



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (01): 321-332.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.054
收稿日期:2019-07-09
修回日期:2020-06-15
出版日期:2022-02-10
发布日期:2022-03-08
作者简介:张红雨,女,实验师,1985年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事元素地球化学和年代学研究。Email: zhanghongyu@cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
ZHANG Hongyu1,2( ), SU Li1,2, QIN Hong1,2
), SU Li1,2, QIN Hong1,2
Received:2019-07-09
Revised:2020-06-15
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2022-03-08
摘要:
对内蒙古大沟井钒矿床的矿石样品进行了系统的常量和微量元素、X射线粉晶衍射以及显微能谱分析,探讨矿石中钒的赋存形式、形成环境以及保存条件等。研究结果表明,矿石样品中P2O5含量变化范围为0.81%~6.14%,显示其磷含量普遍较高,反映地层中较为富集磷;样品烧失量的范围为7.75%~41.24%,比较大,反映云母及泥质胶结物含量较高。矿石的V含量介于1 015.2×10-6~4 162.0×10-6之间,远高于地壳中钒的平均含量。U/Th值指示样品为正常的海相沉积产物;矿石的V/Cr、Ni/Co、δU、δCe、Ce/La及V/(V+Ni)值的计算结果以及黑色岩系中的大部分Fe均已转化为黄铁矿这些信息一致揭示出,该区黑色岩系整体上形成于一种较干燥、缺氧、富H2S、还原和封闭的滞留海盆环境。矿石样品中钒的主要载体矿物为原生矿物相钒云母,为鳞片状矿物,粒度均极细,多型为2M1,矿物化学分子式为K(V,Al,Mg)2AlSi3O10(OH)2。研究认为大量黄铁矿单晶或集合体的存在是钒元素在黑色岩系中富集和保存的有利因素。
中图分类号:
张红雨, 苏犁, 秦红. 内蒙古大沟井寒武纪黑色页岩元素地球化学特征及钒赋存形式[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 321-332.
ZHANG Hongyu, SU Li, QIN Hong. Element Geochemistry and Vanadium Occurrence of the Dagoujing Black Shales, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(01): 321-332.

图1 内蒙古大沟井钒矿床2 350 m中段矿体平面地质图(据金文庆等[12])
Fig.1 Geological map of 2,350 m level for the Dagoujing V deposit, Inner Mongolia (modified from Jin et al.[12])

图2 内蒙古大沟井钒矿床0号勘探线剖面地质图(据金文庆等[12]) 1.第四系黄土及坡积物;2.震旦系草大板组绢云钙质千枚岩;3.震旦系草大坂组炭质千枚岩;4.震旦系草大坂组含炭千枚岩;5.震旦系草大坂组含砾炭质千枚岩;6.震旦系烧火筒沟组绢云钙质千枚岩;7.震旦系烧火筒沟组绢云石英千枚岩;8.震旦系烧火筒沟组炭质板岩;9.震旦系烧火筒沟组砂质板岩;10.震旦系烧火筒沟组碎裂炭质板岩;11.震旦系烧火筒沟组含炭灰岩;12.震旦系烧火筒沟组炭质千枚岩;13.震旦系烧火筒沟组砂质灰岩;14.震旦系烧火筒沟组灰岩;15.钻孔位置及深度(m);16.矿体及编号;17.资源储量估算边界线
Fig.2 Cross section geological map of the number 0 exploration line for the Dagoujing V deposit, Inner Mongolia (modified from Jin et al.[12])
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 采样位置 | 岩石名称 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tc4-3-E1 | 4号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂质板岩 |
| 2 | Tc4-3-E | 4号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂质板岩 |
| 3 | Tc4-3-X | 4号探槽矿层下段 | 粉砂质板岩 |
| 4 | Tc28-2-E1 | 28号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂泥岩 |
| 5 | Tc28-2-E3 | 28号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂泥岩 |
| 6 | Tc28-2-E5 | 28号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂泥岩 |
| 7 | Tc12-2-X | 12号探槽矿层下段 | 含炭千枚岩 |
| 8 | Tc12-S | 12号探槽矿层上段 | 含炭千枚岩 |
| 9 | Tc12-Z | 12号探槽矿层中段 | 含炭千枚岩 |
| 10 | Zk001-1 | 1号钻孔113.09~117.09 m | 含炭粉砂岩 |
| 11 | Zk1802 | 18号钻孔76~80 m | 炭质粉砂泥岩 |
| 12 | Zk301 | 3号钻孔69.86~72.06 m | 含炭粉砂岩 |
| 13 | Zk501 | 5号钻孔30.19~31.34 m | 含炭粉砂岩 |
表1 大沟井钒矿床样品采集信息
Table 1 Sampling information for the Dagoujing vana- dium deposit
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 采样位置 | 岩石名称 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tc4-3-E1 | 4号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂质板岩 |
