



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (06): 1212-1226.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.06.10
收稿日期:2018-03-21
修回日期:2018-09-10
出版日期:2018-12-10
发布日期:2018-12-20
作者简介:徐立明,男,助理工程师,硕士,1989年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事区域地质调查工作。Email:xlmcugb@126.com。
基金资助:
XU Liming( ), WANG Dake, LIU Yu, ZHENG Jilin, ZHANG Wenqiang, LIANG Zhongkai
), WANG Dake, LIU Yu, ZHENG Jilin, ZHANG Wenqiang, LIANG Zhongkai
Received:2018-03-21
Revised:2018-09-10
Online:2018-12-10
Published:2018-12-20
摘要:
以大兴安岭北段塔河南部基性、中性和酸性侵入岩(SiO2=51.27%~74.90%)为研究对象,通过锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和岩石地球化学分析,探讨了其岩石成因和构造环境。测定的2件样品锆石U-Pb定年结果分别是(126.9±0.8) Ma和(123.4±0.9) Ma,侵位于早白垩世。在哈克(Harker)图解中,多数样品主量元素和微量元素随SiO2含量增加具有很好的线性演化趋势(除K2O和Rb外)。微量元素总体显示富集Pb和大离子亲石元素K、Rb、Ba等,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti、P等,并具有相似的Sr、Nd同位素特征((87Sr/86Sr)i=0.705 517~0.706 827,εNd(t)=-6.82~0.79)。综合研究认为,塔河南部早白垩世侵入岩的岩浆源区是与俯冲有关的熔流体交代的石榴子石二辉橄榄岩相和尖晶石二辉橄榄岩相的混合源区,且以石榴子石二辉橄榄岩相为主,在岩浆快速上升的过程中主要经历了分离结晶作用,最后形成一套宽谱系的岩浆演化序列。结合中国东北地区火山岩展布方向、古地磁资料、蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合时间以及古太平洋板块俯冲方向等已有成果,认为大兴安岭北段塔河南部的侵入岩产出在与蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合有关的后碰撞环境。
中图分类号:
徐立明, 王大可, 刘玉, 郑吉林, 张文强, 梁中恺. 大兴安岭北段塔河南部早白垩世侵入岩年代学和地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1212-1226.
XU Liming, WANG Dake, LIU Yu, ZHENG Jilin, ZHANG Wenqiang, LIANG Zhongkai. Age and Geochemistry of the Early Cretaceous Intrusive Rocks in Southern Tahe, Northern Great Xing’an Range[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(06): 1212-1226.

图1 东北地区构造分区((a)据文献[14])主要地理单元((b)据文献[15])和研究区地质简图(c) F1.牡丹江断裂;F2.敦化—密山断裂;F3.伊通—依兰断裂;F4.西拉木伦—长春断裂;F5.贺根山—黑河断裂;F6.塔源—喜桂图断裂;F7.蒙古—鄂霍茨克断裂
Fig.1 Maps showing the tectonic subdivision(a), major geographical units(b) of NE China and geology(c) of the study area

图2 研究区侵入岩野外采样和显微镜下照片 (a)SPM9-5-1石英二长岩侵入中生代安山岩中;(b)样品SPM13TC19取样探槽;(c)细粒辉长岩镜下照片;(d)闪长岩镜下照片;(e)似斑状石英二长岩镜下照片;(f)二长花岗岩镜下照片。Pl.斜长石;Kfs.钾长石;Hbi.角闪石;Bt.黑云母;Px.普通辉石;Q.石英
Fig.2 Field photos and thin section photomicrographs of the intrusive rocks from the study area
| 测点 | wB/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | |||
| SPM3TC27-1 | 3 | 121 | 1.57 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.135 5 | 0.033 8 | 0.048 8 | 0.012 4 | 128.6 | 2.8 | 129.1 | 32.2 | 137.3 | 595.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-2 | 3 | 100 | 1.48 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 7 | 0.015 4 | 0.048 5 | 0.021 8 | 128.5 | 1.9 | 128.3 | 14.7 | 124.6 | 105 6.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-3 | 1 | 47 | 1.10 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.134 3 | 0.023 8 | 0.048 8 | 0.013 9 | 127.3 | 2.8 | 128.0 | 22.7 | 139.7 | 669.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-4 | 1 | 42 | 1.11 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 4 | 0.133 6 | 0.017 8 | 0.049 6 | 0.007 3 | 124.8 | 2.3 | 127.4 | 16.9 | 174.7 | 341.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-5 | 1 | 41 | 1.12 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.135 4 | 0.026 0 | 0.048 5 | 0.011 1 | 129.2 | 3.2 | 128.9 | 24.7 | 123.9 | 539.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-6 | 1 | 49 | 1.19 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.133 8 | 0.017 0 | 0.048 4 | 0.006 5 | 128.0 | 2.2 | 127.5 | 16.2 | 119.6 | 315.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-7 | 1 | 37 | 1.15 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 4 | 0.131 6 | 0.014 1 | 0.048 8 | 0.005 5 | 124.9 | 2.6 | 125.6 | 13.4 | 137.7 | 263.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-8 | 1 | 43 | 1.44 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 8 | 0.133 3 | 0.028 6 | 0.048 6 | 0.011 8 | 126.9 | 5.0 | 127.1 | 27.3 | 129.9 | 572.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-9 | 1 | 40 | 1.11 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.132 0 | 0.026 2 | 0.047 6 | 0.010 4 | 128.5 | 2.7 | 125.9 | 25.0 | 77.5 | 520.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-10 | 1 | 53 | 1.44 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.135 3 | 0.028 9 | 0.048 5 | 0.012 4 | 129.1 | 2.9 | 128.8 | 27.5 | 122.7 | 601.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-11 | 2 | 56 | 1.60 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.138 0 | 0.028 9 | 0.048 3 | 0.011 7 | 132.1 | 2.4 | 131.2 | 27.5 | 115.3 | 570.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-12 | 1 | 42 | 1.21 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.131 9 | 0.013 7 | 0.048 5 | 0.005 6 | 125.9 | 2.1 | 125.8 | 13.1 | 124.3 | 270.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-13 | 3 | 113 | 1.24 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.136 3 | 0.012 8 | 0.048 5 | 0.004 6 | 130.2 | 1.8 | 129.8 | 12.2 | 122.2 | 222.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-14 | 1 | 52 | 1.17 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 0 | 0.011 1 | 0.050 2 | 0.004 3 | 123.6 | 1.9 | 127.7 | 10.6 | 204.1 | 199.7 | |
| SPM3TC27-15 | 2 | 89 | 1.33 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.135 8 | 0.017 5 | 0.048 6 | 0.006 6 | 129.3 | 1.7 | 129.3 | 16.7 | 128.3 | 318.1 | |
| SPM3TC27-16 | 2 | 62 | 1.28 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 7 | 0.010 2 | 0.049 2 | 0.003 8 | 126.9 | 1.9 | 128.3 | 9.7 | 155.9 | 179.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-17 | 11 | 333 | 2.98 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.134 1 | 0.004 6 | 0.048 1 | 0.001 7 | 129.0 | 1.4 | 127.7 | 4.3 | 104.9 | 82.9 | |
| SPM3TC27-18 | 2 | 59 | 1.66 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.133 3 | 0.015 0 | 0.048 9 | 0.006 0 | 126.3 | 2.1 | 127.1 | 14.3 | 142.1 | 285.9 | |
| SPM3TC27-19 | 1 | 47 | 1.18 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.133 4 | 0.025 4 | 0.048 1 | 0.011 8 | 128.5 | 2.4 | 127.2 | 24.2 | 103.4 | 580.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-20 | 1 | 52 | 1.59 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 8 | 0.133 6 | 0.064 5 | 0.049 1 | 0.026 4 | 126.1 | 4.9 | 127.3 | 61.4 | 150.5 | 125 9.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-21 | 1 | 48 | 1.22 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 6 | 0.029 1 | 0.048 6 | 0.010 3 | 128.2 | 2.2 | 128.2 | 27.7 | 129.1 | 498.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-22 | 2 | 61 | 2.89 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.132 8 | 0.021 3 | 0.048 0 | 0.008 2 | 128.2 | 1.8 | 126.6 | 20.3 | 97.4 | 407.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-23 | 1 | 53 | 1.23 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.132 4 | 0.015 0 | 0.049 3 | 0.006 4 | 124.5 | 2.3 | 126.3 | 14.3 | 160.0 | 303.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-24 | 2 | 56 | 1.34 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 0 | 0.013 6 | 0.050 2 | 0.008 3 | 123.7 | 2.0 | 127.7 | 13.0 | 203.5 | 383.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-25 | 1 | 50 | 1.33 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 5 | 0.131 4 | 0.026 1 | 0.049 1 | 0.009 9 | 123.9 | 3.0 | 125.4 | 24.9 | 153.8 | 470.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-26 | 2 | 76 | 1.19 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.134 4 | 0.031 9 | 0.048 2 | 0.013 3 | 129.0 | 3.2 | 128.1 | 30.4 | 110.7 | 653.3 | |
