



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (06): 1114-1130.
李成禄1,2( ), 徐文喜2, 于援帮3, 李光辉2, 李胜荣1, 袁茂文1, 李士胜1, 徐国战2
), 徐文喜2, 于援帮3, 李光辉2, 李胜荣1, 袁茂文1, 李士胜1, 徐国战2
收稿日期:2017-05-04
修回日期:2017-10-22
出版日期:2017-12-10
发布日期:2017-12-25
作者简介:李成禄,男,博士研究生,高级工程师,1984年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事矿产勘查与成矿规律研究工作。Email:LCL230881@163.com。
基金资助:
LI Chenglu1,2( ), XU Wenxi2, YU Yuanbang3, LI Guanghui2, LI Shengrong1, YUAN Maowen1, LI Shisheng1, XU Guozhan2
), XU Wenxi2, YU Yuanbang3, LI Guanghui2, LI Shengrong1, YUAN Maowen1, LI Shisheng1, XU Guozhan2
Received:2017-05-04
Revised:2017-10-22
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-12-25
摘要:
永新金矿是近年发现的大型蚀变岩型脉状金矿床,闪长玢岩脉等与金矿脉相互穿切并侵入于上盘龙江组火山岩中。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年显示,龙江组安山岩结晶年龄为(113.7 ± 1.8)Ma,闪长玢岩结晶年龄为(114.8 ± 1.9)Ma,均形成于早白垩世晚期。二者钠钾含量变化相对较大,相对富铝富铁、钙镁含量中等,从火山岩到脉岩表现为钙碱性向碱性系列过渡特征。火山岩、脉岩与矿石的稀土元素配分曲线有很好的一致性,矿石稀土含量低于岩石。岩石微量元素总体显示Zr、Hf、Nd、U等明显富集,而Nb、Ta、Th、P、Ti等明显亏损。在Sr/Y-Y和(La/Yb)N-(Yb)N图解中,所有样品均落入经典岛弧岩石范围;在Nb-Y、Ta-Yb的构造环境判别图中均处于火山弧岩浆岩区,在(La/Yb)N-δEu变异图上落在壳-幔型岩浆范围。结合矿床稳定同位素及区域金矿时空分布规律等综合特征,认为永新金矿的形成与早白垩世古太平洋板块俯冲所引发的(火山)岩浆活动有关。
中图分类号:
李成禄, 徐文喜, 于援帮, 李光辉, 李胜荣, 袁茂文, 李士胜, 徐国战. 小兴安岭西北部与永新金矿有关岩浆岩的年代学和地球化学及成矿构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1114-1130.
LI Chenglu, XU Wenxi, YU Yuanbang, LI Guanghui, LI Shengrong, YUAN Maowen, LI Shisheng, XU Guozhan. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Ore-related Magmatic Rocks from the Yongxin Gold Deposit, Northwest Xiao Hinggan Mountains and Their Ore-forming Tectonic Implication[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(06): 1114-1130.

图1 中国东北地区构造地质简图(a)及永新金矿床地质简图(b) 1.白垩系光华组流纹岩及流纹质晶屑凝灰岩等; 2.白垩系龙江组安山岩、安粗岩和英安岩等; 3.中侏罗世花岗闪长岩; 4.晚石炭世—早二叠世正长花岗岩; 5.糜棱岩; 6.闪长玢岩; 7.花岗斑岩; 8.微晶闪长岩; 9.矿体
Fig.1 Regional tectonic units of Northeast China(a) and geological sketch map of the Yongxin gold deposit(b)

图3 永新金矿床安山岩、闪长玢岩和矿石标本及对应显微照片 (a)灰褐色安山岩,斑状结构,块状构造,可见少量杏仁体;(b)正交偏光下安山岩,斑晶斜长石双晶明显,表面浑浊,绢云母化、碳酸盐化较强;(c)灰绿色闪长玢岩,斑状结构,块状构造;(d)正交偏光下闪长玢岩,斑晶斜长石形态规则,斜长石解理缝及边部碳酸盐化、绢云母化等蚀变强烈;(e)蚀变构造角砾岩矿石,硅质强烈充填,角砾成分为围岩正长花岗岩与糜棱岩,黄铁矿浸染状、团块状分布;(f)团块状黄铁矿中见有不规则形态的裂隙金;Pl.斜长石;Au.金矿物;Py.黄铁矿
Fig.3 Drill core and microscopic photos of andesite, diorite porphyry and ores in the Yongxin gold deposit
| 测点 | 206Pbt/ 10-6 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | 232Th /238U | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb*/206Pb* 比值 | 1σ | 207Pb*/235U 比值 | 1σ | 206Pb*/238U 比值 | 1σ | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18022-01 | 10.65 | 726 | 381 | 1.769 5 | 117 | 1.6 | 143 | 126 | 119 | 2.6 | 0.048 9 | 0.002 6 | 0.122 9 | 0.006 4 | 0.018 3 | 0.000 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-02 | 63.30 | 777 | 663 | 1.121 4 | 448 | 3.4 | 465 | 52 | 445 | 6.6 | 0.056 3 | 0.001 3 | 0.562 3 | 0.013 4 | 0.072 0 | 0.000 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-03 | 39.20 | 578 | 1 029 | 0.517 1 | 207 | 1.8 | 406 | 69 | 214 | 4.9 | 0.054 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.250 0 | 0.008 0 | 0.032 7 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-04 | 32.90 | 554 | 795 | 0.663 9 | 212 | 2.7 | 809 | 112 | 257 | 10.8 | 0.066 1 | 0.003 4 | 0.315 2 | 0.019 4 | 0.033 4 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-05 | 1.98 | 89 | 85 | 1.002 4 | 115 | 2.9 | 235 | 219 | 117 | 4.9 | 0.050 9 | 0.005 1 | 0.119 6 | 0.010 3 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-06 | 2.51 | 135 | 110 | 1.176 8 | 108 | 2.2 | 456 | 186 | 105 | 3.6 | 0.055 9 | 0.004 8 | 0.128 0 | 0.010 0 | 0.016 8 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-07 | 2.32 | 111 | 88 | 1.182 8 | 113 | 2.3 | 1 263 | 173 | 133 | 5.4 | 0.082 7 | 0.007 3 | 0.196 5 | 0.014 8 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-08 | 3.60 | 217 | 141 | 1.470 3 | 112 | 1.8 | 109 | 224 | 109 | 3.2 | 0.048 2 | 0.003 4 | 0.115 1 | 0.007 7 | 0.017 5 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-09 | 68.90 | 552 | 1 157 | 0.453 7 | 324 | 3.8 | 800 | 74 | 365 | 12.7 | 0.065 8 | 0.002 4 | 0.477 8 | 0.019 6 | 0.051 5 | 0.000 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-10 | 26.55 | 377 | 700 | 0.511 6 | 205 | 2.2 | 276 | 76 | 205 | 5.0 | 0.051 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.231 1 | 0.007 4 | 0.032 2 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-11 | 7.29 | 417 | 236 | 1.643 0 | 116 | 1.8 | 1 544 | 93 | 139 | 3.3 | 0.095 8 | 0.004 7 | 0.238 8 | 0.011 0 | 0.018 2 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-12 | 2.77 | 133 | 114 | 1.112 1 | 116 | 2.4 | 220 | 227 | 109 | 4.0 | 0.050 5 | 0.004 2 | 0.123 3 | 0.009 9 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-13 | 2.88 | 144 | 114 | 1.179 4 | 112 | 2.4 | 833 | 179 | 133 | 9.5 | 0.066 5 | 0.005 7 | 0.160 3 | 0.013 7 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-14 | 2.79 | 113 | 116 | 0.928 7 | 115 | 2.4 | 676 | 172 | 125 | 4.7 | 0.062 1 | 0.005 0 | 0.152 3 | 0.011 9 | 0.018 0 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-15 | 22.45 | 318 | 400 | 0.778 3 | 286 | 3.3 | 483 | 96 | 289 | 6.7 | 0.056 8 | 0.002 5 | 0.356 9 | 0.015 4 | 0.045 4 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-16 | 1.72 | 79 | 72 | 1.065 4 | 116 | 3.2 | 733 | 269 | 106 | 4.6 | 0.061 8 | 0.007 7 | 0.141 4 | 0.015 0 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-17 | 2.34 | 114 | 92 | 1.196 5 | 112 | 2.4 | 922 | 244 | 126 | 4.8 | 0.069 5 | 0.008 0 | 0.166 8 | 0.019 6 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-18 | 3.44 | 166 | 146 | 1.030 4 | 113 | 2.1 | 124 | 193 | 114 | 3.7 | 0.048 5 | 0.004 2 | 0.114 7 | 0.009 1 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-19 | 3.60 | 230 | 133 | 1.555 5 | 111 | 2.3 | 483 | 152 | 112 | 3.4 | 0.056 8 | 0.003 9 | 0.134 0 | 0.008 5 | 0.017 3 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-20 | 2.01 | 88 | 84 | 1.005 7 | 118 | 2.7 | 146 | 215 | 117 | 5.1 | 0.049 0 | 0.004 8 | 0.121 2 | 0.010 4 | 0.018 5 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-21 | 2.22 | 87 | 92 | 0.892 3 | 121 | 2.6 | 235 | 274 | 129 | 5.9 | 0.050 9 | 0.006 6 | 0.121 4 | 0.010 0 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-22 | 2.01 | 76 | 73 | 0.997 5 | 117 | 2.6 | 1 472 | 158 | 157 | 6.9 | 0.092 2 | 0.007 7 | 0.224 9 | 0.014 9 | 0.018 3 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-23 | 119.67 | 45 | 733 | 0.057 7 | 907 | 7.7 | 1 161 | 75 | 2 480 | 152.3 | 0.078 5 | 0.001 7 | 1.652 1 | 0.037 8 | 0.151 0 | 0.001 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-24 | 32.50 | 243 | 366 | 0.638 1 | 440 | 4.9 | 524 | 63 | 563 | 17.4 | 0.057 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.567 5 | 0.016 5 | 0.070 6 | 0.000 8 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-25 | 14.63 | 175 | 385 | 0.442 6 | 208 | 2.1 | 272 | 83 | 222 | 7.3 | 0.051 7 | 0.001 9 | 0.234 9 | 0.008 2 | 0.032 8 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-26 | 3.17 | 168 | 129 | 1.260 8 | 111 | 2.2 | 457 | 170 | 113 | 3.8 | 0.056 1 | 0.004 3 | 0.130 8 | 0.008 9 | 0.017 3 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-27 | 1.70 | 62 | 73 | 0.839 3 | 118 | 2.1 | 283 | 236 | 114 | 5.5 | 0.052 0 | 0.005 4 | 0.125 8 | 0.010 8 | 0.018 4 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-28 | 34.70 | 413 | 556 | 0.735 3 | 307 | 3.2 | 833 | 63 | 373 | 8.2 | 0.066 8 | 0.002 0 | 0.450 2 | 0.012 8 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-29 | 30.10 | 392 | 533 | 0.714 5 | 291 | 2.9 | 283 | 72 | 292 | 7.3 | 0.052 0 | 0.001 6 | 0.333 2 | 0.010 5 | 0.046 1 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
