



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (01): 31-45.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.024
出版日期:2025-02-10
发布日期:2025-02-20
通信作者:
田 伟,男,副教授,1976年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事火山学研究。Email:davidtian@pku.edu.cn。作者简介:许 鑫,男,博士研究生,1992年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事火山岩中熔体包裹体研究。Email:xuxin@stu.pku.edu.cn。
基金资助:
XU Xin( ), ZHANG Lifei, TIAN Wei(
), ZHANG Lifei, TIAN Wei( ), ZHU Jintao, HE Yanxin
), ZHU Jintao, HE Yanxin
Published:2025-02-10
Online:2025-02-20
摘要:
熔体包裹体记录了岩浆喷发前的演化、去气过程以及岩浆中挥发分等重要信息,是研究玄武质岩浆系统及其地幔源区强有力的工具,被广泛应用于探索地幔岩浆的起源和演化。然而,关于熔体包裹体均一化加热前后的玻璃成分差异目前研究较少。本文选择海南岛蓬莱地区新生代玄武岩橄榄石斑晶中熔体包裹体为研究对象,采用电子探针对熔体包裹体玻璃及其寄主矿物进行元素组成分析。结果显示,寄主矿物橄榄石的Fo值为70~85,CaO含量大于0.1%,为典型的橄榄石斑晶。室温下,熔体包裹体由熔体(玻璃)、气泡和子矿物(辉石、斜长石、钛铁矿)组成。熔体包裹体玻璃成分为英安质熔体。通过高温炉对含熔体包裹体的橄榄石进行均一化加热后,包裹体中未见子矿物,包裹体玻璃成分为玄武质、玄武安山质熔体,少数为安山质熔体,与海南岛蓬莱地区新生代玄武岩全岩成分相近。本文认为海南岛蓬莱地区新生代玄武岩橄榄石斑晶中存在富硅熔体包裹体的原因是包裹体被捕获后冷却速率缓慢导致熔体内部发生分离结晶,进而残余熔体不断向富硅方向演化而形成。因此,对熔体包裹体进行研究时首先观察熔体包裹体内部结构特征,必要时进行均一化加热实验。
中图分类号:
许鑫, 张立飞, 田伟, 朱金涛, 何衍鑫. 海南岛新生代玄武岩中富硅熔体包裹体特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 31-45.
XU Xin, ZHANG Lifei, TIAN Wei, ZHU Jintao, HE Yanxin. Characteristics of Silicon-rich Melt Inclusions in the Cenozoic Basalts from Hainan Island and Their Genesis[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(01): 31-45.

图1 海南岛周边地质简图(a)(底图据文献[15]修改)和琼北新生代火山岩分布图(b)(底图据文献[23]修改)
Fig.1 Small sketch map showing the tectonic situation of the Hainan Island (a)(base map modified from reference [15]) and distribution and sample locations of late Cenozoic volcanic rocks on Hainan Island (b)(base map modified from reference [23])

图2 野外样品宏观外貌及熔体和流体包裹体岩相学特征 (a)玄武岩柱状节理;(b)(c)新鲜无蚀变玄武岩;(d)(e)未均一化加热的橄榄石熔体包裹体在光学显微镜下的特征,熔体+气泡+子矿物(透射光);(f)(g)未均一化加热的熔体包裹体在背散射图像下的形态特征;(h)(i)均一化加热的熔体包裹体在背散射图像下的形态特征;(j)(k)橄榄石中的流体包裹体(透射光);Ol.橄榄石;MI.熔体包裹体;FI.流体包裹体
Fig.2 Field photographs of Cenozoic basalts and photomicrographs of melt/fluid inclusions
| 样品号 | SiO2 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | NiO | Al2O3 | P2O5 | TiO2 | Cr2O3 | 总量 | Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL28-5a | 36.54 | 27.33 | 0.33 | 35.89 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 0.02 | - | - | - | 100.49 | 70 |
| PL28-8a | 37.17 | 25.89 | 0.17 | 37.24 | 0.21 | 0.20 | - | 0.03 | 0.12 | - | 101.03 | 72 |
| PL28-9 | 36.67 | 27.76 | 0.20 | 35.88 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100.90 | 70 |
| PL28-13 | 37.35 | 22.29 | 0.18 | 39.55 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.03 | - | - | - | 99.84 | 76 |
| PL28-13a | 37.66 | 20.96 | 0.26 | 40.54 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.01 | - | 0.06 | - | 99.89 | 78 |
| PL28-27 | 38.18 | 19.81 | 0.21 | 41.15 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | 0.01 | 99.70 | 79 |
| PL28-35 | 37.44 | 21.27 | 0.23 | 40.19 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.01 | 99.55 | 77 |
| PLTW-7 | 37.36 | 25.02 | 0.23 | 37.11 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.01 | - | - | 100.14 | 73 |
| PLTW-14 | 37.55 | 24.07 | 0.29 | 38.22 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.03 | 100.53 | 74 |
| PLTW-23 | 36.62 | 25.21 | 0.32 | 37.43 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 99.97 | 73 |
| PL13-1 | 37.15 | 25.66 | 0.24 | 36.87 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.03 | - | - | 0.05 | 100.37 | 72 |
| PL13-1a | 37.01 | 25.58 | 0.21 | 36.79 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 100.20 | 72 |
| PL13-25 | 37.04 | 25.87 | 0.23 | 36.58 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 | - | 100.26 | 72 |
| PL13-12 | 36.77 | 26.39 | 0.18 | 36.53 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | 0.01 | 100.34 | 71 |
| PL13-12a | 36.67 | 26.40 | 0.18 | 36.54 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.02 | - | - | 100.24 | 71 |
| PL13-36 | 37.28 | 24.13 | 0.23 | 38.04 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.07 | - | 0.02 | 100.15 | 74 |
| PL13-36a | 37.24 | 24.76 | 0.23 | 37.57 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.04 | - | - | 100.28 | 73 |
| PL39-12 | 37.41 | 23.98 | 0.24 | 38.10 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | - | 100.16 | 74 |
| PL39-21 | 37.56 | 23.53 | 0.26 | 38.04 | 0.15 | 0.17 | - | - | - | 0.02 | 99.75 | 74 |
| PL25-5 | 37.33 | 25.30 | 0.20 | 37.36 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.03 | - | 0.02 | 100.68 | 73 |
| PL25-17 | 36.93 | 26.46 | 0.33 | 36.06 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.01 | - | 0.02 | 0.02 | 100.26 | 71 |
| PL25-28 | 37.22 | 24.32 | 0.25 | 37.82 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 | 99.99 | 74 |
| PL35-1 | 37.23 | 21.92 | 0.22 | 39.32 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | - | 99.06 | 76 |
| PL35-8 | 37.17 | 25.43 | 0.28 | 37.23 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 | 100.58 | 72 |
| PL35-11 | 37.89 | 21.92 | 0.20 | 39.67 | 0.12 | 0.18 | - | 0.01 | - | - | 99.99 | 76 |
| PL35-12 | 37.44 | 25.06 | 0.26 | 36.89 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 100.19 | 72 |
| PL35-28 | 37.16 | 25.02 | 0.24 | 37.70 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | - | 100.56 | 73 |
| PL26-16 | 37.24 | 24.74 | 0.20 | 37.45 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | 0.03 | 100.03 | 73 |
| PL26-17 | 37.09 | 25.34 | 0.29 | 37.65 | 0.20 | 0.13 | - | - | - | 0.02 | 100.74 | 73 |
| PLTW-2* | 37.51 | 23.01 | 0.30 | 39.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.02 | 100.28 | 75 |
| PLTW-9* | 37.37 | 24.57 | 0.21 | 38.08 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.04 | - | 0.02 | - | 100.72 | 73 |
| PLTW-22* | 37.32 | 24.20 | 0.18 | 38.55 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.02 | - | 0.07 | 0.03 | 100.71 | 74 |
| PLTW-28* | 36.98 | 25.21 | 0.24 | 37.59 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.02 | 100.40 | 73 |
| PLTW-32* | 37.29 | 25.28 | 0.27 | 37.61 | 0.18 | 0.22 | - | - | - | - | 100.84 | 73 |
| PLTW-33* | 37.67 | 24.38 | 0.21 | 38.35 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 101.12 | 74 |
| PL28-9* | 36.67 | 27.07 | 0.26 | 35.50 | 0.20 | 0.17 | - | 0.05 | 0.03 | - | 99.96 | 70 |
| PL28-12* | 38.86 | 15.13 | 0.10 | 44.65 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.03 | - | - | - | 99.11 | 84 |
| PL28-14* | 37.15 | 25.46 | 0.20 | 37.45 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100.65 | 72 |
| PL28-20* | 37.47 | 25.10 | 0.31 | 37.89 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.02 | - | 0.03 | - | 101.24 | 73 |
| PL28-27* | 37.55 | 23.12 | 0.21 | 39.03 | 0.12 | 0.19 | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | 100.29 | 75 |