| SPM3TC27-27 | 2 | 79 | 1.65 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.132 3 | 0.008 9 | 0.049 1 | 0.003 2 | 124.9 | 1.7 | 126.2 | 8.5 | 150.6 | 152.1 | |
| SPM3TC27-28 | 21 | 272 | 12.24 | 0.018 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.136 5 | 0.007 6 | 0.052 8 | 0.003 0 | 119.7 | 2.4 | 130.0 | 7.3 | 322.2 | 128.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-29 | 8 | 268 | 2.99 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 8 | 0.014 8 | 0.048 8 | 0.005 2 | 127.8 | 1.6 | 128.4 | 14.1 | 138.9 | 250.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-30 | 1 | 61 | 1.38 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.133 9 | 0.029 6 | 0.049 0 | 0.011 6 | 126.5 | 2.0 | 127.6 | 28.2 | 146.9 | 555.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-31 | 1 | 40 | 1.13 | 0.019 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.129 4 | 0.015 4 | 0.048 8 | 0.006 0 | 122.8 | 2.6 | 123.6 | 14.7 | 139.5 | 289.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-32 | 1 | 55 | 1.16 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 4 | 0.130 9 | 0.013 7 | 0.048 4 | 0.005 3 | 125.2 | 2.3 | 124.9 | 13.1 | 120.8 | 257.8 | |
| SPM13TC19-1 | 4 | 164 | 1.05 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.197 6 | 0.010 8 | 0.073 8 | 0.004 0 | 123.9 | 1.3 | 183.1 | 10.0 | 1 037.0 | 108.7 | |
| SPM13TC19-2 | 4 | 145 | 0.87 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.168 9 | 0.011 5 | 0.062 9 | 0.004 3 | 124.4 | 1.3 | 158.5 | 10.8 | 704.4 | 146.2 | |
| SPM13TC19-3 | 2 | 84 | 0.74 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.210 0 | 0.020 6 | 0.077 2 | 0.007 9 | 125.9 | 1.6 | 193.6 | 19.0 | 1 127.2 | 204.3 | |
| SPM13TC19-4 | 2 | 85 | 0.65 | 0.019 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.159 1 | 0.019 1 | 0.059 7 | 0.007 8 | 123.3 | 1.6 | 149.9 | 18.0 | 593.7 | 282.9 | |
| SPM13TC19-5 | 4 | 175 | 1.10 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.145 7 | 0.009 7 | 0.053 8 | 0.003 6 | 125.5 | 1.3 | 138.1 | 9.2 | 360.6 | 151.5 | |
| SPM13TC19-6 | 16 | 605 | 1.49 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.168 0 | 0.004 1 | 0.061 9 | 0.001 5 | 125.6 | 1.2 | 157.7 | 3.9 | 670.7 | 51.4 | |
| SPM13TC19-7 | 11 | 393 | 1.40 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.314 6 | 0.007 1 | 0.112 6 | 0.002 5 | 129.3 | 1.3 | 277.8 | 6.3 | 1 842.1 | 39.4 | |
| SPM13TC19-8 | 3 | 134 | 1.13 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.212 5 | 0.015 9 | 0.078 9 | 0.005 9 | 124.7 | 1.4 | 195.7 | 14.7 | 1 170.5 | 148.5 | |
| SPM13TC19-9 | 4 | 183 | 0.89 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.218 7 | 0.009 8 | 0.080 8 | 0.003 5 | 125.4 | 1.3 | 200.8 | 9.0 | 1 215.7 | 86.1 | |
| SPM13TC19-10 | 9 | 334 | 1.36 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.227 2 | 0.006 2 | 0.082 5 | 0.002 2 | 127.5 | 1.2 | 207.9 | 5.7 | 1 257.3 | 51.8 | |
| SPM13TC19-11 | 5 | 205 | 0.79 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.307 5 | 0.012 2 | 0.108 5 | 0.004 1 | 131.2 | 1.4 | 272.2 | 10.8 | 1 774.4 | 68.9 | |
| SPM13TC19-12 | 6 | 201 | 1.27 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.317 1 | 0.010 5 | 0.111 0 | 0.003 6 | 132.2 | 1.4 | 279.6 | 9.3 | 1 816.3 | 59.0 | |
| SPM13TC19-13 | 3 | 105 | 1.01 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.152 0 | 0.016 6 | 0.056 4 | 0.006 6 | 124.7 | 1.5 | 143.6 | 15.7 | 468.4 | 260.1 | |
| SPM13TC19-14 | 13 | 478 | 2.06 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.139 4 | 0.004 6 | 0.051 9 | 0.001 6 | 124.3 | 1.2 | 132.5 | 4.3 | 283.1 | 72.4 | |
| SPM13TC19-15 | 3 | 129 | 1.12 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.173 4 | 0.015 1 | 0.064 0 | 0.005 7 | 125.4 | 1.4 | 162.4 | 14.1 | 741.7 | 188.7 | |
| SPM13TC19-16 | 4 | 161 | 1.21 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.319 0 | 0.014 5 | 0.113 0 | 0.005 0 | 130.7 | 1.4 | 281.1 | 12.8 | 1 848.0 | 79.6 | |
| SPM13TC19-17 | 4 | 167 | 0.87 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.182 2 | 0.012 2 | 0.067 4 | 0.004 5 | 125.2 | 1.3 | 170.0 | 11.4 | 849.2 | 138.3 | |
| SPM13TC19-18 | 9 | 362 | 1.39 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.142 0 | 0.006 1 | 0.053 0 | 0.002 3 | 124.1 | 1.2 | 134.8 | 5.8 | 327.5 | 97.0 | |
| SPM13TC19-19 | 3 | 135 | 0.95 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.227 5 | 0.018 0 | 0.083 7 | 0.006 5 | 125.8 | 1.5 | 208.2 | 16.5 | 1 286.0 | 151.6 | |
| SPM13TC19-20 | 6 | 229 | 1.12 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.146 1 | 0.008 2 | 0.054 3 | 0.003 0 | 124.6 | 1.3 | 138.5 | 7.8 | 382.4 | 125.5 | |
| SPM13TC19-21 | 2 | 98 | 0.62 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.233 5 | 0.024 2 | 0.084 5 | 0.008 9 | 127.9 | 1.7 | 213.1 | 22.1 | 1 303.8 | 204.4 | |
表1 研究区侵入岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon analytical data of the intrusive rocks from the study area
| 测点 | wB/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | ±1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | ±1σ | |||
| SPM3TC27-1 | 3 | 121 | 1.57 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.135 5 | 0.033 8 | 0.048 8 | 0.012 4 | 128.6 | 2.8 | 129.1 | 32.2 | 137.3 | 595.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-2 | 3 | 100 | 1.48 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 7 | 0.015 4 | 0.048 5 | 0.021 8 | 128.5 | 1.9 | 128.3 | 14.7 | 124.6 | 105 6.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-3 | 1 | 47 | 1.10 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.134 3 | 0.023 8 | 0.048 8 | 0.013 9 | 127.3 | 2.8 | 128.0 | 22.7 | 139.7 | 669.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-4 | 1 | 42 | 1.11 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 4 | 0.133 6 | 0.017 8 | 0.049 6 | 0.007 3 | 124.8 | 2.3 | 127.4 | 16.9 | 174.7 | 341.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-5 | 1 | 41 | 1.12 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.135 4 | 0.026 0 | 0.048 5 | 0.011 1 | 129.2 | 3.2 | 128.9 | 24.7 | 123.9 | 539.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-6 | 1 | 49 | 1.19 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.133 8 | 0.017 0 | 0.048 4 | 0.006 5 | 128.0 | 2.2 | 127.5 | 16.2 | 119.6 | 315.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-7 | 1 | 37 | 1.15 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 4 | 0.131 6 | 0.014 1 | 0.048 8 | 0.005 5 | 124.9 | 2.6 | 125.6 | 13.4 | 137.7 | 263.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-8 | 1 | 43 | 1.44 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 8 | 0.133 3 | 0.028 6 | 0.048 6 | 0.011 8 | 126.9 | 5.0 | 127.1 | 27.3 | 129.9 | 572.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-9 | 1 | 40 | 1.11 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.132 0 | 0.026 2 | 0.047 6 | 0.010 4 | 128.5 | 2.7 | 125.9 | 25.0 | 77.5 | 520.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-10 | 1 | 53 | 1.44 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.135 3 | 0.028 9 | 0.048 5 | 0.012 4 | 129.1 | 2.9 | 128.8 | 27.5 | 122.7 | 601.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-11 | 2 | 56 | 1.60 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.138 0 | 0.028 9 | 0.048 3 | 0.011 7 | 132.1 | 2.4 | 131.2 | 27.5 | 115.3 | 570.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-12 | 1 | 42 | 1.21 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.131 9 | 0.013 7 | 0.048 5 | 0.005 6 | 125.9 | 2.1 | 125.8 | 13.1 | 124.3 | 270.2 | |