表1 安山岩(18022)锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 1 U-Th-Pb compositions of the zircon samples from the andesite (18022)
| 测点 | 206Pbt/ 10-6 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | 232Th /238U | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb*/206Pb* 比值 | 1σ | 207Pb*/235U 比值 | 1σ | 206Pb*/238U 比值 | 1σ | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18022-01 | 10.65 | 726 | 381 | 1.769 5 | 117 | 1.6 | 143 | 126 | 119 | 2.6 | 0.048 9 | 0.002 6 | 0.122 9 | 0.006 4 | 0.018 3 | 0.000 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-02 | 63.30 | 777 | 663 | 1.121 4 | 448 | 3.4 | 465 | 52 | 445 | 6.6 | 0.056 3 | 0.001 3 | 0.562 3 | 0.013 4 | 0.072 0 | 0.000 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-03 | 39.20 | 578 | 1 029 | 0.517 1 | 207 | 1.8 | 406 | 69 | 214 | 4.9 | 0.054 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.250 0 | 0.008 0 | 0.032 7 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-04 | 32.90 | 554 | 795 | 0.663 9 | 212 | 2.7 | 809 | 112 | 257 | 10.8 | 0.066 1 | 0.003 4 | 0.315 2 | 0.019 4 | 0.033 4 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-05 | 1.98 | 89 | 85 | 1.002 4 | 115 | 2.9 | 235 | 219 | 117 | 4.9 | 0.050 9 | 0.005 1 | 0.119 6 | 0.010 3 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-06 | 2.51 | 135 | 110 | 1.176 8 | 108 | 2.2 | 456 | 186 | 105 | 3.6 | 0.055 9 | 0.004 8 | 0.128 0 | 0.010 0 | 0.016 8 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-07 | 2.32 | 111 | 88 | 1.182 8 | 113 | 2.3 | 1 263 | 173 | 133 | 5.4 | 0.082 7 | 0.007 3 | 0.196 5 | 0.014 8 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-08 | 3.60 | 217 | 141 | 1.470 3 | 112 | 1.8 | 109 | 224 | 109 | 3.2 | 0.048 2 | 0.003 4 | 0.115 1 | 0.007 7 | 0.017 5 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-09 | 68.90 | 552 | 1 157 | 0.453 7 | 324 | 3.8 | 800 | 74 | 365 | 12.7 | 0.065 8 | 0.002 4 | 0.477 8 | 0.019 6 | 0.051 5 | 0.000 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-10 | 26.55 | 377 | 700 | 0.511 6 | 205 | 2.2 | 276 | 76 | 205 | 5.0 | 0.051 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.231 1 | 0.007 4 | 0.032 2 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-11 | 7.29 | 417 | 236 | 1.643 0 | 116 | 1.8 | 1 544 | 93 | 139 | 3.3 | 0.095 8 | 0.004 7 | 0.238 8 | 0.011 0 | 0.018 2 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-12 | 2.77 | 133 | 114 | 1.112 1 | 116 | 2.4 | 220 | 227 | 109 | 4.0 | 0.050 5 | 0.004 2 | 0.123 3 | 0.009 9 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-13 | 2.88 | 144 | 114 | 1.179 4 | 112 | 2.4 | 833 | 179 | 133 | 9.5 | 0.066 5 | 0.005 7 | 0.160 3 | 0.013 7 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-14 | 2.79 | 113 | 116 | 0.928 7 | 115 | 2.4 | 676 | 172 | 125 | 4.7 | 0.062 1 | 0.005 0 | 0.152 3 | 0.011 9 | 0.018 0 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-15 | 22.45 | 318 | 400 | 0.778 3 | 286 | 3.3 | 483 | 96 | 289 | 6.7 | 0.056 8 | 0.002 5 | 0.356 9 | 0.015 4 | 0.045 4 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-16 | 1.72 | 79 | 72 | 1.065 4 | 116 | 3.2 | 733 | 269 | 106 | 4.6 | 0.061 8 | 0.007 7 | 0.141 4 | 0.015 0 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-17 | 2.34 | 114 | 92 | 1.196 5 | 112 | 2.4 | 922 | 244 | 126 | 4.8 | 0.069 5 | 0.008 0 | 0.166 8 | 0.019 6 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-18 | 3.44 | 166 | 146 | 1.030 4 | 113 | 2.1 | 124 | 193 | 114 | 3.7 | 0.048 5 | 0.004 2 | 0.114 7 | 0.009 1 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-19 | 3.60 | 230 | 133 | 1.555 5 | 111 | 2.3 | 483 | 152 | 112 | 3.4 | 0.056 8 | 0.003 9 | 0.134 0 | 0.008 5 | 0.017 3 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-20 | 2.01 | 88 | 84 | 1.005 7 | 118 | 2.7 | 146 | 215 | 117 | 5.1 | 0.049 0 | 0.004 8 | 0.121 2 | 0.010 4 | 0.018 5 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-21 | 2.22 | 87 | 92 | 0.892 3 | 121 | 2.6 | 235 | 274 | 129 | 5.9 | 0.050 9 | 0.006 6 | 0.121 4 | 0.010 0 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-22 | 2.01 | 76 | 73 | 0.997 5 | 117 | 2.6 | 1 472 | 158 | 157 | 6.9 | 0.092 2 | 0.007 7 | 0.224 9 | 0.014 9 | 0.018 3 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-23 | 119.67 | 45 | 733 | 0.057 7 | 907 | 7.7 | 1 161 | 75 | 2 480 | 152.3 | 0.078 5 | 0.001 7 | 1.652 1 | 0.037 8 | 0.151 0 | 0.001 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-24 | 32.50 | 243 | 366 | 0.638 1 | 440 | 4.9 | 524 | 63 | 563 | 17.4 | 0.057 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.567 5 | 0.016 5 | 0.070 6 | 0.000 8 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-25 | 14.63 | 175 | 385 | 0.442 6 | 208 | 2.1 | 272 | 83 | 222 | 7.3 | 0.051 7 | 0.001 9 | 0.234 9 | 0.008 2 | 0.032 8 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-26 | 3.17 | 168 | 129 | 1.260 8 | 111 | 2.2 | 457 | 170 | 113 | 3.8 | 0.056 1 | 0.004 3 | 0.130 8 | 0.008 9 | 0.017 3 | 0.000 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-27 | 1.70 | 62 | 73 | 0.839 3 | 118 | 2.1 | 283 | 236 | 114 | 5.5 | 0.052 0 | 0.005 4 | 0.125 8 | 0.010 8 | 0.018 4 | 0.000 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-28 | 34.70 | 413 | 556 | 0.735 3 | 307 | 3.2 | 833 | 63 | 373 | 8.2 | 0.066 8 | 0.002 0 | 0.450 2 | 0.012 8 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18022-29 | 30.10 | 392 | 533 | 0.714 5 | 291 | 2.9 | 283 | 72 | 292 | 7.3 | 0.052 0 | 0.001 6 | 0.333 2 | 0.010 5 | 0.046 1 | 0.000 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 测点 | 206Pbt/ 10-6 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | 232Th /238U | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb*/206Pb* 比值 | 1σ | 207Pb*/235U 比值 | 1σ | 206Pb*/238U 比值 | 1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17001-2-01 | 390 | 327 | 583 | 0.549 1 | 446 | 7.7 | 345 | 106 | 469 | 16.1 | 0.053 2 | 0.002 5 | 0.538 4 | 0.024 0 | 0.071 6 | 0.001 3 |
| 17001-2-02 | 509 | 352 | 518 | 0.688 5 | 195 | 5.7 | 2 948 | 107 | 575 | 38.0 | 0.215 6 | 0.014 3 | 0.956 5 | 0.075 2 | 0.030 7 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-03 | 91 | 304 | 191 | 1.617 7 | 117 | 3.7 | 339 | 264 | 118 | 5.0 | 0.053 2 | 0.006 3 | 0.121 2 | 0.012 2 | 0.018 3 | 0.000 6 |
| 17001-2-04 | 104 | 312 | 207 | 1.539 2 | 121 | 5.3 | 306 | 348 | 129 | 8.3 | 0.052 4 | 0.009 0 | 0.129 1 | 0.016 9 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-05 | 98 | 225 | 271 | 0.836 7 | 166 | 5.1 | 309 | 231 | 166 | 7.8 | 0.052 5 | 0.005 3 | 0.180 9 | 0.015 7 | 0.026 1 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-06 | 31 | 40 | 59 | 0.676 9 | 137 | 7.0 | 2 595 | 268 | 245 | 30.6 | 0.173 8 | 0.027 6 | 0.388 5 | 0.050 8 | 0.021 5 | 0.001 1 |
| 17001-2-07 | 47 | 100 | 84 | 1.163 6 | 139 | 6.3 | 2 027 | 293 | 171 | 11.3 | 0.124 9 | 0.020 5 | 0.303 5 | 0.048 0 | 0.021 7 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-08 | 55 | 184 | 134 | 1.381 9 | 113 | 4.4 | 295 | 278 | 108 | 6.5 | 0.052 2 | 0.007 0 | 0.117 7 | 0.013 5 | 0.017 7 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-09 | 27 | 85 | 68 | 1.287 6 | 110 | 6.6 | 1 302 | 478 | 111 | 8.1 | 0.084 4 | 0.020 2 | 0.155 0 | 0.034 8 | 0.017 2 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-10 | 40 | 118 | 117 | 1.045 8 | 109 | 6.0 | 33 | 372 | 119 | 9.4 | 0.046 5 | 0.008 4 | 0.112 5 | 0.018 0 | 0.017 1 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-11 | 67 | 250 | 167 | 1.554 8 | 112 | 4.6 | 120 | 296 | 96 | 5.2 | 0.048 5 | 0.006 6 | 0.116 4 | 0.016 3 | 0.017 5 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-12 | 66 | 204 | 161 | 1.268 0 | 116 | 5.0 | 1 133 | 319 | 115 | 5.7 | 0.074 9 | 0.011 7 | 0.173 3 | 0.023 5 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-13 | 28 | 41 | 51 | 0.828 4 | 134 | 7.8 | 2 881 | 281 | 223 | 17.3 | 0.206 8 | 0.035 3 | 0.421 5 | 0.046 5 | 0.021 0 | 0.001 2 |