| 2 | Tc4-3-E | 4号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂质板岩 |
| 3 | Tc4-3-X | 4号探槽矿层下段 | 粉砂质板岩 |
| 4 | Tc28-2-E1 | 28号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂泥岩 |
| 5 | Tc28-2-E3 | 28号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂泥岩 |
| 6 | Tc28-2-E5 | 28号探槽矿层东段 | 含炭粉砂泥岩 |
| 7 | Tc12-2-X | 12号探槽矿层下段 | 含炭千枚岩 |
| 8 | Tc12-S | 12号探槽矿层上段 | 含炭千枚岩 |
| 9 | Tc12-Z | 12号探槽矿层中段 | 含炭千枚岩 |
| 10 | Zk001-1 | 1号钻孔113.09~117.09 m | 含炭粉砂岩 |
| 11 | Zk1802 | 18号钻孔76~80 m | 炭质粉砂泥岩 |
| 12 | Zk301 | 3号钻孔69.86~72.06 m | 含炭粉砂岩 |
| 13 | Zk501 | 5号钻孔30.19~31.34 m | 含炭粉砂岩 |
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc4-3-E1 | 51.77 | 0.57 | 9.03 | 7.57 | 0.04 | 1.21 | 5.79 | 0.7 | 3.03 | 2.35 | 13.46 | 95.52 |
| Tc4-3-E | 65.47 | 0.42 | 6.65 | 2.93 | 0.03 | 1.11 | 8.29 | 0.19 | 2.4 | 1.53 | 9.15 | 98.17 |
| Tc4-3-X | 60.28 | 0.70 | 8.73 | 3.12 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 8.69 | 0.22 | 3.43 | 2.19 | 7.75 | 96.58 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 65.45 | 0.82 | 7.10 | 5.60 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 4.52 | 0.25 | 3.08 | 1.81 | 9.02 | 98.66 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 34.65 | 0.29 | 3.65 | 5.64 | 0.02 | 0.38 | 16.09 | 0.16 | 0.85 | 6.14 | 21.54 | 89.40 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 50.45 | 0.42 | 5.91 | 5.61 | 0.03 | 0.81 | 9.45 | 0.19 | 1.96 | 3.96 | 16.10 | 94.90 |
| Tc12-2-X | 49.08 | 0.84 | 10.30 | 5.71 | 0.03 | 1.62 | 6.29 | 0.02 | 3.67 | 4.17 | 17.54 | 99.26 |
| Tc12-S | 63.54 | 0.91 | 10.14 | 6.45 | 0.03 | 1.41 | 3.04 | 0.20 | 4.24 | 0.81 | 8.54 | 99.31 |
| Tc12-Z | 52.51 | 0.52 | 7.96 | 10.92 | 0.02 | 1.27 | 6.73 | 0.40 | 4.16 | 1.84 | 11.89 | 98.20 |
| Zk001-1 | 40.79 | 0.41 | 6.70 | 4.06 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 1.88 | 0.08 | 2.42 | 1.16 | 41.24 | 99.75 |
| Zk1802 | 54.30 | 0.77 | 7.35 | 4.08 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 8.54 | 0.29 | 2.97 | 2.17 | 12.74 | 94.11 |
| Zk301 | 42.19 | 0.34 | 6.75 | 3.68 | 0.03 | 1.50 | 2.74 | 0.05 | 2.49 | 1.10 | 38.04 | 98.90 |
| Zk501 | 55.89 | 0.77 | 11.52 | 5.95 | 0.02 | 2.05 | 4.46 | 0.27 | 4.14 | 3.20 | 9.08 | 97.34 |
表2 大沟井钒矿床样品主量元素分析结果(%)
Table 2 Major element analytical results of the Dagoujing vanadium deposit (%)
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc4-3-E1 | 51.77 | 0.57 | 9.03 | 7.57 | 0.04 | 1.21 | 5.79 | 0.7 | 3.03 | 2.35 | 13.46 | 95.52 |
| Tc4-3-E | 65.47 | 0.42 | 6.65 | 2.93 | 0.03 | 1.11 | 8.29 | 0.19 | 2.4 | 1.53 | 9.15 | 98.17 |
| Tc4-3-X | 60.28 | 0.70 | 8.73 | 3.12 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 8.69 | 0.22 | 3.43 | 2.19 | 7.75 | 96.58 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 65.45 | 0.82 | 7.10 | 5.60 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 4.52 | 0.25 | 3.08 | 1.81 | 9.02 | 98.66 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 34.65 | 0.29 | 3.65 | 5.64 | 0.02 | 0.38 | 16.09 | 0.16 | 0.85 | 6.14 | 21.54 | 89.40 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 50.45 | 0.42 | 5.91 | 5.61 | 0.03 | 0.81 | 9.45 | 0.19 | 1.96 | 3.96 | 16.10 | 94.90 |
