



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (05): 1354-1369.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.116
邓硕1,2( ), 李素梅1,2(
), 李素梅1,2( ), 曹敬涛3, 黄太明3, 刘佳1,2, 张建淼1,2, 施倩倩1,2
), 曹敬涛3, 黄太明3, 刘佳1,2, 张建淼1,2, 施倩倩1,2
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-11-13
通信作者:
李素梅,女,研究员,1968年出生,主要从事油气地质地球化学研究工作。Email: smli@cup.edu.cn。作者简介:邓硕,男,博士研究生,1990年出生,主要从事油气地质地球化学研究工作。Email: ds901007@163.com。
基金资助:
DENG Shuo1,2( ), LI Sumei1,2(
), LI Sumei1,2( ), CAO Jingtao3, HUANG Taiming3, LIU Jia1,2, ZHANG Jianmiao1,2, SHI Qianqian1,2
), CAO Jingtao3, HUANG Taiming3, LIU Jia1,2, ZHANG Jianmiao1,2, SHI Qianqian1,2
Published:2024-10-10
Online:2024-11-13
摘要:
辽河西部凹陷低熟油资源丰富,不同类型稠油的成因机制差异尚不清楚,解决上述问题对辽河稠油的勘探工作具有指导意义。本文采用色谱/质谱(GC/MS)结合傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱(FT-ICR MS)技术对辽河西部凹陷北部高升和牛心坨油田低熟油的特征及其成因机制进行研究。高升原油形成于强还原咸水水体,有机质为菌藻类低等生物与陆源的双重贡献。牛心坨原油形成于还原性半咸水水体,有机质来源为低等微生物和陆源有机质双重输入,具有高蜡特征。成熟度参数表明二者均为低熟油。两种低熟油中均检测到N1、N1O1、N1O2、O1、O2、O3、O4化合物,高升低熟油以N1类为主,牛心坨低熟油以O2类为主;前者富含脂肪酸和藿烷酸,后者富含脂肪酸,藿烷酸含量较低,反映两种原油成因机制的差异。高升低熟油中大量的藿烷酸表明其生烃母质在早期成岩作用阶段经历了细菌改造作用,低熟油为细菌改造有机质低温生烃和藻类类脂低温生烃混合成因机制。牛心坨低熟油富含脂肪酸和高等植物蜡质,成因机制为生物类脂物早期低温生烃。两种低熟油的成因机制,为低熟油成因理论提供了研究方法,有助于完善低熟油成因理论并指导类似盆地低熟油油气勘探。
中图分类号:
邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 黄太明, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1354-1369.
DENG Shuo, LI Sumei, CAO Jingtao, HUANG Taiming, LIU Jia, ZHANG Jianmiao, SHI Qianqian. High-Resolution Mass Spectrum Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Low Maturity Oil in the Liaohe Western Depression[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1354-1369.

图1 辽河西部凹陷构造位置图(a)、构造特征示意图(b)和构造剖面图(c)
Fig.1 Structural location map of the Western Liaohe Depression (a), comprehensive map of structural characteristics (b), and structural section (c)
| 井号 | 油田 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | 降解 程度 | 密度 (g/cm3) | 黏度 (mPa·s) | 凝固点 (℃) | 含蜡量 (%) | 含硫量 (%) | 饱和烃 (%) | 芳烃 (%) | 非烃 (%) | 沥青质 (%) | 非烃+ 沥青质(%) | 饱/芳 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z17-23 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1753.00 | 未 | 0.89 | 414 | 31 | 11.45 | 0.48 | 35.90 | 20.70 | 28.60 | 14.90 | 43.50 | 1.58 |