| 17001-2-14 | 42 | 156 | 123 | 1.303 8 | 119 | 5.3 | 433 | 383 | 97 | 6.7 | 0.055 3 | 0.011 0 | 0.126 2 | 0.022 1 | 0.018 6 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-15 | 65 | 226 | 161 | 1.448 2 | 119 | 5.1 | 87 | 356 | 109 | 6.5 | 0.047 7 | 0.008 0 | 0.124 5 | 0.023 7 | 0.018 6 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-16 | 25 | 85 | 84 | 1.049 3 | 129 | 6.9 | 1 524 | 550 | 109 | 7.1 | 0.094 7 | 0.026 7 | 0.134 6 | 0.033 9 | 0.020 2 | 0.001 1 |
| 17001-2-17 | 37 | 117 | 106 | 1.173 9 | 123 | 5.2 | 80 | 330 | 115 | 8.2 | 0.047 6 | 0.007 4 | 0.129 7 | 0.017 9 | 0.019 3 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-18 | 59 | 211 | 154 | 1.429 9 | 123 | 5.6 | 456 | 361 | 111 | 7.5 | 0.055 9 | 0.010 5 | 0.130 0 | 0.027 9 | 0.019 2 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-19 | 44 | 138 | 114 | 1.303 1 | 122 | 6.5 | 972 | 410 | 123 | 8.8 | 0.071 5 | 0.014 1 | 0.155 8 | 0.026 9 | 0.019 1 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-20 | 150 | 259 | 432 | 0.656 4 | 228 | 6.9 | 139 | 270 | 217 | 14.6 | 0.048 8 | 0.006 1 | 0.238 0 | 0.025 7 | 0.036 0 | 0.001 1 |
| 17001-2-21 | 66 | 234 | 176 | 1.411 5 | 115 | 4.9 | 109 | 341 | 108 | 5.6 | 0.048 2 | 0.007 7 | 0.117 8 | 0.018 2 | 0.018 0 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-22 | 29 | 90 | 90 | 1.048 1 | 115 | 5.5 | 1 276 | 333 | 126 | 9.0 | 0.083 3 | 0.014 0 | 0.167 5 | 0.027 4 | 0.017 9 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-23 | 64 | 193 | 121 | 1.650 1 | 132 | 5.3 | 587 | 425 | 128 | 7.4 | 0.059 5 | 0.011 4 | 0.145 1 | 0.025 9 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-24 | 57 | 215 | 160 | 1.403 7 | 120 | 3.8 | 189 | 272 | 102 | 5.5 | 0.049 7 | 0.006 5 | 0.132 2 | 0.014 5 | 0.018 8 | 0.000 6 |
| 17001-2-25 | 61 | 203 | 136 | 1.541 3 | 123 | 6.0 | 1 220 | 349 | 114 | 6.7 | 0.080 9 | 0.014 1 | 0.178 8 | 0.019 0 | 0.019 3 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-26 | 70 | 251 | 158 | 1.644 3 | 107 | 4.3 | 1 106 | 347 | 107 | 5.6 | 0.076 4 | 0.013 2 | 0.144 3 | 0.020 0 | 0.016 7 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-27 | 151 | 519 | 298 | 1.736 9 | 112 | 3.4 | 354 | 233 | 111 | 4.9 | 0.053 6 | 0.005 5 | 0.120 0 | 0.009 6 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 5 |
| 17001-2-28 | 131 | 384 | 240 | 1.637 0 | 120 | 4.2 | 1 013 | 225 | 130 | 6.6 | 0.073 0 | 0.008 0 | 0.192 1 | 0.020 2 | 0.018 7 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-29 | 73 | 245 | 168 | 1.499 6 | 116 | 4.9 | 261 | 381 | 109 | 8.0 | 0.051 5 | 0.009 6 | 0.123 8 | 0.020 0 | 0.018 2 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-30 | 67 | 231 | 152 | 1.528 1 | 110 | 4.6 | 467 | 302 | 107 | 7.2 | 0.054 8 | 0.010 0 | 0.111 5 | 0.014 4 | 0.017 3 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-31 | 100 | 138 | 123 | 1.148 4 | 148 | 6.2 | 2 506 | 239 | 279 | 27.9 | 0.164 9 | 0.023 2 | 0.537 0 | 0.080 4 | 0.023 2 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-32 | 40 | 126 | 110 | 1.188 1 | 114 | 5.8 | 280 | 422 | 112 | 9.6 | 0.051 9 | 0.010 9 | 0.121 9 | 0.034 3 | 0.017 8 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-33 | 37 | 124 | 90 | 1.392 7 | 114 | 5.7 | 635 | 372 | 104 | 6.8 | 0.060 9 | 0.010 3 | 0.145 5 | 0.019 8 | 0.017 8 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-34 | 70 | 149 | 118 | 1.256 4 | 123 | 4.7 | 2 106 | 212 | 169 | 10.3 | 0.130 5 | 0.015 7 | 0.314 5 | 0.034 1 | 0.019 3 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-35 | 48 | 114 | 100 | 1.181 6 | 124 | 5.9 | 2 147 | 272 | 144 | 9.0 | 0.133 7 | 0.020 5 | 0.279 7 | 0.030 9 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-36 | 36 | 128 | 107 | 1.250 8 | 112 | 5.0 | 367 | 356 | 99 | 8.1 | 0.053 7 | 0.009 4 | 0.122 4 | 0.021 6 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-37 | 36 | 47.5 | 58 | 0.845 7 | 146 | 7.6 | 3 033 | 283 | 260 | 16.8 | 0.227 3 | 0.039 6 | 0.538 6 | 0.048 6 | 0.022 9 | 0.001 2 |
| 17001-2-38 | 50 | 129 | 101 | 1.257 3 | 122 | 6.1 | 1 533 | 313 | 153 | 10.6 | 0.095 3 | 0.015 6 | 0.244 0 | 0.041 0 | 0.019 0 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-39 | 68 | 214 | 148 | 1.494 3 | 118 | 5.7 | 322 | 328 | 117 | 6.6 | 0.052 6 | 0.008 6 | 0.119 7 | 0.014 9 | 0.018 4 | 0.000 9 |
表2 闪长玢岩(17001-2)锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 2 U-Th-Pb composition of the zircon samples from the diorite porphyry(17001-2)
| 测点 | 206Pbt/ 10-6 | Th/ 10-6 | U/ 10-6 | 232Th /238U | 206Pb/238U 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th 年龄/Ma | 1σ | 207Pb*/206Pb* 比值 | 1σ | 207Pb*/235U 比值 | 1σ | 206Pb*/238U 比值 | 1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17001-2-01 | 390 | 327 | 583 | 0.549 1 | 446 | 7.7 | 345 | 106 | 469 | 16.1 | 0.053 2 | 0.002 5 | 0.538 4 | 0.024 0 | 0.071 6 | 0.001 3 |
| 17001-2-02 | 509 | 352 | 518 | 0.688 5 | 195 | 5.7 | 2 948 | 107 | 575 | 38.0 | 0.215 6 | 0.014 3 | 0.956 5 | 0.075 2 | 0.030 7 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-03 | 91 | 304 | 191 | 1.617 7 | 117 | 3.7 | 339 | 264 | 118 | 5.0 | 0.053 2 | 0.006 3 | 0.121 2 | 0.012 2 | 0.018 3 | 0.000 6 |
| 17001-2-04 | 104 | 312 | 207 | 1.539 2 | 121 | 5.3 | 306 | 348 | 129 | 8.3 | 0.052 4 | 0.009 0 | 0.129 1 | 0.016 9 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-05 | 98 | 225 | 271 | 0.836 7 | 166 | 5.1 | 309 | 231 | 166 | 7.8 | 0.052 5 | 0.005 3 | 0.180 9 | 0.015 7 | 0.026 1 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-06 | 31 | 40 | 59 | 0.676 9 | 137 | 7.0 | 2 595 | 268 | 245 | 30.6 | 0.173 8 | 0.027 6 | 0.388 5 | 0.050 8 | 0.021 5 | 0.001 1 |
| 17001-2-07 | 47 | 100 | 84 | 1.163 6 | 139 | 6.3 | 2 027 | 293 | 171 | 11.3 | 0.124 9 | 0.020 5 | 0.303 5 | 0.048 0 | 0.021 7 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-08 | 55 | 184 | 134 | 1.381 9 | 113 | 4.4 | 295 | 278 | 108 | 6.5 | 0.052 2 | 0.007 0 | 0.117 7 | 0.013 5 | 0.017 7 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-09 | 27 | 85 | 68 | 1.287 6 | 110 | 6.6 | 1 302 | 478 | 111 | 8.1 | 0.084 4 | 0.020 2 | 0.155 0 | 0.034 8 | 0.017 2 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-10 | 40 | 118 | 117 | 1.045 8 | 109 | 6.0 | 33 | 372 | 119 | 9.4 | 0.046 5 | 0.008 4 | 0.112 5 | 0.018 0 | 0.017 1 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-11 | 67 | 250 | 167 | 1.554 8 | 112 | 4.6 | 120 | 296 | 96 | 5.2 | 0.048 5 | 0.006 6 | 0.116 4 | 0.016 3 | 0.017 5 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-12 | 66 | 204 | 161 | 1.268 0 | 116 | 5.0 | 1 133 | 319 | 115 | 5.7 | 0.074 9 | 0.011 7 | 0.173 3 | 0.023 5 | 0.018 1 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-13 | 28 | 41 | 51 | 0.828 4 | 134 | 7.8 | 2 881 | 281 | 223 | 17.3 | 0.206 8 | 0.035 3 | 0.421 5 | 0.046 5 | 0.021 0 | 0.001 2 |
| 17001-2-14 | 42 | 156 | 123 | 1.303 8 | 119 | 5.3 | 433 | 383 | 97 | 6.7 | 0.055 3 | 0.011 0 | 0.126 2 | 0.022 1 | 0.018 6 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-15 | 65 | 226 | 161 | 1.448 2 | 119 | 5.1 | 87 | 356 | 109 | 6.5 | 0.047 7 | 0.008 0 | 0.124 5 | 0.023 7 | 0.018 6 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-16 | 25 | 85 | 84 | 1.049 3 | 129 | 6.9 | 1 524 | 550 | 109 | 7.1 | 0.094 7 | 0.026 7 | 0.134 6 | 0.033 9 | 0.020 2 | 0.001 1 |