| Tc12-2-X | 49.08 | 0.84 | 10.30 | 5.71 | 0.03 | 1.62 | 6.29 | 0.02 | 3.67 | 4.17 | 17.54 | 99.26 |
| Tc12-S | 63.54 | 0.91 | 10.14 | 6.45 | 0.03 | 1.41 | 3.04 | 0.20 | 4.24 | 0.81 | 8.54 | 99.31 |
| Tc12-Z | 52.51 | 0.52 | 7.96 | 10.92 | 0.02 | 1.27 | 6.73 | 0.40 | 4.16 | 1.84 | 11.89 | 98.20 |
| Zk001-1 | 40.79 | 0.41 | 6.70 | 4.06 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 1.88 | 0.08 | 2.42 | 1.16 | 41.24 | 99.75 |
| Zk1802 | 54.30 | 0.77 | 7.35 | 4.08 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 8.54 | 0.29 | 2.97 | 2.17 | 12.74 | 94.11 |
| Zk301 | 42.19 | 0.34 | 6.75 | 3.68 | 0.03 | 1.50 | 2.74 | 0.05 | 2.49 | 1.10 | 38.04 | 98.90 |
| Zk501 | 55.89 | 0.77 | 11.52 | 5.95 | 0.02 | 2.05 | 4.46 | 0.27 | 4.14 | 3.20 | 9.08 | 97.34 |
| 样品编号 | Li | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc4-3-E1 | 31.98 | 12.12 | 3 210.00 | 3 362.00 | 153.30 | 270.20 | 34.64 | 475.80 | 47.44 | 114.50 | 14.88 |
| Tc4-3-E | 19.55 | 8.43 | 2 338.00 | 1 767.40 | 98.70 | 198.20 | 4.17 | 79.42 | 24.58 | 58.62 | 11.38 |
| Tc4-3-X | 17.86 | 9.30 | 2 754.00 | 2 362.00 | 116.30 | 96.20 | 1.05 | 60.38 | 27.50 | 28.94 | 11.82 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 17.77 | 11.70 | 4 188.00 | 1 355.80 | 142.60 | 99.36 | 2.65 | 106.80 | 67.76 | 110.50 | 11.92 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 6.72 | 5.61 | 1 423.00 | 774.60 | 60.16 | 104.10 | 0.62 | 13.19 | 22.92 | 49.90 | 5.76 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 16.73 | 13.24 | 2 194.00 | 1 469.60 | 84.16 | 178.40 | 5.85 | 116.30 | 33.12 | 76.10 | 9.18 |
| Tc12-2-X | 29.10 | 13.26 | 4 086.00 | 3 540.00 | 175.20 | 199.00 | 15.38 | 516.20 | 130.00 | 639.80 | 17.85 |
| Tc12-S | 38.04 | 10.12 | 4 624.00 | 1 806.00 | 156.10 | 226.80 | 13.52 | 391.60 | 98.72 | 553.00 | 15.51 |
| Tc12-Z | 26.86 | 12.30 | 2 916.00 | 1 015.20 | 127.30 | 183.10 | 4.06 | 112.50 | 41.16 | 139.80 | 16.74 |
| Zk001-1 | 13.89 | 6.95 | 2 168.00 | 3 424.00 | 85.98 | 146.50 | 12.25 | 435.00 | 76.24 | 262.40 | 16.92 |
| Zk1802 | 14.58 | 13.66 | 3 740.00 | 3 094.00 | 133.30 | 92.62 | 0.73 | 38.66 | 92.50 | 77.24 | 12.89 |
| Zk301 | 24.02 | 8.37 | 1 994.20 | 2 544.00 | 73.14 | 202.20 | 10.91 | 386.20 | 42.32 | 269.00 | 14.12 |
| Zk501 | 38.16 | 14.74 | 4 016.00 | 4 162.00 | 182.00 | 102.30 | 4.47 | 153.80 | 108.80 | 36.16 | 17.76 |
| 样品编号 | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U |
| Tc4-3-E1 | 96.86 | 241.40 | 196.80 | 10.61 | 4.78 | 449.60 | 4.19 | 0.66 | 38.94 | 9.66 | 5.21 |
| Tc4-3-E | 84.04 | 169.60 | 153.70 | 8.20 | 4.08 | 345.80 | 2.94 | 0.50 | 15.80 | 4.98 | 2.32 |
