | 2.13 | 0.1613 | 0.0150 | 0.0165 | 0.0007 | 0.4897 | 152 | 13 | 105 | 5 | 63 | ||
| MJS1-33 | 331 | 411 | 0.81 | 1.3094 | 0.0498 | 0.1418 | 0.0041 | 0.7624 | 850 | 22 | 855 | 23 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-34 | 317 | 237 | 1.34 | 0.2417 | 0.0170 | 0.0146 | 0.0007 | 0.6568 | 220 | 14 | 93 | 4 | 19 | ||
| MJS1-35 | 158 | 470 | 0.34 | 9.3187 | 0.3125 | 0.4470 | 0.0128 | 0.8506 | 2370 | 31 | 2382 | 57 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-36 | 103 | 59.3 | 1.74 | 0.5912 | 0.0435 | 0.0199 | 0.0010 | 0.6665 | 472 | 28 | 127 | 6 | -15 | ||
| MJS1-37 | 247 | 126 | 1.96 | 0.1697 | 0.0192 | 0.0170 | 0.0007 | 0.3798 | 159 | 17 | 109 | 5 | 62 | ||
| MJS1-38 | 48.0 | 2889 | 0.02 | 4.5771 | 0.1530 | 0.2801 | 0.0079 | 0.8461 | 1745 | 28 | 1592 | 40 | 90 | ||
| MJS1-39 | 83.2 | 46.9 | 1.77 | 0.8321 | 0.1436 | 0.0210 | 0.0013 | 0.3580 | 615 | 80 | 134 | 8 | -29 | ||
| MJS1-40 | 28.7 | 98.8 | 0.29 | 4.3474 | 0.1725 | 0.2537 | 0.0078 | 0.7774 | 1702 | 33 | 1457 | 40 | 84 | ||
| MJS1-41 | 139 | 156 | 0.89 | 1.1492 | 0.0430 | 0.1105 | 0.0035 | 0.8357 | 777 | 20 | 675 | 20 | 86 | ||
| MJS1-42 | 69.6 | 56.0 | 1.24 | 0.5077 | 0.0402 | 0.0187 | 0.0008 | 0.5328 | 417 | 27 | 120 | 5 | -11 | ||
| MJS1-43 | 141 | 45.1 | 3.13 | 1.1436 | 0.1011 | 0.0255 | 0.0013 | 0.5728 | 774 | 48 | 162 | 8 | -31 | ||
| MJS1-44 | 161 | 82.7 | 1.95 | 0.2798 | 0.0241 | 0.0167 | 0.0007 | 0.4544 | 250 | 19 | 106 | 4 | 19 | ||
| MJS1-45 | 114 | 68.9 | 1.66 | 0.3890 | 0.0393 | 0.0169 | 0.0009 | 0.5013 | 334 | 29 | 108 | 5 | -3 | ||
| MJS1-46 | 66.4 | 60.5 | 1.10 | 0.0909 | 0.0127 | 0.0146 | 0.0006 | 0.3046 | 88 | 12 | 93 | 4 | 94 | ||
| MJS1-47 | 225 | 103 | 2.18 | 0.2056 | 0.0256 | 0.0172 | 0.0008 | 0.3627 | 190 | 22 | 110 | 5 | 46 | ||
| MJS1-48 | 136 | 84.1 | 1.61 | 0.2183 | 0.0183 | 0.0150 | 0.0005 | 0.4174 | 200 | 15 | 96 | 3 | 29 | ||
| MJS1-49 | 94.2 | 77.7 | 1.21 | 0.2549 | 0.0265 | 0.0170 | 0.0007 | 0.4050 | 231 | 21 | 109 | 5 | 28 | ||
| MJS1-50 | 138 | 74.3 | 1.86 | 1.5439 | 0.1082 | 0.0285 | 0.0013 | 0.6395 | 948 | 43 | 181 | 8 | -36 | ||
| MJS1-51 | 114 | 81.3 | 1.41 | 0.3728 | 0.0307 | 0.0174 | 0.0007 | 0.4926 | 322 | 23 | 111 | 4 | 2 | ||
| MJS1-52 | 76.9 | 55.5 | 1.39 | 0.6765 | 0.0601 | 0.0189 | 0.0009 | 0.5201 | 525 | 36 | 121 | 6 | -26 | ||
| MJS1-53 | 95.7 | 67.6 | 1.41 | 1.6108 | 0.0844 | 0.0272 | 0.0011 | 0.7843 | 974 | 33 | 173 | 7 | -40 | ||
| MJS1-54 | 268 | 122 | 2.20 | 0.1795 | 0.0133 | 0.0155 | 0.0006 | 0.5023 | 168 | 11 | 99 | 4 | 48 | ||
| MJS1-55 | 61.2 | 47.8 | 1.28 | 0.2149 | 0.0292 | 0.0157 | 0.0008 | 0.3572 | 198 | 24 | 100 | 5 | 34 | ||
| MJS1-56 | 91.1 | 64.3 | 1.42 | 1.5957 | 0.0904 | 0.0282 | 0.0012 | 0.7587 | 969 | 35 | 179 | 8 | -38 | ||
| MJS2 (马脊山, GPS: 31°38'21.51″; E117°52'13.30″) | |||||||||||||||
| MJS2-01 | 619 | 1120 | 0.55 | 1.0239 | 0.0343 | 0.1117 | 0.0030 | 0.8150 | 716 | 17 | 683 | 18 | 95 | ||
| MJS2-02 | 107 | 67.5 | 1.59 | 0.2105 | 0.0241 | 0.0161 | 0.0008 | 0.4494 | 194 | 20 | 103 | 5 | 38 | ||
| MJS2-03 | 62.9 | 34.2 | 1.84 | 5.7043 | 0.2586 | 0.3455 | 0.0111 | 0.7077 | 1932 | 39 | 1913 | 53 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-04 | 421 | 164 | 2.57 | 0.2052 | 0.0227 | 0.0126 | 0.0009 | 0.6550 | 190 | 19 | 81 | 6 | 19 | ||
| MJS2-05 | 161 | 101 | 1.60 | 0.1911 | 0.0283 | 0.0170 | 0.0008 | 0.3200 | 178 | 24 | 109 | 5 | 51 | ||
| MJS2-06 | 1449 | 2244 | 0.65 | 0.3766 | 0.0170 | 0.0356 | 0.0012 | 0.7597 | 325 | 13 | 226 | 8 | 64 | ||
| MJS2-07 | 1871 | 1786 | 1.05 | 1.2222 | 0.0412 | 0.1290 | 0.0036 | 0.8235 | 811 | 19 | 782 | 20 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-08 | 240 | 494 | 0.49 | 1.6106 | 0.0614 | 0.1563 | 0.0046 | 0.7686 | 974 | 24 | 936 | 26 | 95 | ||
| MJS2-10 | 89.6 | 59.4 | 1.51 | 0.8602 | 0.0797 | 0.0197 | 0.0012 | 0.6789 | 630 | 43 | 125 | 8 | -34 | ||
| MJS2-11 | 79.4 | 54.7 | 1.45 | 0.4564 | 0.0689 | 0.0163 | 0.0014 | 0.5566 | 382 | 48 | 104 | 9 | -15 | ||
| MJS2-12 | 768 | 1801 | 0.43 | 1.0012 | 0.0426 | 0.1016 | 0.0034 | 0.7843 | 704 | 22 | 624 | 20 | 87 | ||
| MJS2-13 | 186 | 112 | 1.67 | 0.6444 | 0.0958 | 0.0181 | 0.0014 | 0.5183 | 505 | 59 | 115 | 9 | -26 | ||
| MJS2-14 | 2168 | 2028 | 1.07 | 0.3912 | 0.0228 | 0.0397 | 0.0015 | 0.6534 | 335 | 17 | 251 | 9 | 71 | ||
| MJS2-15 | 137 | 84.3 | 1.62 | 0.2406 | 0.0270 | 0.0160 | 0.0011 | 0.5944 | 219 | 22 | 102 | 7 | 27 | ||
| MJS2-16 | 20.7 | 39.8 | 0.52 | 1.3106 | 0.1138 | 0.1460 | 0.0053 | 0.4208 | 850 | 50 | 878 | 30 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-17 | 61.7 | 53.6 | 1.15 | 0.2366 | 0.0319 | 0.0175 | 0.0011 | 0.4663 | 216 | 26 | 112 | 7 | 36 | ||
| MJS2-18 | 212 | 185 | 1.14 | 0.2460 | 0.0366 | 0.0164 | 0.0010 | 0.4023 | 223 | 30 | 105 | 6 | 27 | ||
| MJS2-19 | 246 | 115 | 2.13 | 0.1256 | 0.0208 | 0.0134 | 0.0007 | 0.3030 | 120 | 19 | 86 | 4 | 67 | ||
| MJS2-20 | 84.2 | 291 | 0.29 | 1.1521 | 0.0673 | 0.1350 | 0.0058 | 0.7380 | 778 | 32 | 816 | 33 | 95 | ||
| MJS2-21 | 382 | 1352 | 0.28 | 0.2889 | 0.0160 | 0.0384 | 0.0015 | 0.7250 | 258 | 13 | 243 | 10 | 94 | ||