| 17001-2-17 | 37 | 117 | 106 | 1.173 9 | 123 | 5.2 | 80 | 330 | 115 | 8.2 | 0.047 6 | 0.007 4 | 0.129 7 | 0.017 9 | 0.019 3 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-18 | 59 | 211 | 154 | 1.429 9 | 123 | 5.6 | 456 | 361 | 111 | 7.5 | 0.055 9 | 0.010 5 | 0.130 0 | 0.027 9 | 0.019 2 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-19 | 44 | 138 | 114 | 1.303 1 | 122 | 6.5 | 972 | 410 | 123 | 8.8 | 0.071 5 | 0.014 1 | 0.155 8 | 0.026 9 | 0.019 1 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-20 | 150 | 259 | 432 | 0.656 4 | 228 | 6.9 | 139 | 270 | 217 | 14.6 | 0.048 8 | 0.006 1 | 0.238 0 | 0.025 7 | 0.036 0 | 0.001 1 |
| 17001-2-21 | 66 | 234 | 176 | 1.411 5 | 115 | 4.9 | 109 | 341 | 108 | 5.6 | 0.048 2 | 0.007 7 | 0.117 8 | 0.018 2 | 0.018 0 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-22 | 29 | 90 | 90 | 1.048 1 | 115 | 5.5 | 1 276 | 333 | 126 | 9.0 | 0.083 3 | 0.014 0 | 0.167 5 | 0.027 4 | 0.017 9 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-23 | 64 | 193 | 121 | 1.650 1 | 132 | 5.3 | 587 | 425 | 128 | 7.4 | 0.059 5 | 0.011 4 | 0.145 1 | 0.025 9 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-24 | 57 | 215 | 160 | 1.403 7 | 120 | 3.8 | 189 | 272 | 102 | 5.5 | 0.049 7 | 0.006 5 | 0.132 2 | 0.014 5 | 0.018 8 | 0.000 6 |
| 17001-2-25 | 61 | 203 | 136 | 1.541 3 | 123 | 6.0 | 1 220 | 349 | 114 | 6.7 | 0.080 9 | 0.014 1 | 0.178 8 | 0.019 0 | 0.019 3 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-26 | 70 | 251 | 158 | 1.644 3 | 107 | 4.3 | 1 106 | 347 | 107 | 5.6 | 0.076 4 | 0.013 2 | 0.144 3 | 0.020 0 | 0.016 7 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-27 | 151 | 519 | 298 | 1.736 9 | 112 | 3.4 | 354 | 233 | 111 | 4.9 | 0.053 6 | 0.005 5 | 0.120 0 | 0.009 6 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 5 |
| 17001-2-28 | 131 | 384 | 240 | 1.637 0 | 120 | 4.2 | 1 013 | 225 | 130 | 6.6 | 0.073 0 | 0.008 0 | 0.192 1 | 0.020 2 | 0.018 7 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-29 | 73 | 245 | 168 | 1.499 6 | 116 | 4.9 | 261 | 381 | 109 | 8.0 | 0.051 5 | 0.009 6 | 0.123 8 | 0.020 0 | 0.018 2 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-30 | 67 | 231 | 152 | 1.528 1 | 110 | 4.6 | 467 | 302 | 107 | 7.2 | 0.054 8 | 0.010 0 | 0.111 5 | 0.014 4 | 0.017 3 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-31 | 100 | 138 | 123 | 1.148 4 | 148 | 6.2 | 2 506 | 239 | 279 | 27.9 | 0.164 9 | 0.023 2 | 0.537 0 | 0.080 4 | 0.023 2 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-32 | 40 | 126 | 110 | 1.188 1 | 114 | 5.8 | 280 | 422 | 112 | 9.6 | 0.051 9 | 0.010 9 | 0.121 9 | 0.034 3 | 0.017 8 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-33 | 37 | 124 | 90 | 1.392 7 | 114 | 5.7 | 635 | 372 | 104 | 6.8 | 0.060 9 | 0.010 3 | 0.145 5 | 0.019 8 | 0.017 8 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-34 | 70 | 149 | 118 | 1.256 4 | 123 | 4.7 | 2 106 | 212 | 169 | 10.3 | 0.130 5 | 0.015 7 | 0.314 5 | 0.034 1 | 0.019 3 | 0.000 7 |
| 17001-2-35 | 48 | 114 | 100 | 1.181 6 | 124 | 5.9 | 2 147 | 272 | 144 | 9.0 | 0.133 7 | 0.020 5 | 0.279 7 | 0.030 9 | 0.019 4 | 0.000 9 |
| 17001-2-36 | 36 | 128 | 107 | 1.250 8 | 112 | 5.0 | 367 | 356 | 99 | 8.1 | 0.053 7 | 0.009 4 | 0.122 4 | 0.021 6 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 8 |
| 17001-2-37 | 36 | 47.5 | 58 | 0.845 7 | 146 | 7.6 | 3 033 | 283 | 260 | 16.8 | 0.227 3 | 0.039 6 | 0.538 6 | 0.048 6 | 0.022 9 | 0.001 2 |
| 17001-2-38 | 50 | 129 | 101 | 1.257 3 | 122 | 6.1 | 1 533 | 313 | 153 | 10.6 | 0.095 3 | 0.015 6 | 0.244 0 | 0.041 0 | 0.019 0 | 0.001 0 |
| 17001-2-39 | 68 | 214 | 148 | 1.494 3 | 118 | 5.7 | 322 | 328 | 117 | 6.6 | 0.052 6 | 0.008 6 | 0.119 7 | 0.014 9 | 0.018 4 | 0.000 9 |
| 岩石 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/CNK | σ | DI | Na2O/K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闪长玢岩 | 17010-1 | 53.92 | 1.04 | 16.13 | 1.48 | 4.34 | 0.14 | 1.80 | 5.34 | 1.66 | 4.99 | 0.51 | 1.58 | 0.58 | 8.06 | 99.42 | 0.90 | 4.05 | 58.90 | 0.33 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 17001-2 | 58.36 | 0.92 | 16.08 | 1.98 | 3.51 | 0.23 | 1.73 | 4.30 | 0.40 | 3.63 | 0.39 | 3.32 | 0.60 | 8.26 | 99.78 | 1.29 | 1.06 | 59.49 | 0.11 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 18003-5 | 50.70 | 1.16 | 17.45 | 1.92 | 4.84 | 0.30 | 2.44 | 4.31 | 0.08 | 4.28 | 0.42 | 3.20 | 0.26 | 10.96 | 98.87 | 1.38 | 2.47 | 51.51 | 0.02 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 19003-2 | 60.78 | 1.41 | 16.94 | 2.20 | 5.16 | 0.07 | 1.87 | 1.05 | 0.13 | 4.44 | 0.72 | 0.94 | 0.39 | 4.22 | 98.98 | 2.44 | 1.17 | 68.25 | 0.03 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 18006-5 | 51.56 | 1.15 | 16.44 | 2.50 | 4.44 | 0.13 | 2.70 | 6.03 | 3.00 | 3.80 | 0.59 | 1.26 | 0.75 | 7.34 | 99.68 | 0.82 | 5.40 | 55.56 | 0.79 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 17003-2 | 48.00 | 1.03 | 18.01 | 2.00 | 5.11 | 0.11 | 3.49 | 6.95 | 3.00 | 3.22 | 0.49 | 3.00 | 0.08 | 8.08 | 99.49 | 0.85 | 7.74 | 48.64 | 0.93 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 19003-6 | 49.60 | 1.42 | 16.43 | 2.19 | 5.77 | 0.21 | 2.78 | 4.50 | 0.05 | 5.10 | 0.72 | 1.98 | 0.49 | 10.02 | 98.79 | 1.19 | 4.02 | 51.00 | 0.01 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 17011-4 | 49.64 | 1.61 | 18.73 | 2.06 | 6.38 | 0.13 | 4.01 | 3.86 | 0.34 | 4.68 | 0.80 | 3.86 | 0.96 | 6.88 | 99.12 | 1.48 | 3.80 | 48.34 | 0.07 |
| 安粗岩 | 18022 | 56.92 | 1.15 | 16.59 | 6.46 | 4.07 | 0.13 | 1.66 | 5.35 | 4.01 | 3.05 | 0.43 | 1.80 | 0.60 | 3.82 | 103.64 | 0.84 | 3.58 | 60.22 | 1.31 |
| 安山岩 | 18017-5 | 56.00 | 0.69 | 15.70 | 1.07 | 5.28 | 0.30 | 2.95 | 5.08 | 2.44 | 2.79 | 0.15 | 3.10 | 0.51 | 7.08 | 99.53 | 0.96 | 2.10 | 53.81 | 0.87 |
| 安山岩 | 18007-1 | 58.80 | 0.74 | 14.44 | 1.01 | 5.44 | 0.22 | 2.86 | 5.22 | 2.58 | 2.35 | 0.17 | 2.22 | 0.28 | 5.02 | 98.86 | 0.89 | 1.54 | 56.02 | 1.10 |
| 安山岩 | 17012-1 | 60.16 | 0.62 | 13.92 | 3.36 | 2.54 | 0.45 | 2.00 | 6.31 | 2.26 | 2.20 | 0.13 | 2.82 | 0.54 | 6.18 | 100.13 | 0.79 | 1.16 | 58.33 | 1.03 |
| 英安岩 | 18006-1 | 61.60 | 0.84 | 13.57 | 1.98 | 4.20 | 0.25 | 2.18 | 4.49 | 1.61 | 1.69 | 0.30 | 2.88 | 0.49 | 6.52 | 99.23 | 1.07 | 0.59 | 59.23 | 0.95 |
表3 火山岩和脉岩主量元素分析结果(wB/%)
Table 3 Major element compositions for volcanic rocks and dyke(%)
| 岩石 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/CNK | σ | DI | Na2O/K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闪长玢岩 | 17010-1 | 53.92 | 1.04 | 16.13 | 1.48 | 4.34 | 0.14 | 1.80 | 5.34 | 1.66 | 4.99 | 0.51 | 1.58 | 0.58 | 8.06 | 99.42 | 0.90 | 4.05 | 58.90 | 0.33 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 17001-2 | 58.36 | 0.92 | 16.08 | 1.98 | 3.51 | 0.23 | 1.73 | 4.30 | 0.40 | 3.63 | 0.39 | 3.32 | 0.60 | 8.26 | 99.78 | 1.29 | 1.06 | 59.49 | 0.11 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 18003-5 | 50.70 | 1.16 | 17.45 | 1.92 | 4.84 | 0.30 | 2.44 | 4.31 | 0.08 | 4.28 | 0.42 | 3.20 | 0.26 | 10.96 | 98.87 | 1.38 | 2.47 | 51.51 | 0.02 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 19003-2 | 60.78 | 1.41 | 16.94 | 2.20 | 5.16 | 0.07 | 1.87 | 1.05 | 0.13 | 4.44 | 0.72 | 0.94 | 0.39 | 4.22 | 98.98 | 2.44 | 1.17 | 68.25 | 0.03 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 18006-5 | 51.56 | 1.15 | 16.44 | 2.50 | 4.44 | 0.13 | 2.70 | 6.03 | 3.00 | 3.80 | 0.59 | 1.26 | 0.75 | 7.34 | 99.68 | 0.82 | 5.40 | 55.56 | 0.79 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 17003-2 | 48.00 | 1.03 | 18.01 | 2.00 | 5.11 | 0.11 | 3.49 | 6.95 | 3.00 | 3.22 | 0.49 | 3.00 | 0.08 | 8.08 | 99.49 | 0.85 | 7.74 | 48.64 | 0.93 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 19003-6 | 49.60 | 1.42 | 16.43 | 2.19 | 5.77 | 0.21 | 2.78 | 4.50 | 0.05 | 5.10 | 0.72 | 1.98 | 0.49 | 10.02 | 98.79 | 1.19 | 4.02 | 51.00 | 0.01 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 17011-4 | 49.64 | 1.61 | 18.73 | 2.06 | 6.38 | 0.13 | 4.01 | 3.86 | 0.34 | 4.68 | 0.80 | 3.86 | 0.96 | 6.88 | 99.12 | 1.48 | 3.80 | 48.34 | 0.07 |
