



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (06): 1131-1146.
袁建国1( ), 任永健2(
), 任永健2( ), 姜振宁2, 屈云燕3, 魏浩4
), 姜振宁2, 屈云燕3, 魏浩4
收稿日期:2016-12-10
修回日期:2017-07-10
出版日期:2017-12-10
发布日期:2017-12-25
通讯作者:
任永健,男,工程师,1986年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,主要从事区域地质矿产调查工作。Email: 作者简介:袁建国,男,博士研究生,1988年出生,区域成矿学专业,主要从事矿床学和岩石学研究。Email:yuanjg0112@163.com。
基金资助:
YUAN Jianguo1( ), REN Yongjian2(
), REN Yongjian2( ), JIANG Zhenning2, QU Yunyan3, WEI Hao4
), JIANG Zhenning2, QU Yunyan3, WEI Hao4
Received:2016-12-10
Revised:2017-07-10
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-12-25
摘要:
通过对内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场早石炭世花岗岩体进行野外观察、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年以及地球化学测试,讨论其构造环境,进一步为研究古亚洲洋闭合时限提供依据。测年结果表明:花岗闪长岩为(330.6±1.8) Ma,二长花岗岩为(327.7±2.6) Ma,成岩时代为早石炭世。岩石地球化学分析表明:花岗闪长岩为强过铝质、钙碱性系列岩石,具有活动大陆边缘的亲缘性特征。微量元素特征指示花岗闪长岩具有典型下地壳来源特征并伴有部分幔源岩浆混合作用,为弧岩浆岩。二长花岗岩为具高硅、富碱、相对低铝特征的高钾钙碱性系列岩石。两类差异明显的岩石稀土配分曲线表明二长花岗岩具有下地壳岩浆重熔的演化特征。微量元素特征指示样品为大陆弧环境下壳源重熔的成熟弧花岗岩。构造判别图显示花岗闪长岩为代表活动大陆边缘环境的I型花岗岩,而二长花岗岩则为指示活动大陆边缘弧后伸展环境的A2型花岗岩,二者构成I-A型复合岩体,说明研究区在早石炭世仍存在古亚洲洋向西伯利亚板块的俯冲作用,推测古亚洲洋此时尚未闭合。
中图分类号:
袁建国, 任永健, 姜振宁, 屈云燕, 魏浩. 内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场早石炭世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1131-1146.
YUAN Jianguo, REN Yongjian, JIANG Zhenning, QU Yunyan, WEI Hao. Zircon U-Pb Dating and Geochemistry of Granites in Early Carboniferous in Maodeng of Xilin Hot, Inner Mongolia and Their Geological Implications[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(06): 1131-1146.

图2 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩野外及镜下特征 (a)二长花岗岩侵入花岗闪长岩;(b)花岗闪长岩露头;(c)花岗闪长岩镜下特征;(d)二长花岗岩镜下特征
Fig.2 The photograghs and microscope photograghs of granites in Maodeng of Xilin Hot
| 分析点号 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 207Pb/206Pb | 208Pb/232Th | 232Th/238U | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | ||
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.1 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 327.33 | 3.15 | 347.90 | 14.58 | 494.79 | 91.54 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.2 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 328.88 | 3.22 | 362.24 | 20.27 | 419.61 | 122.09 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.3 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 332.80 | 2.66 | 349.77 | 21.04 | 381.29 | 130.06 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.4 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.55 | 338.89 | 3.19 | 344.07 | 11.92 | 2 023.01 | 57.35 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.5 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.59 | 330.35 | 3.20 | 358.42 | 19.35 | 1 171.08 | 99.00 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.6 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.49 | 338.64 | 2.63 | 348.63 | 17.91 | 758.01 | 103.05 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.7 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.67 | 333.39 | 3.88 | 336.93 | 17.44 | 1 753.65 | 92.68 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.8 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 333.30 | 2.77 | 340.92 | 21.04 | 603.64 | 123.30 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.9 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 335.55 | 3.49 | 347.49 | 24.00 | 897.71 | 132.53 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.10 | 0.05 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 333.95 | 3.21 | 369.06 | 19.10 | 595.93 | 105.70 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.11 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 329.14 | 3.58 | 349.29 | 24.75 | 907.86 | 135.61 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.12 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 328.61 | 3.22 | 346.26 | 20.15 | 466.44 | 119.27 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.13 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 327.51 | 3.25 | 336.55 | 12.97 | 399.54 | 81.92 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.14 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.62 | 326.51 | 2.78 | 362.32 | 21.08 | 598.46 | 121.26 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.15 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 331.90 | 3.12 | 343.16 | 17.96 | 420.18 | 109.55 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.16 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.53 | 328.57 | 3.25 | 364.06 | 19.46 | 596.82 | 109.90 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.17 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 326.02 | 3.07 | 350.73 | 18.16 | 517.72 | 109.83 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.18 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 323.77 | 2.84 | 337.76 | 24.30 | 435.21 | 153.57 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.19 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 328.83 | 3.00 | 339.30 | 11.98 | 411.62 | 76.10 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.20 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 331.24 | 3.17 | 348.04 | 17.25 | 608.18 | 100.52 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.21 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 329.37 | 3.07 | 336.84 | 17.22 | 431.78 | 110.95 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.22 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.87 | 329.04 | 2.98 | 335.54 | 13.16 | 380.86 | 87.16 | |
表1 花岗闪长岩(WHHS-46-U.Pb02)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of granodiorite(WHHS-46-U.Pb02)
| 分析点号 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 207Pb/206Pb | 208Pb/232Th | 232Th/238U | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | ||
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.1 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 327.33 | 3.15 | 347.90 | 14.58 | 494.79 | 91.54 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.2 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 328.88 | 3.22 | 362.24 | 20.27 | 419.61 | 122.09 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.3 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 332.80 | 2.66 | 349.77 | 21.04 | 381.29 | 130.06 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.4 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.55 | 338.89 | 3.19 | 344.07 | 11.92 | 2 023.01 | 57.35 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.5 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.59 | 330.35 | 3.20 | 358.42 | 19.35 | 1 171.08 | 99.00 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.6 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.49 | 338.64 | 2.63 | 348.63 | 17.91 | 758.01 | 103.05 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.7 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.67 | 333.39 | 3.88 | 336.93 | 17.44 | 1 753.65 | 92.68 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.8 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 333.30 | 2.77 | 340.92 | 21.04 | 603.64 | 123.30 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.9 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 335.55 | 3.49 | 347.49 | 24.00 | 897.71 | 132.53 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.10 | 0.05 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 333.95 | 3.21 | 369.06 | 19.10 | 595.93 | 105.70 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.11 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 329.14 | 3.58 | 349.29 | 24.75 | 907.86 | 135.61 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.12 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 328.61 | 3.22 | 346.26 | 20.15 | 466.44 | 119.27 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.13 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 327.51 | 3.25 | 336.55 | 12.97 | 399.54 | 81.92 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.14 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.62 | 326.51 | 2.78 | 362.32 | 21.08 | 598.46 | 121.26 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.15 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 331.90 | 3.12 | 343.16 | 17.96 | 420.18 | 109.55 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.16 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.53 | 328.57 | 3.25 | 364.06 | 19.46 | 596.82 | 109.90 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.17 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 326.02 | 3.07 | 350.73 | 18.16 | 517.72 | 109.83 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.18 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 323.77 | 2.84 | 337.76 | 24.30 | 435.21 | 153.57 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.19 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 328.83 | 3.00 | 339.30 | 11.98 | 411.62 | 76.10 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.20 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 331.24 | 3.17 | 348.04 | 17.25 | 608.18 | 100.52 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.21 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 329.37 | 3.07 | 336.84 | 17.22 | 431.78 | 110.95 | |
| WHHS.46.U.Pb02.22 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.87 | 329.04 | 2.98 | 335.54 | 13.16 | 380.86 | 87.16 | |
| 分析点号 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 207Pb/206Pb | 208Pb/232Th | 232Th/238U | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | ||
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.1 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 328.51 | 3.07 | 348.22 | 5.73 | 481.89 | 30.08 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.2 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 360.99 | 4.33 | 346.36 | 4.44 | 249.29 | 27.70 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.3 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 323.31 | 2.37 | 325.45 | 3.52 | 340.75 | 23.82 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.4 | 0.24 | 4.94 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 1 394.32 | 14.23 | 1 809.80 | 15.86 | 2 328.69 | 13.24 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.5 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 348.74 | 3.58 | 349.11 | 15.29 | 351.63 | 94.79 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.6 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.35 | 334.24 | 2.97 | 326.61 | 2.92 | 272.57 | 19.81 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.7 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 328.68 | 2.80 | 335.90 | 8.17 | 386.21 | 53.03 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.8 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.56 | 329.70 | 2.56 | 346.90 | 5.58 | 463.76 | 31.94 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.9 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.50 | 323.08 | 3.62 | 326.72 | 6.46 | 352.73 | 41.66 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.10 | 0.07 | 1.76 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 426.96 | 3.02 | 1 032.54 | 9.35 | 2 715.09 | 15.37 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.11 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.59 | 333.33 | 3.83 | 345.42 | 6.30 | 427.55 | 38.09 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.12 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 327.51 | 3.25 | 344.30 | 6.99 | 459.22 | 40.90 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.13 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 1.03 | 324.91 | 3.10 | 324.29 | 6.78 | 319.86 | 46.35 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.14 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 331.32 | 3.24 | 333.75 | 6.69 | 350.66 | 43.85 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.15 | 0.05 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 322.37 | 2.81 | 320.97 | 11.89 | 310.83 | 78.46 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.16 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 324.40 | 2.52 | 335.77 | 4.25 | 415.23 | 27.70 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.17 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 327.87 | 3.25 | 345.27 | 5.63 | 464.12 | 35.16 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.18 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 321.27 | 3.44 | 333.47 | 9.17 | 419.45 | 59.52 | |
表2 二长花岗岩(WHEH-47-U.Pb06)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of monzonite granite(WHEH-47-U.Pb06)
| 分析点号 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 207Pb/206Pb | 208Pb/232Th | 232Th/238U | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | ||
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.1 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 328.51 | 3.07 | 348.22 | 5.73 | 481.89 | 30.08 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.2 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 360.99 | 4.33 | 346.36 | 4.44 | 249.29 | 27.70 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.3 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 323.31 | 2.37 | 325.45 | 3.52 | 340.75 | 23.82 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.4 | 0.24 | 4.94 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 1 394.32 | 14.23 | 1 809.80 | 15.86 | 2 328.69 | 13.24 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.5 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 348.74 | 3.58 | 349.11 | 15.29 | 351.63 | 94.79 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.6 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.35 | 334.24 | 2.97 | 326.61 | 2.92 | 272.57 | 19.81 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.7 