



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (06): 1095-1113.
余超1( ), 柳振江1(
), 柳振江1( ), 宓奎峰1, 王常波2, 张杰2, 王建平1, 刘家军1, 张梅3
), 宓奎峰1, 王常波2, 张杰2, 王建平1, 刘家军1, 张梅3
收稿日期:2017-03-15
修回日期:2017-07-07
出版日期:2017-12-10
发布日期:2017-12-25
通讯作者:
柳振江,男,讲师,博士,1983年出生,矿床学专业,主要从事区域成矿学研究。Email:作者简介:余 超,男,硕士研究生,1993年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床学与矿床地球化学研究。Email:yuchao0927@yeah.net。
基金资助:
YU Chao1( ), LIU Zhenjiang1(
), LIU Zhenjiang1( ), MI Kuifeng1, WANG Changbo2, ZHANG Jie2, WANG Jianping1, LIU Jiajun1, ZHANG Mei3
), MI Kuifeng1, WANG Changbo2, ZHANG Jie2, WANG Jianping1, LIU Jiajun1, ZHANG Mei3
Received:2017-03-15
Revised:2017-07-07
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-12-25
摘要:
巴彦都兰铜矿是内蒙古二连浩特—东乌旗成矿带近年来新发现的一处中—高温热液脉型铜多金属矿床。通过对矿区内与成矿关系密切的花岗岩岩体开展同位素年代学、岩石地球化学和Hf同位素测试,据此探讨了该矿床的成因机制。分析结果显示,黑云母二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(300.2±2.2) Ma和(300.0±2.0) Ma;具有富硅、高钾钙碱性、弱过铝质,富集轻稀土元素及Rb、K等大离子亲石元素,亏损Sr、Nb、Ta等高场强元素的特征;锆石Hf同位素εHf(t)=6.1~10.7,TDM2=632~924 Ma,表现出洋壳俯冲形成的新生下地壳部分熔融的特征。综合研究认为,巴彦都兰铜矿形成的大地构造背景处于晚石炭世—早二叠世二连—贺根山洋盆闭合、区域构造环境逐渐由挤压转为后碰撞的伸展环境,在此期间碰撞后的岩石圈拆沉作用以及拉张机制下上涌的地幔物质使得新生下地壳得到再活化,产生的混合有基性幔源物质的酸性岩浆体系为成矿系统提供了主要成矿物质与流体。
中图分类号:
余超, 柳振江, 宓奎峰, 王常波, 张杰, 王建平, 刘家军, 张梅. 内蒙古巴彦都兰铜矿地质特征及矿床成因——岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1095-1113.
YU Chao, LIU Zhenjiang, MI Kuifeng, WANG Changbo, ZHANG Jie, WANG Jianping, LIU Jiajun, ZHANG Mei. U-Pb Zircon, Geochemical and Hf Isotopic Constraints on Origin of the Bayandulan Copper Deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(06): 1095-1113.

图1 内蒙古二连浩特—东乌旗地区地质矿产略图(据文献[16]修编) 1.第四系;2.中生界;3.古生界;4.中生代花岗岩类;5.古生代花岗岩类;6.古生代超基性岩;7.新生代玄武岩;8.断层;9.地质界线;10.地标;11.铁多金属矿;12.银-铅-锌矿;13.铁-锌矿;14.银-金矿;15.钨矿;16.铅-锌矿;17.铜-锌矿;18.铜矿
Fig.1 Sketch map of regional geology and ore deposits distribution in Erenhot-East Ujimqin banner, Inner Mongolia (modified after reference[16])

图2 巴彦都兰铜矿床平面(a)及剖面地质图(b)① ① 内蒙古赤峰地质矿产勘查开发院.内蒙古自治区东乌珠穆沁旗巴彦都兰矿区铜矿资源储量核实报告[R].2013.
Fig.2 Plan(a)and cross-section geological map(b) of the Bayandulan copper deposit①

图3 巴彦都兰铜矿床野外及手标本特征 a.粉砂岩地层中发育NEE向断裂;b.黑云母二长花岗岩;c.黑云母二长花岗岩中的暗色微粒包体;d.黑云母二长花岗岩侵入粉砂岩地层,后者发生角岩化;e.毒砂-白钨矿矿体呈脉状产于粉砂岩中,并夹有围岩角砾;f.黄铜矿-毒砂-白钨矿矿石呈团块状产出;g. 呈脉状产出的毒砂-磁黄铁矿以及呈细脉状产出的石英-黄铜矿;h.毒砂-磁黄铁矿-黄铜矿呈网脉状产出于粉砂岩中,并伴生有石英颗粒;i.毒砂、白钨矿(紫光灯下具蓝色荧光效应)和少量黄铜矿呈浸染状产出于粉砂岩中,并伴生有石英颗粒。矿物代号:Qtz.石英;Py.黄铁矿;Ccp.黄铜矿;Apy.毒砂;Po.磁黄铁矿;Sh.白钨矿
Fig.3 Field and hand specimen feature of the Bayandulan copper deposit

图4 巴彦都兰铜多金属矿床岩矿石显微特征 a.黑云母二长花岗岩(正交偏光);b.暗色微粒包体(正交偏光);c.暗色微粒包体,发育有绿泥石化和黄铁矿化(正交偏光);d.黄铜矿-磁黄铁矿对毒砂有交代熔蚀作用,并形成毒砂骸晶;e.磁黄铁矿-黄铜矿-石英交代毒砂-白钨矿,并沿白钨矿裂隙填充,构成它形填隙结构;f.粒状白钨矿包含有黑钨矿颗粒,具Ⅱ级黄色—Ⅱ级紫红色干涉色,并与其他石英硫化物共生(左:正交偏光,右:反射光);g.磁黄铁矿-黄铜矿-石英交代并穿切毒砂-白钨矿-石英;h.磁黄铁矿-黄铜矿-石英呈网脉状产出于粉砂岩中;i.辉锑银矿交代磁黄铁矿;闪锌矿呈乳滴状分布在黄铜矿与磁黄铁矿中,构成固溶体分离结构。矿物代号:Qtz.石英;Ms.白云母;Kfs.正长石;Mic.微斜长石;Pl.斜长石;Bt.黑云母;Amp.角闪石;Py.黄铁矿;Ccp.黄铜矿;Apy.毒砂;Po.磁黄铁矿;Sh.白钨矿;Wf.黑钨矿;Sp.闪锌矿;Mpy.辉锑银矿
Fig.4 Microscopic features of ore and rock samples in the Bayandulan copper deposit
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL1-1 | 黑云母二 长花岗岩 | 70.39 | 0.41 | 14.99 | 2.26 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.79 | 0.48 | 4.50 | 4.28 | 0.11 | (0.06) | 98.66 | |||||||||||
| BL1-2 | 69.16 | 0.38 | 15.32 | 2.07 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 1.20 | 4.09 | 4.36 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 98.74 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z1 | 68.33 | 0.40 | 15.44 | 2.29 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 0.51 | 1.20 | 4.16 | 4.77 | 0.09 | 1.26 | 99.06 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z2 | 68.69 | 0.44 | 15.55 | 2.20 | 0.93 | 0.08 | 0.93 | 2.00 | 3.94 | 4.01 | 0.11 | 0.87 | 99.75 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z1BT | 暗色微粒 包体 | 52.49 | 1.34 | 17.54 | 8.35 | 2.33 | 0.22 | 3.45 | 3.35 | 4.33 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 2.82 | 97.15 | |||||||||||
| BL-Z2BT | 52.65 | 1.34 | 17.57 | 8.20 | 2.51 | 0.23 | 3.46 | 3.35 | 4.33 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 2.77 | 97.38 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-1 | 二长花岗 岩 | 72.44 | 0.15 | 15.52 | 0.12 | 0.74 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.67 | 4.83 | 4.26 | 0.07 | 0.67 | 99.81 | |||||||||||
| 4437-2 | 74.22 | 0.13 | 14.71 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.59 | 4.35 | 4.28 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 99.88 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-3 | 73.59 | 0.17 | 14.56 | 0.47 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 4.48 | 3.57 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 99.97 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-4 | 71.56 | 0.15 | 16.38 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.58 | 4.94 | 4.35 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 99.86 | ||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Pr | Sr | Nd | Sm | ||||||||||||
| BL1-1 | 黑云母二 长花岗岩 | 113.50 | 892.00 | 14.10 | 2.30 | 10.20 | 1.20 | 24.50 | 52.20 | 5.93 | 205.00 | 22.10 | 5.56 | ||||||||||||
