



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (03): 790-800.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.041
杜古尔·卫卫( ), 石海涛(
), 石海涛( ), 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特
), 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特
收稿日期:2022-09-15
修回日期:2023-04-19
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-07-20
通讯作者:
石海涛,男,工程师,1991年出生,资源勘查工程专业,从事生态地质调查和综合地质调查研究。Email:shihaitao@mail.cgs.gov.cn。
作者简介:杜古尔·卫卫,男,工程师,1989年出生,地球化学专业,从事环境地球化学和生态地球化学研究。 Email:dgeww@mail.cgs.gov.cn。
基金资助:
DUGUER Weiwei( ), SHI Haitao(
), SHI Haitao( ), XING Hao, LOU Xuecong, HU Hongli, BULONG Bate
), XING Hao, LOU Xuecong, HU Hongli, BULONG Bate
Received:2022-09-15
Revised:2023-04-19
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-07-20
摘要:
查明戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源及其空间分布特征是准确判断和制定土壤污染治理方案的前提,然而系统的研究工作依然薄弱。本文以新疆戈壁荒漠区典型煤矿周边土壤为研究对象,系统的布设和采集了266件土壤样品,测试分析了As、Cd、Co、Cu、Cr、Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn共9种元素含量及土壤pH值。通过利用描述性统计分析、相关性分析、聚类分析以及主成分分析等多元地学统计分析方法分析研究了土壤重金属含量特征并初步识别了土壤重金属来源,使用绝对主成分-多元线性回归受体模型(APCS-MLR)和反距离加权法定量分析各污染源贡献率和重金属元素空间分布特征。结果表明:(1)研究区土壤pH平均值为8.31,9种元素含量低于土壤环境质量农业用地、建设用地筛选值,同时也低于新疆土壤重金属背景值;从各功能分区来看,仅废污水排放区As、Cd、Cu、Ni和Pb元素含量高于新疆背景值;(2)Cr、Ni、Zn、Co、Cu、As、Cd元素两两之间具有中等以上相关性,Cd与Pb具有中等程度相关性,Hg与其他8种元素相关性较弱;(3)聚类分析结果将研究区土壤重金属分为Cr-Ni-Zn-Co-Cu-As、Cd-Pb和Hg三类;(4)源解析结果表明研究区土壤重金属主要来源为成土母质源(50.902%)、废污水与煤尘源(31.507%)。
中图分类号:
杜古尔·卫卫, 石海涛, 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特. 新疆戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 790-800.
DUGUER Weiwei, SHI Haitao, XING Hao, LOU Xuecong, HU Hongli, BULONG Bate. Source Analysis and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Soil from Typical Open-pit Coal Mines in the Gobi Desert, Xinjiang[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 790-800.

图1 新疆哈密位置图(a)、哈密地区南湖乡大南湖七号井田位置图(b)及土壤采样点分布示意图(c)
Fig.1 Location map of Hami, Xinjiang (a) and the Dananhu No.7 coal mine in Hami (b) and distribution of soil sampling sites (c)
| 元素 (参数) | 最小值 (mg·kg-1) | 最大值 (mg·kg-1) | 平均值 (mg·kg-1) | 标准偏差 (mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 | 新疆背景值 (mg·kg-1) | GB 15618-2018 (pH>7.5)(mg·kg-1) | GB 36600-2018 (pH>7.5)(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 2.95 | 22.14 | 8.09 | 2.819 | 0.3487 | 11.20 | 25 | 60 |
| Cd | 0.03 | 0.43 | 0.1 | 0.050 | 0.5021 | 0.12 | 0.6 | 65 |