| 安粗岩 | 18022 | 56.92 | 1.15 | 16.59 | 6.46 | 4.07 | 0.13 | 1.66 | 5.35 | 4.01 | 3.05 | 0.43 | 1.80 | 0.60 | 3.82 | 103.64 | 0.84 | 3.58 | 60.22 | 1.31 |
| 安山岩 | 18017-5 | 56.00 | 0.69 | 15.70 | 1.07 | 5.28 | 0.30 | 2.95 | 5.08 | 2.44 | 2.79 | 0.15 | 3.10 | 0.51 | 7.08 | 99.53 | 0.96 | 2.10 | 53.81 | 0.87 |
| 安山岩 | 18007-1 | 58.80 | 0.74 | 14.44 | 1.01 | 5.44 | 0.22 | 2.86 | 5.22 | 2.58 | 2.35 | 0.17 | 2.22 | 0.28 | 5.02 | 98.86 | 0.89 | 1.54 | 56.02 | 1.10 |
| 安山岩 | 17012-1 | 60.16 | 0.62 | 13.92 | 3.36 | 2.54 | 0.45 | 2.00 | 6.31 | 2.26 | 2.20 | 0.13 | 2.82 | 0.54 | 6.18 | 100.13 | 0.79 | 1.16 | 58.33 | 1.03 |
| 英安岩 | 18006-1 | 61.60 | 0.84 | 13.57 | 1.98 | 4.20 | 0.25 | 2.18 | 4.49 | 1.61 | 1.69 | 0.30 | 2.88 | 0.49 | 6.52 | 99.23 | 1.07 | 0.59 | 59.23 | 0.95 |
| 岩石 | 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ∑REE | ∑Ce/∑Y | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闪长玢岩 | 17010-1 | 44.19 | 86.86 | 10.52 | 41.56 | 7.55 | 1.91 | 6.27 | 0.93 | 4.89 | 0.97 | 2.76 | 0.41 | 2.43 | 0.44 | 25.28 | 236.97 | 4.34 | 0.83 | 13.02 | 3.78 | 2.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | 17001-2 | 34.75 | 66.55 | 8.44 | 33.89 | 6.34 | 1.72 | 5.32 | 0.80 | 4.39 | 0.88 | 2.57 | 0.38 | 2.34 | 0.42 | 22.79 | 191.58 | 3.80 | 0.88 | 10.64 | 3.54 | 1.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | 18003-5 | 26.26 | 53.21 | 7.10 | 29.34 | 5.81 | 1.74 | 4.72 | 0.70 | 3.90 | 0.76 | 2.18 | 0.31 | 1.91 | 0.34 | 19.60 | 157.88 | 3.59 | 0.98 | 9.84 | 2.92 | 2.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | 19003-2 | 39.78 | 82.76 | 10.33 | 42.25 | 8.35 | 2.20 | 6.84 | 1.05 | 5.39 | 1.09 | 3.01 | 0.42 | 2.54 | 0.42 | 27.32 | 233.75 | 3.86 | 0.86 | 11.24 | 3.08 | 2.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 18006-5 | 34.90 | 68.67 | 8.77 | 35.90 | 6.89 | 2.00 | 5.57 | 0.83 | 4.48 | 0.82 | 2.41 | 0.33 | 1.99 | 0.35 | 22.18 | 196.08 | 4.03 | 0.96 | 12.61 | 3.27 | 2.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 17003-2 | 30.57 | 59.75 | 7.64 | 31.12 | 6.20 | 1.80 | 5.12 | 0.77 | 3.97 | 0.77 | 2.03 | 0.27 | 1.63 | 0.27 | 18.15 | 170.07 | 4.16 | 0.95 | 13.45 | 3.18 | 2.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 19003-6 | 39.92 | 82.50 | 10.16 | 42.37 | 8.29 | 2.23 | 6.89 | 1.07 | 5.61 | 1.05 | 2.97 | 0.42 | 2.55 | 0.47 | 28.13 | 234.63 | 3.77 | 0.88 | 11.24 | 3.11 | 2.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 17011-4 | 50.22 | 104.41 | 12.69 | 50.30 | 9.39 | 2.41 | 7.68 | 1.15 | 6.16 | 1.18 | 3.33 | 0.47 | 2.84 | 0.52 | 30.26 | 282.99 | 4.28 | 0.84 | 12.68 | 3.45 | 2.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安粗岩 | 18022 | 45.00 | 91.40 | 11.20 | 44.80 | 8.60 | 2.49 | 6.87 | 1.03 | 5.63 | 1.05 | 3.00 | 0.46 | 3.09 | 0.51 | 29.20 | 254.33 | 4.00 | 0.96 | 10.45 | 3.38 | 1.84 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安山岩 | 18017-5 | 49.78 | 99.22 | 11.17 | 42.89 | 8.36 | 2.10 | 7.37 | 1.15 | 6.43 | 1.32 | 3.76 | 0.56 | 3.42 | 0.59 | 34.48 | 272.60 | 3.61 | 0.80 | 10.43 | 3.84 | 1.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安山岩 | 18007-1 | 47.58 | 95.06 | 11.00 | 43.26 | 8.93 | 2.01 | 7.87 | 1.28 | 7.23 | 1.46 | 4.18 | 0.61 | 3.78 | 0.67 | 38.70 | 273.63 | 3.16 | 0.72 | 9.04 | 3.44 | 1.72 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安山岩 | 17012-1 | 32.54 | 76.54 | 7.41 | 28.48 | 5.53 | 1.42 | 4.91 | 0.78 | 4.38 | 0.90 | 2.65 | 0.40 | 2.47 | 0.44 | 23.94 | 192.78 | 3.72 | 0.81 | 9.47 | 3.80 | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 英安岩 | 18006-1 | 36.92 | 73.65 | 8.77 | 34.74 | 7.02 | 1.91 | 6.00 | 0.95 | 5.43 | 1.05 | 3.03 | 0.43 | 2.57 | 0.43 | 28.21 | 211.13 | 3.39 | 0.88 | 10.29 | 3.39 | 1.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18005-4 | 21.59 | 40.63 | 4.69 | 17.23 | 3.25 | 0.88 | 2.64 | 0.40 | 2.24 | 0.46 | 1.53 | 0.23 | 1.53 | 0.30 | 12.43 | 110.02 | 4.06 | 0.89 | 10.15 | 4.30 | 1.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18006-4 | 21.08 | 40.78 | 4.81 | 18.04 | 3.30 | 0.91 | 2.82 | 0.44 | 2.49 | 0.52 | 1.55 | 0.25 | 1.62 | 0.31 | 13.63 | 112.55 | 3.76 | 0.88 | 9.33 | 4.12 | 1.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18006-6 | 25.81 | 47.63 | 5.54 | 19.89 | 3.81 | 0.96 | 3.34 | 0.50 | 2.84 | 0.58 | 1.81 | 0.29 | 1.95 | 0.31 | 16.29 | 131.55 | 3.71 | 0.80 | 9.52 | 4.37 | 1.42 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 17004-1 | 21.21 | 38.62 | 4.72 | 15.89 | 3.26 | 0.82 | 2.73 | 0.49 | 2.78 | 0.59 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 1.92 | 0.37 | 16.34 | 111.83 | 3.10 | 0.82 | 7.90 | 4.20 | 1.17 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18005-6 | 15.46 | 29.22 | 3.47 | 12.62 | 2.38 | 0.68 | 2.12 | 0.33 | 1.89 | 0.39 | 1.20 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 0.23 | 10.90 | 82.34 | 3.45 | 0.91 | 8.92 | 4.19 | 1.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18017-2 | 12.14 | 22.69 | 2.64 | 9.51 | 1.82 | 0.58 | 1.79 | 0.33 | 2.01 | 0.41 | 1.14 | 0.19 | 1.42 | 0.25 | 11.26 | 68.19 | 2.63 | 0.97 | 6.11 | 4.31 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||
表4 火山岩、脉岩和矿石稀土元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 4 REE compositions of volcanic rocks, dyke and gold ores(10-6)
| 岩石 | 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ∑REE | ∑Ce/∑Y | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闪长玢岩 | 17010-1 | 44.19 | 86.86 | 10.52 | 41.56 | 7.55 | 1.91 | 6.27 | 0.93 | 4.89 | 0.97 | 2.76 | 0.41 | 2.43 | 0.44 | 25.28 | 236.97 | 4.34 | 0.83 | 13.02 | 3.78 | 2.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | 17001-2 | 34.75 | 66.55 | 8.44 | 33.89 | 6.34 | 1.72 | 5.32 | 0.80 | 4.39 | 0.88 | 2.57 | 0.38 | 2.34 | 0.42 | 22.79 | 191.58 | 3.80 | 0.88 | 10.64 | 3.54 | 1.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | 18003-5 | 26.26 | 53.21 | 7.10 | 29.34 | 5.81 | 1.74 | 4.72 | 0.70 | 3.90 | 0.76 | 2.18 | 0.31 | 1.91 | 0.34 | 19.60 | 157.88 | 3.59 | 0.98 | 9.84 | 2.92 | 2.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 闪长玢岩 | 19003-2 | 39.78 | 82.76 | 10.33 | 42.25 | 8.35 | 2.20 | 6.84 | 1.05 | 5.39 | 1.09 | 3.01 | 0.42 | 2.54 | 0.42 | 27.32 | 233.75 | 3.86 | 0.86 | 11.24 | 3.08 | 2.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 18006-5 | 34.90 | 68.67 | 8.77 | 35.90 | 6.89 | 2.00 | 5.57 | 0.83 | 4.48 | 0.82 | 2.41 | 0.33 | 1.99 | 0.35 | 22.18 | 196.08 | 4.03 | 0.96 | 12.61 | 3.27 | 2.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 17003-2 | 30.57 | 59.75 | 7.64 | 31.12 | 6.20 | 1.80 | 5.12 | 0.77 | 3.97 | 0.77 | 2.03 | 0.27 | 1.63 | 0.27 | 18.15 | 170.07 | 4.16 | 0.95 | 13.45 | 3.18 | 2.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 19003-6 | 39.92 | 82.50 | 10.16 | 42.37 | 8.29 | 2.23 | 6.89 | 1.07 | 5.61 | 1.05 | 2.97 | 0.42 | 2.55 | 0.47 | 28.13 | 234.63 | 3.77 | 0.88 | 11.24 | 3.11 | 2.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 17011-4 | 50.22 | 104.41 | 12.69 | 50.30 | 9.39 | 2.41 | 7.68 | 1.15 | 6.16 | 1.18 | 3.33 | 0.47 | 2.84 | 0.52 | 30.26 | 282.99 | 4.28 | 0.84 | 12.68 | 3.45 | 2.