| BL1-2 | 122.00 | 917.00 | 13.95 | 2.71 | 9.90 | 1.20 | 34.20 | 69.70 | 7.44 | 354.00 | 27.60 | 5.88 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1 | 117.50 | 817.00 | 10.55 | 7.76 | 8.90 | 0.70 | 48.50 | 95.40 | 10.80 | 229.00 | 39.80 | 6.85 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z2 | 165.50 | 615.00 | 14.90 | 8.17 | 11.90 | 1.70 | 26.70 | 51.20 | 6.38 | 256.00 | 24.60 | 5.05 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1BT | 暗色微粒 包体 | 212.00 | 161.50 | 11.25 | 20.20 | 23.70 | 1.30 | 45.60 | 102.00 | 13.90 | 383.00 | 57.20 | 13.95 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z2BT | 251.00 | 187.00 | 13.30 | 25.20 | 28.60 | 1.50 | 53.00 | 116.00 | 16.20 | 441.00 | 66.50 | 16.15 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-1 | 二长花岗 岩 | 177.00 | 706.00 | 6.63 | 3.18 | 10.50 | 0.97 | 5.50 | 17.20 | 1.28 | 203.00 | 4.39 | 0.86 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-2 | 162.00 | 298.00 | 12.40 | 5.33 | 10.50 | 2.31 | 16.90 | 31.40 | 3.65 | 135.00 | 12.90 | 2.47 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-3 | 190.00 | 475.00 | 15.50 | 4.65 | 7.91 | 1.51 | 14.10 | 28.60 | 2.70 | 101.00 | 9.11 | 1.61 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-4 | 174.00 | 468.00 | 14.80 | 4.47 | 9.51 | 1.85 | 31.50 | 60.40 | 6.26 | 110.00 | 21.30 | 3.66 | |||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Zr | Hf | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Y | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||||||||||
| BL1-1 | 黑云母二 长花岗岩 | 386.00 | 10.50 | 1.29 | 4.67 | 0.79 | 4.17 | 24.30 | 0.94 | 2.84 | 0.47 | 3.05 | 0.55 | ||||||||||||
| BL1-2 | 369.00 | 10.00 | 1.36 | 4.73 | 0.78 | 4.43 | 25.70 | 0.97 | 2.71 | 0.49 | 2.96 | 0.53 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1 | 493.00 | 10.70 | 1.31 | 5.23 | 0.73 | 4.06 | 28.20 | 0.85 | 2.20 | 0.31 | 2.08 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z2 | 316.00 | 7.50 | 0.88 | 4.35 | 0.72 | 4.15 | 30.20 | 0.88 | 2.63 | 0.42 | 2.78 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1BT | 暗色微粒 包体 | 306.00 | 7.40 | 1.37 | 11.95 | 1.92 | 10.60 | 68.00 | 2.23 | 6.14 | 0.89 | 6.17 | 0.92 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z2BT | 336.00 | 8.40 | 1.56 | 14.40 | 2.42 | 13.30 | 78.00 | 2.68 | 7.56 | 1.08 | 7.03 | 1.11 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-1 | 二长花岗 岩 | 149.00 | 11.50 | 0.33 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 1.02 | 5.30 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 0.77 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-2 | 68.90 | 2.70 | 0.32 | 2.19 | 0.34 | 1.89 | 11.00 | 0.40 | 1.15 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-3 | 73.80 | 2.86 | 0.30 | 1.58 | 0.23 | 1.23 | 6.39 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-4 | 62.60 | 2.70 | 0.44 | 3.21 | 0.41 | 1.92 | 9.54 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||
表2 巴彦都兰地区二长花岗岩与暗色微粒包体主量元素(wB/%)、微量元素(wB/10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major elements(%)and trace elements(10-6) for monzogranite and its enclaves from Bayandulan area
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL1-1 | 黑云母二 长花岗岩 | 70.39 | 0.41 | 14.99 | 2.26 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.79 | 0.48 | 4.50 | 4.28 | 0.11 | (0.06) | 98.66 | |||||||||||
| BL1-2 | 69.16 | 0.38 | 15.32 | 2.07 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 1.20 | 4.09 | 4.36 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 98.74 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z1 | 68.33 | 0.40 | 15.44 | 2.29 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 0.51 | 1.20 | 4.16 | 4.77 | 0.09 | 1.26 | 99.06 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z2 | 68.69 | 0.44 | 15.55 | 2.20 | 0.93 | 0.08 | 0.93 | 2.00 | 3.94 | 4.01 | 0.11 | 0.87 | 99.75 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z1BT | 暗色微粒 包体 | 52.49 | 1.34 | 17.54 | 8.35 | 2.33 | 0.22 | 3.45 | 3.35 | 4.33 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 2.82 | 97.15 | |||||||||||
| BL-Z2BT | 52.65 | 1.34 | 17.57 | 8.20 | 2.51 | 0.23 | 3.46 | 3.35 | 4.33 | 2.07 | 0.35 | 2.77 | 97.38 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-1 | 二长花岗 岩 | 72.44 | 0.15 | 15.52 | 0.12 | 0.74 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.67 | 4.83 | 4.26 | 0.07 | 0.67 | 99.81 | |||||||||||
| 4437-2 | 74.22 | 0.13 | 14.71 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.59 | 4.35 | 4.28 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 99.88 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-3 | 73.59 | 0.17 | 14.56 | 0.47 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 4.48 | 3.57 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 99.97 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-4 | 71.56 | 0.15 | 16.38 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.58 | 4.94 | 4.35 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 99.86 | ||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Pr | Sr | Nd | Sm | ||||||||||||
| BL1-1 | 黑云母二 长花岗岩 | 113.50 | 892.00 | 14.10 | 2.30 | 10.20 | 1.20 | 24.50 | 52.20 | 5.93 | 205.00 | 22.10 | 5.56 | ||||||||||||
| BL1-2 | 122.00 | 917.00 | 13.95 | 2.71 | 9.90 | 1.20 | 34.20 | 69.70 | 7.44 | 354.00 | 27.60 | 5.88 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1 | 117.50 | 817.00 | 10.55 | 7.76 | 8.90 | 0.70 | 48.50 | 95.40 | 10.80 | 229.00 | 39.80 | 6.85 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z2 | 165.50 | 615.00 | 14.90 | 8.17 | 11.90 | 1.70 | 26.70 | 51.20 | 6.38 | 256.00 | 24.60 | 5.05 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1BT | 暗色微粒 包体 | 212.00 | 161.50 | 11.25 | 20.20 | 23.70 | 1.30 | 45.60 | 102.00 | 13.90 | 383.00 | 57.20 | 13.95 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z2BT | 251.00 | 187.00 | 13.30 | 25.20 | 28.60 | 1.50 | 53.00 | 116.00 | 16.20 | 441.00 | 66.50 | 16.15 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-1 | 二长花岗 岩 | 177.00 | 706.00 | 6.63 | 3.18 | 10.50 | 0.97 | 5.50 | 17.20 | 1.28 | 203.00 | 4.39 | 0.86 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-2 | 162.00 | 298.00 | 12.40 | 5.33 | 10.50 | 2.31 | 16.90 | 31.40 | 3.65 | 135.00 | 12.90 | 2.47 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-3 | 190.00 | 475.00 | 15.50 | 4.65 | 7.91 | 1.51 | 14.10 | 28.60 | 2.70 | 101.00 | 9.11 | 1.61 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-4 | 174.00 | 468.00 | 14.80 | 4.47 | 9.51 | 1.85 | 31.50 | 60.40 | 6.26 | 110.00 | 21.30 | 3.66 | |||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Zr | Hf | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Y | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||||||||||