| G1-5-13 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1337.00 | 轻微 | 0.90 | 1935 | 26 | 10.00 | 0.63 | 37.80 | 18.50 | 26.80 | 16.90 | 43.70 | 2.04 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1788.00 | 中等 | 0.94 | 3524 | 6 | 5.10 | 0.53 | 27.50 | 21.10 | 29.30 | 22.10 | 51.40 | 1.31 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1641.95 | 中等 | 0.93 | 2585 | 9 | 6.68 | 0.51 | 24.00 | 19.60 | 30.90 | 25.50 | 56.40 | 1.23 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | Es4下 | 1909.55 | 未 | 0.88 | 1178 | 39 | 13.43 | 0.40 | 37.80 | 17.20 | 24.80 | 20.20 | 45.00 | 2.20 |
| T35-29 | 牛心坨 | 潜山 | 2170.00 | 未 | - | - | - | - | - | 37.25 | 9.02 | 40.39 | 13.33 | 53.73 | 4.13 |
表1 原油物理性质与族组分组成[7]
Table 1 Physical properties and group composition of oils from Gaosheng and Niuxintuo[7]
| 井号 | 油田 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | 降解 程度 | 密度 (g/cm3) | 黏度 (mPa·s) | 凝固点 (℃) | 含蜡量 (%) | 含硫量 (%) | 饱和烃 (%) | 芳烃 (%) | 非烃 (%) | 沥青质 (%) | 非烃+ 沥青质(%) | 饱/芳 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z17-23 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1753.00 | 未 | 0.89 | 414 | 31 | 11.45 | 0.48 | 35.90 | 20.70 | 28.60 | 14.90 | 43.50 | 1.58 |
| G1-5-13 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1337.00 | 轻微 | 0.90 | 1935 | 26 | 10.00 | 0.63 | 37.80 | 18.50 | 26.80 | 16.90 | 43.70 | 2.04 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1788.00 | 中等 | 0.94 | 3524 | 6 | 5.10 | 0.53 | 27.50 | 21.10 | 29.30 | 22.10 | 51.40 | 1.31 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1641.95 | 中等 | 0.93 | 2585 | 9 | 6.68 | 0.51 | 24.00 | 19.60 | 30.90 | 25.50 | 56.40 | 1.23 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | Es4下 | 1909.55 | 未 | 0.88 | 1178 | 39 | 13.43 | 0.40 | 37.80 | 17.20 | 24.80 | 20.20 | 45.00 | 2.20 |
| T35-29 | 牛心坨 | 潜山 | 2170.00 | 未 | - | - | - | - | - | 37.25 | 9.02 | 40.39 | 13.33 | 53.73 | 4.13 |
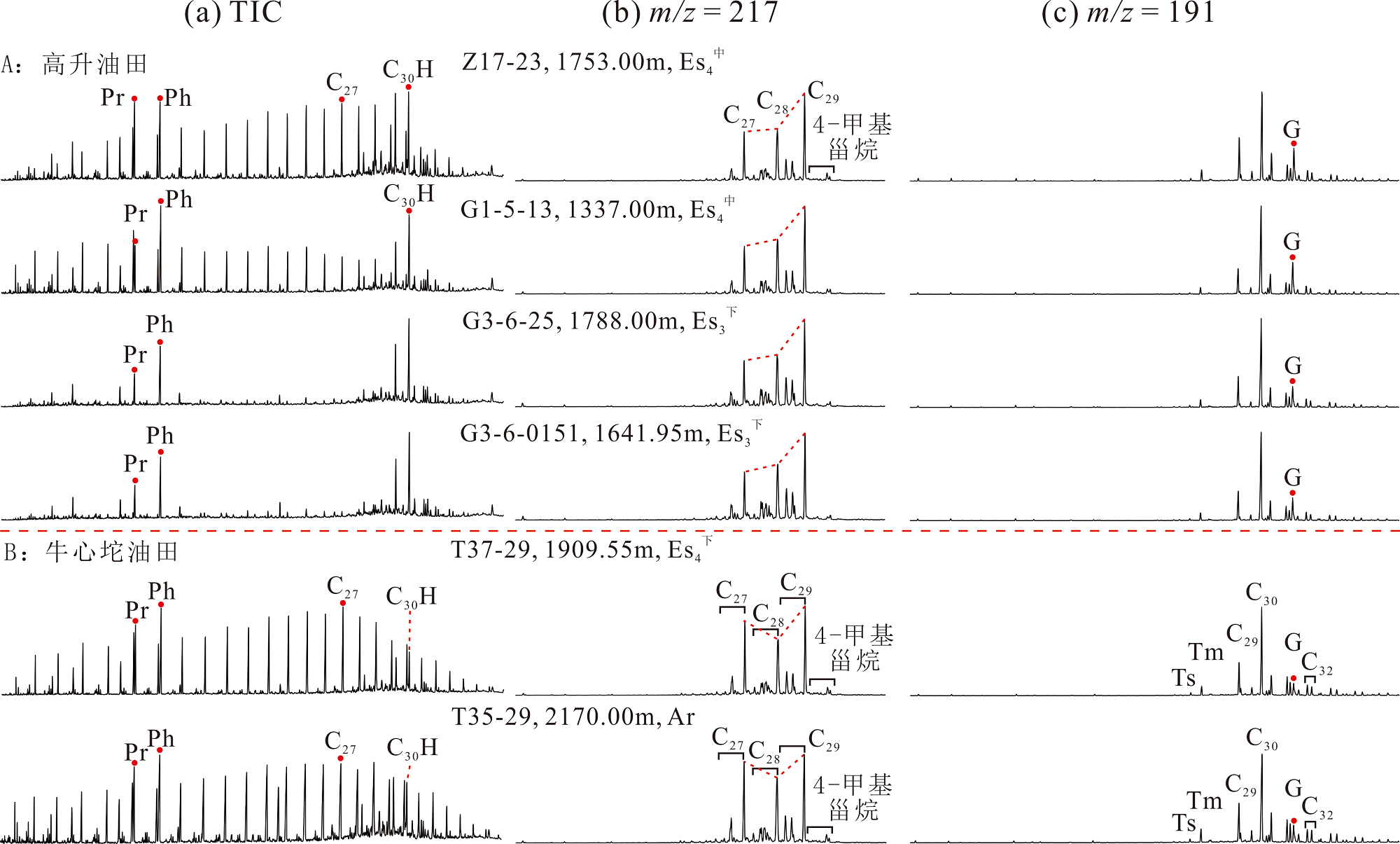
图2 原油饱和烃总离子流图(a)、m/z =217质量色谱图(b)和 m/z =191质量色谱图(c)
Fig.2 TIC (a), m/z=217 (b) and m/z=191 (c) mass chromatograms of saturated hydrocarbon fractions from selected oils
| 井号 | 深度 (m) | Pr/ Ph | Pr/ C17 | Ph/ C18 | CPI | OEP | C27 (%) | C28 (%) | C29 (%) | C27/C29 规则 甾烷 | 4-甲基 甾烷/ C29规 则甾烷 | 伽马蜡 烷/C30 藿烷 | 甾烷/ 藿烷 | C29甾烷 20S/ (S+R) | C29甾烷 αββ/ (ααα+ αββ) | C21+22/ C29 甾烷 | 三环萜 烷/五环 萜烷 | DBT/ P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z17-23 | 1753.00 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 2.28 | 1.21 | 21.86 | 35.49 | 42.65 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.13 |
