



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (02): 425-433.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.02.12
成晓梦1,2,3( ), 吴超1,2,3(
), 吴超1,2,3( ), 孙彬彬1,2,3, 贺灵1,2,3, 曾道明1,2,3
), 孙彬彬1,2,3, 贺灵1,2,3, 曾道明1,2,3
收稿日期:2020-04-29
修回日期:2020-07-07
出版日期:2021-04-25
发布日期:2021-05-25
通讯作者:
吴超
作者简介:吴超,男,助理工程师,1990年出生,地球探测与信息技术专业,主要从事生态地球化学调查与评价方面的研究工作。Email: wchao@mail.cgs.gov.cn。基金资助:
CHENG Xiaomeng1,2,3( ), WU Chao1,2,3(
), WU Chao1,2,3( ), SUN Binbin1,2,3, HE Ling1,2,3, ZENG Daoming1,2,3
), SUN Binbin1,2,3, HE Ling1,2,3, ZENG Daoming1,2,3
Received:2020-04-29
Revised:2020-07-07
Online:2021-04-25
Published:2021-05-25
Contact:
WU Chao
摘要:
富硒土地是生产富硒农产品的宝贵资源,黑色岩系形成的土壤通常富含硒和重金属元素。为了指导这类富硒土地资源的安全开发利用,选择浙江中部典型黑色岩系分布区,通过调查土壤-作物中硒和重金属的浓度及生物有效性,评价农产品富硒率,识别作物重金属超标风险。结果显示:研究区富硒土壤占38%,足硒土壤占62%,水稻和莲子富硒率分别为85.71%和100%;受黑色岩系风化成土影响,研究区土壤镉含量介于污染筛选值和风险管控值之间的样品比例为26%,且Cd活动态和潜在活动态所占比例分别为57%和40%,水稻籽实中Cd超标率为31%,莲子Cd含量均不超标。基于土壤重金属总量和形态的风险评价表明,富硒土壤开发利用的风险区主要位于西皮山岗和腰塘边一带,建议禁止种植农产品,其他黑色岩系发育的富硒丘陵地区,虽然土壤镉含量较高,但因土壤Cd的生物有效性和水稻中Cd的超标率较低,应加以保护和合理开发利用。
中图分类号:
成晓梦, 吴超, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 曾道明. 浙江中部典型黑色岩系分布区土壤-作物富硒特征与重金属风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 425-433.
CHENG Xiaomeng, WU Chao, SUN Binbin, HE Ling, ZENG Daoming. Selenium-rich Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Crop in A Typical Black Shale Area of the Central Part of Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 425-433.
| 序号 | 形态 | 提取剂 | 测试方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 水溶态 | 蒸馏水 | 氢化物-原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS):As 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS):Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn 冷蒸汽-原子荧光光谱法(CV-AFS):Hg |
| 2 | 离子交换态 | 1.0 mol/L氯化镁溶液 | |
| 3 | 碳酸盐结合态 | 1.0 mol/L醋酸钠溶液 | |
| 4 | 腐殖酸结合态 | 1.0 mol/L焦磷酸钠溶液 | |
| 5 | 铁锰氧化物结合态 | 0.25 mol/L盐酸羟胺-盐酸溶液 | |
| 6 | 强有机结合态 | 30%过氧化氢溶液,2.5 mol/L醋酸铵-硝酸溶液 | |
| 7 | 残渣态 | HCl-HNO3溶液 |
表1 土壤元素形态提取步骤及测定方法
Table 1 Sequential extraction and determination methods of heavy metals in soil
| 序号 | 形态 | 提取剂 | 测试方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 水溶态 | 蒸馏水 | 氢化物-原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS):As 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS):Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn 冷蒸汽-原子荧光光谱法(CV-AFS):Hg |
| 2 | 离子交换态 | 1.0 mol/L氯化镁溶液 | |
| 3 | 碳酸盐结合态 | 1.0 mol/L醋酸钠溶液 | |
| 4 | 腐殖酸结合态 | 1.0 mol/L焦磷酸钠溶液 | |
| 5 | 铁锰氧化物结合态 | 0.25 mol/L盐酸羟胺-盐酸溶液 | |