| BL1-1 | 黑云母二 长花岗岩 | 386.00 | 10.50 | 1.29 | 4.67 | 0.79 | 4.17 | 24.30 | 0.94 | 2.84 | 0.47 | 3.05 | 0.55 | ||||||||||||
| BL1-2 | 369.00 | 10.00 | 1.36 | 4.73 | 0.78 | 4.43 | 25.70 | 0.97 | 2.71 | 0.49 | 2.96 | 0.53 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1 | 493.00 | 10.70 | 1.31 | 5.23 | 0.73 | 4.06 | 28.20 | 0.85 | 2.20 | 0.31 | 2.08 | 0.35 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z2 | 316.00 | 7.50 | 0.88 | 4.35 | 0.72 | 4.15 | 30.20 | 0.88 | 2.63 | 0.42 | 2.78 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||
| BL-Z1BT | 暗色微粒 包体 | 306.00 | 7.40 | 1.37 | 11.95 | 1.92 | 10.60 | 68.00 | 2.23 | 6.14 | 0.89 | 6.17 | 0.92 | ||||||||||||
| BL-Z2BT | 336.00 | 8.40 | 1.56 | 14.40 | 2.42 | 13.30 | 78.00 | 2.68 | 7.56 | 1.08 | 7.03 | 1.11 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-1 | 二长花岗 岩 | 149.00 | 11.50 | 0.33 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 1.02 | 5.30 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 0.77 | 0.12 | ||||||||||||
| 4437-2 | 68.90 | 2.70 | 0.32 | 2.19 | 0.34 | 1.89 | 11.00 | 0.40 | 1.15 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 0.19 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-3 | 73.80 | 2.86 | 0.30 | 1.58 | 0.23 | 1.23 | 6.39 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||
| 4437-4 | 62.60 | 2.70 | 0.44 | 3.21 | 0.41 | 1.92 | 9.54 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||

图7 巴彦都兰地区二长花岗岩及其暗色微粒包体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化图解(b)(球粒陨石标准值、原始地幔标准化值据文献[33])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements patterns(b) of monzogranite and its enclaves in Bayandulan area(chondrite-normalized values and primitive mantle-normalized values after reference[33])
| 测试 点号 | Th/10-6 | U/10-6 | Pb/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||||||
| BL1-02 | 158.56 | 381.55 | 19.10 | 0.42 | 0.343 92 | 0.012 05 | 0.047 90 | 0.000 66 | 300 | 9 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL1-03 | 103.84 | 228.17 | 11.61 | 0.46 | 0.343 24 | 0.020 28 | 0.047 67 | 0.000 75 | 300 | 15 | 300 | 5 | |
| BL1-04 | 141.01 | 361.77 | 17.98 | 0.39 | 0.340 40 | 0.012 07 | 0.047 28 | 0.000 63 | 297 | 9 | 298 | 4 | |
| BL1-05 | 113.38 | 236.93 | 12.11 | 0.48 | 0.340 96 | 0.015 88 | 0.047 61 | 0.000 70 | 298 | 12 | 300 | 4 | |
| BL1-08 | 226.42 | 383.68 | 20.25 | 0.59 | 0.345 99 | 0.011 48 | 0.047 71 | 0.000 63 | 302 | 9 | 300 | 4 | |
| BL1-10 | 75.99 | 276.89 | 14.18 | 0.27 | 0.367 37 | 0.015 50 | 0.047 09 | 0.000 63 | 318 | 12 | 297 | 4 | |
| BL1-11 | 119.22 | 242.37 | 13.04 | 0.49 | 0.363 79 | 0.018 47 | 0.047 82 | 0.000 70 | 315 | 14 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL1-12 | 109.67 | 166.53 | 9.73 | 0.66 | 0.358 41 | 0.020 61 | 0.047 14 | 0.000 75 | 311 | 15 | 297 | 5 | |
| BL1-18 | 382.47 | 1 420.89 | 72.04 | 0.27 | 0.352 21 | 0.010 35 | 0.048 27 | 0.000 59 | 306 | 8 | 304 | 4 | |
| BL1-20 | 65.31 | 629.05 | 30.57 | 0.10 | 0.349 42 | 0.009 16 | 0.048 35 | 0.000 60 | 304 | 7 | 304 | 4 | |
| BL1-26 | 110.78 | 356.60 | 17.93 | 0.31 | 0.354 06 | 0.010 52 | 0.047 31 | 0.000 60 | 308 | 8 | 298 | 4 | |
| BL1-27 | 48.78 | 124.22 | 6.40 | 0.39 | 0.344 00 | 0.015 79 | 0.047 38 | 0.000 67 | 300 | 12 | 298 | 4 | |
| BL1-28 | 58.24 | 153.42 | 7.94 | 0.38 | 0.343 43 | 0.011 69 | 0.047 77 | 0.000 64 | 300 | 9 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL1-29 | 76.28 | 214.89 | 11.12 | 0.35 | 0.346 31 | 0.011 11 | 0.047 92 | 0.000 62 | 302 | 8 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL2-01 | 390.64 | 1241.56 | 75.02 | 0.31 | 0.336 86 | 0.016 23 | 0.046 02 | 0.000 56 | 295 | 12 | 290 | 3 | |
| BL2-06 | 45.92 | 118.34 | 5.86 | 0.39 | 0.348 09 | 0.021 83 | 0.048 38 | 0.000 83 | 303 | 16 | 305 | 5 | |
| BL2-07 | 95.76 | 209.94 | 24.94 | 0.46 | 0.339 91 | 0.018 41 | 0.047 21 | 0.000 77 | 297 | 14 | 297 | 5 | |
| BL2-08 | 38.33 | 101.05 | 5.14 | 0.38 | 0.344 18 | 0.030 08 | 0.047 65 | 0.000 85 | 300 | 23 | 300 | 5 | |
| BL2-09 | 91.05 | 267.87 | 13.83 | 0.34 | 0.345 68 | 0.012 33 | 0.047 76 | 0.000 65 | 301 | 9 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL2-10 | 98.96 | 291.63 | 14.47 | 0.34 | 0.347 12 | 0.017 65 | 0.048 00 | 0.000 66 | 303 | 13 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL2-11 | 79.50 | 181.09 | 9.38 | 0.44 | 0.342 00 | 0.022 42 | 0.047 46 | 0.000 71 | 299 | 17 | 299 | 4 | |
| BL2-13 | 102.03 | 236.30 | 13.85 | 0.43 | 0.340 33 | 0.022 64 | 0.046 14 | 0.000 67 | 297 | 17 | 291 | 4 | |
| BL2-15 | 136.33 | 288.44 | 14.74 | 0.47 | 0.346 03 | 0.013 20 | 0.047 81 | 0.000 63 | 302 | 10 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL2-17 | 65.25 | 162.95 | 8.35 | 0.40 | 0.343 77 | 0.024 67 | 0.047 63 | 0.000 83 | 300 | 19 | 300 | 5 | |