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 328.68 | 2.80 | 335.90 | 8.17 | 386.21 | 53.03 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.8 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.56 | 329.70 | 2.56 | 346.90 | 5.58 | 463.76 | 31.94 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.9 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.50 | 323.08 | 3.62 | 326.72 | 6.46 | 352.73 | 41.66 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.10 | 0.07 | 1.76 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 426.96 | 3.02 | 1 032.54 | 9.35 | 2 715.09 | 15.37 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.11 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.59 | 333.33 | 3.83 | 345.42 | 6.30 | 427.55 | 38.09 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.12 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 327.51 | 3.25 | 344.30 | 6.99 | 459.22 | 40.90 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.13 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 1.03 | 324.91 | 3.10 | 324.29 | 6.78 | 319.86 | 46.35 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.14 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 331.32 | 3.24 | 333.75 | 6.69 | 350.66 | 43.85 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.15 | 0.05 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 322.37 | 2.81 | 320.97 | 11.89 | 310.83 | 78.46 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.16 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 324.40 | 2.52 | 335.77 | 4.25 | 415.23 | 27.70 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.17 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 327.87 | 3.25 | 345.27 | 5.63 | 464.12 | 35.16 | |
| WHEH.47.U.Pb06.18 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 321.27 | 3.44 | 333.47 | 9.17 | 419.45 | 59.52 | |
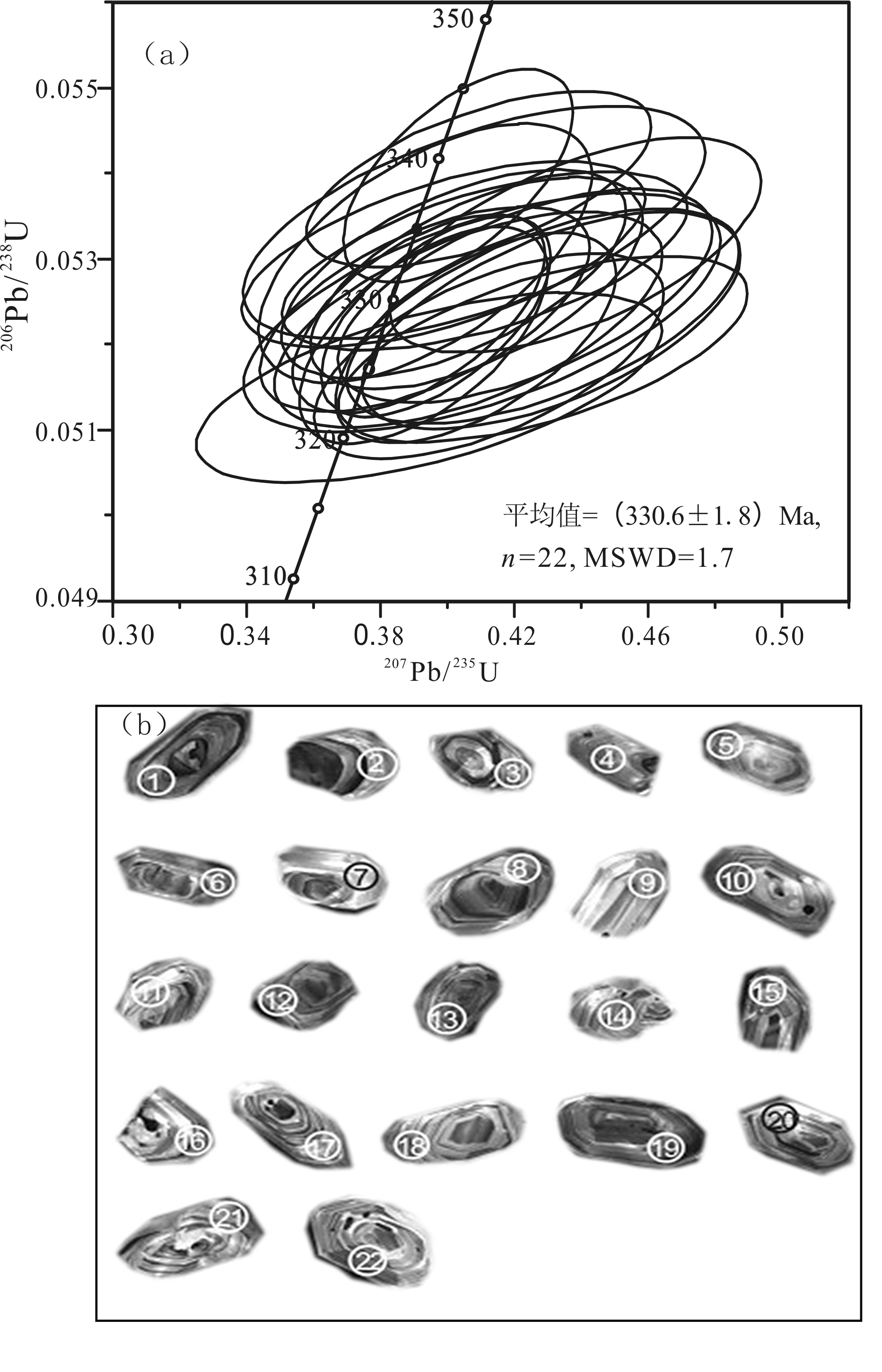
图3 花岗闪长岩(WHHS-46-U.Pb02)锆石U-Pb谐和曲线图(a)及CL图像(b)
Fig. 3 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagram(a) and cathodolum inescence (CL) images(b) of granodiorite(WHHS-46-U.Pb02)
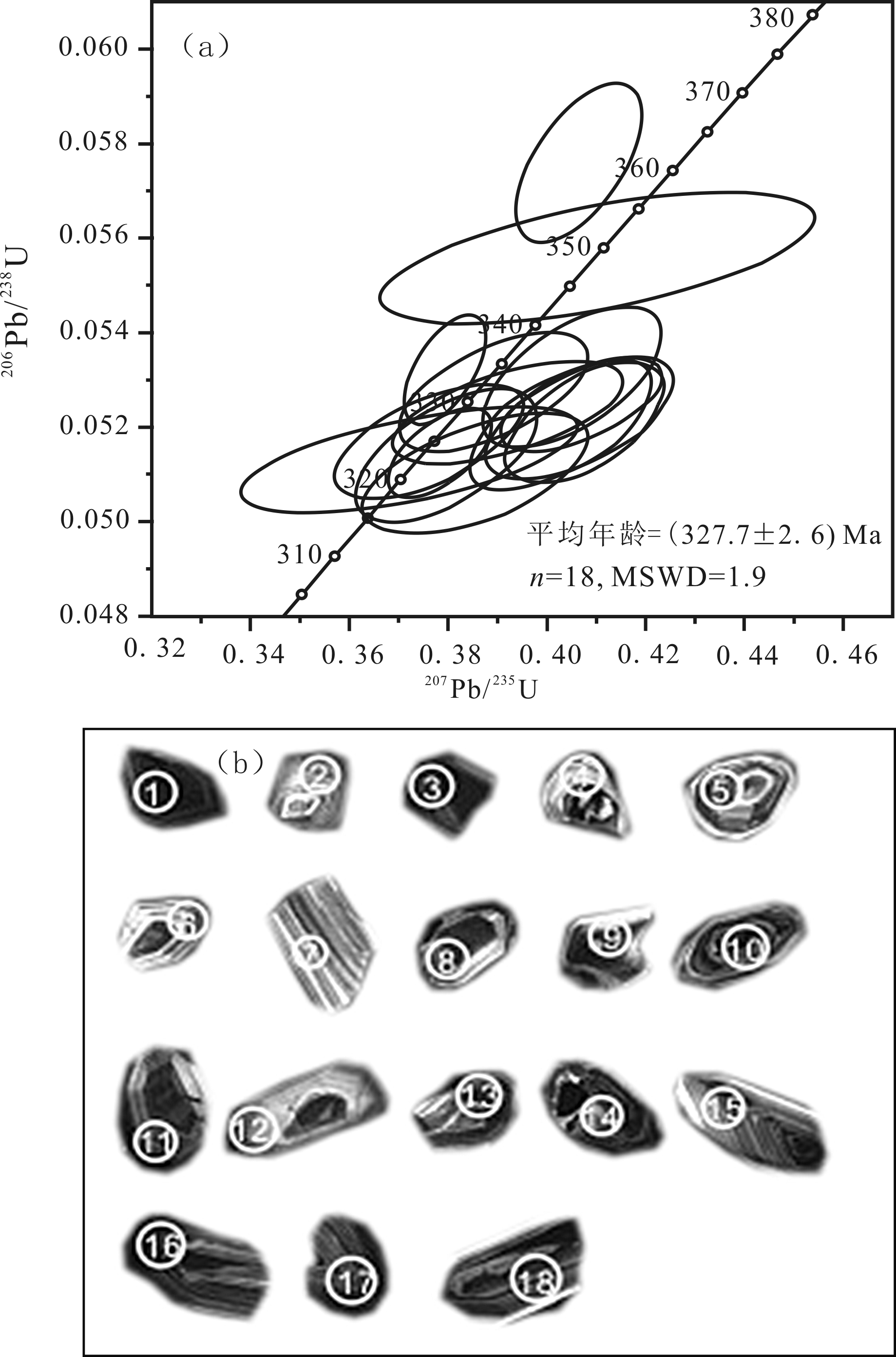
图4 二长花岗岩(WHEH-47-U.Pb06)锆石U-Pb谐和曲线图(a)及CL图像(b)
Fig.4 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagram(a) and cathodolum inescence (CL) images(b) of monzonite granite (WHEH-47-U.Pb06)
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 样品名称 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 总计 | A/CNK | ANK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM25-3-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 66.37 | 0.45 | 17.66 | 1.85 | 2.00 | 0.07 | 1.63 | 4.48 | 4.34 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 99.99 | 1.09 | 2.15 |
| 2 | PM25-5-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 69.26 | 0.37 | 16.58 | 1.25 | 1.68 | 0.05 | 1.18 | 3.34 | 4.72 | 1.44 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 1.09 | 1.78 |
| 3 | P1YQ01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 72.20 | 0.32 | 14.31 | 0.94 | 1.73 | 0.06 | 1.25 | 1.84 | 3.65 | 1.69 | 0.18 | 98.17 | 1.30 | 1.83 |
| 平均值 | 69.28 | 0.38 | 16.18 | 1.35 | 1.80 | 0.06 | 1.35 | 3.22 | 4.24 | 1.38 | 0.15 | 99.39 | 1.16 | 1.92 | ||
| 4 | WHHS-47-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.67 | 0.21 | 13.50 | 0.54 | 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 1.37 | 3.55 | 3.81 | 0.05 | 100.00 | 1.09 | 1.35 |
| 5 | PM25-6-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.06 | 0.01 | 14.35 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 3.07 | 4.12 | 0.04 | 98.59 | 1.48 | 1.51 |
| 6 | WHEH-46-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.31 | 0.06 | 13.18 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 3.56 | 5.51 | 0.05 | 99.54 | 1.06 | 1.11 |
| 7 | WHEH-47-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.75 | 0.11 | 12.53 | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.52 | 2.80 | 5.73 | 0.02 | 99.43 | 1.07 | 1.16 |
| 8 | WHEH-47-GSY09 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.31 | 0.04 | 13.38 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.59 | 3.57 | 5.39 | 0.02 | 99.65 | 1.05 | 1.14 |
| 9 | WHEH-49-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.41 | 0.15 | 13.70 | 0.71 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 3.62 | 5.05 | 0.04 | 99.14 | 1.15 | 1.20 |
| 10 | WHEH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 74.11 | 0.05 | 14.88 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 4.56 | 4.78 | 0.03 | 99.37 | 1.12 | 1.17 |
| 11 | WHZH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 72.47 | 0.18 | 15.54 | 0.97 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.59 | 4.45 | 4.70 | 0.04 | 99.12 | 1.16 | 1.25 |
| 平均值 | 75.39 | 0.10 | 13.88 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 3.65 | 4.89 | 0.04 | 99.36 | 1.15 | 1.24 | ||
| 12 | WHZH-50-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 74.45 | 0.18 | 14.35 | 1.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.69 | 4.14 | 4.08 | 0.06 | 99.13 | 1.16 | 1.28 |
| 13 | WHZH-50-GSY03 | 二长花岗岩 | 74.98 | 0.13 | 14.05 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 3.79 | 4.85 | 0.03 | 99.39 | 1.11 | 1.22 |
| 14 | WHZH-50-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.17 | 0.16 | 13.95 | 0.90 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 3.75 | 4.48 | 0.03 | 99.22 | 1.15 | 1.26 |
| 15 | WHZH-50-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.08 | 0.13 | 14.18 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.42 | 3.84 | 4.96 | 0.02 | 99.32 | 1.14 | 1.21 |
| 16 | PM25-6-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.64 | 0.04 | 13.49 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.59 | 4.21 | 4.36 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 1.06 | 1.16 |
| 17 | PM25-8-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 77.09 | 0.06 | 13.08 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 3.38 | 5.37 | 0.02 | 100.01 | 1.08 | 1.15 |
| 18 | PM25-9-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.69 | 0.04 | 13.48 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 4.02 | 4.78 | 0.02 | 100.00 | 1.04 | 1.14 |
| 19 | WHEH-49-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 77.31 | 0.04 | 12.92 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 4.13 | 4.74 | 0.05 | 100.01 | 1.05 | 1.08 |
| 20 | WHEH-46-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.91 | 0.04 | 13.24 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 3.64 | 4.93 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 1.07 | 1.17 |
| 21 | WHEH-47-GSY07 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.84 | 0.04 | 13.46 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 3.77 | 4.41 | 0.02 | 100.00 | 1.07 | 1.23 |
| 22 | WHEH-47-GSY08 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.98 | 0.05 | 13.20 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 4.09 | 4.29 | 0.01 | 99.99 | 1.04 | 1.16 |