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安粗岩 | 18022 | 45.00 | 91.40 | 11.20 | 44.80 | 8.60 | 2.49 | 6.87 | 1.03 | 5.63 | 1.05 | 3.00 | 0.46 | 3.09 | 0.51 | 29.20 | 254.33 | 4.00 | 0.96 | 10.45 | 3.38 | 1.84 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安山岩 | 18017-5 | 49.78 | 99.22 | 11.17 | 42.89 | 8.36 | 2.10 | 7.37 | 1.15 | 6.43 | 1.32 | 3.76 | 0.56 | 3.42 | 0.59 | 34.48 | 272.60 | 3.61 | 0.80 | 10.43 | 3.84 | 1.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安山岩 | 18007-1 | 47.58 | 95.06 | 11.00 | 43.26 | 8.93 | 2.01 | 7.87 | 1.28 | 7.23 | 1.46 | 4.18 | 0.61 | 3.78 | 0.67 | 38.70 | 273.63 | 3.16 | 0.72 | 9.04 | 3.44 | 1.72 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 安山岩 | 17012-1 | 32.54 | 76.54 | 7.41 | 28.48 | 5.53 | 1.42 | 4.91 | 0.78 | 4.38 | 0.90 | 2.65 | 0.40 | 2.47 | 0.44 | 23.94 | 192.78 | 3.72 | 0.81 | 9.47 | 3.80 | 1.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 英安岩 | 18006-1 | 36.92 | 73.65 | 8.77 | 34.74 | 7.02 | 1.91 | 6.00 | 0.95 | 5.43 | 1.05 | 3.03 | 0.43 | 2.57 | 0.43 | 28.21 | 211.13 | 3.39 | 0.88 | 10.29 | 3.39 | 1.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18005-4 | 21.59 | 40.63 | 4.69 | 17.23 | 3.25 | 0.88 | 2.64 | 0.40 | 2.24 | 0.46 | 1.53 | 0.23 | 1.53 | 0.30 | 12.43 | 110.02 | 4.06 | 0.89 | 10.15 | 4.30 | 1.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18006-4 | 21.08 | 40.78 | 4.81 | 18.04 | 3.30 | 0.91 | 2.82 | 0.44 | 2.49 | 0.52 | 1.55 | 0.25 | 1.62 | 0.31 | 13.63 | 112.55 | 3.76 | 0.88 | 9.33 | 4.12 | 1.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18006-6 | 25.81 | 47.63 | 5.54 | 19.89 | 3.81 | 0.96 | 3.34 | 0.50 | 2.84 | 0.58 | 1.81 | 0.29 | 1.95 | 0.31 | 16.29 | 131.55 | 3.71 | 0.80 | 9.52 | 4.37 | 1.42 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 17004-1 | 21.21 | 38.62 | 4.72 | 15.89 | 3.26 | 0.82 | 2.73 | 0.49 | 2.78 | 0.59 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 1.92 | 0.37 | 16.34 | 111.83 | 3.10 | 0.82 | 7.90 | 4.20 | 1.17 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18005-6 | 15.46 | 29.22 | 3.47 | 12.62 | 2.38 | 0.68 | 2.12 | 0.33 | 1.89 | 0.39 | 1.20 | 0.19 | 1.24 | 0.23 | 10.90 | 82.34 | 3.45 | 0.91 | 8.92 | 4.19 | 1.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 矿石 | 18017-2 | 12.14 | 22.69 | 2.64 | 9.51 | 1.82 | 0.58 | 1.79 | 0.33 | 2.01 | 0.41 | 1.14 | 0.19 | 1.42 | 0.25 | 11.26 | 68.19 | 2.63 | 0.97 | 6.11 | 4.31 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石 | 样号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Sr | P | Zr | Hf | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Ga | Au | Ag | Zn | Cu | Pb | Zr/Hf | Rb/Sr | Nb/Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闪长玢岩 | 17010-1 | 122 | 1117 | 3.33 | 1.54 | 12.9 | 0.26 | 457 | 1 950 | 297 | 7.3 | 6 671 | 31.7 | 12.72 | 7.64 | 18.8 | 6.0 | 0.09 | 87.5 | 14.8 | 19.8 | 40.68 | 0.27 | 49.05 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 17001-2 | 102 | 465 | 4.71 | 1.86 | 11.0 | 0.56 | 160 | 1 338 | 206 | 4.8 | 5 498 | 33.6 | 12.01 | 8.46 | 18.9 | 120.4 | 0.27 | 75.7 | 19.0 | 19.5 | 42.92 | 0.64 | 19.57 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 18003-5 | 159 | 487 | 2.93 | 2.35 | 7.7 | 0.21 | 169 | 1 427 | 150 | 3.9 | 7 717 | 91.6 | 17.61 | 13.10 | 22.2 | 33.2 | 0.25 | 132.7 | 7.4 | 23.5 | 38.46 | 0.94 | 36.67 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 19003-2 | 171 | 162 | 4.73 | 1.81 | 13.3 | 0.47 | 131 | 2 612 | 249 | 6.4 | 7 953 | 33.9 | 25.42 | 13.38 | 26.0 | 67.0 | 0.44 | 118.5 | 8.3 | 14.6 | 38.91 | 1.31 | 28.12 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 18006-5 | 111 | 853 | 4.02 | 1.20 | 10.4 | 0.26 | 546 | 2 205 | 204 | 6.0 | 7 068 | 22.7 | 18.13 | 7.24 | 19.4 | 4.6 | 0.09 | 82.8 | 7.9 | 14.8 | 34.00 | 0.20 | 40.31 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 17003-2 | 109 | 473 | 2.99 | 1.21 | 7.0 | 0.29 | 630 | 1 893 | 138 | 5.7 | 6 883 | 40.6 | 22.91 | 19.30 | 18.7 | 32.4 | 0.20 | 108.5 | 9.7 | 26.3 | 24.21 | 0.17 | 24.39 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 19003-6 | 188 | 131 | 2.95 | 3.50 | 13.3 | 0.30 | 216 | 2 555 | 228 | 6.9 | 9 056 | 42.6 | 20.9 | 11.47 | 22.3 | 58.2 | 0.23 | 99.8 | 14.3 | 15.2 | 33.04 | 0.87 | 43.75 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 17011-4 | 119 | 953 | 3.17 | 1.15 | 17.7 | 1.04 | 387 | 2 775 | 335 | 7.3 | 9 323 | 126.0 | 30.67 | 42.20 | 23.3 | 49.2 | 0.26 | 94.0 | 27.5 | 22.3 | 45.89 | 0.31 | 17.02 |
| 安粗岩 | 18022 | 54 | 1067 | 8.98 | 2.68 | 10.5 | 1.10 | 765 | 2 203 | 207 | 7.5 | 7 713 | 2.8 | 12.30 | 1.78 | 22.0 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 87.1 | 10.0 | 22.4 | 27.60 | 0.07 | 9.55 |
| 安山岩 | 18017-5 | 102 | 456 | 5.34 | 1.86 | 10.2 | 0.31 | 311 | 580 | 143 | 3.9 | 4 282 | 78.3 | 26.59 | 66.54 | 20.7 | 2.5 | 0.27 | 124.2 | 34.9 | 25.6 | 36.67 | 0.33 | 32.59 |
| 安山岩 | 18007-1 | 70 | 581 | 4.07 | 2.26 | 10.2 | 0.25 | 307 | 736 | 157 | 6.8 | 4 532 | 90.9 | 24.03 | 59.31 | 17.5 | 2.1 | 0.16 | 97.5 | 39.6 | 24.9 | 23.09 | 0.23 | 41.13 |
| 安山岩 | 17012-1 | 70 | 548 | 5.48 | 1.95 | 9.5 | 0.18 | 367 | 484 | 139 | 4.8 | 3 487 | 48.4 | 51.91 | 88.30 | 17.1 | 5.6 | 0.2 | 144.1 | 46.4 | 28.2 | 28.96 | 0.19 | 51.91 |
| 英安岩 | 18006-1 | 83 | 300 | 4.09 | 2.39 | 11.2 | 0.41 | 241 | 1 140 | 172 | 5.5 | 5 176 | 95.9 | 21.49 | 57.32 | 17.2 | 9.1 | 0.25 | 122.2 | 38.6 | 24.7 | 31.27 | 0.34 | 27.59 |
| 矿石 | 18005-4 | 146 | 639 | 5.10 | 3.07 | 11.7 | 0.34 | 157 | 390 | 111 | 4.5 | 1 500 | 26.0 | 6.48 | 13.14 | 15.4 | 662.8 | 1.61 | 30.3 | 1.8 | 21.6 | 24.67 | 0.93 | 34.01 |
| 矿石 | 18006-4 | 163 | 721 | 2.65 | 2.49 | 7.7 | 0.19 | 132 | 599 | 126 | 5.5 | 2 334 | 27.8 | 7.95 | 9.16 | 18.7 | 402.4 | 1.96 | 35.4 | 6.1 | 27.9 | 22.91 | 1.23 | 41.18 |
| 矿石 | 18006-6 | 145 | 533 | 5.65 | 3.39 | 9.6 | 0.25 | 58 | 506 | 159 | 3.3 | 2 570 | 35.4 | 11.58 | 11.53 | 18.8 | 1 647.5 | 5.26 | 39.3 | 3.8 | 33.6 | 48.18 | 2.50 | 38.55 |
| 矿石 | 17004-1 | 133 | 641 | 7.60 | 2.73 | 14.2 | 0.12 | 173 | 463 | 130 | 4.8 | 1 910 | 10.8 | 14.60 | 8.97 | 17.2 | 2 523.8 | 7.07 | 24.4 | 2.6 | 45.1 | 27.08 | 0.77 | 120.34 |
| 矿石 | 18005-6 | 108 | 560 | 5.57 | 2.72 | 6.4 | 0.26 | 157 | 440 | 92 | 2.6 | 2 107 | 27.3 | 11.25 | 10.05 | 16.1 | 1 352.0 | 2.84 | 20.2 | 2.5 | 25.2 | 35.38 | 0.69 | 24.90 |
| 矿石 | 18017-2 | 75 | 351 | 3.81 | 2.30 | 3.4 | 0.11 | 119 | 248 | 43 | 0.3 | 693 | 7.4 | 15.14 | 5.07 | 9.2 | 6 219.4 | 32.1 | 69.5 | 2.5 | 78.1 | 143.33 | 0.63 | 30.63 |
表5 火山岩、脉岩和矿石微量元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 5 Trace element compositions of volcanic rocks, dyke and gold ores(10-6)
| 岩石 | 样号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Sr | P | Zr | Hf | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Ga | Au | Ag | Zn | Cu | Pb | Zr/Hf | Rb/Sr | Nb/Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闪长玢岩 | 17010-1 | 122 | 1117 | 3.33 | 1.54 | 12.9 | 0.26 | 457 | 1 950 | 297 | 7.3 | 6 671 | 31.7 | 12.72 | 7.64 | 18.8 | 6.0 | 0.09 | 87.5 | 14.8 | 19.8 | 40.68 | 0.27 | 49.05 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 17001-2 | 102 | 465 | 4.71 | 1.86 | 11.0 | 0.56 | 160 | 1 338 | 206 | 4.8 | 5 498 | 33.6 | 12.01 | 8.46 | 18.9 | 120.4 | 0.27 | 75.7 | 19.0 | 19.5 | 42.92 | 0.64 | 19.57 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 18003-5 | 159 | 487 | 2.93 | 2.35 | 7.7 | 0.21 | 169 | 1 427 | 150 | 3.9 | 7 717 | 91.6 | 17.61 | 13.10 | 22.2 | 33.2 | 0.25 | 132.7 | 7.4 | 23.5 | 38.46 | 0.94 | 36.67 |