| Co | 4.40 | 21.90 | 8.56 | 2.614 | 0.3055 | 15.90 | - | 70 |
| Cr | 13.10 | 79.30 | 28.15 | 10.240 | 0.3637 | 49.30 | 250 | - |
| Cu | 8.94 | 52.60 | 17.97 | 6.958 | 0.3873 | 26.70 | 100 | 18000 |
| Hg | 0 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.010 | 1.4150 | 0.02 | 3.4 | 38 |
| Ni | 7.43 | 43.50 | 14.55 | 5.766 | 0.3964 | 25.20 | 190 | 900 |
| Pb | 10.10 | 48.70 | 15.16 | 4.029 | 0.2658 | 19.40 | 170 | 800 |
| Zn | 23.20 | 112.00 | 39.39 | 13.920 | 0.3534 | 68.80 | 300 | - |
| pH | 7.82 | 8.95 | 8.31 | 0.140 | 0.0168 | - | - | - |
表1 大南湖七号煤矿土壤重金属及pH值特征及背景值 (mg·kg-1)
Table 1 Parameters and background of soil heavy metals and pH in the Dananhu No.7 coal mine ( mg·kg-1)
| 元素 (参数) | 最小值 (mg·kg-1) | 最大值 (mg·kg-1) | 平均值 (mg·kg-1) | 标准偏差 (mg·kg-1) | 变异系数 | 新疆背景值 (mg·kg-1) | GB 15618-2018 (pH>7.5)(mg·kg-1) | GB 36600-2018 (pH>7.5)(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 2.95 | 22.14 | 8.09 | 2.819 | 0.3487 | 11.20 | 25 | 60 |
| Cd | 0.03 | 0.43 | 0.1 | 0.050 | 0.5021 | 0.12 | 0.6 | 65 |
| Co | 4.40 | 21.90 | 8.56 | 2.614 | 0.3055 | 15.90 | - | 70 |
| Cr | 13.10 | 79.30 | 28.15 | 10.240 | 0.3637 | 49.30 | 250 | - |
| Cu | 8.94 | 52.60 | 17.97 | 6.958 | 0.3873 | 26.70 | 100 | 18000 |
| Hg | 0 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.010 | 1.4150 | 0.02 | 3.4 | 38 |
| Ni | 7.43 | 43.50 | 14.55 | 5.766 | 0.3964 | 25.20 | 190 | 900 |
| Pb | 10.10 | 48.70 | 15.16 | 4.029 | 0.2658 | 19.40 | 170 | 800 |
| Zn | 23.20 | 112.00 | 39.39 | 13.920 | 0.3534 | 68.80 | 300 | - |
| pH | 7.82 | 8.95 | 8.31 | 0.140 | 0.0168 | - | - | - |
| 功能分区 | 元素 | As | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 露天矿坑 | 平均值 | 7.506 | 0.106 | 7.354 | 22.712 | 19.155 | 0.010 | 11.650 | 16.022 | 34.988 |
| 最大值 | 22.14 | 0.43 | 15.9 | 34 | 51 | 0.131 | 19.4 | 48.7 | 72.8 | |
| 最小值 | 4.52 | 0.03 | 4.4 | 13.1 | 8.94 | 0 | 7.48 | 10.8 | 24.3 | |
| 标准偏差 | 3.317 | 0.079 | 1.798 | 4.355 | 7.441 | 0.020 | 2.122 | 8.013 | 9.140 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.442 | 0.741 | 0.244 | 0.192 | 0.388 | 1.949 | 0.182 | 0.500 | 0.261 | |
| 样本数量 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | |
| 废污水排放区 | 平均值 | 12.72 | 0.18 | 13.29 | 48.65 | 30.41 | 0.017 | 26.65 | 19.97 | 68.76 |
| 最大值 | 21.20 | 0.33 | 20.40 | 79.30 | 52.60 | 0.04 | 43.50 | 27.20 | 112.00 | |
| 最小值 | 5.77 | 0.06 | 5.54 | 16.4 | 10.8 | 0 | 9.03 | 11.7 | 26.20 | |
