



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (05): 1338-1353.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.106
李小冬1( ), 李志军1, 李熹微1, 马学峰1, 李晓燕1, 陈柯童1, 张霁潮1, 许梦婷1, 张瑞雪1, 秦梦华1, 王成云1, 刘佳2, 张建淼2, 施倩倩2, 李素梅2,3(
), 李志军1, 李熹微1, 马学峰1, 李晓燕1, 陈柯童1, 张霁潮1, 许梦婷1, 张瑞雪1, 秦梦华1, 王成云1, 刘佳2, 张建淼2, 施倩倩2, 李素梅2,3( )
)
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-11-13
通信作者:
李素梅,女,教授,1968年出生,主要从事油气地质地球化学研究工作。Email: smli@cup.edu.cn。作者简介:李小冬,男,高级工程师,1980年出生,主要从事油气地质勘探工作。Email: wty_lxd@petrochina.com.cn。
基金资助:
LI Xiaodong1( ), LI Zhijun1, LI Xiwei1, MA Xuefeng1, LI Xiaoyan1, CHEN Ketong1, ZHANG Jichao1, XU Mengting1, ZHANG Ruixue1, QIN Menghua1, WANG Chengyun1, LIU Jia2, ZHANG Jianmiao2, SHI Qianqian2, LI Sumei2,3(
), LI Zhijun1, LI Xiwei1, MA Xuefeng1, LI Xiaoyan1, CHEN Ketong1, ZHANG Jichao1, XU Mengting1, ZHANG Ruixue1, QIN Menghua1, WANG Chengyun1, LIU Jia2, ZHANG Jianmiao2, SHI Qianqian2, LI Sumei2,3( )
)
Published:2024-10-10
Online:2024-11-13
摘要:
冀中坳陷保定凹陷清苑构造带近年取得了重大油气勘探突破,油气的来源及其成因有待进一步确认。采用色谱-质谱、高分辨率质谱等地球化学途径,对该区油气的主力烃源岩及油气成因进行了精细剖析。清苑构造带主体原油为含蜡(均值8.12%)、含硫(均值0.81%)的重质油,具有低Pr/Ph (0.14~0.24)、高甾烷/藿烷(3.3~5.6)、高伽马蜡烷和三芳甾烷相对丰度(40%~61%)、低甾烷异构化程度(C29甾烷ααα20S/(S+R)=0.23~0.28)等特征,为典型的强还原咸水相原油。油-油、油源对比表明,清苑构造带主体原油和相邻的蠡县斜坡原油特征相似,与蠡县斜坡沙一段咸水相泥页岩具有较好的亲缘关系,主力烃源岩埋深>3000 m,与保定凹陷烃源岩未显示相关性。高分辨率质谱分析表明,清苑构造带原油富含O1、O2类化合物,特别是等效双键数(DBE)为1、5的O2类化合物(分别主要为脂肪酸和甾烷酸),其低温降解成烃是低熟油形成的重要机制,饶阳凹陷蠡县斜坡及相邻的生油洼陷发育处于生油窗阶段的、热演化程度相对不高的沙一段烃源岩是该区低熟油形成的前提。
中图分类号:
李小冬, 李志军, 李熹微, 马学峰, 李晓燕, 陈柯童, 张霁潮, 许梦婷, 张瑞雪, 秦梦华, 王成云, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩, 李素梅. 冀中坳陷保定凹陷清苑构造带低熟油成因解析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1338-1353.
LI Xiaodong, LI Zhijun, LI Xiwei, MA Xuefeng, LI Xiaoyan, CHEN Ketong, ZHANG Jichao, XU Mengting, ZHANG Ruixue, QIN Menghua, WANG Chengyun, LIU Jia, ZHANG Jianmiao, SHI Qianqian, LI Sumei. Genetic Mechanism of Low-Maturity Oil in the Qingyuan Tectonic Belt, Baoding Sag, Jizhong Depression[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1338-1353.

图1 冀中坳陷保定—饶阳凹陷区域构造图(a)及油气分布(b)
Fig.1 Illustration of the regional structure skeleton (a) and hydrocarbon distribution (b) of the Baoding-Raoyang Sag in the Jizhong Depression
| 数值类型 | 密度(g/cm3)(20 ℃) | 黏度(mPa·s) | 凝固点(℃) | 含蜡(%) | 含硫(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分布范围 | 0.9079~0.9472 | 421~6397 | 18~36 | 4.86~12.83 | 0.55~1.11 |
| 均值(个数) | 0.9805(22) | 1965(22) | 27(22) | 8.12(22) | 0.81(22) |
表1 清苑构造带原油物性特征(据华北油田勘探开发研究院数据库,2022)
Table 1 Physical properties of crude oils from the Qingyuan Tectonic Belt
| 数值类型 | 密度(g/cm3)(20 ℃) | 黏度(mPa·s) | 凝固点(℃) | 含蜡(%) | 含硫(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分布范围 | 0.9079~0.9472 | 421~6397 | 18~36 | 4.86~12.83 | 0.55~1.11 |
| 均值(个数) | 0.9805(22) | 1965(22) | 27(22) | 8.12(22) | 0.81(22) |
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 深度(m) | 层位 | Sat (%) | Ar (%) | Re (%) | Asp (%) | CPI | OEP | Pr/ nC17 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保定 | 清苑构造 北侧 | 1 | GB1X | 2194.0~2198.0 | Es1 | 44.90 | 17.60 | 24.20 | 13.30 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 0.56 | ||||||
| 2 | G66 | 2622.2~2626.2 | Es1 | 60.40 | 17.00 | 20.00 | 2.60 | 1.15 | 1.07 | 0.60 | ||||||||
| 3 | D20X | 3071.0~3079.0 | Es1 | 55.10 | 16.80 | 21.40 | 6.70 | 1.17 | 1.08 | 0.68 | ||||||||
| 清苑构造 主体带 | 4 | G77-2X | 1385.4~1395.8 | Ed | 22.90 | 25.80 | 49.00 | 2.40 | 3.62 | 6.11 | 2.04 | |||||||
| 5 | G77-1X | 1737.0~1778.8 | E | 27.71 | 19.18 | 9.54 | 43.56 | 1.02 | 0.90 | 1.91 | ||||||||
| 6 | G77-10X | 1701.0~1778.0 | E | 23.58 | 16.87 | 10.32 | 49.24 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 2.63 | ||||||||
| 7 | G77-11X | 1320.8~1352.0 | Ed3 | 17.55 | 20.86 | 13.77 | 47.83 | 1.16 | 1.00 | 4.24 | ||||||||
| 8 | G77X | 1594.0~1600.4 | Ed3 | 20.78 | 24.36 | 23.87 | 30.99 | 1.23 | 1.71 | 4.94 | ||||||||
| 9 | G79X | 1568.0~1585.0 | Ed3 | 25.19 | 19.65 | 11.63 | 43.53 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 2.23 | ||||||||
| 10 | BQ2 | 2086.4~2121.0 | Ed3 | 18.36 | 14.09 | 11.31 | 56.25 | 1.03 | 1.90 | 1.23 | ||||||||
| 11 | BQ1X | 1035.8~1054.4 | Ed | 41.50 | 23.30 | 31.30 | 4.44 | 1.07 | 0.90 | 3.06 | ||||||||
| 饶阳 | 蠡县斜坡 | 12 | N721X | 3429.4~3457.0 | E | 57.30 | 19.60 | 16.20 | 6.90 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.92 | ||||||
| 13 | G684 | 2423.0~2430.0 | E | 12.20 | 32.30 | 54.00 | 1.50 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 1.52 | ||||||||
| 14 | XL1 | 3266.0~3330.0 | E | 41.30 | 16.20 | 41.30 | 1.20 | 1.08 | 1.01 | 1.47 | ||||||||
| 15 | XL25X | 3328.2~3342.1 | E | 69.90 | 12.50 | 17.30 | 0.30 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 1.07 | ||||||||
