



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (06): 1551-1562.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.222
张金晴1,2( ), 李贤庆1,2(
), 李贤庆1,2( ), 张博翔1,2, 张学庆1,2, 杨经纬1,2, 于振锋3
), 张博翔1,2, 张学庆1,2, 杨经纬1,2, 于振锋3
收稿日期:2022-05-06
修回日期:2022-07-08
出版日期:2022-12-10
发布日期:2023-01-11
通讯作者:
李贤庆
作者简介:李贤庆,男,教授,博士生导师,1967年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,从事煤油气地质、有机地球化学和有机岩石学等方面的教学与科研工作。Email:lixq@cumtb.edu.cn。基金资助:
ZHANG Jinqing1,2( ), LI Xianqing1,2(
), LI Xianqing1,2( ), ZHANG Boxiang1,2, ZHANG Xueqing1,2, YANG Jingwei1,2, YU Zhenfeng3
), ZHANG Boxiang1,2, ZHANG Xueqing1,2, YANG Jingwei1,2, YU Zhenfeng3
Received:2022-05-06
Revised:2022-07-08
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2023-01-11
Contact:
LI Xianqing
摘要:
储层孔隙特征和孔隙结构是影响页岩气赋存与储集的重要因素。为评价海陆过渡相高演化煤系页岩储层性质与页岩气储集性能,应用扫描电子显微镜、高压压汞、低温N2和 CO2气体吸附、微米CT扫描、核磁共振实验方法,对沁水盆地武乡区块上古生界煤系页岩气储层孔隙微观特征和孔隙结构进行了研究。结果表明,沁水盆地武乡区块上古生界煤系页岩样品中发育多种类型微观孔隙,常见粒间孔、粒内孔和微裂缝,有机质孔几乎不发育;武乡区块煤系页岩气储层样品孔隙总孔容分布在0.021 9~0.073 5 mL/g之间,平均值为0.039 9 mL/g,总比表面积主要分布在11.94~46.83 m2/g之间,平均为29.16 m2/g,其中介孔(2~50 nm)和微孔(<2 nm)是煤系页岩气储集的主要载体。煤系页岩中的高配位数孔隙数量越多,相应的孔容和孔比表面积越大,孔隙连通性越好;在孔隙数量和总孔容相差不大的前提下,山西组煤系页岩储层孔隙结构与连通性比太原组煤系页岩稍好。
中图分类号:
张金晴, 李贤庆, 张博翔, 张学庆, 杨经纬, 于振锋. 沁水盆地武乡区块上古生界煤系页岩气储层孔隙特征和孔隙结构[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1551-1562.
ZHANG Jinqing, LI Xianqing, ZHANG Boxiang, ZHANG Xueqing, YANG Jingwei, YU Zhenfeng. Pore Characteristics and Pore Structure of the Upper Paleozoic Coal-bearing Shale Gas Reservoir in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(06): 1551-1562.