| SPM3TC27-13 | 3 | 113 | 1.24 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.136 3 | 0.012 8 | 0.048 5 | 0.004 6 | 130.2 | 1.8 | 129.8 | 12.2 | 122.2 | 222.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-14 | 1 | 52 | 1.17 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 0 | 0.011 1 | 0.050 2 | 0.004 3 | 123.6 | 1.9 | 127.7 | 10.6 | 204.1 | 199.7 | |
| SPM3TC27-15 | 2 | 89 | 1.33 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.135 8 | 0.017 5 | 0.048 6 | 0.006 6 | 129.3 | 1.7 | 129.3 | 16.7 | 128.3 | 318.1 | |
| SPM3TC27-16 | 2 | 62 | 1.28 | 0.019 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 7 | 0.010 2 | 0.049 2 | 0.003 8 | 126.9 | 1.9 | 128.3 | 9.7 | 155.9 | 179.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-17 | 11 | 333 | 2.98 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.134 1 | 0.004 6 | 0.048 1 | 0.001 7 | 129.0 | 1.4 | 127.7 | 4.3 | 104.9 | 82.9 | |
| SPM3TC27-18 | 2 | 59 | 1.66 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.133 3 | 0.015 0 | 0.048 9 | 0.006 0 | 126.3 | 2.1 | 127.1 | 14.3 | 142.1 | 285.9 | |
| SPM3TC27-19 | 1 | 47 | 1.18 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.133 4 | 0.025 4 | 0.048 1 | 0.011 8 | 128.5 | 2.4 | 127.2 | 24.2 | 103.4 | 580.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-20 | 1 | 52 | 1.59 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 8 | 0.133 6 | 0.064 5 | 0.049 1 | 0.026 4 | 126.1 | 4.9 | 127.3 | 61.4 | 150.5 | 125 9.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-21 | 1 | 48 | 1.22 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 6 | 0.029 1 | 0.048 6 | 0.010 3 | 128.2 | 2.2 | 128.2 | 27.7 | 129.1 | 498.6 | |
| SPM3TC27-22 | 2 | 61 | 2.89 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.132 8 | 0.021 3 | 0.048 0 | 0.008 2 | 128.2 | 1.8 | 126.6 | 20.3 | 97.4 | 407.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-23 | 1 | 53 | 1.23 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.132 4 | 0.015 0 | 0.049 3 | 0.006 4 | 124.5 | 2.3 | 126.3 | 14.3 | 160.0 | 303.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-24 | 2 | 56 | 1.34 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 0 | 0.013 6 | 0.050 2 | 0.008 3 | 123.7 | 2.0 | 127.7 | 13.0 | 203.5 | 383.4 | |
| SPM3TC27-25 | 1 | 50 | 1.33 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 5 | 0.131 4 | 0.026 1 | 0.049 1 | 0.009 9 | 123.9 | 3.0 | 125.4 | 24.9 | 153.8 | 470.8 | |
| SPM3TC27-26 | 2 | 76 | 1.19 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 5 | 0.134 4 | 0.031 9 | 0.048 2 | 0.013 3 | 129.0 | 3.2 | 128.1 | 30.4 | 110.7 | 653.3 | |
| SPM3TC27-27 | 2 | 79 | 1.65 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.132 3 | 0.008 9 | 0.049 1 | 0.003 2 | 124.9 | 1.7 | 126.2 | 8.5 | 150.6 | 152.1 | |
| SPM3TC27-28 | 21 | 272 | 12.24 | 0.018 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.136 5 | 0.007 6 | 0.052 8 | 0.003 0 | 119.7 | 2.4 | 130.0 | 7.3 | 322.2 | 128.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-29 | 8 | 268 | 2.99 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.134 8 | 0.014 8 | 0.048 8 | 0.005 2 | 127.8 | 1.6 | 128.4 | 14.1 | 138.9 | 250.5 | |
| SPM3TC27-30 | 1 | 61 | 1.38 | 0.019 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.133 9 | 0.029 6 | 0.049 0 | 0.011 6 | 126.5 | 2.0 | 127.6 | 28.2 | 146.9 | 555.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-31 | 1 | 40 | 1.13 | 0.019 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.129 4 | 0.015 4 | 0.048 8 | 0.006 0 | 122.8 | 2.6 | 123.6 | 14.7 | 139.5 | 289.0 | |
| SPM3TC27-32 | 1 | 55 | 1.16 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 4 | 0.130 9 | 0.013 7 | 0.048 4 | 0.005 3 | 125.2 | 2.3 | 124.9 | 13.1 | 120.8 | 257.8 | |
| SPM13TC19-1 | 4 | 164 | 1.05 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.197 6 | 0.010 8 | 0.073 8 | 0.004 0 | 123.9 | 1.3 | 183.1 | 10.0 | 1 037.0 | 108.7 | |
| SPM13TC19-2 | 4 | 145 | 0.87 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.168 9 | 0.011 5 | 0.062 9 | 0.004 3 | 124.4 | 1.3 | 158.5 | 10.8 | 704.4 | 146.2 | |
| SPM13TC19-3 | 2 | 84 | 0.74 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 3 | 0.210 0 | 0.020 6 | 0.077 2 | 0.007 9 | 125.9 | 1.6 | 193.6 | 19.0 | 1 127.2 | 204.3 | |
| SPM13TC19-4 | 2 | 85 | 0.65 | 0.019 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.159 1 | 0.019 1 | 0.059 7 | 0.007 8 | 123.3 | 1.6 | 149.9 | 18.0 | 593.7 | 282.9 | |
| SPM13TC19-5 | 4 | 175 | 1.10 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.145 7 | 0.009 7 | 0.053 8 | 0.003 6 | 125.5 | 1.3 | 138.1 | 9.2 | 360.6 | 151.5 | |
| SPM13TC19-6 | 16 | 605 | 1.49 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.168 0 | 0.004 1 | 0.061 9 | 0.001 5 | 125.6 | 1.2 | 157.7 | 3.9 | 670.7 | 51.4 | |
| SPM13TC19-7 | 11 | 393 | 1.40 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.314 6 | 0.007 1 | 0.112 6 | 0.002 5 | 129.3 | 1.3 | 277.8 | 6.3 | 1 842.1 | 39.4 | |
| SPM13TC19-8 | 3 | 134 | 1.13 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.212 5 | 0.015 9 | 0.078 9 | 0.005 9 | 124.7 | 1.4 | 195.7 | 14.7 | 1 170.5 | 148.5 | |
| SPM13TC19-9 | 4 | 183 | 0.89 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.218 7 | 0.009 8 | 0.080 8 | 0.003 5 | 125.4 | 1.3 | 200.8 | 9.0 | 1 215.7 | 86.1 | |
| SPM13TC19-10 | 9 | 334 | 1.36 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.227 2 | 0.006 2 | 0.082 5 | 0.002 2 | 127.5 | 1.2 | 207.9 | 5.7 | 1 257.3 | 51.8 | |
| SPM13TC19-11 | 5 | 205 | 0.79 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.307 5 | 0.012 2 | 0.108 5 | 0.004 1 | 131.2 | 1.4 | 272.2 | 10.8 | 1 774.4 | 68.9 | |
| SPM13TC19-12 | 6 | 201 | 1.27 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.317 1 | 0.010 5 | 0.111 0 | 0.003 6 | 132.2 | 1.4 | 279.6 | 9.3 | 1 816.3 | 59.0 | |
| SPM13TC19-13 | 3 | 105 | 1.01 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.152 0 | 0.016 6 | 0.056 4 | 0.006 6 | 124.7 | 1.5 | 143.6 | 15.7 | 468.4 | 260.1 | |
| SPM13TC19-14 | 13 | 478 | 2.06 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.139 4 | 0.004 6 | 0.051 9 | 0.001 6 | 124.3 | 1.2 | 132.5 | 4.3 | 283.1 | 72.4 | |