| 16 | G67X | 1571.0~1574.1 | Ng | 57.30 | 14.90 | 24.40 | 3.30 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 1.06 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 17 | WA102X | 3162.6~3165.9 | E | 57.30 | 19.10 | 22.10 | 1.50 | 1.15 | 1.01 | 0.80 | |||||||
| 18 | M25-18X | 3382.2~3402.9 | Es3 | 67.20 | 16.40 | 14.40 | 2.00 | 1.15 | 1.07 | 0.48 | ||||||||
| 19 | Q104X | 3935.1~3946.4 | E | 63.50 | 14.60 | 19.60 | 2.20 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 0.43 | ||||||||
| 20 | Q105X | 2720.0~2773.8 | E | 66.40 | 15.50 | 14.40 | 3.60 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 0.63 | ||||||||
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 井深(m) | 层位 | Ph/ nC18 | Pr/ Ph | C29S/R | abb | S/H | G/ C31H | C31 S/R | C29Ts/ C30H | |||||
| 保定 | 清苑构造 北侧 | 1 | GB1X | 2194.0~2198.0 | Es1 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 0.57 | 0.26 | |||||
| 2 | G66 | 2622.2~2626.2 | Es1 | 1.01 | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.93 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.25 | |||||||
| 3 | D20X | 3071.0~3079.0 | Es1 | 1.71 | 0.43 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.25 | |||||||
| 清苑构造 主体带 | 4 | G77-2X | 1385.4~1395.8 | Ed | 102.37 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 4.28 | 1.59 | 0.52 | 0.06 | ||||||
| 5 | G77-1X | 1737.0~1778.8 | E | 13.70 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 4.48 | 0.98 | 0.51 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 6 | G77-10X | 1701.0~1778.0 | E | 21.34 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 4.64 | 1.02 | 0.50 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 7 | G77-11X | 1320.8~1352.0 | Ed3 | 67.82 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 5.62 | 1.38 | 0.48 | 0.03 | |||||||
| 8 | G77X | 1594.0~1600.4 | Ed3 | 71.55 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 4.27 | 0.97 | 0.51 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 9 | G79X | 1568.0~1585.0 | Ed3 | 13.26 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 3.66 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 0.05 | |||||||
| 10 | BQ2 | 2086.4~2121.0 | Ed3 | 18.00 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 4.24 | 0.95 | 0.50 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 11 | BQ1X | 1035.8~1054.4 | Ed | 14.90 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 3.30 | 1.04 | 0.56 | 0.07 | |||||||
| 饶阳 | 蠡县斜坡 | 12 | N721X | 3429.4~3457.0 | E | 2.64 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 1.72 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.10 | |||||
| 13 | G684 | 2423.0~2430.0 | E | 8.54 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 3.46 | 1.25 | 0.54 | 0.07 | |||||||
| 14 | XL1 | 3266.0~3330.0 | E | 7.20 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 3.59 | 1.39 | 0.51 | 0.07 | |||||||
| 15 | XL25X | 3328.2~3342.1 | E | 3.59 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 2.31 | 0.78 | 0.57 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 16 | G67X | 1571.0~1574.1 | Ng | 3.87 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 2.31 | 0.78 | 0.58 | 0.10 | |||||||
| 洼陷带 | 17 | WA102X | 3162.6~3165.9 | E | 2.29 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 1.88 | 0.79 | 0.56 | 0.14 | ||||||
| 18 | M25-18X | 3382.2~3402.9 | Es3 | 0.37 | 1.32 | 0.39 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.58 | 0.32 | |||||||
| 19 | Q104X | 3935.1~3946.4 | E | 0.25 | 1.91 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.57 | 0.20 | |||||||
| 20 | Q105X | 2720.0~2773.8 | E | 0.35 | 2.06 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.58 | 0.22 | |||||||
表2 保定—饶阳凹陷部分第三系原油基本地球化学参数
Table 2 Basic geochemical parameters of Tertiary crude oils from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 深度(m) | 层位 | Sat (%) | Ar (%) | Re (%) | Asp (%) | CPI | OEP | Pr/ nC17 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保定 | 清苑构造 北侧 | 1 | GB1X | 2194.0~2198.0 | Es1 | 44.90 | 17.60 | 24.20 | 13.30 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 0.56 | ||||||
| 2 | G66 | 2622.2~2626.2 | Es1 | 60.40 | 17.00 | 20.00 | 2.60 | 1.15 | 1.07 | 0.60 | ||||||||
| 3 | D20X | 3071.0~3079.0 | Es1 | 55.10 | 16.80 | 21.40 | 6.70 | 1.17 | 1.08 | 0.68 | ||||||||
| 清苑构造 主体带 | 4 | G77-2X | 1385.4~1395.8 | Ed | 22.90 | 25.80 | 49.00 | 2.40 | 3.62 | 6.11 | 2.04 | |||||||
| 5 | G77-1X | 1737.0~1778.8 | E | 27.71 | 19.18 | 9.54 | 43.56 | 1.02 | 0.90 | 1.91 | ||||||||
| 6 | G77-10X | 1701.0~1778.0 | E | 23.58 | 16.87 | 10.32 | 49.24 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 2.63 | ||||||||
| 7 | G77-11X | 1320.8~1352.0 | Ed3 | 17.55 | 20.86 | 13.77 | 47.83 | 1.16 | 1.00 | 4.24 | ||||||||
| 8 | G77X | 1594.0~1600.4 | Ed3 | 20.78 | 24.36 | 23.87 | 30.99 | 1.23 | 1.71 | 4.94 | ||||||||
