



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (01): 188-198.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.015
收稿日期:2020-10-08
修回日期:2020-12-16
出版日期:2021-02-12
发布日期:2021-03-12
作者简介:张 薇,女,高级工程师,博士,1981年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事地热地质方面的研究。Email: 18879003@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Wei( ), WANG Guiling, ZHAO Jiayi, LIU Feng
), WANG Guiling, ZHAO Jiayi, LIU Feng
Received:2020-10-08
Revised:2020-12-16
Online:2021-02-12
Published:2021-03-12
摘要:
四川西部是我国主要的高温地热资源分布区之一,水热活动的时空分布、物质来源与深部水热岩作用密切相关,地热流体化学特征可反映流体上升至近地表过程中发生的深部地球化学过程信息。通过分析鲜水河地热带、甘孜-理塘地热带和金沙江地热带典型地热田的地热流体化学组分特征,认为研究区地下水类型基本为HCO3-Na型水。其中甘孜-理塘地热带地下热水中的K +、Na +、HCO3 -和Mg 2+与Cl -有相似物质来源,除了来自矿物溶解外,还来源于地球深部物质。研究区地热流体径流较长,深度为2 189.93~5 620.52 m,地热流体在上升过程中冷水混入比例为 56%~78%,水岩作用仍未达到平衡状态。在循环过程中,受到含钙、镁的硅酸盐矿物溶解的影响。厘清区域内地热流体汇聚的路径及其控制因素,提高对四川西部地区地热资源分布规律和成因的认识,可为区域内工程建设施工提供参考依据。
中图分类号:
张薇, 王贵玲, 赵佳怡, 刘峰. 四川西部中高温地热流体地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 188-198.
ZHANG Wei, WANG Guiling, ZHAO Jiayi, LIU Feng. Geochemical Characteristics of Medium-high Temperature Geothermal Fluids in West Sichuan and Their Geological Implications[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 188-198.

图1 研究区断裂构造、地热带分布及采样点位置示意图 (a)断裂构造;(b)金沙江地热带;(c)甘孜—理塘地热带;(d)鲜水河地热带
Fig.1 Fault structure, distribution of geothermal zone and location of sampling points in the study area
| 区域 | 编号 | 水温/℃ | pH | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl- | S | HC | TDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜水河 地热带 | KD01 | 68.0 | 6.8 | 31.00 | 320.00 | 86.17 | 23.32 | 85.10 | 19.04 | 1 159.30 | 1 268.20 |
| KD02 | 47.0 | 6.9 | 30.00 | 270.00 | 71.14 | 16.42 | 64.89 | 6.48 | 897.00 | 1 009.30 | |
| KD03 | 26.0 | 7.1 | 26.00 | 200.00 | 62.12 | 26.14 | 46.80 | 3.76 | 784.10 | 846.50 | |
| KD04 | 32.0 | 6.8 | 12.00 | 185.00 | 40.08 | 4.26 | 35.45 | 3.00 | 549.20 | 584.10 | |
| KD05 | 47.0 | 7.0 | 34.00 | 290.00 | 45.09 | 7.90 | 76.22 | 8.60 | 915.30 | 1 132.00 | |
| KD06 | 61.0 | 7.1 | 36.00 | 370.00 | 90.18 | 21.28 | 85.09 | 2.90 | 1 305.80 | 1 222.00 | |
| KD07 | 46.0 | 7.4 | 34.00 | 338.00 | 86.17 | 22.50 | 88.63 | 1.35 | 1 220.30 | 1 275.40 | |
| KD08 | 70.0 | 8.7 | 56.00 | 550.00 | 12.02 | 29.18 | 260.60 | <0.10 | 1 019.00 | 1 649.60 | |
| KD09 | 81.0 | 7.6 | 55.00 | 400.00 | 40.08 | 14.59 | 294.30 | 75.80 | 720.00 | 1 430.80 | |
| 甘孜—理塘 地热带 | LT10 | 54.0 | 8.2 | 1.92 | 53.57 | 3.92 | 0.18 | 7.00 | 16.50 | 128.10 | 202.80 |
| LT11 | 72.0 | 8.1 | 2.48 | 63.66 | 3.82 | 0.02 | 1.75 | 15.28 | 140.30 | 238.00 | |