| 标准偏差 | 5.61 | 0.09 | 5.26 | 23.05 | 15.17 | 0.01 | 13.26 | 5.52 | 31.98 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.47 | |
| 样本数量 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| 生活区 | 平均值 | 7.25 | 0.09 | 8.09 | 25.77 | 15.60 | 0.01 | 13.57 | 14.87 | 38.50 |
| 最大值 | 9.08 | 0.11 | 8.99 | 30.7 | 18.1 | 0.02 | 16 | 15.9 | 44.1 | |
| 最小值 | 6.05 | 0.07 | 6.89 | 23.2 | 13.5 | 0 | 11.6 | 14.3 | 35.1 | |
| 标准偏差 | 1.61 | 0.02 | 1.08 | 4.27 | 2.33 | 0.01 | 2.24 | 0.90 | 4.89 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.13 | |
| 样本数量 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 煤电厂 | 平均值 | 8.10 | 0.10 | 8.63 | 28.59 | 16.29 | 0.00 | 14.76 | 14.86 | 39.87 |
| 最大值 | 9.96 | 0.13 | 10 | 33.8 | 19.4 | 0.01 | 18 | 16.4 | 47.1 | |
| 最小值 | 5.89 | 0.07 | 7.6 | 24.1 | 13.9 | 0 | 12.4 | 13.6 | 35 | |
| 标准偏差 | 1.50 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 3.98 | 2.04 | 0.01 | 2.19 | 0.93 | 5.12 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.13 | |
| 样本数量 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| 灰场 | 平均值 | 8.624 | 0.088 | 9.2405 | 30.605 | 17.305 | 0.005 | 15.645 | 15.185 | 39.33 |
| 最大值 | 11 | 0.11 | 12.9 | 36.8 | 20.4 | 0.01 | 17.8 | 17 | 48.1 | |
| 最小值 | 6.3 | 0.07 | 7.52 | 22.3 | 12.3 | 0 | 10 | 13.8 | 33.6 | |
| 标准偏差 | 1.25 | 0.01 | 1.13 | 3.70 | 1.90 | 0.01 | 1.79 | 0.88 | 4.01 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.10 | |
| 样本数量 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | |
| 新疆背景值 | 11.2 | 0.12 | 15.9 | 49.3 | 26.7 | 0.017 | 25.2 | 19.4 | 68.8 | |
| GB 15618-2018(pH>7.5) | 25 | 0.6 | - | 250 | 100 | 3.4 | 190 | 170 | 300 | |
| GB 36600-2018(pH>7.5) | 60 | 65 | 70 | - | 18000 | 38 | 900 | 800 | - | |
表2 吐哈煤田大南湖七号煤矿各功能分区土壤重金属含量特征及背景值 (mg·kg-1)
Table 2 Soil heavy metal parameters and background values of different functional zones in the Dananhu No.7 coal mine of Turpan-Hami coalfield (mg·kg-1)
| 功能分区 | 元素 | As | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 露天矿坑 | 平均值 | 7.506 | 0.106 | 7.354 | 22.712 | 19.155 | 0.010 | 11.650 | 16.022 | 34.988 |
| 最大值 | 22.14 | 0.43 | 15.9 | 34 | 51 | 0.131 | 19.4 | 48.7 | 72.8 | |
| 最小值 | 4.52 | 0.03 | 4.4 | 13.1 | 8.94 | 0 | 7.48 | 10.8 | 24.3 | |
| 标准偏差 | 3.317 | 0.079 | 1.798 | 4.355 | 7.441 | 0.020 | 2.122 | 8.013 | 9.140 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.442 | 0.741 | 0.244 | 0.192 | 0.388 | 1.949 | 0.182 | 0.500 | 0.261 | |