| 9 | G79X | 1568.0~1585.0 | Ed3 | 25.19 | 19.65 | 11.63 | 43.53 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 2.23 | ||||||||
| 10 | BQ2 | 2086.4~2121.0 | Ed3 | 18.36 | 14.09 | 11.31 | 56.25 | 1.03 | 1.90 | 1.23 | ||||||||
| 11 | BQ1X | 1035.8~1054.4 | Ed | 41.50 | 23.30 | 31.30 | 4.44 | 1.07 | 0.90 | 3.06 | ||||||||
| 饶阳 | 蠡县斜坡 | 12 | N721X | 3429.4~3457.0 | E | 57.30 | 19.60 | 16.20 | 6.90 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.92 | ||||||
| 13 | G684 | 2423.0~2430.0 | E | 12.20 | 32.30 | 54.00 | 1.50 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 1.52 | ||||||||
| 14 | XL1 | 3266.0~3330.0 | E | 41.30 | 16.20 | 41.30 | 1.20 | 1.08 | 1.01 | 1.47 | ||||||||
| 15 | XL25X | 3328.2~3342.1 | E | 69.90 | 12.50 | 17.30 | 0.30 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 1.07 | ||||||||
| 16 | G67X | 1571.0~1574.1 | Ng | 57.30 | 14.90 | 24.40 | 3.30 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 1.06 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 17 | WA102X | 3162.6~3165.9 | E | 57.30 | 19.10 | 22.10 | 1.50 | 1.15 | 1.01 | 0.80 | |||||||
| 18 | M25-18X | 3382.2~3402.9 | Es3 | 67.20 | 16.40 | 14.40 | 2.00 | 1.15 | 1.07 | 0.48 | ||||||||
| 19 | Q104X | 3935.1~3946.4 | E | 63.50 | 14.60 | 19.60 | 2.20 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 0.43 | ||||||||
| 20 | Q105X | 2720.0~2773.8 | E | 66.40 | 15.50 | 14.40 | 3.60 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 0.63 | ||||||||
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 井深(m) | 层位 | Ph/ nC18 | Pr/ Ph | C29S/R | abb | S/H | G/ C31H | C31 S/R | C29Ts/ C30H | |||||
| 保定 | 清苑构造 北侧 | 1 | GB1X | 2194.0~2198.0 | Es1 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 0.57 | 0.26 | |||||
| 2 | G66 | 2622.2~2626.2 | Es1 | 1.01 | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.93 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.25 | |||||||
| 3 | D20X | 3071.0~3079.0 | Es1 | 1.71 | 0.43 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.25 | |||||||
| 清苑构造 主体带 | 4 | G77-2X | 1385.4~1395.8 | Ed | 102.37 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 4.28 | 1.59 | 0.52 | 0.06 | ||||||
| 5 | G77-1X | 1737.0~1778.8 | E | 13.70 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 4.48 | 0.98 | 0.51 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 6 | G77-10X | 1701.0~1778.0 | E | 21.34 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 4.64 | 1.02 | 0.50 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 7 | G77-11X | 1320.8~1352.0 | Ed3 | 67.82 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 5.62 | 1.38 | 0.48 | 0.03 | |||||||
| 8 | G77X | 1594.0~1600.4 | Ed3 | 71.55 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 4.27 | 0.97 | 0.51 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 9 | G79X | 1568.0~1585.0 | Ed3 | 13.26 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 3.66 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 0.05 | |||||||
| 10 | BQ2 | 2086.4~2121.0 | Ed3 | 18.00 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 4.24 | 0.95 | 0.50 | 0.04 | |||||||
| 11 | BQ1X | 1035.8~1054.4 | Ed | 14.90 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 3.30 | 1.04 | 0.56 | 0.07 | |||||||
| 饶阳 | 蠡县斜坡 | 12 | N721X | 3429.4~3457.0 | E | 2.64 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 1.72 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.10 | |||||
| 13 | G684 | 2423.0~2430.0 | E | 8.54 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 3.46 | 1.25 | 0.54 | 0.07 | |||||||
| 14 | XL1 | 3266.0~3330.0 | E | 7.20 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 3.59 | 1.39 | 0.51 | 0.07 | |||||||
| 15 | XL25X | 3328.2~3342.1 | E | 3.59 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 2.31 | 0.78 | 0.57 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 16 | G67X | 1571.0~1574.1 | Ng | 3.87 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 2.31 | 0.78 | 0.58 | 0.10 | |||||||
| 洼陷带 | 17 | WA102X | 3162.6~3165.9 | E | 2.29 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 1.88 | 0.79 | 0.56 | 0.14 | ||||||
| 18 | M25-18X | 3382.2~3402.9 | Es3 | 0.37 | 1.32 | 0.39 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.58 | 0.32 | |||||||
| 19 | Q104X | 3935.1~3946.4 | E | 0.25 | 1.91 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.57 | 0.20 | |||||||
| 20 | Q105X | 2720.0~2773.8 | E | 0.35 | 2.06 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.58 | 0.22 | |||||||

图3 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系原油基本特征与成因类型分类 (a)Pr/nC17-Ph/nC18关系图;(b) Pr/Ph-DBT/P关系图,DBT为二苯并噻吩,P为菲
Fig.3 Basic geochemical characteristics and genetic types of Tertiary crude oils from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag
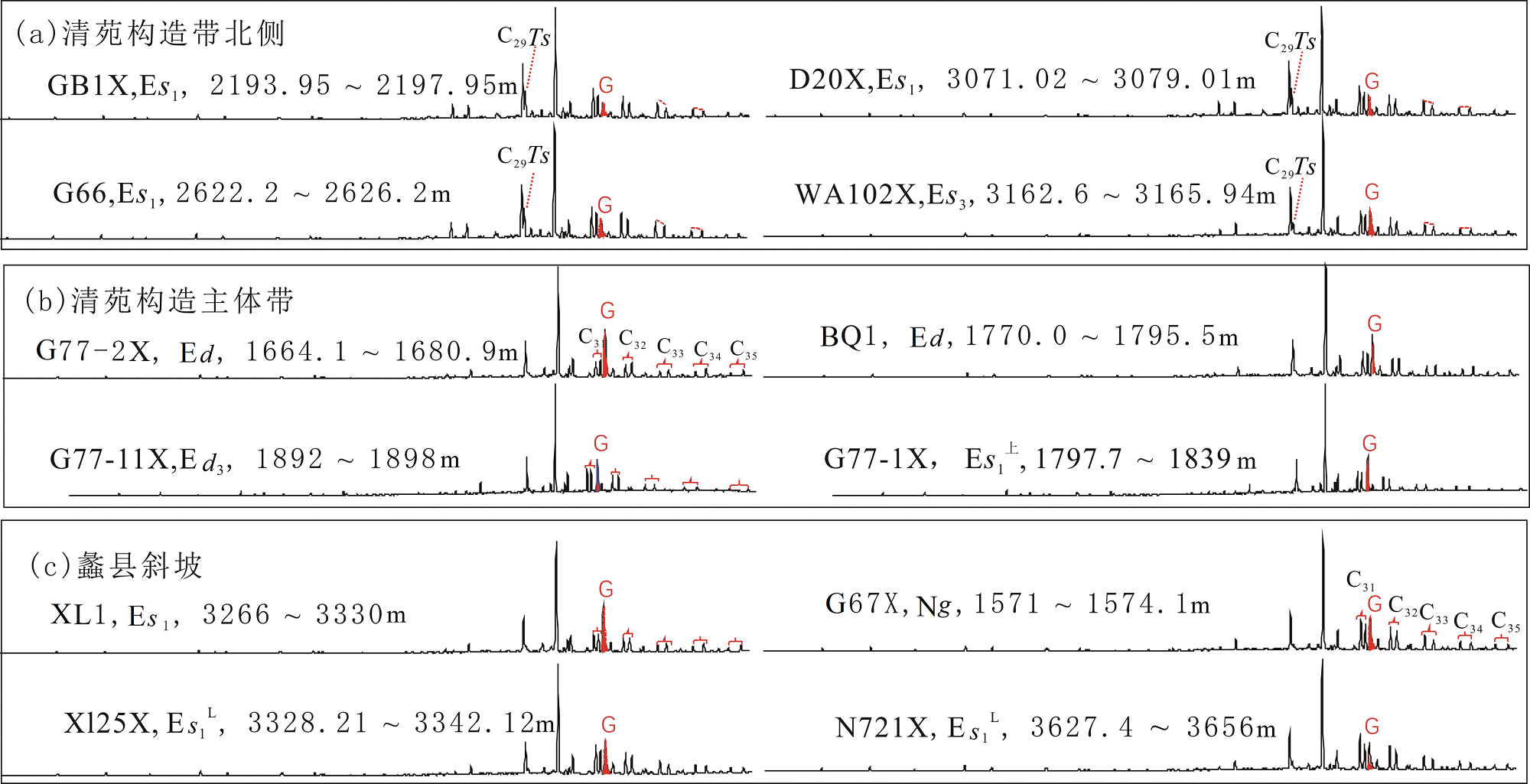