| MJS2-22 | 270 | 318 | 0.85 | 9.4692 | 0.3211 | 0.4513 | 0.0132 | 0.8601 | 2385 | 31 | 2401 | 58 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-23 | 247 | 440 | 0.56 | 1.1030 | 0.0625 | 0.1197 | 0.0062 | 0.9149 | 755 | 30 | 729 | 36 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-24 | 67.3 | 54.9 | 1.22 | 0.2509 | 0.0387 | 0.0213 | 0.0014 | 0.4368 | 227 | 31 | 136 | 9 | 49 | ||
| MJS2-26 | 73.1 | 74.2 | 0.99 | 0.3368 | 0.0542 | 0.0170 | 0.0012 | 0.4339 | 295 | 41 | 109 | 8 | 7 | ||
| MJS2-27 | 2687 | 2631 | 1.02 | 0.4015 | 0.0254 | 0.0289 | 0.0012 | 0.6544 | 343 | 18 | 184 | 8 | 39 | ||
| MJS2-28 | 48.6 | 72.0 | 0.68 | 1.4242 | 0.0847 | 0.1521 | 0.0049 | 0.5398 | 899 | 35 | 913 | 27 | 98 | ||
| MJS2-29 | 59.2 | 52.7 | 1.12 | 0.4309 | 0.0777 | 0.0171 | 0.0013 | 0.4147 | 364 | 55 | 109 | 8 | -8 | ||
| MJS2-30 | 57.6 | 88.0 | 0.65 | 1.4370 | 0.0818 | 0.1564 | 0.0050 | 0.5607 | 904 | 34 | 937 | 28 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-31 | 1254 | 1765 | 0.71 | 0.5073 | 0.0202 | 0.0554 | 0.0017 | 0.7707 | 417 | 14 | 348 | 10 | 81 | ||
| MJS2-33 | 413 | 2720 | 0.15 | 0.1947 | 0.0124 | 0.0258 | 0.0012 | 0.7230 | 181 | 11 | 164 | 7 | 90 | ||
| MJS2-35 | 295 | 1255 | 0.23 | 5.9728 | 0.3726 | 0.2984 | 0.0175 | 0.9386 | 1972 | 54 | 1683 | 87 | 84 | ||
| MJS2-36 | 32.4 | 40.0 | 0.81 | 1.9744 | 0.4067 | 0.0475 | 0.0066 | 0.6741 | 1107 | 139 | 299 | 41 | -15 | ||
| MJS2-37 | 173 | 131 | 1.32 | 0.3733 | 0.0559 | 0.0170 | 0.0016 | 0.6294 | 322 | 41 | 109 | 10 | 1 | ||
| MJS2-38 | 88.1 | 82.1 | 1.07 | 0.8060 | 0.1138 | 0.0172 | 0.0017 | 0.6957 | 600 | 64 | 110 | 11 | -39 | ||
| MJS2-39 | 49.9 | 53.8 | 0.93 | 1.8502 | 0.5916 | 0.0465 | 0.0102 | 0.6832 | 1064 | 211 | 293 | 63 | -14 | ||
| MJS2-40 | 172 | 120 | 1.44 | 0.1565 | 0.0167 | 0.0170 | 0.0008 | 0.4646 | 148 | 15 | 109 | 5 | 69 | ||
| MJS2-41 | 73.4 | 55.7 | 1.32 | 3.0716 | 0.3355 | 0.0398 | 0.0032 | 0.7284 | 1426 | 84 | 252 | 20 | -40 | ||
| MJS2-42 | 113 | 76.0 | 1.49 | 0.2898 | 0.0274 | 0.0163 | 0.0007 | 0.4407 | 258 | 22 | 104 | 4 | 14 | ||
| MJS2-43 | 123 | 48.2 | 2.56 | 1.8676 | 0.2755 | 0.0345 | 0.0029 | 0.5757 | 1070 | 98 | 218 | 18 | -33 | ||
| MJS2-44 | 74.8 | 58.4 | 1.28 | 0.1424 | 0.0149 | 0.0154 | 0.0007 | 0.4435 | 135 | 13 | 99 | 5 | 68 | ||
| MJS2-45 | 187 | 112 | 1.67 | 1.2328 | 0.0487 | 0.1448 | 0.0040 | 0.6916 | 816 | 22 | 872 | 22 | 93 | ||
| MJS2-46 | 292 | 278 | 1.05 | 1.2332 | 0.0388 | 0.1341 | 0.0037 | 0.8820 | 816 | 18 | 811 | 21 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-47 | 316 | 252 | 1.25 | 1.3348 | 0.0432 | 0.1437 | 0.0039 | 0.8323 | 861 | 19 | 866 | 22 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-48 | 70.2 | 52.0 | 1.35 | 0.3528 | 0.0250 | 0.0173 | 0.0008 | 0.6649 | 307 | 19 | 110 | 5 | 5 | ||
| MJS2-49 | 51.1 | 45.3 | 1.13 | 0.2009 | 0.0212 | 0.0160 | 0.0008 | 0.4471 | 186 | 18 | 102 | 5 | 41 | ||
| MJS2-50 | 78.4 | 74.0 | 1.06 | 0.3824 | 0.0261 | 0.0164 | 0.0007 | 0.6084 | 329 | 19 | 105 | 4 | -4 | ||
| MJS2-51 | 84.3 | 91.9 | 0.92 | 0.3858 | 0.0496 | 0.0198 | 0.0010 | 0.4086 | 331 | 36 | 126 | 7 | 10 | ||
| MJS2-52 | 143 | 179 | 0.80 | 0.9318 | 0.0424 | 0.0997 | 0.0029 | 0.6448 | 669 | 22 | 612 | 17 | 91 | ||
| MJS2-53 | 107 | 83.4 | 1.29 | 0.9195 | 0.1921 | 0.0212 | 0.0025 | 0.5613 | 662 | 102 | 135 | 16 | -33 | ||
| MJS2-54 | 182 | 154 | 1.18 | 0.2028 | 0.0275 | 0.0173 | 0.0008 | 0.3618 | 188 | 23 | 110 | 5 | 48 | ||
| MJS2-55 | 101 | 60.3 | 1.68 | 0.9474 | 0.1023 | 0.0248 | 0.0016 | 0.5927 | 677 | 53 | 158 | 10 | -25 | ||
| MJS2-56 | 91.6 | 70.3 | 1.30 | 0.3993 | 0.0412 | 0.0173 | 0.0010 | 0.5423 | 341 | 30 | 111 | 6 | -3 | ||
| XHS2 (向核山南坡, GPS: 31°40'46.51″; E117°50'36.57″) | |||||||||||||||
| XHS2-01 | 321 | 181 | 1.77 | 0.2175 | 0.0295 | 0.0153 | 0.0008 | 0.3901 | 200 | 25 | 98 | 5 | 31 | ||
| XHS2-02 | 56.0 | 297 | 0.19 | 0.1271 | 0.0096 | 0.0175 | 0.0006 | 0.4300 | 121 | 9 | 112 | 4 | 91 | ||
| XHS2-03 | 366 | 339 | 1.08 | 1.0247 | 0.0643 | 0.1293 | 0.0049 | 0.6070 | 716 | 32 | 784 | 28 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-04 | 172 | 97.4 | 1.77 | 0.1088 | 0.0113 | 0.0164 | 0.0007 | 0.3964 | 105 | 10 | 105 | 4 | 99 | ||
| XHS2-05 | 146 | 84.9 | 1.72 | 0.3934 | 0.0669 | 0.0158 | 0.0012 | 0.4509 | 337 | 49 | 101 | 8 | -8 | ||
| XHS2-06 | 2927 | 3045 | 0.96 | 0.7190 | 0.0439 | 0.0806 | 0.0046 | 0.9268 | 550 | 26 | 500 | 27 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-07 | 202 | 701 | 0.29 | 1.0071 | 0.0497 | 0.1045 | 0.0047 | 0.9065 | 707 | 25 | 641 | 27 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-08 | 170 | 131 | 1.30 | 0.4198 | 0.0540 | 0.0126 | 0.0010 | 0.6361 | 356 | 39 | 80 | 7 | -27 | ||
| XHS2-09 | 83.7 | 140 | 0.60 | 4.2314 | 0.2153 | 0.2493 | 0.0091 | 0.7133 | 1680 | 42 | 1435 | 47 | 84 | ||
| XHS2-10 | 63.1 | 60.9 | 1.04 | 0.7145 | 0.1272 | 0.0235 | 0.0025 | 0.6018 | 547 | 75 | 150 | 16 | -15 | ||
| XHS2-11 | 70.8 | 61.9 | 1.14 | 0.3267 | 0.0793 | 0.0161 | 0.0011 | 0.2788 | 287 | 61 | 103 | 7 | 5 | ||
| XHS2-12 | 54.2 | 57.1 | 0.95 | 0.1978 | 0.0309 | 0.0176 | 0.0012 | 0.4285 | 183 | 26 | 112 | 7 | 51 | ||
| XHS2-13 | 345 | 579 | 0.60 | 1.2627 | 0.0566 | 0.1376 | 0.0046 | 0.7435 | 829 | 25 | 831 | 26 | 99 | ||
