



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (03): 662-673.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.009
收稿日期:2022-10-28
修回日期:2023-03-09
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-07-20
通讯作者:
张德会,男,教授,博士生导师,1955年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事成矿作用地球化学研究。Email:1978011191@cugb.edu.cn。
作者简介:李 柱,男,博士,高级工程师,1987年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿床地球化学研究。Email:867113514@qq.com。
基金资助:
LI Zhu1,2( ), ZHANG Dehui1(
), ZHANG Dehui1( ), YANG Fan3, LIU Xiangchong4
), YANG Fan3, LIU Xiangchong4
Received:2022-10-28
Revised:2023-03-09
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-07-20
摘要:
区域化探数据是典型的成分数据,等距对数比变换(ILR)可以有效构建化探数据的标准正交基,消除其闭合效应,解释数据的组成性质,但是解释ILR转换的变量仍然很困难。为使ILR转换更容易理解,本研究利用地质知识和数据驱动的方法构建可解释的ILR转换变量,并将该方法应用于从大兴安岭中南段水系沉积物地球化学数据中提取地质信息。基于地质知识和层次聚类分析,构建了Sn、W、Cr和Ni元素浓度之间的顺序二元划分(SBP),并经ILR转换后表示为变量b1、b2和b3。此外,还采用了由最小信息长度准则(MML)改进的期望最大化(EM)算法,研究上述变量的混合分布。ILR转换的变量具有镁铁质岩浆作用、Sn-W热液成矿和后期地质作用的信息,服从双正态分布或三正态分布。其中b1、b2和b3的高平均值分组对应于锡钨成矿的异常,综合圈定4个锡钨找矿潜力较高的预测区。本研究表明,ILR转换和MML-EM算法在从区域化探数据中提取地质信息和圈定异常方面是一种很有前途的方法。
中图分类号:
李柱, 张德会, 杨帆, 刘向冲. 等距对数比变换及混合分布在区域化探数据分析中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 662-673.
LI Zhu, ZHANG Dehui, YANG Fan, LIU Xiangchong. Regional Geochemical Data Analysis Using Isometric Log-ratio Transformation and Mixture Distribution[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 662-673.

图1 大兴安岭中南段大地构造位置(a)及区域地质简图(b)(底图据文献[17])
Fig.1 Tectonic map (a) and generalized regional geologic map (b) of the central and southern Da Hinggan Mountains (after reference [17])

图2 大兴安岭中南段代表性矿床的矿体、矿石及主要围岩岩性特征 (a)元古宙斜长片麻岩;(b)古生界林西组变质砂岩;(c)中生界白音高老组晶屑岩屑凝灰岩;(d)二叠纪辉长岩;(e)石炭纪二长花岗岩;(f)早白垩世黑云母二长花岗岩和细晶岩脉;(g)早白垩世石英斑岩;(h)拜仁达坝Zn-Pb-Cu-Ag多金属矿体;(i)维拉斯托角砾岩型锂多金属矿体;(j)维拉斯托石英脉型锡多金属矿体;(k)大井Cu-Sn矿石手标本;(l)白音查干斑岩型锡多金属矿石手标本;Apy.毒砂;Clp.黄铜矿;Cst.锡石;Fl.萤石;Gn.方铅矿;Lpd.锂云母;Po.磁黄铁矿;Py.黄铁矿;Qtz.石英;Sp.方铅矿
Fig.2 Photos showing the major wall rock and features of ore body and ore of representative deposits in the central and southern Da Hinggan Mountains
| Ag | As | Au | Bi | Cr | Cu | F | Li | Mo | Nb | Ni | Pb | Sn | W | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 1.12 | 0.79 | 0.50 | 0.46 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 1.26 | 0.30 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.40 | |
| As | -1.62 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 1.09 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 1.10 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 0.54 | |
| Au | -5.05 | -3.44 | 1.01 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.63 | 0.35 | 1.04 | 0.48 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.54 | |
| Bi | -5.52 | -3.91 | -0.47 | 1.57 | 1.13 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 1.74 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.82 | |
| Cr | -1.41 | 0.21 | 3.64 | 4.11 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.09 | 0.84 | 0.29 | 1.03 | 1.41 | 1.29 | 0.72 | |