图5 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系原油饱和烃m/z 191质量色谱图 (a)清苑构造带北侧; (b)清苑构造主体带; (c)蠡县斜坡
Fig.5 Mass chromatograms of m/z 191 for saturates from partial crude oils from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag
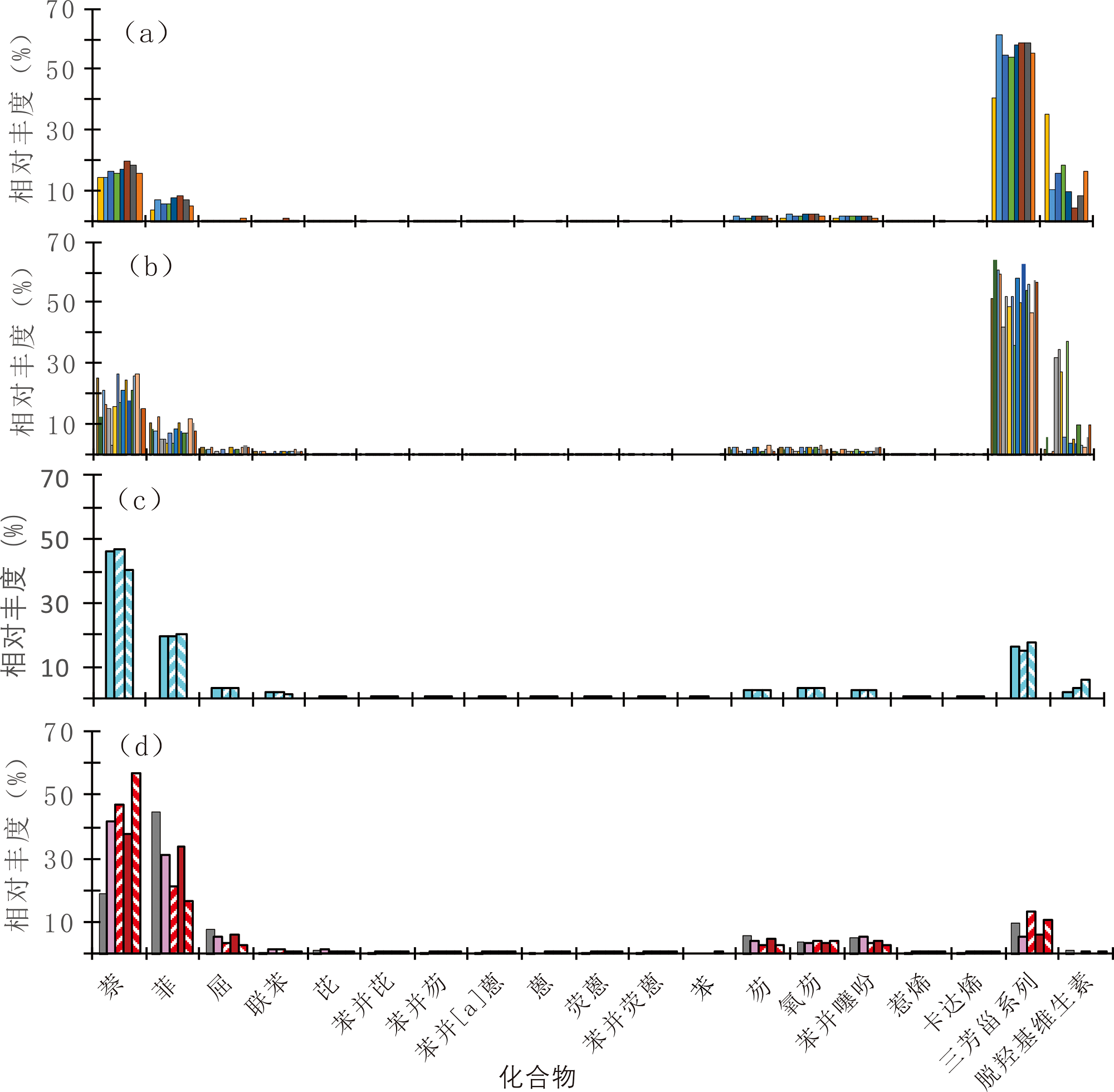
图6 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系原油芳烃组成与分布特征 (a)清苑构造主体带原油; (b)蠡县斜坡原油; (c)清苑构造带北侧原油; (d)饶阳凹陷沙三段原油
Fig.6 Composition and distribution of aromatic hydrocarbons in Tertiary crude oils from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag

图7 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系烃源岩饱和烃m/z 218、m/z 191质量色谱图 (a)清苑构造带—蠡县斜坡Es1浅埋源岩(Es1); (b)蠡县斜坡Es1深埋源岩;(c)保定—蠡县斜坡Es2+3烃源岩
Fig.7 Mass chromatograms of m/z 218 and m/z191 for saturates from partial Tertiary source rocks from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag

图8 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系原油、烃源岩生标成熟度、沉积环境参数纵向对比
Fig.8 Thermal maturity and paleoenvironment longitudinal correlation for crude oils and source rocks from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 深度(m) | 层位 | 岩性 | Sat (%) | Ar (%) | Re (%) | Asp (%) | CPI | OEP | Pr/nC17 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保定 凹陷 | 清苑构 造带 | 1 | GB1X | 2114 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 50.59 | 6.45 | 25.41 | 17.55 | 1.84 | 2.03 | 0.99 | ||||||
| 2 | GB1X | 2130 | Es1 | 灰褐色油页岩 | 48.37 | 11.83 | 27.33 | 12.47 | 1.42 | 1.65 | 1.46 | ||||||||
| 3 | GB1X | 2138.3 | Es1 | 灰褐色油页岩 | 40.15 | 7.03 | 35.51 | 17.31 | 1.74 | 2.63 | 0.37 | ||||||||
| 4 | GB1X | 2138.6 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 33.88 | 5.99 | 44.17 | 15.96 | 2.00 | 3.53 | 0.46 | ||||||||
| 5 | GB1X | 2151 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 44.63 | 10.77 | 38.21 | 6.39 | 1.99 | 3.65 | 0.45 | ||||||||
| 6 | GB1X | 2183 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 42.83 | 12.48 | 26.62 | 18.07 | 1.65 | 2.75 | 0.86 | ||||||||
| 7 | GB1X | 2237 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 46.32 | 4.55 | 32.13 | 17.00 | 1.59 | 2.44 | 0.79 | ||||||||
| 8 | GB1X | 2138 | E | 青灰色泥岩 | 17.52 | 10.58 | 59.85 | 12.04 | 1.08 | 1.42 | 0.65 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 9 | BS2 | 2678.65 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 26.31 | 14.04 | 26.15 | 33.50 | 2.25 | 1.11 | 0.60 | |||||||
| 10 | BS2 | 2473.54 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 25.91 | 6.21 | 35.63 | 32.25 | 3.42 | 4.64 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| 11 | BS2 | 2474.04 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 32.78 | 4.12 | 49.31 | 13.79 | 2.12 | 4.72 | 1.37 | ||||||||
| 12 | BS2 | 2481.64 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 33.69 | 11.54 | 39.58 | 15.19 | 1.37 | 1.66 | 0.97 | ||||||||
| 13 | BS2 | 2478.3 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 19.87 | 10.09 | 41.96 | 28.08 | 2.30 | 1.22 | 0.87 | ||||||||
| 14 | BS2 | 2681.5 | Es1 | 灰色泥页岩 | 14.05 | 11.35 | 28.65 | 45.95 | 1.24 | 1.02 | 1.02 | ||||||||
| 饶阳 凹陷 | 蠡县 斜坡 | 15 | XL25X | 3337.7 | E | 深灰色泥页岩 | 14.71 | 27.31 | 40.76 | 17.23 | 1.16 | 1.57 | 4.24 | ||||||
| 16 | XL25X | 3340.9 | E | 深灰色泥页岩 | 24.49 | 28.57 | 40.41 | 6.53 | 1.23 | 1.71 | 4.94 | ||||||||
| 17 | B11X | 3331.3 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 31.79 | 13.85 | 32.31 | 22.05 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.49 | ||||||||
| 18 | B11X | 3365.3 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 29.88 | 18.29 | 36.89 | 14.94 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| 19 | G34 | 2513.8 | E | 深灰色页岩 | 26.42 | 11.70 | 41.89 | 20.00 | 1.23 | 0.98 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 20 | G52 | 3095.5 | E | 深灰色页岩 | 28.97 | 13.40 | 50.78 | 6.85 | 1.15 | 1.06 | 0.50 | ||||||||
| 21 | G24 | 2615.7 | E | 灰黑色页岩 | 23.34 | 14.41 | 53.31 | 8.93 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| 22 | GB1X | 2138.0 | E | 青灰色泥岩 | 17.52 | 10.58 | 59.85 | 12.04 | 1.08 | 1.42 | 0.65 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 23 | M40 | 3653.7 | Es2-3 | 灰黑色泥岩 | 10.42 | 20.83 | 30.21 | 38.54 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 1.31 | |||||||
| 24 | M40 | 3763.1 | Es2-3 | 灰黑色页岩 | 30.53 | 25.19 | 29.26 | 15.01 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 2.23 | ||||||||
| 25 | M40 | 3792.6 | Es2-3 | 灰黑色泥岩 | 26.18 | 24.29 | 29.97 | 19.56 | 0.82 | 0.64 | 0.76 | ||||||||
| 26 | M305 | 3458.8 | Es2-3 | 深灰色泥岩 | 23.26 | 11.63 | 37.21 | 27.91 | 2.02 | 2.57 | 2.62 | ||||||||
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 深度(m) | 层位 | Ph/nC18 | Pr/Ph | C29S/R | abb | S/H | G/C31H | C31S/R | C29Ts/ C30H | ||||||
| 保定 凹陷 | 清苑构 造带 | 1 | GB1X | 2114.00 | Es1 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.27 | ||||||