| XHS2-14 | 79.3 | 71.7 | 1.11 | 0.2270 | 0.0438 | 0.0130 | 0.0009 | 0.3696 | 208 | 36 | 83 | 6 | 14 | ||
| XHS2-15 | 312 | 254 | 1.23 | 1.3651 | 0.0675 | 0.1404 | 0.0044 | 0.6332 | 874 | 29 | 847 | 25 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-16 | 130 | 131 | 1.00 | 1.3025 | 0.0801 | 0.1367 | 0.0042 | 0.4991 | 847 | 35 | 826 | 24 | 97 | ||
| XHS2-17 | 198 | 275 | 0.72 | 7.1593 | 0.2446 | 0.3331 | 0.0096 | 0.8479 | 2131 | 30 | 1853 | 47 | 86 | ||
| XHS2-18 | 230 | 449 | 0.51 | 0.1133 | 0.0069 | 0.0173 | 0.0005 | 0.5075 | 109 | 6 | 111 | 3 | 98 | ||
| XHS2-19 | 101 | 201 | 0.50 | 1.2685 | 0.0593 | 0.1326 | 0.0046 | 0.7476 | 832 | 27 | 803 | 26 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-20 | 220 | 331 | 0.67 | 1.1818 | 0.0505 | 0.1355 | 0.0040 | 0.6870 | 792 | 24 | 819 | 23 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-21 | 93.7 | 940 | 0.10 | 4.9467 | 0.1667 | 0.2891 | 0.0086 | 0.8788 | 1810 | 28 | 1637 | 43 | 89 | ||
| XHS2-22 | 94.7 | 154 | 0.62 | 1.3617 | 0.0703 | 0.1359 | 0.0042 | 0.6021 | 873 | 30 | 821 | 24 | 93 | ||
| XHS2-23 | 516 | 1414 | 0.36 | 0.8242 | 0.0444 | 0.0767 | 0.0036 | 0.8694 | 610 | 25 | 476 | 21 | 75 | ||
| XHS2-24 | 50.5 | 51.6 | 0.98 | 0.7983 | 0.2211 | 0.0176 | 0.0021 | 0.4280 | 596 | 125 | 113 | 13 | -37 | ||
| XHS2-25 | 166 | 147 | 1.13 | 0.3882 | 0.0781 | 0.0150 | 0.0010 | 0.3480 | 333 | 57 | 96 | 7 | -11 | ||
| XHS2-26 | 284 | 503 | 0.57 | 0.9429 | 0.0588 | 0.0999 | 0.0052 | 0.8288 | 674 | 31 | 614 | 30 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-27 | 45.9 | 67.8 | 0.68 | 0.4698 | 0.0778 | 0.0144 | 0.0012 | 0.5127 | 391 | 54 | 92 | 8 | -24 | ||
| XHS2-28 | 250 | 138 | 1.80 | 0.3236 | 0.0588 | 0.0159 | 0.0009 | 0.3026 | 285 | 45 | 102 | 6 | 5 | ||
| XHS2-29 | 16604 | 10800 | 1.54 | 0.1277 | 0.0075 | 0.0139 | 0.0005 | 0.6530 | 122 | 7 | 89 | 3 | 68 | ||
| XHS2-30 | 444 | 360 | 1.23 | 1.4073 | 0.0987 | 0.1352 | 0.0060 | 0.6317 | 892 | 42 | 817 | 34 | 91 | ||
| XHS2-41 | 58.4 | 46.4 | 1.26 | 0.2751 | 0.0233 | 0.0152 | 0.0007 | 0.5644 | 247 | 19 | 97 | 5 | 12 | ||
| XHS2-42 | 89.7 | 76.3 | 1.18 | 0.3364 | 0.0293 | 0.0170 | 0.0006 | 0.4392 | 294 | 22 | 109 | 4 | 7 | ||
| XHS2-43 | 79.1 | 64.3 | 1.23 | 0.2362 | 0.0168 | 0.0160 | 0.0006 | 0.5300 | 215 | 14 | 102 | 4 | 28 | ||
| XHS2-44 | 68.8 | 81.4 | 0.85 | 0.0933 | 0.0120 | 0.0150 | 0.0006 | 0.2908 | 91 | 11 | 96 | 4 | 94 | ||
| XHS2-45 | 56.4 | 51.1 | 1.10 | 0.1615 | 0.0177 | 0.0163 | 0.0007 | 0.3919 | 152 | 15 | 104 | 4 | 62 | ||
| XHS2-46 | 162 | 178 | 0.91 | 1.3464 | 0.0458 | 0.1410 | 0.0038 | 0.8002 | 866 | 20 | 850 | 22 | 98 | ||
| XHS2-47 | 71.9 | 46.7 | 1.54 | 0.2669 | 0.0240 | 0.0162 | 0.0007 | 0.4624 | 240 | 19 | 104 | 4 | 20 | ||
| XHS2-48 | 153 | 182 | 0.84 | 1.3558 | 0.0471 | 0.1337 | 0.0037 | 0.7893 | 870 | 20 | 809 | 21 | 92 | ||
| XHS2-49 | 350 | 415 | 0.84 | 1.1808 | 0.0410 | 0.1259 | 0.0034 | 0.7885 | 792 | 19 | 764 | 20 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-50 | 67.7 | 57.4 | 1.18 | 0.2220 | 0.0214 | 0.0158 | 0.0006 | 0.4232 | 204 | 18 | 101 | 4 | 32 | ||
| XHS2-51 | 45.0 | 40.0 | 1.13 | 1.3322 | 0.2838 | 0.0309 | 0.0030 | 0.4622 | 860 | 124 | 196 | 19 | -26 | ||
| XHS2-52 | 89.4 | 81.7 | 1.09 | 0.2364 | 0.0203 | 0.0144 | 0.0005 | 0.4148 | 215 | 17 | 92 | 3 | 19 | ||
| XHS2-53 | 81.8 | 75.0 | 1.09 | 0.2252 | 0.0180 | 0.0159 | 0.0006 | 0.4388 | 206 | 15 | 102 | 4 | 32 | ||
| XHS2-54 | 268 | 153 | 1.75 | 0.1666 | 0.0120 | 0.0158 | 0.0006 | 0.4861 | 156 | 10 | 101 | 4 | 57 | ||
| XHS2-55 | 206 | 93.4 | 2.20 | 0.1449 | 0.0128 | 0.0167 | 0.0007 | 0.4791 | 137 | 11 | 107 | 4 | 75 | ||
| XHS2-56 | 341 | 213 | 1.60 | 0.2150 | 0.0130 | 0.0169 | 0.0006 | 0.5423 | 198 | 11 | 108 | 4 | 41 | ||
表3 巢北花岗斑岩的锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 3 Zircon U-Pb dating results of the Chaobei granitic porphyries
| 点号 | Th | U | Th/U | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | rho | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 谐和度 (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/g | μg/g | 比例 | 1σ | 比例 | 1σ | 年龄 (Ma) | 1σ | 年龄 (Ma) | 1σ | ||||||
| MJS1 (马脊山, GPS: 31°38'21.51″; E117°52'13.30″) | |||||||||||||||
| MJS1-01 | 39.9 | 129 | 0.31 | 0.1641 | 0.0245 | 0.0141 | 0.0008 | 0.3510 | 154 | 21 | 90 | 5 | 47 | ||
| MJS1-02 | 212 | 122 | 1.74 | 0.1345 | 0.0144 | 0.0161 | 0.0008 | 0.4450 | 128 | 13 | 103 | 5 | 78 | ||
| MJS1-03 | 118 | 74.9 | 1.57 | 0.2030 | 0.0310 | 0.0133 | 0.0011 | 0.5350 | 188 | 26 | 85 | 7 | 24 | ||
| MJS1-04 | 113 | 62.6 | 1.80 | 0.3676 | 0.0503 | 0.0165 | 0.0010 | 0.4350 | 318 | 37 | 105 | 6 | -1 | ||
| MJS1-05 | 116 | 62.8 | 1.84 | 0.5571 | 0.0656 | 0.0202 | 0.0011 | 0.4610 | 450 | 43 | 129 | 7 | -11 | ||
| MJS1-06 | 194 | 91.9 | 2.11 | 0.6845 | 0.0832 | 0.0183 | 0.0011 | 0.4851 | 529 | 50 | 117 | 7 | -28 | ||
| MJS1-07 | 1.40 | 308 | 0.00 | 0.1629 | 0.0104 | 0.0156 | 0.0005 | 0.5326 | 153 | 9 | 100 | 3 | 57 | ||
| MJS1-08 | 64.4 | 67.1 | 0.96 | 0.1083 | 0.0172 | 0.0146 | 0.0007 | 0.2866 | 104 | 16 | 93 | 4 | 88 | ||
| MJS1-09 | 65.1 | 73.6 | 0.88 | 0.4006 | 0.0599 | 0.0174 | 0.0010 | 0.3797 | 342 | 43 | 111 | 6 | -2 | ||