| 样本数量 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | |
| 废污水排放区 | 平均值 | 12.72 | 0.18 | 13.29 | 48.65 | 30.41 | 0.017 | 26.65 | 19.97 | 68.76 |
| 最大值 | 21.20 | 0.33 | 20.40 | 79.30 | 52.60 | 0.04 | 43.50 | 27.20 | 112.00 | |
| 最小值 | 5.77 | 0.06 | 5.54 | 16.4 | 10.8 | 0 | 9.03 | 11.7 | 26.20 | |
| 标准偏差 | 5.61 | 0.09 | 5.26 | 23.05 | 15.17 | 0.01 | 13.26 | 5.52 | 31.98 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.47 | |
| 样本数量 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| 生活区 | 平均值 | 7.25 | 0.09 | 8.09 | 25.77 | 15.60 | 0.01 | 13.57 | 14.87 | 38.50 |
| 最大值 | 9.08 | 0.11 | 8.99 | 30.7 | 18.1 | 0.02 | 16 | 15.9 | 44.1 | |
| 最小值 | 6.05 | 0.07 | 6.89 | 23.2 | 13.5 | 0 | 11.6 | 14.3 | 35.1 | |
| 标准偏差 | 1.61 | 0.02 | 1.08 | 4.27 | 2.33 | 0.01 | 2.24 | 0.90 | 4.89 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.13 | |
| 样本数量 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 煤电厂 | 平均值 | 8.10 | 0.10 | 8.63 | 28.59 | 16.29 | 0.00 | 14.76 | 14.86 | 39.87 |
| 最大值 | 9.96 | 0.13 | 10 | 33.8 | 19.4 | 0.01 | 18 | 16.4 | 47.1 | |
| 最小值 | 5.89 | 0.07 | 7.6 | 24.1 | 13.9 | 0 | 12.4 | 13.6 | 35 | |
| 标准偏差 | 1.50 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 3.98 | 2.04 | 0.01 | 2.19 | 0.93 | 5.12 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.13 | |
| 样本数量 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| 灰场 | 平均值 | 8.624 | 0.088 | 9.2405 | 30.605 | 17.305 | 0.005 | 15.645 | 15.185 | 39.33 |
| 最大值 | 11 | 0.11 | 12.9 | 36.8 | 20.4 | 0.01 | 17.8 | 17 | 48.1 | |
| 最小值 | 6.3 | 0.07 | 7.52 | 22.3 | 12.3 | 0 | 10 | 13.8 | 33.6 | |
| 标准偏差 | 1.25 | 0.01 | 1.13 | 3.70 | 1.90 | 0.01 | 1.79 | 0.88 | 4.01 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 1.03 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.10 | |
| 样本数量 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | |
| 新疆背景值 | 11.2 | 0.12 | 15.9 | 49.3 | 26.7 | 0.017 | 25.2 | 19.4 | 68.8 | |
| GB 15618-2018(pH>7.5) | 25 | 0.6 | - | 250 | 100 | 3.4 | 190 | 170 | 300 | |
| GB 36600-2018(pH>7.5) | 60 | 65 | 70 | - | 18000 | 38 | 900 | 800 | - | |
| 元素 组合 | Cr-Ni | Cr-Zn | Co-Cr | Cd-Pb | Co-Cu | As-Co | As-Cd | As-Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚类关 系值 | 0.9765 | 0.9287 | 0.9121 | 0.8413 | 0.832 | 0.8022 | 0.658 | 0.485 |
表3 大南湖七号煤矿元素相关性分析结果