| 2 | GB1X | 2130.00 | Es1 | 2.04 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 2.13 | 1.89 | 0.45 | 0.09 | ||||||||
| 3 | GB1X | 2138.30 | Es1 | 4.93 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 2.02 | 2.46 | 0.49 | 0.33 | ||||||||
| 4 | GB1X | 2138.60 | Es1 | 4.20 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 5.12 | 1.56 | 0.42 | 0.38 | ||||||||
| 5 | GB1X | 2151.00 | Es1 | 4.00 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 5.68 | 1.51 | 0.42 | 0.17 | ||||||||
| 6 | GB1X | 2183.00 | Es1 | 2.59 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 2.63 | 1.50 | 0.43 | 0.27 | ||||||||
| 7 | GB1X | 2237.00 | Es1 | 2.12 | 0.36 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 2.86 | 1.47 | 0.44 | 0.10 | ||||||||
| 8 | GB1X | 2138.00 | E | 3.42 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 7.78 | 2.05 | 0.28 | 0.34 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 9 | BS2 | 2678.65 | Es1 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.19 | |||||||
| 10 | BS2 | 2473.54 | Es1 | 1.28 | 0.78 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.37 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| 11 | BS2 | 2474.04 | Es1 | 1.78 | 0.74 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.04 | ||||||||
| 12 | BS2 | 2481.64 | Es1 | 3.35 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.48 | 0.12 | ||||||||
| 13 | BS2 | 2478.30 | Es1 | 2.07 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.77 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.06 | ||||||||
| 14 | BS2 | 2681.50 | Es1 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 1.45 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.16 | ||||||||
| 饶阳 凹陷 | 蠡县 斜坡 | 15 | XL25X | 3337.70 | E | 67.80 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.12 | ||||||
| 16 | XL25X | 3340.90 | E | 71.60 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 1.81 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.12 | ||||||||
| 17 | B11X | 3331.30 | Es1 | 7.24 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.52 | 0.21 | ||||||||
| 18 | B11X | 3365.30 | Es1 | 1.59 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.79 | 0.35 | 0.51 | 0.07 | ||||||||
| 19 | G34 | 2513.80 | E | 0.60 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 4.27 | 2.99 | 0.45 | 0.16 | ||||||||
| 20 | G52 | 3095.50 | E | 0.36 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 5.23 | 1.65 | 0.41 | 0.11 | ||||||||
| 21 | G24 | 2615.70 | E | 1.44 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 8.03 | 2.16 | 0.42 | 0.22 | ||||||||
| 22 | GB1X | 2138.00 | E | 3.42 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 7.78 | 2.05 | 0.28 | 0.34 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 23 | M40 | 3653.70 | Es2-3 | 6.43 | 0.23 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 24 | M40 | 3763.10 | Es2-3 | 5.16 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 1.66 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 0.16 | ||||||||
| 25 | M40 | 3792.60 | Es2-3 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.56 | 0.26 | ||||||||
| 26 | M305 | 3458.80 | Es2-3 | 1.54 | 1.68 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 1.04 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.10 | ||||||||
表3 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系烃源岩地球化学参数
Table 3 Geochemical parameters of Tertiary source rocks from the Baoding-Raoyang Sag
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 深度(m) | 层位 | 岩性 | Sat (%) | Ar (%) | Re (%) | Asp (%) | CPI | OEP | Pr/nC17 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保定 凹陷 | 清苑构 造带 | 1 | GB1X | 2114 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 50.59 | 6.45 | 25.41 | 17.55 | 1.84 | 2.03 | 0.99 | ||||||
| 2 | GB1X | 2130 | Es1 | 灰褐色油页岩 | 48.37 | 11.83 | 27.33 | 12.47 | 1.42 | 1.65 | 1.46 | ||||||||
| 3 | GB1X | 2138.3 | Es1 | 灰褐色油页岩 | 40.15 | 7.03 | 35.51 | 17.31 | 1.74 | 2.63 | 0.37 | ||||||||
| 4 | GB1X | 2138.6 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 33.88 | 5.99 | 44.17 | 15.96 | 2.00 | 3.53 | 0.46 | ||||||||
| 5 | GB1X | 2151 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 44.63 | 10.77 | 38.21 | 6.39 | 1.99 | 3.65 | 0.45 | ||||||||
| 6 | GB1X | 2183 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 42.83 | 12.48 | 26.62 | 18.07 | 1.65 | 2.75 | 0.86 | ||||||||
| 7 | GB1X | 2237 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 46.32 | 4.55 | 32.13 | 17.00 | 1.59 | 2.44 | 0.79 | ||||||||
| 8 | GB1X | 2138 | E | 青灰色泥岩 | 17.52 | 10.58 | 59.85 | 12.04 | 1.08 | 1.42 | 0.65 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 9 | BS2 | 2678.65 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 26.31 | 14.04 | 26.15 | 33.50 | 2.25 | 1.11 | 0.60 | |||||||