| SPM13TC19-15 | 3 | 129 | 1.12 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.173 4 | 0.015 1 | 0.064 0 | 0.005 7 | 125.4 | 1.4 | 162.4 | 14.1 | 741.7 | 188.7 | |
| SPM13TC19-16 | 4 | 161 | 1.21 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.319 0 | 0.014 5 | 0.113 0 | 0.005 0 | 130.7 | 1.4 | 281.1 | 12.8 | 1 848.0 | 79.6 | |
| SPM13TC19-17 | 4 | 167 | 0.87 | 0.019 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.182 2 | 0.012 2 | 0.067 4 | 0.004 5 | 125.2 | 1.3 | 170.0 | 11.4 | 849.2 | 138.3 | |
| SPM13TC19-18 | 9 | 362 | 1.39 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.142 0 | 0.006 1 | 0.053 0 | 0.002 3 | 124.1 | 1.2 | 134.8 | 5.8 | 327.5 | 97.0 | |
| SPM13TC19-19 | 3 | 135 | 0.95 | 0.019 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.227 5 | 0.018 0 | 0.083 7 | 0.006 5 | 125.8 | 1.5 | 208.2 | 16.5 | 1 286.0 | 151.6 | |
| SPM13TC19-20 | 6 | 229 | 1.12 | 0.019 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.146 1 | 0.008 2 | 0.054 3 | 0.003 0 | 124.6 | 1.3 | 138.5 | 7.8 | 382.4 | 125.5 | |
| SPM13TC19-21 | 2 | 98 | 0.62 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.233 5 | 0.024 2 | 0.084 5 | 0.008 9 | 127.9 | 1.7 | 213.1 | 22.1 | 1 303.8 | 204.4 | |
| 测点 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | 2σ | (176Hf/177Hf)i | εHf(0) | εHf(t) | TDM/Ma | fLu/Hf | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM13TC19-1 | 124.4 | 0.034 486 | 0.001 143 | 0.282 788 | 0.000 023 | 0.282 785 | 0.6 | 3.2 | 660 | 978 | -0.97 |
| SPM13TC19-2 | 125.9 | 0.031 751 | 0.001 047 | 0.282 736 | 0.000 019 | 0.282 733 | -1.3 | 1.4 | 732 | 1 094 | -0.97 |
| SPM13TC19-3 | 123.3 | 0.048 326 | 0.001 598 | 0.282 741 | 0.000 022 | 0.282 738 | -1.1 | 1.5 | 735 | 1 086 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-4 | 125.4 | 0.051 590 | 0.001 555 | 0.282 774 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 770 | 0.1 | 2.7 | 687 | 1 010 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-5 | 124.7 | 0.048 914 | 0.001 511 | 0.282 765 | 0.000 022 | 0.282 761 | -0.3 | 2.4 | 700 | 1 031 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-6 | 124.3 | 0.054 456 | 0.001 697 | 0.282 753 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 749 | -0.7 | 1.9 | 721 | 1 060 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-7 | 125.4 | 0.084 832 | 0.002 566 | 0.282 724 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 718 | -1.7 | 0.8 | 781 | 1 129 | -0.92 |
| SPM13TC19-8 | 124.1 | 0.102 235 | 0.003 124 | 0.282 767 | 0.000 019 | 0.282 760 | -0.2 | 2.3 | 729 | 1 035 | -0.91 |
| SPM13TC19-9 | 125.8 | 0.049 982 | 0.001 541 | 0.282 772 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 769 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 690 | 1 014 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-10 | 124.6 | 0.085 726 | 0.002 616 | 0.282 822 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 816 | 1.8 | 4.3 | 636 | 907 | -0.92 |
| SPM13TC19-11 | 127.9 | 0.030 372 | 0.000 971 | 0.282 741 | 0.000 017 | 0.282 739 | -1.1 | 1.6 | 723 | 1 080 | -0.97 |
表2 研究区侵入岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2 Zircon Hf isotopic data of the intrusive rocks from the study area
| 测点 | 年龄/Ma | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | 2σ | (176Hf/177Hf)i | εHf(0) | εHf(t) | TDM/Ma | fLu/Hf | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM13TC19-1 | 124.4 | 0.034 486 | 0.001 143 | 0.282 788 | 0.000 023 | 0.282 785 | 0.6 | 3.2 | 660 | 978 | -0.97 |
| SPM13TC19-2 | 125.9 | 0.031 751 | 0.001 047 | 0.282 736 | 0.000 019 | 0.282 733 | -1.3 | 1.4 | 732 | 1 094 | -0.97 |
| SPM13TC19-3 | 123.3 | 0.048 326 | 0.001 598 | 0.282 741 | 0.000 022 | 0.282 738 | -1.1 | 1.5 | 735 | 1 086 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-4 | 125.4 | 0.051 590 | 0.001 555 | 0.282 774 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 770 | 0.1 | 2.7 | 687 | 1 010 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-5 | 124.7 | 0.048 914 | 0.001 511 | 0.282 765 | 0.000 022 | 0.282 761 | -0.3 | 2.4 | 700 | 1 031 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-6 | 124.3 | 0.054 456 | 0.001 697 | 0.282 753 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 749 | -0.7 | 1.9 | 721 | 1 060 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-7 | 125.4 | 0.084 832 | 0.002 566 | 0.282 724 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 718 | -1.7 | 0.8 | 781 | 1 129 | -0.92 |
| SPM13TC19-8 | 124.1 | 0.102 235 | 0.003 124 | 0.282 767 | 0.000 019 | 0.282 760 | -0.2 | 2.3 | 729 | 1 035 | -0.91 |
| SPM13TC19-9 | 125.8 | 0.049 982 | 0.001 541 | 0.282 772 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 769 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 690 | 1 014 | -0.95 |
| SPM13TC19-10 | 124.6 | 0.085 726 | 0.002 616 | 0.282 822 | 0.000 018 | 0.282 816 | 1.8 | 4.3 | 636 | 907 | -0.92 |
| SPM13TC19-11 | 127.9 | 0.030 372 | 0.000 971 | 0.282 741 | 0.000 017 | 0.282 739 | -1.1 | 1.6 | 723 | 1 080 | -0.97 |
| 样品号 | wB/% | Mg# | A/CNK | wB/10-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Li | Be | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC28 | 52.07 | 1.21 | 18.51 | 3.79 | 4.86 | 0.12 | 4.42 | 8.16 | 3.72 | 1.38 | 0.33 | 1.11 | 99.69 | 49.03 | 0.83 | 7.81 | 1.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC54 | 51.27 | 1.10 | 17.84 | 4.64 | 3.50 | 0.11 | 3.71 | 8.06 | 2.78 | 2.15 | 0.36 | 4.16 | 99.68 | 46.53 | 0.83 | 15.9 | 1.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC8 | 59.72 | 0.73 | 16.93 | 2.99 | 2.69 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 4.48 | 4.31 | 3.32 | 0.38 | 2.06 | 99.73 | 40.10 | 0.90 | 22.2 | 2.78 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC19 | 57.40 | 0.92 | 18.83 | 2.87 | 2.69 | 0.10 | 2.06 | 4.68 | 4.81 | 3.26 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 99.61 | 41.32 | 0.94 | 17.9 | 2.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC92 | 58.89 | 0.80 | 17.13 | 3.78 | 3.05 | 0.11 | 2.14 | 5.21 | 4.55 | 2.34 | 0.38 | 1.30 | 99.70 | 37.33 | 0.88 | 10.6 | 1.66 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC66 | 58.38 | 0.94 | 17.01 | 4.32 | 2.42 | 0.12 | 2.58 | 4.53 | 4.17 | 2.93 | 0.30 | 1.99 | 99.69 | 42.41 | 0.93 | 14.0 | 2.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC86 | 59.28 | 0.80 | 16.97 | 4.84 | 1.68 | 0.14 | 2.30 | 4.41 | 4.13 | 2.82 | 0.32 | 2.02 | 99.71 | 40.69 | 0.95 | 10.5 | 1.95 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM9-5-1 | 68.18 | 0.44 | 15.60 | 1.73 | 1.21 | 0.06 | 0.90 | 2.24 | 4.44 | 3.89 | 0.14 | 0.91 | 99.74 | 36.91 | 1.00 | 12.6 | 2.42 | |||||||||||||||||