Table 3 Elemental correlation of the Dananhu No.7 coalmine
| 元素 组合 | Cr-Ni | Cr-Zn | Co-Cr | Cd-Pb | Co-Cu | As-Co | As-Cd | As-Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚类关 系值 | 0.9765 | 0.9287 | 0.9121 | 0.8413 | 0.832 | 0.8022 | 0.658 | 0.485 |
| 元素 | 旋转前因子 | 旋转后因子 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | |
| As | 0.840 | -0.170 | 0.782 | 0.351 |
| Cd | 0.774 | 0.540 | 0.315 | 0.890 |
| Co | 0.905 | -0.280 | 0.899 | 0.299 |
| Cr | 0.918 | -0.296 | 0.919 | 0.293 |
| Cu | 0.914 | 0.111 | 0.678 | 0.622 |
| Hg | 0.551 | 0.249 | 0.303 | 0.523 |
| Ni | 0.937 | -0.285 | 0.928 | 0.314 |
| Pb | 0.715 | 0.585 | 0.241 | 0.891 |
| Zn | 0.957 | -0.146 | 0.864 | 0.438 |
| 方差贡献率(%) | 71.237 | 11.172 | 50.902 | 31.507 |
| 累积方差贡献率(%) | 71.237 | 82.409 | 50.902 | 82.409 |
表4 大南湖七号煤矿土壤重金属正交旋转因子荷载
Table 4 Orthogonal rotation factor loading of soil heavy metals in the Dananhu No.7 coal mine
| 元素 | 旋转前因子 | 旋转后因子 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | |
| As | 0.840 | -0.170 | 0.782 | 0.351 |
| Cd | 0.774 | 0.540 | 0.315 | 0.890 |
| Co | 0.905 | -0.280 | 0.899 | 0.299 |
| Cr | 0.918 | -0.296 | 0.919 | 0.293 |
| Cu | 0.914 | 0.111 | 0.678 | 0.622 |
| Hg | 0.551 | 0.249 | 0.303 | 0.523 |
| Ni | 0.937 | -0.285 | 0.928 | 0.314 |
| Pb | 0.715 | 0.585 | 0.241 | 0.891 |
| Zn | 0.957 | -0.146 | 0.864 | 0.438 |
| 方差贡献率(%) | 71.237 | 11.172 | 50.902 | 31.507 |
| 累积方差贡献率(%) | 71.237 | 82.409 | 50.902 | 82.409 |
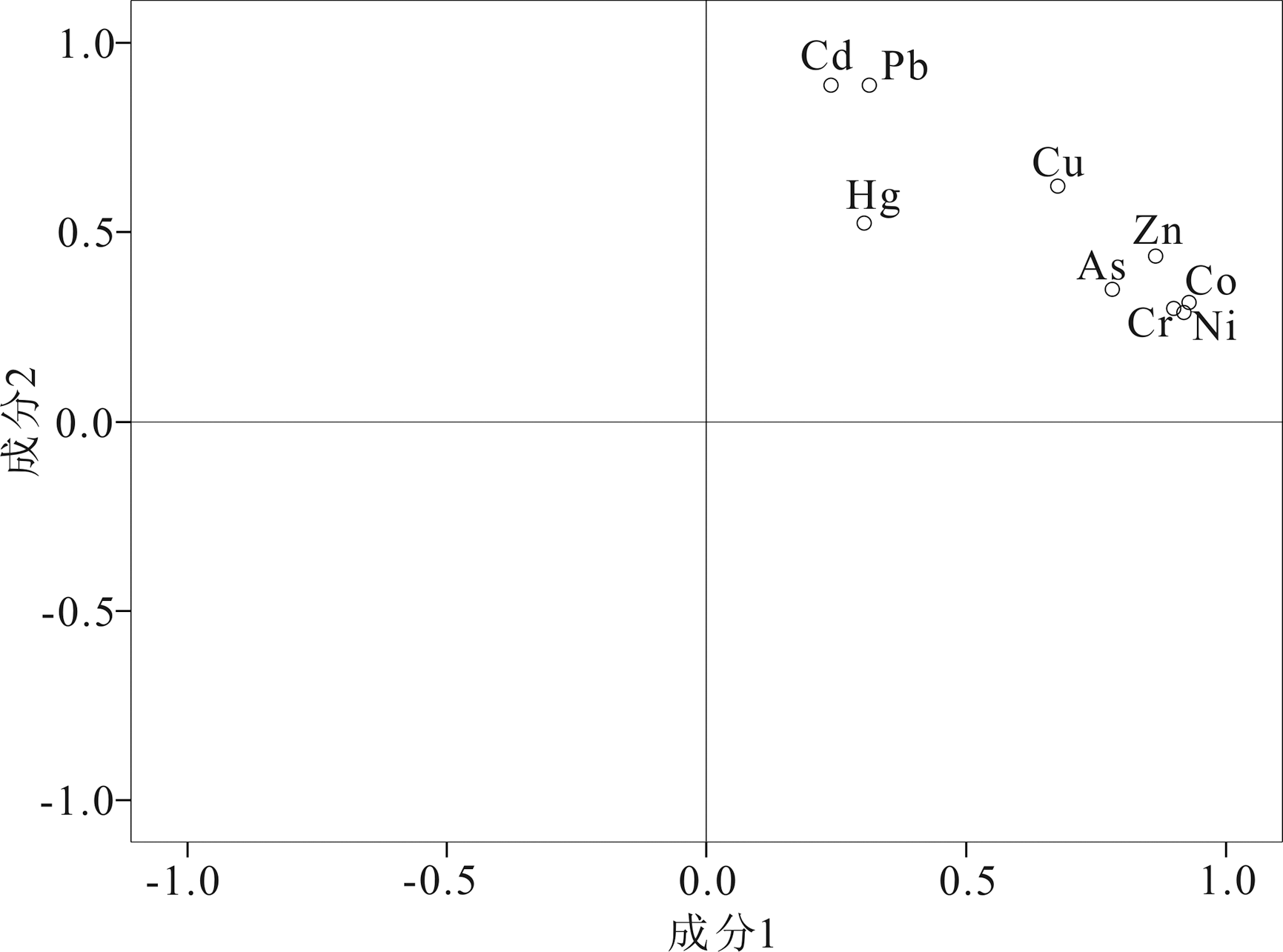
图6 大南湖七号煤矿土壤重金属主成分荷载图(主成分1代表成土母质;主成分2代表废污水排放与煤尘)
Fig.6 Factors matrix of heavy metals of the Dananhu No.7 coal mine (PC1 represents soil-forming parent material; PC2 represents waste water discharge and coal dust)
| 元素 | 贡献率(%) | E/O | 调整 后R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 | 主成分2 | 其他因子 | |||
| As | 62.37 | 24.99 | 12.64 | 1 | 0.733 |
| Cd | 23.52 | 59.12 | 17.36 | 1 | 0.890 |
| Co | 62.75 | 18.68 | 18.57 | 1 | 0.896 |
| Cr | 76.40 | 21.79 | 1.82 | 1 | 0.930 |
| Cu | 50.65 | 41.52 | 7.83 | 1 | 0.846 |
| Hg | 24.43 | 36.39 | 39.18 | 1 | 0.360 |
| Ni | 70.66 | 21.36 | 7.98 | 0.999 | 0.959 |
| Pb | 14.67 | 48.43 | 36.90 | 1 | 0.852 |
| Zn | 67.86 | 30.77 | 1.38 | 1.001 | 0.938 |
表5 大南湖七号煤矿土壤重金属污染源贡献率
Table 5 Contribution rate of heavy metal pollution sources in the soil of Dananhu No.7 coal mine
| 元素 | 贡献率(%) | E/O | 调整 后R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 | 主成分2 | 其他因子 | |||