| 10 | BS2 | 2473.54 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 25.91 | 6.21 | 35.63 | 32.25 | 3.42 | 4.64 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| 11 | BS2 | 2474.04 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 32.78 | 4.12 | 49.31 | 13.79 | 2.12 | 4.72 | 1.37 | ||||||||
| 12 | BS2 | 2481.64 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 33.69 | 11.54 | 39.58 | 15.19 | 1.37 | 1.66 | 0.97 | ||||||||
| 13 | BS2 | 2478.3 | Es1 | 灰色泥岩 | 19.87 | 10.09 | 41.96 | 28.08 | 2.30 | 1.22 | 0.87 | ||||||||
| 14 | BS2 | 2681.5 | Es1 | 灰色泥页岩 | 14.05 | 11.35 | 28.65 | 45.95 | 1.24 | 1.02 | 1.02 | ||||||||
| 饶阳 凹陷 | 蠡县 斜坡 | 15 | XL25X | 3337.7 | E | 深灰色泥页岩 | 14.71 | 27.31 | 40.76 | 17.23 | 1.16 | 1.57 | 4.24 | ||||||
| 16 | XL25X | 3340.9 | E | 深灰色泥页岩 | 24.49 | 28.57 | 40.41 | 6.53 | 1.23 | 1.71 | 4.94 | ||||||||
| 17 | B11X | 3331.3 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 31.79 | 13.85 | 32.31 | 22.05 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.49 | ||||||||
| 18 | B11X | 3365.3 | Es1 | 深灰色泥岩 | 29.88 | 18.29 | 36.89 | 14.94 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| 19 | G34 | 2513.8 | E | 深灰色页岩 | 26.42 | 11.70 | 41.89 | 20.00 | 1.23 | 0.98 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 20 | G52 | 3095.5 | E | 深灰色页岩 | 28.97 | 13.40 | 50.78 | 6.85 | 1.15 | 1.06 | 0.50 | ||||||||
| 21 | G24 | 2615.7 | E | 灰黑色页岩 | 23.34 | 14.41 | 53.31 | 8.93 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| 22 | GB1X | 2138.0 | E | 青灰色泥岩 | 17.52 | 10.58 | 59.85 | 12.04 | 1.08 | 1.42 | 0.65 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 23 | M40 | 3653.7 | Es2-3 | 灰黑色泥岩 | 10.42 | 20.83 | 30.21 | 38.54 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 1.31 | |||||||
| 24 | M40 | 3763.1 | Es2-3 | 灰黑色页岩 | 30.53 | 25.19 | 29.26 | 15.01 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 2.23 | ||||||||
| 25 | M40 | 3792.6 | Es2-3 | 灰黑色泥岩 | 26.18 | 24.29 | 29.97 | 19.56 | 0.82 | 0.64 | 0.76 | ||||||||
| 26 | M305 | 3458.8 | Es2-3 | 深灰色泥岩 | 23.26 | 11.63 | 37.21 | 27.91 | 2.02 | 2.57 | 2.62 | ||||||||
| 凹陷 | 构造 单元 | 编号 | 井号 | 深度(m) | 层位 | Ph/nC18 | Pr/Ph | C29S/R | abb | S/H | G/C31H | C31S/R | C29Ts/ C30H | ||||||
| 保定 凹陷 | 清苑构 造带 | 1 | GB1X | 2114.00 | Es1 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.27 | ||||||
| 2 | GB1X | 2130.00 | Es1 | 2.04 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 2.13 | 1.89 | 0.45 | 0.09 | ||||||||
| 3 | GB1X | 2138.30 | Es1 | 4.93 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 2.02 | 2.46 | 0.49 | 0.33 | ||||||||
| 4 | GB1X | 2138.60 | Es1 | 4.20 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 5.12 | 1.56 | 0.42 | 0.38 | ||||||||
| 5 | GB1X | 2151.00 | Es1 | 4.00 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 5.68 | 1.51 | 0.42 | 0.17 | ||||||||
| 6 | GB1X | 2183.00 | Es1 | 2.59 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 2.63 | 1.50 | 0.43 | 0.27 | ||||||||
| 7 | GB1X | 2237.00 | Es1 | 2.12 | 0.36 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 2.86 | 1.47 | 0.44 | 0.10 | ||||||||
| 8 | GB1X | 2138.00 | E | 3.42 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 7.78 | 2.05 | 0.28 | 0.34 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 9 | BS2 | 2678.65 | Es1 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 1.33 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.19 | |||||||
| 10 | BS2 | 2473.54 | Es1 | 1.28 | 0.78 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.37 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| 11 | BS2 | 2474.04 | Es1 | 1.78 | 0.74 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.04 | ||||||||
| 12 | BS2 | 2481.64 | Es1 | 3.35 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.48 | 0.12 | ||||||||
| 13 | BS2 | 2478.30 | Es1 | 2.07 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.77 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.06 | ||||||||
| 14 | BS2 | 2681.50 | Es1 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 1.45 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.16 | ||||||||
| 饶阳 凹陷 | 蠡县 斜坡 | 15 | XL25X | 3337.70 | E | 67.80 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.12 | ||||||
| 16 | XL25X | 3340.90 | E | 71.60 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 1.81 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.12 | ||||||||
| 17 | B11X | 3331.30 | Es1 | 7.24 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.52 | 0.21 | ||||||||
| 18 | B11X | 3365.30 | Es1 | 1.59 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.79 | 0.35 | 0.51 | 0.07 | ||||||||
| 19 | G34 | 2513.80 | E | 0.60 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 4.27 | 2.99 | 0.45 | 0.16 | ||||||||