| Tc4-3-X | 90.18 | 81.48 | 160.40 | 9.57 | 4.03 | 474.80 | 3.11 | 0.60 | 16.56 | 5.25 | 2.16 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 86.40 | 363.00 | 352.20 | 13.71 | 4.73 | 1 624.20 | 7.31 | 0.97 | 47.96 | 10.08 | 2.62 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 24.08 | 503.20 | 87.32 | 4.67 | 1.12 | 4 062.00 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 27.90 | 3.65 | 1.87 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 50.16 | 309.00 | 165.40 | 7.28 | 2.00 | 2 716.00 | 2.57 | 0.46 | 65.58 | 6.75 | 1.70 |
| Tc12-2-X | 115.90 | 311.40 | 301.80 | 14.34 | 6.81 | 1 485.00 | 6.17 | 0.90 | 24.10 | 10.87 | 3.73 |
| Tc12-S | 130.80 | 114.80 | 378.60 | 15.39 | 8.78 | 711.60 | 8.09 | 1.09 | 24.04 | 10.84 | 1.93 |
| Tc12-Z | 141.70 | 180.30 | 144.50 | 9.63 | 6.09 | 864.40 | 3.13 | 0.62 | 14.08 | 11.00 | 1.08 |
| Zk001-1 | 66.04 | 103.50 | 106.40 | 10.63 | 2.22 | 2 336.00 | 2.02 | 0.46 | 32.32 | 5.14 | 8.54 |
| Zk1802 | 93.70 | 85.84 | 211.40 | 13.05 | 8.28 | 1 059.80 | 4.22 | 0.78 | 30.22 | 8.31 | 4.51 |
| Zk301 | 86.02 | 98.96 | 111.00 | 9.09 | 4.78 | 787.40 | 2.12 | 0.40 | 25.56 | 4.90 | 7.17 |
| Zk501 | 127.00 | 194.40 | 287.20 | 14.62 | 4.18 | 3 706.00 | 5.81 | 0.90 | 27.86 | 10.48 | 3.57 |
表3 大沟井钒矿床样品微量元素分析结果(10-6)
Table 3 Trace elements analytical results of the Dagoujing vanadium deposit (10-6)
| 样品编号 | Li | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc4-3-E1 | 31.98 | 12.12 | 3 210.00 | 3 362.00 | 153.30 | 270.20 | 34.64 | 475.80 | 47.44 | 114.50 | 14.88 |
| Tc4-3-E | 19.55 | 8.43 | 2 338.00 | 1 767.40 | 98.70 | 198.20 | 4.17 | 79.42 | 24.58 | 58.62 | 11.38 |
| Tc4-3-X | 17.86 | 9.30 | 2 754.00 | 2 362.00 | 116.30 | 96.20 | 1.05 | 60.38 | 27.50 | 28.94 | 11.82 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 17.77 | 11.70 | 4 188.00 | 1 355.80 | 142.60 | 99.36 | 2.65 | 106.80 | 67.76 | 110.50 | 11.92 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 6.72 | 5.61 | 1 423.00 | 774.60 | 60.16 | 104.10 | 0.62 | 13.19 | 22.92 | 49.90 | 5.76 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 16.73 | 13.24 | 2 194.00 | 1 469.60 | 84.16 | 178.40 | 5.85 | 116.30 | 33.12 | 76.10 | 9.18 |
| Tc12-2-X | 29.10 | 13.26 | 4 086.00 | 3 540.00 | 175.20 | 199.00 | 15.38 | 516.20 | 130.00 | 639.80 | 17.85 |
| Tc12-S | 38.04 | 10.12 | 4 624.00 | 1 806.00 | 156.10 | 226.80 | 13.52 | 391.60 | 98.72 | 553.00 | 15.51 |
| Tc12-Z | 26.86 | 12.30 | 2 916.00 | 1 015.20 | 127.30 | 183.10 | 4.06 | 112.50 | 41.16 | 139.80 | 16.74 |
| Zk001-1 | 13.89 | 6.95 | 2 168.00 | 3 424.00 | 85.98 | 146.50 | 12.25 | 435.00 | 76.24 | 262.40 | 16.92 |
| Zk1802 | 14.58 | 13.66 | 3 740.00 | 3 094.00 | 133.30 | 92.62 | 0.73 | 38.66 | 92.50 | 77.24 | 12.89 |
| Zk301 | 24.02 | 8.37 | 1 994.20 | 2 544.00 | 73.14 | 202.20 | 10.91 | 386.20 | 42.32 | 269.00 | 14.12 |
| Zk501 | 38.16 | 14.74 | 4 016.00 | 4 162.00 | 182.00 | 102.30 | 4.47 | 153.80 | 108.80 | 36.16 | 17.76 |
| 样品编号 | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U |