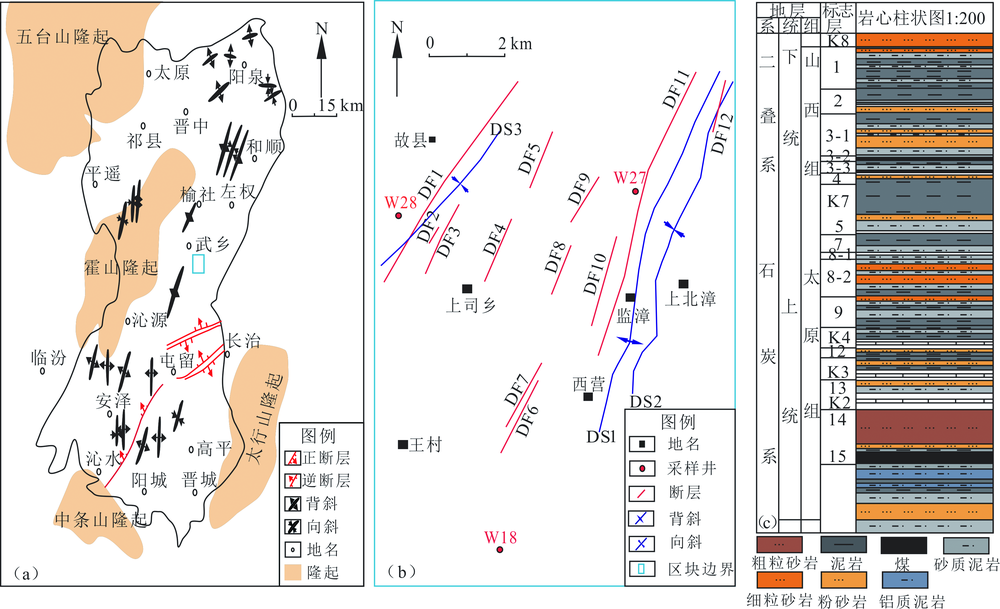
图1 沁水盆地区域构造(a)、武乡区块取样井分布(b)与研究区地层柱状图(c)
Fig.1 Regional structure of Qinshui Basin(a), well location map of the Wuxiang Block(b), and stratigraphic histogram of the study area(c)
| 样品号 | 层位 | 埋深/m | TOC/% | Ro/% | 全岩矿物成分含量 /% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石英 | 碳酸盐矿物 | 黏土矿物 | 其它矿物 | |||||
| W18-03 | 山西组 | 1 581.6 | 6.61 | 2.35 | 34.2 | 2.9 | 54.2 | 8.7 |
| W18-06 | 山西组 | 1 600.3 | 0.29 | 2.41 | 63.0 | 2.0 | 32.5 | 2.5 |
| W18-08 | 山西组 | 1 614.4 | 7.42 | 2.48 | 60.6 | 0.0 | 28.3 | 11.1 |
| W18-11 | 山西组 | 1 652.7 | 1.74 | 2.33 | 51.8 | 2.2 | 40.7 | 5.3 |
| W27-02 | 山西组 | 1 502.3 | 2.23 | 2.61 | 49.1 | 19.7 | 20.5 | 10.7 |
| W27-07 | 山西组 | 1 623.5 | 2.75 | 2.55 | 55.6 | 1.8 | 33.2 | 9.4 |
| W27-09 | 太原组 | 1 677.9 | 1.81 | 2.63 | 48.5 | 0.0 | 47.3 | 4.2 |
| W28-02 | 山西组 | 1 738.2 | 2.01 | 2.39 | 56.0 | 0.9 | 35.3 | 7.8 |
| W28-07 | 山西组 | 1 748.5 | 8.36 | 2.33 | 46.5 | 23.1 | 22.0 | 8.4 |
| W28-13 | 太原组 | 1 884.4 | 1.57 | 2.59 | 59.8 | 2.4 | 34.1 | 3.7 |
| W28-15 | 太原组 | 1 888.0 | 2.82 | 2.54 | 57.5 | 5.1 | 35.3 | 2.1 |
| W28-19 | 太原组 | 1 900.6 | 6.30 | 2.63 | 59.7 | 0.0 | 36.4 | 3.9 |
表1 沁水盆地武乡区块煤系页岩样品的基本地球化学特征
Table 1 Basic geochemical characteristics of coal-bearing shale samples in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin
| 样品号 | 层位 | 埋深/m | TOC/% | Ro/% | 全岩矿物成分含量 /% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石英 | 碳酸盐矿物 | 黏土矿物 | 其它矿物 | |||||
| W18-03 | 山西组 | 1 581.6 | 6.61 | 2.35 | 34.2 | 2.9 | 54.2 | 8.7 |
| W18-06 | 山西组 | 1 600.3 | 0.29 | 2.41 | 63.0 | 2.0 | 32.5 | 2.5 |
| W18-08 | 山西组 | 1 614.4 | 7.42 | 2.48 | 60.6 | 0.0 | 28.3 | 11.1 |
| W18-11 | 山西组 | 1 652.7 | 1.74 | 2.33 | 51.8 | 2.2 | 40.7 | 5.3 |
| W27-02 | 山西组 | 1 502.3 | 2.23 | 2.61 | 49.1 | 19.7 | 20.5 | 10.7 |
| W27-07 | 山西组 | 1 623.5 | 2.75 | 2.55 | 55.6 | 1.8 | 33.2 | 9.4 |
| W27-09 | 太原组 | 1 677.9 | 1.81 | 2.63 | 48.5 | 0.0 | 47.3 | 4.2 |
| W28-02 | 山西组 | 1 738.2 | 2.01 | 2.39 | 56.0 | 0.9 | 35.3 | 7.8 |
| W28-07 | 山西组 | 1 748.5 | 8.36 | 2.33 | 46.5 | 23.1 | 22.0 | 8.4 |
| W28-13 | 太原组 | 1 884.4 | 1.57 | 2.59 | 59.8 | 2.4 | 34.1 | 3.7 |
| W28-15 | 太原组 | 1 888.0 | 2.82 | 2.54 | 57.5 | 5.1 | 35.3 | 2.1 |
| W28-19 | 太原组 | 1 900.6 | 6.30 | 2.63 | 59.7 | 0.0 | 36.4 | 3.9 |

图2 沁水盆地武乡区块煤系页岩样品孔隙特征扫描电镜图像 (a)-(d)为氩离子抛光-场发射扫描电镜下图像;(e)-(h)为自然断面-扫描电镜下图像(a) W28-07,微裂缝,1 748.5 m;(b) W18-08,黄铁矿晶间孔,1 614.4 m;(c) W28-07,有机质孔,1 748.5 m;(d) W28-07,粒间孔和粒内孔,1 748.5 m;(e) W18-11,微裂缝,1 652.7 m;(f) W28-02,有机质孔,1 738.2 m;(g)W18-11,微裂缝,1 652.7 m;(h) W28-19,微裂缝,1 900.6 m
Fig.2 Image analysis of scanning electron microscopy from coal-bearing shale samples in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin
| 样品号 | 粒间孔 | 粒内孔 | 有机质孔 | 微裂缝 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发育程度 | 大小/nm | 发育程度 | 大小/nm | 发育程度 | 大小/nm | 发育程度 | 长度/μm | 宽度/nm | ||||
| W18-08 | +++ | 80~430 | ++ | 70~530 | - | - | + | 13~42 | 70~310 | |||
| W18-11 | +++ | 90~530 | ++ | 80~610 | - | - | + | 7~28 | 40~290 | |||
| W28-02 | +++ | 110~440 | + | 110~730 | + | 30~370 | + | 11~59 | 60~510 | |||
| W28-07 | +++ | 50~330 | ++ | 50~520 | + | 50~160 | + | 7~31 | 110~370 | |||
| W28-19 | +++ | 110~630 | ++ | 80~210 | - | - | + | 2~14 | 30~430 | |||
表2 沁水盆地武乡区块煤系页岩中不同类型孔隙发育程度
Table 2 Development degree of different types of coal-bearing shale in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin
| 样品号 | 粒间孔 | 粒内孔 | 有机质孔 | 微裂缝 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发育程度 | 大小/nm | 发育程度 | 大小/nm | 发育程度 | 大小/nm | 发育程度 | 长度/μm | 宽度/nm | ||||
| W18-08 | +++ | 80~430 | ++ | 70~530 | - | - | + | 13~42 | 70~310 | |||
| W18-11 | +++ | 90~530 | ++ | 80~610 | - | - | + | 7~28 | 40~290 | |||
| W28-02 | +++ | 110~440 | + | 110~730 | + | 30~370 | + | 11~59 | 60~510 | |||
| W28-07 | +++ | 50~330 | ++ | 50~520 | + | 50~160 | + | 7~31 | 110~370 | |||
| W28-19 | +++ | 110~630 | ++ | 80~210 | - | - | + | 2~14 | 30~430 | |||
| 样品编号 | 平均孔径 /nm | 总孔容/ (mL·g-1) | 总比表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 孔容/(mL·g-1) | 比表面积/(m2 ·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 介孔 | 宏孔 | 微孔 | 介孔 | 宏孔 | |||||
| W18-03 | 33.46 | 0.043 7 | 46.83 | 0.013 8 | 0.024 3 | 0.005 6 | 29.49 | 16.67 | 0.67 | |
| W18-06 | 25.19 | 0.029 6 | 16.76 | 0.003 9 | 0.019 5 | 0.006 2 | 7.17 | 8.60 | 0.99 | |
| W18-08 | 24.22 | 0.073 5 | 33.91 | 0.009 8 | 0.017 1 | 0.046 6 | 21.68 | 11.46 | 0.77 | |
| W18-11 | 63.13 | 0.056 8 | 42.72 | 0.009 0 | 0.036 9 | 0.010 9 | 16.04 | 25.99 | 0.69 | |
| W28-02 | 29.35 | 0.029 9 | 17.60 | 0.003 9 | 0.021 1 | 0.004 9 | 7.62 | 9.32 | 0.66 | |
| W28-07 | 30.81 | 0.021 9 | 11.94 | 0.003 2 | 0.012 7 | 0.006 0 | 5.94 | 5.22 | 0.78 | |
| W28-13 | 36.52 | 0.031 7 | 25.79 | 0.005 3 | 0.021 6 | 0.004 8 | 12.05 | 13.21 | 0.53 | |
| W28-15 | 40.72 | 0.033 3 | 28.95 | 0.006 3 | 0.021 9 | 0.005 1 | 14.52 | 13.93 | 0.50 | |
| W28-19 | 40.23 | 0.038 8 | 37.92 | 0.009 6 | 0.023 8 | 0.005 4 | 21.63 | 15.76 | 0.53 | |
表3 沁水盆地武乡区块煤系页岩样品孔隙结构特征
Table 3 Pore structure characteristics of coal-bearing shale in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin
| 样品编号 | 平均孔径 /nm | 总孔容/ (mL·g-1) | 总比表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 孔容/(mL·g-1) | 比表面积/(m2 ·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微孔 | 介孔 | 宏孔 | 微孔 | 介孔 | 宏孔 | |||||