| Cu | -1.83 | -0.21 | 3.23 | 3.70 | -0.42 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.41 | 0.77 | 1.10 | 0.99 | 0.42 | |
| F | 1.51 | 3.13 | 6.56 | 7.03 | 2.92 | 3.34 | 0.26 | 0.46 | 0.27 | 0.78 | 0.41 | 0.74 | 0.48 | 0.31 | |
| Li | -1.12 | 0.49 | 3.93 | 4.40 | 0.29 | 0.70 | -2.63 | 0.49 | 0.26 | 0.91 | 0.37 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.32 | |
| Mo | -4.50 | -2.89 | 0.55 | 1.02 | -3.10 | -2.68 | -6.02 | -3.38 | 0.36 | 1.11 | 0.48 | 0.76 | 0.51 | 0.46 | |
| Nb | -1.98 | -0.37 | 3.07 | 3.54 | -0.57 | -0.16 | -3.49 | -0.86 | 2.52 | 0.92 | 0.30 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.30 | |
| Ni | -2.09 | -0.48 | 2.96 | 3.43 | -0.68 | -0.27 | -3.60 | -0.97 | 2.41 | -0.11 | 1.17 | 1.56 | 1.41 | 0.72 | |
| Pb | -1.40 | 0.21 | 3.65 | 4.12 | 0.01 | 0.42 | -2.92 | -0.28 | 3.10 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.30 | |
| Sn | -3.26 | -1.65 | 1.79 | 2.26 | -1.85 | -1.44 | -4.77 | -2.14 | 1.24 | -1.28 | -1.17 | -1.86 | 0.23 | 0.60 | |
| W | -3.96 | -2.34 | 1.10 | 1.56 | -2.55 | -2.13 | -5.47 | -2.84 | 0.55 | -1.98 | -1.87 | -2.55 | -0.70 | 0.54 | |
| Zn | -0.12 | 1.49 | 4.93 | 5.40 | 1.29 | 1.70 | -1.63 | 1.00 | 4.38 | 1.86 | 1.97 | 1.28 | 3.14 | 3.84 |
表1 变异矩阵(右上部)及ln(xi/xj)平均值(左下部)
Table 1 Variation matrix (upper right) and the mean of ln(xi/xj) (lower left)
| Ag | As | Au | Bi | Cr | Cu | F | Li | Mo | Nb | Ni | Pb | Sn | W | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 1.12 | 0.79 | 0.50 | 0.46 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 1.26 | 0.30 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.40 | |
| As | -1.62 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 1.09 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 1.10 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 0.54 | |
| Au | -5.05 | -3.44 | 1.01 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.63 | 0.35 | 1.04 | 0.48 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.54 | |
| Bi | -5.52 | -3.91 | -0.47 | 1.57 | 1.13 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 1.74 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.82 | |
| Cr | -1.41 | 0.21 | 3.64 | 4.11 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.09 | 0.84 | 0.29 | 1.03 | 1.41 | 1.29 | 0.72 | |
| Cu | -1.83 | -0.21 | 3.23 | 3.70 | -0.42 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.41 | 0.77 | 1.10 | 0.99 | 0.42 | |
| F | 1.51 | 3.13 | 6.56 | 7.03 | 2.92 | 3.34 | 0.26 | 0.46 | 0.27 | 0.78 | 0.41 | 0.74 | 0.48 | 0.31 | |
| Li | -1.12 | 0.49 | 3.93 | 4.40 | 0.29 | 0.70 | -2.63 | 0.49 | 0.26 | 0.91 | 0.37 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.32 | |
| Mo | -4.50 | -2.89 | 0.55 | 1.02 | -3.10 | -2.68 | -6.02 | -3.38 | 0.36 | 1.11 | 0.48 | 0.76 | 0.51 | 0.46 | |
| Nb | -1.98 | -0.37 | 3.07 | 3.54 | -0.57 | -0.16 | -3.49 | -0.86 | 2.52 | 0.92 | 0.30 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.30 | |
| Ni | -2.09 | -0.48 | 2.96 | 3.43 | -0.68 | -0.27 | -3.60 | -0.97 | 2.41 | -0.11 | 1.17 | 1.56 | 1.41 | 0.72 | |
