



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 964-980.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.036
潘少军( ), 陈小友*(
), 陈小友*( ), 张建芳, 曾凡飞, 顾明光, 马俊祥
), 张建芳, 曾凡飞, 顾明光, 马俊祥
出版日期:2025-08-10
发布日期:2025-08-27
通信作者:
*陈小友,男,高级工程师,1979年出生,主要从事区域地质调查研究工作。Email: 414177270@qq.com。作者简介:潘少军,男,地质工程师,1986年出生,主要从事区域地质调查研究工作。Email:751151749@qq.com。
基金资助:
PAN Shaojun( ), CHEN Xiaoyou*(
), CHEN Xiaoyou*( ), ZHANG Jianfang, ZENG Fanfei, GU Mingguang, MA Junxiang
), ZHANG Jianfang, ZENG Fanfei, GU Mingguang, MA Junxiang
Published:2025-08-10
Online:2025-08-27
摘要:
浙东南沿海地区是否存在晚白垩世火山岩,以及如何厘定其成岩年龄,一直是该区域地质研究中的难点问题。以南雁荡山地区白云山火山机构为研究对象,开展锆石U-Pb测年工作,获得了8套高精度测年数据,4套火山岩和1套正长斑岩的年龄分布于90.32~98.37 Ma,确认该地区在晚白垩世仍存在强烈的火山活动。对6套晚白垩世火山岩样品开展地球化学特征研究,主量元素呈现高硅、富碱、低铝,贫钙、铁、镁、磷、钛,高分异度等特征;微量及稀土元素呈现出大离子亲石元素Rb、K、Th、U等富集,Co、Ni、Cr等亲铁元素含量低,且贫Ba、Nb、Sr、P、Ti等元素的特征;反映了该套火山岩属于准铝质-过铝质高钾钙碱性岩石,具有高结晶分异演化程度和壳源特征。通过火山岩成因探讨,认为由于太平洋板块的俯冲作用,导致浙江东南部自晚侏罗世以来上地壳挤压-伸展拉张作用一直持续到晚白垩世,造就了南雁荡山地区晚白垩世火山活动。浙江东南区域不断有新的晚白垩世火山岩被发现,且岩性、地球化学组合特征与小雄组并不完全一致,为了更好地“安置”晚白垩世火山岩地层,建议新建“雁荡山群”,并根据岩性组合和地球化学特征在群内建立不同的“组-段”地层单元。
中图分类号:
潘少军, 陈小友, 张建芳, 曾凡飞, 顾明光, 马俊祥. 浙江南雁荡山晚白垩世火山岩及地层厘定[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 964-980.
PAN Shaojun, CHEN Xiaoyou, ZHANG Jianfang, ZENG Fanfei, GU Mingguang, MA Junxiang. Late Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks and Stratigraphic Delimitation in the Nanyandang Mountain Area, Southeastern Zhejiang[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(04): 964-980.

图2 流纹质(熔结)凝灰岩(a)—(f)、流纹岩(g)及正长斑岩(h)显微照片(正交偏光) (a)熔结凝灰结构;(b)凝灰结构;(c)钾长石呈港湾状溶蚀;(d)钾长石呈穿孔状溶蚀;(e)塑性玻屑;(f) 鸡骨状、条纹状等多形状玻屑;(g)流纹构造;(h)斜长石的正边结构;Or.钾长石;Pl.斜长石
Fig.2 Microphotograph of rhyolitic (fused) tuff (a)-(f), rhyolite (g), and syenite porphyry (h)(orthogonally polarized)

图3 研究区火山岩代表性锆石的阴极发光图像、LA-ICP-MS分析点位及206Pb/238U年龄
Fig. 3 CL images, localities of the points for LA-ICP-MS measurements and the 206Pb/238U apparent ages of representative detected zircons in the study area
| 测点编号 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/235U±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | 208Pb/232Th±σ | 207Pb/235U±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | 208Pb/232Th±σ | ||||||||||
| ①样品QD047,流纹岩;采样坐标:120°07'49″E,27°29'12″N;16个点加权平均年龄98.37±0.88 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| QD047-01 | 0.87 | 0.11618±0.00558 | 0.01584±0.00035 | 0.00564±0.00041 | 111.6±5.07 | 101.3±2.22 | 113.8±8.23 | ||||||||
| QD047-02 | 0.73 | 0.10229±0.00395 | 0.01529±0.00028 | 0.0047±0.00028 | 98.9±3.64 | 97.8±1.76 | 94.7±5.65 | ||||||||
| QD047-03 | 0.91 | 0.0982±0.00394 | 0.0152±0.00028 | 0.00484±0.00027 | 95.1±3.64 | 97.3±1.81 | 97.6±5.42 | ||||||||
| QD047-04 | 0.99 | 0.1057±0.00463 | 0.01525±0.00029 | 0.00472±0.00025 | 102±4.25 | 97.6±1.86 | 95.2±5.13 | ||||||||
| QD047-05 | 0.85 | 0.11131±0.00402 | 0.01518±0.00022 | 0.00554±0.00030 | 107.2±3.67 | 97.1±1.41 | 111.7±6.07 | ||||||||
| QD047-06 | 0.74 | 0.09806±0.00323 | 0.01537±0.00025 | 0.00493±0.00028 | 95±2.98 | 98.3±1.58 | 99.4±5.73 | ||||||||
| QD047-07 | 0.80 | 0.10683±0.00489 | 0.01579±0.00039 | 0.00554±0.00038 | 103.1±4.49 | 101±2.49 | 111.6±7.72 | ||||||||
| QD047-08 | 0.90 | 0.10074±0.00345 | 0.01533±0.00029 | 0.00508±0.00022 | 97.5±3.18 | 98.1±1.83 | 102.4±4.34 | ||||||||
| QD047-09 | 0.76 | 0.11046±0.00337 | 0.01527±0.00027 | 0.00494±0.00022 | 106.4±3.09 | 97.7±1.71 | 99.6±4.50 | ||||||||
| QD047-10 | 1.08 | 0.10062±0.00358 | 0.01548±0.00029 | 0.00475±0.00019 | 97.3±3.31 | 99±1.86 | 95.9±3.85 | ||||||||
| QD047-11 | 1.04 | 0.10187±0.00317 | 0.01547±0.00028 | 0.00497±0.00023 | 98.5±2.92 | 99±1.79 | 100.3±4.59 | ||||||||
| QD047-12 | 1.02 | 0.10391±0.00414 | 0.01537±0.00028 | 0.00469±0.00020 | 100.4±3.81 | 98.3±1.78 | 94.5±4.04 | ||||||||
| QD047-13 | 0.95 | 0.10055±0.00369 | 0.01555±0.00032 | 0.00504±0.00021 | 97.3±3.41 | 99.4±2.02 | 101.6±4.17 | ||||||||
| QD047-14 | 1.06 | 0.10612±0.00315 | 0.0152±0.00027 | 0.00485±0.00020 | 102.4±2.89 | 97.3±1.69 | 97.8±4.02 | ||||||||
| QD047-15 | 0.83 | 0.10073±0.00329 | 0.01546±0.00023 | 0.00519±0.00026 | 97.4±3.03 | 98.9±1.44 | 104.7±5.20 | ||||||||
| QD047-16 | 0.76 | 0.11088±0.00787 | 0.01555±0.00038 | 0.00505±0.00044 | 106.8±7.19 | 99.5±2.39 | 101.9±8.93 | ||||||||
| ②样品QD086,流纹质角砾熔结凝灰岩;采样坐标:120°10'41″E,27°34'14″N;10个点加权平均年龄90.32±0.95 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| QD086-01 | 0.85 | 0.10192±0.00212 | 0.01428±0.00010 | 0.00473±0.00006 | 98.5±1.95 | 91.4±0.64 | 95.4±1.17 | ||||||||
| QD086-02 | 0.55 | 0.09413±0.00265 | 0.01429±0.00012 | 0.00441±0.00008 | 91.3±2.46 | 91.5±0.76 | 89±1.59 | ||||||||
| QD086-03 | 0.74 | 0.13398±0.00612 | 0.0143±0.00016 | 0.00504±0.00011 | 127.7±5.48 | 91.5±1.04 | 101.7±2.28 | ||||||||
| QD086-04 | 0.90 | 0.11219±0.00222 | 0.0143±0.00009 | 0.00483±0.00007 | 108±2.03 | 91.6±0.59 | 97.3±1.33 | ||||||||
| QD086-05 | 0.93 | 0.12286±0.00249 | 0.01431±0.00009 | 0.0051±0.00007 | 117.7±2.26 | 91.6±0.58 | 102.8±1.34 | ||||||||
| QD086-06 | 0.90 | 0.10337±0.00229 | 0.01438±0.00013 | 0.00476±0.00007 | 99.9±2.11 | 92±0.83 | 96±1.49 | ||||||||
| QD086-07 | 0.96 | 0.15694±0.00658 | 0.01446±0.00015 | 0.00576±0.00014 | 148±5.78 | 92.5±0.92 | 116±2.82 | ||||||||
| QD086-08 | 0.57 | 0.11388±0.00335 | 0.01446±0.00009 | 0.0052±0.00011 | 109.5±3.05 | 92.6±0.60 | 104.8±2.13 | ||||||||
| QD086-09 | 0.82 | 0.17573±0.00850 | 0.01453±0.00018 | 0.00673±0.00018 | 164.4±7.34 | 93±1.12 | 135.6±3.66 | ||||||||
| QD086-10 | 0.71 | 0.20156±0.00665 | 0.01457±0.00014 | 0.00712±0.00017 | 186.4±5.62 | 93.3±0.89 | 143.4±3.33 | ||||||||
| ③样品D1548,流纹质角砾晶屑熔结凝岩;采样坐标:120°08'39″E,27°31'33″N;19个点加权平均年龄93.3±1.0 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1548-01 | 0.52 | 0.09728±0.00707 | 0.01503±0.00032 | 0.00476±0.00023 | 94.3±6.54 | 96.2±2.02 | 96±4.58 | ||||||||
| D1548-02 | 0.53 | 0.10199±0.00493 | 0.01485±0.00019 | 0.0049±0.00012 | 98.6±4.55 | 95±1.24 | 98.9±2.45 | ||||||||
| D1548-03 | 0.6 | 0.10334±0.00495 | 0.01456±0.00020 | 0.00484±0.00015 | 99.9±4.55 | 93.2±1.25 | 97.6±2.98 | ||||||||
| D1548-04 | 0.59 | 0.09337±0.00559 | 0.01464±0.00022 | 0.00485±0.00017 | 90.6±5.19 | 93.7±1.39 | 97.9±3.44 | ||||||||
| D1548-05 | 0.62 | 0.09947±0.00968 | 0.01398±0.00028 | 0.00442±0.00023 | 96.3±8.94 | 89.5±1.75 | 89.2±4.60 | ||||||||
| D1548-06 | 0.56 | 0.10235±0.00599 | 0.01429±0.00023 | 0.00435±0.00017 | 98.9±5.52 | 91.5±1.44 | 87.7±3.34 | ||||||||
| D1548-07 | 0.65 | 0.09993±0.00701 | 0.01392±0.00026 | 0.0047±0.00020 | 96.7±6.47 | 89.1±1.66 | 94.7±4.04 | ||||||||
| D1548-08 | 1.25 | 0.09263±0.00688 | 0.01462±0.00025 | 0.00456±0.00012 | 90±6.39 | 93.6±1.60 | 92±2.47 | ||||||||
| D1548-09 | 0.66 | 0.10247±0.00509 | 0.01467±0.00021 | 0.00481±0.00015 | 99±4.69 | 93.9±1.31 | 96.9±3.11 | ||||||||
| D1548-10 | 0.68 | 0.09897±0.00345 | 0.01487±0.00017 | 0.00484±0.00010 | 95.8±3.19 | 95.2±1.08 | 97.6±2.06 | ||||||||
| D1548-11 | 0.58 | 0.08559±0.00643 | 0.0139±0.00033 | 0.0044±0.00021 | 83.4±6.01 | 89±2.07 | 88.7±4.17 | ||||||||
| D1548-12 | 0.58 | 0.09985±0.00605 | 0.01447±0.00019 | 0.00472±0.00013 | 96.6±5.59 | 92.6±1.22 | 95.1±2.66 | ||||||||
| D1548-13 | 0.63 | 0.09537±0.00438 | 0.01484±0.00018 | 0.00472±0.00013 | 92.5±4.06 | 94.9±1.17 | 95.1±2.58 | ||||||||