| 平均值 | 76.19 | 0.08 | 13.58 | 0.46 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 3.89 | 4.66 | 0.03 | 99.73 | 1.09 | 1.19 | ||
表3 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩主量元素分析结果(wB/%)
Table 3 Petrochemical analysis and characteristic parameters of granite in Maodeng of Xilin Hot (%)
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 样品名称 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 总计 | A/CNK | ANK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM25-3-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 66.37 | 0.45 | 17.66 | 1.85 | 2.00 | 0.07 | 1.63 | 4.48 | 4.34 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 99.99 | 1.09 | 2.15 |
| 2 | PM25-5-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 69.26 | 0.37 | 16.58 | 1.25 | 1.68 | 0.05 | 1.18 | 3.34 | 4.72 | 1.44 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 1.09 | 1.78 |
| 3 | P1YQ01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 72.20 | 0.32 | 14.31 | 0.94 | 1.73 | 0.06 | 1.25 | 1.84 | 3.65 | 1.69 | 0.18 | 98.17 | 1.30 | 1.83 |
| 平均值 | 69.28 | 0.38 | 16.18 | 1.35 | 1.80 | 0.06 | 1.35 | 3.22 | 4.24 | 1.38 | 0.15 | 99.39 | 1.16 | 1.92 | ||
| 4 | WHHS-47-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.67 | 0.21 | 13.50 | 0.54 | 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 1.37 | 3.55 | 3.81 | 0.05 | 100.00 | 1.09 | 1.35 |
| 5 | PM25-6-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.06 | 0.01 | 14.35 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 3.07 | 4.12 | 0.04 | 98.59 | 1.48 | 1.51 |
| 6 | WHEH-46-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.31 | 0.06 | 13.18 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 3.56 | 5.51 | 0.05 | 99.54 | 1.06 | 1.11 |
| 7 | WHEH-47-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.75 | 0.11 | 12.53 | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.52 | 2.80 | 5.73 | 0.02 | 99.43 | 1.07 | 1.16 |
| 8 | WHEH-47-GSY09 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.31 | 0.04 | 13.38 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.59 | 3.57 | 5.39 | 0.02 | 99.65 | 1.05 | 1.14 |
| 9 | WHEH-49-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.41 | 0.15 | 13.70 | 0.71 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 3.62 | 5.05 | 0.04 | 99.14 | 1.15 | 1.20 |
| 10 | WHEH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 74.11 | 0.05 | 14.88 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 4.56 | 4.78 | 0.03 | 99.37 | 1.12 | 1.17 |
| 11 | WHZH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 72.47 | 0.18 | 15.54 | 0.97 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.59 | 4.45 | 4.70 | 0.04 | 99.12 | 1.16 | 1.25 |
| 平均值 | 75.39 | 0.10 | 13.88 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 3.65 | 4.89 | 0.04 | 99.36 | 1.15 | 1.24 | ||
| 12 | WHZH-50-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 74.45 | 0.18 | 14.35 | 1.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.69 | 4.14 | 4.08 | 0.06 | 99.13 | 1.16 | 1.28 |
| 13 | WHZH-50-GSY03 | 二长花岗岩 | 74.98 | 0.13 | 14.05 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 3.79 | 4.85 | 0.03 | 99.39 | 1.11 | 1.22 |
| 14 | WHZH-50-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.17 | 0.16 | 13.95 | 0.90 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 3.75 | 4.48 | 0.03 | 99.22 | 1.15 | 1.26 |
| 15 | WHZH-50-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.08 | 0.13 | 14.18 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.42 | 3.84 | 4.96 | 0.02 | 99.32 | 1.14 | 1.21 |
| 16 | PM25-6-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.64 | 0.04 | 13.49 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.59 | 4.21 | 4.36 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 1.06 | 1.16 |
| 17 | PM25-8-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 77.09 | 0.06 | 13.08 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.41 | 3.38 | 5.37 | 0.02 | 100.01 | 1.08 | 1.15 |
| 18 | PM25-9-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.69 | 0.04 | 13.48 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 4.02 | 4.78 | 0.02 | 100.00 | 1.04 | 1.14 |
| 19 | WHEH-49-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 77.31 | 0.04 | 12.92 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 4.13 | 4.74 | 0.05 | 100.01 | 1.05 | 1.08 |
| 20 | WHEH-46-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.91 | 0.04 | 13.24 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 3.64 | 4.93 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 1.07 | 1.17 |
| 21 | WHEH-47-GSY07 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.84 | 0.04 | 13.46 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 3.77 | 4.41 | 0.02 | 100.00 | 1.07 | 1.23 |
| 22 | WHEH-47-GSY08 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.98 | 0.05 | 13.20 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 4.09 | 4.29 | 0.01 | 99.99 | 1.04 | 1.16 |
| 平均值 | 76.19 | 0.08 | 13.58 | 0.46 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 3.89 | 4.66 | 0.03 | 99.73 | 1.09 | 1.19 | ||
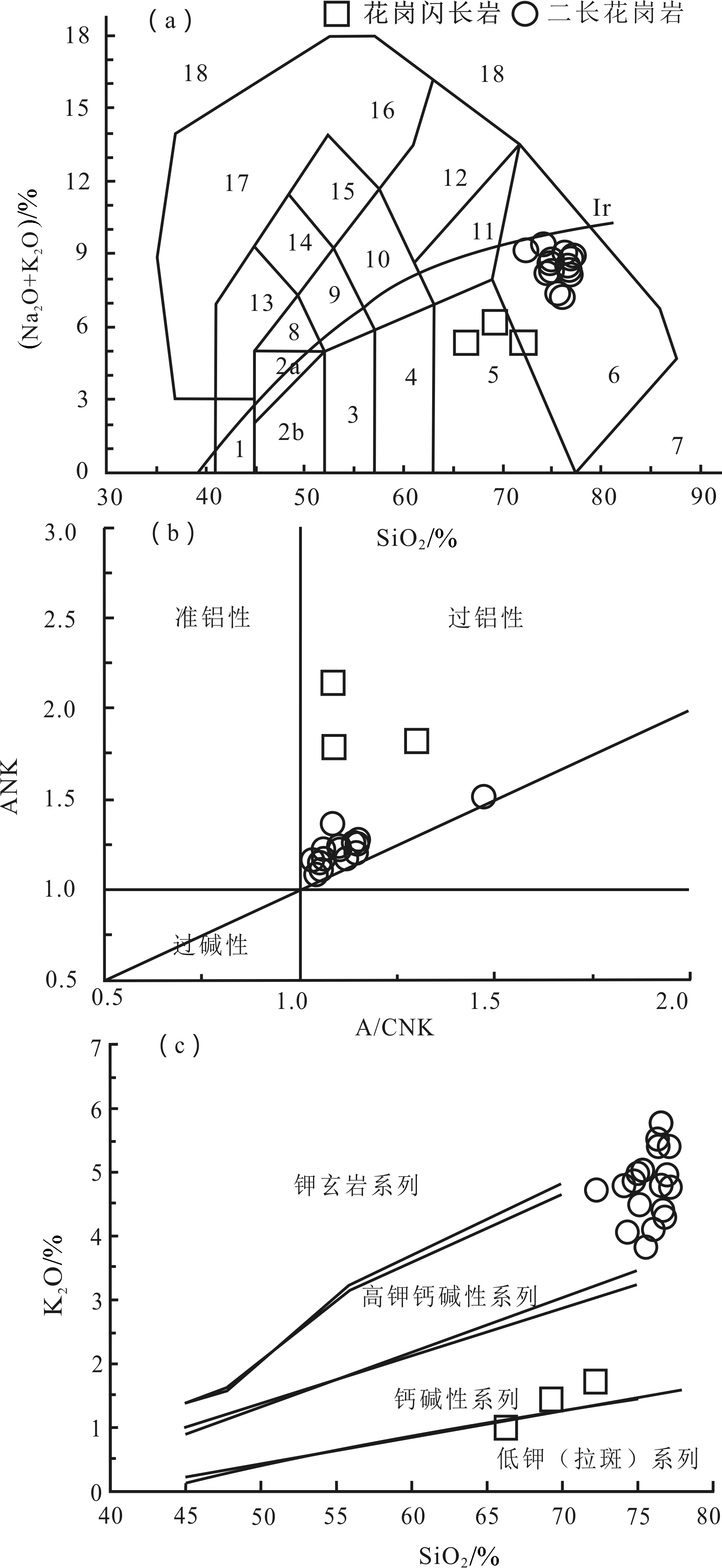
图5 岩浆/火山岩系统全碱-硅(TAS)图(a)、A/CNK-ANK图解(b)和K2O-SiO2图解(c)
Fig.5 TAS classification(a), A/CNK-ANK (b) and K2O-SiO2(c)diagrams of igneous or volcanic rock system
| 序号 | 样品号 | 样品名 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | δEu | δCe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM25-3-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 8.70 | 16.73 | 2.21 | 8.87 | 1.81 | 0.64 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 1.46 | 0.27 | 0.82 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 0.18 | 44.74 | 6.74 | 7.26 | 1.08 | 0.91 |
| 2 | PM25-5-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 14.47 | 27.56 | 3.46 | 13.35 | 2.44 | 0.72 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 1.74 | 0.33 | 1.01 | 0.17 | 1.01 | 0.28 | 69.19 | 8.62 | 10.28 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| 3 | P1YQ01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 19.20 | 37.30 | 4.11 | 14.70 | 2.85 | 0.59 | 2.58 | 0.44 | 2.61 | 0.57 | 1.65 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.33 | 89.02 | 7.67 | 7.57 | 0.65 | 0.98 |
| 平均值 | 14.12 | 27.20 | 3.26 | 12.31 | 2.37 | 0.65 | 2.21 | 0.36 | 1.94 | 0.39 | 1.16 | 0.19 | 1.23 | 0.26 | 67.65 | 7.68 | 8.37 | 0.88 | 0.94 | ||
| 4 | WHHS-47-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 35.30 | 64.35 | 6.77 | 22.11 | 3.47 | 0.91 | 3.03 | 0.42 | 2.31 | 0.43 | 1.33 | 0.22 | 1.38 | 0.25 | 142.28 | 14.18 | 18.35 | 0.84 | 0.95 |
| 5 | WHEH-47-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 22.03 | 47.07 | 4.91 | 16.77 | 3.15 | 0.69 | 2.67 | 0.43 | 2.80 | 0.54 | 1.61 | 0.29 | 1.87 | 0.33 | 105.16 | 8.98 | 8.45 | 0.71 | 1.06 |