| G1-5-13 | 1337.00 | 0.52 | 0.77 | 2.47 | - | - | 22.06 | 37.19 | 40.75 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.10 |
| G3-6-25 | 1788.00 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 24.29 | - | - | 22.98 | 36.80 | 40.22 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| G3-6-0151 | 1641.95 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 18.77 | - | - | 22.90 | 36.64 | 40.46 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| T37-29 | 1909.55 | 0.78 | 1.22 | 1.98 | 2.43 | 1.34 | 33.60 | 29.89 | 36.51 | 0.92 | 0.47 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| T35-29 | 2170.00 | 0.71 | 1.24 | 2.17 | 2.36 | 1.31 | 28.65 | 35.90 | 35.45 | 0.81 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.86 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.16 |
表2 高升、牛心坨原油常规地球化学参数
Table 2 Basic geochemical parameters of oils from Gaosheng and Niuxintuo
| 井号 | 深度 (m) | Pr/ Ph | Pr/ C17 | Ph/ C18 | CPI | OEP | C27 (%) | C28 (%) | C29 (%) | C27/C29 规则 甾烷 | 4-甲基 甾烷/ C29规 则甾烷 | 伽马蜡 烷/C30 藿烷 | 甾烷/ 藿烷 | C29甾烷 20S/ (S+R) | C29甾烷 αββ/ (ααα+ αββ) | C21+22/ C29 甾烷 | 三环萜 烷/五环 萜烷 | DBT/ P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z17-23 | 1753.00 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 2.28 | 1.21 | 21.86 | 35.49 | 42.65 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.13 |
| G1-5-13 | 1337.00 | 0.52 | 0.77 | 2.47 | - | - | 22.06 | 37.19 | 40.75 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.10 |
| G3-6-25 | 1788.00 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 24.29 | - | - | 22.98 | 36.80 | 40.22 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| G3-6-0151 | 1641.95 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 18.77 | - | - | 22.90 | 36.64 | 40.46 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| T37-29 | 1909.55 | 0.78 | 1.22 | 1.98 | 2.43 | 1.34 | 33.60 | 29.89 | 36.51 | 0.92 | 0.47 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| T35-29 | 2170.00 | 0.71 | 1.24 | 2.17 | 2.36 | 1.31 | 28.65 | 35.90 | 35.45 | 0.81 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.86 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.16 |