| D1548-14 | 0.67 | 0.10075±0.00758 | 0.01403±0.00032 | 0.00479±0.00019 | 97.5±6.99 | 89.8±2.03 | 96.6±3.91 | ||||||||
| D1548-15 | 0.48 | 0.1058±0.00922 | 0.01494±0.00038 | 0.00511±0.00033 | 102.1±8.47 | 95.6±2.40 | 103.1±6.56 | ||||||||
| D1548-16 | 0.52 | 0.09688±0.00814 | 0.015±0.00017 | 0.00446±0.00020 | 93.9±7.53 | 96±1.10 | 90±4.06 | ||||||||
| D1548-17 | 0.57 | 0.09886±0.00645 | 0.01415±0.00025 | 0.0048±0.00019 | 95.7±5.96 | 90.5±1.56 | 96.7±3.82 | ||||||||
| D1548-18 | 0.61 | 0.10639±0.00691 | 0.01453±0.00022 | 0.00461±0.00016 | 102.7±6.34 | 93±1.39 | 92.9±3.19 | ||||||||
| D1548-19 | 0.61 | 0.09325±0.00473 | 0.0144±0.00021 | 0.00452±0.00014 | 90.5±4.40 | 92.1±1.30 | 91.1±2.85 | ||||||||
| ④样品PM16TW10,流纹质晶玻屑熔结凝灰岩;采样坐标:120°09'08″E,27°34'47″N;19个点加权平均年龄94.8±1.0Ma | |||||||||||||||
| PM16-10-01 | 1.15 | 0.09904±0.00705 | 0.01479±0.00026 | 0.00482±0.00016 | 95.9±6.51 | 94.6±1.65 | 97.1±3.25 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-02 | 1.19 | 0.10192±0.00729 | 0.01412±0.00027 | 0.0047±0.00016 | 98.5±6.72 | 90.4±1.72 | 94.9±3.22 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-03 | 1.85 | 0.10124±0.00642 | 0.01472±0.00026 | 0.00464±0.00013 | 97.9±5.92 | 94.2±1.68 | 93.6±2.54 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-04 | 1.19 | 0.09752±0.00714 | 0.01469±0.00028 | 0.00498±0.00017 | 94.5±6.61 | 94±1.80 | 100.4±3.34 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-05 | 1.18 | 0.10901±0.00892 | 0.01505±0.00031 | 0.00464±0.00021 | 105.1±8.17 | 96.3±2.00 | 93.5±4.29 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-06 | 1.51 | 0.1091±0.00758 | 0.01508±0.00030 | 0.00491±0.00016 | 105.1±6.94 | 96.5±1.93 | 99±3.30 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-07 | 2.91 | 0.10339±0.00643 | 0.01483±0.00023 | 0.00465±0.00011 | 99.9±5.92 | 94.9±1.49 | 93.8±2.20 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-08 | 1.16 | 0.10929±0.00775 | 0.01537±0.00031 | 0.00478±0.00017 | 105.3±7.10 | 98.3±1.94 | 96.3±3.42 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-09 | 1.40 | 0.10814±0.00682 | 0.01531±0.00035 | 0.00524±0.00016 | 104.3±6.25 | 98±2.19 | 105.7±3.20 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-10 | 1.14 | 0.10692±0.00759 | 0.01498±0.00034 | 0.00465±0.00016 | 103.1±6.97 | 95.9±2.14 | 93.8±3.26 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-11 | 2.40 | 0.09755±0.00725 | 0.01474±0.00024 | 0.00486±0.00012 | 94.5±6.70 | 94.4±1.54 | 98±2.34 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-12 | 1.31 | 0.10514±0.00796 | 0.01442±0.00034 | 0.00502±0.00019 | 101.5±7.31 | 92.3±2.17 | 101.2±3.82 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-13 | 2.68 | 0.10284±0.00702 | 0.01498±0.00027 | 0.00461±0.00011 | 99.4±6.47 | 95.8±1.72 | 93±2.30 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-14 | 0.85 | 0.08625±0.00933 | 0.0144±0.00042 | 0.00459±0.00023 | 84±8.72 | 92.2±2.68 | 92.5±4.53 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-15 | 1.24 | 0.09792±0.00816 | 0.01488±0.00031 | 0.00452±0.00019 | 94.9±7.54 | 95.2±1.99 | 91.1±3.79 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-16 | 1.93 | 0.0975±0.00620 | 0.01437±0.00023 | 0.00473±0.00012 | 94.5±5.74 | 92±1.47 | 95.4±2.39 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-17 | 1.24 | 0.09168±0.00666 | 0.01484±0.00031 | 0.00461±0.00015 | 89.1±6.20 | 94.9±1.97 | 93±3.02 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-18 | 1.49 | 0.109±0.00979 | 0.01542±0.00040 | 0.00485±0.00018 | 105±8.97 | 98.6±2.53 | 97.8±3.66 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-19 | 1.23 | 0.10335±0.00844 | 0.01524±0.00030 | 0.00469±0.00019 | 99.9±7.77 | 97.5±1.89 | 94.5±3.78 | ||||||||
| ⑤样品D1045,正长斑岩;采样坐标:120°09'42″E,27°32'49″N;23个点加权平均年龄94.0±1.4 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1045-01 | 0.73 | 0.10016±0.01581 | 0.01382±0.00058 | 0.00484±0.00039 | 96.9±14.59 | 88.5±3.72 | 97.6±7.86 | ||||||||
| D1045-02 | 0.74 | 0.10391±0.01014 | 0.01481±0.00044 | 0.00547±0.00031 | 100.4±9.33 | 94.8±2.80 | 110.2±6.31 | ||||||||
| D1045-03 | 0.67 | 0.09827±0.01072 | 0.01403±0.00052 | 0.00456±0.00032 | 95.2±9.92 | 89.8±3.30 | 92±6.35 | ||||||||
| D1045-04 | 0.71 | 0.09919±0.01519 | 0.01476±0.00048 | 0.00475±0.00029 | 96±14.03 | 94.5±3.08 | 95.7±5.82 | ||||||||
| D1045-05 | 0.77 | 0.08961±0.01106 | 0.01503±0.00052 | 0.00459±0.00031 | 87.1±10.31 | 96.2±3.28 | 92.7±6.28 | ||||||||
| D1045-06 | 0.73 | 0.10578±0.00758 | 0.01456±0.00027 | 0.00489±0.00018 | 102.1±6.96 | 93.2±1.69 | 98.6±3.68 | ||||||||
| D1045-07 | 1.23 | 0.10097±0.01255 | 0.01426±0.00050 | 0.00525±0.00023 | 97.7±11.58 | 91.3±3.17 | 105.8±4.65 | ||||||||
| D1045-08 | 0.74 | 0.10197±0.01051 | 0.01426±0.00043 | 0.0042±0.00025 | 98.6±9.68 | 91.3±2.75 | 84.8±5.00 | ||||||||
| D1045-09 | 0.98 | 0.09361±0.00816 | 0.01374±0.00036 | 0.00469±0.00025 | 90.9±7.58 | 88±2.27 | 94.5±4.96 | ||||||||
| D1045-10 | 0.83 | 0.09071±0.00649 | 0.01441±0.00029 | 0.00422±0.00016 | 88.2±6.04 | 92.2±1.86 | 85.1±3.16 | ||||||||
| D1045-11 | 0.82 | 0.10602±0.00863 | 0.01484±0.00033 | 0.00462±0.00018 | 102.3±7.92 | 94.9±2.12 | 93.2±3.56 | ||||||||
| D1045-12 | 0.78 | 0.09032±0.00941 | 0.01458±0.00041 | 0.00454±0.00020 | 87.8±8.77 | 93.3±2.63 | 91.5±4.01 | ||||||||
| D1045-13 | 0.78 | 0.09579±0.01045 | 0.01436±0.00036 | 0.00446±0.00023 | 92.9±9.68 | 91.9±2.30 | 90±4.63 | ||||||||
| D1045-14 | 0.84 | 0.10492±0.00868 | 0.01444±0.00037 | 0.00497±0.00021 | 101.3±7.97 | 92.5±2.32 | 100.1±4.24 | ||||||||
| D1045-15 | 0.74 | 0.10672±0.00732 | 0.01554±0.00034 | 0.00493±0.00021 | 103±6.72 | 99.4±2.16 | 99.5±4.14 | ||||||||
| D1045-16 | 0.82 | 0.11381±0.01290 | 0.0157±0.00049 | 0.00469±0.00026 | 109.4±11.76 | 100.4±3.09 | 94.5±5.17 | ||||||||
| D1045-17 | 0.69 | 0.09849±0.00853 | 0.01563±0.00040 | 0.00416±0.00022 | 95.4±7.89 | 100±2.51 | 83.9±4.45 | ||||||||
| D1045-18 | 0.64 | 0.09122±0.00660 | 0.01438±0.00025 | 0.00423±0.00017 | 88.6±6.15 | 92±1.62 | 85.2±3.34 | ||||||||
| D1045-19 | 0.64 | 0.10141±0.00797 | 0.01466±0.00028 | 0.00515±0.00024 | 98.1±7.35 | 93.8±1.80 | 103.9±4.76 | ||||||||
| D1045-20 | 0.76 | 0.09809±0.00846 | 0.01516±0.00033 | 0.00465±0.00020 | 95±7.82 | 97±2.07 | 93.9±4.11 | ||||||||
| D1045-21 | 0.77 | 0.11492±0.01016 | 0.01562±0.00052 | 0.00497±0.00031 | 110.5±9.25 | 99.9±3.30 | 100.2±6.24 | ||||||||
| D1045-22 | 0.80 | 0.09944±0.01005 | 0.01528±0.00044 | 0.00482±0.00024 | 96.3±9.28 | 97.8±2.82 | 97.1±4.91 | ||||||||
| D1045-23 | 0.91 | 0.08616±0.00787 | 0.01429±0.00051 | 0.00525±0.00033 | 83.9±7.35 | 91.5±3.24 | 105.9±6.54 | ||||||||
| ⑥样品QD050,流纹岩;采样坐标:120°05'58″E,27°30'17″N;16个点加权平均年龄114.3±1.3 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| QD050-01 | 1.44 | 0.12284±0.00578 | 0.01781±0.00042 | 0.00552±0.00033 | 117.6±5.23 | 113.8±2.67 | 111.3±6.54 | ||||||||
| QD050-02 | 1.15 | 0.12698±0.00750 | 0.01822±0.00044 | 0.00538±0.00036 | 121.4±6.75 | 116.4±2.79 | 108.4±7.16 | ||||||||
| QD050-03 | 0.66 | 0.13036±0.00895 | 0.01833±0.00053 | 0.00697±0.00073 | 124.4±8.04 | 117.1±3.33 | 140.4±14.72 | ||||||||
| QD050-04 | 0.94 | 0.11331±0.00619 | 0.01777±0.00059 | 0.00605±0.00057 | 109±5.65 | 113.5±3.76 | 121.8±11.50 | ||||||||
| QD050-05 | 0.88 | 0.11487±0.00466 | 0.01782±0.00037 | 0.00547±0.00034 | 110.4±4.25 | 113.9±2.35 | 110.2±6.86 | ||||||||