| 6 | WHEH-49-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 31.85 | 60.75 | 6.35 | 20.40 | 3.49 | 0.62 | 2.92 | 0.41 | 2.26 | 0.43 | 1.28 | 0.22 | 1.46 | 0.28 | 132.72 | 13.33 | 15.65 | 0.58 | 0.99 |
| 7 | WHZH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 19.51 | 43.43 | 4.17 | 13.71 | 2.82 | 0.49 | 2.68 | 0.55 | 3.88 | 0.80 | 2.49 | 0.44 | 2.73 | 0.45 | 98.15 | 6.00 | 5.13 | 0.54 | 1.12 |
| 8 | WHZH-50-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 20.78 | 39.99 | 4.32 | 14.25 | 2.94 | 0.52 | 2.83 | 0.58 | 4.17 | 0.85 | 2.69 | 0.48 | 2.94 | 0.44 | 97.78 | 5.53 | 5.07 | 0.54 | 0.98 |
| 9 | WHZH-50-GSY03 | 二长花岗岩 | 22.31 | 45.14 | 4.73 | 15.56 | 3.10 | 0.52 | 2.77 | 0.46 | 2.97 | 0.59 | 1.79 | 0.30 | 1.94 | 0.34 | 102.52 | 8.19 | 8.25 | 0.53 | 1.02 |
| 10 | WHZH-50-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 26.56 | 53.36 | 5.42 | 17.80 | 3.17 | 0.64 | 2.79 | 0.43 | 2.74 | 0.53 | 1.58 | 0.27 | 1.79 | 0.31 | 117.39 | 10.24 | 10.64 | 0.64 | 1.03 |
| 11 | WHZH-50-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 35.58 | 75.43 | 7.54 | 25.50 | 5.08 | 0.81 | 4.41 | 0.70 | 4.23 | 0.82 | 2.48 | 0.42 | 2.78 | 0.44 | 166.22 | 9.21 | 9.18 | 0.51 | 1.07 |
| 平均值 | 26.74 | 53.69 | 5.53 | 18.26 | 3.40 | 0.65 | 3.01 | 0.50 | 3.17 | 0.62 | 1.91 | 0.33 | 2.11 | 0.36 | 120.28 | 9.46 | 10.09 | 0.61 | 1.03 | ||
| 12 | PM25-6-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 6.38 | 15.11 | 1.85 | 6.52 | 2.40 | 0.04 | 2.55 | 0.63 | 3.54 | 0.58 | 1.53 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 0.34 | 43.18 | 2.97 | 3.18 | 0.05 | 1.06 |
| 13 | WHEH-46-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 7.10 | 13.72 | 1.61 | 5.45 | 1.64 | 0.12 | 1.94 | 0.52 | 4.26 | 0.93 | 2.95 | 0.53 | 3.37 | 0.48 | 44.62 | 1.98 | 1.51 | 0.21 | 0.96 |
| 14 | WHEH-47-GSY09 | 二长花岗岩 | 8.17 | 16.48 | 1.97 | 7.57 | 2.64 | 0.22 | 3.45 | 0.94 | 7.98 | 1.80 | 5.80 | 1.09 | 6.96 | 0.99 | 66.06 | 1.28 | 0.84 | 0.22 | 0.98 |
| 15 | WHEH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 7.14 | 15.74 | 1.71 | 5.65 | 1.69 | 0.09 | 1.80 | 0.46 | 3.63 | 0.77 | 2.41 | 0.42 | 2.60 | 0.38 | 44.49 | 2.57 | 1.97 | 0.16 | 1.07 |
| 16 | PM25-6-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 11.09 | 20.49 | 2.66 | 10.24 | 3.04 | 0.14 | 3.21 | 0.84 | 6.35 | 1.60 | 6.18 | 1.44 | 9.61 | 1.39 | 78.28 | 1.56 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.90 |
| 17 | PM25-8-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 8.70 | 16.29 | 1.92 | 6.69 | 1.89 | 0.18 | 2.41 | 0.61 | 4.26 | 0.94 | 3.07 | 0.61 | 3.67 | 0.59 | 51.83 | 2.21 | 1.70 | 0.26 | 0.94 |
| 18 | PM25-9-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 10.20 | 18.32 | 2.36 | 9.04 | 2.84 | 0.20 | 3.41 | 0.85 | 5.91 | 1.29 | 4.37 | 0.92 | 5.77 | 0.91 | 66.39 | 1.83 | 1.27 | 0.20 | 0.88 |
| 19 | WHEH-49-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 9.77 | 17.61 | 2.12 | 7.66 | 2.22 | 0.21 | 2.37 | 0.60 | 4.84 | 1.05 | 3.57 | 0.71 | 4.87 | 0.73 | 58.33 | 2.11 | 1.44 | 0.28 | 0.91 |
| 20 | WHEH-46-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 6.13 | 11.50 | 1.32 | 4.87 | 1.70 | 0.31 | 2.26 | 0.68 | 5.95 | 1.38 | 4.65 | 0.91 | 5.87 | 0.84 | 48.37 | 1.15 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.95 |
| 21 | WHEH-47-GSY07 | 二长花岗岩 | 8.37 | 15.56 | 1.75 | 6.39 | 1.76 | 0.34 | 2.01 | 0.50 | 3.99 | 0.89 | 2.93 | 0.56 | 3.62 | 0.56 | 49.23 | 2.27 | 1.66 | 0.55 | 0.95 |
| 平均值 | 8.31 | 16.08 | 1.93 | 7.01 | 2.18 | 0.19 | 2.54 | 0.66 | 5.07 | 1.12 | 3.75 | 0.75 | 4.78 | 0.72 | 55.08 | 1.99 | 1.52 | 0.26 | 0.96 | ||
表4 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩稀土元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 4 Rare earth elements aboundance and characteristic parameter ofgranite in Maodeng of Xilin Hot(10-6)
| 序号 | 样品号 | 样品名 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | δEu | δCe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM25-3-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 8.70 | 16.73 | 2.21 | 8.87 | 1.81 | 0.64 | 1.77 | 0.28 | 1.46 | 0.27 | 0.82 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 0.18 | 44.74 | 6.74 | 7.26 | 1.08 | 0.91 |
| 2 | PM25-5-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 14.47 | 27.56 | 3.46 | 13.35 | 2.44 | 0.72 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 1.74 | 0.33 | 1.01 | 0.17 | 1.01 | 0.28 | 69.19 | 8.62 | 10.28 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| 3 | P1YQ01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 19.20 | 37.30 | 4.11 | 14.70 | 2.85 | 0.59 | 2.58 | 0.44 | 2.61 | 0.57 | 1.65 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.33 | 89.02 | 7.67 | 7.57 | 0.65 | 0.98 |
| 平均值 | 14.12 | 27.20 | 3.26 | 12.31 | 2.37 | 0.65 | 2.21 | 0.36 | 1.94 | 0.39 | 1.16 | 0.19 | 1.23 | 0.26 | 67.65 | 7.68 | 8.37 | 0.88 | 0.94 | ||
| 4 | WHHS-47-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 35.30 | 64.35 | 6.77 | 22.11 | 3.47 | 0.91 | 3.03 | 0.42 | 2.31 | 0.43 | 1.33 | 0.22 | 1.38 | 0.25 | 142.28 | 14.18 | 18.35 | 0.84 | 0.95 |
| 5 | WHEH-47-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 22.03 | 47.07 | 4.91 | 16.77 | 3.15 | 0.69 | 2.67 | 0.43 | 2.80 | 0.54 | 1.61 | 0.29 | 1.87 | 0.33 | 105.16 | 8.98 | 8.45 | 0.71 | 1.06 |
| 6 | WHEH-49-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 31.85 | 60.75 | 6.35 | 20.40 | 3.49 | 0.62 | 2.92 | 0.41 | 2.26 | 0.43 | 1.28 | 0.22 | 1.46 | 0.28 | 132.72 | 13.33 | 15.65 | 0.58 | 0.99 |
| 7 | WHZH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 19.51 | 43.43 | 4.17 | 13.71 | 2.82 | 0.49 | 2.68 | 0.55 | 3.88 | 0.80 | 2.49 | 0.44 | 2.73 | 0.45 | 98.15 | 6.00 | 5.13 | 0.54 | 1.12 |
| 8 | WHZH-50-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 20.78 | 39.99 | 4.32 | 14.25 | 2.94 | 0.52 | 2.83 | 0.58 | 4.17 | 0.85 | 2.69 | 0.48 | 2.94 | 0.44 | 97.78 | 5.53 | 5.07 | 0.54 | 0.98 |
| 9 | WHZH-50-GSY03 | 二长花岗岩 | 22.31 | 45.14 | 4.73 | 15.56 | 3.10 | 0.52 | 2.77 | 0.46 | 2.97 | 0.59 | 1.79 | 0.30 | 1.94 | 0.34 | 102.52 | 8.19 | 8.25 | 0.53 | 1.02 |
| 10 | WHZH-50-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 26.56 | 53.36 | 5.42 | 17.80 | 3.17 | 0.64 | 2.79 | 0.43 | 2.74 | 0.53 | 1.58 | 0.27 | 1.79 | 0.31 | 117.39 | 10.24 | 10.64 | 0.64 | 1.03 |
| 11 | WHZH-50-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 35.58 | 75.43 | 7.54 | 25.50 | 5.08 | 0.81 | 4.41 | 0.70 | 4.23 | 0.82 | 2.48 | 0.42 | 2.78 | 0.44 | 166.22 | 9.21 | 9.18 | 0.51 | 1.07 |
| 平均值 | 26.74 | 53.69 | 5.53 | 18.26 | 3.40 | 0.65 | 3.01 | 0.50 | 3.17 | 0.62 | 1.91 | 0.33 | 2.11 | 0.36 | 120.28 | 9.46 | 10.09 | 0.61 | 1.03 | ||
| 12 | PM25-6-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 6.38 | 15.11 | 1.85 | 6.52 | 2.40 | 0.04 | 2.55 | 0.63 | 3.54 | 0.58 | 1.53 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 0.34 | 43.18 | 2.97 | 3.18 | 0.05 | 1.06 |