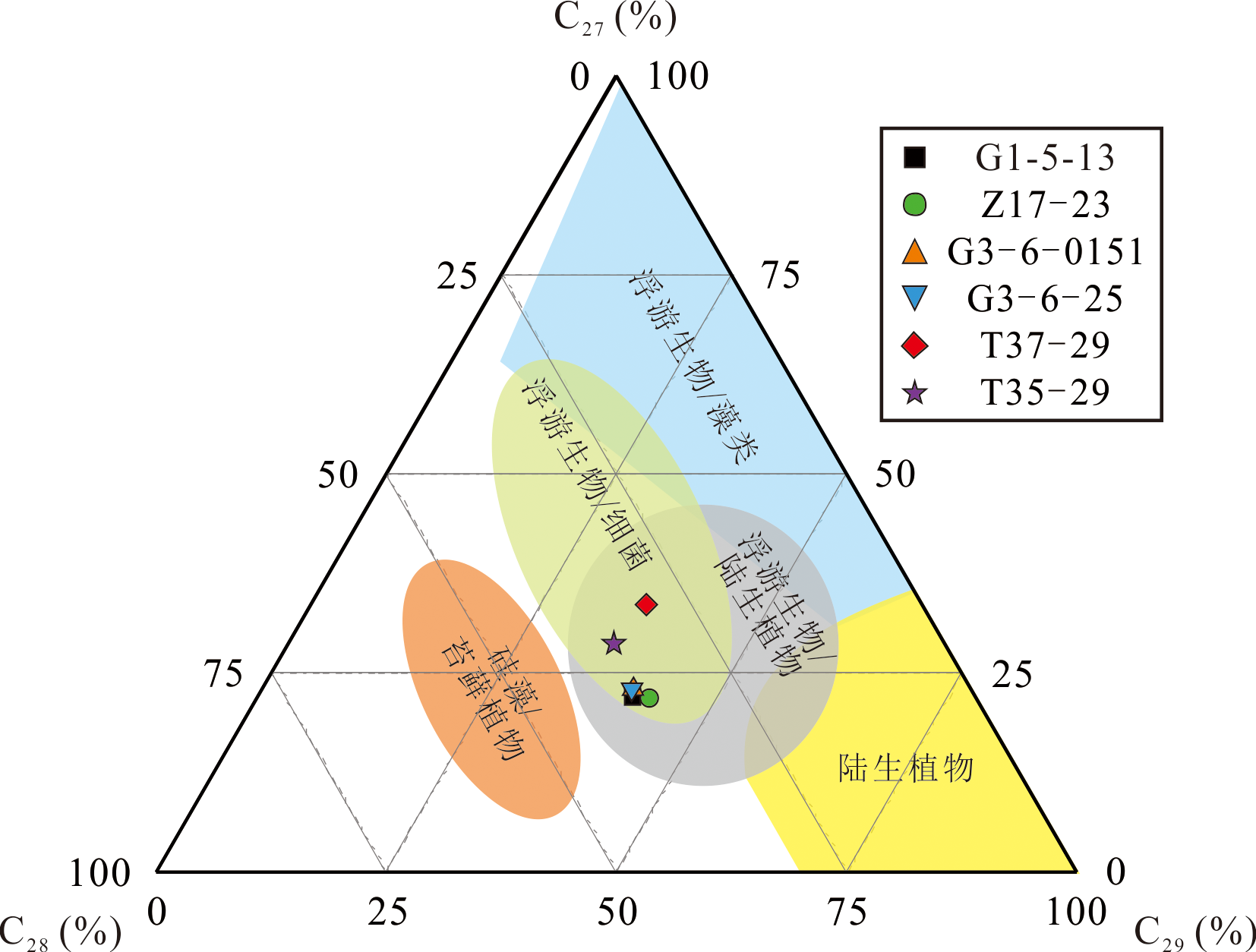
图4 高升、牛心坨原油C27-C28-C29规则甾烷三角图[27]
Fig.4 Ternary plot showing the relative distribution of C27, C28 and C29 steranes in the oils from Gaosheng and Niuxintuo[27]
| 井号 | N1 (%) | N1O1 (%) | N1O2 (%) | O1 (%) | O2 (%) | O3 (%) | O4 (%) | N1 (%) | O1 (%) | O2 (%) | A | B | C | D | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBE9 | DBE12 | DBE15 | DBE4 | DBE5 | DBE1 | DBE5 | DBE6 | ||||||||||||||
| Z17-23 | 40.86 | 6.99 | 5.82 | 25.79 | 19.83 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 22.34 | 14.19 | 5.25 | 37.20 | 20.61 | 34.20 | 15.34 | 11.64 | 1.38 | 1.04 | 0.24 | 0.75 | ||
| G1-5-13 | 36.07 | 3.60 | 3.72 | 21.78 | 27.87 | 6.29 | 0.67 | 19.80 | 12.15 | 4.77 | 44.21 | 19.07 | 22.15 | 17.73 | 14.41 | 0.73 | 1.08 | 0.32 | 0.93 | ||
| G3-6-25 | 54.22 | 5.76 | 2.23 | 23.11 | 14.12 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 17.50 | 12.62 | 5.84 | 34.36 | 19.36 | 19.80 | 17.27 | 14.21 | 0.73 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 0.90 | ||
| G3-6-0151 | 50.46 | 4.42 | 1.49 | 22.45 | 20.06 | 0.00 | 1.12 | 17.73 | 12.64 | 5.70 | 36.74 | 19.43 | 34.24 | 14.50 | 11.24 | 1.45 | 1.52 | 0.51 | 1.04 | ||
| T37-29 | 23.32 | 6.72 | 7.04 | 18.98 | 35.79 | 6.17 | 1.99 | 28.23 | 14.84 | 4.66 | 46.67 | 18.40 | 48.21 | 21.75 | 7.34 | 1.75 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 1.76 | ||
| T35-29 | 17.62 | 1.15 | 0.45 | 16.01 | 63.92 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 30.69 | 12.45 | 3.49 | 61.03 | 18.07 | 85.16 | 3.38 | 2.75 | 13.41 | 0.80 | 1.08 | 1.86 | ||
表3 高升、牛心坨原油负离子ESI FT-ICR MS参数
Table 3 Basic parameters of Gaosheng and Niuxintuo crude oil analyzed by negative-ion ESI FT-ICR MS
| 井号 | N1 (%) | N1O1 (%) | N1O2 (%) | O1 (%) | O2 (%) | O3 (%) | O4 (%) | N1 (%) | O1 (%) | O2 (%) | A | B | C | D | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBE9 | DBE12 | DBE15 | DBE4 | DBE5 | DBE1 | DBE5 | DBE6 | ||||||||||||||
| Z17-23 | 40.86 | 6.99 | 5.82 | 25.79 | 19.83 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 22.34 | 14.19 | 5.25 | 37.20 | 20.61 | 34.20 | 15.34 | 11.64 | 1.38 | 1.04 | 0.24 | 0.75 | ||
| G1-5-13 | 36.07 | 3.60 | 3.72 | 21.78 | 27.87 | 6.29 | 0.67 | 19.80 | 12.15 | 4.77 | 44.21 | 19.07 | 22.15 | 17.73 | 14.41 | 0.73 | 1.08 | 0.32 | 0.93 | ||