| QD050-06 | 1.13 | 0.1234±0.00585 | 0.01788±0.00043 | 0.00569±0.00033 | 118.1±5.28 | 114.2±2.70 | 114.7±6.62 | ||||||||
| QD050-07 | 0.78 | 0.12175±0.00423 | 0.01786±0.00036 | 0.00585±0.00027 | 116.7±3.83 | 114.1±2.27 | 117.9±5.42 | ||||||||
| QD050-08 | 0.99 | 0.12846±0.00628 | 0.01786±0.00040 | 0.00527±0.00026 | 122.7±5.65 | 114.1±2.55 | 106.3±5.25 | ||||||||
| QD050-09 | 2.50 | 0.12228±0.00469 | 0.01782±0.00035 | 0.00529±0.00019 | 117.1±4.24 | 113.9±2.22 | 106.6±3.79 | ||||||||
| QD050-10 | 1.30 | 0.12634±0.00659 | 0.01779±0.00041 | 0.00594±0.00030 | 120.8±5.94 | 113.7±2.61 | 119.8±6.08 | ||||||||
| QD050-11 | 1.12 | 0.12555±0.00503 | 0.0178±0.00039 | 0.00534±0.00027 | 120.1±4.54 | 113.7±2.47 | 107.6±5.34 | ||||||||
| QD050-12 | 0.80 | 0.12482±0.00579 | 0.01788±0.00040 | 0.0061±0.00039 | 119.4±5.23 | 114.3±2.54 | 123±7.93 | ||||||||
| QD050-13 | 1.05 | 0.1262±0.00634 | 0.01769±0.00041 | 0.0056±0.00045 | 120.7±5.72 | 113.1±2.61 | 112.9±9.08 | ||||||||
| QD050-14 | 1.22 | 0.11813±0.00406 | 0.01798±0.00032 | 0.00545±0.00023 | 113.4±3.69 | 114.9±2.05 | 109.9±4.62 | ||||||||
| QD050-15 | 1.65 | 0.11939±0.00680 | 0.01783±0.00044 | 0.0057±0.00035 | 114.5±6.17 | 113.9±2.76 | 114.9±7.06 | ||||||||
| QD050-16 | 1.12 | 0.12392±0.00744 | 0.01798±0.00046 | 0.00618±0.00042 | 118.6±6.72 | 114.9±2.9 | 124.6±8.34 | ||||||||
| ⑦样品D1313,流纹质晶屑熔结凝岩;采样坐标:120°12'17″E,27°35'30″N;25个点加权平均年龄111.2±1.1Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1313-01 | 1.20 | 0.1073±0.00853 | 0.01744±0.00037 | 0.0053±0.00019 | 103.5±7.82 | 111.5±2.36 | 106.8±3.86 | ||||||||
| D1313-02 | 1.09 | 0.11677±0.00980 | 0.01778±0.00035 | 0.00598±0.00019 | 112.1±8.91 | 113.6±2.19 | 120.5±3.81 | ||||||||
| D1313-03 | 1.05 | 0.11417±0.01536 | 0.01797±0.00064 | 0.00555±0.00028 | 109.8±14.00 | 114.8±4.04 | 111.8±5.69 | ||||||||
| D1313-04 | 0.78 | 0.11147±0.00961 | 0.01699±0.00032 | 0.00586±0.00029 | 107.3±8.78 | 108.6±2.03 | 118.2±5.74 | ||||||||
| D1313-05 | 1.36 | 0.11502±0.00858 | 0.01803±0.00034 | 0.00569±0.00016 | 110.5±7.81 | 115.2±2.14 | 114.8±3.31 | ||||||||
| D1313-06 | 0.72 | 0.11626±0.01407 | 0.01783±0.00070 | 0.00592±0.00045 | 111.7±12.79 | 113.9±4.42 | 119.2±8.98 | ||||||||
| D1313-07 | 0.82 | 0.13141±0.00827 | 0.01782±0.00037 | 0.00587±0.00023 | 125.4±7.42 | 113.9±2.32 | 118.2±4.61 | ||||||||
| D1313-08 | 0.75 | 0.13345±0.00887 | 0.01813±0.00042 | 0.00581±0.00029 | 127.2±7.95 | 115.8±2.69 | 117±5.89 | ||||||||
| D1313-09 | 0.75 | 0.1111±0.01616 | 0.01765±0.00062 | 0.00616±0.00052 | 107±14.77 | 112.8±3.94 | 124.1±10.35 | ||||||||
| D1313-10 | 1.01 | 0.11939±0.00998 | 0.01704±0.00039 | 0.00518±0.00021 | 114.5±9.05 | 108.9±2.46 | 104.5±4.24 | ||||||||
| D1313-11 | 1.22 | 0.12903±0.00987 | 0.018±0.00042 | 0.00546±0.00018 | 123.2±8.87 | 115±2.67 | 110.1±3.60 | ||||||||
| D1313-12 | 1.38 | 0.11474±0.00825 | 0.01708±0.00032 | 0.00527±0.00014 | 110.3±7.51 | 109.2±2.00 | 106.2±2.84 | ||||||||
| D1313-13 | 1.26 | 0.11755±0.00854 | 0.01745±0.00032 | 0.00569±0.00018 | 112.9±7.76 | 111.5±2.06 | 114.6±3.63 | ||||||||
| D1313-14 | 0.90 | 0.11188±0.00922 | 0.01735±0.00039 | 0.00557±0.00023 | 107.7±8.42 | 110.9±2.50 | 112.3±4.70 | ||||||||
| D1313-15 | 0.92 | 0.12675±0.00825 | 0.01729±0.00034 | 0.00585±0.00021 | 121.2±7.44 | 110.5±2.15 | 117.9±4.13 | ||||||||
| D1313-16 | 0.81 | 0.11929±0.01081 | 0.01776±0.00038 | 0.00606±0.00027 | 114.4±9.81 | 113.5±2.39 | 122.2±5.36 | ||||||||
| D1313-17 | 0.75 | 0.12202±0.00902 | 0.0171±0.00034 | 0.00546±0.00019 | 116.9±8.16 | 109.3±2.13 | 110.1±3.84 | ||||||||
| D1313-18 | 1.11 | 0.11567±0.00925 | 0.01703±0.00041 | 0.00578±0.00023 | 111.1±8.42 | 108.8±2.60 | 116.4±4.61 | ||||||||
| D1313-19 | 1.14 | 0.12929±0.01308 | 0.01749±0.00048 | 0.00559±0.00027 | 123.5±11.76 | 111.8±3.06 | 112.6±5.45 | ||||||||
| D1313-20 | 0.89 | 0.12494±0.01256 | 0.0174±0.00050 | 0.00516±0.00028 | 119.5±11.34 | 111.2±3.15 | 104.1±5.57 | ||||||||
| D1313-21 | 0.97 | 0.12006±0.00880 | 0.01678±0.00050 | 0.00583±0.00030 | 115.1±7.98 | 107.2±3.14 | 117.5±6.02 | ||||||||
| D1313-22 | 1.19 | 0.11104±0.00676 | 0.01738±0.00032 | 0.00521±0.00015 | 106.9±6.18 | 111.1±2.04 | 105±3.04 | ||||||||
| D1313-23 | 1.41 | 0.10786±0.01542 | 0.01774±0.00070 | 0.00581±0.00030 | 104±14.13 | 113.4±4.42 | 117.1±5.97 | ||||||||
| D1313-24 | 0.67 | 0.12272±0.00738 | 0.01666±0.00027 | 0.00541±0.00020 | 117.5±6.67 | 106.5±1.74 | 109±4.00 | ||||||||
| D1313-25 | 0.64 | 0.11768±0.01070 | 0.01754±0.00039 | 0.00614±0.00029 | 113±9.72 | 112.1±2.48 | 123.6±5.79 | ||||||||
| ⑧样品D1372,流纹质含角砾含晶屑玻屑凝灰岩;采样坐标:120°14'19″E,27°35'43″N;11个点加权平均年龄110.6±1.4 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1372-01 | 1.13 | 0.11271±0.01449 | 0.01788±0.00069 | 0.00592±0.00036 | 108.4±13.22 | 114.2±4.37 | 119.4±7.13 | ||||||||
| D1372-02 | 1.04 | 0.12211±0.01295 | 0.01726±0.00053 | 0.00608±0.00031 | 117±11.72 | 110.3±3.37 | 122.5±6.24 | ||||||||
| D1372-03 | 2.36 | 0.12739±0.00736 | 0.01748±0.00028 | 0.00569±0.00013 | 121.7±6.63 | 111.7±1.76 | 114.7±2.68 | ||||||||
| D1372-04 | 0.82 | 0.12554±0.01073 | 0.01726±0.00033 | 0.0059±0.00025 | 120.1±9.68 | 110.3±2.12 | 119±4.94 | ||||||||
| D1372-05 | 0.66 | 0.12359±0.00784 | 0.01721±0.00028 | 0.00546±0.00017 | 118.3±7.09 | 110±1.79 | 110.1±3.41 | ||||||||
| D1372-06 | 0.89 | 0.1167±0.00792 | 0.01751±0.00032 | 0.00568±0.00019 | 112.1±7.20 | 111.9±2.04 | 114.5±3.83 | ||||||||
| D1372-07 | 1.41 | 0.11973±0.01089 | 0.01699±0.00050 | 0.005±0.00025 | 114.8±9.88 | 108.6±3.19 | 100.8±5.13 | ||||||||
| D1372-08 | 1.14 | 0.12585±0.00997 | 0.01738±0.00032 | 0.00502±0.00016 | 120.4±8.99 | 111.1±2.03 | 101.3±3.13 | ||||||||
| D1372-09 | 0.91 | 0.12624±0.01369 | 0.0172±0.00052 | 0.00545±0.00030 | 120.7±12.34 | 109.9±3.27 | 109.8±6.00 | ||||||||
| D1372-10 | 1.24 | 0.11429±0.00645 | 0.0171±0.00028 | 0.00544±0.00016 | 109.9±5.88 | 109.3±1.77 | 109.6±3.27 | ||||||||
| D1372-11 | 1.30 | 0.12007±0.01515 | 0.01718±0.00059 | 0.00631±0.00031 | 115.1±13.73 | 109.8±3.71 | 127.2±6.32 | ||||||||
表1 研究区火山岩及潜火山岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 年龄分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of volcanic and subvolcanic rocks in the study area
| 测点编号 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄(Ma) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/235U±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | 208Pb/232Th±σ | 207Pb/235U±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | 208Pb/232Th±σ | ||||||||||
| ①样品QD047,流纹岩;采样坐标:120°07'49″E,27°29'12″N;16个点加权平均年龄98.37±0.88 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| QD047-01 | 0.87 | 0.11618±0.00558 | 0.01584±0.00035 | 0.00564±0.00041 | 111.6±5.07 | 101.3±2.22 | 113.8±8.23 | ||||||||
| QD047-02 | 0.73 | 0.10229±0.00395 | 0.01529±0.00028 | 0.0047±0.00028 | 98.9±3.64 | 97.8±1.76 | 94.7±5.65 | ||||||||
| QD047-03 | 0.91 | 0.0982±0.00394 | 0.0152±0.00028 | 0.00484±0.00027 | 95.1±3.64 | 97.3±1.81 | 97.6±5.42 | ||||||||
| QD047-04 | 0.99 | 0.1057±0.00463 | 0.01525±0.00029 | 0.00472±0.00025 | 102±4.25 | 97.6±1.86 | 95.2±5.13 | ||||||||
| QD047-05 | 0.85 | 0.11131±0.00402 | 0.01518±0.00022 | 0.00554±0.00030 | 107.2±3.67 | 97.1±1.41 | 111.7±6.07 | ||||||||