| D2012 | 65.43 | 0.67 | 15.30 | 2.39 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 1.56 | 1.82 | 4.33 | 4.43 | 0.17 | 2.16 | 99.78 | 43.82 | 1.01 | 25.8 | 3.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM7-2-2 | 62.82 | 0.94 | 16.74 | 1.95 | 2.95 | 0.11 | 1.15 | 2.23 | 4.48 | 5.10 | 0.35 | 0.91 | 99.73 | 30.56 | 0.99 | 13.2 | 3.96 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC84 | 66.61 | 0.54 | 16.50 | 2.34 | 0.69 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 4.77 | 5.57 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 99.75 | 30.14 | 1.07 | 10.0 | 3.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM3TC27 | 68.92 | 0.53 | 15.32 | 1.73 | 1.03 | 0.08 | 0.81 | 1.33 | 4.94 | 4.17 | 0.14 | 0.78 | 99.80 | 36.07 | 1.02 | 19.2 | 2.32 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | wB/10-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC28 | 25.3 | 232 | 51.7 | 33.7 | 25.6 | 64.4 | 24.6 | 28.7 | 1351 | 17.8 | 128 | 6.56 | 694 | 19.4 | 41.7 | 5.81 | 25.7 | 5.47 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC54 | 19.8 | 219 | 42.0 | 25.9 | 13.0 | 57.4 | 21.5 | 54.6 | 1330 | 16.1 | 118 | 6.78 | 702 | 22.1 | 45.4 | 6.15 | 25.2 | 5.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC8 | 10.1 | 117 | 14.6 | 11.2 | 1.23 | 20.7 | 21.8 | 103 | 899 | 18.5 | 170 | 11.5 | 728 | 28.2 | 61.8 | 8.05 | 31.4 | 5.82 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC19 | 8.62 | 91.7 | 17.0 | 9.99 | 2.72 | 16.6 | 22.3 | 81.1 | 1245 | 17.0 | 183 | 11.2 | 1141 | 32.0 | 71.0 | 9.19 | 36.3 | 6.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC92 | 12.0 | 125 | 16.0 | 13.0 | 1.97 | 17.8 | 23.2 | 66.8 | 1172 | 19.6 | 134 | 6.91 | 826. | 28.0 | 57.3 | 7.20 | 29.3 | 5.76 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC66 | 15.4 | 167 | 19.4 | 14.9 | 11.8 | 21.7 | 25.5 | 99.6 | 1075 | 19.7 | 250 | 12.1 | 1005 | 28.5 | 63.9 | 8.99 | 36.3 | 6.87 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC86 | 11.7 | 133 | 5.03 | 11.4 | 2.12 | 24.1 | 22.4 | 80.3 | 933 | 21.1 | 164 | 7.95 | 970 | 32.7 | 58.4 | 7.83 | 30.9 | 5.93 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM9-5-1 | 5.57 | 52.4 | 17.1 | 5.16 | 1.98 | 11.6 | 18.6 | 116 | 548 | 13.9 | 222 | 10.9 | 905 | 33.1 | 67.0 | 7.45 | 25.7 | 4.08 | ||||||||||||||||
| D2012 | 7.22 | 81.3 | 43.3 | 11.0 | 18.6 | 27.1 | 22.7 | 187 | 389 | 13.4 | 308 | 11.1 | 725 | 38.9 | 82.7 | 9.78 | 34.0 | 5.37 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM7-2-2 | 10.1 | 48.3 | 5.47 | 7.09 | 1.82 | 5.80 | 21.5 | 92.8 | 505 | 30.7 | 436 | 53.0 | 1006 | 57.5 | 123 | 12.3 | 44.5 | 8.19 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC84 | 6.60 | 35.0 | 4.92 | 2.81 | 1.35 | 3.23 | 22.4 | 197 | 307 | 18.8 | 391 | 19.7 | 1126 | 36.7 | 78.5 | 8.86 | 33.1 | 5.61 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM3TC27 | 5.04 | 40.6 | 3.02 | 3.49 | 1.41 | 4.12 | 21.6 | 88.2 | 460 | 19.0 | 247 | 12.6 | 907 | 40.5 | 74.1 | 10.0 | 36.5 | 6.11 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | wB/10-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Mo | δEu | (La/Yb) N | ||||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC28 | 1.58 | 4.37 | 0.67 | 3.57 | 0.7 | 1.94 | 0.31 | 1.78 | 0.36 | 3.4 | 0.44 | 12.1 | 2.09 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.96 | 7.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC54 | 1.54 | 4.1 | 0.62 | 3.45 | 0.64 | 1.79 | 0.28 | 1.52 | 0.34 | 3.19 | 0.5 | 10.2 | 2.96 | 0.8 | 0.66 | 0.98 | 10.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC8 | 1.49 | 4.64 | 0.73 | 3.89 | 0.71 | 2.10 | 0.34 | 2.25 | 0.40 | 5.24 | 0.79 | 12.5 | 8.43 | 1.08 | 0.4 | 0.85 | 8.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC19 | 1.73 | 4.98 | 0.72 | 3.80 | 0.65 | 1.95 | 0.30 | 1.89 | 0.32 | 4.94 | 0.69 | 12.9 | 5.24 | 1.04 | 0.29 | 0.93 | 12.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC92 | 1.74 | 4.95 | 0.77 | 4.08 | 0.77 | 2.30 | 0.35 | 2.45 | 0.34 | 4.42 | 0.51 | 12.2 | 3.89 | 1.21 | 0.63 | 0.97 | 8.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC66 | 1.56 | 5.23 | 0.74 | 4.11 | 0.74 | 2.14 | 0.34 | 1.84 | 0.46 | 6.08 | 0.77 | 14.1 | 10.9 | 2.2 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 11.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC86 | 1.6 | 4.78 | 0.74 | 4.07 | 0.78 | 2.22 | 0.36 | 2.1 | 0.38 | 5.13 | 0.65 | 10.8 | 8 | 1.01 | 0.47 | 0.89 | 11.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM9-5-1 | 0.96 | 3.37 | 0.48 | 2.58 | 0.49 | 1.52 | 0.25 | 1.83 | 0.33 | 7.21 | 0.82 | 18.1 | 12.7 | 1.68 | 1.06 | 0.77 | 12.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| D2012 | 1.00 | 4.24 | 0.58 | 2.73 | 0.46 | 1.47 | 0.22 | 1.46 | 0.41 | 8.39 | 0.90 | 25.3 | 27.2 | 3.45 | 1.26 | 0.62 | 19.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM7-2-2 | 2.25 | 7.26 | 1.11 | 6.39 | 1.16 | 3.29 | 0.53 | 3 | 0.41 | 18.5 | 2.98 | 19.5 | 11.1 | 1.35 | 0.45 | 0.87 | 13.75 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC84 | 1.04 | 4.49 | 0.66 | 3.58 | 0.68 | 2.05 | 0.35 | 2.08 | 0.62 | 8.71 | 1.15 | 16.8 | 11.7 | 2.42 | 1.83 | 0.61 | 12.66 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM3TC27 | 1.26 | 4.63 | 0.69 | 3.64 | 0.67 | 2.03 | 0.31 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 11.6 | 0.98 | 24.6 | 11.6 | 1.23 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 15.34 | |||||||||||||||||
表3 研究区侵入岩主量元素、稀土元素和微量元素分析结果
Table 3 Major, rare earth and trace element compositions of the intrusive rocks from the study area
| 样品号 | wB/% | Mg# | A/CNK | wB/10-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Li | Be | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC28 | 52.07 | 1.21 | 18.51 | 3.79 | 4.86 | 0.12 | 4.42 | 8.16 | 3.72 | 1.38 | 0.33 | 1.11 | 99.69 | 49.03 | 0.83 | 7.81 | 1.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC54 | 51.27 | 1.10 | 17.84 | 4.64 | 3.50 | 0.11 | 3.71 | 8.06 | 2.78 | 2.15 | 0.36 | 4.16 | 99.68 | 46.53 | 0.83 | 15.9 | 1.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC8 | 59.72 | 0.73 | 16.93 | 2.99 | 2.69 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 4.48 | 4.31 | 3.32 | 0.38 | 2.06 | 99.73 | 40.10 | 0.90 | 22.2 | 2.78 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC19 | 57.40 | 0.92 | 18.83 | 2.87 | 2.69 | 0.10 | 2.06 | 4.68 | 4.81 | 3.26 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 99.61 | 41.32 | 0.94 | 17.9 | 2.07 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC92 | 58.89 | 0.80 | 17.13 | 3.78 | 3.05 | 0.11 | 2.14 | 5.21 | 4.55 | 2.34 | 0.38 | 1.30 | 99.70 | 37.33 | 0.88 | 10.6 | 1.66 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC66 | 58.38 | 0.94 | 17.01 | 4.32 | 2.42 | 0.12 | 2.58 | 4.53 | 4.17 | 2.93 | 0.30 | 1.99 | 99.69 | 42.41 | 0.93 | 14.0 | 2.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC86 | 59.28 | 0.80 | 16.97 | 4.84 | 1.68 | 0.14 | 2.30 | 4.41 | 4.13 | 2.82 | 0.32 | 2.02 | 99.71 | 40.69 | 0.95 | 10.5 | 1.95 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM9-5-1 | 68.18 | 0.44 | 15.60 | 1.73 | 1.21 | 0.06 | 0.90 | 2.24 | 4.44 | 3.89 | 0.14 | 0.91 | 99.74 | 36.91 | 1.00 | 12.6 | 2.42 | |||||||||||||||||