| As | 62.37 | 24.99 | 12.64 | 1 | 0.733 |
| Cd | 23.52 | 59.12 | 17.36 | 1 | 0.890 |
| Co | 62.75 | 18.68 | 18.57 | 1 | 0.896 |
| Cr | 76.40 | 21.79 | 1.82 | 1 | 0.930 |
| Cu | 50.65 | 41.52 | 7.83 | 1 | 0.846 |
| Hg | 24.43 | 36.39 | 39.18 | 1 | 0.360 |
| Ni | 70.66 | 21.36 | 7.98 | 0.999 | 0.959 |
| Pb | 14.67 | 48.43 | 36.90 | 1 | 0.852 |
| Zn | 67.86 | 30.77 | 1.38 | 1.001 | 0.938 |
| [1] | 王鹏. 煤矿开采引发的地质环境问题及其对策研究[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2019(28): 118-120. |
| [2] | 李长春, 张光胜, 姚峰, 等. 新疆准东煤田五彩湾露天矿区土壤重金属污染评估与分析[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(7): 142-146. |
| [3] | 孙芳, 高优娜, 郝琳, 等. 探讨露天煤矿开采酿成的环境问题及防护对策[J]. 环境与发展, 2012, 24(6): 63-64. |
| [4] | 曹彪, 白云岗, 李玉生, 等. 新疆煤矿水土流失及生态环境危害分析[J]. 中国水土保持, 2020(6): 11-15. |
| [5] | 柴磊, 王新, 马良, 等. 基于PMF模型的兰州耕地土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(9): 39119-3929. |
| [6] | 黄华斌, 林承奇, 胡恭任, 等. 基于PMF模型的九龙江流域农田土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 430-437. |
| [7] | 陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 等. 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(10): 2219-2238. |
| [8] |
GUO H, WANG T, LOUIE P K K. Source apportionment of ambient non-methane hydrocarbons in Hong Kong: application of a principal component analysis/absolute principal component scores (PCA/APCS) receptor model[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2004, 129(3): 489-498.
PMID |
| [9] | 邱立民, 刘淼, 王菊, 等. 绝对主因子分析法解析龙岩市大气中的可吸入颗粒物来源[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2012, 50(2): 371-376. |
| [10] | 孟利, 左锐, 王金生, 等. 基于PCA-APCS-MLR的地下水污染源定量解析研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(10): 3773-3786. |
| [11] | 张旺, 高珍冉, 邰粤鹰, 等. 基于APCS-MLR受体模型的贵州喀斯特矿区水田土壤重金属源解析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(3): 212-219. |
| [12] | 后希康, 张凯, 段平洲, 等. 基于APCS-MLR模型的沱河流域污染来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(10): 2350-2357. |
| [13] | 瞿明凯, 李卫东, 张传荣, 等. 基于受体模型和地统计学相结合的土壤镉污染源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(5): 854-860. |
| [14] | 孙丽, 卢喜林, 周佳, 等. 国投哈密能源开发有限责任公司大南湖矿区西区大南湖七号煤矿及选煤厂环境影响报告书[R]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆天合环境技术咨询有限公司, 2015:28-29. |
| [15] | 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 多目标区域地球化学调查规范: DZ/T 0258—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. |