| QD047-06 | 0.74 | 0.09806±0.00323 | 0.01537±0.00025 | 0.00493±0.00028 | 95±2.98 | 98.3±1.58 | 99.4±5.73 | ||||||||
| QD047-07 | 0.80 | 0.10683±0.00489 | 0.01579±0.00039 | 0.00554±0.00038 | 103.1±4.49 | 101±2.49 | 111.6±7.72 | ||||||||
| QD047-08 | 0.90 | 0.10074±0.00345 | 0.01533±0.00029 | 0.00508±0.00022 | 97.5±3.18 | 98.1±1.83 | 102.4±4.34 | ||||||||
| QD047-09 | 0.76 | 0.11046±0.00337 | 0.01527±0.00027 | 0.00494±0.00022 | 106.4±3.09 | 97.7±1.71 | 99.6±4.50 | ||||||||
| QD047-10 | 1.08 | 0.10062±0.00358 | 0.01548±0.00029 | 0.00475±0.00019 | 97.3±3.31 | 99±1.86 | 95.9±3.85 | ||||||||
| QD047-11 | 1.04 | 0.10187±0.00317 | 0.01547±0.00028 | 0.00497±0.00023 | 98.5±2.92 | 99±1.79 | 100.3±4.59 | ||||||||
| QD047-12 | 1.02 | 0.10391±0.00414 | 0.01537±0.00028 | 0.00469±0.00020 | 100.4±3.81 | 98.3±1.78 | 94.5±4.04 | ||||||||
| QD047-13 | 0.95 | 0.10055±0.00369 | 0.01555±0.00032 | 0.00504±0.00021 | 97.3±3.41 | 99.4±2.02 | 101.6±4.17 | ||||||||
| QD047-14 | 1.06 | 0.10612±0.00315 | 0.0152±0.00027 | 0.00485±0.00020 | 102.4±2.89 | 97.3±1.69 | 97.8±4.02 | ||||||||
| QD047-15 | 0.83 | 0.10073±0.00329 | 0.01546±0.00023 | 0.00519±0.00026 | 97.4±3.03 | 98.9±1.44 | 104.7±5.20 | ||||||||
| QD047-16 | 0.76 | 0.11088±0.00787 | 0.01555±0.00038 | 0.00505±0.00044 | 106.8±7.19 | 99.5±2.39 | 101.9±8.93 | ||||||||
| ②样品QD086,流纹质角砾熔结凝灰岩;采样坐标:120°10'41″E,27°34'14″N;10个点加权平均年龄90.32±0.95 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| QD086-01 | 0.85 | 0.10192±0.00212 | 0.01428±0.00010 | 0.00473±0.00006 | 98.5±1.95 | 91.4±0.64 | 95.4±1.17 | ||||||||
| QD086-02 | 0.55 | 0.09413±0.00265 | 0.01429±0.00012 | 0.00441±0.00008 | 91.3±2.46 | 91.5±0.76 | 89±1.59 | ||||||||
| QD086-03 | 0.74 | 0.13398±0.00612 | 0.0143±0.00016 | 0.00504±0.00011 | 127.7±5.48 | 91.5±1.04 | 101.7±2.28 | ||||||||
| QD086-04 | 0.90 | 0.11219±0.00222 | 0.0143±0.00009 | 0.00483±0.00007 | 108±2.03 | 91.6±0.59 | 97.3±1.33 | ||||||||
| QD086-05 | 0.93 | 0.12286±0.00249 | 0.01431±0.00009 | 0.0051±0.00007 | 117.7±2.26 | 91.6±0.58 | 102.8±1.34 | ||||||||
| QD086-06 | 0.90 | 0.10337±0.00229 | 0.01438±0.00013 | 0.00476±0.00007 | 99.9±2.11 | 92±0.83 | 96±1.49 | ||||||||
| QD086-07 | 0.96 | 0.15694±0.00658 | 0.01446±0.00015 | 0.00576±0.00014 | 148±5.78 | 92.5±0.92 | 116±2.82 | ||||||||
| QD086-08 | 0.57 | 0.11388±0.00335 | 0.01446±0.00009 | 0.0052±0.00011 | 109.5±3.05 | 92.6±0.60 | 104.8±2.13 | ||||||||
| QD086-09 | 0.82 | 0.17573±0.00850 | 0.01453±0.00018 | 0.00673±0.00018 | 164.4±7.34 | 93±1.12 | 135.6±3.66 | ||||||||
| QD086-10 | 0.71 | 0.20156±0.00665 | 0.01457±0.00014 | 0.00712±0.00017 | 186.4±5.62 | 93.3±0.89 | 143.4±3.33 | ||||||||
| ③样品D1548,流纹质角砾晶屑熔结凝岩;采样坐标:120°08'39″E,27°31'33″N;19个点加权平均年龄93.3±1.0 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1548-01 | 0.52 | 0.09728±0.00707 | 0.01503±0.00032 | 0.00476±0.00023 | 94.3±6.54 | 96.2±2.02 | 96±4.58 | ||||||||
| D1548-02 | 0.53 | 0.10199±0.00493 | 0.01485±0.00019 | 0.0049±0.00012 | 98.6±4.55 | 95±1.24 | 98.9±2.45 | ||||||||
| D1548-03 | 0.6 | 0.10334±0.00495 | 0.01456±0.00020 | 0.00484±0.00015 | 99.9±4.55 | 93.2±1.25 | 97.6±2.98 | ||||||||
| D1548-04 | 0.59 | 0.09337±0.00559 | 0.01464±0.00022 | 0.00485±0.00017 | 90.6±5.19 | 93.7±1.39 | 97.9±3.44 | ||||||||
| D1548-05 | 0.62 | 0.09947±0.00968 | 0.01398±0.00028 | 0.00442±0.00023 | 96.3±8.94 | 89.5±1.75 | 89.2±4.60 | ||||||||
| D1548-06 | 0.56 | 0.10235±0.00599 | 0.01429±0.00023 | 0.00435±0.00017 | 98.9±5.52 | 91.5±1.44 | 87.7±3.34 | ||||||||
| D1548-07 | 0.65 | 0.09993±0.00701 | 0.01392±0.00026 | 0.0047±0.00020 | 96.7±6.47 | 89.1±1.66 | 94.7±4.04 | ||||||||
| D1548-08 | 1.25 | 0.09263±0.00688 | 0.01462±0.00025 | 0.00456±0.00012 | 90±6.39 | 93.6±1.60 | 92±2.47 | ||||||||
| D1548-09 | 0.66 | 0.10247±0.00509 | 0.01467±0.00021 | 0.00481±0.00015 | 99±4.69 | 93.9±1.31 | 96.9±3.11 | ||||||||
| D1548-10 | 0.68 | 0.09897±0.00345 | 0.01487±0.00017 | 0.00484±0.00010 | 95.8±3.19 | 95.2±1.08 | 97.6±2.06 | ||||||||
| D1548-11 | 0.58 | 0.08559±0.00643 | 0.0139±0.00033 | 0.0044±0.00021 | 83.4±6.01 | 89±2.07 | 88.7±4.17 | ||||||||
| D1548-12 | 0.58 | 0.09985±0.00605 | 0.01447±0.00019 | 0.00472±0.00013 | 96.6±5.59 | 92.6±1.22 | 95.1±2.66 | ||||||||
| D1548-13 | 0.63 | 0.09537±0.00438 | 0.01484±0.00018 | 0.00472±0.00013 | 92.5±4.06 | 94.9±1.17 | 95.1±2.58 | ||||||||
| D1548-14 | 0.67 | 0.10075±0.00758 | 0.01403±0.00032 | 0.00479±0.00019 | 97.5±6.99 | 89.8±2.03 | 96.6±3.91 | ||||||||
| D1548-15 | 0.48 | 0.1058±0.00922 | 0.01494±0.00038 | 0.00511±0.00033 | 102.1±8.47 | 95.6±2.40 | 103.1±6.56 | ||||||||
| D1548-16 | 0.52 | 0.09688±0.00814 | 0.015±0.00017 | 0.00446±0.00020 | 93.9±7.53 | 96±1.10 | 90±4.06 | ||||||||
| D1548-17 | 0.57 | 0.09886±0.00645 | 0.01415±0.00025 | 0.0048±0.00019 | 95.7±5.96 | 90.5±1.56 | 96.7±3.82 | ||||||||
| D1548-18 | 0.61 | 0.10639±0.00691 | 0.01453±0.00022 | 0.00461±0.00016 | 102.7±6.34 | 93±1.39 | 92.9±3.19 | ||||||||
| D1548-19 | 0.61 | 0.09325±0.00473 | 0.0144±0.00021 | 0.00452±0.00014 | 90.5±4.40 | 92.1±1.30 | 91.1±2.85 | ||||||||
| ④样品PM16TW10,流纹质晶玻屑熔结凝灰岩;采样坐标:120°09'08″E,27°34'47″N;19个点加权平均年龄94.8±1.0Ma | |||||||||||||||
| PM16-10-01 | 1.15 | 0.09904±0.00705 | 0.01479±0.00026 | 0.00482±0.00016 | 95.9±6.51 | 94.6±1.65 | 97.1±3.25 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-02 | 1.19 | 0.10192±0.00729 | 0.01412±0.00027 | 0.0047±0.00016 | 98.5±6.72 | 90.4±1.72 | 94.9±3.22 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-03 | 1.85 | 0.10124±0.00642 | 0.01472±0.00026 | 0.00464±0.00013 | 97.9±5.92 | 94.2±1.68 | 93.6±2.54 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-04 | 1.19 | 0.09752±0.00714 | 0.01469±0.00028 | 0.00498±0.00017 | 94.5±6.61 | 94±1.80 | 100.4±3.34 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-05 | 1.18 | 0.10901±0.00892 | 0.01505±0.00031 | 0.00464±0.00021 | 105.1±8.17 | 96.3±2.00 | 93.5±4.29 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-06 | 1.51 | 0.1091±0.00758 | 0.01508±0.00030 | 0.00491±0.00016 | 105.1±6.94 | 96.5±1.93 | 99±3.30 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-07 | 2.91 | 0.10339±0.00643 | 0.01483±0.00023 | 0.00465±0.00011 | 99.9±5.92 | 94.9±1.49 | 93.8±2.20 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-08 | 1.16 | 0.10929±0.00775 | 0.01537±0.00031 | 0.00478±0.00017 | 105.3±7.10 | 98.3±1.94 | 96.3±3.42 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-09 | 1.40 | 0.10814±0.00682 | 0.01531±0.00035 | 0.00524±0.00016 | 104.3±6.25 | 98±2.19 | 105.7±3.20 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-10 | 1.14 | 0.10692±0.00759 | 0.01498±0.00034 | 0.00465±0.00016 | 103.1±6.97 | 95.9±2.14 | 93.8±3.26 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-11 | 2.40 | 0.09755±0.00725 | 0.01474±0.00024 | 0.00486±0.00012 | 94.5±6.70 | 94.4±1.54 | 98±2.34 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-12 | 1.31 | 0.10514±0.00796 | 0.01442±0.00034 | 0.00502±0.00019 | 101.5±7.31 | 92.3±2.17 | 101.2±3.82 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-13 | 2.68 | 0.10284±0.00702 | 0.01498±0.00027 | 0.00461±0.00011 | 99.4±6.47 | 95.8±1.72 | 93±2.30 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-14 | 0.85 | 0.08625±0.00933 | 0.0144±0.00042 | 0.00459±0.00023 | 84±8.72 | 92.2±2.68 | 92.5±4.53 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-15 | 1.24 | 0.09792±0.00816 | 0.01488±0.00031 | 0.00452±0.00019 | 94.9±7.54 | 95.2±1.99 | 91.1±3.79 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-16 | 1.93 | 0.0975±0.00620 | 0.01437±0.00023 | 0.00473±0.00012 | 94.5±5.74 | 92±1.47 | 95.4±2.39 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-17 | 1.24 | 0.09168±0.00666 | 0.01484±0.00031 | 0.00461±0.00015 | 89.1±6.20 | 94.9±1.97 | 93±3.02 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-18 | 1.49 | 0.109±0.00979 | 0.01542±0.00040 | 0.00485±0.00018 | 105±8.97 | 98.6±2.53 | 97.8±3.66 | ||||||||