| D2012 | 65.43 | 0.67 | 15.30 | 2.39 | 1.46 | 0.06 | 1.56 | 1.82 | 4.33 | 4.43 | 0.17 | 2.16 | 99.78 | 43.82 | 1.01 | 25.8 | 3.18 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM7-2-2 | 62.82 | 0.94 | 16.74 | 1.95 | 2.95 | 0.11 | 1.15 | 2.23 | 4.48 | 5.10 | 0.35 | 0.91 | 99.73 | 30.56 | 0.99 | 13.2 | 3.96 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC84 | 66.61 | 0.54 | 16.50 | 2.34 | 0.69 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 4.77 | 5.57 | 0.15 | 0.95 | 99.75 | 30.14 | 1.07 | 10.0 | 3.41 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM3TC27 | 68.92 | 0.53 | 15.32 | 1.73 | 1.03 | 0.08 | 0.81 | 1.33 | 4.94 | 4.17 | 0.14 | 0.78 | 99.80 | 36.07 | 1.02 | 19.2 | 2.32 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | wB/10-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC28 | 25.3 | 232 | 51.7 | 33.7 | 25.6 | 64.4 | 24.6 | 28.7 | 1351 | 17.8 | 128 | 6.56 | 694 | 19.4 | 41.7 | 5.81 | 25.7 | 5.47 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC54 | 19.8 | 219 | 42.0 | 25.9 | 13.0 | 57.4 | 21.5 | 54.6 | 1330 | 16.1 | 118 | 6.78 | 702 | 22.1 | 45.4 | 6.15 | 25.2 | 5.25 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC8 | 10.1 | 117 | 14.6 | 11.2 | 1.23 | 20.7 | 21.8 | 103 | 899 | 18.5 | 170 | 11.5 | 728 | 28.2 | 61.8 | 8.05 | 31.4 | 5.82 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC19 | 8.62 | 91.7 | 17.0 | 9.99 | 2.72 | 16.6 | 22.3 | 81.1 | 1245 | 17.0 | 183 | 11.2 | 1141 | 32.0 | 71.0 | 9.19 | 36.3 | 6.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC92 | 12.0 | 125 | 16.0 | 13.0 | 1.97 | 17.8 | 23.2 | 66.8 | 1172 | 19.6 | 134 | 6.91 | 826. | 28.0 | 57.3 | 7.20 | 29.3 | 5.76 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC66 | 15.4 | 167 | 19.4 | 14.9 | 11.8 | 21.7 | 25.5 | 99.6 | 1075 | 19.7 | 250 | 12.1 | 1005 | 28.5 | 63.9 | 8.99 | 36.3 | 6.87 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC86 | 11.7 | 133 | 5.03 | 11.4 | 2.12 | 24.1 | 22.4 | 80.3 | 933 | 21.1 | 164 | 7.95 | 970 | 32.7 | 58.4 | 7.83 | 30.9 | 5.93 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM9-5-1 | 5.57 | 52.4 | 17.1 | 5.16 | 1.98 | 11.6 | 18.6 | 116 | 548 | 13.9 | 222 | 10.9 | 905 | 33.1 | 67.0 | 7.45 | 25.7 | 4.08 | ||||||||||||||||
| D2012 | 7.22 | 81.3 | 43.3 | 11.0 | 18.6 | 27.1 | 22.7 | 187 | 389 | 13.4 | 308 | 11.1 | 725 | 38.9 | 82.7 | 9.78 | 34.0 | 5.37 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM7-2-2 | 10.1 | 48.3 | 5.47 | 7.09 | 1.82 | 5.80 | 21.5 | 92.8 | 505 | 30.7 | 436 | 53.0 | 1006 | 57.5 | 123 | 12.3 | 44.5 | 8.19 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC84 | 6.60 | 35.0 | 4.92 | 2.81 | 1.35 | 3.23 | 22.4 | 197 | 307 | 18.8 | 391 | 19.7 | 1126 | 36.7 | 78.5 | 8.86 | 33.1 | 5.61 | ||||||||||||||||
| SPM3TC27 | 5.04 | 40.6 | 3.02 | 3.49 | 1.41 | 4.12 | 21.6 | 88.2 | 460 | 19.0 | 247 | 12.6 | 907 | 40.5 | 74.1 | 10.0 | 36.5 | 6.11 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | wB/10-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Mo | δEu | (La/Yb) N | ||||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC28 | 1.58 | 4.37 | 0.67 | 3.57 | 0.7 | 1.94 | 0.31 | 1.78 | 0.36 | 3.4 | 0.44 | 12.1 | 2.09 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.96 | 7.82 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM2TC54 | 1.54 | 4.1 | 0.62 | 3.45 | 0.64 | 1.79 | 0.28 | 1.52 | 0.34 | 3.19 | 0.5 | 10.2 | 2.96 | 0.8 | 0.66 | 0.98 | 10.43 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC8 | 1.49 | 4.64 | 0.73 | 3.89 | 0.71 | 2.10 | 0.34 | 2.25 | 0.40 | 5.24 | 0.79 | 12.5 | 8.43 | 1.08 | 0.4 | 0.85 | 8.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC19 | 1.73 | 4.98 | 0.72 | 3.80 | 0.65 | 1.95 | 0.30 | 1.89 | 0.32 | 4.94 | 0.69 | 12.9 | 5.24 | 1.04 | 0.29 | 0.93 | 12.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC92 | 1.74 | 4.95 | 0.77 | 4.08 | 0.77 | 2.30 | 0.35 | 2.45 | 0.34 | 4.42 | 0.51 | 12.2 | 3.89 | 1.21 | 0.63 | 0.97 | 8.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC66 | 1.56 | 5.23 | 0.74 | 4.11 | 0.74 | 2.14 | 0.34 | 1.84 | 0.46 | 6.08 | 0.77 | 14.1 | 10.9 | 2.2 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 11.11 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM14TC86 | 1.6 | 4.78 | 0.74 | 4.07 | 0.78 | 2.22 | 0.36 | 2.1 | 0.38 | 5.13 | 0.65 | 10.8 | 8 | 1.01 | 0.47 | 0.89 | 11.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM9-5-1 | 0.96 | 3.37 | 0.48 | 2.58 | 0.49 | 1.52 | 0.25 | 1.83 | 0.33 | 7.21 | 0.82 | 18.1 | 12.7 | 1.68 | 1.06 | 0.77 | 12.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| D2012 | 1.00 | 4.24 | 0.58 | 2.73 | 0.46 | 1.47 | 0.22 | 1.46 | 0.41 | 8.39 | 0.90 | 25.3 | 27.2 | 3.45 | 1.26 | 0.62 | 19.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM7-2-2 | 2.25 | 7.26 | 1.11 | 6.39 | 1.16 | 3.29 | 0.53 | 3 | 0.41 | 18.5 | 2.98 | 19.5 | 11.1 | 1.35 | 0.45 | 0.87 | 13.75 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM13TC84 | 1.04 | 4.49 | 0.66 | 3.58 | 0.68 | 2.05 | 0.35 | 2.08 | 0.62 | 8.71 | 1.15 | 16.8 | 11.7 | 2.42 | 1.83 | 0.61 | 12.66 | |||||||||||||||||
| SPM3TC27 | 1.26 | 4.63 | 0.69 | 3.64 | 0.67 | 2.03 | 0.31 | 1.89 | 0.30 | 11.6 | 0.98 | 24.6 | 11.6 | 1.23 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 15.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | 2σ | (87Sr/86Sr)i | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | 2σ | (143Nd/144Nd)i | εNd(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM3TC27 | 酸 性 岩 样 品 | 0.557 0 | 0.706 512 | 6 | 0.705 507 | 0.103 3 | 0.512 472 | 3 | 0.512 386 | -1.72 |
| PM17TC34* | 0.766 6 | 0.707 697 | 6 | 0.706 313 | 0.095 2 | 0.512 438 | 9 | 0.512 359 | -2.26 | |
| 0075-3* | 0.568 2 | 0.706 208 | 14 | 0.705 182 | 0.1 | 0.512 598 | 12 | 0.512 515 | 0.79 | |
| 0075-4* | 3.703 2 | 0.709 796 | 13 | 0.703 112 | 0.09 | 0.512 549 | 13 | 0.512 474 | -0.01 | |
| 0076-2* | 0.814 0 | 0.706 878 | 14 | 0.705 409 | 0.09 | 0.512 541 | 10 | 0.512 466 | -0.16 | |
| 0076-9* | 1.209 3 | 0.707 674 | 11 | 0.705 491 | 0.11 | 0.512 553 | 14 | 0.512 462 | -0.25 | |
| 05TH05* | 基 性 岩 样 品 | 0.238 4 | 0.705 947 | 14 | 0.705 517 | 0.118 4 | 0.512 503 | 12 | 0.512 405 | -1.36 |
| 05TH10* | 0.088 8 | 0.707 665 | 13 | 0.707 505 | 0.115 | 0.512 285 | 15 | 0.512 189 | -5.56 | |
| 05TH11* | 0.122 2 | 0.707 794 | 10 | 0.707 573 | 0.067 8 | 0.512 527 | 13 | 0.512 471 | -0.08 | |
| 05TH12* | 0.345 8 | 0.706 747 | 12 | 0.706 123 | 0.107 4 | 0.512 567 | 18 | 0.512 478 | 0.06 | |
| 05TH14* | 0.262 9 | 0.706 191 | 10 | 0.705 716 | 0.108 1 | 0.512 494 | 15 | 0.512 404 | -1.37 | |
| 05TH16* | 0.217 5 | 0.706 368 | 10 | 0.705 975 | 0.109 9 | 0.512 52 | 12 | 0.512 429 | -0.90 | |
| 05TH17* | 0.166 0 | 0.706 297 | 14 | 0.705 997 | 0.110 7 | 0.5124 93 | 12 | 0.512 401 | -1.44 | |
| 05TH19* | 0.100 1 | 0.706 934 | 12 | 0.706 753 | 0.109 1 | 0.5123 82 | 13 | 0.512 291 | -3.58 | |
| 05TH21* | 0.096 9 | 0.707 002 | 12 | 0.706 827 | 0.067 3 | 0.5125 49 | 13 | 0.512 493 | 0.36 | |
| 05TH23* | 0.112 3 | 0.705 952 | 14 | 0.705 749 | 0.124 1 | 0.5125 26 | 14 | 0.512 423 | -1.01 | |
| 05TH25* | 0.066 2 | 0.705 836 | 10 | 0.705 717 | 0.110 2 | 0.5125 37 | 11 | 0.512 445 | -0.57 | |
| 05TH26* | 0.070 9 | 0.705 816 | 14 | 0.705 688 | 0.178 8 | 0.5124 08 | 13 | 0.512 259 | -4.20 | |