| 13 | WHEH-46-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 7.10 | 13.72 | 1.61 | 5.45 | 1.64 | 0.12 | 1.94 | 0.52 | 4.26 | 0.93 | 2.95 | 0.53 | 3.37 | 0.48 | 44.62 | 1.98 | 1.51 | 0.21 | 0.96 |
| 14 | WHEH-47-GSY09 | 二长花岗岩 | 8.17 | 16.48 | 1.97 | 7.57 | 2.64 | 0.22 | 3.45 | 0.94 | 7.98 | 1.80 | 5.80 | 1.09 | 6.96 | 0.99 | 66.06 | 1.28 | 0.84 | 0.22 | 0.98 |
| 15 | WHEH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 7.14 | 15.74 | 1.71 | 5.65 | 1.69 | 0.09 | 1.80 | 0.46 | 3.63 | 0.77 | 2.41 | 0.42 | 2.60 | 0.38 | 44.49 | 2.57 | 1.97 | 0.16 | 1.07 |
| 16 | PM25-6-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 11.09 | 20.49 | 2.66 | 10.24 | 3.04 | 0.14 | 3.21 | 0.84 | 6.35 | 1.60 | 6.18 | 1.44 | 9.61 | 1.39 | 78.28 | 1.56 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.90 |
| 17 | PM25-8-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 8.70 | 16.29 | 1.92 | 6.69 | 1.89 | 0.18 | 2.41 | 0.61 | 4.26 | 0.94 | 3.07 | 0.61 | 3.67 | 0.59 | 51.83 | 2.21 | 1.70 | 0.26 | 0.94 |
| 18 | PM25-9-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 10.20 | 18.32 | 2.36 | 9.04 | 2.84 | 0.20 | 3.41 | 0.85 | 5.91 | 1.29 | 4.37 | 0.92 | 5.77 | 0.91 | 66.39 | 1.83 | 1.27 | 0.20 | 0.88 |
| 19 | WHEH-49-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 9.77 | 17.61 | 2.12 | 7.66 | 2.22 | 0.21 | 2.37 | 0.60 | 4.84 | 1.05 | 3.57 | 0.71 | 4.87 | 0.73 | 58.33 | 2.11 | 1.44 | 0.28 | 0.91 |
| 20 | WHEH-46-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 6.13 | 11.50 | 1.32 | 4.87 | 1.70 | 0.31 | 2.26 | 0.68 | 5.95 | 1.38 | 4.65 | 0.91 | 5.87 | 0.84 | 48.37 | 1.15 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.95 |
| 21 | WHEH-47-GSY07 | 二长花岗岩 | 8.37 | 15.56 | 1.75 | 6.39 | 1.76 | 0.34 | 2.01 | 0.50 | 3.99 | 0.89 | 2.93 | 0.56 | 3.62 | 0.56 | 49.23 | 2.27 | 1.66 | 0.55 | 0.95 |
| 平均值 | 8.31 | 16.08 | 1.93 | 7.01 | 2.18 | 0.19 | 2.54 | 0.66 | 5.07 | 1.12 | 3.75 | 0.75 | 4.78 | 0.72 | 55.08 | 1.99 | 1.52 | 0.26 | 0.96 | ||

图6 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩稀土配分曲线 (a)花岗闪长岩(1—3); (b)二长花岗岩(4—11); (c)二长花岗岩(12—22); (d)两种二长花岗岩稀土均值
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of granodiorite and monzonite granite in Maodeng of Xilin Hot
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 样品名称 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | Cr | Co | V | Pb | Ga | Zn | Cu | W | Mo | Bi | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM25-3-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 36.00 | 552.00 | 230.60 | 66.00 | 2.10 | 2.50 | 0.80 | 7.30 | 2.90 | 0.30 | 23.10 | 1.50 | 87.50 | 10.00 | 20.50 | 83.70 | 27.60 | 0.10 | 9.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 2.39 | 3.13 |
| 2 | PM25-5-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 38.80 | 484.40 | 359.40 | 101.70 | 2.70 | 3.40 | 1.10 | 8.80 | 3.30 | 0.30 | 20.80 | 0.30 | 52.10 | 12.50 | 18.60 | 50.80 | 68.70 | 0.10 | 12.00 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 1.35 | 3.09 |
| 3 | P1YQ01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 64.40 | 299.00 | 510.00 | 88.70 | 4.00 | 5.30 | 1.20 | 15.80 | 9.00 | - | 59.70 | 24.10 | 190.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.22 | 0.59 | 4.42 |
| 平均 | 46.40 | 445.13 | 366.67 | 85.47 | 2.93 | 3.73 | 1.03 | 10.63 | 5.07 | 0.30 | 34.53 | 8.63 | 109.87 | 11.25 | 19.55 | 67.25 | 48.15 | 0.10 | 10.50 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 1.44 | 3.54 | ||
| 4 | WHHS-47-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 100.60 | 163.10 | 823.70 | 114.00 | 4.30 | 17.30 | 1.10 | 11.70 | 7.40 | 0.60 | 27.30 | 2.30 | 41.80 | 23.00 | 14.00 | 35.20 | 7.40 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.62 | 0.20 | 15.73 |
| 5 | WHEH-47-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 129.90 | 75.70 | 803.30 | 49.30 | 2.30 | 11.10 | 1.40 | 14.60 | 8.90 | 1.10 | 23.30 | 1.00 | 23.40 | 26.30 | 11.90 | 17.10 | 8.70 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 1.72 | 0.09 | 7.93 |
| 6 | WHEH-49-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 126.40 | 65.70 | 401.50 | 87.30 | 3.40 | 21.00 | 2.90 | 11.80 | 7.30 | 0.70 | 24.10 | 0.60 | 30.80 | 24.30 | 13.40 | 23.50 | 5.50 | 0.80 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 1.92 | 0.16 | 7.24 |
| 7 | WHZH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 191.70 | 92.90 | 288.30 | 73.10 | 3.50 | 18.00 | 1.90 | 22.10 | 15.10 | 1.70 | 24.20 | 1.30 | 38.30 | 23.30 | 17.90 | 25.30 | 5.60 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 2.06 | 0.32 | 9.47 |
| 8 | WHZH-50-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 157.80 | 115.50 | 318.00 | 73.70 | 3.20 | 16.50 | 2.20 | 24.80 | 14.30 | 1.60 | 23.60 | 1.30 | 33.70 | 20.70 | 16.80 | 28.30 | 5.80 | 1.10 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 1.37 | 0.36 | 7.50 |
| 9 | WHZH-50-GSY03 | 二长花岗岩 | 153.80 | 74.50 | 290.50 | 60.70 | 2.60 | 20.60 | 1.70 | 16.20 | 10.20 | 1.10 | 24.50 | 0.80 | 34.70 | 28.40 | 15.90 | 21.40 | 5.40 | 2.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 2.06 | 0.26 | 12.12 |
| 10 | WHZH-50-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 120.50 | 95.20 | 810.20 | 70.00 | 3.00 | 19.10 | 1.50 | 14.60 | 8.80 | 1.10 | 22.40 | 0.90 | 32.30 | 21.90 | 13.50 | 19.90 | 5.40 | 6.30 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.27 | 0.12 | 12.73 |
| 11 | WHZH-50-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 152.90 | 75.70 | 361.90 | 68.60 | 3.00 | 20.80 | 1.40 | 21.50 | 8.40 | 0.90 | 24.30 | 0.60 | 34.80 | 26.00 | 15.30 | 14.30 | 5.10 | 1.90 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 2.02 | 0.21 | 14.86 |
| 平均 | 141.70 | 94.79 | 512.18 | 74.59 | 3.16 | 18.05 | 1.76 | 17.16 | 10.05 | 1.10 | 24.21 | 1.10 | 33.73 | 24.24 | 14.84 | 23.13 | 6.11 | 1.84 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 1.63 | 0.22 | 10.95 | ||
| 12 | PM25-6-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 325.40 | 41.90 | 40.90 | 39.50 | 2.80 | 5.60 | 2.50 | 18.10 | 12.60 | 1.90 | 17.90 | 1.70 | 10.40 | 19.40 | 25.10 | 55.80 | 10.00 | 0.10 | 8.00 | 0.00 | 7.77 | 1.02 | 2.24 |
| 13 | WHEH-46-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 227.70 | 26.20 | 47.60 | 32.80 | 1.90 | 6.50 | 1.90 | 26.20 | 14.60 | 2.30 | 21.60 | 0.60 | 16.60 | 33.10 | 13.70 | 10.40 | 5.00 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 8.69 | 0.55 | 3.42 |
| 14 | WHEH-47-GSY09 | 二长花岗岩 | 249.40 | 28.30 | 36.60 | 59.00 | 3.70 | 22.90 | 6.10 | 53.60 | 17.20 | 3.80 | 22.90 | 0.50 | 30.60 | 47.00 | 16.00 | 9.00 | 5.60 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 8.81 | 0.77 | 3.75 |
| 15 | WHEH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 248.10 | 18.30 | 50.00 | 23.30 | 1.40 | 8.60 | 1.70 | 22.70 | 12.80 | 1.80 | 23.20 | 0.80 | 26.40 | 22.50 | 17.00 | 16.30 | 6.10 | 1.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 13.56 | 0.37 | 5.06 |