| PM16-10-19 | 1.23 | 0.10335±0.00844 | 0.01524±0.00030 | 0.00469±0.00019 | 99.9±7.77 | 97.5±1.89 | 94.5±3.78 | ||||||||
| ⑤样品D1045,正长斑岩;采样坐标:120°09'42″E,27°32'49″N;23个点加权平均年龄94.0±1.4 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1045-01 | 0.73 | 0.10016±0.01581 | 0.01382±0.00058 | 0.00484±0.00039 | 96.9±14.59 | 88.5±3.72 | 97.6±7.86 | ||||||||
| D1045-02 | 0.74 | 0.10391±0.01014 | 0.01481±0.00044 | 0.00547±0.00031 | 100.4±9.33 | 94.8±2.80 | 110.2±6.31 | ||||||||
| D1045-03 | 0.67 | 0.09827±0.01072 | 0.01403±0.00052 | 0.00456±0.00032 | 95.2±9.92 | 89.8±3.30 | 92±6.35 | ||||||||
| D1045-04 | 0.71 | 0.09919±0.01519 | 0.01476±0.00048 | 0.00475±0.00029 | 96±14.03 | 94.5±3.08 | 95.7±5.82 | ||||||||
| D1045-05 | 0.77 | 0.08961±0.01106 | 0.01503±0.00052 | 0.00459±0.00031 | 87.1±10.31 | 96.2±3.28 | 92.7±6.28 | ||||||||
| D1045-06 | 0.73 | 0.10578±0.00758 | 0.01456±0.00027 | 0.00489±0.00018 | 102.1±6.96 | 93.2±1.69 | 98.6±3.68 | ||||||||
| D1045-07 | 1.23 | 0.10097±0.01255 | 0.01426±0.00050 | 0.00525±0.00023 | 97.7±11.58 | 91.3±3.17 | 105.8±4.65 | ||||||||
| D1045-08 | 0.74 | 0.10197±0.01051 | 0.01426±0.00043 | 0.0042±0.00025 | 98.6±9.68 | 91.3±2.75 | 84.8±5.00 | ||||||||
| D1045-09 | 0.98 | 0.09361±0.00816 | 0.01374±0.00036 | 0.00469±0.00025 | 90.9±7.58 | 88±2.27 | 94.5±4.96 | ||||||||
| D1045-10 | 0.83 | 0.09071±0.00649 | 0.01441±0.00029 | 0.00422±0.00016 | 88.2±6.04 | 92.2±1.86 | 85.1±3.16 | ||||||||
| D1045-11 | 0.82 | 0.10602±0.00863 | 0.01484±0.00033 | 0.00462±0.00018 | 102.3±7.92 | 94.9±2.12 | 93.2±3.56 | ||||||||
| D1045-12 | 0.78 | 0.09032±0.00941 | 0.01458±0.00041 | 0.00454±0.00020 | 87.8±8.77 | 93.3±2.63 | 91.5±4.01 | ||||||||
| D1045-13 | 0.78 | 0.09579±0.01045 | 0.01436±0.00036 | 0.00446±0.00023 | 92.9±9.68 | 91.9±2.30 | 90±4.63 | ||||||||
| D1045-14 | 0.84 | 0.10492±0.00868 | 0.01444±0.00037 | 0.00497±0.00021 | 101.3±7.97 | 92.5±2.32 | 100.1±4.24 | ||||||||
| D1045-15 | 0.74 | 0.10672±0.00732 | 0.01554±0.00034 | 0.00493±0.00021 | 103±6.72 | 99.4±2.16 | 99.5±4.14 | ||||||||
| D1045-16 | 0.82 | 0.11381±0.01290 | 0.0157±0.00049 | 0.00469±0.00026 | 109.4±11.76 | 100.4±3.09 | 94.5±5.17 | ||||||||
| D1045-17 | 0.69 | 0.09849±0.00853 | 0.01563±0.00040 | 0.00416±0.00022 | 95.4±7.89 | 100±2.51 | 83.9±4.45 | ||||||||
| D1045-18 | 0.64 | 0.09122±0.00660 | 0.01438±0.00025 | 0.00423±0.00017 | 88.6±6.15 | 92±1.62 | 85.2±3.34 | ||||||||
| D1045-19 | 0.64 | 0.10141±0.00797 | 0.01466±0.00028 | 0.00515±0.00024 | 98.1±7.35 | 93.8±1.80 | 103.9±4.76 | ||||||||
| D1045-20 | 0.76 | 0.09809±0.00846 | 0.01516±0.00033 | 0.00465±0.00020 | 95±7.82 | 97±2.07 | 93.9±4.11 | ||||||||
| D1045-21 | 0.77 | 0.11492±0.01016 | 0.01562±0.00052 | 0.00497±0.00031 | 110.5±9.25 | 99.9±3.30 | 100.2±6.24 | ||||||||
| D1045-22 | 0.80 | 0.09944±0.01005 | 0.01528±0.00044 | 0.00482±0.00024 | 96.3±9.28 | 97.8±2.82 | 97.1±4.91 | ||||||||
| D1045-23 | 0.91 | 0.08616±0.00787 | 0.01429±0.00051 | 0.00525±0.00033 | 83.9±7.35 | 91.5±3.24 | 105.9±6.54 | ||||||||
| ⑥样品QD050,流纹岩;采样坐标:120°05'58″E,27°30'17″N;16个点加权平均年龄114.3±1.3 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| QD050-01 | 1.44 | 0.12284±0.00578 | 0.01781±0.00042 | 0.00552±0.00033 | 117.6±5.23 | 113.8±2.67 | 111.3±6.54 | ||||||||
| QD050-02 | 1.15 | 0.12698±0.00750 | 0.01822±0.00044 | 0.00538±0.00036 | 121.4±6.75 | 116.4±2.79 | 108.4±7.16 | ||||||||
| QD050-03 | 0.66 | 0.13036±0.00895 | 0.01833±0.00053 | 0.00697±0.00073 | 124.4±8.04 | 117.1±3.33 | 140.4±14.72 | ||||||||
| QD050-04 | 0.94 | 0.11331±0.00619 | 0.01777±0.00059 | 0.00605±0.00057 | 109±5.65 | 113.5±3.76 | 121.8±11.50 | ||||||||
| QD050-05 | 0.88 | 0.11487±0.00466 | 0.01782±0.00037 | 0.00547±0.00034 | 110.4±4.25 | 113.9±2.35 | 110.2±6.86 | ||||||||
| QD050-06 | 1.13 | 0.1234±0.00585 | 0.01788±0.00043 | 0.00569±0.00033 | 118.1±5.28 | 114.2±2.70 | 114.7±6.62 | ||||||||
| QD050-07 | 0.78 | 0.12175±0.00423 | 0.01786±0.00036 | 0.00585±0.00027 | 116.7±3.83 | 114.1±2.27 | 117.9±5.42 | ||||||||
| QD050-08 | 0.99 | 0.12846±0.00628 | 0.01786±0.00040 | 0.00527±0.00026 | 122.7±5.65 | 114.1±2.55 | 106.3±5.25 | ||||||||
| QD050-09 | 2.50 | 0.12228±0.00469 | 0.01782±0.00035 | 0.00529±0.00019 | 117.1±4.24 | 113.9±2.22 | 106.6±3.79 | ||||||||
| QD050-10 | 1.30 | 0.12634±0.00659 | 0.01779±0.00041 | 0.00594±0.00030 | 120.8±5.94 | 113.7±2.61 | 119.8±6.08 | ||||||||
| QD050-11 | 1.12 | 0.12555±0.00503 | 0.0178±0.00039 | 0.00534±0.00027 | 120.1±4.54 | 113.7±2.47 | 107.6±5.34 | ||||||||
| QD050-12 | 0.80 | 0.12482±0.00579 | 0.01788±0.00040 | 0.0061±0.00039 | 119.4±5.23 | 114.3±2.54 | 123±7.93 | ||||||||
| QD050-13 | 1.05 | 0.1262±0.00634 | 0.01769±0.00041 | 0.0056±0.00045 | 120.7±5.72 | 113.1±2.61 | 112.9±9.08 | ||||||||
| QD050-14 | 1.22 | 0.11813±0.00406 | 0.01798±0.00032 | 0.00545±0.00023 | 113.4±3.69 | 114.9±2.05 | 109.9±4.62 | ||||||||
| QD050-15 | 1.65 | 0.11939±0.00680 | 0.01783±0.00044 | 0.0057±0.00035 | 114.5±6.17 | 113.9±2.76 | 114.9±7.06 | ||||||||
| QD050-16 | 1.12 | 0.12392±0.00744 | 0.01798±0.00046 | 0.00618±0.00042 | 118.6±6.72 | 114.9±2.9 | 124.6±8.34 | ||||||||
| ⑦样品D1313,流纹质晶屑熔结凝岩;采样坐标:120°12'17″E,27°35'30″N;25个点加权平均年龄111.2±1.1Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1313-01 | 1.20 | 0.1073±0.00853 | 0.01744±0.00037 | 0.0053±0.00019 | 103.5±7.82 | 111.5±2.36 | 106.8±3.86 | ||||||||
| D1313-02 | 1.09 | 0.11677±0.00980 | 0.01778±0.00035 | 0.00598±0.00019 | 112.1±8.91 | 113.6±2.19 | 120.5±3.81 | ||||||||
| D1313-03 | 1.05 | 0.11417±0.01536 | 0.01797±0.00064 | 0.00555±0.00028 | 109.8±14.00 | 114.8±4.04 | 111.8±5.69 | ||||||||
| D1313-04 | 0.78 | 0.11147±0.00961 | 0.01699±0.00032 | 0.00586±0.00029 | 107.3±8.78 | 108.6±2.03 | 118.2±5.74 | ||||||||
| D1313-05 | 1.36 | 0.11502±0.00858 | 0.01803±0.00034 | 0.00569±0.00016 | 110.5±7.81 | 115.2±2.14 | 114.8±3.31 | ||||||||
| D1313-06 | 0.72 | 0.11626±0.01407 | 0.01783±0.00070 | 0.00592±0.00045 | 111.7±12.79 | 113.9±4.42 | 119.2±8.98 | ||||||||
| D1313-07 | 0.82 | 0.13141±0.00827 | 0.01782±0.00037 | 0.00587±0.00023 | 125.4±7.42 | 113.9±2.32 | 118.2±4.61 | ||||||||
| D1313-08 | 0.75 | 0.13345±0.00887 | 0.01813±0.00042 | 0.00581±0.00029 | 127.2±7.95 | 115.8±2.69 | 117±5.89 | ||||||||
| D1313-09 | 0.75 | 0.1111±0.01616 | 0.01765±0.00062 | 0.00616±0.00052 | 107±14.77 | 112.8±3.94 | 124.1±10.35 | ||||||||
| D1313-10 | 1.01 | 0.11939±0.00998 | 0.01704±0.00039 | 0.00518±0.00021 | 114.5±9.05 | 108.9±2.46 | 104.5±4.24 | ||||||||
| D1313-11 | 1.22 | 0.12903±0.00987 | 0.018±0.00042 | 0.00546±0.00018 | 123.2±8.87 | 115±2.67 | 110.1±3.60 | ||||||||
| D1313-12 | 1.38 | 0.11474±0.00825 | 0.01708±0.00032 | 0.00527±0.00014 | 110.3±7.51 | 109.2±2.00 | 106.2±2.84 | ||||||||