| BL2-18 | 61.13 | 163.36 | 8.41 | 0.37 | 0.347 48 | 0.015 44 | 0.047 97 | 0.000 65 | 303 | 12 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL2-19 | 249.00 | 798.83 | 40.19 | 0.31 | 0.355 07 | 0.006 89 | 0.049 12 | 0.000 56 | 309 | 5 | 309 | 3 | |
| BL2-21 | 189.26 | 405.58 | 22.24 | 0.47 | 0.341 33 | 0.013 57 | 0.047 08 | 0.000 58 | 298 | 10 | 297 | 4 | |
| BL2-23 | 82.87 | 227.96 | 10.89 | 0.36 | 0.335 95 | 0.018 47 | 0.047 03 | 0.000 74 | 294 | 14 | 296 | 5 | |
| BL2-24 | 268.72 | 1 029.77 | 51.11 | 0.26 | 0.376 44 | 0.009 93 | 0.047 55 | 0.000 56 | 324 | 7 | 299 | 3 | |
| BL2-27 | 316.44 | 741.82 | 40.68 | 0.43 | 0.342 46 | 0.014 46 | 0.047 48 | 0.000 60 | 299 | 11 | 299 | 4 | |
| BL2-29 | 112.13 | 449.76 | 24.43 | 0.25 | 0.362 19 | 0.009 63 | 0.047 96 | 0.000 56 | 314 | 7 | 302 | 3 | |
| BL2-30 | 103.47 | 278.62 | 15.14 | 0.37 | 0.352 11 | 0.013 71 | 0.047 71 | 0.000 61 | 306 | 10 | 300 | 4 | |
| BL2-31 | 91.25 | 290.46 | 13.06 | 0.31 | 0.379 16 | 0.012 64 | 0.048 10 | 0.000 65 | 326 | 9 | 303 | 4 | |
表3 巴彦都兰铜矿床黑云母二长花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测试数据
Table 3 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data for biotite monzogranite samples from the Bayandulan copper deposit
| 测试 点号 | Th/10-6 | U/10-6 | Pb/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | ||||||||
| BL1-02 | 158.56 | 381.55 | 19.10 | 0.42 | 0.343 92 | 0.012 05 | 0.047 90 | 0.000 66 | 300 | 9 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL1-03 | 103.84 | 228.17 | 11.61 | 0.46 | 0.343 24 | 0.020 28 | 0.047 67 | 0.000 75 | 300 | 15 | 300 | 5 | |
| BL1-04 | 141.01 | 361.77 | 17.98 | 0.39 | 0.340 40 | 0.012 07 | 0.047 28 | 0.000 63 | 297 | 9 | 298 | 4 | |
| BL1-05 | 113.38 | 236.93 | 12.11 | 0.48 | 0.340 96 | 0.015 88 | 0.047 61 | 0.000 70 | 298 | 12 | 300 | 4 | |
| BL1-08 | 226.42 | 383.68 | 20.25 | 0.59 | 0.345 99 | 0.011 48 | 0.047 71 | 0.000 63 | 302 | 9 | 300 | 4 | |
| BL1-10 | 75.99 | 276.89 | 14.18 | 0.27 | 0.367 37 | 0.015 50 | 0.047 09 | 0.000 63 | 318 | 12 | 297 | 4 | |
| BL1-11 | 119.22 | 242.37 | 13.04 | 0.49 | 0.363 79 | 0.018 47 | 0.047 82 | 0.000 70 | 315 | 14 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL1-12 | 109.67 | 166.53 | 9.73 | 0.66 | 0.358 41 | 0.020 61 | 0.047 14 | 0.000 75 | 311 | 15 | 297 | 5 | |
| BL1-18 | 382.47 | 1 420.89 | 72.04 | 0.27 | 0.352 21 | 0.010 35 | 0.048 27 | 0.000 59 | 306 | 8 | 304 | 4 | |
| BL1-20 | 65.31 | 629.05 | 30.57 | 0.10 | 0.349 42 | 0.009 16 | 0.048 35 | 0.000 60 | 304 | 7 | 304 | 4 | |
| BL1-26 | 110.78 | 356.60 | 17.93 | 0.31 | 0.354 06 | 0.010 52 | 0.047 31 | 0.000 60 | 308 | 8 | 298 | 4 | |
| BL1-27 | 48.78 | 124.22 | 6.40 | 0.39 | 0.344 00 | 0.015 79 | 0.047 38 | 0.000 67 | 300 | 12 | 298 | 4 | |
| BL1-28 | 58.24 | 153.42 | 7.94 | 0.38 | 0.343 43 | 0.011 69 | 0.047 77 | 0.000 64 | 300 | 9 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL1-29 | 76.28 | 214.89 | 11.12 | 0.35 | 0.346 31 | 0.011 11 | 0.047 92 | 0.000 62 | 302 | 8 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL2-01 | 390.64 | 1241.56 | 75.02 | 0.31 | 0.336 86 | 0.016 23 | 0.046 02 | 0.000 56 | 295 | 12 | 290 | 3 | |
| BL2-06 | 45.92 | 118.34 | 5.86 | 0.39 | 0.348 09 | 0.021 83 | 0.048 38 | 0.000 83 | 303 | 16 | 305 | 5 | |
| BL2-07 | 95.76 | 209.94 | 24.94 | 0.46 | 0.339 91 | 0.018 41 | 0.047 21 | 0.000 77 | 297 | 14 | 297 | 5 | |
| BL2-08 | 38.33 | 101.05 | 5.14 | 0.38 | 0.344 18 | 0.030 08 | 0.047 65 | 0.000 85 | 300 | 23 | 300 | 5 | |
| BL2-09 | 91.05 | 267.87 | 13.83 | 0.34 | 0.345 68 | 0.012 33 | 0.047 76 | 0.000 65 | 301 | 9 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL2-10 | 98.96 | 291.63 | 14.47 | 0.34 | 0.347 12 | 0.017 65 | 0.048 00 | 0.000 66 | 303 | 13 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL2-11 | 79.50 | 181.09 | 9.38 | 0.44 | 0.342 00 | 0.022 42 | 0.047 46 | 0.000 71 | 299 | 17 | 299 | 4 | |
| BL2-13 | 102.03 | 236.30 | 13.85 | 0.43 | 0.340 33 | 0.022 64 | 0.046 14 | 0.000 67 | 297 | 17 | 291 | 4 | |
| BL2-15 | 136.33 | 288.44 | 14.74 | 0.47 | 0.346 03 | 0.013 20 | 0.047 81 | 0.000 63 | 302 | 10 | 301 | 4 | |
| BL2-17 | 65.25 | 162.95 | 8.35 | 0.40 | 0.343 77 | 0.024 67 | 0.047 63 | 0.000 83 | 300 | 19 | 300 | 5 | |
| BL2-18 | 61.13 | 163.36 | 8.41 | 0.37 | 0.347 48 | 0.015 44 | 0.047 97 | 0.000 65 | 303 | 12 | 302 | 4 | |
| BL2-19 | 249.00 | 798.83 | 40.19 | 0.31 | 0.355 07 | 0.006 89 | 0.049 12 | 0.000 56 | 309 | 5 | 309 | 3 | |
| BL2-21 | 189.26 | 405.58 | 22.24 | 0.47 | 0.341 33 | 0.013 57 | 0.047 08 | 0.000 58 | 298 | 10 | 297 | 4 | |
| BL2-23 | 82.87 | 227.96 | 10.89 | 0.36 | 0.335 95 | 0.018 47 | 0.047 03 | 0.000 74 | 294 | 14 | 296 | 5 | |
| BL2-24 | 268.72 | 1 029.77 | 51.11 | 0.26 | 0.376 44 | 0.009 93 | 0.047 55 | 0.000 56 | 324 | 7 | 299 | 3 | |
| BL2-27 | 316.44 | 741.82 | 40.68 | 0.43 | 0.342 46 | 0.014 46 | 0.047 48 | 0.000 60 | 299 | 11 | 299 | 4 | |
| BL2-29 | 112.13 | 449.76 | 24.43 | 0.25 | 0.362 19 | 0.009 63 | 0.047 96 | 0.000 56 | 314 | 7 | 302 | 3 | |
| BL2-30 | 103.47 | 278.62 | 15.14 | 0.37 | 0.352 11 | 0.013 71 | 0.047 71 | 0.000 61 | 306 | 10 | 300 | 4 | |
| BL2-31 | 91.25 | 290.46 | 13.06 | 0.31 | 0.379 16 | 0.012 64 | 0.048 10 | 0.000 65 | 326 | 9 | 303 | 4 | |

图9 巴彦都兰铜矿黑云母二长花岗岩岩体锆石U-Pb谐和图和加权平均年龄图
Fig.9 Zircon U-Pb concordia and weighted average diagrams of biotite monzogranite samples from the Bayandulan copper deposit
| 测试点号 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | 2σ | εHf(0) | fLu/Hf | εHf(t) | TDM1 | TDM2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL1-02 | 302.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 897 | 0.000 009 | 4.4 | -0.98 | 10.9 | 499 | 619 |