| Pb | -1.40 | 0.21 | 3.65 | 4.12 | 0.01 | 0.42 | -2.92 | -0.28 | 3.10 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.30 | |
| Sn | -3.26 | -1.65 | 1.79 | 2.26 | -1.85 | -1.44 | -4.77 | -2.14 | 1.24 | -1.28 | -1.17 | -1.86 | 0.23 | 0.60 | |
| W | -3.96 | -2.34 | 1.10 | 1.56 | -2.55 | -2.13 | -5.47 | -2.84 | 0.55 | -1.98 | -1.87 | -2.55 | -0.70 | 0.54 | |
| Zn | -0.12 | 1.49 | 4.93 | 5.40 | 1.29 | 1.70 | -1.63 | 1.00 | 4.38 | 1.86 | 1.97 | 1.28 | 3.14 | 3.84 |
| Sn | Cr | W | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | + | + | - | - |
| b2 | + | - | ||
| b3 | + | - |
表2 大兴安岭中南段4种元素顺序二元划分
Table 2 Sequential binary partitions of the four elements in the central and southern Da HingganMountains
| Sn | Cr | W | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | + | + | - | - |
| b2 | + | - | ||
| b3 | + | - |
| 变量 | 子分布 | 权重 | 均值 | 方差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.81 | 0.57 |
| 2 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.12 | |
| b2 | 1 | 0.47 | -1.24 | 0.20 |
| 2 | 0.25 | -2.28 | 0.37 | |
| 3 | 0.28 | -0.60 | 0.52 | |
| b3 | 1 | 0.11 | -0.17 | 0.30 |
| 2 | 0.13 | -2.63 | 0.85 | |
| 3 | 0.76 | -1.26 | 0.25 |
表3 大兴安岭中南段变量b1、b2和b3拟合的混合分布结果
Table 3 Results of fitting the mixture distributions of b1, b2 and b3 variables in the central and southern Da Hinggan Mountains
| 变量 | 子分布 | 权重 | 均值 | 方差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.81 | 0.57 |
| 2 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.12 | |
| b2 | 1 | 0.47 | -1.24 | 0.20 |
| 2 | 0.25 | -2.28 | 0.37 | |
| 3 | 0.28 | -0.60 | 0.52 | |
| b3 | 1 | 0.11 | -0.17 | 0.30 |
| 2 | 0.13 | -2.63 | 0.85 | |
| 3 | 0.76 | -1.26 | 0.25 |

图7 大兴安岭中南段变量b1三个分组的空间分布
Fig.7 Map showing the spatial distribution of the three subpopulations of b1 variable in the central and southern Da Hinggan Mountains
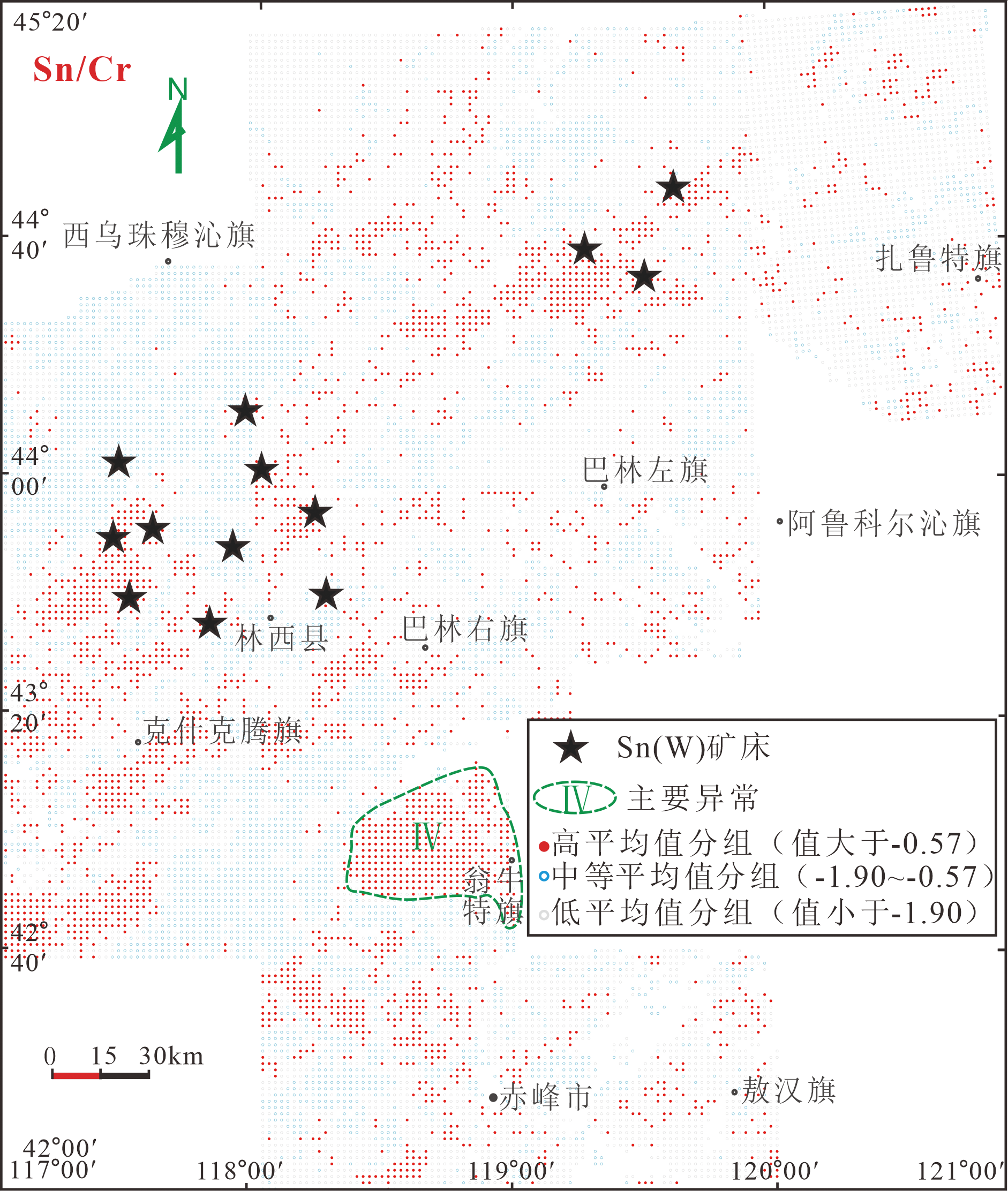
图9 大兴安岭中南段变量b2三个分组的空间分布
Fig.9 Map showing the spatial distribution of the three subpopulations of b2 variable in the central and southern Da Hinggan Mountains

图11 大兴安岭中南段变量b3三个分组的空间分布
Fig.11 Map showing the spatial distribution of the three subpopulations of b3 variable in the central and southern Da Hinggan Mountains
| [1] |
BUCCIANTI A, ZUO R G. Weathering reactions and isometric log-ratio coordinates: Do they speak to each other?[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2016, 75: 189-199.
DOI URL |
| [2] | PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, BUCCIANTI A. Compositional Data Analysis: Theory and Applications[M]. Chicester: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. |
| [3] |
PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, EGOZCUE J J. Compositional data and their analysis: An introduction[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2006, 264(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 刘向冲, 王文磊, 裴英茹. 西藏多龙矿集区水系沉积物地球化学数据定量分析与解释[J]. 地质力学学报, 2017, 23(5): 695-706. |
| [5] |
LIU X C, WANG W L, PEI Y R, et al. A knowledge-driven way to interpret the isometric log-ratio transformation and mixture distributions of geochemical data[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 210: 106417.