| W18-03 | 33.46 | 0.043 7 | 46.83 | 0.013 8 | 0.024 3 | 0.005 6 | 29.49 | 16.67 | 0.67 | |
| W18-06 | 25.19 | 0.029 6 | 16.76 | 0.003 9 | 0.019 5 | 0.006 2 | 7.17 | 8.60 | 0.99 | |
| W18-08 | 24.22 | 0.073 5 | 33.91 | 0.009 8 | 0.017 1 | 0.046 6 | 21.68 | 11.46 | 0.77 | |
| W18-11 | 63.13 | 0.056 8 | 42.72 | 0.009 0 | 0.036 9 | 0.010 9 | 16.04 | 25.99 | 0.69 | |
| W28-02 | 29.35 | 0.029 9 | 17.60 | 0.003 9 | 0.021 1 | 0.004 9 | 7.62 | 9.32 | 0.66 | |
| W28-07 | 30.81 | 0.021 9 | 11.94 | 0.003 2 | 0.012 7 | 0.006 0 | 5.94 | 5.22 | 0.78 | |
| W28-13 | 36.52 | 0.031 7 | 25.79 | 0.005 3 | 0.021 6 | 0.004 8 | 12.05 | 13.21 | 0.53 | |
| W28-15 | 40.72 | 0.033 3 | 28.95 | 0.006 3 | 0.021 9 | 0.005 1 | 14.52 | 13.93 | 0.50 | |
| W28-19 | 40.23 | 0.038 8 | 37.92 | 0.009 6 | 0.023 8 | 0.005 4 | 21.63 | 15.76 | 0.53 | |
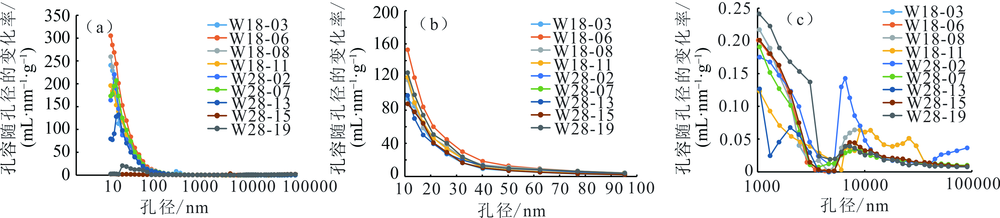
图5 不同孔径对宏孔孔容变化率分布表征(高压压汞法)
Fig.5 Characterization of macropore volume change rate distribution with different pore diameters (high pressure mercury intrusion method)

图7 不同孔径对孔容和比表面积的变化率分布表征(N2吸附法)
Fig.7 Characterization of the change rate distribution of pore volume and specific surface area with different pore diameters (N2 adsorption method)

图9 不同孔径对孔容和比表面积的变化率分布表征(CO2吸附法)
Fig.9 Characterization of the change rate distribution of pore volume and specific surface area with different pore diameters (CO2 adsorption method)

图10 沁水盆地武乡区块煤系页岩全孔径分布及其与北美页岩比较
Fig.10 Full pore size distribution of the coal-bearing shale in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin and its comparison with North American shale

图11 沁水盆地武乡区块煤系页岩孔喉半径分布特征及孔隙配位数
Fig.11 Distribution characteristics of pore roar radius and pore coordination number of coal-bearing shale in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin

图13 沁水盆地武乡区块山西组和太原组煤系页岩样品三维重构喉道分布图
Fig.13 Distribution map of 3D reconstruction of coal-bearing shale samples from Shanxi Formation and Taiyuan Formation in the Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin
| [1] | CURTIS J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938. |
| [2] | 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. |
| [3] | 肖贤明, 宋之光, 朱炎铭, 等. 北美页岩气研究及对我国下古生界页岩气开发的启示[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5):721-727. |
| [4] | 戴金星, 秦胜飞, 胡国艺, 等. 新中国天然气勘探开发70年来的重大进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6):1037-1046. |
| [5] | 郑民, 李建忠, 吴晓智, 等. 我国常规与非常规天然气资源潜力、重点领域与勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(10):1383-1397. |
| [6] |
金之钧, 胡宗全, 高波, 等. 川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气富集与高产控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1):1-10.
DOI |