| 05TH27* | 0.160 1 | 0.708 140 | 12 | 0.707 851 | 0.190 2 | 0.5122 83 | 11 | 0.512 125 | -6.82 |
表4 研究区侵入岩及收集样品全岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果
Table 4 Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the intrusive rocks from the study area
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | 2σ | (87Sr/86Sr)i | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | 2σ | (143Nd/144Nd)i | εNd(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM3TC27 | 酸 性 岩 样 品 | 0.557 0 | 0.706 512 | 6 | 0.705 507 | 0.103 3 | 0.512 472 | 3 | 0.512 386 | -1.72 |
| PM17TC34* | 0.766 6 | 0.707 697 | 6 | 0.706 313 | 0.095 2 | 0.512 438 | 9 | 0.512 359 | -2.26 | |
| 0075-3* | 0.568 2 | 0.706 208 | 14 | 0.705 182 | 0.1 | 0.512 598 | 12 | 0.512 515 | 0.79 | |
| 0075-4* | 3.703 2 | 0.709 796 | 13 | 0.703 112 | 0.09 | 0.512 549 | 13 | 0.512 474 | -0.01 | |
| 0076-2* | 0.814 0 | 0.706 878 | 14 | 0.705 409 | 0.09 | 0.512 541 | 10 | 0.512 466 | -0.16 | |
| 0076-9* | 1.209 3 | 0.707 674 | 11 | 0.705 491 | 0.11 | 0.512 553 | 14 | 0.512 462 | -0.25 | |
| 05TH05* | 基 性 岩 样 品 | 0.238 4 | 0.705 947 | 14 | 0.705 517 | 0.118 4 | 0.512 503 | 12 | 0.512 405 | -1.36 |
| 05TH10* | 0.088 8 | 0.707 665 | 13 | 0.707 505 | 0.115 | 0.512 285 | 15 | 0.512 189 | -5.56 | |
| 05TH11* | 0.122 2 | 0.707 794 | 10 | 0.707 573 | 0.067 8 | 0.512 527 | 13 | 0.512 471 | -0.08 | |
| 05TH12* | 0.345 8 | 0.706 747 | 12 | 0.706 123 | 0.107 4 | 0.512 567 | 18 | 0.512 478 | 0.06 | |
| 05TH14* | 0.262 9 | 0.706 191 | 10 | 0.705 716 | 0.108 1 | 0.512 494 | 15 | 0.512 404 | -1.37 | |
| 05TH16* | 0.217 5 | 0.706 368 | 10 | 0.705 975 | 0.109 9 | 0.512 52 | 12 | 0.512 429 | -0.90 | |
| 05TH17* | 0.166 0 | 0.706 297 | 14 | 0.705 997 | 0.110 7 | 0.5124 93 | 12 | 0.512 401 | -1.44 | |
| 05TH19* | 0.100 1 | 0.706 934 | 12 | 0.706 753 | 0.109 1 | 0.5123 82 | 13 | 0.512 291 | -3.58 | |
| 05TH21* | 0.096 9 | 0.707 002 | 12 | 0.706 827 | 0.067 3 | 0.5125 49 | 13 | 0.512 493 | 0.36 | |
| 05TH23* | 0.112 3 | 0.705 952 | 14 | 0.705 749 | 0.124 1 | 0.5125 26 | 14 | 0.512 423 | -1.01 | |
| 05TH25* | 0.066 2 | 0.705 836 | 10 | 0.705 717 | 0.110 2 | 0.5125 37 | 11 | 0.512 445 | -0.57 | |
| 05TH26* | 0.070 9 | 0.705 816 | 14 | 0.705 688 | 0.178 8 | 0.5124 08 | 13 | 0.512 259 | -4.20 | |
| 05TH27* | 0.160 1 | 0.708 140 | 12 | 0.707 851 | 0.190 2 | 0.5122 83 | 11 | 0.512 125 | -6.82 |
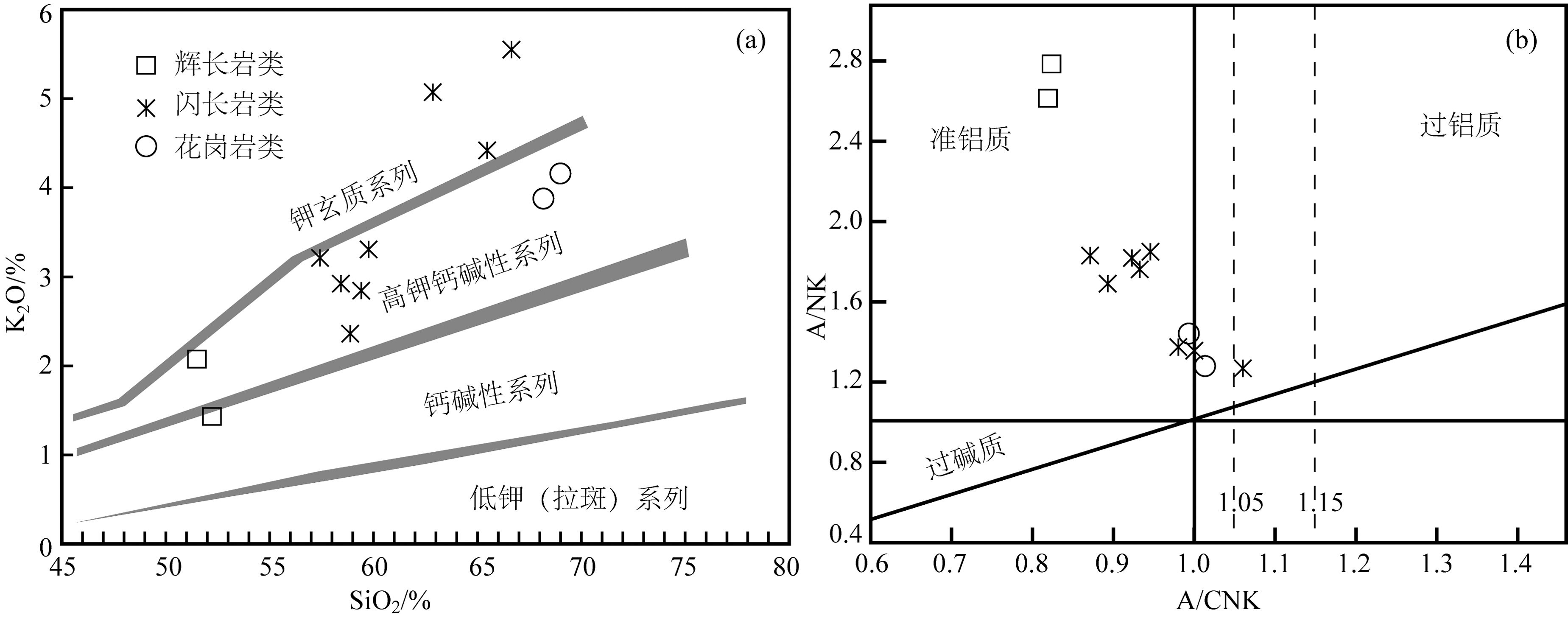
图4 研究区侵入岩SiO2-K2O图解((a)底图据[23])、A/CNK-A/NK图解((b)底图据[24])
Fig.4 SiO2 vs.K2O diagram (a) and A/CNK vs. A/NK diagram (b) of the intrusive rocks from the study area

图5 研究区侵入岩稀土元素配分曲线(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化数值据文献[25])
Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spidergram (b) of intrusive rocks from the study area

图9 Sm-Sm/Yb图解(a)和La/Sm-Sm/Yb图解(b) DMM.亏损地幔[46];PM.原始地幔[25];尖晶石二辉橄榄岩(Ol53+Opx27+Cpx17+Sp11)熔融曲线和石榴子石二辉橄榄岩相(Ol60+Opx20+Cpx10+Gt10)熔融曲线引自文献[43]
Fig.9 Diagrams of Sm vs.Sm/Yb (a) and La/Sm vs. Sm/Yb (b)
| [1] | SOROKIN A A, KUDRYASHOW N M, LI J Y, et al. Early Paleozoic granitoids in the Eastern margin of the Argun Terrane, Amur Area: First geochemical and geochronologic data[J]. Petrology, 2004, 12(4): 367-376. |
| [2] | 武广, 孙丰月, 赵财胜, 等. 额尔古纳地块北缘早古生代后碰撞花岗岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(20): 2279-2288. |
| [3] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 大兴安岭北部塔河花岗岩体的时代及对额尔古纳地块构造归属的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(12): 1239-1247. |
| [4] | 孙德有. 张广才岭中生代花岗岩成因及其地球动力学意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2001:1-112. |
| [5] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J]. 岩石学报, 1999, 15(2): 22-30. |
| [6] |
TANG J, XU W L, WANG F, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, and deformation history of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous intrusive rocks in the Erguna Massif, NE China: Constraints on the Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 658: 91-110.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG T, GUO L, ZHANG L, et al. Timing and evolution of Jurassic-Cretaceous granitoid magmatisms in the Mongol-Okhotsk belt and adjacent areas, NE Asia: Implications for transition from contractional crustal thickening to extensional thinning and geodynamic settings[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 365-392.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 司秋亮, 崔天日, 唐振, 等. 大兴安岭中段柴河地区玛尼吐组火山岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(2): 389-403. |
| [9] | 宋立忠, 赵泽辉, 焦贵浩, 等. 松辽盆地早白垩世火山岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(4): 1182-1194. |
| [10] | 孙德有, 苟军, 任云生, 等. 满洲里南部玛尼吐组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(10): 3083-3094. |
| [11] | 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭东北部侏罗纪花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 461-480. |
| [12] | 张吉衡. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩年代学及地球化学研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2009:1-116. |
| [13] | 曾涛, 王涛, 童英, 等. 俄罗斯远东地区晚中生代花岗岩类的时空分布及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(5): 732-744. |
| [14] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the phanerozoic granitoids in Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 1-30.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MENG Q R. What drove Late Mesozoic extension of the Northern China-Mongolia tract?[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 369(3/4): 155-174.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICP MS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(S1): 600-601. |
| [17] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [18] | LIU Y. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(51): 392-399. |
| [19] | LUDWIG K R. Isoplot/Ex Version 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003:1-60. |
| [20] | 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10): 2595-2604. |
| [21] |
LI X H, LIU D Y, SUN M, et al. Precise Sm-Nd and U-Pb isotopic dating of the super-giant Shizhuyuan polymetallic deposit and its host granite Southeast China[J]. Geological Magazine, 2004, 141: 225-231.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HOSKIN P W O, BLACK L P. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18(4): 423-439.
DOI URL |
| [23] | LE MAITRE R W. Igneous rocks: A classification and glossary of term. Recommendations of the international union of geological sciences, subcommission on the systematics of igneous rocks[J]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002:33-39. |
| [24] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 张彦龙, 葛文春, 柳小明, 等. 大兴安岭新林镇岩体的同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(2): 177-186. |
| [27] | 张玉涛, 张连昌, 英基丰, 等. 大兴安岭北段塔河地区早白垩世火山岩地球化学及源区特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(11): 2811-2822. |
| [28] | KETO L S, JACOBSEN S B. Nd and Sr isotopic variations of Early Paleozoic Oceans[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1987, 84(1): 27-41. |