DOI URL |
| [6] | PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, EGOZCUE J J, TOLOSANA-DELGADO R. Modelling and Analysis of Compositional Data[M]. Chicester: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. |
| [7] |
FILZMOSER P, HRON K, TEMPL M. Discriminant analysis for compositional data and robust parameter estimation[J]. Computational Statistics, 2012, 27(4): 585-604.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FIŠEROVÁ E, HRON K. On the interpretation of orthonormal coordinates for compositional data[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2011, 43(4): 455-468.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ALLÈGREC J, LEWIN E. Scaling laws and geochemical distributions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 132(1/2/3/4): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 刘向冲, 侯翠霞, 申维, 等. MML-EM方法及其在化探数据混合分布中的应用[J]. 地球科学, 2011, 36(2): 355-359. |
| [11] |
SINCLAIR A J. A fundamental approach to threshold estimation in exploration geochemistry: Probability plots revisited[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1991, 41(1/2): 1-22.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 李柱, 张德会, 沈存利, 等. 内蒙古巴彦塔拉—明安图地区地球化学数据分形和混合筛分定量分析及稀有金属找矿预测[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(6):54-63. |
| [13] |
CARRANZA E J M. Geochemical mineral exploration: Should we use enrichment factors or log-ratios?[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2017, 26(4): 411-428.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
GRUNSKY E C, SMEE B W. The differentiation of soil types and mineralization from multi-element geochemistry using multivariate methods and digital topography[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 67(1/2/3): 287-299.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 陈良, 张达, 狄永军, 等. 大兴安岭中南段区域成矿规律初步研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2009, 24(4): 267-271. |
| [16] | 刘建明, 张锐, 张庆洲. 大兴安岭地区的区域成矿特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 269-277. |
| [17] | 杨帆. 大兴安岭中南段铅锌多金属矿地球化学建模及定量预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. |
| [18] | 赵一鸣, 张德全. 大兴安岭及邻区铜多金属矿床成矿规律及远景评价[M]. 北京: 地震出版杜, 1997. |
| [19] | 欧阳荷根. 大兴安岭南段拜仁达坝—维拉斯托银多金属矿床成矿作用及动力学背景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [20] | 翟德高, 刘家军, 杨永强, 等. 内蒙古黄岗梁铁锡矿床成岩、成矿时代与构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4): 513-523. |
| [21] | 翟德高, 刘家军, 李俊明, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托斑岩型锡矿床成岩、成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2016, 35(5): 1011-1022. |
| [22] | 周振华, 吕林素, 冯佳睿, 等. 内蒙古黄岗夕卡岩型锡铁矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(3): 667-679. |
| [23] | 廖震, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等. 内蒙古大井锡多金属矿床岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(7): 2292-2306. |
| [24] |
刘瑞麟, 武广, 李铁刚, 等. 大兴安岭南段维拉斯托锡多金属矿床LA-ICP-MS锡石和锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(5): 183-201.