| G3-6-25 | 54.22 | 5.76 | 2.23 | 23.11 | 14.12 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 17.50 | 12.62 | 5.84 | 34.36 | 19.36 | 19.80 | 17.27 | 14.21 | 0.73 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 0.90 | ||
| G3-6-0151 | 50.46 | 4.42 | 1.49 | 22.45 | 20.06 | 0.00 | 1.12 | 17.73 | 12.64 | 5.70 | 36.74 | 19.43 | 34.24 | 14.50 | 11.24 | 1.45 | 1.52 | 0.51 | 1.04 | ||
| T37-29 | 23.32 | 6.72 | 7.04 | 18.98 | 35.79 | 6.17 | 1.99 | 28.23 | 14.84 | 4.66 | 46.67 | 18.40 | 48.21 | 21.75 | 7.34 | 1.75 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 1.76 | ||
| T35-29 | 17.62 | 1.15 | 0.45 | 16.01 | 63.92 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 30.69 | 12.45 | 3.49 | 61.03 | 18.07 | 85.16 | 3.38 | 2.75 | 13.41 | 0.80 | 1.08 | 1.86 | ||
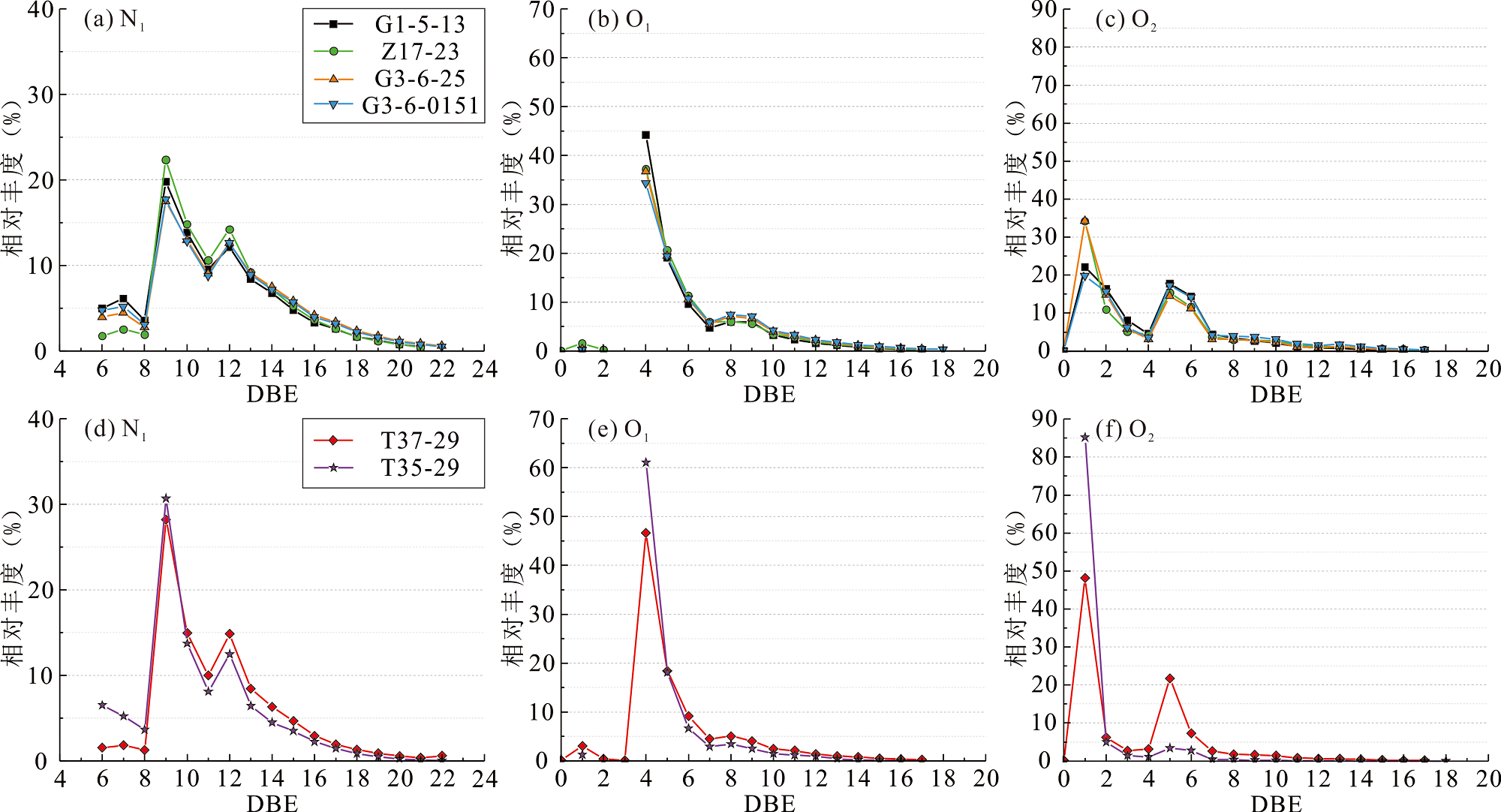
图6 原油中N1、O1和O2类化合物DBE的分布特征
Fig.6 Relative abundance of N1, O1 and O2 class species with various DBE values in the crude oils detected by negative-ion ESI FT-ICR MS

图7 原油中N1类化合物碳数、DBE及其强度关系(左)和原油中不同DBE系列的N1类化合物碳数分布特征(右)
Fig.7 Plots of DBE versus carbon number for N1 class species for the selected oils (left), and carbon curve of N1 class species with DBE=9, 12 and 15 in the selected oils (right)

图8 原油中O1类化合物碳数、DBE及其强度关系(左)和原油中不同DBE系列(DBE为4和5)的O1类化合物碳数分布特征(右)
Fig.8 Plots of DBE versus carbon number for O1 class species in the selected oils (left), and carbon curve of O1 class species with DBE=4 and 5 in the selected oils (right)

图9 原油中O2类化合物碳数、DBE及其强度关系(左)和原油中不同DBE系列(DBE为1、5和6)的O2类化合物碳数分布特征(右)
Fig.9 Plots of DBE versus carbon number for O2 class species in the selected oils (left), and carbon curve of O2 class species with DBE=1, 5 and 6 in the selected oils (right)

图10 基于负离子ESI FT-ICR MS的参数与常规地球化学参数的相互关系
Fig.10 Cross plots of negative-ion ESI FT-ICR MS indices for condensation of O2 species versus GC-MS parameters for the oils
| [1] | 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 金之钧, 等. 未熟-低熟油研究现状与存在的问题[J]. 地质论评, 2003, 49(3): 298-304. |
| [2] | 毛光周, 刘池洋, 高丽华. 中国未熟-低熟油的基本特征及成因[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 31(6): 76-85. |
| [3] | 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 候读杰, 等. 中国低熟油的几种成因机制[J]. 沉积学报, 1997(2): 75-83. |
| [4] |
黄第藩, 李晋超. 陆相沉积中的未熟石油及其意义[J]. 石油学报, 1987, 8(1): 1-9.