| LT12 | 76.0 | 8.0 | 2.63 | 65.40 | 4.06 | 0.03 | 1.75 | 16.66 | 146.40 | 253.90 | |
| LT13 | 75.0 | 7.9 | 2.80 | 72.32 | 3.36 | 0.03 | 1.75 | 15.30 | 161.70 | 275.10 | |
| LT14 | 79.7 | 7.8 | 2.80 | 72.01 | 4.32 | 0.01 | 1.75 | 14.55 | 158.60 | 272.60 | |
| LT15 | 80.0 | 7.1 | 57.69 | 477.50 | 27.52 | 10.92 | 68.28 | 7.72 | 1 522.00 | 1 585.00 | |
| LT16 | 84.0 | 7.0 | 57.40 | 480.20 | 24.05 | 10.43 | 65.83 | 12.07 | 1 483.00 | 1 564.00 | |
| LT17 | 7.1 | 62.41 | 525.70 | 23.44 | 10.53 | 68.28 | 10.97 | 1 488.00 | 1 618.00 | ||
| LT18 | 56.0 | 6.8 | 53.60 | 443.60 | 29.66 | 12.93 | 61.97 | 10.41 | 1 327.00 | 1 442.00 | |
| LT19 | 64.0 | 6.7 | 54.57 | 446.60 | 29.79 | 12.97 | 59.52 | 11.00 | 1 422.00 | 1 469.00 | |
| 金沙江 地热带 | BT20 | 94.0 | 8.6 | 19.94 | 267.20 | 5.60 | 0.23 | 40.88 | 70.14 | 516.60 | 871.50 |
| BT21 | 88.0 | 9.3 | 29.86 | 333.20 | 1.02 | 0.06 | 17.77 | 28.81 | 319.80 | 992.30 | |
| BT22 | 90.0 | 9.3 | 29.98 | 324.80 | 2.06 | 0.08 | 47.99 | 52.71 | 418.80 | 1 047.00 | |
| BT23 | 89.0 | 9.2 | 34.53 | 358.90 | 1.34 | 0.02 | 19.19 | 32.84 | 379.10 | 1 079.00 | |
| BT24 | 81.0 | 9.3 | 29.81 | 317.00 | 0.81 | <0.013 | 39.10 | 30.17 | 365.00 | 991.20 | |
| BT25 | 90.0 | 8.4 | 27.62 | 290.80 | 4.02 | 0.21 | 42.65 | 42.06 | 617.50 | 909.00 | |
| BT26 | 88.0 | 9.4 | 30.48 | 321.80 | 0.69 | <0.013 | 51.54 | 27.50 | 209.70 | 1 065.00 | |
| BT27 | 91.0 | 9.6 | 31.36 | 335.80 | 0.80 | <0.013 | 51.54 | 46.19 | 190.10 | 1 105.00 | |
| BT28 | 89.0 | 9.0 | 28.86 | 343.80 | 0.65 | <0.013 | 51.90 | 25.45 | 428.00 | 1 041.00 | |
| BT29 | 48.0 | 8.4 | 2.60 | 104.50 | 9.34 | 0.70 | 8.89 | 16.33 | 226.20 | 332.10 | |
| BT30 | 53.0 | 8.3 | 2.41 | 90.24 | 11.61 | 0.81 | 8.89 | 20.74 | 217.00 | 305.50 | |
| BT31 | 64.0 | 7.8 | 6.21 | 124.80 | 16.30 | 0.35 | 16.00 | 25.46 | 314.90 | 476.60 | |
| BT32 | 75.0 | 7.5 | 6.69 | 128.90 | 17.11 | 0.39 | 13.86 | 23.52 | 342.40 | 483.20 | |
| BT33 | 86.0 | 8.2 | 26.00 | 353.20 | 6.41 | 2.92 | 33.77 | 19.47 | 679.30 | 1 071.00 | |
| BT34 | 90.0 | 9.1 | 26.23 | 351.60 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 23.10 | 20.30 | 114.30 | 1 039.00 | |
| BT35 | 90.0 | 7.8 | 26.80 | 358.20 | 1.67 | 0.20 | 33.77 | 42.62 | 885.90 | 1 071.00 | |
| BT36 | 90.0 | 8.0 | 25.24 | 345.20 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 33.06 | 42.09 | 862.10 | 1 033.00 | |
| BT37 | 70.0 | 7.6 | 30.51 | 380.40 | 7.77 | 2.51 | 32.70 | 25.90 | 1 015.00 | 1 179.00 |
表1 研究区地下水样的水化学参数
Table 1 Hydrochemical parameters of groundwater samples from the study area