DOI |
| [25] | 张学斌, 周长红, 贾晓青, 等. 内蒙古毛登地区碎斑熔岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(7): 974-983. |
| [26] | AITCHISON J. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data[M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1986. |
| [27] | 耿国帅, 张德会, 杨帆, 等. 东昆仑东段水系沉积物测量数据处理中因子分析法的应用研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(4): 105-117. |
| [28] |
EGOZCUE J J, PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, MATEU-FIGUERAS G, et al. Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis[J]. Mathematical Geology, 2003, 35(3): 279-300.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
EGOZCUE J J, PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V. Groups of parts and their balances in compositional data analysis[J]. Mathematical Geology, 2005, 37(7): 795-828.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MARTÍN-FERNÁNDEZ J A, PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, EGOZCUE J J, et al. Advances in principal balances for compositional data[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2018, 50(3): 273-298.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
THIOMBANE M, ZUZOLO D, CICCHELLA D, et al. Soil geochemical follow-up in the Cilento World Heritage Park (Campania, Italy) through exploratory compositional data analysis and C-A fractal model[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 189: 85-99.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
MURTAGH F, LEGENDRE P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement ward’s criterion?[J]. Journal of Classification, 2014, 31(3): 274-295.
DOI URL |
| [33] | WHITE W M. Geochemistry[M]. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013. |
| [34] |
FIGUEIREDO M A T, JAIN A K. Unsupervised learning of finite mixture models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(3): 381-396.
DOI URL |
| [35] | REINERS P W, CARLSON R W, RENNE P R, et al. Geochronology and Thermochronology[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2017. |
| [36] |
SCHMITZ M D, KUIPER K F. High-precision geochronology[J]. Elements, 2013, 9(1): 25-30.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [2] | 赵保具, 张艳飞, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 大兴安岭中段有色金属矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396. |
| [3] | 杨元江, 李成禄, 邓昌州, 李文龙, 张立, 赵忠海, 赵寒冬. 大兴安岭大洋山钼矿成矿岩体地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及构造背景[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1092-1102. |
| [4] | 王迪, 赵国春, 苏尚国, 李宏星. 大兴安岭南段晚中生代侵入岩时空分布及主脊与东坡岩体特征对比[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 466-482. |
| [5] | 周亚龙, 杨志斌, 张富贵, 张舜尧, 孙忠军, 王惠艳. 祁连山天然气水合物地球化学勘查方法稳定性和异常重现性分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1314-1324. |
| [6] | 徐立明, 王大可, 刘玉, 郑吉林, 张文强, 梁中恺. 大兴安岭北段塔河南部早白垩世侵入岩年代学和地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1212-1226. |
| [7] | 赵胜金, 高利东, 于海洋, 朴丽丽, 柳志辉, 周颖帅, 张猛, 张玉龙, 杨海星, 赵万莉. 大兴安岭北段上侏罗统哈日陶勒盖玄武岩的厘定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 718-726. |
| [8] | 李英雷, 徐国, 刘汇川, 白灵麒, 苏银春, 刘小女. 大兴安岭西缘玛尼吐组火山岩成因及构造指示[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 683-696. |
| [9] | 戴慧敏, 代雅键, 马振东, 杨忠芳, 宫传东, 孙中任. 大兴安岭查巴奇地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 1043-1050. |
| [10] | 张梅, 翟裕生, 沈存利, 刘永慧, 杨帅师, 翟德高, 要梅娟, 王建平, 王守光, 高征西, 张玲. 大兴安岭中南段铜多金属矿床成矿系统[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(5): 819-831. |
| [11] | 曹殿华 王安建 王高尚 李瑞萍 李以科. 勘查地球化学异常多尺度分析方法——以赣东北德兴矿集区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(6): 1028-1033. |
| [12] | 徐毅,张寿庭,王长明,刘晓吉. 大兴安岭南段铜多金属矿构造控矿特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(Suppl): 30-34. |
| [13] | 韩伟民 张滨生 武法东 马庆勋. 大兴安岭东北部兴华渡口群地球物理特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(1): 175-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||