| Tc4-3-E1 | 96.86 | 241.40 | 196.80 | 10.61 | 4.78 | 449.60 | 4.19 | 0.66 | 38.94 | 9.66 | 5.21 |
| Tc4-3-E | 84.04 | 169.60 | 153.70 | 8.20 | 4.08 | 345.80 | 2.94 | 0.50 | 15.80 | 4.98 | 2.32 |
| Tc4-3-X | 90.18 | 81.48 | 160.40 | 9.57 | 4.03 | 474.80 | 3.11 | 0.60 | 16.56 | 5.25 | 2.16 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 86.40 | 363.00 | 352.20 | 13.71 | 4.73 | 1 624.20 | 7.31 | 0.97 | 47.96 | 10.08 | 2.62 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 24.08 | 503.20 | 87.32 | 4.67 | 1.12 | 4 062.00 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 27.90 | 3.65 | 1.87 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 50.16 | 309.00 | 165.40 | 7.28 | 2.00 | 2 716.00 | 2.57 | 0.46 | 65.58 | 6.75 | 1.70 |
| Tc12-2-X | 115.90 | 311.40 | 301.80 | 14.34 | 6.81 | 1 485.00 | 6.17 | 0.90 | 24.10 | 10.87 | 3.73 |
| Tc12-S | 130.80 | 114.80 | 378.60 | 15.39 | 8.78 | 711.60 | 8.09 | 1.09 | 24.04 | 10.84 | 1.93 |
| Tc12-Z | 141.70 | 180.30 | 144.50 | 9.63 | 6.09 | 864.40 | 3.13 | 0.62 | 14.08 | 11.00 | 1.08 |
| Zk001-1 | 66.04 | 103.50 | 106.40 | 10.63 | 2.22 | 2 336.00 | 2.02 | 0.46 | 32.32 | 5.14 | 8.54 |
| Zk1802 | 93.70 | 85.84 | 211.40 | 13.05 | 8.28 | 1 059.80 | 4.22 | 0.78 | 30.22 | 8.31 | 4.51 |
| Zk301 | 86.02 | 98.96 | 111.00 | 9.09 | 4.78 | 787.40 | 2.12 | 0.40 | 25.56 | 4.90 | 7.17 |
| Zk501 | 127.00 | 194.40 | 287.20 | 14.62 | 4.18 | 3 706.00 | 5.81 | 0.90 | 27.86 | 10.48 | 3.57 |
| 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc4-3-E1 | 44.74 | 59.08 | 6.972 | 25.00 | 4.240 | 0.880 | 4.228 | 0.583 | 3.956 | 0.899 |
| Tc4-3-E | 27.90 | 40.86 | 5.034 | 19.65 | 3.556 | 0.712 | 3.272 | 0.428 | 2.820 | 0.622 |
| Tc4-3-X | 35.88 | 50.64 | 6.282 | 24.00 | 4.036 | 0.798 | 3.912 | 0.598 | 4.480 | 1.116 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 30.60 | 56.16 | 6.684 | 25.04 | 4.294 | 0.957 | 3.574 | 0.484 | 3.086 | 0.645 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 25.20 | 38.42 | 5.282 | 21.18 | 4.170 | 1.211 | 4.448 | 0.618 | 3.996 | 0.884 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 29.44 | 44.64 | 6.014 | 23.04 | 2.988 | 0.712 | 2.720 | 0.379 | 2.648 | 0.618 |
| Tc12-2-X | 82.86 | 120.70 | 15.630 | 64.00 | 11.690 | 2.522 | 12.310 | 1.631 | 10.450 | 2.338 |
| Tc12-S | 43.76 | 80.78 | 9.500 | 34.72 | 5.714 | 1.150 | 5.120 | 0.744 | 4.940 | 1.097 |
| Tc12-Z | 51.64 | 100.70 | 9.926 | 29.56 | 4.796 | 0.977 | 4.264 | 0.607 | 4.098 | 0.922 |
| Zk001-1 | 30.96 | 44.82 | 6.110 | 24.74 | 4.678 | 1.133 | 4.836 | 0.661 | 4.308 | 0.953 |
| Zk1802 | 41.76 | 58.54 | 6.236 | 19.94 | 2.644 | 0.591 | 2.578 | 0.400 | 2.978 | 0.729 |
| Zk301 | 42.14 | 66.12 | 7.802 | 31.26 | 5.436 | 1.212 | 5.368 | 0.698 | 4.460 | 0.969 |
| Zk501 | 60.90 | 95.86 | 11.200 | 44.04 | 8.176 | 2.008 | 8.782 | 1.216 | 8.020 | 1.776 |
| 样品编号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe |
| Tc4-3-E1 | 2.774 | 0.372 | 2.178 | 0.305 | 43.44 | 156.21 | 9.21 | 14.73 | 0.63 | 0.74 |