| [7] | 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(4):561-574. |
| [8] | 石强, 蒋春碧, 陈鹏, 等. 基于游离气为核心的页岩气层类型划分方法——以川南地区下志留统龙马溪组海相页岩气层为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(2):37-46. |
| [9] | 熊亮, 魏力民, 史洪亮. 川南龙马溪组储层分级综合评价技术及应用——以四川盆地威荣页岩气田为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(增):60-65. |
| [10] | 雷丹凤, 李熙喆, 位云生, 等. 海相页岩有效产气储层特征——以四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组页岩为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(2):333-343. |
| [11] | 曹代勇, 王崇敬, 李靖, 等. 煤系页岩气的基本特点与聚集规律[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2014, 42(4):25-30. |
| [12] | 代旭光, 王猛. 鄂尔多斯东南缘海陆交互相页岩储层特征及含气性[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(15):26-32. |
| [13] | 谢卫东, 王猛, 代旭光, 等. 山西河东煤田中—南部煤系页岩气储层微观特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(4):512-525. |
| [14] | 朱炎铭, 周晓刚, 胡琳. 沁南地区太原组页岩气成藏的构造控制[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(8):34-38. |
| [15] | ZHANG J Z, LI X Q, WEI Q, et al. Quantitative characterization of pore-fracture system of organic-rich marine-continental shale reservoirs: A case study of the Upper Permian Longtan Formation, Southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Fuel, 2017, 200:272-281. |
| [16] | ZOU X Y, LI X Q, ZHANG J Z, et al. Characteristics of pore structure and gas content of the Lower Paleozoic shale from the Upper Yangtze Plate, South China[J]. Energies, 2021, 14:7603. |
| [17] | 张吉振, 李贤庆, 邹晓艳, 等. 海陆过渡相煤系页岩孔隙结构特征及其对含气性的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2021, 50(5):478-491. |
| [18] | 董大忠, 邹才能, 戴金星, 等. 中国页岩气发展战略对策建议[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3):397-406. |
| [19] | ZHANG J Z, LI X Q, ZOU X Y, et al. Characterization of the full-sized pore structure of coal-bearing shales and its effect on shale gas content[J]. Energy Fuels, 2019, 33:1969-1982. |
| [20] | ZHANG J Z, LI X Q, ZHANG G W, et al. Microstructural investigation of different nanopore types in marine-continental transitional shales: Examples from the Longtan Formation in Southern Sichuan Basin, south China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 110:912-927. |
| [21] | 和钰凯, 李贤庆, 魏强, 等. 淮南潘谢矿区石盒子组煤系页岩气储层孔隙结构特征及影响因素[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(33): 13618-13627. |
| [22] | 赵佩, 李贤庆, 田兴旺, 等. 川南地区龙马溪组页岩气储层微孔隙结构特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(6): 947-956. |
| [23] | 杨景芬, 徐宏杰, 胡宝林, 等. 海陆过渡相煤系页岩气储层压汞孔隙特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(31): 186-192. |
| [24] | 陈尚斌, 朱炎铭, 王红岩, 等. 川南龙马溪组页岩气储层纳米孔隙结构特征及其成藏意义[J]. 煤炭学报, 2012, 37(3): 438-444. |