| 20 | G52 | 3095.50 | E | 0.36 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 5.23 | 1.65 | 0.41 | 0.11 | ||||||||
| 21 | G24 | 2615.70 | E | 1.44 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 8.03 | 2.16 | 0.42 | 0.22 | ||||||||
| 22 | GB1X | 2138.00 | E | 3.42 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 7.78 | 2.05 | 0.28 | 0.34 | ||||||||
| 洼陷带 | 23 | M40 | 3653.70 | Es2-3 | 6.43 | 0.23 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 24 | M40 | 3763.10 | Es2-3 | 5.16 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 1.66 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 0.16 | ||||||||
| 25 | M40 | 3792.60 | Es2-3 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.56 | 0.26 | ||||||||
| 26 | M305 | 3458.80 | Es2-3 | 1.54 | 1.68 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 1.04 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.10 | ||||||||

图9 保定—饶阳凹陷第三系原油、烃源岩沉积环境与生源参数聚类对比((c)(d)图中的彩色阴影为(a)(b)图原油的分布区域)
Fig.9 Correlation based on biomarker indicating paleoenvironment and organic matter for Tertiary oils and source rocks from the Baoding-Raoyang Depression

图10 清苑构造带部分原油O2类化合物高分辨率质谱分布特征 (a)(c)分别为BQ2、G77-10井O2类化合物碳数、等价双键数与强度关系图;(b)O2类化合物不同等价双键数相对丰度;(d)等价双键数为5的O2类化合物不同碳数相对丰度
Fig.10 Distribution of O2 species detected by negative ESI FT-ICR MS in crude oils from the Qingyuan Tectonic Belt

图11 清苑构造带—蠡县斜坡沙一段烃源岩成熟度随埋深变化特征
Fig.11 Variation in thermal maturity with burial depth for Es1 source rocks from the Qingyuan Tectonic Belt to the Lixian Slope
| [1] | PANG X Q, LI M W, LI S M, et al. Origin of crude oils in the Jinhu Depression of North Jiangsu-South Yellow Sea Basin, Eastern China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(4): 553-573. |
| [2] | PANG X Q, LI M W, LI S M, et al. Geochemistry of petroleum systems in the Niuzhuang South Slope of Bohai Bay Basin: Part 2.Evidence for significant contribution of mature source rocks to “immature oils” in the Bamianhe field[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(7): 931-950. |
| [3] | 柯昌炜, 李素梅, 张洪安, 等. 东濮凹陷盐湖相烃源岩有机硫同位素分布特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2):301-314. |
| [4] | 陈湘飞, 李素梅, 张洪安, 等. 东濮凹陷膏盐岩对烃源岩成烃演化的控制作用及其石油地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1125-1136. |
| [5] | 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 侯读杰. 低熟油气形成机理与分布[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1995. |
| [6] | 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 侯读杰, 等. 中国低熟油的几种成因机制[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(2): 75-82. |
| [7] | LARGEAU C, CASADEVALL E, BERKALOFF C. The biosynthesis of long-chain hydrocarbons in the green alga Botryococcus braunii[J]. Phytochemistry, 1980, 19(6): 1081-1085. |
| [8] | SINNINGHE DAMSTÉ J S, EGLINTON T I, DE LEEUW J W, et al. Organic sulphur in macromolecular sedimentary organic matter: I. Structure and origin of sulphur-containing moieties in kerogen, asphaltenes and coal as revealed by flash pyrolysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(4): 873-889. |
| [9] | 邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 等. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5):1354-1369. |
| [10] | 黄第藩. 成烃理论的发展:(I)未熟油及有机质成烃演化模式[J]. 地球科学进展, 1996, 11( 4) : 327-335. |
| [11] | BAZHENOVA O K, AREFIEV O A. Immature oils as the products of early catagenetic transformation of bacterial-algal organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1990, 16(1/2/3): 307-311. |
| [12] | WAN Z H, LI S M, WANG Z J, et al. Characteristics and geochemical significance of heteroatomic compounds by negative-ion ESI FT-ICR MS in crude oils from the Nanpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 111:34-55. |
| [13] | JI H, LI S M, GREENWOOD P, et al. Geochemical characteristics and significance of heteroatom compounds in lacustrine oils of the Dongpu Depression (Bohai Bay Basin, China) by negative-ion Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 568-591. |
| [14] | ZHANG H J, LI S M. GC-MS and ESI FT-ICR MS characterization on two type crude oils from the Dongying depression[J]. Fuel, 2023, 333: 126408. |
| [15] | DENG S, LI S M, LI X D, et al. New geochemical proxies of nitrogen-and oxygen-containing compounds characterized by ESI (-) FT-ICR MS[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(20): 15505-15522. |
| [16] | 张文朝, 杨德相, 陈彦均, 等. 冀中坳陷古近系沉积构造特征与油气分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(8): 1103-1112. |
| [17] | 张文朝, 崔周旗, 韩春元, 等. 冀中坳陷老第三纪湖盆演化与油气[J]. 古地理学报, 2001, 3(1): 45-54. |
| [18] | CHEN X Y, HAO F, GUO L X, et al. Characteristic of source rocks and origin of crude oils in the Raoyang Sag and Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Insights from geochemical and geolo-gical analyses[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 407-421. |