| 16 | PM25-6-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 317.70 | 35.70 | 41.60 | 47.10 | 2.70 | 13.20 | 5.70 | 45.20 | 25.70 | 6.10 | 17.70 | 0.70 | 11.20 | 43.90 | 15.80 | 11.70 | 11.30 | 0.20 | 23.00 | 0.00 | 8.90 | 0.86 | 2.32 |
| 17 | PM25-8-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 340.00 | 31.30 | 65.60 | 43.80 | 2.20 | 9.30 | 2.30 | 28.40 | 15.90 | 2.30 | 19.00 | 0.60 | 12.40 | 41.30 | 14.40 | 12.10 | 10.80 | 0.10 | 8.00 | 0.00 | 10.86 | 0.48 | 4.04 |
| 18 | PM25-9-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 181.40 | 26.30 | 39.60 | 57.70 | 3.30 | 16.90 | 5.80 | 41.20 | 17.90 | 4.70 | 17.80 | 0.20 | 15.80 | 55.60 | 13.80 | 9.10 | 11.50 | 0.10 | 7.00 | 0.00 | 6.90 | 0.66 | 2.91 |
| 19 | WHEH-49-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 250.10 | 60.90 | 166.70 | 49.60 | 3.10 | 21.00 | 5.10 | 29.70 | 16.60 | 3.40 | 24.60 | 0.80 | 34.60 | 29.00 | 11.80 | 11.80 | 9.00 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 4.11 | 0.37 | 4.12 |
| 20 | WHEH-46-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 211.00 | 47.70 | 99.80 | 49.40 | 2.80 | 22.90 | 6.40 | 40.40 | 15.80 | 3.00 | 23.20 | 0.90 | 25.00 | 44.50 | 14.90 | 9.20 | 5.20 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 4.42 | 0.48 | 3.58 |
| 21 | WHEH-47-GSY07 | 二长花岗岩 | 225.70 | 33.40 | 29.60 | 70.90 | 3.00 | 48.40 | 6.80 | 26.00 | 8.90 | 1.30 | 23.70 | 0.50 | 28.30 | 53.30 | 15.90 | 19.00 | 5.20 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 6.76 | 1.13 | 7.12 |
| 22 | WHEH-47-GSY08 | 二长花岗岩 | 225.10 | 32.90 | 21.30 | 48.10 | 2.20 | 35.20 | 4.90 | 26.60 | 15.40 | 3.50 | 23.20 | 0.50 | 25.20 | 47.10 | 14.70 | 17.20 | 5.60 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 6.84 | 1.54 | 7.18 |
| 平均 | 254.69 | 34.81 | 58.12 | 47.38 | 2.65 | 19.14 | 4.47 | 32.55 | 15.76 | 3.10 | 21.35 | 0.71 | 21.50 | 39.70 | 15.74 | 16.51 | 7.75 | 0.36 | 4.37 | 0.10 | 7.97 | 0.75 | 4.16 | ||
表5 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩微量元素分析结果(wB/10-6)
Table 5 Trace elements aboundance and characteristic parameters of granite in Maodeng of Xilin Hot(10-6)
| 序号 | 样品编号 | 样品名称 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | Cr | Co | V | Pb | Ga | Zn | Cu | W | Mo | Bi | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM25-3-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 36.00 | 552.00 | 230.60 | 66.00 | 2.10 | 2.50 | 0.80 | 7.30 | 2.90 | 0.30 | 23.10 | 1.50 | 87.50 | 10.00 | 20.50 | 83.70 | 27.60 | 0.10 | 9.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 2.39 | 3.13 |
| 2 | PM25-5-GSY01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 38.80 | 484.40 | 359.40 | 101.70 | 2.70 | 3.40 | 1.10 | 8.80 | 3.30 | 0.30 | 20.80 | 0.30 | 52.10 | 12.50 | 18.60 | 50.80 | 68.70 | 0.10 | 12.00 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 1.35 | 3.09 |
| 3 | P1YQ01 | 花岗闪长岩 | 64.40 | 299.00 | 510.00 | 88.70 | 4.00 | 5.30 | 1.20 | 15.80 | 9.00 | - | 59.70 | 24.10 | 190.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.22 | 0.59 | 4.42 |
| 平均 | 46.40 | 445.13 | 366.67 | 85.47 | 2.93 | 3.73 | 1.03 | 10.63 | 5.07 | 0.30 | 34.53 | 8.63 | 109.87 | 11.25 | 19.55 | 67.25 | 48.15 | 0.10 | 10.50 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 1.44 | 3.54 | ||
| 4 | WHHS-47-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 100.60 | 163.10 | 823.70 | 114.00 | 4.30 | 17.30 | 1.10 | 11.70 | 7.40 | 0.60 | 27.30 | 2.30 | 41.80 | 23.00 | 14.00 | 35.20 | 7.40 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.62 | 0.20 | 15.73 |
| 5 | WHEH-47-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 129.90 | 75.70 | 803.30 | 49.30 | 2.30 | 11.10 | 1.40 | 14.60 | 8.90 | 1.10 | 23.30 | 1.00 | 23.40 | 26.30 | 11.90 | 17.10 | 8.70 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 1.72 | 0.09 | 7.93 |
| 6 | WHEH-49-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 126.40 | 65.70 | 401.50 | 87.30 | 3.40 | 21.00 | 2.90 | 11.80 | 7.30 | 0.70 | 24.10 | 0.60 | 30.80 | 24.30 | 13.40 | 23.50 | 5.50 | 0.80 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 1.92 | 0.16 | 7.24 |
| 7 | WHZH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 191.70 | 92.90 | 288.30 | 73.10 | 3.50 | 18.00 | 1.90 | 22.10 | 15.10 | 1.70 | 24.20 | 1.30 | 38.30 | 23.30 | 17.90 | 25.30 | 5.60 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 2.06 | 0.32 | 9.47 |
| 8 | WHZH-50-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 157.80 | 115.50 | 318.00 | 73.70 | 3.20 | 16.50 | 2.20 | 24.80 | 14.30 | 1.60 | 23.60 | 1.30 | 33.70 | 20.70 | 16.80 | 28.30 | 5.80 | 1.10 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 1.37 | 0.36 | 7.50 |
| 9 | WHZH-50-GSY03 | 二长花岗岩 | 153.80 | 74.50 | 290.50 | 60.70 | 2.60 | 20.60 | 1.70 | 16.20 | 10.20 | 1.10 | 24.50 | 0.80 | 34.70 | 28.40 | 15.90 | 21.40 | 5.40 | 2.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 2.06 | 0.26 | 12.12 |
| 10 | WHZH-50-GSY04 | 二长花岗岩 | 120.50 | 95.20 | 810.20 | 70.00 | 3.00 | 19.10 | 1.50 | 14.60 | 8.80 | 1.10 | 22.40 | 0.90 | 32.30 | 21.90 | 13.50 | 19.90 | 5.40 | 6.30 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.27 | 0.12 | 12.73 |
| 11 | WHZH-50-GSY05 | 二长花岗岩 | 152.90 | 75.70 | 361.90 | 68.60 | 3.00 | 20.80 | 1.40 | 21.50 | 8.40 | 0.90 | 24.30 | 0.60 | 34.80 | 26.00 | 15.30 | 14.30 | 5.10 | 1.90 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 2.02 | 0.21 | 14.86 |
| 平均 | 141.70 | 94.79 | 512.18 | 74.59 | 3.16 | 18.05 | 1.76 | 17.16 | 10.05 | 1.10 | 24.21 | 1.10 | 33.73 | 24.24 | 14.84 | 23.13 | 6.11 | 1.84 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 1.63 | 0.22 | 10.95 | ||
| 12 | PM25-6-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 325.40 | 41.90 | 40.90 | 39.50 | 2.80 | 5.60 | 2.50 | 18.10 | 12.60 | 1.90 | 17.90 | 1.70 | 10.40 | 19.40 | 25.10 | 55.80 | 10.00 | 0.10 | 8.00 | 0.00 | 7.77 | 1.02 | 2.24 |
| 13 | WHEH-46-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 227.70 | 26.20 | 47.60 | 32.80 | 1.90 | 6.50 | 1.90 | 26.20 | 14.60 | 2.30 | 21.60 | 0.60 | 16.60 | 33.10 | 13.70 | 10.40 | 5.00 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 8.69 | 0.55 | 3.42 |
| 14 | WHEH-47-GSY09 | 二长花岗岩 | 249.40 | 28.30 | 36.60 | 59.00 | 3.70 | 22.90 | 6.10 | 53.60 | 17.20 | 3.80 | 22.90 | 0.50 | 30.60 | 47.00 | 16.00 | 9.00 | 5.60 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 8.81 | 0.77 | 3.75 |
| 15 | WHEH-50-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 248.10 | 18.30 | 50.00 | 23.30 | 1.40 | 8.60 | 1.70 | 22.70 | 12.80 | 1.80 | 23.20 | 0.80 | 26.40 | 22.50 | 17.00 | 16.30 | 6.10 | 1.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 13.56 | 0.37 | 5.06 |
| 16 | PM25-6-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 317.70 | 35.70 | 41.60 | 47.10 | 2.70 | 13.20 | 5.70 | 45.20 | 25.70 | 6.10 | 17.70 | 0.70 | 11.20 | 43.90 | 15.80 | 11.70 | 11.30 | 0.20 | 23.00 | 0.00 | 8.90 | 0.86 | 2.32 |