| [25] | CHENG P, XIAO X M, TIAN H, et al. Differences in the distribution and occurrence phases of pore water in various nanopores of marine-terrestrial transitional shales in the Yangquan area of the northeast Qinshui Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 137:105510. |
| [26] | 闫高原, 张军建, 路冠文, 等. 沁水盆地太原组-山西组页岩孔隙分形特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5):548-553. |
| [27] | 李阳阳, 李贤庆, 张学庆, 等. 沁水盆地阳泉区块太原组煤系页岩孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(4):1033-1042. |
| [28] | 田忠斌, 魏书宏, 王建青, 等. 沁水盆地中东部海陆过渡相页岩微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(7):1818-1827. |
| [29] | 袁余洋, 李卓沛, 钟明洋, 等. 沁水盆地中南部太原组煤系页岩孔隙结构特征[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(9):184-192. |
| [30] | 曹磊, 郭英海. 沁水盆地东部武乡区块泥页岩孔隙结构特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(4):230-236. |
| [31] | 马如英, 张健, 王猛, 等. 沁水盆地海陆过渡相页岩储层微观孔隙特征及含气性特征[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(4):66-77. |
| [32] | SHAO L Y, YANG Z Y, SHANG X X, et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Carboniferous and Permian in the Qinshui basin, Shanxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 4(4): 384-412. |
| [33] | 秦勇, 梁建设, 申建, 等. 沁水盆地南部致密砂岩和页岩的气测显示与气藏类型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8):1559-1565. |
| [34] | YIN L, GUO S. Full-sized pore structure and fractal characteristics of marine-continental transitional shale: A case study in Qinshui Basin, North China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2019, 93(3): 675-691. |
| [35] | 梁建设, 朱学申, 柳迎红, 等. 沁水盆地与鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界致密气成藏条件类比及勘探潜力[J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(1):192-201. |
| [36] | HU B, HU L, SONG H, et al. Ichnoassemblages and their sedimentary environments in limestone of the Upper Carboniferous-Lower Permian Taiyuan Formation, southeastern Shanxi Province[J]. Paleogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 15(6): 809-818. |
| [37] | ZHANG X Q, LI X Q, YANG J W, et al. Characterization of the full-sized pore structure and controlling factors of the coal-bearing shale in the Wuxiang block, south-central Qinshui Basin, China[J]. Frontiers in the Science, 2022, 9:813925. |
| [38] | 赵楷棣, 傅雪海, 张苗, 等. 煤系泥页岩有机地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(11):182-188. |
| [39] | CLARKSON C R, SOLANO N, BUSTIN R M, et al. Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103: 606-616. |
| [40] | 张金川, 金之钧, 袁明生. 页岩气成藏机理和分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, 24(7):15-18. |
| [41] | LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098. |