| MJS1-10 | 377 | 234 | 1.61 | 0.7722 | 0.0995 | 0.0222 | 0.0013 | 0.4393 | 581 | 57 | 141 | 8 | -22 | ||
| MJS1-11 | 97.4 | 225 | 0.43 | 1.3330 | 0.0894 | 0.1368 | 0.0070 | 0.7665 | 860 | 39 | 826 | 40 | 95 | ||
| MJS1-12 | 118 | 250 | 0.47 | 1.1838 | 0.0835 | 0.1316 | 0.0058 | 0.6237 | 793 | 39 | 797 | 33 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-13 | 55.8 | 153 | 0.37 | 3.2401 | 0.3032 | 0.2534 | 0.0141 | 0.5947 | 1467 | 73 | 1456 | 73 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-14 | 158 | 188 | 0.84 | 0.3927 | 0.0722 | 0.0185 | 0.0029 | 0.8407 | 336 | 53 | 118 | 18 | 4 | ||
| MJS1-16 | 232 | 708 | 0.33 | 1.2143 | 0.1007 | 0.1080 | 0.0045 | 0.4997 | 807 | 46 | 661 | 26 | 80 | ||
| MJS1-17 | 174 | 114 | 1.53 | 0.3505 | 0.0682 | 0.0236 | 0.0017 | 0.3656 | 305 | 51 | 150 | 11 | 31 | ||
| MJS1-18 | 69.9 | 60.4 | 1.16 | 0.1899 | 0.0414 | 0.0169 | 0.0015 | 0.4204 | 177 | 35 | 108 | 10 | 51 | ||
| MJS1-19 | 180 | 264 | 0.68 | 1.3451 | 0.0574 | 0.1434 | 0.0043 | 0.6966 | 865 | 25 | 864 | 24 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-20 | 80.5 | 99.6 | 0.81 | 0.3028 | 0.0463 | 0.0190 | 0.0013 | 0.4359 | 269 | 36 | 121 | 8 | 24 | ||
| MJS1-21 | 276 | 111 | 2.50 | 0.1011 | 0.0125 | 0.0161 | 0.0008 | 0.4233 | 98 | 12 | 103 | 5 | 95 | ||
| MJS1-22 | 140 | 88.6 | 1.58 | 1.7836 | 0.2747 | 0.0296 | 0.0034 | 0.7414 | 1040 | 100 | 188 | 21 | -39 | ||
| MJS1-23 | 159 | 80.0 | 1.99 | 0.1082 | 0.0136 | 0.0164 | 0.0009 | 0.4173 | 104 | 13 | 105 | 5 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-24 | 249 | 372 | 0.67 | 1.4254 | 0.0696 | 0.1546 | 0.0050 | 0.6590 | 900 | 29 | 927 | 28 | 97 | ||
| MJS1-25 | 328 | 155 | 2.11 | 0.1606 | 0.0144 | 0.0166 | 0.0008 | 0.5104 | 151 | 13 | 106 | 5 | 64 | ||
| MJS1-26 | 186 | 102 | 1.83 | 0.5000 | 0.0768 | 0.0184 | 0.0012 | 0.4334 | 412 | 52 | 117 | 8 | -12 | ||
| MJS1-27 | 216 | 104 | 2.07 | 0.3448 | 0.0629 | 0.0170 | 0.0010 | 0.3174 | 301 | 47 | 109 | 6 | 6 | ||
| MJS1-28 | 341 | 533 | 0.64 | 10.0890 | 0.3445 | 0.4625 | 0.0130 | 0.8254 | 2443 | 32 | 2451 | 57 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-29 | 111 | 198 | 0.56 | 1.2507 | 0.0517 | 0.1416 | 0.0041 | 0.7004 | 824 | 23 | 854 | 23 | 96 | ||
| MJS1-30 | 41.3 | 29.5 | 1.40 | 0.2502 | 0.0375 | 0.0206 | 0.0014 | 0.4542 | 227 | 30 | 131 | 9 | 46 | ||
| MJS1-31 | 99.9 | 134 | 0.74 | 1.5599 | 0.0745 | 0.1562 | 0.0047 | 0.6289 | 954 | 30 | 936 | 26 | 98 | ||
| MJS1-32 | 421 | 198 | 2.13 | 0.1613 | 0.0150 | 0.0165 | 0.0007 | 0.4897 | 152 | 13 | 105 | 5 | 63 | ||
| MJS1-33 | 331 | 411 | 0.81 | 1.3094 | 0.0498 | 0.1418 | 0.0041 | 0.7624 | 850 | 22 | 855 | 23 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-34 | 317 | 237 | 1.34 | 0.2417 | 0.0170 | 0.0146 | 0.0007 | 0.6568 | 220 | 14 | 93 | 4 | 19 | ||
| MJS1-35 | 158 | 470 | 0.34 | 9.3187 | 0.3125 | 0.4470 | 0.0128 | 0.8506 | 2370 | 31 | 2382 | 57 | 99 | ||
| MJS1-36 | 103 | 59.3 | 1.74 | 0.5912 | 0.0435 | 0.0199 | 0.0010 | 0.6665 | 472 | 28 | 127 | 6 | -15 | ||
| MJS1-37 | 247 | 126 | 1.96 | 0.1697 | 0.0192 | 0.0170 | 0.0007 | 0.3798 | 159 | 17 | 109 | 5 | 62 | ||
| MJS1-38 | 48.0 | 2889 | 0.02 | 4.5771 | 0.1530 | 0.2801 | 0.0079 | 0.8461 | 1745 | 28 | 1592 | 40 | 90 | ||
| MJS1-39 | 83.2 | 46.9 | 1.77 | 0.8321 | 0.1436 | 0.0210 | 0.0013 | 0.3580 | 615 | 80 | 134 | 8 | -29 | ||
| MJS1-40 | 28.7 | 98.8 | 0.29 | 4.3474 | 0.1725 | 0.2537 | 0.0078 | 0.7774 | 1702 | 33 | 1457 | 40 | 84 | ||
| MJS1-41 | 139 | 156 | 0.89 | 1.1492 | 0.0430 | 0.1105 | 0.0035 | 0.8357 | 777 | 20 | 675 | 20 | 86 | ||
| MJS1-42 | 69.6 | 56.0 | 1.24 | 0.5077 | 0.0402 | 0.0187 | 0.0008 | 0.5328 | 417 | 27 | 120 | 5 | -11 | ||
| MJS1-43 | 141 | 45.1 | 3.13 | 1.1436 | 0.1011 | 0.0255 | 0.0013 | 0.5728 | 774 | 48 | 162 | 8 | -31 | ||
| MJS1-44 | 161 | 82.7 | 1.95 | 0.2798 | 0.0241 | 0.0167 | 0.0007 | 0.4544 | 250 | 19 | 106 | 4 | 19 | ||
| MJS1-45 | 114 | 68.9 | 1.66 | 0.3890 | 0.0393 | 0.0169 | 0.0009 | 0.5013 | 334 | 29 | 108 | 5 | -3 | ||
| MJS1-46 | 66.4 | 60.5 | 1.10 | 0.0909 | 0.0127 | 0.0146 | 0.0006 | 0.3046 | 88 | 12 | 93 | 4 | 94 | ||
| MJS1-47 | 225 | 103 | 2.18 | 0.2056 | 0.0256 | 0.0172 | 0.0008 | 0.3627 | 190 | 22 | 110 | 5 | 46 | ||
| MJS1-48 | 136 | 84.1 | 1.61 | 0.2183 | 0.0183 | 0.0150 | 0.0005 | 0.4174 | 200 | 15 | 96 | 3 | 29 | ||
| MJS1-49 | 94.2 | 77.7 | 1.21 | 0.2549 | 0.0265 | 0.0170 | 0.0007 | 0.4050 | 231 | 21 | 109 | 5 | 28 | ||
| MJS1-50 | 138 | 74.3 | 1.86 | 1.5439 | 0.1082 | 0.0285 | 0.0013 | 0.6395 | 948 | 43 | 181 | 8 | -36 | ||
| MJS1-51 | 114 | 81.3 | 1.41 | 0.3728 | 0.0307 | 0.0174 | 0.0007 | 0.4926 | 322 | 23 | 111 | 4 | 2 | ||
| MJS1-52 | 76.9 | 55.5 | 1.39 | 0.6765 | 0.0601 | 0.0189 | 0.0009 | 0.5201 | 525 | 36 | 121 | 6 | -26 | ||
| MJS1-53 | 95.7 | 67.6 | 1.41 | 1.6108 | 0.0844 | 0.0272 | 0.0011 | 0.7843 | 974 | 33 | 173 | 7 | -40 | ||
| MJS1-54 | 268 | 122 | 2.20 | 0.1795 | 0.0133 | 0.0155 | 0.0006 | 0.5023 | 168 | 11 | 99 | 4 | 48 | ||
| MJS1-55 | 61.2 | 47.8 | 1.28 | 0.2149 | 0.0292 | 0.0157 | 0.0008 | 0.3572 | 198 | 24 | 100 | 5 | 34 | ||
| MJS1-56 | 91.1 | 64.3 | 1.42 | 1.5957 | 0.0904 | 0.0282 | 0.0012 | 0.7587 | 969 | 35 | 179 | 8 | -38 | ||