| D1313-13 | 1.26 | 0.11755±0.00854 | 0.01745±0.00032 | 0.00569±0.00018 | 112.9±7.76 | 111.5±2.06 | 114.6±3.63 | ||||||||
| D1313-14 | 0.90 | 0.11188±0.00922 | 0.01735±0.00039 | 0.00557±0.00023 | 107.7±8.42 | 110.9±2.50 | 112.3±4.70 | ||||||||
| D1313-15 | 0.92 | 0.12675±0.00825 | 0.01729±0.00034 | 0.00585±0.00021 | 121.2±7.44 | 110.5±2.15 | 117.9±4.13 | ||||||||
| D1313-16 | 0.81 | 0.11929±0.01081 | 0.01776±0.00038 | 0.00606±0.00027 | 114.4±9.81 | 113.5±2.39 | 122.2±5.36 | ||||||||
| D1313-17 | 0.75 | 0.12202±0.00902 | 0.0171±0.00034 | 0.00546±0.00019 | 116.9±8.16 | 109.3±2.13 | 110.1±3.84 | ||||||||
| D1313-18 | 1.11 | 0.11567±0.00925 | 0.01703±0.00041 | 0.00578±0.00023 | 111.1±8.42 | 108.8±2.60 | 116.4±4.61 | ||||||||
| D1313-19 | 1.14 | 0.12929±0.01308 | 0.01749±0.00048 | 0.00559±0.00027 | 123.5±11.76 | 111.8±3.06 | 112.6±5.45 | ||||||||
| D1313-20 | 0.89 | 0.12494±0.01256 | 0.0174±0.00050 | 0.00516±0.00028 | 119.5±11.34 | 111.2±3.15 | 104.1±5.57 | ||||||||
| D1313-21 | 0.97 | 0.12006±0.00880 | 0.01678±0.00050 | 0.00583±0.00030 | 115.1±7.98 | 107.2±3.14 | 117.5±6.02 | ||||||||
| D1313-22 | 1.19 | 0.11104±0.00676 | 0.01738±0.00032 | 0.00521±0.00015 | 106.9±6.18 | 111.1±2.04 | 105±3.04 | ||||||||
| D1313-23 | 1.41 | 0.10786±0.01542 | 0.01774±0.00070 | 0.00581±0.00030 | 104±14.13 | 113.4±4.42 | 117.1±5.97 | ||||||||
| D1313-24 | 0.67 | 0.12272±0.00738 | 0.01666±0.00027 | 0.00541±0.00020 | 117.5±6.67 | 106.5±1.74 | 109±4.00 | ||||||||
| D1313-25 | 0.64 | 0.11768±0.01070 | 0.01754±0.00039 | 0.00614±0.00029 | 113±9.72 | 112.1±2.48 | 123.6±5.79 | ||||||||
| ⑧样品D1372,流纹质含角砾含晶屑玻屑凝灰岩;采样坐标:120°14'19″E,27°35'43″N;11个点加权平均年龄110.6±1.4 Ma | |||||||||||||||
| D1372-01 | 1.13 | 0.11271±0.01449 | 0.01788±0.00069 | 0.00592±0.00036 | 108.4±13.22 | 114.2±4.37 | 119.4±7.13 | ||||||||
| D1372-02 | 1.04 | 0.12211±0.01295 | 0.01726±0.00053 | 0.00608±0.00031 | 117±11.72 | 110.3±3.37 | 122.5±6.24 | ||||||||
| D1372-03 | 2.36 | 0.12739±0.00736 | 0.01748±0.00028 | 0.00569±0.00013 | 121.7±6.63 | 111.7±1.76 | 114.7±2.68 | ||||||||
| D1372-04 | 0.82 | 0.12554±0.01073 | 0.01726±0.00033 | 0.0059±0.00025 | 120.1±9.68 | 110.3±2.12 | 119±4.94 | ||||||||
| D1372-05 | 0.66 | 0.12359±0.00784 | 0.01721±0.00028 | 0.00546±0.00017 | 118.3±7.09 | 110±1.79 | 110.1±3.41 | ||||||||
| D1372-06 | 0.89 | 0.1167±0.00792 | 0.01751±0.00032 | 0.00568±0.00019 | 112.1±7.20 | 111.9±2.04 | 114.5±3.83 | ||||||||
| D1372-07 | 1.41 | 0.11973±0.01089 | 0.01699±0.00050 | 0.005±0.00025 | 114.8±9.88 | 108.6±3.19 | 100.8±5.13 | ||||||||
| D1372-08 | 1.14 | 0.12585±0.00997 | 0.01738±0.00032 | 0.00502±0.00016 | 120.4±8.99 | 111.1±2.03 | 101.3±3.13 | ||||||||
| D1372-09 | 0.91 | 0.12624±0.01369 | 0.0172±0.00052 | 0.00545±0.00030 | 120.7±12.34 | 109.9±3.27 | 109.8±6.00 | ||||||||
| D1372-10 | 1.24 | 0.11429±0.00645 | 0.0171±0.00028 | 0.00544±0.00016 | 109.9±5.88 | 109.3±1.77 | 109.6±3.27 | ||||||||
| D1372-11 | 1.30 | 0.12007±0.01515 | 0.01718±0.00059 | 0.00631±0.00031 | 115.1±13.73 | 109.8±3.71 | 127.2±6.32 | ||||||||
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD047 | 75.59 | 0.132 | 12.50 | 1.85 | 0.08 | 0.048 | 0.065 | 0.50 | 3.66 | 5.05 |
| QD086 | 77.27 | 0.096 | 11.51 | 1.61 | 0.38 | 0.028 | 0.067 | 0.40 | 3.45 | 5.17 |
| D1548 | 77.68 | 0.120 | 11.57 | 1.76 | 0.21 | 0.044 | 0.046 | 0.13 | 3.32 | 4.39 |
| PM16-10 | 74.91 | 0.260 | 12.86 | 1.59 | <0.10 | 0.081 | 0.140 | 0.59 | 4.52 | 3.97 |
| PM17-7 | 77.13 | 0.150 | 11.50 | 1.76 | 0.14 | 0.018 | 0.059 | 0.17 | 3.56 | 4.49 |
| PM17-10 | 77.64 | 0.140 | 11.30 | 1.83 | 0.46 | 0.052 | 0.059 | 0.41 | 3.55 | 4.65 |
| 样品编号 | P2O5 | 烧失 | ALK | K/Na | AKI | A/NK | A/CNK | τ | σ | D.I |
| QD047 | 0.014 | 0.48 | 8.71 | 1.38 | 0.92 | 1.09 | 1.01 | 122.42 | 2.32 | 95.01 |
| QD086 | 0.013 | 0.33 | 8.62 | 1.50 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 155.83 | 2.17 | 96.35 |
| D1548 | 0.012 | 0.41 | 7.71 | 1.32 | 0.88 | 1.13 | 1.11 | 124.08 | 1.71 | 95.81 |
| PM16-10 | 0.037 | 0.53 | 8.49 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 1.10 | 1.01 | 66.85 | 2.25 | 94.67 |
| PM17-7 | 0.015 | 0.47 | 8.06 | 1.26 | 0.70 | 1.07 | 1.05 | 51.65 | 1.90 | 96.38 |
| PM17-10 | 0.012 | 0.42 | 8.20 | 1.31 | 0.73 | 1.04 | 0.97 | 56.91 | 1.94 | 95.67 |
表2 研究区代表性岩石样品的主量(%)测试结果及主要岩石化学参数
Table 2 Main element content (%) test results and main rock chemical parameters of representative rock samples in the study area
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD047 | 75.59 | 0.132 | 12.50 | 1.85 | 0.08 | 0.048 | 0.065 | 0.50 | 3.66 | 5.05 |
| QD086 | 77.27 | 0.096 | 11.51 | 1.61 | 0.38 | 0.028 | 0.067 | 0.40 | 3.45 | 5.17 |
| D1548 | 77.68 | 0.120 | 11.57 | 1.76 | 0.21 | 0.044 | 0.046 | 0.13 | 3.32 | 4.39 |
| PM16-10 | 74.91 | 0.260 | 12.86 | 1.59 | <0.10 | 0.081 | 0.140 | 0.59 | 4.52 | 3.97 |
| PM17-7 | 77.13 | 0.150 | 11.50 | 1.76 | 0.14 | 0.018 | 0.059 | 0.17 | 3.56 | 4.49 |
| PM17-10 | 77.64 | 0.140 | 11.30 | 1.83 | 0.46 | 0.052 | 0.059 | 0.41 | 3.55 | 4.65 |
| 样品编号 | P2O5 | 烧失 | ALK | K/Na | AKI | A/NK | A/CNK | τ | σ | D.I |
| QD047 | 0.014 | 0.48 | 8.71 | 1.38 | 0.92 | 1.09 | 1.01 | 122.42 | 2.32 | 95.01 |
| QD086 | 0.013 | 0.33 | 8.62 | 1.50 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 155.83 | 2.17 | 96.35 |
| D1548 | 0.012 | 0.41 | 7.71 | 1.32 | 0.88 | 1.13 | 1.11 | 124.08 | 1.71 | 95.81 |
| PM16-10 | 0.037 | 0.53 | 8.49 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 1.10 | 1.01 | 66.85 | 2.25 | 94.67 |
| PM17-7 | 0.015 | 0.47 | 8.06 | 1.26 | 0.70 | 1.07 | 1.05 | 51.65 | 1.90 | 96.38 |
| PM17-10 | 0.012 | 0.42 | 8.20 | 1.31 | 0.73 | 1.04 | 0.97 | 56.91 | 1.94 | 95.67 |

图5 研究区火山岩特征判别图解(底图分别据文献[38-42]) (a)TAS图;(b)A/CNK-A/NK 关系图;(c)SiO2-K2O关系图;(d)FAM图解
Fig.5 Diagram for distinguishing the characteristics of volcanic rocks in the study area (base map after refs.[38-42])
| 样品号 | Ba | Cd | Co | Cr | Cs | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Rb | Sc | Sr | Ta | Th | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD047 | 66.95 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.36 | 3.26 | 8.31 | 4.09 | 27.12 | 0.13 | 280.20 | 2.01 | 30.09 | 1.90 | 40.76 | |||
| QD086 | 38.12 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.98 | 3.64 | 13.01 | 6.76 | 41.35 | 0.39 | 293.89 | 0.62 | 24.45 | 2.68 | 31.63 | |||
| D1548 | 58.80 | 0.48 | 0.20 | 2.75 | 2.55 | 11.40 | 3.18 | 31.40 | 0.52 | 216.00 | 0.86 | 4.12 | 2.00 | 25.60 | |||
| PM16-10 | 124.00 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 6.39 | 4.24 | 10.60 | 5.85 | 27.70 | 1.28 | 160.00 | 4.33 | 58.30 | 1.62 | 21.20 | |||
| PM17-7 | 75.80 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 1.50 | 10.60 | 5.66 | 26.10 | 0.20 | 172.00 | 1.70 | 17.80 | 1.38 | 28.60 | |||
| PM17-10 | 39.50 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 1.60 | 9.77 | 4.09 | 26.50 | 0.12 | 172.00 | 1.17 | 13.40 | 1.39 | 27.60 | |||
| 均值 | 67.20 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 2.00 | 2.80 | 10.62 | 4.94 | 30.03 | 0.44 | 215.68 | 1.78 | 24.69 | 1.83 | 29.23 | |||
| 样品号 | U | V | Zr | K/Rb | Rb/Sr | Rb/Ba | Th/Ta | Ce | Dy | Er | Eu | Gd | Ho | La | |||
| QD047 | 6.51 | 1.08 | 267 | 150 | 9.31 | 4.19 | 21.45 | 174 | 11.1 | 6.32 | 0.35 | 10.40 | 2.21 | 87.9 | |||