| 6 | 强有机结合态 | 30%过氧化氢溶液,2.5 mol/L醋酸铵-硝酸溶液 | |
| 7 | 残渣态 | HCl-HNO3溶液 |
| 土壤环境质量等级 | 污染风险 | 划分标准 |
|---|---|---|
| 一等 | 无风险 | Ci≤Si |
| 二等 | 风险可控 | Si< Ci ≤Gi |
| 三等 | 风险较高 | Ci> Gi |
表2 土壤环境质量与风险等级划分
Table 2 Comprehensive grading classi?cation of soil environmental quality and risk
| 土壤环境质量等级 | 污染风险 | 划分标准 |
|---|---|---|
| 一等 | 无风险 | Ci≤Si |
| 二等 | 风险可控 | Si< Ci ≤Gi |
| 三等 | 风险较高 | Ci> Gi |
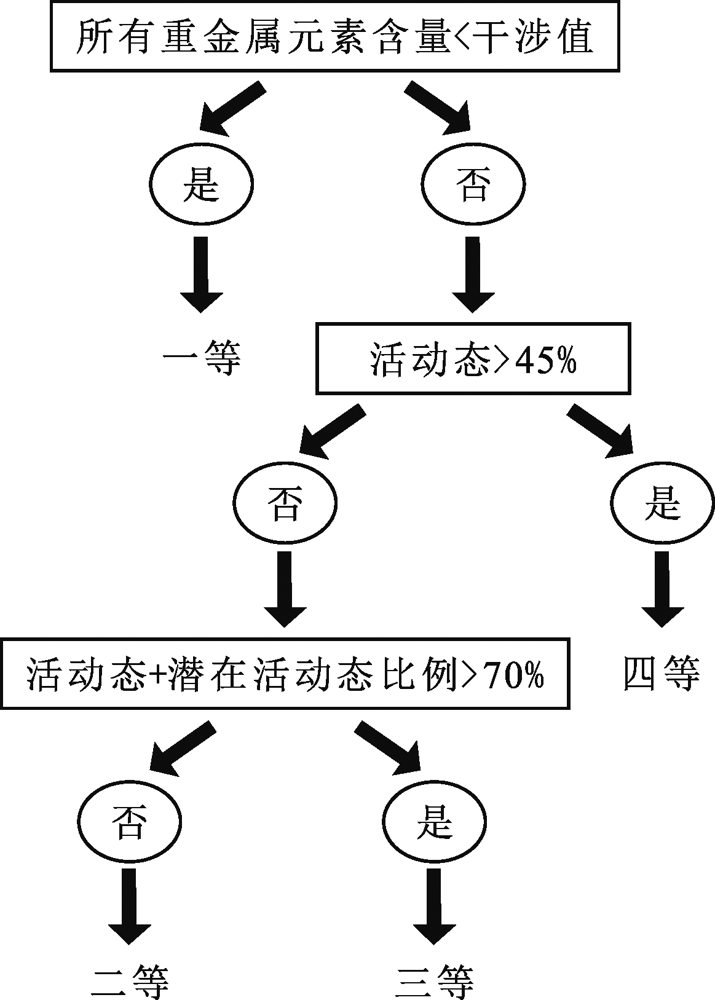
图2 土壤重金属环境潜在风险分类流程图(据文献[24]修改)
Fig.2 Classification of soil heavy metal according to their potential risks of environment(modified after reference [24])
| 作物(样品数) | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 作物富硒标准值[ | 富硒率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻(n=35) | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.04~0.30 | 85.71 |
| 莲子(n=15) | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.04~1.00 | 100 |
表3 水稻籽实、莲子果实的硒含量与富硒率(wB/(mg?kg-1))
Table 3 Concentrations of Se and the rate of selenium-rich in rice seed and lotus seed
| 作物(样品数) | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 作物富硒标准值[ | 富硒率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻(n=35) | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.04~0.30 | 85.71 |
| 莲子(n=15) | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.04~1.00 | 100 |
| 统计参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 2.05 | 0.123 | 28 | 14 | 0.070 | 8.87 | 19.70 | 54 |
| 最大值 | 20.87 | 0.954 | 88 | 87 | 1.075 | 43.75 | 58.66 | 137 |
| 平均值 | 7.64 | 0.287 | 54 | 26 | 0.199 | 20.88 | 35.72 | 81 |
| 标准偏差 | 4.37 | 0.17 | 17.07 | 9.23 | 0.15 | 10.46 | 7.28 | 21 |
| 变异系数/% | 57 | 59 | 32 | 35 | 73 | 50 | 20 | 26 |
| 浙江省表层土壤[ | 9.2 | 0.07 | 52.9 | 17.6 | 0.086 | 24.6 | 23.7 | 70.6 |
| 全国表层土壤[ | 11 | 0.097 | 61 | 23 | 0.065 | 27 | 26 | 74 |
| ≤ 筛选值/% | 100 | 74 | 100 | 98 | 98 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 筛选值—管控值/% | 0 | 26 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表4 土壤重金属含量统计参数表(wB/(mg·kg-1)(n=50))
Table 4 Statistical parameters of heavy metal concentrations in soil
| 统计参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 2.05 | 0.123 | 28 | 14 | 0.070 | 8.87 | 19.70 | 54 |
| 最大值 | 20.87 | 0.954 | 88 | 87 | 1.075 | 43.75 | 58.66 | 137 |
| 平均值 | 7.64 | 0.287 | 54 | 26 | 0.199 | 20.88 | 35.72 | 81 |
| 标准偏差 | 4.37 | 0.17 | 17.07 | 9.23 | 0.15 | 10.46 | 7.28 | 21 |
| 变异系数/% | 57 | 59 | 32 | 35 | 73 | 50 | 20 | 26 |
| 浙江省表层土壤[ | 9.2 | 0.07 | 52.9 | 17.6 | 0.086 | 24.6 | 23.7 | 70.6 |