| [29] |
JAHN B M, WU F Y, CAPDEVILA R, et al. Highly evolved juvenile granites with tetrad REE patterns: The Woduhe and Baerzhe granites from the Great Xing’an Mountains in NE China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 59(4): 171-198.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (i): Geochronology and Petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003, 66(3): 241-273.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 李竞妍, 郭锋, 李超文, 等. 东北地区晚古生代-中生代I型和A型花岗岩Nd同位素变化趋势及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1995-2008. |
| [32] |
CLEMENS J D. S-type granitic magmas-petrogenetic issues, models and evidence[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 61(1/2): 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
DEPAOLO D J, DALEY E E. Neodymium isotopes in basalts of the southwest basin and range and lithospheric thinning during continental extension[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 169(1/2): 157-185.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
HOOPER P R, BAILEY D G, HOLDER M C. Tertiary calc-alkaline magmatism associated with lithospheric extension in the Pacific Northwest[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1995, 100(B6): 10303-10319.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
ARCULUS R J. Aspects of magma genesis in arcs[J]. Lithos, 1994, 33(1/3): 189-208.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
DAVIES J H, STEVENSON D J. Physical model of source region of subduction zone volcanics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1992, 97(B2): 2037-2070.
DOI URL |
| [37] | HUNTER A G, BLAKE S. Petrogenetic evolution of a transitional tholeiitic-calc-alkaline series: Towada volcano, Japan[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(6): 1579-1605. |
| [38] |
GUO Z, HERTOGEN J, LIU J, et al. Potassic magmatism in western Sichuan and Yunnan Provinces, SE Tibet, China: Petrological and geochemical constraints on petrogenesis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 46(1): 33-78.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
HAWKESWORTH C J, TURNER S P, MCDERMOTT F, et al. U-Th isotopes in arc magmas: Implications for element transfer from the subducted crust[J]. Science, 1997, 276: 551-555.
PMID |
| [40] |
CASTILLO P R, NEEHALL C G. Geochemical constraints on possible subduction components in lavas of mayon and Taal Volcanoes, Southern Luzon, Philippines[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 45(6): 1089-1108.
DOI URL |
| [41] | KELEMEN P B, HANGHØJ K, GREENE A R. One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[J]. Treatise onGeochemistry, 2003, 138: 1-70. |
| [42] |
PEATE D W, KOKFELT T F, HAWKESWORTH C J, et al. U-series isotope data on Lau Basin Glasses: the role of subduction-related fluids during melt generation in back-arc basins[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(8): 1449-1470.
DOI URL |
| [43] | ALDANMAZ E, PEARCE J A, THIRLWALL M F, et al. Petrogenetic evolution of late Cenozoic, post-collision volcanism in Western Anatolia, Turkey[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 2000, 102(1/2): 67-95. |
| [44] |
JOHNSON K T M. Experimental cpx/ and garnet/melt partitioning of REE and other trace elements at high pressures: petrogenetic implications[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1994, 58A(1): 454-455.
DOI URL |
| [45] | ANNEN C, BLUNDY J D, SPARKS R J S. The sources of granitic melt in deep hot zones[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh, 2006, 97(4): 297-309. |
| [46] |
MCKENZIE D, O’NIONS R K. Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1991, 32(5): 1021-1091.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
CHARLES N, AUGIER R, GUMIAUX C, et al. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula (China, East Asia)[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24(1): 412-428.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DAOUDENE Y, RUFFET G, COCHERIE A, et al. Timing of exhumation of the Ereendavaa metamorphic core complex (NorthEastern Mongolia)U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar constraints[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62: 98-116.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
DONSKAYA T V, GLADKOCHUB D P, MAZUKABZOV A M, et al. Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic subduction-related magmatism at the southern margin of the Siberian Continent and the 150 million-year history of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62: 79-97.
DOI URL |
| [50] | WU F Y, LIN J Q, WILDE S A, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in Eastern China[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1/2): 103-119. |
| [51] | 张兴洲. 中国兴蒙—吉黑地区岩石圈三维结构及演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011:103-105. |
| [52] | KIRILLOVA G L. The Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary basins at the continental margin of southeastern Russia: Geodynamic evolution and coal and petroleum potential[J]. Geotectonics, 2005, 39(5): 389-407. |
| [53] | XU W L, WANG F, PEI F P, et al. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional ore-forming background in NE China: Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock associations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(2): 339-353. |
| [54] | 张旗. 中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1): 113-128. |
| [55] | WANG W, TANG J, XU W L, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Jurassic volcanic rocks in the Erguna Massif, Northeast China: Petrogenesis and implications for the tectonic evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk suture belt[J]. Lithos, 2015, 218: 73-86. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [3] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| [4] | 李柱, 张德会, 杨帆, 刘向冲. 等距对数比变换及混合分布在区域化探数据分析中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 662-673. |
| [5] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [6] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [7] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [8] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [9] | 李柱, 张德会, 张荣臻, 沈存利, 焦世豪, 李林, 朱鹏龙. 内蒙古那仁乌拉早白垩世高分异花岗岩年代学及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 848-861. |
| [10] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [11] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [12] | 欧伟程, 李承东, 张永清, 赵利刚, 许腾, 许雅雯, 孙烜烨. 北秦岭二郎坪群抱树坪组碎屑锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及物源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 347-361. |
| [13] | 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 郑艳荣, 李晓东, 武海文, 张龙. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1633-1650. |
| [14] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [15] | 刘爱荣, 徐永婧, 刘成林, 庞尔成. 大同盆地地质特征及构造演化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1296-1310. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||