| MJS2 (马脊山, GPS: 31°38'21.51″; E117°52'13.30″) | |||||||||||||||
| MJS2-01 | 619 | 1120 | 0.55 | 1.0239 | 0.0343 | 0.1117 | 0.0030 | 0.8150 | 716 | 17 | 683 | 18 | 95 | ||
| MJS2-02 | 107 | 67.5 | 1.59 | 0.2105 | 0.0241 | 0.0161 | 0.0008 | 0.4494 | 194 | 20 | 103 | 5 | 38 | ||
| MJS2-03 | 62.9 | 34.2 | 1.84 | 5.7043 | 0.2586 | 0.3455 | 0.0111 | 0.7077 | 1932 | 39 | 1913 | 53 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-04 | 421 | 164 | 2.57 | 0.2052 | 0.0227 | 0.0126 | 0.0009 | 0.6550 | 190 | 19 | 81 | 6 | 19 | ||
| MJS2-05 | 161 | 101 | 1.60 | 0.1911 | 0.0283 | 0.0170 | 0.0008 | 0.3200 | 178 | 24 | 109 | 5 | 51 | ||
| MJS2-06 | 1449 | 2244 | 0.65 | 0.3766 | 0.0170 | 0.0356 | 0.0012 | 0.7597 | 325 | 13 | 226 | 8 | 64 | ||
| MJS2-07 | 1871 | 1786 | 1.05 | 1.2222 | 0.0412 | 0.1290 | 0.0036 | 0.8235 | 811 | 19 | 782 | 20 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-08 | 240 | 494 | 0.49 | 1.6106 | 0.0614 | 0.1563 | 0.0046 | 0.7686 | 974 | 24 | 936 | 26 | 95 | ||
| MJS2-10 | 89.6 | 59.4 | 1.51 | 0.8602 | 0.0797 | 0.0197 | 0.0012 | 0.6789 | 630 | 43 | 125 | 8 | -34 | ||
| MJS2-11 | 79.4 | 54.7 | 1.45 | 0.4564 | 0.0689 | 0.0163 | 0.0014 | 0.5566 | 382 | 48 | 104 | 9 | -15 | ||
| MJS2-12 | 768 | 1801 | 0.43 | 1.0012 | 0.0426 | 0.1016 | 0.0034 | 0.7843 | 704 | 22 | 624 | 20 | 87 | ||
| MJS2-13 | 186 | 112 | 1.67 | 0.6444 | 0.0958 | 0.0181 | 0.0014 | 0.5183 | 505 | 59 | 115 | 9 | -26 | ||
| MJS2-14 | 2168 | 2028 | 1.07 | 0.3912 | 0.0228 | 0.0397 | 0.0015 | 0.6534 | 335 | 17 | 251 | 9 | 71 | ||
| MJS2-15 | 137 | 84.3 | 1.62 | 0.2406 | 0.0270 | 0.0160 | 0.0011 | 0.5944 | 219 | 22 | 102 | 7 | 27 | ||
| MJS2-16 | 20.7 | 39.8 | 0.52 | 1.3106 | 0.1138 | 0.1460 | 0.0053 | 0.4208 | 850 | 50 | 878 | 30 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-17 | 61.7 | 53.6 | 1.15 | 0.2366 | 0.0319 | 0.0175 | 0.0011 | 0.4663 | 216 | 26 | 112 | 7 | 36 | ||
| MJS2-18 | 212 | 185 | 1.14 | 0.2460 | 0.0366 | 0.0164 | 0.0010 | 0.4023 | 223 | 30 | 105 | 6 | 27 | ||
| MJS2-19 | 246 | 115 | 2.13 | 0.1256 | 0.0208 | 0.0134 | 0.0007 | 0.3030 | 120 | 19 | 86 | 4 | 67 | ||
| MJS2-20 | 84.2 | 291 | 0.29 | 1.1521 | 0.0673 | 0.1350 | 0.0058 | 0.7380 | 778 | 32 | 816 | 33 | 95 | ||
| MJS2-21 | 382 | 1352 | 0.28 | 0.2889 | 0.0160 | 0.0384 | 0.0015 | 0.7250 | 258 | 13 | 243 | 10 | 94 | ||
| MJS2-22 | 270 | 318 | 0.85 | 9.4692 | 0.3211 | 0.4513 | 0.0132 | 0.8601 | 2385 | 31 | 2401 | 58 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-23 | 247 | 440 | 0.56 | 1.1030 | 0.0625 | 0.1197 | 0.0062 | 0.9149 | 755 | 30 | 729 | 36 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-24 | 67.3 | 54.9 | 1.22 | 0.2509 | 0.0387 | 0.0213 | 0.0014 | 0.4368 | 227 | 31 | 136 | 9 | 49 | ||
| MJS2-26 | 73.1 | 74.2 | 0.99 | 0.3368 | 0.0542 | 0.0170 | 0.0012 | 0.4339 | 295 | 41 | 109 | 8 | 7 | ||
| MJS2-27 | 2687 | 2631 | 1.02 | 0.4015 | 0.0254 | 0.0289 | 0.0012 | 0.6544 | 343 | 18 | 184 | 8 | 39 | ||
| MJS2-28 | 48.6 | 72.0 | 0.68 | 1.4242 | 0.0847 | 0.1521 | 0.0049 | 0.5398 | 899 | 35 | 913 | 27 | 98 | ||
| MJS2-29 | 59.2 | 52.7 | 1.12 | 0.4309 | 0.0777 | 0.0171 | 0.0013 | 0.4147 | 364 | 55 | 109 | 8 | -8 | ||
| MJS2-30 | 57.6 | 88.0 | 0.65 | 1.4370 | 0.0818 | 0.1564 | 0.0050 | 0.5607 | 904 | 34 | 937 | 28 | 96 | ||
| MJS2-31 | 1254 | 1765 | 0.71 | 0.5073 | 0.0202 | 0.0554 | 0.0017 | 0.7707 | 417 | 14 | 348 | 10 | 81 | ||
| MJS2-33 | 413 | 2720 | 0.15 | 0.1947 | 0.0124 | 0.0258 | 0.0012 | 0.7230 | 181 | 11 | 164 | 7 | 90 | ||
| MJS2-35 | 295 | 1255 | 0.23 | 5.9728 | 0.3726 | 0.2984 | 0.0175 | 0.9386 | 1972 | 54 | 1683 | 87 | 84 | ||
| MJS2-36 | 32.4 | 40.0 | 0.81 | 1.9744 | 0.4067 | 0.0475 | 0.0066 | 0.6741 | 1107 | 139 | 299 | 41 | -15 | ||
| MJS2-37 | 173 | 131 | 1.32 | 0.3733 | 0.0559 | 0.0170 | 0.0016 | 0.6294 | 322 | 41 | 109 | 10 | 1 | ||
| MJS2-38 | 88.1 | 82.1 | 1.07 | 0.8060 | 0.1138 | 0.0172 | 0.0017 | 0.6957 | 600 | 64 | 110 | 11 | -39 | ||
| MJS2-39 | 49.9 | 53.8 | 0.93 | 1.8502 | 0.5916 | 0.0465 | 0.0102 | 0.6832 | 1064 | 211 | 293 | 63 | -14 | ||
| MJS2-40 | 172 | 120 | 1.44 | 0.1565 | 0.0167 | 0.0170 | 0.0008 | 0.4646 | 148 | 15 | 109 | 5 | 69 | ||
| MJS2-41 | 73.4 | 55.7 | 1.32 | 3.0716 | 0.3355 | 0.0398 | 0.0032 | 0.7284 | 1426 | 84 | 252 | 20 | -40 | ||
| MJS2-42 | 113 | 76.0 | 1.49 | 0.2898 | 0.0274 | 0.0163 | 0.0007 | 0.4407 | 258 | 22 | 104 | 4 | 14 | ||
| MJS2-43 | 123 | 48.2 | 2.56 | 1.8676 | 0.2755 | 0.0345 | 0.0029 | 0.5757 | 1070 | 98 | 218 | 18 | -33 | ||
| MJS2-44 | 74.8 | 58.4 | 1.28 | 0.1424 | 0.0149 | 0.0154 | 0.0007 | 0.4435 | 135 | 13 | 99 | 5 | 68 | ||
| MJS2-45 | 187 | 112 | 1.67 | 1.2328 | 0.0487 | 0.1448 | 0.0040 | 0.6916 | 816 | 22 | 872 | 22 | 93 | ||
| MJS2-46 | 292 | 278 | 1.05 | 1.2332 | 0.0388 | 0.1341 | 0.0037 | 0.8820 | 816 | 18 | 811 | 21 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-47 | 316 | 252 | 1.25 | 1.3348 | 0.0432 | 0.1437 | 0.0039 | 0.8323 | 861 | 19 | 866 | 22 | 99 | ||
| MJS2-48 | 70.2 | 52.0 | 1.35 | 0.3528 | 0.0250 | 0.0173 | 0.0008 | 0.6649 | 307 | 19 | 110 | 5 | 5 | ||
| MJS2-49 | 51.1 | 45.3 | 1.13 | 0.2009 | 0.0212 | 0.0160 | 0.0008 | 0.4471 | 186 | 18 | 102 | 5 | 41 | ||