| 全国表层土壤[ | 11 | 0.097 | 61 | 23 | 0.065 | 27 | 26 | 74 |
| ≤ 筛选值/% | 100 | 74 | 100 | 98 | 98 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 筛选值—管控值/% | 0 | 26 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

图4 土壤中重金属元素赋存形态分布图 F1.水溶态;F2.离子交换态;F3.碳酸盐结合态;F4.腐殖酸结合态;F5.铁锰氧化物结合态;F6.强有机结合态;F7.残渣态。
Fig.4 Fractions of heavy metals in soil samples (F1.water-soluble; F2.ion-exchange; F3.carbonate; F4.humic acid; F5.Fe-Mn oxidation; F6.strong organic; F7.residual)
| 作物 | 参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 (n=35) | 最大值 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 1.55 | 4.47 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.38 | 20.33 |
| 最小值 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 1.20 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 10.03 | |
| 平均数 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 2.53 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 15.20 | |
| 限量值[ | 0.5 | 0.2 | 1.0 | — | 0.02 | — | 0.2 | — | |
| 超标率/% | 0 | 31.42 | 8.57 | — | 0 | — | 5.71 | — | |
| 莲子 (n=15) | 最大值 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 29.20 | 0.10 | 2.39 | 0.08 | 31.46 |
| 最小值 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 5.83 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 0.04 | 19.52 | |
| 平均数 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 13.60 | 0.06 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 26.07 | |
| 限量值[ | — | 0.5 | — | — | — | — | 0.2 | — | |
| 超标率/% | — | 0 | — | — | — | — | 0 | — |
表5 研究区作物中重金属含量特征(wB/(mg·kg-1))
Table 5 Heavy metals concentrations in crops in the study area
| 作物 | 参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 (n=35) | 最大值 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 1.55 | 4.47 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.38 | 20.33 |
| 最小值 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 1.20 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 10.03 | |
| 平均数 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 2.53 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 15.20 | |
| 限量值[ | 0.5 | 0.2 | 1.0 | — | 0.02 | — | 0.2 | — | |
| 超标率/% | 0 | 31.42 | 8.57 | — | 0 | — | 5.71 | — | |
| 莲子 (n=15) | 最大值 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 29.20 | 0.10 | 2.39 | 0.08 | 31.46 |
| 最小值 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 5.83 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 0.04 | 19.52 | |
| 平均数 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 13.60 | 0.06 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 26.07 | |