| Tc4-3-E | 1.861 | 0.237 | 1.434 | 0.199 | 30.30 | 108.58 | 8.99 | 13.95 | 0.63 | 0.78 |
| Tc4-3-X | 3.512 | 0.472 | 2.690 | 0.378 | 57.86 | 138.79 | 7.09 | 9.57 | 0.61 | 0.76 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 2.022 | 0.302 | 2.044 | 0.299 | 23.22 | 136.19 | 9.93 | 10.74 | 0.73 | 0.92 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 2.494 | 0.317 | 1.865 | 0.271 | 45.04 | 110.36 | 6.41 | 9.69 | 0.85 | 0.78 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 1.919 | 0.259 | 1.596 | 0.231 | 31.54 | 117.20 | 10.30 | 13.23 | 0.75 | 0.78 |
| Tc12-2-X | 6.664 | 0.797 | 4.332 | 0.588 | 119.90 | 336.51 | 7.61 | 13.72 | 0.64 | 0.77 |
| Tc12-S | 3.410 | 0.479 | 3.094 | 0.452 | 44.58 | 194.96 | 9.08 | 10.15 | 0.64 | 0.93 |
| Tc12-Z | 2.878 | 0.411 | 2.578 | 0.360 | 38.36 | 213.76 | 12.26 | 14.37 | 0.65 | 1.02 |
| Zk001-1 | 2.794 | 0.354 | 2.016 | 0.284 | 45.70 | 128.65 | 6.94 | 11.02 | 0.72 | 0.75 |
| Zk1802 | 2.398 | 0.349 | 2.198 | 0.310 | 33.96 | 141.65 | 10.86 | 13.63 | 0.68 | 0.79 |
| Zk301 | 2.748 | 0.344 | 1.927 | 0.262 | 47.24 | 170.74 | 9.18 | 15.68 | 0.68 | 0.83 |
| Zk501 | 5.092 | 0.639 | 3.702 | 0.503 | 82.26 | 251.91 | 7.47 | 11.80 | 0.72 | 0.84 |
表4 大沟井钒矿床样品稀土元素分析结果
Table 4 REE analytical results of the Dagoujing vanadium deposit
| 样品编号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc4-3-E1 | 44.74 | 59.08 | 6.972 | 25.00 | 4.240 | 0.880 | 4.228 | 0.583 | 3.956 | 0.899 |
| Tc4-3-E | 27.90 | 40.86 | 5.034 | 19.65 | 3.556 | 0.712 | 3.272 | 0.428 | 2.820 | 0.622 |
| Tc4-3-X | 35.88 | 50.64 | 6.282 | 24.00 | 4.036 | 0.798 | 3.912 | 0.598 | 4.480 | 1.116 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 30.60 | 56.16 | 6.684 | 25.04 | 4.294 | 0.957 | 3.574 | 0.484 | 3.086 | 0.645 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 25.20 | 38.42 | 5.282 | 21.18 | 4.170 | 1.211 | 4.448 | 0.618 | 3.996 | 0.884 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 29.44 | 44.64 | 6.014 | 23.04 | 2.988 | 0.712 | 2.720 | 0.379 | 2.648 | 0.618 |
| Tc12-2-X | 82.86 | 120.70 | 15.630 | 64.00 | 11.690 | 2.522 | 12.310 | 1.631 | 10.450 | 2.338 |
| Tc12-S | 43.76 | 80.78 | 9.500 | 34.72 | 5.714 | 1.150 | 5.120 | 0.744 | 4.940 | 1.097 |
| Tc12-Z | 51.64 | 100.70 | 9.926 | 29.56 | 4.796 | 0.977 | 4.264 | 0.607 | 4.098 | 0.922 |
| Zk001-1 | 30.96 | 44.82 | 6.110 | 24.74 | 4.678 | 1.133 | 4.836 | 0.661 | 4.308 | 0.953 |
| Zk1802 | 41.76 | 58.54 | 6.236 | 19.94 | 2.644 | 0.591 | 2.578 | 0.400 | 2.978 | 0.729 |
| Zk301 | 42.14 | 66.12 | 7.802 | 31.26 | 5.436 | 1.212 | 5.368 | 0.698 | 4.460 | 0.969 |
| Zk501 | 60.90 | 95.86 | 11.200 | 44.04 | 8.176 | 2.008 | 8.782 | 1.216 | 8.020 | 1.776 |
| 样品编号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe |
| Tc4-3-E1 | 2.774 | 0.372 | 2.178 | 0.305 | 43.44 | 156.21 | 9.21 | 14.73 | 0.63 | 0.74 |
| Tc4-3-E | 1.861 | 0.237 | 1.434 | 0.199 | 30.30 | 108.58 | 8.99 | 13.95 | 0.63 | 0.78 |
| Tc4-3-X | 3.512 | 0.472 | 2.690 | 0.378 | 57.86 | 138.79 | 7.09 | 9.57 | 0.61 | 0.76 |