DOI |
| [5] | 葛海霞, 张枝焕, 闵伟, 等. 济阳坳陷青东凹陷低熟油生烃机理研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1105-1114. |
| [6] | 史建南, 邹华耀, 郝芳. 辽河坳陷西部凹陷低熟油成藏机理[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2007, 14(1): 36-39. |
| [7] | 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 高先志, 等. 辽河西部凹陷稠油成因机制[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2008, 38(增): 138-49. |
| [8] | LI S M, PANG X Q, SHI Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics of crude oils from the Tarim Basin by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2011, 29(6): 711-741. |
| [9] | 李素梅, 孟祥兵, 张宝收, 等. 傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱的地球化学意义及其在油气勘探中的应用前景[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1): 124-132. |
| [10] | 李素梅, 徐田武, 史权, 等. 东濮凹陷盐湖相原油氮/氧化合物分布特征及其应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(6): 1137-1150. |
| [11] | 李素梅, 张宝收, 张海祖, 等. 塔中原油超高二苯并噻吩硫特征及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(6): 1108-1120. |
| [12] | 朱芳冰. 辽河盆地西部凹陷源岩特征及低熟油分布规律研究[J]. 地球科学, 2002, 27(1): 25-29. |
| [13] | 史权, 张亚和, 徐春明, 等. 石油组分高分辨质谱分析进展与展望[J]. 中国科学(化学), 2014, 44(5): 694-700. |
| [14] | 漆家福, 邓荣敬, 周心怀, 等. 渤海海域新生代盆地中的郯庐断裂带构造[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2008, 38(增): 19-29. |
| [15] | 漆家福, 李晓光, 于福生, 等. 辽河西部凹陷新生代构造变形及“郯庐断裂带” 的表现[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2013, 43(8): 1324-1337. |
| [16] | 李明刚, 漆家福, 童亨茂, 等. 辽河西部凹陷新生代断裂构造特征与油气成藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(3): 281-288. |
| [17] | 冷济高, 庞雄奇, 李晓光, 等. 辽河断陷西部凹陷油气成藏主控因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, 10(5): 473-480. |
| [18] | 胡英杰, 王延山, 黄双泉, 等. 辽河坳陷石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 43-54. |
| [19] |
王延山, 胡英杰, 黄双泉, 等. 渤海湾盆地辽河坳陷天然气地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(10): 1422-1432.
DOI |
| [20] | 惠沙沙, 庞雄奇, 柳广弟, 等. 辽河西部凹陷沙河街组烃源岩特征及油源精细对比[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(8): 3081-3098. |
| [21] | 周晓龙. 辽河西部凹陷雷家—高升地区原油物性特征及影响因素[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2017, 31(1): 22-25. |
| [22] | 李秀娟. 国内外稠油资源的分类评价方法[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2008, 34(21): 61-62. |
| [23] | PETERS K E, WALTERS CC, MOLDOWAN J M. The Biomarker Guide[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. |
| [24] |
SINNINGHE DAMSTE J S, KENIG F, KOOPMANS M P, et al. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(9): 1895-1900.
PMID |
| [25] | CONNAN J, CASSOU A M. Properties of gases and petroleum liquids derived from terrestrial kerogen at various maturation levels[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(1): 1-23. |
| [26] | HUGHES W B, HOLBA A G, DZOU L I P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3581-3598. |
| [27] | HUANG W Y, MEINSCHEIN W G. Sterols as ecological indicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(5): 739-745. |
| [28] | HUGHEY C A, RODGERS R P, MARSHALL A G, et al. Identification of acidic NSO compounds in crude oils of different geochemical origins by negative ion electrospray Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(7): 743-759. |
| [29] | HUGHEY C A, RODGERS R P, MARSHALL A G, et al. Acidic and neutral polar NSO compounds in Smackover oils of different thermal maturity revealed by electrospray high field Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(7): 863-880. |
| [30] | QIAN K N, ROBBINS W K, HUGHEY C A, et al. Resolution and identification of elemental compositions for more than 3000 crude acids in heavy petroleum by negative-ion microelectrospray high-field Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2001, 15(6): 1505-1511. |
| [31] | JI H, LI S M, GREENWOOD P, et al. Geochemical characteristics and significance of heteroatom compounds in lacustrine oils of the Dongpu Depression (Bohai Bay Basin, China) by negative-ion Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 568-591. |
| [32] | CLEGG H, WILKES H, HORSFIELD B. Carbazole distributions in carbonate and clastic source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(24): 5335-5345. |
| [33] |
张宝, 包建平. 有机含氮化合物研究新进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2004, 15(2): 182-186.