| PL35-13* | 38.01 | 20.35 | 0.20 | 40.92 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 | 99.95 | 78 |
| PL39-12* | 37.07 | 25.92 | 0.30 | 36.90 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 | - | 100.73 | 72 |
| PL39-29* | 36.94 | 26.58 | 0.37 | 36.08 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | - | 0.02 | 100.47 | 71 |
| PL39-30* | 36.82 | 25.75 | 0.24 | 36.75 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.02 | - | - | - | 100.02 | 72 |
| PL12-4* | 37.45 | 24.35 | 0.19 | 38.17 | 0.14 | 0.21 | - | 0.02 | 0.02 | - | 100.56 | 74 |
| PL12-7* | 37.51 | 24.99 | 0.25 | 37.54 | 0.24 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.11 | 0.02 | 100.85 | 73 |
| PL12-9* | 37.32 | 24.96 | 0.24 | 37.57 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 100.71 | 73 |
| PL12-12* | 37.03 | 24.93 | 0.27 | 37.39 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 | 100.12 | 73 |
| PL12-15* | 37.41 | 24.97 | 0.33 | 37.74 | 0.22 | 0.22 | - | 0.01 | 0.07 | - | 101.00 | 73 |
| PL12-25* | 37.07 | 25.18 | 0.33 | 37.89 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.02 | - | 0.01 | 101.00 | 73 |
| PL12-30* | 37.47 | 25.09 | 0.25 | 37.39 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 100.59 | 73 |
| PL26-9* | 38.04 | 21.73 | 0.20 | 40.19 | 0.16 | 0.24 | - | - | - | - | 100.57 | 77 |
| PL26-21* | 39.28 | 14.37 | 0.14 | 45.18 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.02 | - | 0.10 | 0.01 | 99.46 | 85 |
| PL13-2* | 37.10 | 25.69 | 0.29 | 37.14 | 0.23 | 0.17 | - | - | - | 0.01 | 100.66 | 72 |
| PL13-4* | 37.31 | 25.30 | 0.27 | 37.64 | 0.20 | 0.14 | - | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 100.97 | 73 |
| PL13-9* | 37.20 | 25.32 | 0.25 | 37.38 | 0.20 | 0.24 | - | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100.66 | 73 |
| PL13-9a* | 37.21 | 25.21 | 0.23 | 37.79 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.02 | - | 0.03 | - | 100.91 | 73 |
| PL13-15* | 38.34 | 18.64 | 0.17 | 42.77 | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 100.62 | 80 |
| PL13-27* | 37.65 | 20.94 | 0.13 | 40.93 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 100.11 | 78 |
| PL13-29* | 37.97 | 19.62 | 0.17 | 41.50 | 0.11 | 0.25 | - | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 99.74 | 79 |
| PL13-34* | 37.57 | 23.20 | 0.20 | 38.91 | 0.13 | 0.16 | - | - | 0.06 | - | 100.27 | 75 |
表1 海南岛蓬莱地区橄榄石电子探针数据(%)
Table 1 Electron probe microanalysis of olivines in Penglai area, Hainan Island(%)
| 样品号 | SiO2 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | NiO | Al2O3 | P2O5 | TiO2 | Cr2O3 | 总量 | Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL28-5a | 36.54 | 27.33 | 0.33 | 35.89 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 0.02 | - | - | - | 100.49 | 70 |
| PL28-8a | 37.17 | 25.89 | 0.17 | 37.24 | 0.21 | 0.20 | - | 0.03 | 0.12 | - | 101.03 | 72 |
| PL28-9 | 36.67 | 27.76 | 0.20 | 35.88 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100.90 | 70 |
| PL28-13 | 37.35 | 22.29 | 0.18 | 39.55 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.03 | - | - | - | 99.84 | 76 |
| PL28-13a | 37.66 | 20.96 | 0.26 | 40.54 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.01 | - | 0.06 | - | 99.89 | 78 |
| PL28-27 | 38.18 | 19.81 | 0.21 | 41.15 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | 0.01 | 99.70 | 79 |
| PL28-35 | 37.44 | 21.27 | 0.23 | 40.19 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.01 | 99.55 | 77 |
| PLTW-7 | 37.36 | 25.02 | 0.23 | 37.11 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.01 | - | - | 100.14 | 73 |
| PLTW-14 | 37.55 | 24.07 | 0.29 | 38.22 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.03 | 100.53 | 74 |
| PLTW-23 | 36.62 | 25.21 | 0.32 | 37.43 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 99.97 | 73 |
| PL13-1 | 37.15 | 25.66 | 0.24 | 36.87 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.03 | - | - | 0.05 | 100.37 | 72 |
| PL13-1a | 37.01 | 25.58 | 0.21 | 36.79 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 100.20 | 72 |
| PL13-25 | 37.04 | 25.87 | 0.23 | 36.58 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 | - | 100.26 | 72 |
| PL13-12 | 36.77 | 26.39 | 0.18 | 36.53 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | 0.01 | 100.34 | 71 |
| PL13-12a | 36.67 | 26.40 | 0.18 | 36.54 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.02 | - | - | 100.24 | 71 |
| PL13-36 | 37.28 | 24.13 | 0.23 | 38.04 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.07 | - | 0.02 | 100.15 | 74 |
| PL13-36a | 37.24 | 24.76 | 0.23 | 37.57 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.04 | - | - | 100.28 | 73 |
| PL39-12 | 37.41 | 23.98 | 0.24 | 38.10 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | - | 100.16 | 74 |
| PL39-21 | 37.56 | 23.53 | 0.26 | 38.04 | 0.15 | 0.17 | - | - | - | 0.02 | 99.75 | 74 |
| PL25-5 | 37.33 | 25.30 | 0.20 | 37.36 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.03 | - | 0.02 | 100.68 | 73 |
| PL25-17 | 36.93 | 26.46 | 0.33 | 36.06 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.01 | - | 0.02 | 0.02 | 100.26 | 71 |
| PL25-28 | 37.22 | 24.32 | 0.25 | 37.82 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 | 99.99 | 74 |
| PL35-1 | 37.23 | 21.92 | 0.22 | 39.32 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | - | 99.06 | 76 |
| PL35-8 | 37.17 | 25.43 | 0.28 | 37.23 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 | 100.58 | 72 |
| PL35-11 | 37.89 | 21.92 | 0.20 | 39.67 | 0.12 | 0.18 | - | 0.01 | - | - | 99.99 | 76 |
| PL35-12 | 37.44 | 25.06 | 0.26 | 36.89 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 100.19 | 72 |
| PL35-28 | 37.16 | 25.02 | 0.24 | 37.70 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.05 | - | - | 100.56 | 73 |
| PL26-16 | 37.24 | 24.74 | 0.20 | 37.45 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | 0.03 | 100.03 | 73 |
| PL26-17 | 37.09 | 25.34 | 0.29 | 37.65 | 0.20 | 0.13 | - | - | - | 0.02 | 100.74 | 73 |
| PLTW-2* | 37.51 | 23.01 | 0.30 | 39.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.02 | 100.28 | 75 |
| PLTW-9* | 37.37 | 24.57 | 0.21 | 38.08 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.04 | - | 0.02 | - | 100.72 | 73 |
| PLTW-22* | 37.32 | 24.20 | 0.18 | 38.55 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.02 | - | 0.07 | 0.03 | 100.71 | 74 |
| PLTW-28* | 36.98 | 25.21 | 0.24 | 37.59 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.02 | - | - | 0.02 | 100.40 | 73 |
| PLTW-32* | 37.29 | 25.28 | 0.27 | 37.61 | 0.18 | 0.22 | - | - | - | - | 100.84 | 73 |
| PLTW-33* | 37.67 | 24.38 | 0.21 | 38.35 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 101.12 | 74 |