| [42] | IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied chemistry). Physical chemistry division commission on colloid and surface chemistry,subcommittee on characterization of porous solids: Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739-1758. |
| [43] | 张明扬, 李贤庆, 王哲, 等. 皖南地区古生界页岩孔隙特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1):172-180. |
| [44] | 张林彦, 包友书, 习成威, 等. 东营凹陷古近系泥页岩孔隙结构特征及连通性[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(2):134-139. |
| [45] | CAO T T, SONG Z G, WANG S B, et al. Characterizing the pore structure in the Silurian and Permian shales of the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 61: 140-150. |
| [1] | 李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 刘若冰, 蔡益栋, 李刚, 周秦, 肖贤明. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1293-1305. |
| [2] | 李庆, 李江山, 卢浩, 齐奉强, 何羽, 安可钦, 李隆禹, 张厚民, 伍岳. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部长73页岩层系储层特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1254-1270. |
| [3] | 漆洋, 吕春研, 王宇慧, 唐书恒, 郗兆栋. 生物地层格架下湘西北地区五峰组—龙马溪组孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1292-1303. |
| [4] | 姜秉仁, 邓恩德, 韩明辉, 马子杰. 黔西北地区石炭系祥摆组页岩微观孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1065-1073. |
| [5] | 崔维平, 杨玉卿, 刘建新. 基于岩性相单元和孔隙结构的低孔低渗储层有效性测井识别方法:以西湖凹陷NB1构造为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 140-148. |
| [6] | 杨毅, 张恒荣, 袁伟, 杨冬, 胡德胜. 常规砂岩与砂砾岩分形特征对比及成因分析:以乌石凹陷X构造流沙港组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 149-158. |
| [7] | 刘文锋, 张小栓, 刘谨铭, 艾力曼·道尔吉, 杨远峰, 张曦文, 祁利祺, 于景维. AH5井区八道湾组砂质和砾质储层孔隙结构特征及评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1844-1853. |
| [8] | 李阳阳, 李贤庆, 张学庆, 杨经纬, 张博翔, 肖贤明, 于振锋. 沁水盆地阳泉区块太原组煤系页岩孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 1033-1042. |
| [9] | 于景维, 牛志杰, 祁利祺, 孙新铭, 柳妮, 张进, 曹嵩. 准噶尔盆地阜北地区头屯河组非均质性综合研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 819-831. |
| [10] | 姜秉仁, 杨通保, 石富伦, 韩明辉, 付炜. 黔西地区下石炭统旧司组页岩气聚集条件及含气性分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 338-348. |
| [11] | 王欢, 马立元, 罗清清, 陈纯芳, 韩波, 李超, 郑晓薇. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界地层压力演化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1166-1180. |
| [12] | 赵建鹏, 崔利凯, 陈惠, 李宁, 王自亮, 马瑶, 杜贵超. 基于CT扫描数字岩心的岩石微观结构定量表征方法[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1205-1213. |
| [13] | 黄宇琪, 张鹏, 张金川, 杨军伟. 湖北来凤LD-1井龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 828-836. |
| [14] | 戴朝霞, 孙蓓蕾, 曾凡桂. 沁水盆地南部长治区块煤层气田的地应力特征[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 266-272. |
| [15] | 胡向阳, 梁玉楠, 吴丰, 廖明光, 张恒荣, 杨冬, 杨毅, 代槿, 钟华明, 吴一雄. 珠江口盆地文昌X-2油田新近系珠江组低阻油层成因机理[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 390-398. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||