| 区域 | 编号 | 水温/℃ | pH | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl- | S | HC | TDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜水河 地热带 | KD01 | 68.0 | 6.8 | 31.00 | 320.00 | 86.17 | 23.32 | 85.10 | 19.04 | 1 159.30 | 1 268.20 |
| KD02 | 47.0 | 6.9 | 30.00 | 270.00 | 71.14 | 16.42 | 64.89 | 6.48 | 897.00 | 1 009.30 | |
| KD03 | 26.0 | 7.1 | 26.00 | 200.00 | 62.12 | 26.14 | 46.80 | 3.76 | 784.10 | 846.50 | |
| KD04 | 32.0 | 6.8 | 12.00 | 185.00 | 40.08 | 4.26 | 35.45 | 3.00 | 549.20 | 584.10 | |
| KD05 | 47.0 | 7.0 | 34.00 | 290.00 | 45.09 | 7.90 | 76.22 | 8.60 | 915.30 | 1 132.00 | |
| KD06 | 61.0 | 7.1 | 36.00 | 370.00 | 90.18 | 21.28 | 85.09 | 2.90 | 1 305.80 | 1 222.00 | |
| KD07 | 46.0 | 7.4 | 34.00 | 338.00 | 86.17 | 22.50 | 88.63 | 1.35 | 1 220.30 | 1 275.40 | |
| KD08 | 70.0 | 8.7 | 56.00 | 550.00 | 12.02 | 29.18 | 260.60 | <0.10 | 1 019.00 | 1 649.60 | |
| KD09 | 81.0 | 7.6 | 55.00 | 400.00 | 40.08 | 14.59 | 294.30 | 75.80 | 720.00 | 1 430.80 | |
| 甘孜—理塘 地热带 | LT10 | 54.0 | 8.2 | 1.92 | 53.57 | 3.92 | 0.18 | 7.00 | 16.50 | 128.10 | 202.80 |
| LT11 | 72.0 | 8.1 | 2.48 | 63.66 | 3.82 | 0.02 | 1.75 | 15.28 | 140.30 | 238.00 | |
| LT12 | 76.0 | 8.0 | 2.63 | 65.40 | 4.06 | 0.03 | 1.75 | 16.66 | 146.40 | 253.90 | |
| LT13 | 75.0 | 7.9 | 2.80 | 72.32 | 3.36 | 0.03 | 1.75 | 15.30 | 161.70 | 275.10 | |
| LT14 | 79.7 | 7.8 | 2.80 | 72.01 | 4.32 | 0.01 | 1.75 | 14.55 | 158.60 | 272.60 | |
| LT15 | 80.0 | 7.1 | 57.69 | 477.50 | 27.52 | 10.92 | 68.28 | 7.72 | 1 522.00 | 1 585.00 | |
| LT16 | 84.0 | 7.0 | 57.40 | 480.20 | 24.05 | 10.43 | 65.83 | 12.07 | 1 483.00 | 1 564.00 | |
| LT17 | 7.1 | 62.41 | 525.70 | 23.44 | 10.53 | 68.28 | 10.97 | 1 488.00 | 1 618.00 | ||
| LT18 | 56.0 | 6.8 | 53.60 | 443.60 | 29.66 | 12.93 | 61.97 | 10.41 | 1 327.00 | 1 442.00 | |
| LT19 | 64.0 | 6.7 | 54.57 | 446.60 | 29.79 | 12.97 | 59.52 | 11.00 | 1 422.00 | 1 469.00 | |
| 金沙江 地热带 | BT20 | 94.0 | 8.6 | 19.94 | 267.20 | 5.60 | 0.23 | 40.88 | 70.14 | 516.60 | 871.50 |
| BT21 | 88.0 | 9.3 | 29.86 | 333.20 | 1.02 | 0.06 | 17.77 | 28.81 | 319.80 | 992.30 | |
| BT22 | 90.0 | 9.3 | 29.98 | 324.80 | 2.06 | 0.08 | 47.99 | 52.71 | 418.80 | 1 047.00 | |
| BT23 | 89.0 | 9.2 | 34.53 | 358.90 | 1.34 | 0.02 | 19.19 | 32.84 | 379.10 | 1 079.00 | |
| BT24 | 81.0 | 9.3 | 29.81 | 317.00 | 0.81 | <0.013 | 39.10 | 30.17 | 365.00 | 991.20 | |
| BT25 | 90.0 | 8.4 | 27.62 | 290.80 | 4.02 | 0.21 | 42.65 | 42.06 | 617.50 | 909.00 | |
| BT26 | 88.0 | 9.4 | 30.48 | 321.80 | 0.69 | <0.013 | 51.54 | 27.50 | 209.70 | 1 065.00 | |
| BT27 | 91.0 | 9.6 | 31.36 | 335.80 | 0.80 | <0.013 | 51.54 | 46.19 | 190.10 | 1 105.00 | |