| MJS2-50 | 78.4 | 74.0 | 1.06 | 0.3824 | 0.0261 | 0.0164 | 0.0007 | 0.6084 | 329 | 19 | 105 | 4 | -4 | ||
| MJS2-51 | 84.3 | 91.9 | 0.92 | 0.3858 | 0.0496 | 0.0198 | 0.0010 | 0.4086 | 331 | 36 | 126 | 7 | 10 | ||
| MJS2-52 | 143 | 179 | 0.80 | 0.9318 | 0.0424 | 0.0997 | 0.0029 | 0.6448 | 669 | 22 | 612 | 17 | 91 | ||
| MJS2-53 | 107 | 83.4 | 1.29 | 0.9195 | 0.1921 | 0.0212 | 0.0025 | 0.5613 | 662 | 102 | 135 | 16 | -33 | ||
| MJS2-54 | 182 | 154 | 1.18 | 0.2028 | 0.0275 | 0.0173 | 0.0008 | 0.3618 | 188 | 23 | 110 | 5 | 48 | ||
| MJS2-55 | 101 | 60.3 | 1.68 | 0.9474 | 0.1023 | 0.0248 | 0.0016 | 0.5927 | 677 | 53 | 158 | 10 | -25 | ||
| MJS2-56 | 91.6 | 70.3 | 1.30 | 0.3993 | 0.0412 | 0.0173 | 0.0010 | 0.5423 | 341 | 30 | 111 | 6 | -3 | ||
| XHS2 (向核山南坡, GPS: 31°40'46.51″; E117°50'36.57″) | |||||||||||||||
| XHS2-01 | 321 | 181 | 1.77 | 0.2175 | 0.0295 | 0.0153 | 0.0008 | 0.3901 | 200 | 25 | 98 | 5 | 31 | ||
| XHS2-02 | 56.0 | 297 | 0.19 | 0.1271 | 0.0096 | 0.0175 | 0.0006 | 0.4300 | 121 | 9 | 112 | 4 | 91 | ||
| XHS2-03 | 366 | 339 | 1.08 | 1.0247 | 0.0643 | 0.1293 | 0.0049 | 0.6070 | 716 | 32 | 784 | 28 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-04 | 172 | 97.4 | 1.77 | 0.1088 | 0.0113 | 0.0164 | 0.0007 | 0.3964 | 105 | 10 | 105 | 4 | 99 | ||
| XHS2-05 | 146 | 84.9 | 1.72 | 0.3934 | 0.0669 | 0.0158 | 0.0012 | 0.4509 | 337 | 49 | 101 | 8 | -8 | ||
| XHS2-06 | 2927 | 3045 | 0.96 | 0.7190 | 0.0439 | 0.0806 | 0.0046 | 0.9268 | 550 | 26 | 500 | 27 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-07 | 202 | 701 | 0.29 | 1.0071 | 0.0497 | 0.1045 | 0.0047 | 0.9065 | 707 | 25 | 641 | 27 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-08 | 170 | 131 | 1.30 | 0.4198 | 0.0540 | 0.0126 | 0.0010 | 0.6361 | 356 | 39 | 80 | 7 | -27 | ||
| XHS2-09 | 83.7 | 140 | 0.60 | 4.2314 | 0.2153 | 0.2493 | 0.0091 | 0.7133 | 1680 | 42 | 1435 | 47 | 84 | ||
| XHS2-10 | 63.1 | 60.9 | 1.04 | 0.7145 | 0.1272 | 0.0235 | 0.0025 | 0.6018 | 547 | 75 | 150 | 16 | -15 | ||
| XHS2-11 | 70.8 | 61.9 | 1.14 | 0.3267 | 0.0793 | 0.0161 | 0.0011 | 0.2788 | 287 | 61 | 103 | 7 | 5 | ||
| XHS2-12 | 54.2 | 57.1 | 0.95 | 0.1978 | 0.0309 | 0.0176 | 0.0012 | 0.4285 | 183 | 26 | 112 | 7 | 51 | ||
| XHS2-13 | 345 | 579 | 0.60 | 1.2627 | 0.0566 | 0.1376 | 0.0046 | 0.7435 | 829 | 25 | 831 | 26 | 99 | ||
| XHS2-14 | 79.3 | 71.7 | 1.11 | 0.2270 | 0.0438 | 0.0130 | 0.0009 | 0.3696 | 208 | 36 | 83 | 6 | 14 | ||
| XHS2-15 | 312 | 254 | 1.23 | 1.3651 | 0.0675 | 0.1404 | 0.0044 | 0.6332 | 874 | 29 | 847 | 25 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-16 | 130 | 131 | 1.00 | 1.3025 | 0.0801 | 0.1367 | 0.0042 | 0.4991 | 847 | 35 | 826 | 24 | 97 | ||
| XHS2-17 | 198 | 275 | 0.72 | 7.1593 | 0.2446 | 0.3331 | 0.0096 | 0.8479 | 2131 | 30 | 1853 | 47 | 86 | ||
| XHS2-18 | 230 | 449 | 0.51 | 0.1133 | 0.0069 | 0.0173 | 0.0005 | 0.5075 | 109 | 6 | 111 | 3 | 98 | ||
| XHS2-19 | 101 | 201 | 0.50 | 1.2685 | 0.0593 | 0.1326 | 0.0046 | 0.7476 | 832 | 27 | 803 | 26 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-20 | 220 | 331 | 0.67 | 1.1818 | 0.0505 | 0.1355 | 0.0040 | 0.6870 | 792 | 24 | 819 | 23 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-21 | 93.7 | 940 | 0.10 | 4.9467 | 0.1667 | 0.2891 | 0.0086 | 0.8788 | 1810 | 28 | 1637 | 43 | 89 | ||
| XHS2-22 | 94.7 | 154 | 0.62 | 1.3617 | 0.0703 | 0.1359 | 0.0042 | 0.6021 | 873 | 30 | 821 | 24 | 93 | ||
| XHS2-23 | 516 | 1414 | 0.36 | 0.8242 | 0.0444 | 0.0767 | 0.0036 | 0.8694 | 610 | 25 | 476 | 21 | 75 | ||
| XHS2-24 | 50.5 | 51.6 | 0.98 | 0.7983 | 0.2211 | 0.0176 | 0.0021 | 0.4280 | 596 | 125 | 113 | 13 | -37 | ||
| XHS2-25 | 166 | 147 | 1.13 | 0.3882 | 0.0781 | 0.0150 | 0.0010 | 0.3480 | 333 | 57 | 96 | 7 | -11 | ||
| XHS2-26 | 284 | 503 | 0.57 | 0.9429 | 0.0588 | 0.0999 | 0.0052 | 0.8288 | 674 | 31 | 614 | 30 | 90 | ||
| XHS2-27 | 45.9 | 67.8 | 0.68 | 0.4698 | 0.0778 | 0.0144 | 0.0012 | 0.5127 | 391 | 54 | 92 | 8 | -24 | ||
| XHS2-28 | 250 | 138 | 1.80 | 0.3236 | 0.0588 | 0.0159 | 0.0009 | 0.3026 | 285 | 45 | 102 | 6 | 5 | ||
| XHS2-29 | 16604 | 10800 | 1.54 | 0.1277 | 0.0075 | 0.0139 | 0.0005 | 0.6530 | 122 | 7 | 89 | 3 | 68 | ||
| XHS2-30 | 444 | 360 | 1.23 | 1.4073 | 0.0987 | 0.1352 | 0.0060 | 0.6317 | 892 | 42 | 817 | 34 | 91 | ||
| XHS2-41 | 58.4 | 46.4 | 1.26 | 0.2751 | 0.0233 | 0.0152 | 0.0007 | 0.5644 | 247 | 19 | 97 | 5 | 12 | ||
| XHS2-42 | 89.7 | 76.3 | 1.18 | 0.3364 | 0.0293 | 0.0170 | 0.0006 | 0.4392 | 294 | 22 | 109 | 4 | 7 | ||
| XHS2-43 | 79.1 | 64.3 | 1.23 | 0.2362 | 0.0168 | 0.0160 | 0.0006 | 0.5300 | 215 | 14 | 102 | 4 | 28 | ||
| XHS2-44 | 68.8 | 81.4 | 0.85 | 0.0933 | 0.0120 | 0.0150 | 0.0006 | 0.2908 | 91 | 11 | 96 | 4 | 94 | ||
| XHS2-45 | 56.4 | 51.1 | 1.10 | 0.1615 | 0.0177 | 0.0163 | 0.0007 | 0.3919 | 152 | 15 | 104 | 4 | 62 | ||
| XHS2-46 | 162 | 178 | 0.91 | 1.3464 | 0.0458 | 0.1410 | 0.0038 | 0.8002 | 866 | 20 | 850 | 22 | 98 | ||
| XHS2-47 | 71.9 | 46.7 | 1.54 | 0.2669 | 0.0240 | 0.0162 | 0.0007 | 0.4624 | 240 | 19 | 104 | 4 | 20 | ||
| XHS2-48 | 153 | 182 | 0.84 | 1.3558 | 0.0471 | 0.1337 | 0.0037 | 0.7893 | 870 | 20 | 809 | 21 | 92 | ||