| [19] | YIN J, WANG Q, HAO F, et al. Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of lacustrine source rocks in the lower 1st Member of the Shahejie Formation in the Raoyang Sag and the Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 495: 87-104. |
| [20] | YIN J, HAO F, WANG Z Q, et al. Lacustrine conditions control on the distribution of organic-rich source rocks: An instance analysis of the lower 1st member of the Shahejie Formation in the Raoyang Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 78: 103320. |
| [21] | 徐田武, 李素梅, 张洪安, 等. 东濮凹陷原油含硫化合物的分布特征及其应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(3): 629-642. |
| [22] | 侯读杰, 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 等. 低熟油的富硫大分子早期降解生烃机制:以临清坳陷德南洼陷低熟原油和烃源岩为例[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1996, 18(1):30-36. |
| [23] | HUGHES W B, HOLBA A G, DZOU L I P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3581-3598. |
| [24] | CONNAN J, CASSOU A M. Properties of gases and petroleum liquids derived from terrestrial kerogen at various maturation levels[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(1): 0016703780901738. |
| [25] | PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, MOLDOWAN J M. The Biomarker Guide[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. |
| [26] | 彭光荣, 张丽丽, 许新明, 等. 珠江口盆地西江主洼烃源岩属性、原油分类及成藏主控因素[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(6): 2361-2375. |
| [27] |
SINNINGHE DAMSTE J S, KENIG F, KOOPMANS M P, et al. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(9): 1895-1900.
PMID |
| [28] | 杨帆, 王权, 郝芳, 等. 冀中坳陷饶阳凹陷北部烃源岩生物标志物特征与油源对比[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1):263-274. |
| [29] | 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 金之钧, 等. 未熟—低熟油研究现状与存在的问题[J]. 地质论评, 2003, 49(3): 298-304. |
| [30] | SHI J Y, XIANG M J, QU D C. Simulation experiments for evolution of fatty acids in immature source rocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(24): 2092-2096. |
| [31] | KAMGA A W, BEHAR F, HATCHER P G. Quantitative analysis of long chain fatty acids present in a type I kerogen using electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: Compared with BF3/MeOH methylation/GC-FID[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2014, 25(5): 880-890. |
| [32] | TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1984. |
| [33] | NASCIMENTO L R, REBOUÇAS L M C, KOIKE L, et al. Acidic biomarkers from albacora oils, Campos Basin, Brazil[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1999, 30(9): 1175-1191. |
| [34] | POETZ S, HORSFIELD B, WILKES H. Maturity-driven generation and transformation of acidic compounds in the organic-rich posidonia shale as revealed by electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(8): 4877-4888. |
| [35] | SHI Q, ZHAO S Q, XU Z M, et al. Distribution of acids and neutral nitrogen compounds in a Chinese crude oil and its fractions: Characterized by negative-ion electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(7): 4005-4011. |
| [1] | 邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 黄太明, 刘佳, 张建淼, 施倩倩. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1354-1369. |
| [2] | 李杰豪, 侯读杰, 曹兰柱, 吴飘, 赵喆, 马潇潇. 二连盆地赛汉塔拉凹陷腾二段低熟油地球化学特征和油源对比[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 315-325. |
| [3] | 李素梅, 徐田武, 史权, 张云献, 吴建勋, 柯昌炜. 东濮凹陷盐湖相原油氮/氧化合物分布特征及其应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1137-1150. |
| [4] | 徐田武, 李素梅, 张洪安, 张云献, 吴建勋, 史权, 陈湘飞, 纪红, 万中华. 东濮凹陷原油含硫化合物的分布特征及其应用[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 629-642. |
| [5] | 李蕾, 李素梅, 张洪安, 徐田武, 张云献, 纪红. 东濮凹陷西斜坡盐湖相原油地球化学特征与油源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1109-1124. |
| [6] | 王元, 李贤庆, 王刚, 徐新德, 刘海钰. 莺琼盆地中新统海相羟源岩地球化学特征及生经潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 500-510. |
| [7] | 张洪安, 李素梅, 徐田武, 庞雄奇, 张云献, 万中华, 纪红. 东濮凹陷北部盐湖相原油特征与成因[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 768-778. |
| [8] | 葛海霞 ,张枝焕 ,闵伟 ,张琳璞 ,柳东 ,章成进. 济阳坳陷青东凹陷低熟油生烃机理研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1105-1114. |
| [9] | 万中华, 李素梅. 渤海湾盆地南堡油田原油特征与油源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(3): 599-607. |
| [10] | 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 杨海军, 肖中尧, 顾乔元, 张玮娜. 塔里木盆地英买力地区原油地球化学特征与族群划分[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(4): 643-653. |
| [11] | 李素梅 姜振学 董月霞 王旭东. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷原油成因类型及其分布规律[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(5): 817-823. |
| [12] | 郑艳红,于学峰. 木质素在古植被重建中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(Suppl): 193-197. |
| [13] | 李伟,张枝焕,李海平,韩立国,王青. 准噶尔盆地中部Ⅰ区侏罗系油藏古今油水界面及成藏史分析[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(3): 432-440. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||