| BT28 | 89.0 | 9.0 | 28.86 | 343.80 | 0.65 | <0.013 | 51.90 | 25.45 | 428.00 | 1 041.00 | |
| BT29 | 48.0 | 8.4 | 2.60 | 104.50 | 9.34 | 0.70 | 8.89 | 16.33 | 226.20 | 332.10 | |
| BT30 | 53.0 | 8.3 | 2.41 | 90.24 | 11.61 | 0.81 | 8.89 | 20.74 | 217.00 | 305.50 | |
| BT31 | 64.0 | 7.8 | 6.21 | 124.80 | 16.30 | 0.35 | 16.00 | 25.46 | 314.90 | 476.60 | |
| BT32 | 75.0 | 7.5 | 6.69 | 128.90 | 17.11 | 0.39 | 13.86 | 23.52 | 342.40 | 483.20 | |
| BT33 | 86.0 | 8.2 | 26.00 | 353.20 | 6.41 | 2.92 | 33.77 | 19.47 | 679.30 | 1 071.00 | |
| BT34 | 90.0 | 9.1 | 26.23 | 351.60 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 23.10 | 20.30 | 114.30 | 1 039.00 | |
| BT35 | 90.0 | 7.8 | 26.80 | 358.20 | 1.67 | 0.20 | 33.77 | 42.62 | 885.90 | 1 071.00 | |
| BT36 | 90.0 | 8.0 | 25.24 | 345.20 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 33.06 | 42.09 | 862.10 | 1 033.00 | |
| BT37 | 70.0 | 7.6 | 30.51 | 380.40 | 7.77 | 2.51 | 32.70 | 25.90 | 1 015.00 | 1 179.00 |
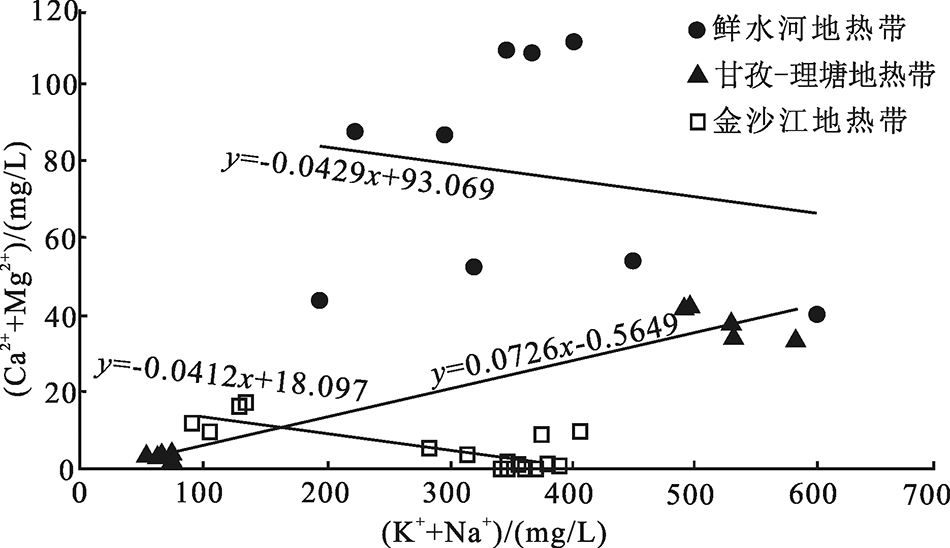
图4 研究区水样的(Ca2++Mg2+)与(K++Na+)阳离子交替吸附作用
Fig.4 Relations between(Ca2++Mg2+)and(K++Na+) cation alternation adsorption diagram of water samples from the study area
| 地理位置 | T石英(无损) | T石英(最大蒸汽损失) | T玉髓 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜水河地热带 | 121.75~172.27 | 119.65~161.85 | 93.49~150.00 |
| 甘孜—理塘地热带 | 101.85~132.36 | 102.59~128.64 | 71.92~105.14 |
| 金沙江地热带 | 98.81~185.92 | 99.96~173.00 | 68.66~165.74 |
表2 地球化学温标计算的热储温度(℃)
Table 2 Estimated temperatures of the geothermal reservoir (℃)
| 地理位置 | T石英(无损) | T石英(最大蒸汽损失) | T玉髓 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜水河地热带 | 121.75~172.27 | 119.65~161.85 | 93.49~150.00 |
| 甘孜—理塘地热带 | 101.85~132.36 | 102.59~128.64 | 71.92~105.14 |
| 金沙江地热带 | 98.81~185.92 | 99.96~173.00 | 68.66~165.74 |
| 温度/℃ | 焓/(J/g) | SiO2/(mg/L) | 温度/℃ | 焓/(J/g) | SiO2 /(mg/L) | 温度/℃ | 焓/(J/g) | SiO2/(mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 50.0 | 13.5 | 150 | 151.0 | 125.0 | 250 | 259.2 | 486.0 |
| 75 | 75.0 | 26.6 | 175 | 177.0 | 185.0 | 275 | 289.0 | 614.0 |
| 100 | 100.1 | 48.0 | 200 | 203.6 | 265.0 | 300 | 321.0 | 692.0 |
| 125 | 125.1 | 80.0 | 225 | 230.9 | 365.0 |
表3 温度、焓和SiO2含量的关系
Table 3 Relations between temperature, enthalpy and SiO2 content
| 温度/℃ | 焓/(J/g) | SiO2/(mg/L) | 温度/℃ | 焓/(J/g) | SiO2 /(mg/L) | 温度/℃ | 焓/(J/g) | SiO2/(mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 50.0 | 13.5 | 150 | 151.0 | 125.0 | 250 | 259.2 | 486.0 |
| 75 | 75.0 | 26.6 | 175 | 177.0 | 185.0 | 275 | 289.0 | 614.0 |
| 100 | 100.1 | 48.0 | 200 | 203.6 | 265.0 | 300 | 321.0 | 692.0 |