| 限量值[ | — | 0.5 | — | — | — | — | 0.2 | — | |
| 超标率/% | — | 0 | — | — | — | — | 0 | — |
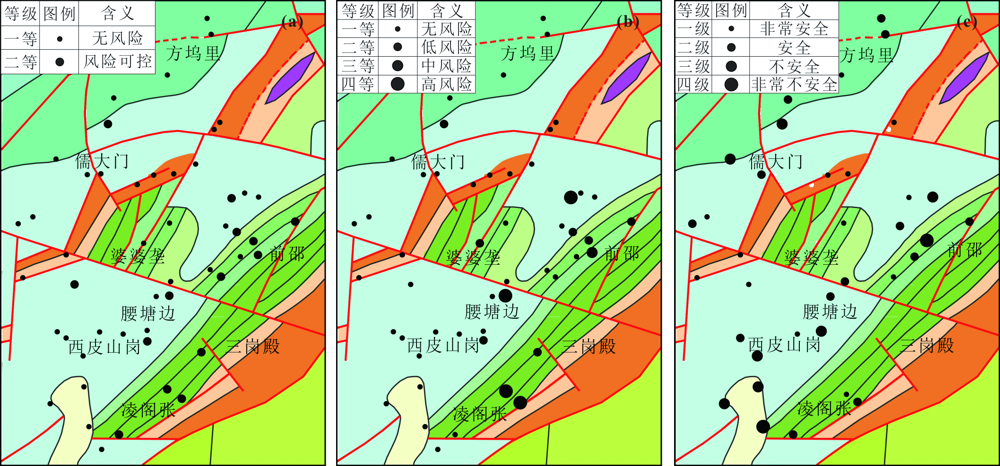
图5 研究区土壤-作物重金属风险评价图 (a)土壤重金属总量评价图;(b)环境潜在风险分类图;(c)水稻安全性评价图。
Fig.5 Risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and crop in the study area ((a) Risk assessment of total concentration of heavy metals in soil; (b) Classification of soil heavy metal according to their potential risk of environment;(c) Safety evaluation of rice)
| [1] |
MCLAUGHLIN M J, PARKER D R, CLARKE J M. Metals and micronutrients-food safety issues[J]. Field Crops Research, 1999,60(1):143-164.
DOI URL |
| [2] | BOWEN H J M. Trace Elements in Biochemisty[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1996: 1-124. |
| [3] | LEVENTHAL J. Metals in black shales[M]//ENGEL M H, MACKO S A. Organic Geochemistry: Principles and Applications. Boston: Springer, 1993: 581-592. |
| [4] |
MAO J W, LEHMANN B, DU A D, et al. Re-Os dating of polymetallic Ni-Mo-PGE-Au mineralization in Lower Cambrian black shales of South China and its geologic significance[J]. Economic Geology, 2002,97:1051-1061.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SHPIRT M Y, PUNANOVA S A, STRIZHAKOVA Y A. Trace elements in black and oil shales[J]. Soil Fuel Chemistry, 2007,41(2):119-127.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LEE J S, CHON H T, KIM K W. Migration and dispersion of trace elements in the rock-soil-plant system in areas underlain by black shales and slates of the Okchon Zone, Korea[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1998,65(1):61-78.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LEE J S, CHON H T, KIM J S, et al. Enrichment of potentially toxic elements in areas underlain by black shales and slates in Korea[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 1998,20(3):135-147.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
PAŠAVA J, KRÍBEK B, VYMAZALOVÁ A, et al. Multiple sources of metals of mineralization in Lower Cambrian black shales of South China: Evidence from geochemical and petrographic study[J]. Resource Geology, 2008,58(1):25-42.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PENG B, PIESTRZYNSKI A, PIECZONKA J, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on environmental impacts from waste rock at Taojiang Mn ore deposit, central Hunan, China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2007,52(7):1277-1296.