| 闪长玢岩 | 19003-2 | 171 | 162 | 4.73 | 1.81 | 13.3 | 0.47 | 131 | 2 612 | 249 | 6.4 | 7 953 | 33.9 | 25.42 | 13.38 | 26.0 | 67.0 | 0.44 | 118.5 | 8.3 | 14.6 | 38.91 | 1.31 | 28.12 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 18006-5 | 111 | 853 | 4.02 | 1.20 | 10.4 | 0.26 | 546 | 2 205 | 204 | 6.0 | 7 068 | 22.7 | 18.13 | 7.24 | 19.4 | 4.6 | 0.09 | 82.8 | 7.9 | 14.8 | 34.00 | 0.20 | 40.31 |
| 二长闪长玢岩 | 17003-2 | 109 | 473 | 2.99 | 1.21 | 7.0 | 0.29 | 630 | 1 893 | 138 | 5.7 | 6 883 | 40.6 | 22.91 | 19.30 | 18.7 | 32.4 | 0.20 | 108.5 | 9.7 | 26.3 | 24.21 | 0.17 | 24.39 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 19003-6 | 188 | 131 | 2.95 | 3.50 | 13.3 | 0.30 | 216 | 2 555 | 228 | 6.9 | 9 056 | 42.6 | 20.9 | 11.47 | 22.3 | 58.2 | 0.23 | 99.8 | 14.3 | 15.2 | 33.04 | 0.87 | 43.75 |
| 辉长闪长玢岩 | 17011-4 | 119 | 953 | 3.17 | 1.15 | 17.7 | 1.04 | 387 | 2 775 | 335 | 7.3 | 9 323 | 126.0 | 30.67 | 42.20 | 23.3 | 49.2 | 0.26 | 94.0 | 27.5 | 22.3 | 45.89 | 0.31 | 17.02 |
| 安粗岩 | 18022 | 54 | 1067 | 8.98 | 2.68 | 10.5 | 1.10 | 765 | 2 203 | 207 | 7.5 | 7 713 | 2.8 | 12.30 | 1.78 | 22.0 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 87.1 | 10.0 | 22.4 | 27.60 | 0.07 | 9.55 |
| 安山岩 | 18017-5 | 102 | 456 | 5.34 | 1.86 | 10.2 | 0.31 | 311 | 580 | 143 | 3.9 | 4 282 | 78.3 | 26.59 | 66.54 | 20.7 | 2.5 | 0.27 | 124.2 | 34.9 | 25.6 | 36.67 | 0.33 | 32.59 |
| 安山岩 | 18007-1 | 70 | 581 | 4.07 | 2.26 | 10.2 | 0.25 | 307 | 736 | 157 | 6.8 | 4 532 | 90.9 | 24.03 | 59.31 | 17.5 | 2.1 | 0.16 | 97.5 | 39.6 | 24.9 | 23.09 | 0.23 | 41.13 |
| 安山岩 | 17012-1 | 70 | 548 | 5.48 | 1.95 | 9.5 | 0.18 | 367 | 484 | 139 | 4.8 | 3 487 | 48.4 | 51.91 | 88.30 | 17.1 | 5.6 | 0.2 | 144.1 | 46.4 | 28.2 | 28.96 | 0.19 | 51.91 |
| 英安岩 | 18006-1 | 83 | 300 | 4.09 | 2.39 | 11.2 | 0.41 | 241 | 1 140 | 172 | 5.5 | 5 176 | 95.9 | 21.49 | 57.32 | 17.2 | 9.1 | 0.25 | 122.2 | 38.6 | 24.7 | 31.27 | 0.34 | 27.59 |
| 矿石 | 18005-4 | 146 | 639 | 5.10 | 3.07 | 11.7 | 0.34 | 157 | 390 | 111 | 4.5 | 1 500 | 26.0 | 6.48 | 13.14 | 15.4 | 662.8 | 1.61 | 30.3 | 1.8 | 21.6 | 24.67 | 0.93 | 34.01 |
| 矿石 | 18006-4 | 163 | 721 | 2.65 | 2.49 | 7.7 | 0.19 | 132 | 599 | 126 | 5.5 | 2 334 | 27.8 | 7.95 | 9.16 | 18.7 | 402.4 | 1.96 | 35.4 | 6.1 | 27.9 | 22.91 | 1.23 | 41.18 |
| 矿石 | 18006-6 | 145 | 533 | 5.65 | 3.39 | 9.6 | 0.25 | 58 | 506 | 159 | 3.3 | 2 570 | 35.4 | 11.58 | 11.53 | 18.8 | 1 647.5 | 5.26 | 39.3 | 3.8 | 33.6 | 48.18 | 2.50 | 38.55 |
| 矿石 | 17004-1 | 133 | 641 | 7.60 | 2.73 | 14.2 | 0.12 | 173 | 463 | 130 | 4.8 | 1 910 | 10.8 | 14.60 | 8.97 | 17.2 | 2 523.8 | 7.07 | 24.4 | 2.6 | 45.1 | 27.08 | 0.77 | 120.34 |
| 矿石 | 18005-6 | 108 | 560 | 5.57 | 2.72 | 6.4 | 0.26 | 157 | 440 | 92 | 2.6 | 2 107 | 27.3 | 11.25 | 10.05 | 16.1 | 1 352.0 | 2.84 | 20.2 | 2.5 | 25.2 | 35.38 | 0.69 | 24.90 |
| 矿石 | 18017-2 | 75 | 351 | 3.81 | 2.30 | 3.4 | 0.11 | 119 | 248 | 43 | 0.3 | 693 | 7.4 | 15.14 | 5.07 | 9.2 | 6 219.4 | 32.1 | 69.5 | 2.5 | 78.1 | 143.33 | 0.63 | 30.63 |

图9 火山岩、脉岩和矿石的稀土配分曲线(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)
Fig.9 Chondrite-normalized REE pattern(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram(b) of volcanic rocks,dyke and gold ores
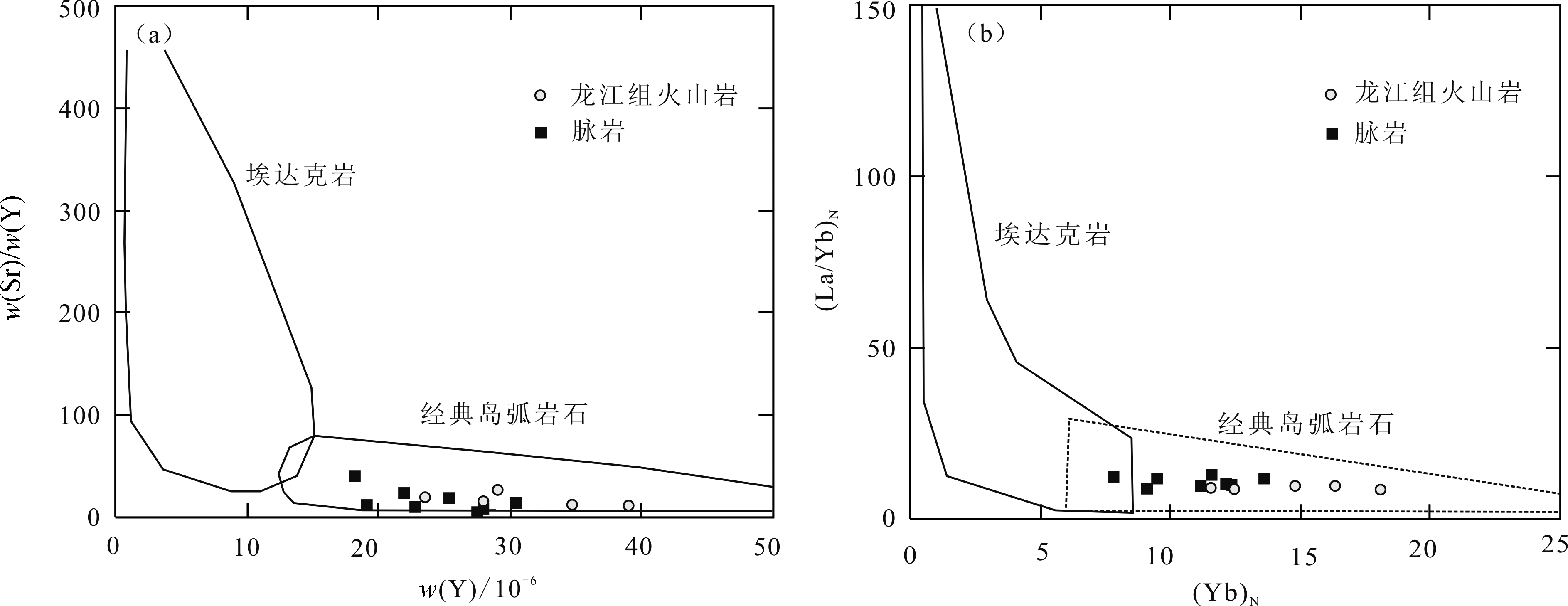
图10 火山岩和脉岩的w(Sr)/w(Y)-w(Y)图解(a)和(La/Yb)N-(Yb)N图解(b)(底图据文献[35])
Fig.10 w(Sr)/w(Y)-w(Y) diagram(a) and (La/Yb)N-(Yb)N diagram(b) for volcanic rocks and dykes
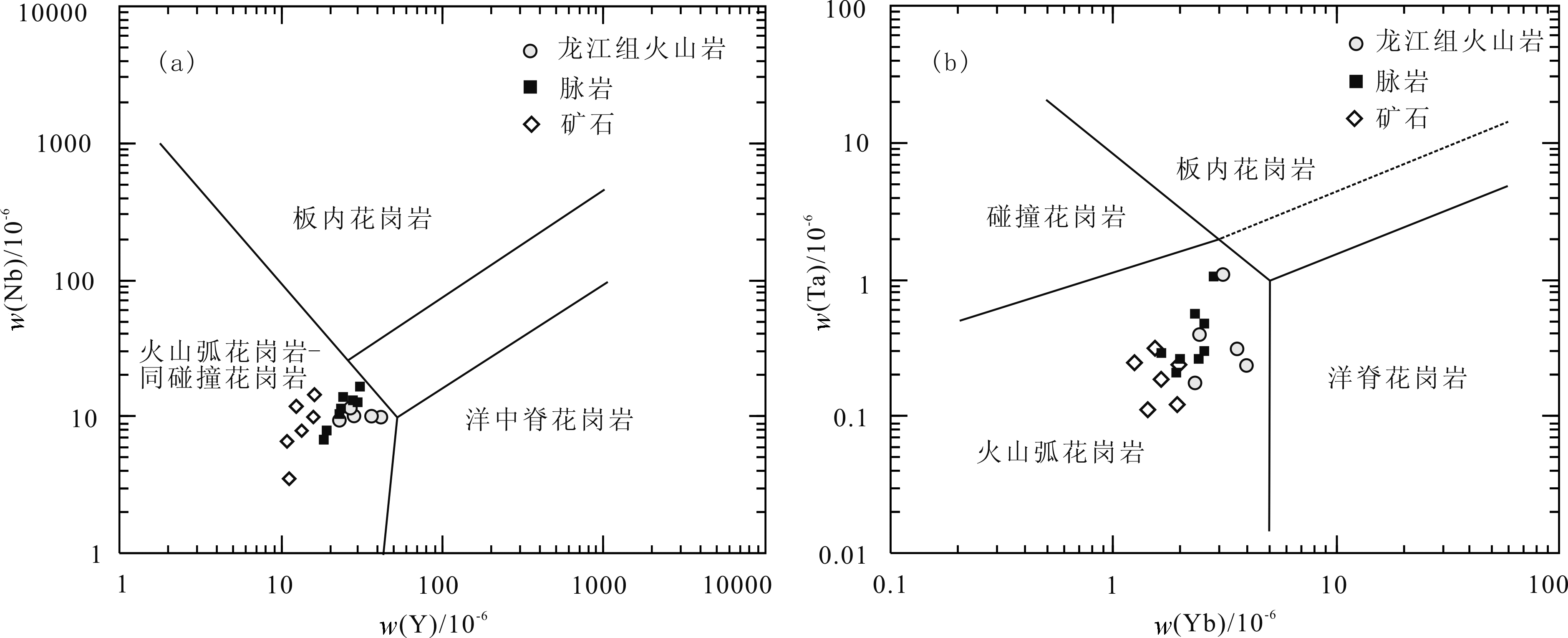
图11 火山岩、脉岩和矿石的w(Nb)-w(Y)(a) 和w(Ta)-w(Yb)(b)构造判别图解(底图据文献[36])
Fig.11 Nb-Y(a) and Ta-Yb(b) discrimination diagram for volcanic rocks, dyke and gold ores
| [1] |
LIU J L, ZHAO S J, COOK N J, et al. Bonanza-grade accumulations of gold tellurides in the Early Cretaceous Sandaowanzi deposit, northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 54(8): 110-126.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 李成禄, 曲晖, 赵忠海, 等. 黑龙江省霍龙门地区成矿地质特征及潜力分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2013, 22(4):273-278. |
| [3] | 曲晖, 赵忠海, 李成禄, 等. 黑龙江永新金矿地质特征及成因[J]. 地质与资源, 2014, 23(6): 520-524. |
| [4] | 袁茂文, 曾勇杰, 李成禄, 等. 黑龙江省嫩江—黑河构造混杂岩区永新金矿热液蚀变与矿化关系定量及定位研究[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(2): 278-289. |
| [5] | 李成禄, 曲晖, 赵忠海, 等. 黑龙江霍龙门地区早石炭世花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(3): 859-868. |
| [6] | 曲晖, 李成禄, 杨福深. 小兴安岭西北部霍龙门地区花岗质杂岩锆石U-Pb 年龄、岩石地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(1): 34-43. |
| [7] |
ZONG K Q, KLEMD R, YUAN Y, et al. The assembly of Rodinia: The correlation of early Neoproterozoic (ca. 900 Ma) high-grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB)[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 290: 32-48.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HU Z C, ZHANG W, LIU Y S, et al. “Wave” signal smoothing and mercury removing device for laser ablation quadrupole and multiple collector ICP-MS analysis: application to lead isotope analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(2): 1152-1157.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51: 537-571.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LUDWIG K R. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003:39. |
| [12] | 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等. 关于火成岩常用图解的正确使用:讨论与建议[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(4):717-734. |
| [13] | LE Maitre R W. Igneous Rocks, A Classification and Glossary of Terms[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002: 1-236. |
| [14] |
WRIGHT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969, 106:370-384.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 刘宝山, 王少轶, 牛延宏, 等. 黑龙江黑河大新屯金矿区地质特征及成因机理初探[J]. 黄金, 2013, 34(11): 16-19. |
| [16] | 王凤博, 杨言辰, 薄军委, 等. 大兴安岭北段上马场金矿床成矿特征及找矿标志[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(9): 10-14. |
| [17] | 郭奎城, 吕军, 谷华娟, 等. 黑龙江省北大沟金矿床矿石特征及金的赋存状态研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(4): 616-621. |
| [18] | 余宇星, 许虹, 吴祥珂, 等. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿Au-Ag-Te 系列矿物特征及其成矿流体[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1): 345-356. |
| [19] | 闫文强, 高树学, 杨凤喜, 等. 五道沟金矿床控矿因素及找矿方向[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2008, 16(3):43-44. |
| [20] | 刘宝山. 黑龙江黑河孟德河金矿床控矿因素及找矿标志[J]. 黄金, 2015, 36(1): 18-21. |
| [21] | 林超, 谈艳, 郭宇飞, 等. 黑龙江省科洛河韧性剪切带型金矿床地质、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 黄金, 2015, 36(4): 31-37. |
| [22] | 白相东. 大兴安岭北段三道湾子碲化物型金矿床:矿床地质与成矿年代学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010: 36-42. |
| [23] |
LIU J L, BAI X D, ZHAO S J, et al. Geology of the Sandaowanzi telluride gold deposit of the northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Geochronology and tectonic controls[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(2):107-118.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 赵天宇, 赵海滨, 孙丰月, 等. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿床同位素年龄对成矿时代的约束[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(4): 1202-1208. |
| [25] | 陈静, 孙丰月. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿床锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 黄金, 2011, 32(5): 18-22. |
| [26] | 吕军. 黑龙江省黑河市三道湾子金矿床地质特征、成矿条件及矿床模型[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011:102-104. |
| [27] |
ZHAI D G, LIU J J, EDWARD M. et al. Geochronological and He-Ar-S isotopic constraints on the origin of the Sandaowanzi gold-telluride deposit, northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 2015, 212/215:338-352.
DOI URL |
| [28 ] | 高燊. 黑龙江省黑河北部中生代金成矿研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017: 124-125. |