DOI |
| [34] | 李素梅, 王铁冠, 张爱云, 等. 原油中吡咯类化合物的地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(2): 312. |
| [35] | WAN Z H, LI S M, PANG X Q, et al. Characteristics and geochemical significance of heteroatom compounds in terrestrial oils by negative-ion electrospray Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 111: 34-55. |
| [36] | KIM S, STANFORD L A, RODGERS R P, et al. Microbial alteration of the acidic and neutral polar NSO compounds revealed by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(8): 1117-1134. |
| [37] | LIAO Y H, SHI Q, HSU C S, et al. Distribution of acids and nitrogen-containing compounds in biodegraded oils of the Liaohe Basin by negative ion ESI FT-ICR MS[J]. Organic Geoche-mistry, 2012, 47: 51-65. |
| [38] | LIU Y, WAN Y Y, ZHU Y J, et al. Impact of biodegradation on polar compounds in crude oil: Comparative simulation of biodegradation from two aerobic bacteria using ultrahigh-resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(5): 5553-5565. |
| [39] | BAKR M M Y, WILKES H. The influence of facies and depositional environment on the occurrence and distribution of carbazoles and benzocarbazoles in crude oils: A case study from the Gulf of Suez, Egypt[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(5): 561-580. |
| [40] | ZHANG C M, ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG M, et al. Carbazole distributions in rocks from non-marine depositional environments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2008, 39(7): 868-878. |
| [41] | SCHIMMELMANN A, WINTSCH R, LEWAN M. From mo-dern chitin to thermally mature kerogen: Lessons from nitrogen isotope ratios[M]// Proceedings of the Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society. Washington: Amer Chemical Soc,20036. |
| [42] | LI M W, FOWLER M G, OBERMAJER M, et al. Geochemical characterisation of Middle Devonian oils in NW Alberta, Canada: Possible source and maturity effect on pyrrolic nitrogen compounds[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1999, 30(9): 1039-1057. |
| [43] | LI M W, LARTER S R, STODDART D, et al. Fractionation of pyrrolic nitrogen compounds in petroleum during migration: Deri-vation of migration-related geochemical parameters[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1995, 86(1): 103-123. |
| [44] | SNYDER L R. Distribution of benzcarbazole isomers in petro-leum as evidence for their biogenic origin[J]. Nature, 1965, 205: 277. |
| [45] | BENNETT B, CHEN M, BRINCAT D, et al. Fractionation of benzocarbazoles between source rocks and petroleums[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(5): 545-559. |
| [46] | SHI Q, HOU D J, CHUNG K H, et al. Characterization of heteroatom compounds in a crude oil and its saturates, aroma-tics, resins, and asphaltenes (SARA) and non-basic nitrogen fractions analyzed by negative-ion electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(4): 2545-2553. |
| [47] | SHI Q, ZHAO S Q, XU Z M, et al. Distribution of acids and neutral nitrogen compounds in a Chinese crude oil and its fractions: Characterized by negative-ion electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(7): 4005-4011. |
| [48] | POETZ S, HORSFIELD B, WILKES H. Maturity-driven generation and transformation of acidic compounds in the organic-richposidonia shale as revealed by electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(8): 4877-4888. |
| [49] | KAMGA A W, BEHAR F, HATCHER P G. Quantitative ana-lysis of long chain fatty acids present in a type I kerogen using electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: Compared with BF3/MeOH methylation/GC-FID[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2014, 25(5): 880-890. |
| [50] | AMRANI A, AIZENSHTAT Z. Photosensitized oxidation of naturally occurring isoprenoid allyl alcohols as a possible pathway for their transformation to thiophenes in sulfur rich depositional environments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(6): 693-712. |
| [51] | ROJAS-RUIZ F A, ORREGO-RUIZ J A. Distribution of oxygen-containing compounds and its significance on total organic acid content in crude oils by ESI negative ion FT-ICR MS[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(10): 8185-8191. |
| [52] | LIU W M, LIAO Y H, PAN Y H, et al. Use of ESI FT-ICR MS to investigate molecular transformation in simulated aerobic biodegradation of a sulfur-rich crude oil[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 123: 17-26. |
| [53] | HEADLEY J V, PERU K M, BARROW M P. Advances in mass spectrometric characterization of naphthenic acids fraction compounds in oil sands environmental samples and crude oil—a review[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2016, 35(2): 311-328. |
| [54] | 段毅, 周世新, 孟自芳. 塔里木盆地群5井和曲1井原油的油源研究——脂肪酸及烷基环己烷系列化合物提供的新证据[J]. 石油实验地质, 2001(4): 433-447. |
| [55] | PAN Y H, LIAO Y H, SHI Q, et al. Acidic and neutral polar NSO compounds in heavily biodegraded oils characterized by negative-ion ESI FT-ICR MS[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(6): 2960-2973. |
| [56] | MARTINS L L, PUDENZI M A, DA CRUZ G F, et al. Asses-sing biodegradation of Brazilian crude oils via characteristic profiles of O1 and O2 compound classes: Petroleomics by negative-ion mode electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(7): 6649-6657. |
| [57] | BOON A R, DUINEVELD G C A. Phytopigments and fatty acids as molecular markers for the quality of near-bottom particulate organic matter in the North Sea[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 1996, 35(4): 279-291. |
| [58] | VOLKMAN J K, BARRETT S M, BLACKBURN S I, et al. Microalgal biomarkers: A review of recent research developments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(5/6/7): 1163-1179. |
| [59] | MEYERS P A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanogra-phic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 27(5/6): 213-250. |