| XHS2-49 | 350 | 415 | 0.84 | 1.1808 | 0.0410 | 0.1259 | 0.0034 | 0.7885 | 792 | 19 | 764 | 20 | 96 | ||
| XHS2-50 | 67.7 | 57.4 | 1.18 | 0.2220 | 0.0214 | 0.0158 | 0.0006 | 0.4232 | 204 | 18 | 101 | 4 | 32 | ||
| XHS2-51 | 45.0 | 40.0 | 1.13 | 1.3322 | 0.2838 | 0.0309 | 0.0030 | 0.4622 | 860 | 124 | 196 | 19 | -26 | ||
| XHS2-52 | 89.4 | 81.7 | 1.09 | 0.2364 | 0.0203 | 0.0144 | 0.0005 | 0.4148 | 215 | 17 | 92 | 3 | 19 | ||
| XHS2-53 | 81.8 | 75.0 | 1.09 | 0.2252 | 0.0180 | 0.0159 | 0.0006 | 0.4388 | 206 | 15 | 102 | 4 | 32 | ||
| XHS2-54 | 268 | 153 | 1.75 | 0.1666 | 0.0120 | 0.0158 | 0.0006 | 0.4861 | 156 | 10 | 101 | 4 | 57 | ||
| XHS2-55 | 206 | 93.4 | 2.20 | 0.1449 | 0.0128 | 0.0167 | 0.0007 | 0.4791 | 137 | 11 | 107 | 4 | 75 | ||
| XHS2-56 | 341 | 213 | 1.60 | 0.2150 | 0.0130 | 0.0169 | 0.0006 | 0.5423 | 198 | 11 | 108 | 4 | 41 | ||

图9 巢北花岗斑岩的成因判别图解 ((a)Na2O-K2O图解[29];(b)Zr+Nb+Ce+Y与FeOt/MgO、(Na2O+K2O)/CaO图解[30];(c)Rb-Ba-Sr图解[32];(d)A-C-F图解[35];(e)CaO/Na2O-Al2O3/TiO2图解[16];(f)Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr比值图解[16] ;(g)锆石继承年龄的频率直方图和概率密度图)
Fig.9 Genetic discrimination diagrams of the Chaobei granitic porphyries

图10 巢北花岗斑岩的构造背景判别图解 (a)Yb-Ta图解[47];(b)Rb/30-Hf-3Ta图解[48];(c)R1-R2图解[49];(d)Sr/Y-Y图解[51]
Fig.10 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of the Chaobei granitic porphyries
| [1] | ZHU G, LIU C, GU C C, et al. Oceanic plate subduction history in the western Pacific Ocean: Constraint from late Mesozoic evolution of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone[J]. SCIENCE CHINA (Earth Sciences), 2018, 61(4): 386-405. |
| [2] | LI Y X, YAN J, SONG C Z, et al. Petrogenesis of late Mesozoic granitoids from the southern segment of the Tan-Lu Fault, eastern China: implications for the tectonic affinity of the Zhangbaling Uplift[J]. International Geology Review, 2021, 63(4): 453-475. |
| [3] | 胡生平, 韩善楚, 张洪求, 等. 庐枞盆地西湾铅锌矿床黄铁矿微量元素组成特征及成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(1): 183-197. |
| [4] | SUN Y, MA C Q, LIU Y Y. The latest Yanshanian magmatic and metallogenic events in the middle-lower Yangtze River belt: Evidence from the Ningzhen region[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(34): 4308-4318. |
| [5] | 薛怀民. 长江下游宁镇地区晚中生代侵入岩:同位素年龄、地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(1): 147-169. |
| [6] | LUO Z, LING M, LU W, et al. The Genesis of A-Type Granites in Lower Yangtze River Belt: Evidence From Calcium Isotopes[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2024, 25(6):e2023GC011347. |
| [7] | LING M X, WANG F Y, DING X, et al. Different origins of adakites from the Dabie Mountains and the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China: geochemical constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 2011, 53(5/6): 727-740. |
| [8] | 牛漫兰, 朱光, 谢成龙, 等. 郯庐断裂带张八岭隆起南段晚中生代侵入岩地球化学及其对岩石圈减薄的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(9): 2783-2804. |
| [9] | LUO Z B, XUE S, ZHANG L P, et al. Origin of Early Cretaceous Guandian adakitic pluton in central eastern China: partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust triggered by ridge subduction[J]. International Geology Review, 2018, 60(11/14): 1707-1720. |
| [10] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 等. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(6): 1435-1448. |
| [11] | WANG T, NIU M L, WU Q, et al. Episodic bimodal magmatism at an active continental margin due to Paleo-Pacific Plate subduction: A case study from the southern segment of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone, eastern China[J]. Lithos, 2019, 328-329: 159-181. |
| [12] | 李三忠, 李安龙, 范德江, 等. 安徽巢北地区的中生代构造变形及其大地构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(2): 208-217. |
| [13] | 姜子朝, 闫峻, 贾志海, 等. 巢湖地区侵入岩锆石定年[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 37(12): 1493-1498. |
| [14] | MCLENNAN S M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2(4): 203-236. |
| [15] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. A simple classification of volcanic rocks[J]. Bulletin Volcanologique, 1972, 36(2): 382-397. |
| [16] | PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81. |
| [17] | SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1): 29-44. |
| [18] | CHAPPELL B W, BRYANT C J, WYBORN D. Peraluminous I-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2012, 153: 142-153. |
| [19] | WU F Y, LIU X C, JI W Q, et al. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(7): 1201-1219. |
| [20] | BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies[M]// HENDERSONP. Rareearth element geochemistry (Developmentsin Geochemistry, volume 2).Amstenlam; Elsevier. 1984,63-114. |
| [21] | 董国强, 余君鹏, 吴义布, 等. 甘肃合黎山古元古代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学特征及其对阿拉善地块南缘构造环境的约束[J]. 地质通报, 2024, 43(10):1830-1840. |
| [22] | WU Y B, ZHENG Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15): 1554-1569. |
| [23] | 刘建敏, 闫峻, 李全忠, 等. 宁镇地区安基山岩体锆石LA-ICPMSU-Pb定年及意义[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(1): 190-200. |
| [24] | 赵枫, 李龚健, 张鹏飞, 等. 西南三江临沧花岗岩基成因与构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(5): 1397-1412. |