| PL28-9* | 36.67 | 27.07 | 0.26 | 35.50 | 0.20 | 0.17 | - | 0.05 | 0.03 | - | 99.96 | 70 |
| PL28-12* | 38.86 | 15.13 | 0.10 | 44.65 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.03 | - | - | - | 99.11 | 84 |
| PL28-14* | 37.15 | 25.46 | 0.20 | 37.45 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100.65 | 72 |
| PL28-20* | 37.47 | 25.10 | 0.31 | 37.89 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.02 | - | 0.03 | - | 101.24 | 73 |
| PL28-27* | 37.55 | 23.12 | 0.21 | 39.03 | 0.12 | 0.19 | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | - | 100.29 | 75 |
| PL35-13* | 38.01 | 20.35 | 0.20 | 40.92 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 | 99.95 | 78 |
| PL39-12* | 37.07 | 25.92 | 0.30 | 36.90 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 | - | 100.73 | 72 |
| PL39-29* | 36.94 | 26.58 | 0.37 | 36.08 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | - | 0.02 | 100.47 | 71 |
| PL39-30* | 36.82 | 25.75 | 0.24 | 36.75 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.02 | - | - | - | 100.02 | 72 |
| PL12-4* | 37.45 | 24.35 | 0.19 | 38.17 | 0.14 | 0.21 | - | 0.02 | 0.02 | - | 100.56 | 74 |
| PL12-7* | 37.51 | 24.99 | 0.25 | 37.54 | 0.24 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.11 | 0.02 | 100.85 | 73 |
| PL12-9* | 37.32 | 24.96 | 0.24 | 37.57 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 100.71 | 73 |
| PL12-12* | 37.03 | 24.93 | 0.27 | 37.39 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 | 100.12 | 73 |
| PL12-15* | 37.41 | 24.97 | 0.33 | 37.74 | 0.22 | 0.22 | - | 0.01 | 0.07 | - | 101.00 | 73 |
| PL12-25* | 37.07 | 25.18 | 0.33 | 37.89 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.02 | - | 0.01 | 101.00 | 73 |
| PL12-30* | 37.47 | 25.09 | 0.25 | 37.39 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 100.59 | 73 |
| PL26-9* | 38.04 | 21.73 | 0.20 | 40.19 | 0.16 | 0.24 | - | - | - | - | 100.57 | 77 |
| PL26-21* | 39.28 | 14.37 | 0.14 | 45.18 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.02 | - | 0.10 | 0.01 | 99.46 | 85 |
| PL13-2* | 37.10 | 25.69 | 0.29 | 37.14 | 0.23 | 0.17 | - | - | - | 0.01 | 100.66 | 72 |
| PL13-4* | 37.31 | 25.30 | 0.27 | 37.64 | 0.20 | 0.14 | - | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 100.97 | 73 |
| PL13-9* | 37.20 | 25.32 | 0.25 | 37.38 | 0.20 | 0.24 | - | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100.66 | 73 |
| PL13-9a* | 37.21 | 25.21 | 0.23 | 37.79 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.02 | - | 0.03 | - | 100.91 | 73 |
| PL13-15* | 38.34 | 18.64 | 0.17 | 42.77 | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 100.62 | 80 |
| PL13-27* | 37.65 | 20.94 | 0.13 | 40.93 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.01 | - | - | - | 100.11 | 78 |
| PL13-29* | 37.97 | 19.62 | 0.17 | 41.50 | 0.11 | 0.25 | - | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 99.74 | 79 |
| PL13-34* | 37.57 | 23.20 | 0.20 | 38.91 | 0.13 | 0.16 | - | - | 0.06 | - | 100.27 | 75 |

图3 海南岛蓬莱地区新生代玄武岩橄榄石Fo与其代表性主量元素图解(地幔橄榄岩橄榄石数据为未发表数据)
Fig.3 Fo vs. representative major elements for olivines of basalts in Penglai area, Hainan Island (olivines in peridotite data are unpublished)
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | SO3 | F | Cl | 总量 | 寄主橄榄 石Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLTW-2 | 69.87 | 0.49 | 17.89 | 1.18 | - | 0.14 | 2.15 | 2.72 | 3.60 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 98.48 | 75 |
| PLTW-9 | 71.20 | 0.74 | 17.02 | 1.35 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 2.55 | 2.08 | 2.20 | 0.10 | 0.01 | - | 0.08 | 97.53 | 73 |
| PLTW-22 | 70.91 | 0.44 | 16.75 | 1.10 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 2.35 | 1.81 | 2.20 | 0.41 | 0.01 | - | 0.08 | 96.16 | 74 |
| PLTW-22a | 70.99 | 0.44 | 17.29 | 1.08 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 2.80 | 2.01 | 1.99 | 0.13 | - | 0.31 | 0.10 | 97.17 | 74 |
| PLTW-28 | 69.02 | 0.81 | 18.01 | 1.22 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 2.85 | 2.48 | 2.88 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 97.72 | 73 |
| PLTW-32 | 67.88 | 1.55 | 18.70 | 1.15 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 4.27 | 2.49 | 2.42 | 0.26 | - | - | 0.06 | 98.87 | 73 |
| PLTW-33 | 64.73 | 0.95 | 17.70 | 1.83 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 7.06 | 2.60 | 2.16 | 0.07 | 0.17 | - | 0.12 | 97.78 | 74 |
| PL28-9 | 65.78 | 0.91 | 17.07 | 2.29 | - | 0.35 | 5.43 | 3.11 | 2.79 | 0.53 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 98.58 | 70 |
| PL28-12 | 66.68 | 1.39 | 18.39 | 1.41 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 3.08 | 2.74 | 2.99 | 1.24 | - | 0.05 | 0.07 | 98.25 | 84 |
| PL28-14 | 68.02 | 1.04 | 17.03 | 1.92 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 3.65 | 2.36 | 2.98 | 0.39 | 0.03 | - | 0.10 | 97.76 | 72 |
| PL28-20 | 65.02 | 1.74 | 17.10 | 2.60 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 5.94 | 2.55 | 2.46 | 0.72 | 0.10 | - | 0.12 | 98.87 | 73 |
| PL28-27 | 70.74 | 1.18 | 16.23 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 2.39 | 1.07 | 1.53 | 0.51 | - | 0.15 | 0.04 | 95.47 | 75 |
| PL28-27a | 70.31 | 1.07 | 16.57 | 1.59 | - | 0.22 | 3.41 | 1.59 | 1.54 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 97.19 | 75 |
| PL35-13 | 65.06 | 1.16 | 17.87 | 2.00 | - | 0.44 | 5.50 | 2.46 | 2.59 | 1.35 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 98.72 | 78 |
| PL35-13a | 68.02 | 0.60 | 18.26 | 1.55 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 3.62 | 2.24 | 2.34 | 0.54 | - | - | 0.06 | 97.57 | 78 |
| PL39-12 | 64.69 | 0.23 | 19.84 | 1.44 | - | 0.13 | 0.87 | 2.34 | 7.38 | 0.08 | 0.01 | - | 0.09 | 97.08 | 72 |
| PL39-12a | 62.54 | 0.95 | 20.46 | 1.46 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1.21 | 2.74 | 6.25 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 96.29 | 72 |
| PL39-29 | 69.06 | 0.58 | 18.71 | 0.97 | 0.02 | - | 2.98 | 2.37 | 2.22 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 97.14 | 71 |
| PL39-29a | 66.58 | 0.97 | 17.79 | 1.87 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 6.30 | 2.68 | 1.82 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 98.51 | 71 |
| PL12-4 | 70.34 | 0.88 | 18.35 | 1.21 | - | 0.09 | 2.19 | 2.82 | 3.07 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 99.35 | 74 |
| PL12-7 | 61.63 | 0.23 | 16.81 | 1.03 | - | 0.11 | 7.59 | 1.95 | 2.54 | 4.94 | 0.02 | 1.08 | 0.17 | 97.60 | 73 |
| PL12-9 | 68.88 | 0.67 | 18.56 | 1.12 | - | 0.02 | 2.62 | 2.65 | 3.20 | 0.09 | - | - | 0.08 | 97.87 | 73 |
| PL12-12 | 69.25 | 0.81 | 18.51 | 1.22 | - | 0.01 | 3.64 | 1.88 | 1.77 | 0.88 | 0.06 | - | 0.10 | 98.11 | 73 |