| BL1-03 | 300.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 885 | 0.000 010 | 4.0 | -0.97 | 10.4 | 521 | 652 |
| BL1-04 | 298.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 829 | 0.000 008 | 2.0 | -0.97 | 8.4 | 599 | 775 |
| BL1-05 | 300.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 866 | 0.000 007 | 3.3 | -0.98 | 9.8 | 545 | 691 |
| BL1-08 | 300.00 | 0.04 | 0.001 3 | 0.282 840 | 0.000 010 | 2.4 | -0.96 | 8.8 | 588 | 754 |
| BL1-10 | 297.00 | 0.04 | 0.001 3 | 0.282 836 | 0.000 010 | 2.2 | -0.96 | 8.5 | 595 | 766 |
| BL1-11 | 301.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 9 | 0.282 863 | 0.000 009 | 3.2 | -0.97 | 9.7 | 550 | 699 |
| BL1-18 | 304.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 866 | 0.000 007 | 3.3 | -0.97 | 9.8 | 547 | 693 |
| BL1-20 | 304.00 | 0.05 | 0.001 7 | 0.282 761 | 0.000 007 | -0.4 | -0.95 | 6.0 | 709 | 939 |
| BL1-26 | 298.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 6 | 0.282 803 | 0.000 009 | 1.1 | -0.98 | 7.5 | 630 | 830 |
| BL1-27 | 298.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 866 | 0.000 010 | 3.3 | -0.98 | 9.7 | 543 | 690 |
| BL1-28 | 301.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 851 | 0.000 012 | 2.8 | -0.97 | 9.2 | 566 | 726 |
| BL1-29 | 302.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 843 | 0.000 008 | 2.5 | -0.98 | 9.0 | 576 | 742 |
| BL2-01 | 290.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 847 | 0.000 008 | 2.7 | -0.98 | 9.1 | 569 | 732 |
| BL2-06 | 305.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 867 | 0.000 009 | 3.4 | -0.98 | 9.8 | 541 | 687 |
| BL2-09 | 301.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 821 | 0.000 010 | 1.7 | -0.98 | 8.2 | 605 | 790 |
| BL2-10 | 302.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 893 | 0.000 009 | 4.3 | -0.98 | 10.7 | 506 | 629 |
| BL2-11 | 299.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 859 | 0.000 009 | 3.1 | -0.98 | 9.5 | 552 | 705 |
| BL2-13 | 291.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 779 | 0.000 012 | 0.2 | -0.97 | 6.6 | 671 | 890 |
| BL2-17 | 300.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 6 | 0.282 850 | 0.000 009 | 2.7 | -0.98 | 9.2 | 564 | 725 |
| BL2-18 | 302.00 | 0.01 | 0.000 5 | 0.282 881 | 0.000 011 | 3.8 | -0.99 | 10.3 | 519 | 654 |
| BL2-19 | 309.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 895 | 0.000 008 | 4.3 | -0.98 | 10.8 | 503 | 626 |
| BL2-21 | 297.00 | 0.05 | 0.001 5 | 0.282 894 | 0.000 009 | 4.3 | -0.96 | 10.6 | 513 | 635 |
| BL2-24 | 299.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 846 | 0.000 008 | 2.6 | -0.98 | 9.1 | 570 | 734 |
| BL2-27 | 299.00 | 0.04 | 0.001 5 | 0.282 856 | 0.000 022 | 3.0 | -0.95 | 9.3 | 568 | 722 |
| BL2-29 | 302.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 9 | 0.282 814 | 0.000 008 | 1.5 | -0.97 | 7.9 | 618 | 808 |
| BL2-30 | 300.00 | 0.06 | 0.001 6 | 0.282 831 | 0.000 009 | 2.1 | -0.95 | 8.4 | 605 | 778 |
表4 巴彦都兰铜矿黑云母二长花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析数据
Table 4 Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions for biotite monzogranite samples from the Bayandulan copper deposit
| 测试点号 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | 2σ | εHf(0) | fLu/Hf | εHf(t) | TDM1 | TDM2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL1-02 | 302.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 897 | 0.000 009 | 4.4 | -0.98 | 10.9 | 499 | 619 |
| BL1-03 | 300.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 885 | 0.000 010 | 4.0 | -0.97 | 10.4 | 521 | 652 |
| BL1-04 | 298.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 829 | 0.000 008 | 2.0 | -0.97 | 8.4 | 599 | 775 |
| BL1-05 | 300.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 866 | 0.000 007 | 3.3 | -0.98 | 9.8 | 545 | 691 |
| BL1-08 | 300.00 | 0.04 | 0.001 3 | 0.282 840 | 0.000 010 | 2.4 | -0.96 | 8.8 | 588 | 754 |
| BL1-10 | 297.00 | 0.04 | 0.001 3 | 0.282 836 | 0.000 010 | 2.2 | -0.96 | 8.5 | 595 | 766 |
| BL1-11 | 301.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 9 | 0.282 863 | 0.000 009 | 3.2 | -0.97 | 9.7 | 550 | 699 |
| BL1-18 | 304.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 866 | 0.000 007 | 3.3 | -0.97 | 9.8 | 547 | 693 |
| BL1-20 | 304.00 | 0.05 | 0.001 7 | 0.282 761 | 0.000 007 | -0.4 | -0.95 | 6.0 | 709 | 939 |
| BL1-26 | 298.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 6 | 0.282 803 | 0.000 009 | 1.1 | -0.98 | 7.5 | 630 | 830 |
| BL1-27 | 298.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 866 | 0.000 010 | 3.3 | -0.98 | 9.7 | 543 | 690 |
| BL1-28 | 301.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 851 | 0.000 012 | 2.8 | -0.97 | 9.2 | 566 | 726 |
| BL1-29 | 302.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 843 | 0.000 008 | 2.5 | -0.98 | 9.0 | 576 | 742 |
| BL2-01 | 290.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 847 | 0.000 008 | 2.7 | -0.98 | 9.1 | 569 | 732 |
| BL2-06 | 305.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 867 | 0.000 009 | 3.4 | -0.98 | 9.8 | 541 | 687 |
| BL2-09 | 301.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 821 | 0.000 010 | 1.7 | -0.98 | 8.2 | 605 | 790 |
| BL2-10 | 302.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 893 | 0.000 009 | 4.3 | -0.98 | 10.7 | 506 | 629 |
| BL2-11 | 299.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 859 | 0.000 009 | 3.1 | -0.98 | 9.5 | 552 | 705 |