| [25] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 王翠彭, 等. 大兴安岭北段呼玛地区晚石炭世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征:对古亚洲洋构造演化的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(1):62-82. |
| [26] | BONIN B, JANOUŠEK V, MOYEN J-F. Chemical variation, modal composition and classification of granitoids[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2020, 491(1): 9-51. |
| [27] | CLARKE D B. Granitoid Rocks[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Science & Business Media, 1992. |
| [28] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1992, 83(1/2): 1-26. |
| [29] | 王国辉, 王志忠, 严城民. 花岗岩成因类型划分与地球化学图解判别综述[J]. 云南地质, 2019, 38(1): 28-37. |
| [30] | COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200. |
| [31] | WHALEN J, CURRIE K, CHAPPELL B. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. |
| [32] | BONIN B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1): 1-29. |
| [33] | EL BOUSEILY A M, EL SOKKARY A A. The relation between Rb, Ba and Sr in granitic rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 1975, 16(3): 207-219. |
| [34] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 等. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(1): 169-182. |
| [35] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [36] |
尹青青, 唐菊兴, 项新葵, 等. 赣北彭山还原性S型花岗岩成因及其对Sn富集的启示:来自锆石微量元素的证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(3):133-149.
DOI |
| [37] | BROWN M. Granite: From genesis to emplacement[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2013, 125(7/8): 1079-1113. |
| [38] | 钟长汀, 邓晋福, 万渝生, 等. 华北克拉通北缘中段古元古代造山作用的岩浆记录:S型花岗岩地球化学特征及锆石SHRIMP年龄[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(6): 585-600. |
| [39] | MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6): 529-532. |
| [40] | 谢成龙, 陈娟, 刘友勤, 等. 郯庐断裂带张八岭隆起段晚中生代岩浆岩继承锆石U-Pb年代学:源区属性及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(4): 976-1000. |
| [41] | MAO J R, LI Z L, YE H M. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in South China: Retrospect and prospect[J]. SCIENCE CHINA (Earth Sciences), 2014, 57(12): 2853-2877. |
| [42] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 等. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(6): 1609-1623. |
| [43] | 郭锋, 赵亮, 张晓兵, 等. 华南陆块东部晚中生代岩浆作用的深部动力学过程[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2022, 46(3): 416-434. |
| [44] | BAI J H, LING M X, YANG X Y, et al. Yangshan A-Type Granites in the Lower Yangtze River Belt Formed by Ridge Subduction: Radiogenic Ca and Nd Isotopic Constraints[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2022, 33(3): 581-590. |
| [45] | LING M X, WANG F Y, DING X, et al. Cretaceous Ridge Subduction Along the Lower Yangtze River Belt, Eastern China[J]. Economic Geology, 2009, 104(2): 303-321. |
| [46] | 巫建华, 郭国林, 郭佳磊, 等. 中国东部中生代岩浆岩的时空分布及其与热液型铀矿的关系[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5): 1591-1614. |
| [47] | SUN W, DING X, HU Y H, et al. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(3): 533-542. |
| [48] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. |
| [49] | HARRIS N B W, PEARCE J A, TINDLE A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 19(1): 67-81. |
| [50] | BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1): 43-55. |
| [51] | CASTILLO P R. An overview of adakite petrogenesis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(3): 257-268. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 张一范, 高远, 陈积权, 黄帅, 海伦, 毋正轩, 杨柳, 董甜. 松辽盆地晚白垩世湖相白云岩碳氧同位素特征及其古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1243-1253. |
| [4] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [5] | 杨文鹏, 李成禄, 杨元江, 符安宗, 郑博, 周腾飞, 赵瑞君. 黑龙江塔溪地区中侏罗世侵入岩地球化学特征、成因及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 390-403. |
| [6] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [7] | 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 王建田, 王利鹏, 赵鹏飞. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 876-897. |
| [8] | 符安宗, 杨文鹏, 刘渊, 赵寒冬, 王贵鹏, 石国明, 李金明, 邓昌州. 大兴安岭中段碾子山地区晚三叠世埃达克质侵入岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 266-281. |
| [9] | 李秀章, 王立功, 李衣鑫, 王英鹏, 于晓卫, 张文, 郭瑞朋, 刘汉栋. 胶东艾山岩体二长花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Lu-Hf同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 333-346. |
| [10] | 张宏辉, 袁永盛, 余杨忠, 李鸿, 张沥元, 李致伟, 郭太堂, 潘江涛, 詹华思, 石海涛. 扬子板块西缘中生代—新生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自峨眉山玄武岩的锆石U-Pb同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1155-1177. |
| [11] | 刘洋, 方念乔, 强萌麟, 贾磊, 宋超杰. 粤桂地区白垩纪中期安山岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 968-980. |
| [12] | 张宇, 唐名鹰, 崔霄峰, 何玉良, 董卫东. 西昆仑东段苏巴什洋向北俯冲:来自早—中二叠世火山岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 763-775. |
| [13] | 刘畅, 杨竹森, 徐培言, 赵晓燕, 夏文杰, 杨晓旭. 冈底斯西段麻木矽卡岩型铅锌矿化区岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 466-476. |
| [14] | 寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260. |
| [15] | 李岱鲜, 康志强, 刘迪, 陈欢, 曹延, 韦乃韶, 韦天伟, 王睿, 刘冬梅, 周桐, 蓝海洋. 桂东南云开地区回龙岩体的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1015-1027. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||