| PL12-15 | 69.42 | 0.16 | 18.96 | 1.19 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 1.06 | 2.75 | 2.90 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 97.32 | 73 |
| PL12-25 | 68.27 | 0.46 | 19.23 | 1.38 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 3.37 | 2.07 | 2.62 | 0.50 | - | - | 0.12 | 98.34 | 73 |
| PL12-30 | 67.09 | 0.51 | 20.67 | 1.36 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.98 | 2.73 | 4.55 | 0.31 | - | 0.05 | 0.14 | 98.44 | 73 |
| PL26-9 | 66.93 | 3.51 | 17.18 | 2.16 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 2.25 | 1.76 | 2.62 | 0.83 | - | - | 0.08 | 97.56 | 77 |
| PL26-21 | 68.63 | 1.95 | 18.48 | 1.45 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 1.48 | 1.60 | 2.75 | 1.24 | - | - | 0.16 | 98.07 | 85 |
| PL13-2 | 62.47 | 0.82 | 17.74 | 1.40 | - | 0.17 | 7.53 | 2.42 | 2.65 | 2.35 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 98.15 | 72 |
| PL13-4 | 68.18 | 0.51 | 18.64 | 1.78 | - | 0.24 | 4.61 | 2.68 | 2.73 | 0.17 | - | - | 0.08 | 99.60 | 73 |
| PL13-9 | 62.39 | 0.91 | 16.98 | 1.96 | - | 0.43 | 9.24 | 2.52 | 2.20 | 4.20 | - | 0.83 | 0.11 | 101.39 | 73 |
| PL13-15 | 68.86 | 0.51 | 17.91 | 1.05 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 3.79 | 2.70 | 2.97 | - | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 98.26 | 80 |
| PL13-27 | 68.25 | 1.07 | 19.20 | 0.91 | - | 0.01 | 3.56 | 2.77 | 2.70 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 98.95 | 78 |
| PL13-29 | 70.37 | 0.46 | 18.45 | 0.88 | - | 0.11 | 1.01 | 1.92 | 3.09 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 97.05 | 79 |
| PL13-34 | 69.36 | 0.63 | 18.56 | 1.20 | - | 0.16 | 2.43 | 2.71 | 3.31 | 0.17 | 0.02 | - | 0.08 | 98.60 | 75 |
表2 未均一化加热熔体包裹体电子探针数据(%)
Table 2 Unheated melt inclusions electron microprobe analyses (%)
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | SO3 | F | Cl | 总量 | 寄主橄榄 石Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLTW-2 | 69.87 | 0.49 | 17.89 | 1.18 | - | 0.14 | 2.15 | 2.72 | 3.60 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 98.48 | 75 |
| PLTW-9 | 71.20 | 0.74 | 17.02 | 1.35 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 2.55 | 2.08 | 2.20 | 0.10 | 0.01 | - | 0.08 | 97.53 | 73 |
| PLTW-22 | 70.91 | 0.44 | 16.75 | 1.10 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 2.35 | 1.81 | 2.20 | 0.41 | 0.01 | - | 0.08 | 96.16 | 74 |
| PLTW-22a | 70.99 | 0.44 | 17.29 | 1.08 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 2.80 | 2.01 | 1.99 | 0.13 | - | 0.31 | 0.10 | 97.17 | 74 |
| PLTW-28 | 69.02 | 0.81 | 18.01 | 1.22 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 2.85 | 2.48 | 2.88 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 97.72 | 73 |
| PLTW-32 | 67.88 | 1.55 | 18.70 | 1.15 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 4.27 | 2.49 | 2.42 | 0.26 | - | - | 0.06 | 98.87 | 73 |
| PLTW-33 | 64.73 | 0.95 | 17.70 | 1.83 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 7.06 | 2.60 | 2.16 | 0.07 | 0.17 | - | 0.12 | 97.78 | 74 |
| PL28-9 | 65.78 | 0.91 | 17.07 | 2.29 | - | 0.35 | 5.43 | 3.11 | 2.79 | 0.53 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 98.58 | 70 |
| PL28-12 | 66.68 | 1.39 | 18.39 | 1.41 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 3.08 | 2.74 | 2.99 | 1.24 | - | 0.05 | 0.07 | 98.25 | 84 |
| PL28-14 | 68.02 | 1.04 | 17.03 | 1.92 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 3.65 | 2.36 | 2.98 | 0.39 | 0.03 | - | 0.10 | 97.76 | 72 |
| PL28-20 | 65.02 | 1.74 | 17.10 | 2.60 | 0.11 | 0.44 | 5.94 | 2.55 | 2.46 | 0.72 | 0.10 | - | 0.12 | 98.87 | 73 |
| PL28-27 | 70.74 | 1.18 | 16.23 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 2.39 | 1.07 | 1.53 | 0.51 | - | 0.15 | 0.04 | 95.47 | 75 |
| PL28-27a | 70.31 | 1.07 | 16.57 | 1.59 | - | 0.22 | 3.41 | 1.59 | 1.54 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 97.19 | 75 |
| PL35-13 | 65.06 | 1.16 | 17.87 | 2.00 | - | 0.44 | 5.50 | 2.46 | 2.59 | 1.35 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 98.72 | 78 |
| PL35-13a | 68.02 | 0.60 | 18.26 | 1.55 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 3.62 | 2.24 | 2.34 | 0.54 | - | - | 0.06 | 97.57 | 78 |
| PL39-12 | 64.69 | 0.23 | 19.84 | 1.44 | - | 0.13 | 0.87 | 2.34 | 7.38 | 0.08 | 0.01 | - | 0.09 | 97.08 | 72 |
| PL39-12a | 62.54 | 0.95 | 20.46 | 1.46 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1.21 | 2.74 | 6.25 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 96.29 | 72 |
| PL39-29 | 69.06 | 0.58 | 18.71 | 0.97 | 0.02 | - | 2.98 | 2.37 | 2.22 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 97.14 | 71 |
| PL39-29a | 66.58 | 0.97 | 17.79 | 1.87 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 6.30 | 2.68 | 1.82 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 98.51 | 71 |
| PL12-4 | 70.34 | 0.88 | 18.35 | 1.21 | - | 0.09 | 2.19 | 2.82 | 3.07 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 99.35 | 74 |
| PL12-7 | 61.63 | 0.23 | 16.81 | 1.03 | - | 0.11 | 7.59 | 1.95 | 2.54 | 4.94 | 0.02 | 1.08 | 0.17 | 97.60 | 73 |
| PL12-9 | 68.88 | 0.67 | 18.56 | 1.12 | - | 0.02 | 2.62 | 2.65 | 3.20 | 0.09 | - | - | 0.08 | 97.87 | 73 |
| PL12-12 | 69.25 | 0.81 | 18.51 | 1.22 | - | 0.01 | 3.64 | 1.88 | 1.77 | 0.88 | 0.06 | - | 0.10 | 98.11 | 73 |
| PL12-15 | 69.42 | 0.16 | 18.96 | 1.19 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 1.06 | 2.75 | 2.90 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 97.32 | 73 |
| PL12-25 | 68.27 | 0.46 | 19.23 | 1.38 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 3.37 | 2.07 | 2.62 | 0.50 | - | - | 0.12 | 98.34 | 73 |
| PL12-30 | 67.09 | 0.51 | 20.67 | 1.36 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.98 | 2.73 | 4.55 | 0.31 | - | 0.05 | 0.14 | 98.44 | 73 |
| PL26-9 | 66.93 | 3.51 | 17.18 | 2.16 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 2.25 | 1.76 | 2.62 | 0.83 | - | - | 0.08 | 97.56 | 77 |
| PL26-21 | 68.63 | 1.95 | 18.48 | 1.45 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 1.48 | 1.60 | 2.75 | 1.24 | - | - | 0.16 | 98.07 | 85 |
| PL13-2 | 62.47 | 0.82 | 17.74 | 1.40 | - | 0.17 | 7.53 | 2.42 | 2.65 | 2.35 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 98.15 | 72 |
| PL13-4 | 68.18 | 0.51 | 18.64 | 1.78 | - | 0.24 | 4.61 | 2.68 | 2.73 | 0.17 | - | - | 0.08 | 99.60 | 73 |
| PL13-9 | 62.39 | 0.91 | 16.98 | 1.96 | - | 0.43 | 9.24 | 2.52 | 2.20 | 4.20 | - | 0.83 | 0.11 | 101.39 | 73 |
| PL13-15 | 68.86 | 0.51 | 17.91 | 1.05 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 3.79 | 2.70 | 2.97 | - | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 98.26 | 80 |