| BL2-13 | 291.00 | 0.03 | 0.001 0 | 0.282 779 | 0.000 012 | 0.2 | -0.97 | 6.6 | 671 | 890 |
| BL2-17 | 300.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 6 | 0.282 850 | 0.000 009 | 2.7 | -0.98 | 9.2 | 564 | 725 |
| BL2-18 | 302.00 | 0.01 | 0.000 5 | 0.282 881 | 0.000 011 | 3.8 | -0.99 | 10.3 | 519 | 654 |
| BL2-19 | 309.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 8 | 0.282 895 | 0.000 008 | 4.3 | -0.98 | 10.8 | 503 | 626 |
| BL2-21 | 297.00 | 0.05 | 0.001 5 | 0.282 894 | 0.000 009 | 4.3 | -0.96 | 10.6 | 513 | 635 |
| BL2-24 | 299.00 | 0.02 | 0.000 7 | 0.282 846 | 0.000 008 | 2.6 | -0.98 | 9.1 | 570 | 734 |
| BL2-27 | 299.00 | 0.04 | 0.001 5 | 0.282 856 | 0.000 022 | 3.0 | -0.95 | 9.3 | 568 | 722 |
| BL2-29 | 302.00 | 0.03 | 0.000 9 | 0.282 814 | 0.000 008 | 1.5 | -0.97 | 7.9 | 618 | 808 |
| BL2-30 | 300.00 | 0.06 | 0.001 6 | 0.282 831 | 0.000 009 | 2.1 | -0.95 | 8.4 | 605 | 778 |
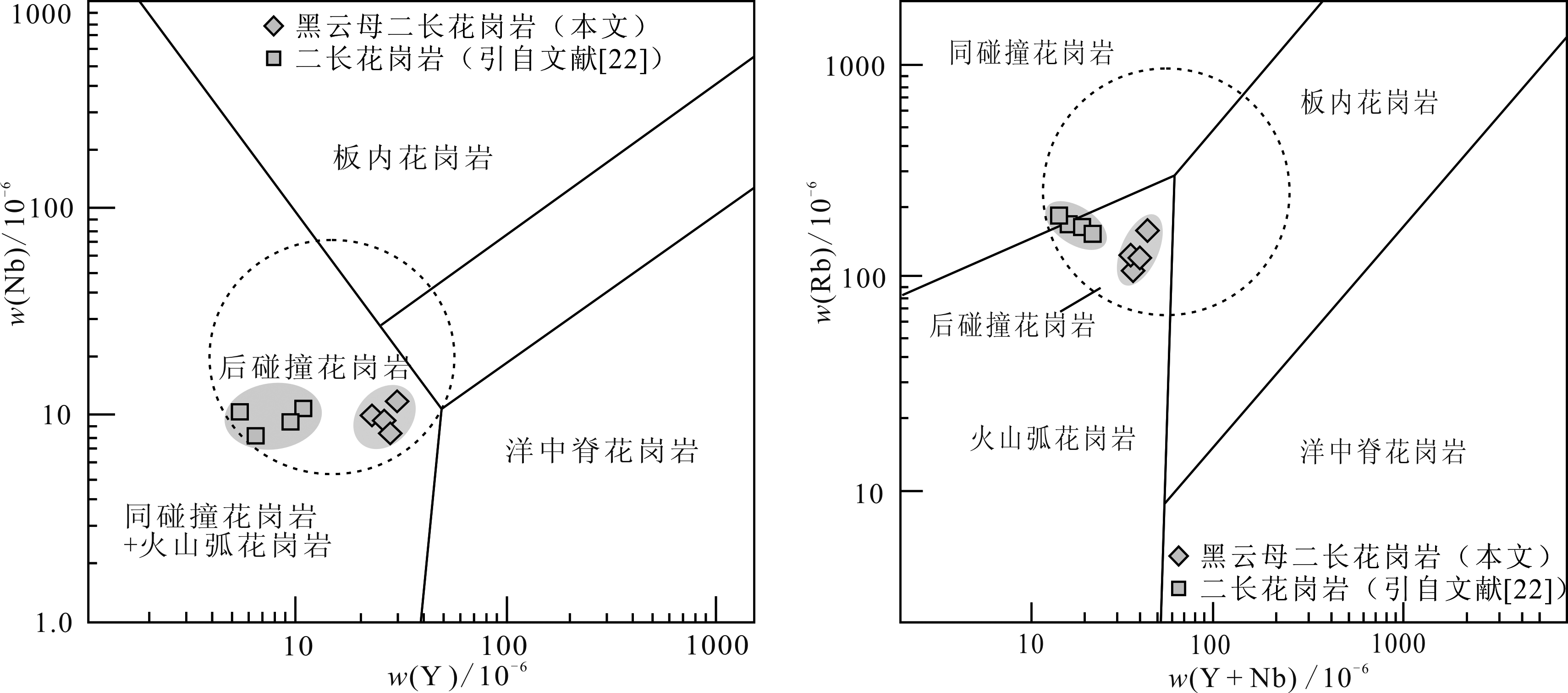
图10 巴彦都兰铜矿床黑云母二长花岗岩Y-Nb、(Y+Nb)-Rb构造判别图(底图据文献[40])
Fig.10 Y-Nb, (Y+Nb)-Rb tectonic discrimination diagram for biotite monzogranite in the Bayandulan copper deposit (after reference[40])

图11 巴彦都兰黑云母二长花岗岩R2-R1构造环境判别图(底图据文献[42])
Fig.11 R2-R1 tectonic discrimination diagram for biotite monzogranite in the Bayandulan copper deposit(after reference[42])
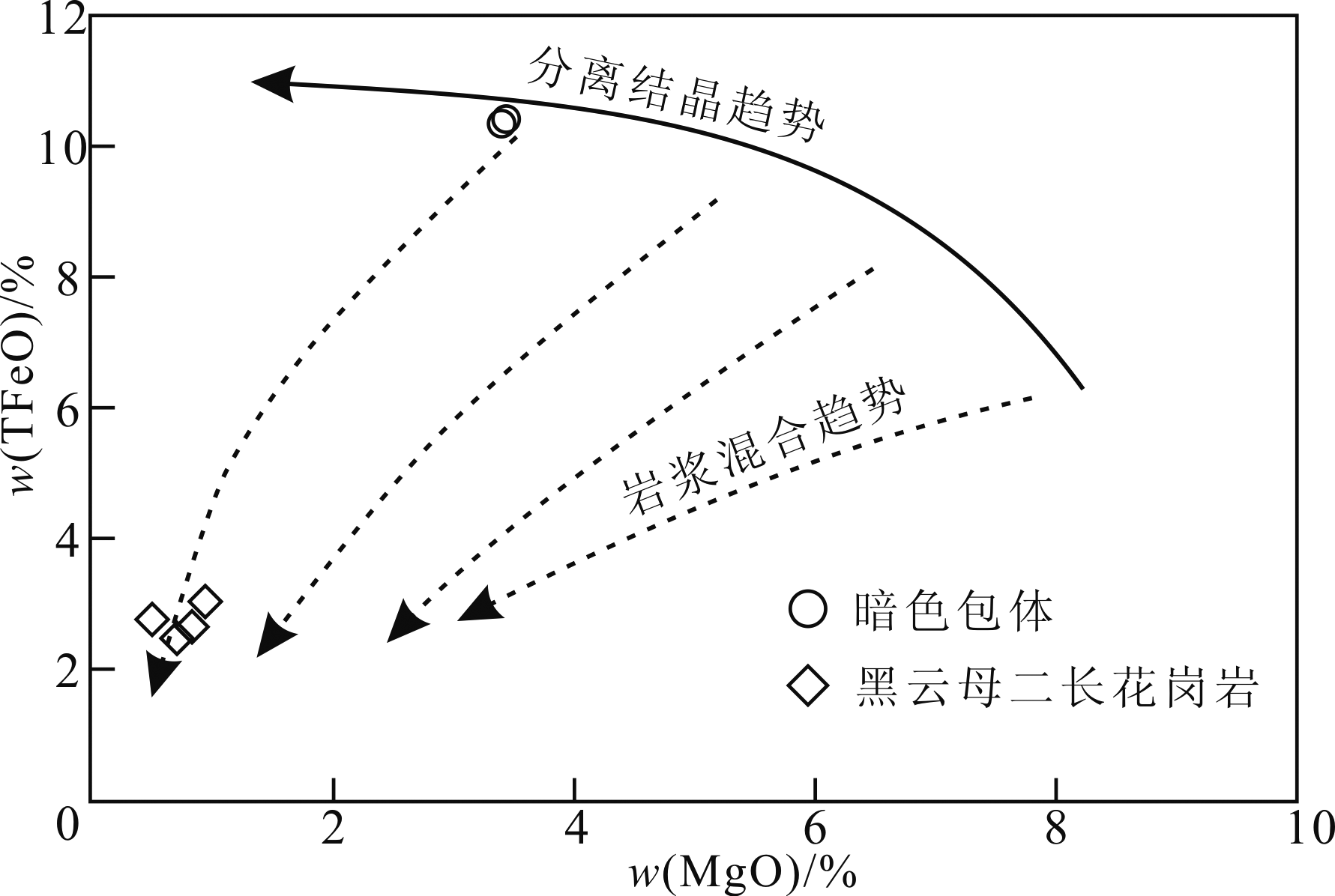
图13 巴彦都兰铜矿黑云母二长花岗岩及其暗色微粒包体TFeO-MgO演化图解(底图据文献[66])
Fig.13 TFeO-MgO diagram of biotite monzogranite and its enclaves in the Bayandulan copper deposit (after refe-rence[66])
| 构造背景 | 矿床(点) | 矿床类型 | 测试岩石/矿物 | 测试方法 | 成岩/成矿时代 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 同造山 | 欧玉陶勒盖 | 斑岩型矿床 | 辉石玄武岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb | 371~390 Ma | [ |
| 辉钼矿 | Re-Os等时线法 | 371~374 Ma | ||||
| 石英闪长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb | (374±3) Ma | ||||
| 石英长石斑岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb | (372±1) Ma | ||||
| 查干苏布尔加 | 斑岩型矿床 | 正长花岗斑岩 | K-Ar法 | 265~339 Ma | [ | |
| 辉钼矿 | Re-Os等时线法 | (370.0±0.8) Ma | ||||
| 绢云母 | 40Ar-39Ar法 | (369.4±7) Ma | ||||
| 白山 | 块状硫化物矿床 | 无 | 无 | 早—中泥盆世 | [ | |
| 造山后 | 奥尤特 | 火山-次火山热 液型矿床 | 流纹岩 | 锆石U-Pb | 320 Ma | 未发表 |
| 绢云母 | 40Ar-39Ar法 | (287±10) Ma | [ | |||
| 巴彦都兰 | 热液型矿床 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石U-Pb | 300 Ma | 本文 | |
| 小坝梁 | 喷流沉积型矿床 | 凝灰岩 | 锆石U-Pb | 314 Ma | 未发表 |
表5 二连—东乌旗及其邻区主要铜金属矿床成因类型及成矿时代
Table 5 The mineralization age of the major copper deposits in Erenhot-East Ujimqin and their adjacent areas
| 构造背景 | 矿床(点) | 矿床类型 | 测试岩石/矿物 | 测试方法 | 成岩/成矿时代 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 同造山 | 欧玉陶勒盖 | 斑岩型矿床 | 辉石玄武岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb | 371~390 Ma | [ |
| 辉钼矿 | Re-Os等时线法 | 371~374 Ma | ||||
| 石英闪长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb | (374±3) Ma | ||||
| 石英长石斑岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb | (372±1) Ma | ||||
| 查干苏布尔加 | 斑岩型矿床 | 正长花岗斑岩 | K-Ar法 | 265~339 Ma | [ | |
| 辉钼矿 | Re-Os等时线法 | (370.0±0.8) Ma | ||||
| 绢云母 | 40Ar-39Ar法 | (369.4±7) Ma | ||||
| 白山 | 块状硫化物矿床 | 无 | 无 | 早—中泥盆世 | [ | |
| 造山后 | 奥尤特 | 火山-次火山热 液型矿床 | 流纹岩 | 锆石U-Pb | 320 Ma | 未发表 |
| 绢云母 | 40Ar-39Ar法 | (287±10) Ma | [ | |||
| 巴彦都兰 | 热液型矿床 | 二长花岗岩 | 锆石U-Pb | 300 Ma | 本文 | |
| 小坝梁 | 喷流沉积型矿床 | 凝灰岩 | 锆石U-Pb | 314 Ma | 未发表 |
| [1] | 童英, 洪大卫, 王涛, 等. 中蒙边境中段花岗岩时空分布特征及构造和找矿意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 395-412. |
| [2] | 李可, 张志诚, 冯志硕, 等. 兴蒙造山带中段北部晚古生代两期岩浆活动及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(2): 272-288. |
| [3] |
CHENG Y, TENG X, LI Y, et al. Early Permian East-Ujimqin mafic-ultramafic and granitic rocks from the Xing’an-Mongolian Orogenic Belt, North China: Origin, chronology, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 96: 361-373.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 赵一鸣, 王大畏, 张德全, 等. 内蒙古东南部铜多金属成矿地质条件及找矿模式[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1994: 1-234. |
| [5] | 赵一鸣, 张德全, 徐志刚. 大兴安岭及其邻区铜多金属矿床成矿规律与远景评价[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1997: 1-318. |
| [6] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 张义, 等. 中蒙边境中东段金属矿床成矿规律和找矿方向[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-574. |
| [7] |
ZHANG W, NIE F, LIU S, et al. Characteristics and genesis of mineral deposits in East Ujimqin Banner, western segment of the Great Xing’an Mountains, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 459-471.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 王建平. 内蒙古东乌旗铜、银多金属成矿带成矿类型分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2003, 17(2): 132-135. |
| [9] | 王守光, 黄占起, 苏新旭, 等. 一条值得重视的跨国境成矿带——南戈壁—东乌旗铜多金属成矿带[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 249-255. |
| [10] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等. 蒙古国南部及邻区金属矿床类型及其时空分布特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3):267-288. |
| [11] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 刘树文, 等. 大兴安岭南段西坡金属矿床特征及成矿规律[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(5): 1583-1599. |
| [12] | 常春郊, 王治华, 王梁, 等. 内蒙东乌珠穆沁旗地区多金属矿床类型与成矿规律[J]. 矿产与地质, 2014(5): 536-545. |
| [13] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 刘妍, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗吉林宝力格银(金)矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 2007, 27(s1): 178-180. |
| [14] | 张万益. 内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗岩浆活动与金属成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2008: 1-169. |
| [15] |