| [29] |
CHEN C, REN Y S, ZHAO H L, et al. Age, tectonic setting, and metallogenic implication of Phanerozoic granitic magmatism at the eastern margin of the Xing’an-Mongolian Orogenic Belt, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 144(15):368-383.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 孟凡超, 刘嘉麒, 崔岩, 等. 中国东北地区中生代构造体制的转变: 来自火山岩时空分布与岩石组合的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(12): 3569-3586. |
| [31] | 李云峰, 赵玥, 孙春林, 等. 黑龙江北部新生地区早白垩世龙江组火山岩年代学地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(1): 12-24. |
| [32] | 赵书跃, 庞雪娇, 李德胜. 黑龙江三道湾子金矿含金石英脉与围岩地球化学及地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2016, 25(2): 130-136. |
| [33] | 翟德高. 黑龙江省碲化物型金矿床地质地球化学特征与成矿机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014: 29-42. |
| [34] | 刘宝山, 吕军. 黑河市三道湾子金矿床地质、地球化学和成因探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(4):481-485. |
| [35] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665.
DOI |
| [36] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 曾涛, 王涛, 郭磊, 等. 东北新开岭地区晚中生代花岗岩类时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(6): 1881-1900. |
| [38] | 刘廷海, 佟卉, 李桂范, 等. 大杨树盆地中生代岩相特征及沉积模式[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2008, 32(6): 9-11. |
| [39] |
WU F Y, LIN J Q, WILDE S A, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in Eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1): 103-119.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 宋立忠, 赵泽辉, 焦贵浩, 等. 松辽盆地早白垩世火山岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(4): 1182-1194. |
| [41] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, LI H M, et al. A-type granites in Northeastern China: age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2): 143-173.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZHANG Y B, WU F Y, WILDE S A, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications of ‘Early Paleozoic’ granitoids at Yanbian, Jilin Province, northeast China[J]. Island Arc, 2004, 13(4): 484-505.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 1-30.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 江国明, 张贵宾, 徐峣. 中国东北地区太平洋板块精细俯冲特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(6): 1125-1135. |
| [45] |
MA X H, CAO R, ZHOU Z H, et al. Early Cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Yanji area,northeastern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 393-405.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3): 749-762. |
| [47] |
MA X H, CHEN B, YANG M C. Magma mixing origin for the Aolunhua porphyry related to Mo-Cu mineralization, eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24(3/4): 1152-1171.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
ZHANG F Q, CHEN H L, YU X, et al. Early Cretaceous volcanism in the northern Songliao Basin, NE China, and its geodynamic implication[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(1):163-176.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Phanerozoic continental crustal growth: U-Pb and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the granites in northeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1/2): 89-113.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
JAHN B M, WU F Y, CAPDEVILA R, et al. Highly evolved juvenile granites with tetrad REE patterns: the Woduhe and Baerzhe granites from the Great Xing’an Mountain in NE China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 59(4):171-198.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 袁建国, 顾玉超, 肖荣阁, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特东部地区早白垩世花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(1): 20-32. |
| [52] | 罗飞, 罗照华, 李达靖, 等. 内蒙古中部白垩纪碱性花岗岩的发现及意义[J]. 现代地质, 1995, 9(2): 203-211. |
| [53] | 杨增海, 王建平, 刘家军, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗乌日尼图钨钼矿床同位素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1):13-23. |
| [54] | WANG T, ZHENG Y D, ZHANG J J, et al. Pattern and kinematic polarity of late Mesozoic extension in continental NE Asia: perspectives from metamorphic core complexes[J]. Tectonics, 2011, 30(6): TC6007. |
| [55] |
SUN W D, DING X, HU Y H, et al. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(3/4) : 533-542.
DOI URL |
| [56] | 包汉勇, 杨风丽, 王丹萍. 苏南地区中、古生界沉积岩地球化学特征——以圣科1井为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(1): 29-38. |
| [57] |
SHU L S, ZHOU X M, DENG P, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Southeast China Block: New insights from basin analysis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 376-391.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ZHANG Z C, MAO J W, WANG Y B, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of the volcanic rocks associated with the Dong’an adularia-sericite epithermal gold deposit, Lesser Hinggan Range, Heilongjiang province, NE China: Constraints on the metallogenesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2010, 37(3/4): 158-174.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
WANG Y B, ZENG Q D, LIU J M, et al. Rb-Sr dating of gold-bearing pyrites from Wulaga gold deposit and its geological significance[J]. Resource Geology, 2014, 64 (3): 262-270.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
WANG Y B, ZENG Q D, ZHOU L L, et al. The sources of ore-forming material in the low-sulfidation epithermal Wulaga gold deposit, NE China: Constraints from S, Pb isotopes and REE pattern[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 76: 140-151.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
SUN J G, HAN S J, ZHANG Y, et al. Diagenesis and metallogenetic mechanisms of the Tuanjiegou gold deposit from the Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62: 373-388.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
HAO B W, DENG J, BAGAS L, et al. The Gaosongshan epithermal gold deposit in the Lesser Hinggan Range of the Heilongjiang Province, NE China: Implications for Early Cretaceous mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 73: 179-197.
DOI URL |
| [63] | 刘瑞萍, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 等. 黑龙江张三沟金矿区赋矿岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(5):645-653. |
| [64] |
ZHANG P, HUANG X W, CUI B, et al. Re-Os isotopic and trace element compositions of pyrite and origin of the Cretaceous Jinchang porphyry Cu-Au deposit, Heilongjiang Province, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 129(1): 67-80.
DOI URL |
| [65] | 柴鹏, 孙景贵, 门兰静, 等. 延边地区九三沟金矿床赋矿围岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄与成岩成矿时代[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(5):633-640. |
| [66] | 孙明道. 中国东北及邻区白垩纪岩浆活动与古太平洋板块俯冲的关系[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(6): 1090-1097. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [3] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [4] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [5] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [6] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [7] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [8] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [9] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [10] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [11] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [12] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [13] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [14] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [15] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||