| QD086 | 8.09 | 2.72 | 337 | 146 | 12.01 | 7.71 | 11.80 | 87 | 15.1 | 9.20 | 0.11 | 12.60 | 3.16 | 40.5 | |||
| D1548 | 4.02 | 11.60 | 320 | 169 | 52.42 | 3.67 | 12.80 | 92 | 10.6 | 6.67 | 0.11 | 9.84 | 2.12 | 56.7 | |||
| PM16-10 | 3.28 | 18.90 | 289 | 206 | 2.74 | 1.29 | 13.09 | 98 | 8.9 | 5.44 | 0.57 | 8.90 | 1.76 | 42.1 | |||
| PM17-7 | 4.20 | 2.47 | 378 | 217 | 9.66 | 2.27 | 20.72 | 150 | 10.6 | 5.67 | 0.27 | 12.4 | 1.96 | 111.0 | |||
| PM17-10 | 3.63 | 1.32 | 351 | 224 | 12.84 | 4.35 | 19.86 | 167 | 9.7 | 5.32 | 0.17 | 10.2 | 1.82 | 84.0 | |||
| 均值 | 4.96 | 6.35 | 324 | 185 | 16.50 | 3.91 | 16.62 | 128 | 11.0 | 6.44 | 0.26 | 10.7 | 2.17 | 70.4 | |||
| 样品号 | Lu | Nd | Pr | Sm | Tb | Tm | Y | Yb | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | TZr(℃) | ||||
| QD047 | 0.89 | 64.8 | 18.6 | 12.5 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 63.1 | 6.04 | 397.80 | 9.05 | 10.43 | 0.09 | 833 | ||||
| QD086 | 1.26 | 40.3 | 10.8 | 11.5 | 2.38 | 1.37 | 94.0 | 8.89 | 244.10 | 3.53 | 3.26 | 0.03 | 852 | ||||
| D1548 | 0.98 | 48.4 | 13.6 | 10.6 | 1.72 | 1.03 | 55.6 | 6.52 | 261.30 | 5.62 | 6.24 | 0.03 | 865 | ||||
| PM16-10 | 0.80 | 42.1 | 11.4 | 9.72 | 1.53 | 0.82 | 46.9 | 5.16 | 237.20 | 6.12 | 5.85 | 0.19 | 839 | ||||
| PM17-7 | 0.81 | 87.1 | 28.7 | 15.7 | 1.79 | 0.86 | 51.9 | 5.38 | 432.20 | 9.95 | 14.80 | 0.06 | 874 | ||||
| PM17-10 | 0.81 | 70.7 | 22.7 | 13.2 | 1.64 | 0.82 | 49.3 | 5.35 | 393.40 | 10.04 | 11.26 | 0.04 | 859 | ||||
| 均值 | 0.93 | 58.9 | 17.6 | 12.2 | 1.80 | 0.97 | 60.1 | 6.22 | 327.67 | 7.39 | 8.64 | 0.07 | 854 | ||||
表3 研究区晚白垩世火山岩微量元素(10-6)、稀土元素测试结果(10-6)及特征值
Table 3 Trace elements (10-6), rare earth elements (10-6) test results and characteristics of Late Cretaceous volcanic rocks in the study area
| 样品号 | Ba | Cd | Co | Cr | Cs | Hf | Li | Nb | Ni | Rb | Sc | Sr | Ta | Th | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD047 | 66.95 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.36 | 3.26 | 8.31 | 4.09 | 27.12 | 0.13 | 280.20 | 2.01 | 30.09 | 1.90 | 40.76 | |||
| QD086 | 38.12 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.98 | 3.64 | 13.01 | 6.76 | 41.35 | 0.39 | 293.89 | 0.62 | 24.45 | 2.68 | 31.63 | |||
| D1548 | 58.80 | 0.48 | 0.20 | 2.75 | 2.55 | 11.40 | 3.18 | 31.40 | 0.52 | 216.00 | 0.86 | 4.12 | 2.00 | 25.60 | |||
| PM16-10 | 124.00 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 6.39 | 4.24 | 10.60 | 5.85 | 27.70 | 1.28 | 160.00 | 4.33 | 58.30 | 1.62 | 21.20 | |||
| PM17-7 | 75.80 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 1.50 | 10.60 | 5.66 | 26.10 | 0.20 | 172.00 | 1.70 | 17.80 | 1.38 | 28.60 | |||
| PM17-10 | 39.50 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 1.60 | 9.77 | 4.09 | 26.50 | 0.12 | 172.00 | 1.17 | 13.40 | 1.39 | 27.60 | |||
| 均值 | 67.20 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 2.00 | 2.80 | 10.62 | 4.94 | 30.03 | 0.44 | 215.68 | 1.78 | 24.69 | 1.83 | 29.23 | |||
| 样品号 | U | V | Zr | K/Rb | Rb/Sr | Rb/Ba | Th/Ta | Ce | Dy | Er | Eu | Gd | Ho | La | |||
| QD047 | 6.51 | 1.08 | 267 | 150 | 9.31 | 4.19 | 21.45 | 174 | 11.1 | 6.32 | 0.35 | 10.40 | 2.21 | 87.9 | |||
| QD086 | 8.09 | 2.72 | 337 | 146 | 12.01 | 7.71 | 11.80 | 87 | 15.1 | 9.20 | 0.11 | 12.60 | 3.16 | 40.5 | |||
| D1548 | 4.02 | 11.60 | 320 | 169 | 52.42 | 3.67 | 12.80 | 92 | 10.6 | 6.67 | 0.11 | 9.84 | 2.12 | 56.7 | |||
| PM16-10 | 3.28 | 18.90 | 289 | 206 | 2.74 | 1.29 | 13.09 | 98 | 8.9 | 5.44 | 0.57 | 8.90 | 1.76 | 42.1 | |||
| PM17-7 | 4.20 | 2.47 | 378 | 217 | 9.66 | 2.27 | 20.72 | 150 | 10.6 | 5.67 | 0.27 | 12.4 | 1.96 | 111.0 | |||
| PM17-10 | 3.63 | 1.32 | 351 | 224 | 12.84 | 4.35 | 19.86 | 167 | 9.7 | 5.32 | 0.17 | 10.2 | 1.82 | 84.0 | |||
| 均值 | 4.96 | 6.35 | 324 | 185 | 16.50 | 3.91 | 16.62 | 128 | 11.0 | 6.44 | 0.26 | 10.7 | 2.17 | 70.4 | |||
| 样品号 | Lu | Nd | Pr | Sm | Tb | Tm | Y | Yb | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | TZr(℃) | ||||
| QD047 | 0.89 | 64.8 | 18.6 | 12.5 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 63.1 | 6.04 | 397.80 | 9.05 | 10.43 | 0.09 | 833 | ||||
| QD086 | 1.26 | 40.3 | 10.8 | 11.5 | 2.38 | 1.37 | 94.0 | 8.89 | 244.10 | 3.53 | 3.26 | 0.03 | 852 | ||||
| D1548 | 0.98 | 48.4 | 13.6 | 10.6 | 1.72 | 1.03 | 55.6 | 6.52 | 261.30 | 5.62 | 6.24 | 0.03 | 865 | ||||
| PM16-10 | 0.80 | 42.1 | 11.4 | 9.72 | 1.53 | 0.82 | 46.9 | 5.16 | 237.20 | 6.12 | 5.85 | 0.19 | 839 | ||||
| PM17-7 | 0.81 | 87.1 | 28.7 | 15.7 | 1.79 | 0.86 | 51.9 | 5.38 | 432.20 | 9.95 | 14.80 | 0.06 | 874 | ||||
| PM17-10 | 0.81 | 70.7 | 22.7 | 13.2 | 1.64 | 0.82 | 49.3 | 5.35 | 393.40 | 10.04 | 11.26 | 0.04 | 859 | ||||
| 均值 | 0.93 | 58.9 | 17.6 | 12.2 | 1.80 | 0.97 | 60.1 | 6.22 | 327.67 | 7.39 | 8.64 | 0.07 | 854 | ||||
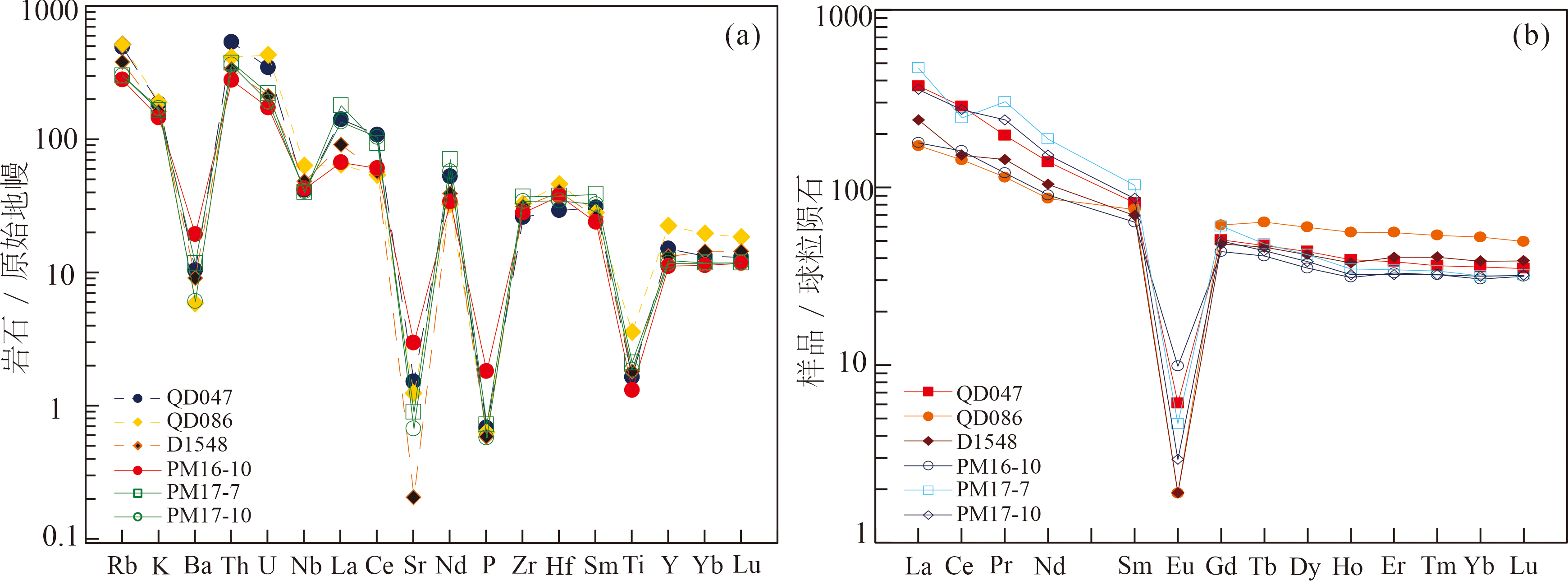
图6 研究区晚白垩世火山岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(a)和稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分配曲线(b)(原始地幔标准化值据文献[43],球粒陨石标准化值据文献[44])
Fig.6 Primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spider diagram (a) and chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (b) (primitive mantle after reference [43], and normalizing values of chondrite after reference [44])
| [1] | 浙江省地质矿产局. 浙江省岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1996. |
| [2] | 冯长明. 浙东沿海燕山期花岗岩类岩石谱系单位特征及成因机制[J]. 中国区域地质, 2001, 20(2): 170-177. |
| [3] | XU K Q, HU S X, SUN M Z, et al. On the two genetic series of granites in Southeastern China and their metallogenic characteristics[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1982, 2: 1-14. |
| [4] | CHARVET J, LAPIERRE H, YU Y W. Geodynamic significance of the Mesozoic volcanism of southeastern China[J]. Jounal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1994, 9(4) : 387-396. |
| [5] | LIN J, XU M, ZHOU Z Y, et al. Ocean dilling invesigation of the global subduction processes[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(12) : 1253-1266. |
| [6] | ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 326(3) : 269-287. |
| [7] | 邢光福, 陈荣, 杨祝良, 等. 东南沿海晚白垩世火山岩浆活动特征及其构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(1):77-91. |
| [8] | 张朝锋, 张玲娟, 强利刚, 等. 青海省曲麻莱县活塔加查岩浆岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 46(3): 201-210. |
| [9] | 李良林, 周汉文, 陈植华, 等. 福建太姥山地区和鼓山地区A型花岗岩对比及其地球动力学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3):509-524. |
| [10] | 舒良树, 周新民, 邓平, 等. 中国东南部中、新生代盆地特征与构造演化[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10): 876-884. |
| [11] | 徐鸣洁, 舒良树. 中国东南部晚中生代岩浆作用的深部条件制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001, 7(1): 21-33. |
| [12] | 徐春强, 王晨杰, 王蔚. 渤中凹陷北部中生界火山岩储层发育特征及油气成藏条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2024, 54(6): 1801-1814. |
| [13] | 王亚妹, 万天丰. 中国东部新生代岩石圈构造滑脱、岩浆活动和地震[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 207-229. |
| [14] | 曹明轩, 褚平利, 段政, 等. 华南中生代火山活动时空演化及其问题探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(4):795-812. |
| [15] | 陶奎元, 邢光福, 杨祝良, 等. 浙江中生代火山岩时代厘定和问题讨论——兼评Lapierre 等关于浙江中生代火山岩活动时代的论述[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(1):14-21. |
| [16] | 王加恩, 刘远栋, 王振. 浙江省丽水地区白垩纪红层盆地火山岩年龄及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(4): 873-883. |