JIANG S H, BAGAS L, HU P, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of the highly fractionated granite with tetrad REE patterns in the Shamai tungsten deposit in eastern Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for the timing of mineralization and ore genesis[J]. Lithos, 2016, 261: 322-339.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 胡朋, 聂凤军, 赫英, 等. 内蒙古沙麦岩体:正εNd(t)值的过铝质花岗岩[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(11): 2781-2790. |
| [17] | 许立权, 陈志勇, 陈郑辉, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗朝不楞铁矿区中粗粒花岗岩SHRIMP定年及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(2): 317-322. |
| [18] | 聂秀兰, 侯万荣. 内蒙古迪彦钦阿木大型钼-银矿床的发现及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 469-472. |
| [19] | 孙艳霞, 张达, 张寿庭, 等. 内蒙古小坝梁铜金矿床的硫、铅同位素特征和喷流沉积成因[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2009, 24(4): 282-285. |
| [20] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 刘妍, 等. 内蒙古奥尤特铜-锌矿床绢云母40Ar-39Ar同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(5): 592-598. |
| [21] | 李敏, 程银行, 李艳锋. 内蒙古东乌旗巴彦都兰二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(4): 6-14. |
| [22] | 李敏, 程银行, 任邦方, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗晚古生代闪长岩、二长花岗岩年代学特征及岩石成因[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(2):380-394. |
| [23] | 洪大卫, 王式洸, 谢锡林, 等. 试析地幔来源物质成矿域——以中亚造山带为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 22(1): 41-55. |
| [24] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YUAN H, GAO S, LIU X, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3): 353-370.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WU F Y, YANG Y H, XIE L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochrono-logy[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234(1): 105-126.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [28] | MIDDLEMOST E A. Magmatic Rocks[M]. London:Logman, 1995: 1-266. |
| [29] |
Middlemost E A. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
DOI URL |
| [30] | RUBATTO D, GEBAUER D. Use of cathodoluminescence for U-Pb zircon dating by ion Microprobe: Some examples from the Western Alps[M]// PAGELM, BARBINV, BLANCP, et al.Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2000: 373-400. |
| [31] |
HANCHAR J M, MILLER C F. Zircon zonation patterns as revealed by cathodoluminescence and backscattered electron images: implications for interpretation of complex crustal histories[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 110(1): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
BELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
BLICHERT-TOFT J, ALBARÈDE F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1): 243-258.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
GRIFFIN W L, PEARSON N J, BELOUSOVA E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LA-MC-ICP-MS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1): 133-147.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 程银行, 李艳锋, 李敏, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗碱性侵入岩的时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(11): 2086-2096. |
| [37] | 王治华, 常春郊, 丛润祥, 等. 内蒙古阿钦楚鲁二长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(1): 166-187. |
| [38] | 王继春, 王银宏, 张梅, 等. 内蒙古高尔旗银铅锌矿区花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 961-980. |
| [39] | 云飞, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 内蒙古莫若格钦地区二长闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(3): 504-510. |
| [40] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [41] | 韩宝福. 后碰撞花岗岩类的多样性及其构造环境判别的复杂性[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(3): 64-72. |
| [42] |
BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1/4): 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [43] | XIAO W, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the Central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectoni-cs, 2003, 22(6): 8-1. |
| [44] |
XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HUANG B C, et al. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 98(6): 1189-1217.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
WINDLEY B F, ALEXEIEV D, XIAO W, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1): 31-47.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ROBINSON P T, ZHOU M, HU X F, et al. Geochemical constraints on the origin of the Hegenshan ophiolite, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1999, 17(4): 423-442.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
JIAN P, LIU D, KRÖNER A, et al. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China: implications for continental growth[J]. Lithos, 2008, 101(3): 233-259.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 苏美霞, 赵文涛, 张慧聪, 等. 华北板块与西伯利亚板块缝合带之地球物理特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(5): 949-955. |
| [49] |
EIZENHÖFER P R, ZHAO G, ZHANG J, et al. Final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean along the Solonker Suture Zone: Constraints from geochronological and geochemical data of Permian volcanic and sedimentary rocks[J]. Tectonics, 2014, 33(4): 441-463.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
JIAN P, KRÖNER A, WINDLEY B F, et al. Carboniferous and Cretaceous mafic-ultramafic massifs in Inner Mongolia (China): A SHRIMP zircon and geochemical study of the previously presumed integral “Hegenshan ophiolite”[J]. Lithos, 2012, 142/143: 48-66.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
ZHANG Z, LI K, LI J, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Eastern Erenhot ophiolitic complex: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 279-293.