| [60] | SINNINGHE DAMSTÉ J S, VERSCHUREN D, OSSEBAAR J, et al. A 25,000-year record of climate-induced changes in lowland vegetation of eastern equatorial Africa revealed by the stable carbon-isotopic composition of fossil plant leaf waxes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 302(1/2): 236-246. |
| [61] | TIERNEY J E, RUSSELL J M, SINNINGHE DAMSTÉ J S, et al. Late Quaternary behavior of the East African monsoon and the importance of the Congo Air Boundary[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(7/8): 798-807. |
| [62] | OLDENBURG T B P, BROWN M, BENNETT B, et al. The impact of thermal maturity level on the composition of crude oils, assessed using ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 75: 151-168. |
| [63] | HOSSEINI S H, HORSFIELD B, POETZ S, et al. Role of maturity in controlling the composition of solid bitumens in veins and vugs from SE Turkey as revealed by conventional and advanced geochemical tools[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(3): 2398-2413. |
| [64] | FARRIMOND P, GRIFFITHS T, EVDOKIADIS E. Hopanoic acids in Mesozoic sedimentary rocks[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(8): 965-977. |
| [65] | 任平. 高升—雷家地区未熟油藏形成条件分析[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2015, 29(2): 38-41. |
| [66] | 曲彦胜, 钟宁宁, 刘岩, 等. 辽河西部凹陷富有机质沉积识别及控制因素探讨[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 11(5): 18-22. |
| [67] | WATSON J S, JONES D M, SWANNELL R P J, et al. Formation of carboxylic acids during aerobic biodegradation of crude oil and evidence of microbial oxidation of hopanes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(10): 1153-1169. |
| [68] | 黄第藩, 张大江, 张林晔. 中国未成熟石油成因机制和成藏条件[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003. |
| [69] | LUCACH S O, BOWLER B F J, FREWIN N, et al. Variation in alkylphenol distributions in a homogenous oil suite from the Dhahaban petroleum system of Oman[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(5): 581-594. |
| [70] | 史继扬, 向明菊, 屈定创. 未熟-低熟烃源岩中脂肪酸的热模拟实验及演化[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(18): 1567-1572. |
| [71] | 张松林, 崔明中, 李振西, 等. 盐湖相低熟油脂肪酸的组成与分布特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 130-135. |
| [72] | SHI J Y, XIANG M J, QU D C. Simulation experiments for evolution of fatty acids in immature source rocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(24): 2092-2096. |
| [73] | TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer,1984. |
| [74] | WILSON H H. The case for early generation and accumulation of oil[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1990, 13(2): 127-156. |
| [75] | 屈定创, 史继扬, 向明菊. 一类新的藿烯化合物的发现及其在地质藿类成因上的意义[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1995, 25(6): 665-72. |
| [76] | NASCIMENTO L R, REBOUÇAS L M C, KOIKE L, et al. Acidic biomarkers from albacora oils, Campos Basin, Brazil[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1999, 30(9): 1175-1191. |
| [77] | INNES H E, BISHOP A N, HEAD I M, et al. Preservation and diagenesis of hopanoids in recent lacustrine sediments of Priest Pot, England[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 26(9/10): 565-576. |
| [78] | WATSON D F, FARRIMOND P. Novel polyfunctionalised geohopanoids in a recent lacustrine sediment (Priest Pot, UK)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(11): 1247-1252. |
| [79] | 管红香, 吴能友, 茅晟懿, 等. 南海北部冷泉碳酸盐岩中系列藿烷酸的检出及意义[J]. 地球科学, 2013, 38(5): 1014-1022. |
| [80] | 王广源, 周心怀, 王昕, 等. 蓬莱19-3/25-6油田未熟-低熟油特征与成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(2): 230-237. |
| [81] | LIU H, LIU W G. N-Alkane distributions and concentrations in algae, submerged plants and terrestrial plants from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 99: 10-22. |
| [1] | 李小冬, 李志军, 李熹微, 马学峰, 李晓燕, 陈柯童, 张霁潮, 许梦婷, 张瑞雪, 秦梦华, 王成云, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩, 李素梅. 冀中坳陷保定凹陷清苑构造带低熟油成因解析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1338-1353. |
| [2] | 王金雨, 刘永顺, 潘美慧, 聂保锋, 邹望, 路智, 张心怡. 黑龙江五大连池火山群的地貌形态和分形特征及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 793-806. |
| [3] | 周小蓉, 陈石, 张新顺, 丁宝通, 宋兴国, 潘楚琦, 彭梓俊. 南乍得盆地Doseo坳陷背形负花状构造成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1146-1154. |
| [4] | 曾帅, 马志刚, 赵聪, 杨磊, 张肃, 董继红, 梁京涛, 鄢圣武. 青藏高原东部大渡河流域太平桥乡古滑坡群复活特征多源遥感识别[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 994-1003. |
| [5] | 张银涛, 陈石, 刘强, 冯光, 谢舟, 梁鑫鑫, 李婷, 宋兴国, 康鹏飞, 彭梓俊. 塔里木盆地富满油田FⅠ19断裂发育特征及演化模式[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 283-295. |
| [6] | 唐名鹰, 华磊, 丁正江, 董振昆, 王炜晓, 翟孝志, 王汝杰, 郑成龙. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区乌腊德石墨矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1475-1485. |
| [7] | 黄少英, 宋兴国, 罗彩明, 能源, 马小丹, 漆家福, 陈石. 塔北隆起X型走滑断裂成因机制的新解释[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1797-1808. |
| [8] | 李杰豪, 侯读杰, 曹兰柱, 吴飘, 赵喆, 马潇潇. 二连盆地赛汉塔拉凹陷腾二段低熟油地球化学特征和油源对比[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 315-325. |
| [9] | 张薇, 王贵玲, 赵佳怡, 刘峰. 四川西部中高温地热流体地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 188-198. |
| [10] | 张江涛, 郭涛, 王冰洁, 李虹霖, 王茂桢. 渤海辽北地区新生代断裂特征及其演变过程[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1110-1118. |
| [11] | 李素梅, 徐田武, 史权, 张云献, 吴建勋, 柯昌炜. 东濮凹陷盐湖相原油氮/氧化合物分布特征及其应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1137-1150. |
| [12] | 徐田武, 李素梅, 张洪安, 张云献, 吴建勋, 史权, 陈湘飞, 纪红, 万中华. 东濮凹陷原油含硫化合物的分布特征及其应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 629-642. |
| [13] | 梁杰, 张向涛, 许新明, 罗泽, 吴静. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼古近系文昌组构造变形特征及成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 750-757. |
| [14] | 张洪安, 李素梅, 徐田武, 庞雄奇, 张云献, 万中华, 纪红. 东濮凹陷北部盐湖相原油特征与成因[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 768-778. |
| [15] | 葛海霞 ,张枝焕 ,闵伟 ,张琳璞 ,柳东 ,章成进. 济阳坳陷青东凹陷低熟油生烃机理研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1105-1114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||