DOI URL |
| [10] | PENG B, TANG X Y, YU C X, et al. Geochemical study of heavy metal contamination of soils derived from black shales at the HJC uranium mine in central Hunan,China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009,83(1):89-106. |
| [11] | YU C X, PENG B, TANG X Y, et al. The black shale and relative heavy metal contamination of soils derived from the black shale[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008,27(2):137-145. |
| [12] | 宋成祖. 鄂西南渔塘坝沉积型硒矿化区概况[J]. 矿床地质, 1989,8(3):83-89. |
| [13] |
ZHU J M, WANG N, LI S H, et al. Distribution and transport of selenium in Yutangba, China: Impact of human activities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008,392(2):252-261.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HAN T, FAN S F, ZHU X Q, et al. Submarine hydrothermal contribution for the extreme element accumulation during the Early Cambrian, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017,86:297-308.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PAGÈS A, BARNES S, SCHMID S, et al. Geochemical investigation of the Lower Cambrian mineralised black shales of South China and the Late Devonian Nick deposit, Canada[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018,94:396-413.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YU C, PENG B, PELTOLA P, et al. Effect of weathering on abundance and release of potentially toxic elements in soils deve-loped on Lower Cambrian black shales, P.R.China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2012,34(3):375-390.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 宋明义, 李恒溪, 魏迎春, 等. 浙江省龙游志棠地区硒的地球化学研究[J]. 贵州地质, 2005,22(3):176-180. |
| [18] | 中国地质调查局. 生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(试行)(DD 2005—03)[S]. 北京: 中国地质调查局, 2005:9-11. |
| [19] | 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)(GB 15618—2018)[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2018: 1-3. |
| [20] | 周国华. 土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(6):1097-1106. |
| [21] | 王蕊, 陈明, 陈楠, 等. 基于总量及形态的土壤重金属生态风险评价对比:以龙岩市适中镇为例[J]. 环境科学, 2017,38(10):4348-4359. |
| [22] | 李小平, 徐长林, 刘献宇, 等. 宝鸡城市土壤重金属生物活性与环境风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015,35(4):1241-1249. |
| [23] |
KIM R Y, YOON J K, KIM T S, et al. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: definitions and practical implementation—a critical review[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2015,37(6):1041-1061.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CAPPUYNS V, SWENNEN R. Classification of alluvial soils according to their potential environmental risk: A case study for Belgian catchments[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2007,9(4):319-328.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量(GB 2762—2017)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 2-8. |
| [26] | 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 82-83. |
| [27] | ALLOWAY B J. Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils[M]//ALLOWAY B J, TREVORS J T. Heavy Metals in Soils. Dordrecht:Springer, 2013: 11-50. |
| [28] |
QIN H B, ZHU J M, LIANG L, et al. The bioavailability of selenium and risk assessment for human selenium poisoning in high-Se areas, China[J]. Environment International, 2013,52:66-74.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 董岩翔, 郑文, 周建华, 等. 浙江省土壤地球化学背景值[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 130-131. |
| [30] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 富硒稻谷(GB/T 22499—2008)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008: 1-2. |
| [31] | 江西省质量技术监督局. 富硒食品硒含量分类标准(DB36/T 566—2017)[S]. 南昌: 江西省质量技术监督局, 2017: 3-4. |
| [32] |