| PL13-27 | 68.25 | 1.07 | 19.20 | 0.91 | - | 0.01 | 3.56 | 2.77 | 2.70 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 98.95 | 78 |
| PL13-29 | 70.37 | 0.46 | 18.45 | 0.88 | - | 0.11 | 1.01 | 1.92 | 3.09 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 97.05 | 79 |
| PL13-34 | 69.36 | 0.63 | 18.56 | 1.20 | - | 0.16 | 2.43 | 2.71 | 3.31 | 0.17 | 0.02 | - | 0.08 | 98.60 | 75 |
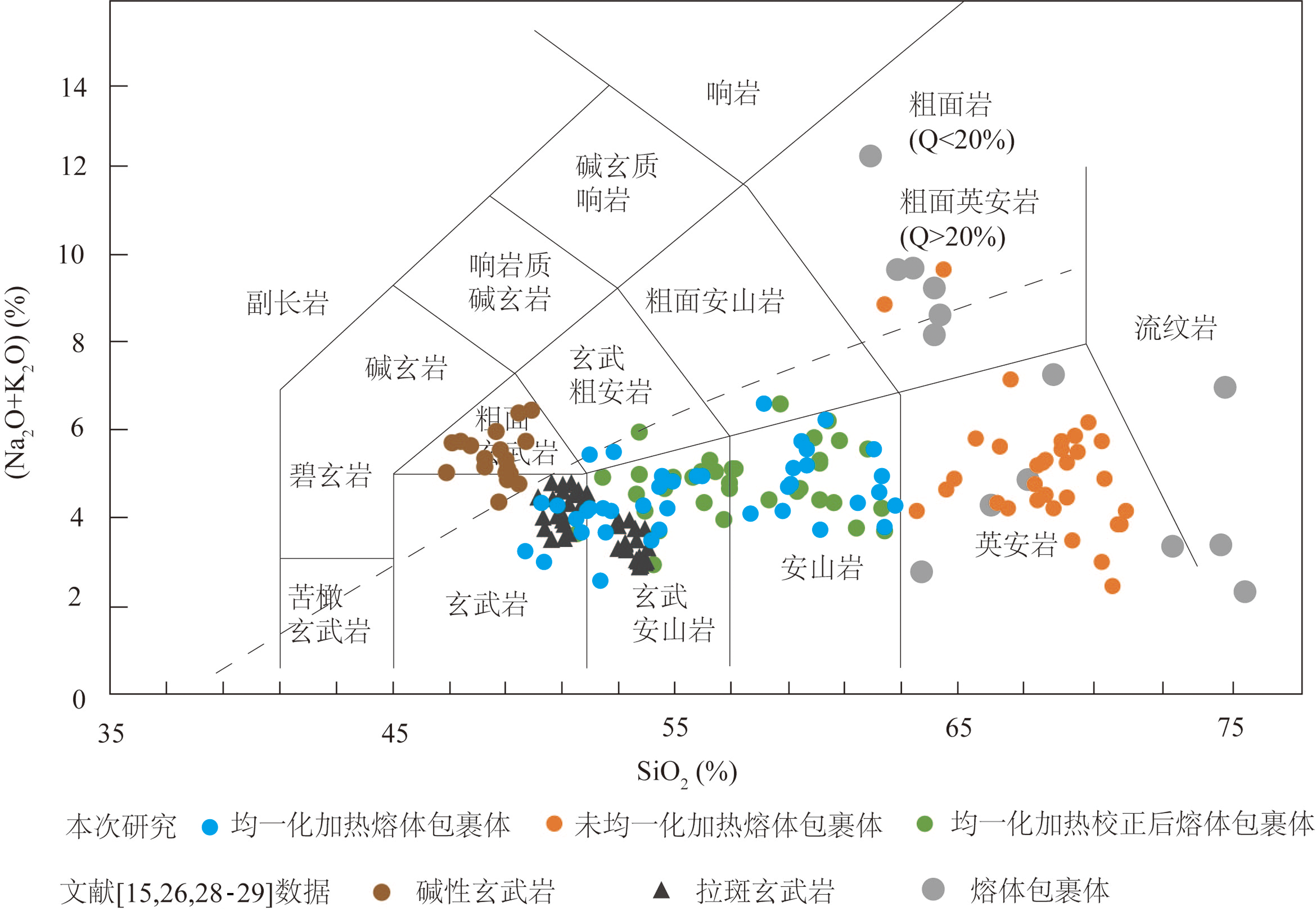
图4 海南岛蓬莱地区橄榄石中熔体包裹体SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(底图据文献[27],收集数据来自文献[15,26,28-29])
Fig.4 SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) diagram for olivine-hosted melt inclusions of basalts in Penglai area, Hainan Island (base map from reference [27], data from references [15,26,28 and 29]
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | SO3 | F | Cl | 总量 | 寄主橄榄 石Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL28-5 | 52.40 | 1.72 | 16.72 | 10.72 | 0.17 | 6.48 | 6.65 | 1.52 | 1.20 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 98.37 | 70 |
| PL28-5(1) | 50.36 | 1.77 | 16.65 | 10.66 | 0.10 | 6.27 | 6.68 | 3.42 | 1.08 | 0.37 | 0.01 | - | 0.03 | 97.39 | 70 |
| PL28-8 | 51.78 | 1.32 | 16.06 | 10.64 | 0.07 | 6.64 | 6.65 | 2.52 | 1.28 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 97.68 | 72 |
| PL28-8(1) | 51.56 | 1.35 | 16.04 | 10.56 | 0.18 | 6.77 | 6.45 | 2.84 | 1.31 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 97.77 | 72 |
| PL28-9 | 52.57 | 3.32 | 12.08 | 12.67 | 0.11 | 6.14 | 5.89 | 2.56 | 1.79 | 0.66 | - | 0.10 | 0.06 | 97.88 | 70 |
| PL28-13 | 53.92 | 2.30 | 12.31 | 12.23 | 0.10 | 5.52 | 5.07 | 2.48 | 1.95 | 0.64 | 0.10 | 0.38 | 0.10 | 96.90 | 76 |
| PL28-13(1) | 60.23 | 1.38 | 13.94 | 7.48 | 0.11 | 4.34 | 3.41 | 2.09 | 1.78 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 95.24 | 76 |
| PL28-13a | 62.53 | 1.29 | 13.55 | 6.86 | 0.06 | 5.40 | 2.51 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 0.38 | - | - | 0.02 | 96.52 | 78 |
| PL28-27 | 59.14 | 2.11 | 14.03 | 7.31 | 0.02 | 5.30 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.54 | 1.21 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 96.63 | 79 |
| PL28-27a | 59.24 | 2.04 | 14.11 | 7.66 | 0.09 | 4.95 | 2.28 | 2.32 | 2.58 | 1.12 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 96.57 | 79 |
| PL28-35 | 56.06 | 2.41 | 13.73 | 8.67 | 0.02 | 5.84 | 4.70 | 2.79 | 2.29 | 0.63 | 0.03 | - | 0.07 | 97.24 | 77 |
| PL28-35a | 55.84 | 2.17 | 13.66 | 8.66 | 0.04 | 5.81 | 4.76 | 2.83 | 2.24 | 0.56 | - | 0.43 | 0.06 | 96.86 | 77 |
| PLTW-7 | 52.04 | 1.78 | 13.07 | 11.40 | 0.14 | 5.58 | 6.60 | 2.44 | 3.12 | 1.98 | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 98.78 | 73 |
| PLTW-14 | 59.57 | 0.78 | 14.26 | 7.53 | - | 4.84 | 3.35 | 2.74 | 3.16 | 0.95 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 97.44 | 74 |
| PLTW-14a | 59.80 | 1.01 | 14.55 | 7.17 | 0.04 | 4.59 | 3.22 | 2.39 | 2.96 | 1.30 | 0.01 | - | 0.12 | 97.12 | 73 |
| PLTW-23 | 54.53 | 2.17 | 13.31 | 10.12 | 0.05 | 4.92 | 6.04 | 2.53 | 2.31 | 0.86 | - | 0.15 | 0.06 | 96.96 | 73 |
| PL13-1 | 54.81 | 1.53 | 13.34 | 9.89 | 0.16 | 5.78 | 6.35 | 2.52 | 1.87 | 0.61 | 0.06 | - | 0.03 | 96.92 | 72 |
| PL13-12 | 52.60 | 2.12 | 12.38 | 11.14 | 0.02 | 7.08 | 6.84 | 2.64 | 1.16 | 0.52 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 96.70 | 71 |
| PL13-25 | 51.92 | 2.24 | 12.81 | 10.71 | - | 6.87 | 6.98 | 2.65 | 1.68 | 0.74 | 0.05 | - | 0.06 | 96.69 | 72 |
| PL13-36 | 52.79 | 1.80 | 13.13 | 11.42 | 0.07 | 6.58 | 6.93 | 2.56 | 1.75 | 1.38 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 98.54 | 73 |
| PL13-36a | 54.99 | 1.37 | 13.59 | 10.06 | 0.02 | 6.08 | 5.72 | 2.57 | 2.42 | 1.11 | - | - | 0.05 | 97.98 | 78 |
| PL39-12 | 54.63 | 1.46 | 14.13 | 9.86 | 0.07 | 5.71 | 5.49 | 3.20 | 1.90 | 1.06 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 97.99 | 74 |
| PL39-12a | 58.92 | 0.53 | 13.24 | 9.16 | 0.08 | 4.87 | 4.62 | 2.85 | 1.45 | 0.56 | - | 0.14 | 0.03 | 96.38 | 74 |
| PL39-21 | 58.30 | 1.54 | 14.73 | 7.62 | 0.06 | 4.65 | 3.16 | 3.04 | 3.65 | 0.42 | - | 0.10 | 0.07 | 97.26 | 74 |
| PL39-25 | 50.87 | 2.30 | 12.61 | 12.40 | 0.21 | 6.37 | 7.30 | 2.75 | 1.69 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 97.33 | 74 |
| PL25-5 | 59.77 | 0.73 | 14.16 | 9.50 | 0.12 | 4.44 | 3.02 | 2.51 | 3.18 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 98.01 | 73 |
| PL25-17 | 54.57 | 1.98 | 12.05 | 12.17 | 0.17 | 6.04 | 5.22 | 2.64 | 1.27 | 0.54 | 0.24 | - | 0.02 | 96.90 | 71 |
| PL25-28 | 62.20 | 0.87 | 13.80 | 7.59 | - | 4.79 | 2.59 | 2.78 | 2.94 | 0.71 | - | - | 0.06 | 98.31 | 74 |
| PL35-1 | 49.76 | 0.99 | 17.83 | 9.34 | 0.05 | 7.67 | 7.42 | 2.56 | 0.86 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 96.91 | 76 |
| PL35-8 | 50.40 | 2.97 | 13.20 | 14.50 | 0.05 | 6.14 | 6.52 | 1.47 | 1.70 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.19 | - | 97.22 | 72 |
| PL35-11 | 60.50 | 1.45 | 14.08 | 7.28 | 0.15 | 5.22 | 2.41 | 2.58 | 3.80 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 0.04 | 97.99 | 76 |
| PL35-12 | 54.26 | 2.24 | 12.51 | 10.61 | 0.11 | 6.78 | 6.94 | 2.68 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 97.82 | 72 |
| PL35-28 | 57.77 | 1.10 | 13.17 | 9.27 | 0.01 | 5.30 | 4.65 | 2.51 | 1.72 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 96.10 | 73 |
| PL26-16 | 62.95 | 0.64 | 14.21 | 8.31 | 0.11 | 4.35 | 3.01 | 2.60 | 1.82 | 0.49 | - | - | 0.04 | 98.51 | 73 |
| PL26-17 | 59.35 | 1.28 | 13.88 | 8.30 | 0.05 | 4.94 | 3.79 | 2.72 | 2.56 | 0.57 | 0.09 | - | 0.03 | 97.55 | 73 |
表3 均一化加热熔体包裹体电子探针数据(%)
Table 3 Heated melt inclusions electron microprobe analyses (%)
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | SO3 | F | Cl | 总量 | 寄主橄榄 石Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL28-5 | 52.40 | 1.72 | 16.72 | 10.72 | 0.17 | 6.48 | 6.65 | 1.52 | 1.20 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 98.37 | 70 |
| PL28-5(1) | 50.36 | 1.77 | 16.65 | 10.66 | 0.10 | 6.27 | 6.68 | 3.42 | 1.08 | 0.37 | 0.01 | - | 0.03 | 97.39 | 70 |
| PL28-8 | 51.78 | 1.32 | 16.06 | 10.64 | 0.07 | 6.64 | 6.65 | 2.52 | 1.28 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 97.68 | 72 |
| PL28-8(1) | 51.56 | 1.35 | 16.04 | 10.56 | 0.18 | 6.77 | 6.45 | 2.84 | 1.31 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 97.77 | 72 |
| PL28-9 | 52.57 | 3.32 | 12.08 | 12.67 | 0.11 | 6.14 | 5.89 | 2.56 | 1.79 | 0.66 | - | 0.10 | 0.06 | 97.88 | 70 |
| PL28-13 | 53.92 | 2.30 | 12.31 | 12.23 | 0.10 | 5.52 | 5.07 | 2.48 | 1.95 | 0.64 | 0.10 | 0.38 | 0.10 | 96.90 | 76 |
| PL28-13(1) | 60.23 | 1.38 | 13.94 | 7.48 | 0.11 | 4.34 | 3.41 | 2.09 | 1.78 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 95.24 | 76 |