| [16] | THURSTON G D, SPENGLER J D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1985, 19(1): 9-25. |
| [17] | 马杰, 沈智杰, 张萍萍, 等. 基于APCS-MLR和PMF模型的煤矸山周边耕地土壤重金属污染特征及源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4): 2192-2203. |
| [18] | 霍明珠, 高秉博, 乔冬云, 等. 基于APCS-MLR受体模型的农田土壤重金属源解析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(5): 978-986. |
| [19] | 国家环境保护局主持, 中国环境监测总站主编. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990. |
| [20] | 李玲, 邵龙美, 李永武, 等. 新疆某多金属矿土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境与发展, 2020, 32(8): 23-26. |
| [21] | 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准: GB 15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. |
| [22] | 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准: GB 36600—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. |
| [23] | 韩小孩, 张耀辉, 孙福军, 等. 基于主成分分析的指标权重确定方法[J]. 四川兵工学报, 2012, 33(10): 124-126. |
| [24] | 张文彤, 董伟. SPSS统计分析高级教程第2版[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013: 213-233. |
| [25] | 乔雯, 王议, 张德强, 等. 某矿区土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 543-551. |
| [26] |
KORRE A. Statistical and spatial assessment of soil heavy metal contamination in areas of poorly recorded, complex sources of pollution[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 1999, 13(4): 260-287.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 王乔林, 宋云涛, 王成文, 等. 滇西地区土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(8): 3693-3703. |
| [28] | 杨磊, 熊黑刚. 新疆准东煤田土壤重金属来源分析及风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(15): 273-281. |
| [29] | 吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(7): 971-984. |
| [30] |
LV J S, LIU Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 387-397.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | 胡潇涵, 张琳, 孔利锋, 等. 新疆准东露天煤矿降尘、土壤以及植物中的重金属污染风险研究[J]. 新疆环境保护, 2020, 42(4): 24-32. |
| [32] | 邢浩, 杜古尔·卫卫, 薛娜娜, 等. 哈密露天煤矿不同环境介质微生物群落特征分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(11): 4525-4537. |
| [33] | 袁宏, 钟红梅, 赵利, 等. 基于PCA/APCS受体模型的崇州市典型农田土壤重金属污染源解析[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(6): 35-43. |
| [34] | 吕建树, 何华春. 江苏海岸带土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2853-2864. |
| [35] | 吴攀, 裴廷权, 冯丽娟, 等. 贵州兴仁煤矿区土壤表土与沉积物中砷的环境调查研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2006, 34(4) :31-35. |
| [36] | 缪成波, 于萌, 卢刚, 等. 干旱区露天煤矿降尘重金属分布特征及来源分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(22): 295-300. |