| Tc28-2-E1 | 2.022 | 0.302 | 2.044 | 0.299 | 23.22 | 136.19 | 9.93 | 10.74 | 0.73 | 0.92 |
| Tc28-2-E3 | 2.494 | 0.317 | 1.865 | 0.271 | 45.04 | 110.36 | 6.41 | 9.69 | 0.85 | 0.78 |
| Tc28-2-E5 | 1.919 | 0.259 | 1.596 | 0.231 | 31.54 | 117.20 | 10.30 | 13.23 | 0.75 | 0.78 |
| Tc12-2-X | 6.664 | 0.797 | 4.332 | 0.588 | 119.90 | 336.51 | 7.61 | 13.72 | 0.64 | 0.77 |
| Tc12-S | 3.410 | 0.479 | 3.094 | 0.452 | 44.58 | 194.96 | 9.08 | 10.15 | 0.64 | 0.93 |
| Tc12-Z | 2.878 | 0.411 | 2.578 | 0.360 | 38.36 | 213.76 | 12.26 | 14.37 | 0.65 | 1.02 |
| Zk001-1 | 2.794 | 0.354 | 2.016 | 0.284 | 45.70 | 128.65 | 6.94 | 11.02 | 0.72 | 0.75 |
| Zk1802 | 2.398 | 0.349 | 2.198 | 0.310 | 33.96 | 141.65 | 10.86 | 13.63 | 0.68 | 0.79 |
| Zk301 | 2.748 | 0.344 | 1.927 | 0.262 | 47.24 | 170.74 | 9.18 | 15.68 | 0.68 | 0.83 |
| Zk501 | 5.092 | 0.639 | 3.702 | 0.503 | 82.26 | 251.91 | 7.47 | 11.80 | 0.72 | 0.84 |
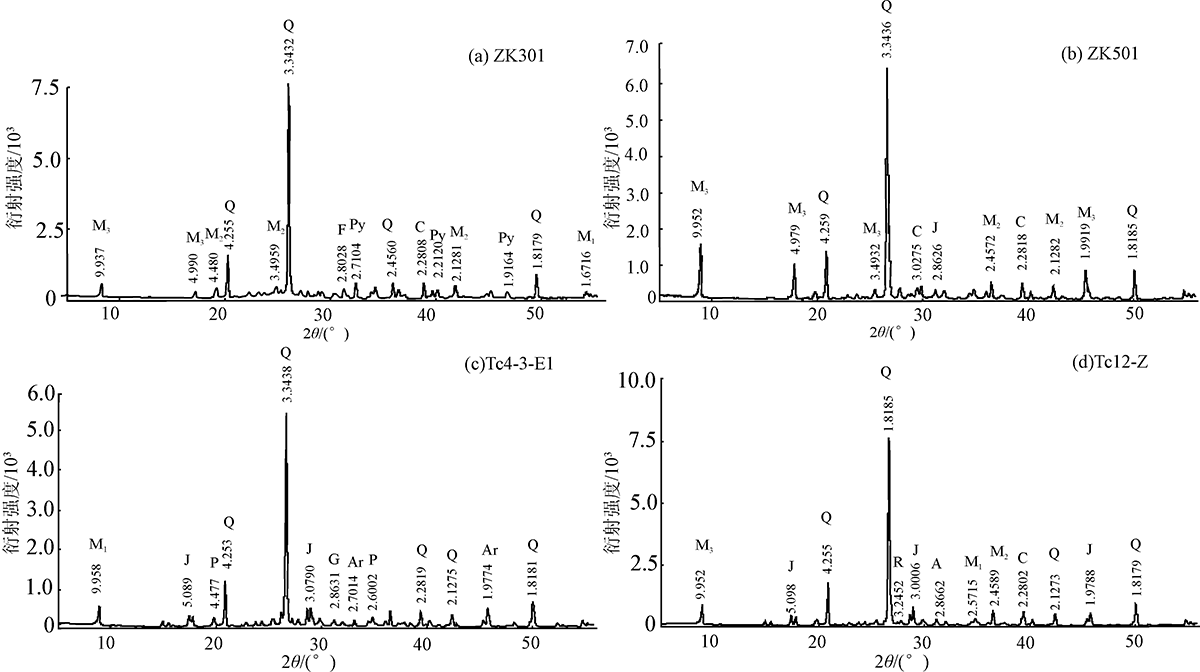
图3 大沟井钒矿床黑色岩系样品X粉晶衍射图谱 Q.石英;M1.含钒云母;M2.多硅白云母;M3.含钒云母+多硅白云母;Py.黄铁矿;J.黄钾铁钒;C.方解石; F.氟磷灰石;P.非晶相;G.石膏;A.硬石膏;Ar.文石;R.金红石
Fig.3 XRD patterns of samples from the Dagoujing vanadium deposit

图4 大沟井钒矿床样品电子扫描图像 (a)云母类矿物和含钒泥质条带共生,样号Tc-12-Z;(b)含钒云母微晶集合体的泥质条带与云母共生,样号Tc-12-Z;(c)黄铁矿集合体与云母类矿物共生,样号Tc-12-Z ;(d)黄铁矿单晶与集合体,样号Tc-12-Z ;(e)浅灰色束状集合体的云母类矿物与深灰色隐晶泥质条带及黄铁矿集合体共生产出,样号Zk001;(f)浅灰色束状集合体的云母类矿物与深灰色隐晶泥质条带共生产出,样号Zk001
Fig.4 SEM photos of samples from the Dagoujing vanadium deposit
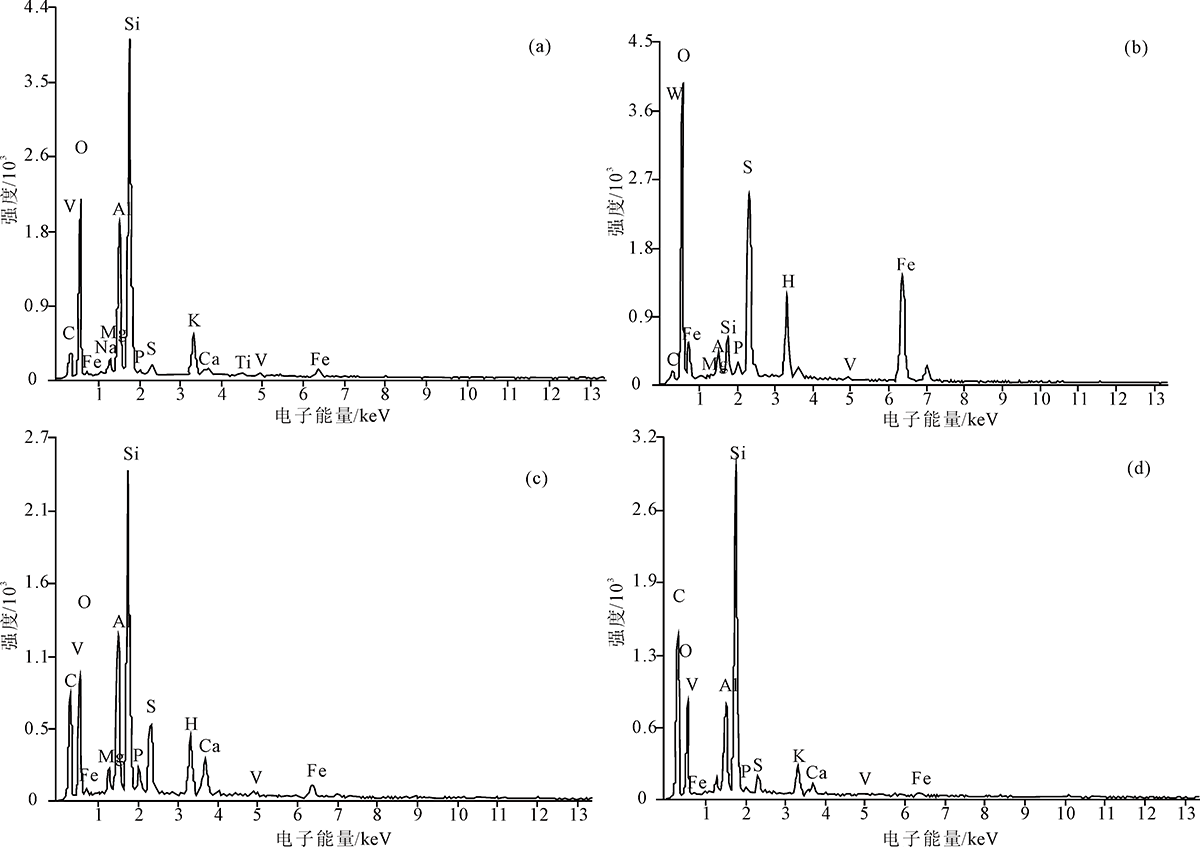
图5 大沟井钒矿床样品能谱图 (a)黏土矿物集合体能谱分析图(图4(b)中部的黏土矿物),样号Tc-12-Z;(b)黄铁矿单晶能谱分析图(图4(d)中的黄铁矿),样号Tc-12-Z;(c)灰色束状集合体的云母类矿物与深灰色隐晶泥质条带能谱分析图(图4(f)),样号Zk001;(d)浅灰色束状集合体的云母类矿物与深灰色隐晶泥质条带区域能谱分析图(图4(f)),样号Zk001
Fig.5 Energy dispersive spectra of samples from the Dagoujing vanadium deposit
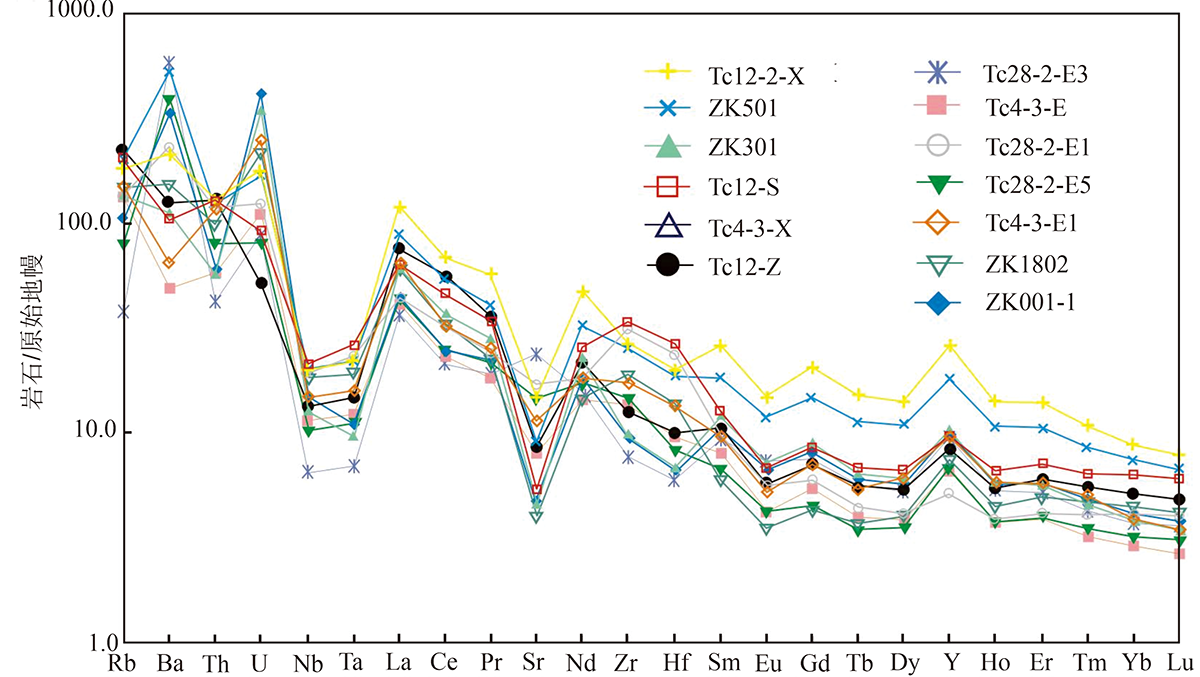
图6 大沟井钒矿床样品微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(原始地幔标准化数据据Sun和McDonough[14])
Fig.6 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram of samples from the Dagoujing vanadium deposit (primitive mantle data based on Sun and McDonough[14])
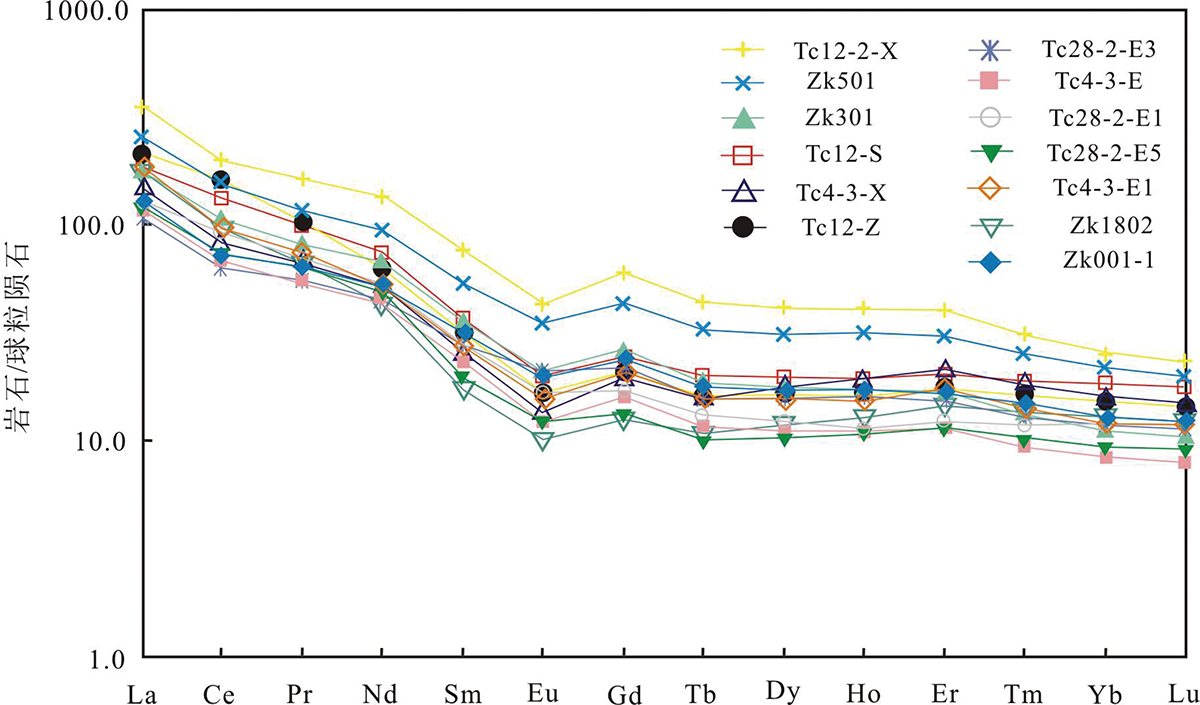
图7 大沟井钒矿床样品稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(球粒陨石标准化数据据Sun和McDonough[14])
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of samples from the Dagoujing vanadium deposit (chondrite-normalized data after Sun and McDonough[14])
| [1] | 王玉往, 王京彬, 王莉娟. 东天山地区两类钒钛磁铁矿型矿床含矿岩石对比[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5): 1425-1436. |
| [2] | 杨富全, 王义天, 李蒙文, 等. 新疆天山黑色岩系型矿床的地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(5):462-469. |
| [3] | MEYERS P A, PRATT L M, NAGY B. Introduction to geochemistry of metalliferous black shales[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/2/3): 7-11. |
| [4] |
WILDE A R, LAYER P, MERNAGH T, et al. The giant Muruntau gold deposit: Geologic, geochronologic, and fluid inclusion constraints on ore genesis[J]. Economic Geology, 2001, 96(3): 633-644.