| PL28-13a | 62.53 | 1.29 | 13.55 | 6.86 | 0.06 | 5.40 | 2.51 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 0.38 | - | - | 0.02 | 96.52 | 78 |
| PL28-27 | 59.14 | 2.11 | 14.03 | 7.31 | 0.02 | 5.30 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.54 | 1.21 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 96.63 | 79 |
| PL28-27a | 59.24 | 2.04 | 14.11 | 7.66 | 0.09 | 4.95 | 2.28 | 2.32 | 2.58 | 1.12 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 96.57 | 79 |
| PL28-35 | 56.06 | 2.41 | 13.73 | 8.67 | 0.02 | 5.84 | 4.70 | 2.79 | 2.29 | 0.63 | 0.03 | - | 0.07 | 97.24 | 77 |
| PL28-35a | 55.84 | 2.17 | 13.66 | 8.66 | 0.04 | 5.81 | 4.76 | 2.83 | 2.24 | 0.56 | - | 0.43 | 0.06 | 96.86 | 77 |
| PLTW-7 | 52.04 | 1.78 | 13.07 | 11.40 | 0.14 | 5.58 | 6.60 | 2.44 | 3.12 | 1.98 | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 98.78 | 73 |
| PLTW-14 | 59.57 | 0.78 | 14.26 | 7.53 | - | 4.84 | 3.35 | 2.74 | 3.16 | 0.95 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 97.44 | 74 |
| PLTW-14a | 59.80 | 1.01 | 14.55 | 7.17 | 0.04 | 4.59 | 3.22 | 2.39 | 2.96 | 1.30 | 0.01 | - | 0.12 | 97.12 | 73 |
| PLTW-23 | 54.53 | 2.17 | 13.31 | 10.12 | 0.05 | 4.92 | 6.04 | 2.53 | 2.31 | 0.86 | - | 0.15 | 0.06 | 96.96 | 73 |
| PL13-1 | 54.81 | 1.53 | 13.34 | 9.89 | 0.16 | 5.78 | 6.35 | 2.52 | 1.87 | 0.61 | 0.06 | - | 0.03 | 96.92 | 72 |
| PL13-12 | 52.60 | 2.12 | 12.38 | 11.14 | 0.02 | 7.08 | 6.84 | 2.64 | 1.16 | 0.52 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 96.70 | 71 |
| PL13-25 | 51.92 | 2.24 | 12.81 | 10.71 | - | 6.87 | 6.98 | 2.65 | 1.68 | 0.74 | 0.05 | - | 0.06 | 96.69 | 72 |
| PL13-36 | 52.79 | 1.80 | 13.13 | 11.42 | 0.07 | 6.58 | 6.93 | 2.56 | 1.75 | 1.38 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 98.54 | 73 |
| PL13-36a | 54.99 | 1.37 | 13.59 | 10.06 | 0.02 | 6.08 | 5.72 | 2.57 | 2.42 | 1.11 | - | - | 0.05 | 97.98 | 78 |
| PL39-12 | 54.63 | 1.46 | 14.13 | 9.86 | 0.07 | 5.71 | 5.49 | 3.20 | 1.90 | 1.06 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 97.99 | 74 |
| PL39-12a | 58.92 | 0.53 | 13.24 | 9.16 | 0.08 | 4.87 | 4.62 | 2.85 | 1.45 | 0.56 | - | 0.14 | 0.03 | 96.38 | 74 |
| PL39-21 | 58.30 | 1.54 | 14.73 | 7.62 | 0.06 | 4.65 | 3.16 | 3.04 | 3.65 | 0.42 | - | 0.10 | 0.07 | 97.26 | 74 |
| PL39-25 | 50.87 | 2.30 | 12.61 | 12.40 | 0.21 | 6.37 | 7.30 | 2.75 | 1.69 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 97.33 | 74 |
| PL25-5 | 59.77 | 0.73 | 14.16 | 9.50 | 0.12 | 4.44 | 3.02 | 2.51 | 3.18 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 98.01 | 73 |
| PL25-17 | 54.57 | 1.98 | 12.05 | 12.17 | 0.17 | 6.04 | 5.22 | 2.64 | 1.27 | 0.54 | 0.24 | - | 0.02 | 96.90 | 71 |
| PL25-28 | 62.20 | 0.87 | 13.80 | 7.59 | - | 4.79 | 2.59 | 2.78 | 2.94 | 0.71 | - | - | 0.06 | 98.31 | 74 |
| PL35-1 | 49.76 | 0.99 | 17.83 | 9.34 | 0.05 | 7.67 | 7.42 | 2.56 | 0.86 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 96.91 | 76 |
| PL35-8 | 50.40 | 2.97 | 13.20 | 14.50 | 0.05 | 6.14 | 6.52 | 1.47 | 1.70 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.19 | - | 97.22 | 72 |
| PL35-11 | 60.50 | 1.45 | 14.08 | 7.28 | 0.15 | 5.22 | 2.41 | 2.58 | 3.80 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 0.04 | 97.99 | 76 |
| PL35-12 | 54.26 | 2.24 | 12.51 | 10.61 | 0.11 | 6.78 | 6.94 | 2.68 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 97.82 | 72 |
| PL35-28 | 57.77 | 1.10 | 13.17 | 9.27 | 0.01 | 5.30 | 4.65 | 2.51 | 1.72 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 96.10 | 73 |
| PL26-16 | 62.95 | 0.64 | 14.21 | 8.31 | 0.11 | 4.35 | 3.01 | 2.60 | 1.82 | 0.49 | - | - | 0.04 | 98.51 | 73 |
| PL26-17 | 59.35 | 1.28 | 13.88 | 8.30 | 0.05 | 4.94 | 3.79 | 2.72 | 2.56 | 0.57 | 0.09 | - | 0.03 | 97.55 | 73 |
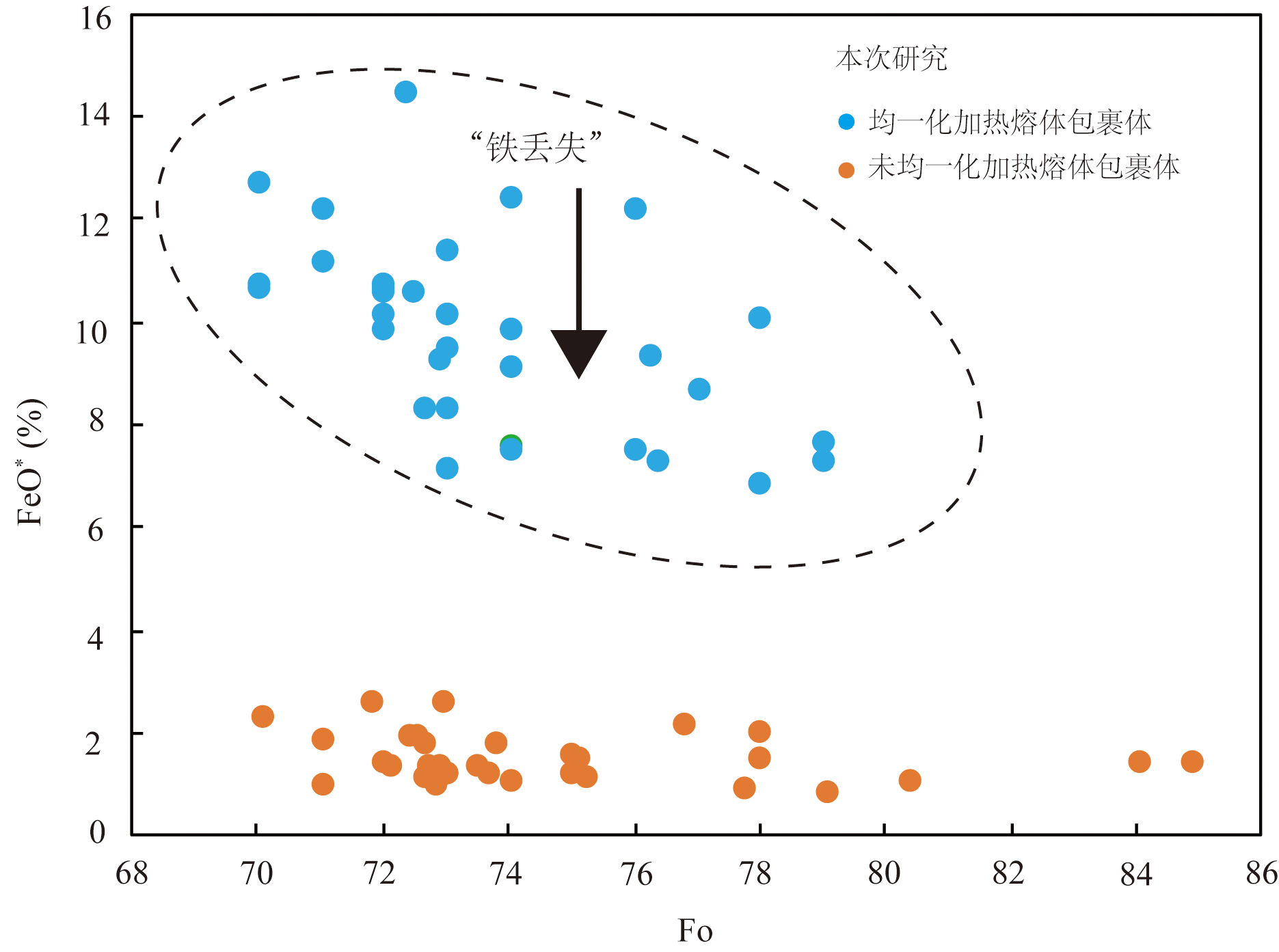
图5 海南岛蓬莱地区橄榄石中未经校正的熔体包裹体FeO*与寄主橄榄石Fo值关系图
Fig.5 FeO* vs.Fo values for uncorrected olivine-hosted melt inclusions composition of Penglai area, Hainan Island
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL28-5 | 53.94 | 1.83 | 17.83 | 1.25 | 9.87 | 0.18 | 4.56 | 7.09 | 1.62 | 1.28 | 0.55 |
| PL28-5(1) | 52.25 | 1.92 | 18.03 | 1.58 | 9.57 | 0.11 | 4.03 | 7.23 | 3.70 | 1.17 | 0.40 |
| PL28-8 | 53.65 | 1.42 | 17.27 | 1.33 | 9.73 | 0.08 | 4.72 | 7.15 | 2.71 | 1.38 | 0.57 |
| PL28-8(1) | 53.38 | 1.45 | 17.26 | 1.40 | 9.74 | 0.19 | 4.66 | 6.94 | 3.06 | 1.41 | 0.52 |
| PL28-9 | 55.33 | 3.72 | 13.52 | 2.02 | 9.12 | 0.12 | 3.97 | 6.59 | 2.87 | 2.00 | 0.74 |
| PL28-13 | 56.51 | 2.45 | 13.10 | 1.56 | 9.72 | 0.11 | 5.78 | 5.39 | 2.64 | 2.08 | 0.68 |
| PL28-13(1) | 60.76 | 1.32 | 13.35 | 1.31 | 9.84 | 0.11 | 6.11 | 3.27 | 2.00 | 1.71 | 0.23 |
| PL28-13a | 61.70 | 1.21 | 12.66 | 1.33 | 9.80 | 0.06 | 6.87 | 2.35 | 1.83 | 1.85 | 0.36 |
| PL28-27 | 58.83 | 1.99 | 13.20 | 1.38 | 9.74 | 0.02 | 6.97 | 2.17 | 2.17 | 2.39 | 1.14 |
| PL28-27a | 58.88 | 1.91 | 13.23 | 1.39 | 9.76 | 0.08 | 6.98 | 2.14 | 2.18 | 2.42 | 1.05 |
| PL28-35 | 56.63 | 2.39 | 13.60 | 1.51 | 9.63 | 0.02 | 5.93 | 4.65 | 2.76 | 2.27 | 0.62 |
| PL28-35a | 56.76 | 2.16 | 13.62 | 1.50 | 9.63 | 0.04 | 5.94 | 4.75 | 2.82 | 2.23 | 0.56 |
| PLTW-7 | 53.50 | 1.88 | 13.77 | 1.80 | 9.29 | 0.15 | 4.72 | 6.95 | 2.57 | 3.29 | 2.09 |
| PLTW-14 | 59.40 | 0.75 | 13.78 | 1.52 | 9.61 | - | 5.09 | 3.24 | 2.65 | 3.05 | 0.92 |
| PLTW-14a | 59.56 | 0.97 | 14.00 | 1.45 | 9.57 | 0.04 | 4.91 | 3.10 | 2.30 | 2.85 | 1.25 |
| PLTW-23 | 56.03 | 2.23 | 13.65 | 1.64 | 9.52 | 0.05 | 4.85 | 6.19 | 2.59 | 2.37 | 0.88 |
| PL13-1 | 56.56 | 1.60 | 13.93 | 1.53 | 9.61 | 0.17 | 4.75 | 6.63 | 2.63 | 1.95 | 0.64 |
| PL13-12 | 55.66 | 2.37 | 13.86 | 1.66 | 9.50 | 0.02 | 4.44 | 7.66 | 2.96 | 1.30 | 0.58 |
| PL13-25 | 54.52 | 2.46 | 14.09 | 1.73 | 9.40 | - | 4.53 | 7.68 | 2.92 | 1.85 | 0.81 |
| PL13-36 | 54.37 | 1.92 | 14.04 | 1.60 | 9.56 | 0.08 | 4.94 | 7.41 | 2.74 | 1.87 | 1.48 |
| PL13-36a | 55.58 | 1.37 | 13.55 | 1.46 | 9.74 | 0.02 | 6.50 | 5.70 | 2.56 | 2.41 | 1.11 |
| PL39-12 | 55.85 | 1.50 | 14.52 | 1.52 | 9.53 | 0.07 | 5.03 | 5.64 | 3.29 | 1.95 | 1.09 |
| PL39-12a | 60.07 | 0.53 | 13.22 | 1.38 | 9.80 | 0.08 | 5.46 | 4.61 | 2.85 | 1.45 | 0.56 |
| PL39-21 | 58.26 | 1.49 | 14.29 | 1.63 | 9.53 | 0.06 | 4.78 | 3.07 | 2.95 | 3.54 | 0.41 |
| PL39-25 | 53.50 | 2.54 | 13.93 | 1.76 | 9.42 | 0.23 | 4.95 | 8.06 | 3.04 | 1.87 | 0.71 |
| PL25-5 | 60.26 | 0.72 | 14.05 | 1.50 | 9.64 | 0.12 | 4.81 | 3.00 | 2.49 | 3.16 | 0.25 |
| PL25-17 | 57.86 | 2.20 | 13.37 | 1.58 | 9.57 | 0.19 | 4.50 | 5.79 | 2.93 | 1.41 | 0.60 |
| PL25-28 | 61.22 | 0.83 | 13.15 | 1.53 | 9.61 | - | 5.08 | 2.47 | 2.65 | 2.80 | 0.68 |
| PL35-1 | 51.38 | 1.05 | 18.86 | 1.15 | 9.95 | 0.05 | 5.81 | 7.85 | 2.71 | 0.91 | 0.29 |
| PL35-8 | 54.13 | 3.45 | 15.32 | 1.65 | 9.41 | 0.06 | 4.60 | 7.57 | 1.71 | 1.97 | 0.15 |