| 125 | 125.1 | 80.0 | 225 | 230.9 | 365.0 |
| 区域 | 冷水混入 比例/% | 循环深度范围/m | 混入前循环 深度/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜水河地热带 | 72~78 | 1 925.02~3 114.82 | 3 866.12~5 620.52 |
| 甘孜—理塘地热带 | 56~65 | 1 470.95~3 160.92 | 2 189.93~3 624.05 |
| 金沙江地热带 | 65~68 | 1 402.41~3 446.09 | 3 318.15~5 471.50 |
表4 研究区热循环深度计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of the thermal cycle depth in west Sichuan
| 区域 | 冷水混入 比例/% | 循环深度范围/m | 混入前循环 深度/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜水河地热带 | 72~78 | 1 925.02~3 114.82 | 3 866.12~5 620.52 |
| 甘孜—理塘地热带 | 56~65 | 1 470.95~3 160.92 | 2 189.93~3 624.05 |
| 金沙江地热带 | 65~68 | 1 402.41~3 446.09 | 3 318.15~5 471.50 |
| [1] | 沈照理. 水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985. |
| [2] | 任福弘, 沈照理. 水文地球化学: 中国大百科全书——地质学[M]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1993: 507-508. |
| [3] | 赵平, 金建, 张海政, 等. 西藏羊八井地热田热水的化学组成[J]. 地质科学, 1998,33(1):61-72. |
| [4] | 赵平, 多吉, 梁廷立, 等. 西藏羊八井地热田气体地球化学特征[J]. 科学通报, 1998,43(7):691-696. |
| [5] | 赵平, KENNEDY Mack, 多吉, 等. 西藏羊八井热田地热流体成因及演化的惰性气体制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2001,17(3):497-503. |
| [6] | 刘虹, 张国平, 金志升, 等. 云南腾冲地区地热流体的地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2009,29(4):496-501. |
| [7] | 张萌, 蔺文静, 刘昭, 等. 西藏谷露高温地热系统水文地球化学特征及成因模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,41(3):382-392. |
| [8] | 刘昭, 蔺文静, 谢鄂军, 等. 西藏尼木-那曲热水氘过量参数及其指示作用[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,41(2):251-256. |
| [9] | BULL I A S H. Hydrogeochemistry of ground water in central Israel[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1967,5:94-95. |
| [10] | MAYO A L, MULLER A B, RALSTON D R. Hydrogeochemistry of the Meade thrust allochthon, southeastern Idaho, U.S.A., and its relevance to stratigraphic and structural groundwater flow control[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1985,76(1/2):27-61. |
| [11] | CHENAKER H, HOUHA B, VINCENT V. Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of thermal water from north-eastern Algeria[J]. Geothermics, 2018,75:137-145. |
| [12] | REZAEI A, REZAEIAN M, PORKHIAL S. The hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of the thermal waters in the Mouil Graben, Sabalan volcano, NW Iran[J]. Geothermics, 2019,78:9-27. |
| [13] | 徐明, 朱传庆, 田云涛, 等. 四川盆地钻孔温度测量及现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011,54(4):1052-1060. |
| [14] | 罗敏, 任蕊, 袁伟. 四川地热资源类型、分布及成因模式[J]. 四川地质学报, 2016,36(1):47-50. |
| [15] | 倪高倩, 张恒, 韦玉婷, 等. 四川地热流体水文地球化学及同位素特征简析[J]. 新能源进展, 2016,4(3):184-194. |