DOI URL |
| [5] | MICHALIK M, SAWLOWICZ Z. Multi-stage and long term origin of the kupferschirfer copper deposits in Poland [M]//PIESTRZYNSKI A. Mineral Deposits at the Beginning of the 21th Century. Liss: A. A. Balkema Publishers, 2001: 235-238. |
| [6] | 游先军, 孙际茂, 陈明辉, 等. 湘西北下寒武统黑色岩系中的钒矿床[J]. 矿产与地质, 2008, 22(1): 20-26. |
| [7] | 张伦尉, 杭家华, 梁琼, 等. 贵州陡山沱组和牛蹄塘组中黑层的地质特征与找矿前景[J]. 矿物学报, 2007, 27(3/4): 456-459. |
| [8] | 张乾, 董振生, 战新志. 鄂西白果园黑色页岩型银钒矿床地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 1995, 15(2): 185-190. |
| [9] | 卢家烂, 庄汉平, 傅家谟, 等. 湖北兴山白果园黑色页岩型银钒矿床中银钒赋存状态研究[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(3): 222-229. |
| [10] | 庄汉平, 卢家烂, 傅家谟, 等. 湖北兴山白果园黑色页岩型银钒矿床改造成矿作用的证据[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(12): 1328-1331. |
| [11] | 谢成连, 刘蕾, 冷莹莹, 等. 内蒙阿右旗铁板井镍矿矿床特征及成因探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 2008, 44(6): 27-30. |
| [12] | 金文庆, 王治文, 马云青. 内蒙古自治区阿拉善右旗大沟井矿区钒矿详查报告(档号cgdoi.n0001/x00111119)[R]. 北京: 全国地质图书馆, 2008. |
| [13] |
HANS WEDEPOHL K. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217-1232.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 李胜荣. 湘黔地区下寒武统黑色岩系金银铂族元素地球化学研究[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所, 1994: 1-118. |
| [16] |
JONES B J, MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/2/3/4): 111-129.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HATCH J R, LEVENTHAL J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U.S.A.[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/2/3): 65-82.
DOI URL |
| [18] | WIGNALL P B. Black Shales[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1994: 46. |
| [19] | 吴朝东, 杨承运, 陈其英. 湘西黑色岩系地球化学特征和成因意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1999, 18(1): 26-38. |
| [20] | 范德廉, 张焘, 叶杰, 等. 中国的黑色岩系及其有关矿床[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 1-48. |
| [21] | 王立社, 侯俊富, 张复新, 等. 北秦岭庙湾组黑色岩系稀土元素地球化学特征及成因意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(1): 73-82. |
| [22] |
WILDE P, QUINBY-HUNT M S, ERDTMANN B D. The whole-rock cerium anomaly: A potential indicator of eustatic sea-level changes in shales of the anoxic facies[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1996, 101(1/2):43-53.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
MURRAY R W, BUCHHOLTZ TEN BRINK M R, GERLACH D C, et al. Rare earth, major, and trace elements in chert from the Franciscan Complex and Monterey Group, California: Assessing REE sources to fine-grained marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(7): 1875-1895.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 吕志成, 刘丛强, 刘家军, 等. 北大巴山下寒武统毒重石矿床赋矿硅质岩地球化学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(3): 390-406. |
| [25] | BAI S L, BAI Z Q, MA X P, et al. Devonian Events and Biostratigraphy of South China, Chapter 3: Ce/La Ratio as Marker of Palacoredox[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1994: 21-24. |
| [26] | 李赛赛, 魏刚锋, 聂江涛, 等. 南秦岭水沟钒矿床地质地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2):243-253. |
| [27] | 侯读杰, 冯子辉, 黄清华. 松辽盆地白垩纪缺氧地质事件的地质地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2003, 17(3):311-317. |
| [28] | 庄汉平, 卢家烂, 傅家谟, 等. 白果园黑色岩系型银(钒)矿床沉积古环境与银(钒)初始富集[J]. 地质论评, 1997, 43(4): 373-380. |
| [1] | 李厚民, 李立兴, 李以科, 柯昌辉, 李瑞萍, 李小赛, 王亿. 内蒙古白云鄂博铁-铌-稀土矿床矿化蚀变矿物组合及流体组成[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 13-24. |
| [2] | 刘金宝, 朱洛婷, 李龙雪, 侯青叶. 内蒙古艾力格庙地区卫境岩体的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 419-432. |
| [3] | 李柱, 张德会, 张荣臻, 沈存利, 焦世豪, 李林, 朱鹏龙. 内蒙古那仁乌拉早白垩世高分异花岗岩年代学及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 848-861. |
| [4] | 王美华. 浙西典型石煤矿山周边耕地富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [5] | 刘健, 汪一凡, 林钟扬, 潘少军. 浙江建德市耕地表层土壤硒分布、来源及生态效应[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 953-962. |
| [6] | 杨培奇, 刘敬党, 刘淑梅, 杨飞, 杨孝伟. 内蒙古乌拉特中旗大乌淀石墨矿床石英片岩地球化学特征与SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 672-681. |
| [7] | 程先钰, 田健, 段霄龙, 赵泽南, 任邦方, 张永. 北山洋晚志留世—早泥盆世构造演化:内蒙古白云山蛇绿混杂岩带南部侵入岩年代学、地球化学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 295-306. |
| [8] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [9] | 孙晓东, 陈海云, 于光宁. 内蒙古海拉斯图乌拉A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1218-1230. |
| [10] | 赵保具, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 一种稀土参数图解新方法:以内蒙古拜仁达坝-维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 608-624. |
| [11] | 成晓梦, 吴超, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 曾道明. 浙江中部典型黑色岩系分布区土壤-作物富硒特征与重金属风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 425-433. |
| [12] | 胡二红, 张善明, 贺中银, 张华, 刘瑞钦, 胡宇超, 何世明, 刘婷, 孙浩. 内蒙古额济纳旗微波山地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1303-1317. |
| [13] | 欧阳鑫, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 刘丽, 刘涛, 王文东. 内蒙古撰山子金矿床成岩成矿年代学与地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 635-652. |
| [14] | 柳志华, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 王佳琳, 刘涛, 王文东, 赵伟, 陈洋. 内蒙古索伦山蛇绿岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 399-417. |
| [15] | 张云, 孙立新, 张天福, 孙义伟, 张祺, 李艳锋, 杨泽黎, 刘文刚. 内蒙古狼山地区乌花辉长岩的年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成:对地幔源区特征和岩石成因的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 450-465. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||