| PL35-11 | 59.90 | 1.39 | 13.47 | 1.57 | 9.58 | 0.14 | 5.44 | 2.31 | 2.47 | 3.64 | 0.11 |
| PL35-12 | 56.33 | 2.42 | 13.49 | 1.57 | 9.49 | 0.12 | 4.70 | 7.48 | 2.89 | 1.01 | 0.51 |
| PL35-28 | 59.61 | 1.13 | 13.51 | 1.40 | 9.72 | 0.01 | 5.09 | 4.77 | 2.57 | 1.76 | 0.43 |
| PL26-16 | 61.68 | 0.60 | 13.39 | 1.40 | 10.04 | 0.10 | 5.31 | 2.84 | 2.45 | 1.72 | 0.46 |
| PL26-17 | 59.54 | 1.26 | 13.64 | 1.51 | 9.64 | 0.05 | 4.88 | 3.73 | 2.67 | 2.52 | 0.56 |
表4 均一化加热校正后的熔体包裹体成分数据(%)
Table 4 Compositional data of heated melt inclusions after correction (%)
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL28-5 | 53.94 | 1.83 | 17.83 | 1.25 | 9.87 | 0.18 | 4.56 | 7.09 | 1.62 | 1.28 | 0.55 |
| PL28-5(1) | 52.25 | 1.92 | 18.03 | 1.58 | 9.57 | 0.11 | 4.03 | 7.23 | 3.70 | 1.17 | 0.40 |
| PL28-8 | 53.65 | 1.42 | 17.27 | 1.33 | 9.73 | 0.08 | 4.72 | 7.15 | 2.71 | 1.38 | 0.57 |
| PL28-8(1) | 53.38 | 1.45 | 17.26 | 1.40 | 9.74 | 0.19 | 4.66 | 6.94 | 3.06 | 1.41 | 0.52 |
| PL28-9 | 55.33 | 3.72 | 13.52 | 2.02 | 9.12 | 0.12 | 3.97 | 6.59 | 2.87 | 2.00 | 0.74 |
| PL28-13 | 56.51 | 2.45 | 13.10 | 1.56 | 9.72 | 0.11 | 5.78 | 5.39 | 2.64 | 2.08 | 0.68 |
| PL28-13(1) | 60.76 | 1.32 | 13.35 | 1.31 | 9.84 | 0.11 | 6.11 | 3.27 | 2.00 | 1.71 | 0.23 |
| PL28-13a | 61.70 | 1.21 | 12.66 | 1.33 | 9.80 | 0.06 | 6.87 | 2.35 | 1.83 | 1.85 | 0.36 |
| PL28-27 | 58.83 | 1.99 | 13.20 | 1.38 | 9.74 | 0.02 | 6.97 | 2.17 | 2.17 | 2.39 | 1.14 |
| PL28-27a | 58.88 | 1.91 | 13.23 | 1.39 | 9.76 | 0.08 | 6.98 | 2.14 | 2.18 | 2.42 | 1.05 |
| PL28-35 | 56.63 | 2.39 | 13.60 | 1.51 | 9.63 | 0.02 | 5.93 | 4.65 | 2.76 | 2.27 | 0.62 |
| PL28-35a | 56.76 | 2.16 | 13.62 | 1.50 | 9.63 | 0.04 | 5.94 | 4.75 | 2.82 | 2.23 | 0.56 |
| PLTW-7 | 53.50 | 1.88 | 13.77 | 1.80 | 9.29 | 0.15 | 4.72 | 6.95 | 2.57 | 3.29 | 2.09 |
| PLTW-14 | 59.40 | 0.75 | 13.78 | 1.52 | 9.61 | - | 5.09 | 3.24 | 2.65 | 3.05 | 0.92 |
| PLTW-14a | 59.56 | 0.97 | 14.00 | 1.45 | 9.57 | 0.04 | 4.91 | 3.10 | 2.30 | 2.85 | 1.25 |
| PLTW-23 | 56.03 | 2.23 | 13.65 | 1.64 | 9.52 | 0.05 | 4.85 | 6.19 | 2.59 | 2.37 | 0.88 |
| PL13-1 | 56.56 | 1.60 | 13.93 | 1.53 | 9.61 | 0.17 | 4.75 | 6.63 | 2.63 | 1.95 | 0.64 |
| PL13-12 | 55.66 | 2.37 | 13.86 | 1.66 | 9.50 | 0.02 | 4.44 | 7.66 | 2.96 | 1.30 | 0.58 |
| PL13-25 | 54.52 | 2.46 | 14.09 | 1.73 | 9.40 | - | 4.53 | 7.68 | 2.92 | 1.85 | 0.81 |
| PL13-36 | 54.37 | 1.92 | 14.04 | 1.60 | 9.56 | 0.08 | 4.94 | 7.41 | 2.74 | 1.87 | 1.48 |
| PL13-36a | 55.58 | 1.37 | 13.55 | 1.46 | 9.74 | 0.02 | 6.50 | 5.70 | 2.56 | 2.41 | 1.11 |
| PL39-12 | 55.85 | 1.50 | 14.52 | 1.52 | 9.53 | 0.07 | 5.03 | 5.64 | 3.29 | 1.95 | 1.09 |
| PL39-12a | 60.07 | 0.53 | 13.22 | 1.38 | 9.80 | 0.08 | 5.46 | 4.61 | 2.85 | 1.45 | 0.56 |
| PL39-21 | 58.26 | 1.49 | 14.29 | 1.63 | 9.53 | 0.06 | 4.78 | 3.07 | 2.95 | 3.54 | 0.41 |
| PL39-25 | 53.50 | 2.54 | 13.93 | 1.76 | 9.42 | 0.23 | 4.95 | 8.06 | 3.04 | 1.87 | 0.71 |
| PL25-5 | 60.26 | 0.72 | 14.05 | 1.50 | 9.64 | 0.12 | 4.81 | 3.00 | 2.49 | 3.16 | 0.25 |
| PL25-17 | 57.86 | 2.20 | 13.37 | 1.58 | 9.57 | 0.19 | 4.50 | 5.79 | 2.93 | 1.41 | 0.60 |
| PL25-28 | 61.22 | 0.83 | 13.15 | 1.53 | 9.61 | - | 5.08 | 2.47 | 2.65 | 2.80 | 0.68 |
| PL35-1 | 51.38 | 1.05 | 18.86 | 1.15 | 9.95 | 0.05 | 5.81 | 7.85 | 2.71 | 0.91 | 0.29 |
| PL35-8 | 54.13 | 3.45 | 15.32 | 1.65 | 9.41 | 0.06 | 4.60 | 7.57 | 1.71 | 1.97 | 0.15 |
| PL35-11 | 59.90 | 1.39 | 13.47 | 1.57 | 9.58 | 0.14 | 5.44 | 2.31 | 2.47 | 3.64 | 0.11 |
| PL35-12 | 56.33 | 2.42 | 13.49 | 1.57 | 9.49 | 0.12 | 4.70 | 7.48 | 2.89 | 1.01 | 0.51 |
| PL35-28 | 59.61 | 1.13 | 13.51 | 1.40 | 9.72 | 0.01 | 5.09 | 4.77 | 2.57 | 1.76 | 0.43 |
| PL26-16 | 61.68 | 0.60 | 13.39 | 1.40 | 10.04 | 0.10 | 5.31 | 2.84 | 2.45 | 1.72 | 0.46 |
| PL26-17 | 59.54 | 1.26 | 13.64 | 1.51 | 9.64 | 0.05 | 4.88 | 3.73 | 2.67 | 2.52 | 0.56 |
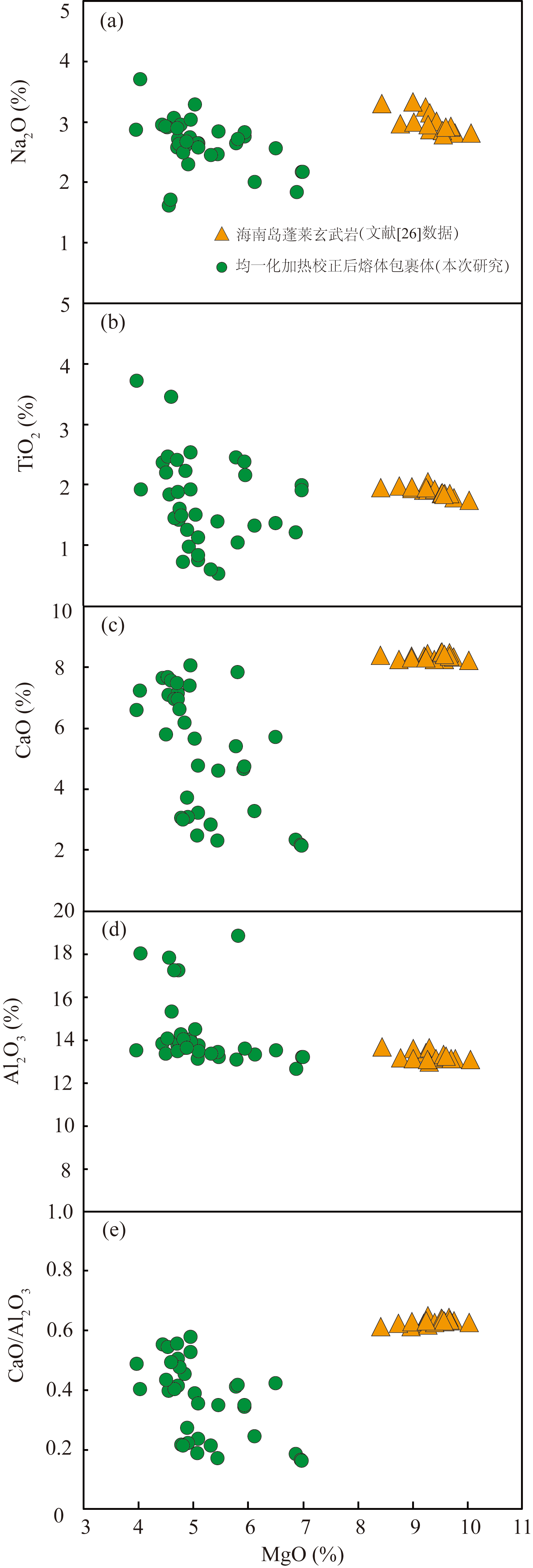
图7 海南岛蓬莱地区橄榄石中校正熔体包裹体MgO-Na2O, TiO2, CaO, Al2O3, CaO/Al2O3图解
Fig.7 MgO vs. Na2O, TiO2, CaO, Al2O3, CaO/Al2O3 diagrams for corrected olivine-hosted melt inclusions, Penglai area, Hainan Island
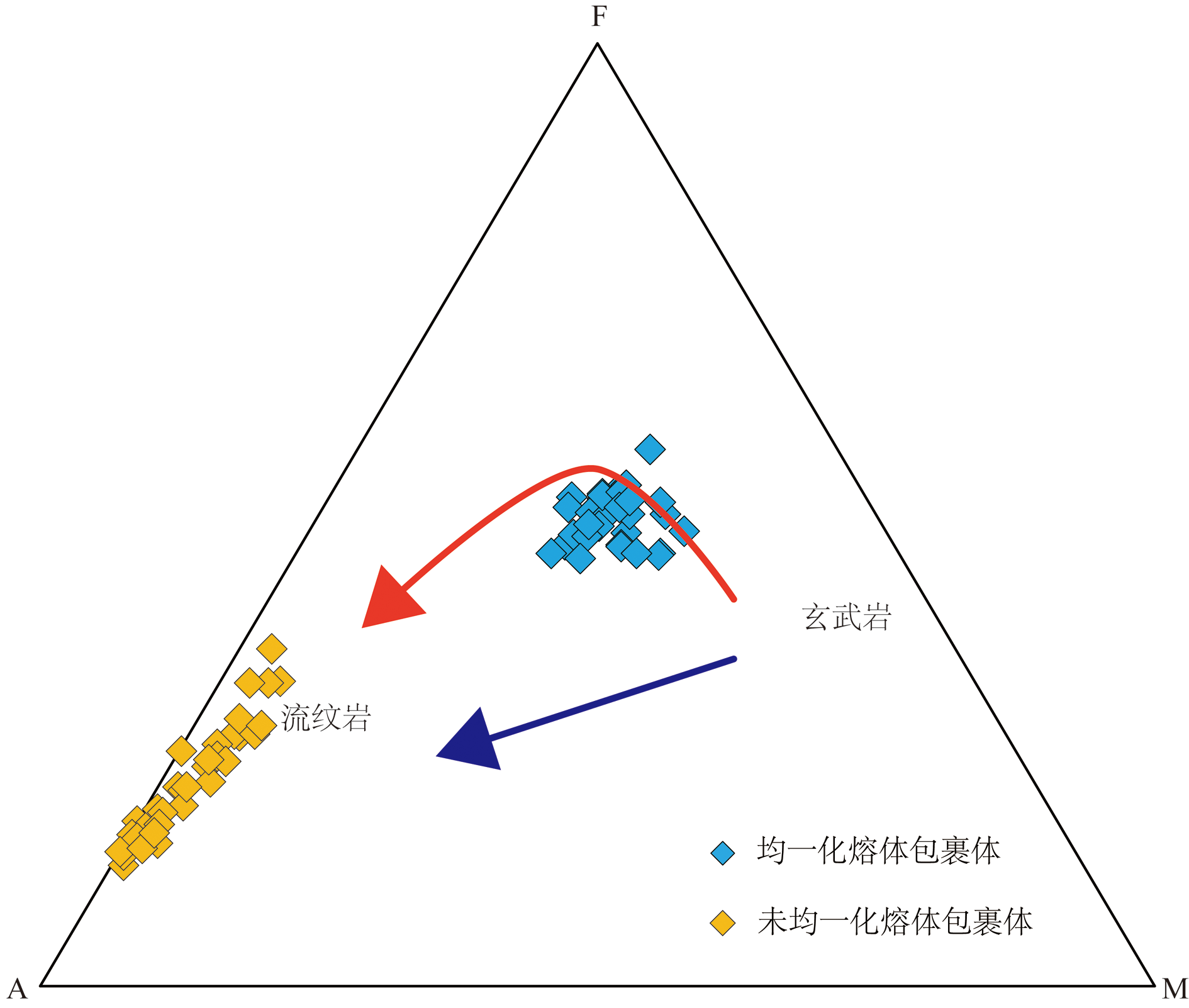
图8 海南岛蓬莱地区橄榄石中均一化熔体包裹体和未均一化熔体包裹体AFM图解
Fig.8 AFM diagram for olivine-hosted heated melt inclusions and unheated melt inclusions A.Na2O+K2O; F.FeOT; M.MgO
| [1] | ROEDDER E. Origin and significance of magmatic inclusions[J]. Bulletin de Mineralogie, 1979, 102: 487-510. |
| [2] | ROEDDER E. Fluid Inclusions[M]. Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter, 1984. |
| [3] | LOWENSTERN J B. Applications of silicate-melt inclusions to the study of magmatic volatiles[J]. Magmas Fluids Ore Deposit, 1995, 23: 71-99. |
| [4] | ANDERSON A T, DAVIS A M, LU F Q. Evolution of Bishop Tuff rhyolitic magma based on melt and magnetite inclusions and zoned phenocrysts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41: 449-473. |
| [5] | HAURI E. SIMS analysis of volatiles in silicate glasses, 2: isotopes and abundances in Hawaiian melt inclusions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 183: 115-141. |
| [6] | LOWENSTERN J B. Melt Inclusions Come of Age: Volatiles, Volcanoes, and Sorby’s Legacy[J]. Developments in Volcanology, 2003, 5:1-21. |
| [7] | WALLACE P J. Volatiles in subduction zone magmas: concentrations and fluxes based on melt inclusion and volcanic gas data[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2005, 140: 217-240. |
| [8] | BODNAR R J, STUDENT J J. Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks: Petrography and Micro Thermometry[M]//WEBSTER J D. Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Short Course, 2006, 36: 1-26. |
| [9] | GAZEL E, PLANK T, FORSYTH D W, et al. Lithosphere versus asthenosphere mantle sources at the Big Pine Volcanic Field, California[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2012, 13: 1-25. |
| [10] | 王蝶, 卢焕章, 单强. 岩浆熔体包裹体研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(2): 653-666. |
| [11] | 张道涵, 魏俊浩, 付乐兵. 熔体包裹体的形成、改造和分析方法及其矿床学应用[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2017, 42(6) : 990-1007. |
| [12] | 李霓, 孙嘉祥. 火山岩中熔体包裹体研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(3): 414-423. |
| [13] | 任钟元, 张乐, 吴亚东, 等. 熔体包裹体在镁铁质火山岩成因研究中的应用[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(3): 395-413. |
| [14] | 丁一, 刘吉强, 李正刚. 橄榄石及其熔体包裹体地球化学约束冲绳海槽岩浆水含量[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(6):1208-1207. |
| [15] | WANG X C, LI Z, LI X, et al. Identification of an ancient mantle reservoir and young recycled materials in the source region of a young mantle plume: implications for potential linkages between plume and plate tectonics[J]. Earth Planet Science Letter, 2013, 377: 248-259. |
| [16] | 温淑女. 海南岛二叠纪—三叠纪岩浆作用的年代学与地球化学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013. |