DOI URL |
| [52] | 黄波, 付冬, 李树才, 等. 内蒙古贺根山蛇绿岩形成时代及构造启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(1): 158-176. |
| [53] | 洪大卫, 王式洸, 韩宝福, 等. 碱性花岗岩的构造环境分类及其鉴别标志[J]. 中国科学:化学, 1995(4):418-426. |
| [54] | 辛后田, 滕学建. 内蒙古东乌旗宝力高庙组地层划分及其同位素年代学研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2011, 34(1): 1-9. |
| [55] | 程银行, 滕学建, 辛后田, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗狠麦温都尔花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(3): 323-334. |
| [56] | 邓晋福, 赵海玲, 莫宣学. 中国大陆根-柱构造:大陆动力学的钥匙[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-110. |
| [57] |
BROWN M. The generation, segregation, ascent and emplacement of granite magma: the migmatite-to-crustally-derived granite connection in thickened orogens[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 36(1/2): 83-130.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩结晶分离作用问题——关于花岗岩研究的思考之二[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1239-1251. |
| [59] |
SCHERER E E, CAMERON K L, BLICHERT-TOFT J. Lu-Hf garnet geochronology: closure temperature relative to the Sm-Nd system and the effects of trace mineral inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(19): 3413-3432.
DOI URL |
| [60] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. |
| [61] |
GRIFFIN W L, WANG X, JACKSON S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: in-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3): 237-269.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
DOBRETSOV N L, BERZIN N A, BUSLOV M M. Opening and tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. International Geology Review, 1995, 37(4): 335-360.
DOI URL |
| [63] | DEBON F. Comparative major element chemistry in various “microgranular enclave-plutonic host” pairs[M]// DIDIERJ, BARBARINB.Enclaves and Granite Petrology. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1991: 293-312. |
| [64] |
KOCAK K, ZEDEF V, KANSUN G. Magma mixing/mingling in the Eocene Horoz (Nigde) granitoids, central southern Turkey: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 103(1/4): 149-167.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
MÜNKER C, PFÄNDER J A, WEYER S, et al. Evolution of planetary cores and the Earth-Moon system from Nb/Ta systema-tics[J]. Science, 2003, 301:84.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
ZORPI M J, COULON C, ORSINI J B, et al. Magma mingling, zoning and emplacement in calc-alkaline granitoid plutons[J]. Tectonophysics, 1989, 157(4):315-329.
DOI URL |
| [67] | 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩混合问题:与玄武岩对比的启示——关于花岗岩研究的思考之一[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(5): 1141-1152. |
| [68] | 华仁民, 王登红. 关于花岗岩与成矿作用若干基本概念的再认识[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, 31(1): 165-175. |
| [69] | 聂凤军, 曹毅, 丁成武, 等. 论兴蒙造山带叠生成矿作用——以锡林浩特和额尔古纳地块为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 2063-2080. |
| [70] | 葛良胜, 张文钊, 袁士松, 等. 蒙古南戈壁—中国东乌旗跨国境成矿带东段金多金属成矿与找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 1-209. |
| [71] |
PERELLO J, COX D, GARAMJAV D, et al. Oyu Tolgoi, Mongolia: Siluro-Devonian porphyry Cu-Au-(Mo) and high-sulfidation Cu mineralization with a Cretaceous Chalcocite Blanket[J]. Economic Geology, 2001, 96(6):1407-1428.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
KHASHGEREL B E, RYE R O, HEDENQUIST J W, et al. Geology and reconnaissance stable isotope study of the Oyu Tolgoi porphyry Cu-Au system, South Gobi, Mongolia[J]. Economic Geology, 2006, 101(3):503-522.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
WAINWRIGHT A J, TOSDAL R M, WOODEN J L, et al. U-Pb (zircon) and geochemical constraints on the age, origin, and evolution of Paleozoic arc magmas in the Oyu Tolgoi porphyry Cu-Au district, southern Mongolia[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(3):764-787.
DOI URL |
| [74] | WATANABE Y, STEIN H J. Re-Os ages for the Erdenet and Tsagaan Suvarga porphyry Cu-Mo deposits, Mongolia, and tectonic implications[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95(7): 1537-1542. |
| [75] | 聂凤军, 云飞. 蒙古国南部又发现一处大型铜-锌矿床[J]. 地球学报, 2009, 30(1): 127-128. |
| [1] | 李厚民, 李立兴, 李以科, 柯昌辉, 李瑞萍, 李小赛, 王亿. 内蒙古白云鄂博铁-铌-稀土矿床矿化蚀变矿物组合及流体组成[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 13-24. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [4] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [5] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [6] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [7] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [8] | 刘金宝, 朱洛婷, 李龙雪, 侯青叶. 内蒙古艾力格庙地区卫境岩体的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 419-432. |
| [9] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [10] | 吕云鹤, 董国臣, 赵丽玮, 苏麟, 殷国栋, 汤家辉. 内蒙古沙章土矿区闪长玢岩成岩时代及岩浆源区探讨:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 836-847. |
| [11] | 李柱, 张德会, 张荣臻, 沈存利, 焦世豪, 李林, 朱鹏龙. 内蒙古那仁乌拉早白垩世高分异花岗岩年代学及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 848-861. |
| [12] | 杨培奇, 刘敬党, 刘淑梅, 杨飞, 杨孝伟. 内蒙古乌拉特中旗大乌淀石墨矿床石英片岩地球化学特征与SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 672-681. |
| [13] | 程先钰, 田健, 段霄龙, 赵泽南, 任邦方, 张永. 北山洋晚志留世—早泥盆世构造演化:内蒙古白云山蛇绿混杂岩带南部侵入岩年代学、地球化学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 295-306. |
| [14] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [15] | 张红雨, 苏犁, 秦红. 内蒙古大沟井寒武纪黑色页岩元素地球化学特征及钒赋存形式[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 321-332. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||