| [37] | 黄大伟, 桂和荣. 宿南矿区土壤重金属含量特征及其来源解析[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(5): 546-554. |
| [38] | 姚峰, 包安明, 古丽·加帕尔, 等. 新疆准东煤田土壤重金属来源与污染评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(10): 1821-1828. |
| [39] | 秦先燕, 李运怀, 孙跃, 等. 环巢湖典型农业区土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(4): 455-463. |
| [40] | 李超, 栾文楼, 蔡奎, 等. 石家庄近地表降尘重金属的分布特征及来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2): 415-420. |
| [41] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 等. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 634-644. |
| [1] | 李楠, 曹明杰, 郝喆, 侯永莉, 陈红丹, 张颖. 基于不同土地利用方式的土壤重金属污染与潜在风险评价:以辽河流域(浑太水系)山水林田湖草沙一体化保护和修复工程为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1655-1664. |
| [2] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [3] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 李欢, 张沁瑞. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 634-644. |
| [4] | 于璐, 郑天元, 郑西来. 地下水硝酸盐污染源解析及氮同位素分馏效应研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 563-573. |
| [5] | 乔雯, 王议, 张德强, 殷秀兰, 白光宇, 何培雍. 某矿区土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 543-551. |
| [6] | 臧传子, 温汉辉, 蔡立梅, 罗杰, 徐述邦, 梅敬娴. 广东省揭阳市土壤铅的空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1425-1432. |
| [7] | 唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 徐进力, 徐仁廷, 张富贵. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 917-927. |
| [8] | 李朋飞, 刘超, 陶春军, 汪晶, 吴正. 再生铅工业园周边土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 663-671. |
| [9] | 王娟恒, 温汉辉, 蔡立梅, 罗杰, 王硕, 王秋爽, 穆桂珍, 蒋慧豪. 广东揭阳土壤镉含量的空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 88-96. |
| [10] | 刘海, 康博, 沈军辉. 基于反向地球化学模拟的地下水形成作用:以安徽省泗县为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 440-450. |
| [11] | 孙凯, 孙彬彬, 周国华, 贺灵, 曾道明, 吴超, 成晓梦. 福建龙海土壤重金属含量特征及影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1302-1310. |
| [12] | 汪名鹏. 江苏泗阳城区浅层地下水化学特征及其影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1329-1336. |
| [13] | 邱海军,曹明明,刘闻,郝俊卿,胡胜,高宇,刘琪. 区域滑坡空间分布的变维分形特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 443-448. |
| [14] | 钟聪, 杨忠芳, 夏学齐, 侯青叶, 姜伟. 青海省土壤有机碳储量估算及其源汇因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 896-909. |
| [15] | 傅倩倩, 王广才. 华北地区某工业场地土壤重金属分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 829-836. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||