| [17] | ZOU H B, FAN Q C. U-Th isotopes in Hainan basalts: Implications for sub-asthenospheric origin of EM2 mantle endmember and the dynamics of melting beneath Hainan Island[J]. Lithos, 2010, 116: 145-152. |
| [18] | 龙文国, 符策锐, 朱耀. 海南岛东部黄竹岭地区“抱板群”的解体[J]. 地层学杂志, 2002, 26(3): 212-215. |
| [19] | 广东省地质矿产局. 海南岛区域地质调查报告(1∶200000). 1964. |
| [20] | 李薇, 贾丽云, 胡道功, 等. 琼北老城剖面记录的马袅—铺前断裂西段晚更新世活动历史[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5): 970-978. |
| [21] |
袁晓博, 方念乔, 董海龙. 海南岛高峰、保城地区花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 85-97.
DOI |
| [22] | 舒斌, 王平安, 李中坚, 等. 海南抱伦金矿的成矿时代研究及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(3): 316-320. |
| [23] | 孙谦. 琼北第四纪火山活动与岩浆演化[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2003. |
| [24] | 樊祺诚, 孙谦, 李霓, 等. 琼北火山活动分期与全新世岩浆演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(3): 533-544. |
| [25] | NIELSEN R L, MICHAEL P J, SOURS P R. Chemical and physical indicators of compromised melt inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 62(5): 831-839. |
| [26] | REN Z Y, HANYU T, MIYAZAKI T, et al. Geochemical differences of the Hawaiian shield lavas: Implications for melting process in the heterogeneous Hawaiian plume[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2009, 50(8): 1553-1573. |
| [27] |
SOBOLEV A V, HOFMANN A W, KUZMIN D V, et al. The amount of recycled crust in sources of mantle-derived melts[J]. Science, 2007, 316: 412-417.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | WANG Z, GAETANI G A. Partitioning of Ni between olivine and siliceous eclogite partial melt: experimental constraints on the mantle source of Hawaiian basalts[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2008, 156(5), 661-678. |
| [29] | XU X, TIAN W, ZHANG L F, et al. Carbon Enrichment in the Lithospheric Mantle: Evidence from the Melt Inclusions in Mantle Xenoliths from the Hainan Basalts[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2023, 97: 358-375. |
| [30] | LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A, et al. A Chemical Classification of Volcanic Rocks Based on the Total Alkali-Silica Diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27: 745-750. |
| [31] | LIU J Q, REN Z Y, NICHOLS A R L, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Cenozoic basalts from North Hainan Island: Constraints from melt inclusions and their host olivines[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 152: 89-121. |
| [32] | WANG P Y, GU X Y, KURITANI T, et al. Highly variable H2O/Ce ratios in the Hainan mantle plume[J]. Lithos, 2021, 406-407. |
| [33] | KENT A J R. Melt Inclusions in Basaltic and Related Volcanic Rocks[M]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2008, 69(1): 273-331. |
| [34] | DANYUSHEVSKY L V, DELLA-PASQUA F N, SOKOLOV S. Re-equilibration of melt inclusions trapped by magnesian olivine phenocrysts from subduction-related magmas: petrological implications[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2000, 138(1): 68-83. |
| [35] | DANYUSHEVSKY L V, PLECHOV P. Petrolog3: Integrated software for modeling crystallization processes[J]. Geocchemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(7): 1-32. |
| [36] | QIAN S P, REN Z Y, RICHARD W, et al. Petrogenesis of early cretaceous basaltic lavas from the north China craton: implications for cratonic destruction[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 2017, 122: 1900-1918. |
| [37] | FORD C E, RUSSEL D G, CRAVEN J A, et al. Olivine-liquid equilibria: temperature, pressure and composition dependence of the crystal/liquid cation partition coeffcients for Mg, Fe2+, Ca and Mn[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1983, 24: 256-265. |
| [38] | 刘建强, 任钟元. 玄武岩源区母岩的多样性和识别特征:以海南岛玄武岩为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿, 2015, 37(3): 471-488. |
| [39] | SCHIANO P, CLOCCHIATTI R. Worldwide occurrence of silica rich melts in sub-continental and sub-oceanic mantle minerals[J]. Nature, 1994, 368: 621-624. |
| [40] | PUTIRKA K D. Thermometers and Barometers for Volcanic Systems[J]. Reviews Mineralogy Geochemistry, 2008, 69: 61-120. |
| [41] | 杜星星, 樊祺诚. 汉诺坝地幔捕虏体中富硅熔体的成因及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1267-1274. |
| [42] | 刘勇, 杨庆坤, 郭福生, 等. 赣南大洲塘中生代高镁安山岩地球化学特征及年代学意义[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 46(1): 48-60. |
| [43] | ROSE-KOGA E F, BOUVIER A S, GAETANI G A, et al. Silicate melt inclusions in the new millennium: A review of recommended practices for preparation, analysis, and data presentation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 570: 1-26. |
| [1] | 刘子安, 王达, 马国桃, 魏守才, 史功文, 贾蓝翔, 蒋成凯. 西藏扎西康锑铅锌银矿床金属硫化物微量元素特征及指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 115-132. |
| [2] | 刘富康, 郭颖, 赵贝, 刘美颖. 不同色调红宝石的致色成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(01): 158-166. |
| [3] | 贺婷婷, 杜利, 谈心, 刘均荣, 罗璐, 章惠, 李昊. 开封坳陷中牟凹陷馆陶组砂岩热储地热系统成因模式及开发潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(06): 1557-1570. |
| [4] | 李小冬, 李志军, 李熹微, 马学峰, 李晓燕, 陈柯童, 张霁潮, 许梦婷, 张瑞雪, 秦梦华, 王成云, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩, 李素梅. 冀中坳陷保定凹陷清苑构造带低熟油成因解析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1338-1353. |
| [5] | 邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 黄太明, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1354-1369. |
| [6] | 周游, 李斌, 吴中海, 左嘉梦, 邹任洲, 郑丽萍. 川西龙门山前陆盆地南段前缘砾石层成因及青衣江演化过程:基于宇宙成因核素26Al/10Be埋藏年龄[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 1121-1133. |
| [7] | 王佳新, 焦建刚, 马云飞, 李峰, 高超. 内蒙古中部乌兰陶勒盖铜镍矿床形成时代与岩浆源区[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 991-1012. |
| [8] | 王金雨, 刘永顺, 潘美慧, 聂保锋, 邹望, 路智, 张心怡. 黑龙江五大连池火山群的地貌形态和分形特征及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 793-806. |
| [9] | 王亿, 李立兴, 李厚民, 李小赛, 马兰晶, 邢玉亮, 孙欣宇, 戴阳, 王小慧. 冀北招兵沟铁磷矿床成矿时代及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 46-55. |
| [10] | 侯婷婷, 姚玉增, 付建飞, 刘静, 张永利, 郭荣荣. 辽宁弓长岭富铁矿成矿过程元素迁移特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 56-67. |
| [11] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [12] | 胡生平, 韩善楚, 张洪求, 张勇, 潘家永, 钟福军, 卢建研, 李惟鑫. 庐枞盆地西湾铅锌矿床黄铁矿微量元素组成特征及成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 183-197. |
| [13] | 刘金波, 张德贤, 胡子奇, 陈绍炜, 谢小雨. 豫西熊耳山蒿坪沟Ag-Au-Pb-Zn多金属矿床闪锌矿矿物学和微量元素组成特征及其成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 198-213. |
| [14] | 周小蓉, 陈石, 张新顺, 丁宝通, 宋兴国, 潘楚琦, 彭梓俊. 南乍得盆地Doseo坳陷背形负花状构造成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1146-1154. |
| [15] | 于景维, 丁韦, 张欣, 祁利祺, 黄舒雅, 张智越, 张以勒. 准噶尔盆地AH5井区八道湾组碳酸盐胶结物成因及对储层影响分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1336-1344. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||