OLAJIRE A A, AYODELE E T, OYEDIRDAN G O, et al. Levels and speciation of heavy metals in soils of industrial Southern Nigeria[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2003,113(2):135-155.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
KEEFER R F, CODLING E E, SINGH R N. Fractionation of metal organic components extracted from a sludge-amended soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1984,48(5):1054-1059.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 宋明义. 浙西地区下寒武统黑色岩系中硒与重金属的表生地球化学及环境效应[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2009: 103-104. |
| [35] | 刘意章, 肖唐付, 熊燕, 等. 西南高镉地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019,40(6):387-394. |
| [36] | 生态环境部, 自然资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[EB/OL] (2014- 04- 17) [2020-6-25]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2014-04/17/content_2661765.htm. |
| [37] | GRANT C A, BAILEY L D, MCLAUGHLIN M J, et al. Mana-gement factors which influence cadmium con centrations in crops[M]//MCLAUGHLIN M J, SINGH B R. Cadmium in Soils and Plants. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic, 1999: 151-198. |
| [38] |
LIN L, ZHOU W H, DAI H X, et al. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012,235/236(2):343-351.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SUN H W, HA J, LIANG S X, et al. Protective role of selenium on garlic growth under cadmium stress[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2010,41(10):1195-1204.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
FILEK M, KESKINEN R, HARTIKAINEN H, et al. The protective role of selenium in rape seedlings subjected to cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2008,165(8):833-844.
DOI URL |
| [41] | 胡居吾, 熊华. 天然富硒土壤的性质及硒对重金属的拮抗研究[J]. 生物化工, 2019,5(2):11-16. |
| [1] | 李楠, 曹明杰, 郝喆, 侯永莉, 陈红丹, 张颖. 基于不同土地利用方式的土壤重金属污染与潜在风险评价:以辽河流域(浑太水系)山水林田湖草沙一体化保护和修复工程为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1655-1664. |
| [2] | 胡庆海, 王学求, 韩志轩, 成晓梦, 吴慧, 田密, 刘福田, 孙彬彬, 陈卫明, 杜雪苗, 刘彬, 崔邢涛. 京津冀地区永清县土壤重金属地球化学特征及绿色食品产地的土壤质量评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 778-789. |
| [3] | 杜古尔·卫卫, 石海涛, 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特. 新疆戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 790-800. |
| [4] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [5] | 朱英海, 施泽明, 王新宇, 张凯亮, 朱伯丞. 攀西大梁子铅锌矿区水系沉积物重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 923-932. |
| [6] | 刘阳, 姜冰, 张海瑞, 孙增兵, 王松涛. 山东省青州市表层土壤硒元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 933-940. |
| [7] | 王美华. 浙西典型石煤矿山周边耕地富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [8] | 刘健, 汪一凡, 林钟扬, 潘少军. 浙江建德市耕地表层土壤硒分布、来源及生态效应[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 953-962. |
| [9] | 吴通航, 刘海燕, 张卫民, 孙占学, 王振, 刘茂涵. 鄱阳湖流域赣江下游水化学特征及人类健康风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 427-438. |
| [10] | 郭正材, 郭华明, 魏亮, 高志鹏. 河北保定典型污灌区土壤Cu吸附特性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 524-532. |
| [11] | 乔雯, 王议, 张德强, 殷秀兰, 白光宇, 何培雍. 某矿区土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 543-551. |
| [12] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 李欢, 张沁瑞. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 634-644. |
| [13] | 张红雨, 苏犁, 秦红. 内蒙古大沟井寒武纪黑色页岩元素地球化学特征及钒赋存形式[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 321-332. |
| [14] | 朱超, 文美兰, 刘攀峰, 陈斌艳, 鲍厚银, 赵银强, 陈昊, 杨奕波. 桂林灵川县典型有机水稻田重金属元素分布特征及污染评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1433-1440. |
| [15] | 李金哲, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 李承柱. 广东汕头市内海湾沉积物重金属环境质量调查与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1441-1449. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||