| [17] | 高丽, 洪文涛, 杨祝良, 等. 浙东小雄破火山晚白垩世火山-侵入杂岩成因及岩浆演化[J]. 华东地质, 2019, 40(3): 161-169. |
| [18] | 舒良树, 周新民. 中国东南部晚中生代构造格架[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(3): 249-260. |
| [19] | 刘远栋, 李翔, 徐磊, 等. 浙南龙泉地区晚侏罗世火山岩的厘定及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(6):1530-1546. |
| [20] | 段政, 邢光福, 余明刚, 等. 浙闽边界区晚中生代火山作用时序与过程分析[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(3):454-469. |
| [21] | 余明刚, 邢光福, 沈加林, 等. 雁荡山世界地质公园火山岩年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(11): 1683-l690. |
| [22] | 贺振宇, 颜丽丽, 褚平利, 等. 中国东南沿海晚白垩世长屿火山的活动过程与古环境意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(5):1419-1442. |
| [23] | 夏炎, 刘磊, 徐夕生. 中国东南部晚中生代A型花岗岩类与古太平洋板块俯冲-后撤[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(6):1109-1119. |
| [24] | 孙卫东, 凌明星, 汪方跃, 等. 太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(3):218-225. |
| [25] | LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43. |
| [26] | LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571. |
| [27] | LUDWIJK R. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel berkeley geochronology center[M]. Berkeley, California: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003. |
| [28] | LI X L, YU J H, JIANG D S, et al. Linking ocean subduction with Eary Paleozoic intracontinental orogeny in South China: Insights from the Xiaying complex in eastern Guangxi Province[J]. Lithos, 2021, 398-399. |
| [29] | RUBATTO D, GEBAUER D. Use of Cathodoluminescence for U-Pb Zircon Dating by Ion Microprobe: Some Examples from the Western Alps. (In: Pagel, M., Barbin, V., Blanc, P., Ohnenstetter, D.(Eds.), Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences)[J]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2002,373-400. |
| [30] | MOLLER A, OBRIEN P J, KENNEDY A, et al. Linking growth episodes of zircon and metamorphic textures to zircon chemistry: an example from the ultrahigh-temperature granulites of Rogaland (SW Norway)[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2003, 220(1): 65. |
| [31] | ROWLEY D B. Ages of ultrahigh pressure metamorphism and protolith orthogneisses from the eastern Dabie Shan: U/Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 151(3): 191-203. |
| [32] | MOJZSIS S J, HARRISON T M. Establishment of a 3.83 Ga magmatic age for the Akilia tonalite (southern West Greenland)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 202(3): 563-576. |
| [33] | WU Y B, ZHENG Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Sci. Bull., 2004, 49: 1554-1569. |
| [34] | CONNELLY J N. Degree of preservation of igneous zonation in zircon as a signpost for concordancy in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chem.Geol., 2000, 172: 25-39. |
| [35] | COMPSTON W, WILLIAMS I S, KIRSCHVINK J L, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian time-scale[J]. Geol. Soc.London, 1992, 149: 171-184. |
| [36] | GRIFFIN W L, BELOUSOVA E A, SHEE S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton: U-Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J]. Precam. Res., 2004, 131: 231-282. |
| [37] | 邱检生, 刘亮, 李真. 浙江黄岩望海岗石英正长岩的锆石U-Pb 年代学与Sr-Nd-Hf 同位素地球化学及其对岩石成因的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(6):1557-1572. |
| [38] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma igneous rock system[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 1994, 37(3-4):215-224. |
| [39] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643. |
| [40] | PECCERILLO R, TAYLOE S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58:63-81. |
| [41] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks[M]. London: Longman, 1985. |
| [42] | IRVINE T N, BARAGER W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8: 523-548. |
| [43] | MCDONOUGH W F, SUN S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chem.Geol., 1995, 120: 223-253. |
| [44] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[J]. Geological Society of London,Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. |
| [45] | WATSON E B, HRRISON T M. Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1983, 64: 295-304. |
| [46] | GORTON M P, SCHANDL E S. From Continents to Island Arcs: A Geochemical Index of Tectonic Setting for Arc-Related and within-Plate Felsic to Intermediate Volcanic Rocks[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2000, 38 (5) : 1065-1073. |
| [47] | SCHANDL E S, GORTON M P. Application of high field strengthelements to discriminate tectonic settings in VMS environments[J]. Econ Geol, 2002, 97:629-642. |
| [48] | WOOD D A. Avariably veined suboceanic uppermantle-genetic significance for mid-ocean ridge basalts from geochemical evidence[J]. Geology, 1979, 7:499-503. |
| [49] | WOOD D A. The application of a Th-Hf-Nb diagram to problems of tectomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of the British Tertiary volcanic provinic[J]. Earth Plant Sci Lett, 1980, 50:11-30. |
| [50] | HARRIS N B W, Pearce J A, Tindle A G. Geochemical Characteristics of Collision-zone Magmatism[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 19(1): 67-81. |
| [51] | WALSON E B, HARRISON T M. Zircon saluralion revisited:Temperature and composilion effects in a variely of crustal magmatypes. Earh and Planelary Science Lellers, 1983, 64(2):295-304. |
| [52] | 翁祖山, 俞方明. 浙东沿海上白垩统小雄组的建立[J]. 火山地质与矿产, 1999, 20(3):197-204. |
| [1] | 武将伟, 胡浩, 张富臣, 牛毅, 周志广, 张达. 内蒙古集宁地区小大青山中生代花岗岩岩石特征及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 995-1015. |
| [2] | 牛花朋, 刘姗, 焦小芹, 张关龙, 王千军, 周健, 赵贤, 于洪洲, 熊峥嵘, 何晓. 准噶尔盆地西北缘石炭系火山岩地球化学特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 588-597. |
| [3] | 黎敬, 时国, 楼法生, 杨玲, 许梦园, 于娟. 江西省赣州市章贡区晚白垩世莲荷组恐龙蛋化石显微结构及古环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 350-360. |
| [4] | 郑英, 韩杰, 张小永, 缑明亮, 王明, 袁博武. 柴达木盆地东北部拉合根地区中生代火山岩的发现及其地质意义:来自地球化学与锆石年代学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1147-1161. |
| [5] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [6] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [7] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [8] | 陈宇航, 张新涛, 余一欣, 杨帆, 柳永军, 张震, 丁康. 渤中凹陷北部中生界顶面断层破碎带量化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1035-1042. |
| [9] | 张宏辉, 谢财富, 陈凯, 袁永盛, 余杨忠, 张沥元, 陈贵仁, 李鸿, 詹华思, 石海涛, 蔡泉宇, 于一帆. 粤西北大桂山岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、岩石成因及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 862-875. |
| [10] | 刘建栋, 李五福, 王国良, 董进生, 曹锦山, 李红刚, 赵忠国. 北祁连东段柏木峡—门岗峡地区蛇绿岩的识别及其区域构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 244-258. |
| [11] | 杨维刚, 李永胜, 李通元, 张俊, 任鹏飞. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世板块碰撞事件的记录:来自合作地区火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1691-1701. |
| [12] | 谢亘, 喻光明, 路英川, 冯欣, 田光昊, 王然, 王建. 华北克拉通南缘小秦岭地区花岗质片麻岩年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712. |
| [13] | 陈澍民, 缪宇, 廖驾, 贺前平, 成明, 张珍力, 吴绍安, 章志明. 中拉萨地块南缘孔隆晚白垩世火山岩成因及对地壳演化的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1713-1726. |
| [14] | 潘力, 何青林, 梁生贤, 陈先洁, 陈文, 谢光华, 黎洋, 夏青, 马乾. 基于正演模拟的火山岩重磁响应特征研究:以川西地区二叠系为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1471-1479. |
| [15] | 王玉平, 吴文彬, 刘永俊, 李海洋, 王晓亮, 李超. 辽东岫岩地区晚侏罗世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 955-967. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||