| [16] | 张健, 李午阳, 唐显春, 等. 川西高温水热活动区的地热学分析[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017,47(8):899-915. |
| [17] | LI J X, YANG G, SAGOE G, et al. Major hydrogeochemical processes controlling the composition of geothermal waters in the Kangding geothermal field, western Sichuan Province[J]. Geothermics , 2018,75:154-163. |
| [18] | 罗来麟. 四川西部温泉分布及成因初探[J]. 重庆师范学院学报(自然科学版), 1994,11(2):39-47. |
| [19] | 四川省地质工程勘察院. 川西地区深部水文地质调查报告[R]. 成都: 四川省地质工程勘察院, 2017. |
| [20] | 强利刚, 周伟, 宋宪生. 甘肃东南地区地球化学特点及其地质意义研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018 ( 1):224-225. |
| [21] | 张未, 程东会, 齐丽军. 吉林省长岭县浅层地下水水文地球化学演化规律分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2016,27(5):59-63. |
| [22] | 陶广斌. 川西淡矿化温泉地球化学特征及成因研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019. |
| [23] | 张保建. 鲁西北地区地下热水的水文地球化学特征及形成条件研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011. |
| [24] | 汪啸. 广东沿海典型深大断裂带地热水系统形成条件及水文地球化学特征[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉), 2018. |
| [25] | 刘军强. 应用地热温标估算热储温度——以嵊州崇仁热水为例[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2014,26(5):129-132. |
| [26] | 佟伟, 章铭陶, 张知非, 等. 西藏地热[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981: 74-100. |
| [27] | 张锡根. 同位素地球化学在地热勘探中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1988,15(1):28-31. |
| [28] | 张洪平, 刘恩凯, 王东升, 等. 中国大气降水稳定同位素组成及影响因素[J]. 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所所刊, 1991(7):101-109. |
| [29] | 孙占学, 李学礼, 史维浚. 江西中低温地热水的同位素水文地球化学[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 1992,15(3):243-248. |
| [30] | 四川省地质工程勘察院. 川西地区高温地热资源调查评价报告[R]. 成都: 四川省地质工程勘察院, 2017. |
| [31] | 周小波, 李纯, 李育昆. 青海省贵德县扎仓地热田成因探讨[J]. 青海科技, 2005 ( 2):18-20. |
| [32] | 曹烈. 致密砂岩天然气成藏动力学研究:以川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组为例[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2010: 41-43. |
| [33] | 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所. 全国大地热流值测量与靶区优选[R]. 石家庄: 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所, 2020. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 周小蓉, 陈石, 张新顺, 丁宝通, 宋兴国, 潘楚琦, 彭梓俊. 南乍得盆地Doseo坳陷背形负花状构造成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1146-1154. |
| [10] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [11] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [12] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [13] | 曾帅, 马志刚, 赵聪, 杨磊, 张肃, 董继红, 梁京涛, 鄢圣武. 青藏高原东部大渡河流域太平桥乡古滑坡群复活特征多源遥感识别[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 994-1003. |
| [14] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [15] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||