| 17 | PM25-8-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 340.00 | 31.30 | 65.60 | 43.80 | 2.20 | 9.30 | 2.30 | 28.40 | 15.90 | 2.30 | 19.00 | 0.60 | 12.40 | 41.30 | 14.40 | 12.10 | 10.80 | 0.10 | 8.00 | 0.00 | 10.86 | 0.48 | 4.04 |
| 18 | PM25-9-GSY01 | 二长花岗岩 | 181.40 | 26.30 | 39.60 | 57.70 | 3.30 | 16.90 | 5.80 | 41.20 | 17.90 | 4.70 | 17.80 | 0.20 | 15.80 | 55.60 | 13.80 | 9.10 | 11.50 | 0.10 | 7.00 | 0.00 | 6.90 | 0.66 | 2.91 |
| 19 | WHEH-49-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 250.10 | 60.90 | 166.70 | 49.60 | 3.10 | 21.00 | 5.10 | 29.70 | 16.60 | 3.40 | 24.60 | 0.80 | 34.60 | 29.00 | 11.80 | 11.80 | 9.00 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 4.11 | 0.37 | 4.12 |
| 20 | WHEH-46-GSY02 | 二长花岗岩 | 211.00 | 47.70 | 99.80 | 49.40 | 2.80 | 22.90 | 6.40 | 40.40 | 15.80 | 3.00 | 23.20 | 0.90 | 25.00 | 44.50 | 14.90 | 9.20 | 5.20 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 4.42 | 0.48 | 3.58 |
| 21 | WHEH-47-GSY07 | 二长花岗岩 | 225.70 | 33.40 | 29.60 | 70.90 | 3.00 | 48.40 | 6.80 | 26.00 | 8.90 | 1.30 | 23.70 | 0.50 | 28.30 | 53.30 | 15.90 | 19.00 | 5.20 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 6.76 | 1.13 | 7.12 |
| 22 | WHEH-47-GSY08 | 二长花岗岩 | 225.10 | 32.90 | 21.30 | 48.10 | 2.20 | 35.20 | 4.90 | 26.60 | 15.40 | 3.50 | 23.20 | 0.50 | 25.20 | 47.10 | 14.70 | 17.20 | 5.60 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 6.84 | 1.54 | 7.18 |
| 平均 | 254.69 | 34.81 | 58.12 | 47.38 | 2.65 | 19.14 | 4.47 | 32.55 | 15.76 | 3.10 | 21.35 | 0.71 | 21.50 | 39.70 | 15.74 | 16.51 | 7.75 | 0.36 | 4.37 | 0.10 | 7.97 | 0.75 | 4.16 | ||
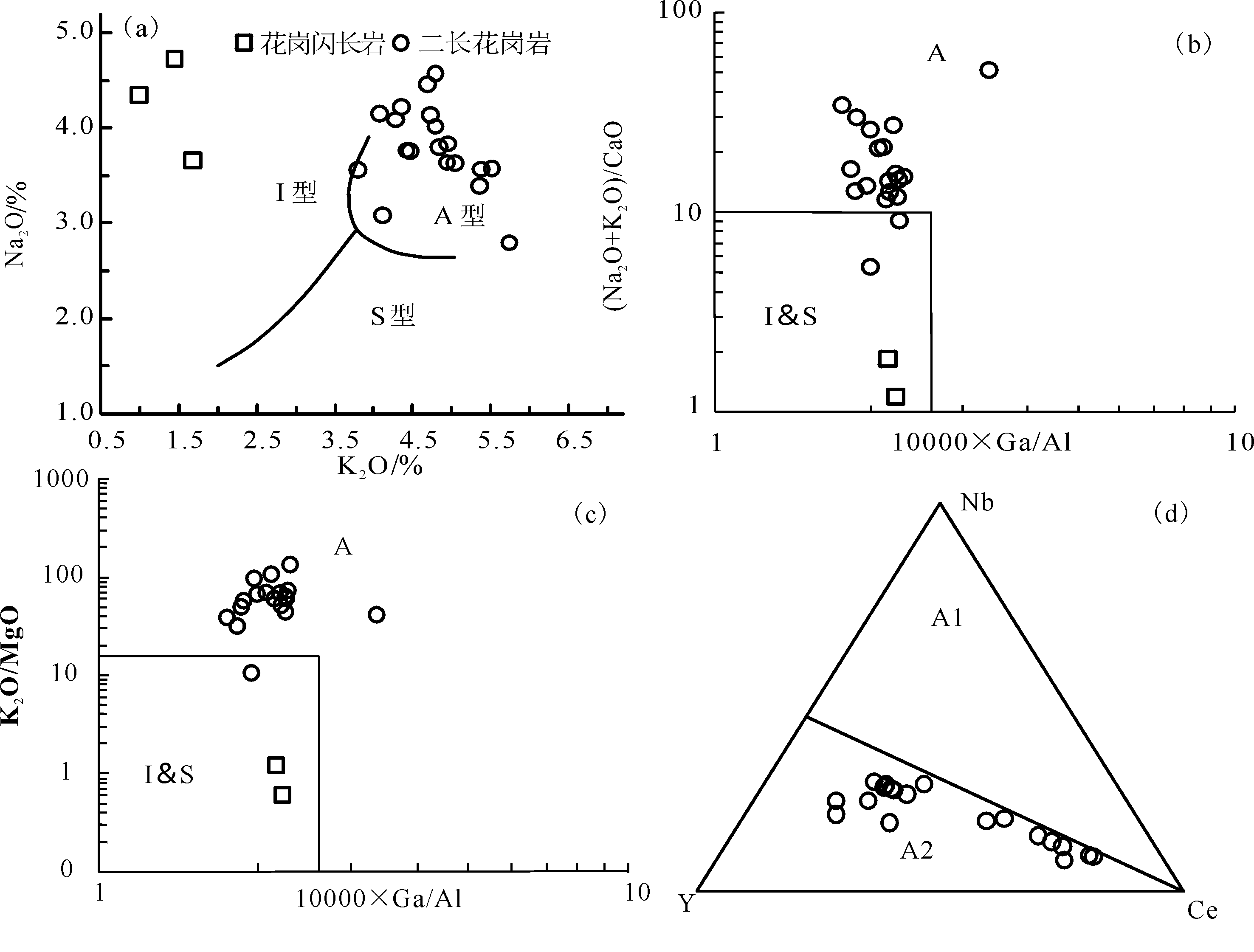
图8 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩类型判别图 (a)岩石系列K2O-Na2O图解;(b)10000×Ga/Al-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO判别图解;(c)10000×Ga/Al-K2O/MgO判别图解;(d)花岗岩Nb-Y-Ce构造环境判别图(A2-造山后花岗岩)
Fig.8 Classification diagrams of granite in Maodeng of Xinlin Hot
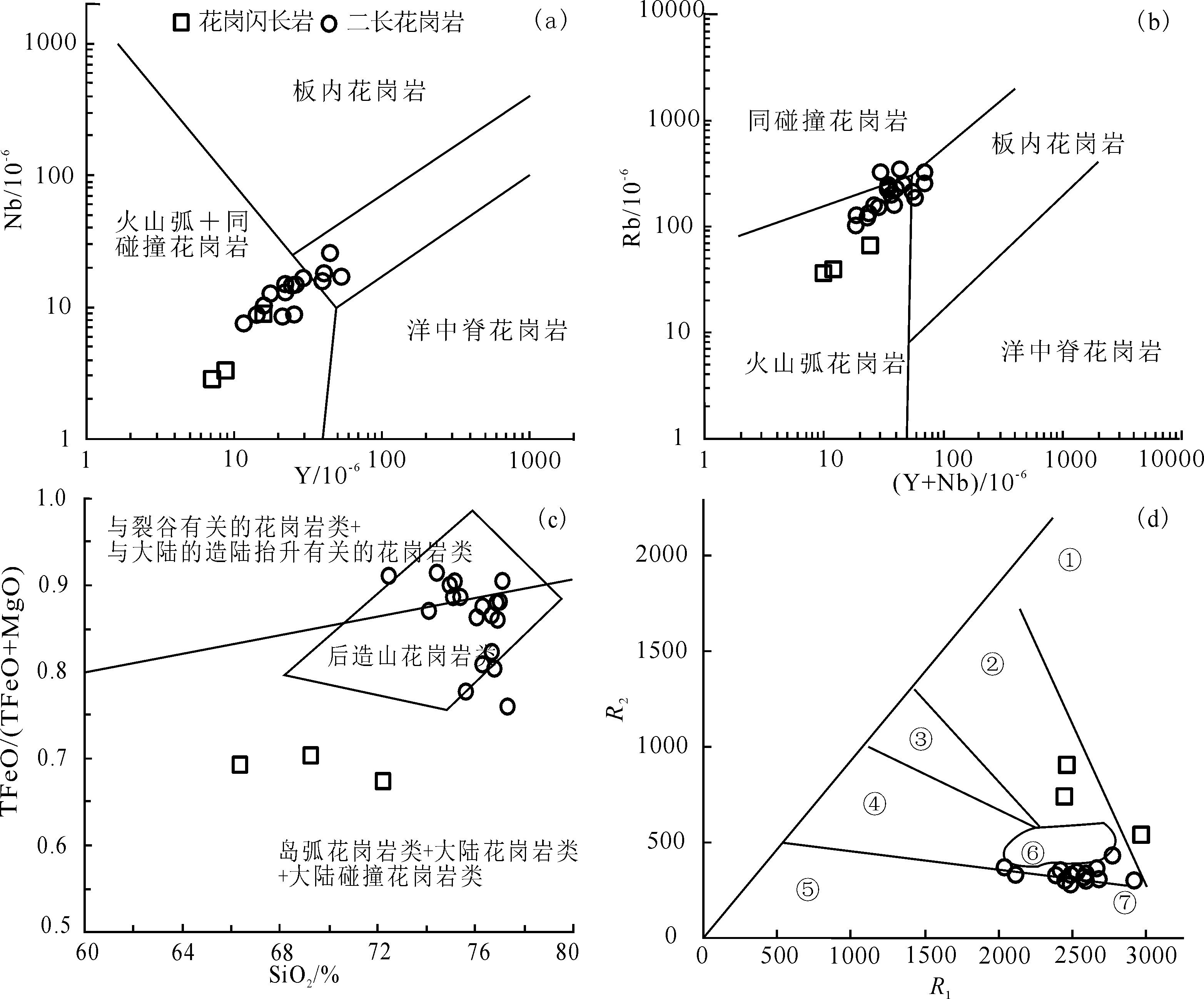
图9 锡林浩特毛登牧场花岗岩岩浆来源及构造环境判别图 ①地幔斜长花岗岩;②破坏性活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④晚造期花岗岩;⑤非造山区A型花岗岩;⑥同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦造山期后A型花岗岩
Fig.9 Discrimination diagrams for the source and tectonic environments of granites in Maodeng of Xilin Hot
| [1] | 李双林, 欧阳自远. 兴蒙造山带及邻区的构造格局与构造演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18 (3) : 46-55. |
| [2] | 刘永江, 张兴洲, 金巍, 等. 东北地区晚古生代区域构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37 (4) : 943-951. |
| [3] | 邵济安, 牟保磊, 何国琦, 等. 华北北部在古亚洲域与古太平洋域构造叠加过程中的地质作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27 (5) : 390-394. |
| [4] | 唐克东, 邵济安. 中亚褶皱区构造演化问题——俄罗斯学者近年研究成果评价[J]. 现代地质, 1997, 11 (1): 22-29. |
| [5] | 朱永峰, 孙世华, 毛骞, 等. 内蒙古锡林格勒杂岩的地球化学研究:从Rodinia聚合到古亚洲洋闭合后碰撞造山的历史记录[J]. 高校地质学报, 2004, 10 (3): 343-355. |
| [6] | 梁玉伟, 余存林, 沈国珍, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗索纳嘠铅锌银矿区花岗岩地球化学特征及其构造与成矿意义[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40 (3): 767-779. |
| [7] |
ZHOU X M, SUN T, SHEN W Z, et al. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 2006, 29 (1): 26-33.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 陈斌, 赵国春, WILDE S. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47 (4): 361-367. |
| [9] | 王成文, 金巍, 张兴洲, 等. 东北及邻区晚古生代大地构造属性新认识[J]. 地层学杂志, 2008, 32 (2): 119-136. |
| [10] | 王成文, 孙跃武, 李宁, 等. 中国东北及邻区晚古生代地层分布规律的大地构造意义[J]. 中国科学 (D辑), 2009, 39 (10): 1429-1437. |
| [11] | 谷丛楠, 周志广, 张有宽, 等. 内蒙古白乃庙地区白音都西群的碎屑锆石年龄及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26 (1): 1-9. |
| [12] | 徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 等. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30 (7): 1841-1857. |
| [13] | 刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83 (3): 365-376. |
| [14] | 朱伟. 内蒙古克什克腾旗晚中生代花岗岩地质特征及其构造意义[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2011:1-84. |
| [15] | 张磊, 吕新彪, 刘阁, 等. 兴蒙造山带东段大陆弧后A型花岗岩特征与成因[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40 (3): 869-884. |
| [16] |
SLÁMA J, JAN K, DANIEL J C, et al. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249(s 1/2): 1-35.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SCHERER E E, CAMERON K L, BLICHERT-TOFT J. Lu-Hf garnet geochronology: closure temperature relative to the Sm-Nd system and the effects of trace mineral inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(19): 3413-3432.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 肖成东, 等. 太行山—大兴安岭构造岩浆带中生代侵入岩Nd、Sr、Pb同位素特征及物质来源探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20 (5): 236-240,242-253. |
| [20] | 袁玲玲, 张晓晖, 薛富红. 内蒙古中北部二连浩特地区晚古生代花岗岩的岩石成因及其地质意义[M]// 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会. 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第15届学术年会论文集. 长春: 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会, 2015: 1. |
| [21] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23 (6): 1217-1238. |
| [22] | 杨帆, 肖荣阁, 李娜, 等. 内蒙古宝音图钼矿床花岗岩稀土元素地球化学特征及花岗岩成因[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27 (4): 831-840. |
| [23] | 赵俊香, 陈岳龙, 李志红. 康定杂岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20 (3): 378-385. |
| [24] | 程银行, 滕学建, 辛后田, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗狠麦温都尔花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31 (3): 323-334. |
| [25] | 李昌年. 火成岩微量元素地球化学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992: 1-195. |
| [26] | 施光海, 刘敦一, 张福勤, 等. 中国内蒙古锡林郭勒杂岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及意义[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48 (20): 2187-2192. |
| [27] | 鲍庆中, 张长捷, 吴之理, 等. 内蒙古白音高勒地区石炭纪石英闪长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37 (1): 15-23. |
| [28] | 辛后田, 滕学建, 程银行. 内蒙古东乌旗宝力高庙组地层划分及其同位素年代学研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2011, 34 (1): 1-9. |
| [29] | 周志广, 张华峰, 刘还林, 等. 内蒙中部四子王旗地区基性侵入岩锆石定年及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25 (6): 1519-1528. |
| [30] | 汪岩, 付俊彧, 那福超, 等. 内蒙古扎赉特旗辉长岩-闪长岩地球化学特征和LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32 (10): 1525-1535. |
| [31] | 许立权. 内蒙古白云鄂博-满都拉地区加里东期—华力西期—印支期岩浆岩特征与大地构造演化探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2005: 1-124. |
| [32] | 庞迎春, 程顺波. 花岗岩分类问题研究现状[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2009, 23 (2): 119-122,137. |
| [33] | 陈建林, 郭原生, 付善明. 花岗岩研究进展——ISMA花岗岩类分类综述[J]. 甘肃地质学报, 2004, 13 (1): 67-73. |
| [34] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 王登红. 内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场大石寨组细碧-角斑岩系地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27 (3): 525-536. |
| [35] |
EBY G N. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26 (1/2): 115-134.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of A-type granitoids: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20 (7): 641.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
CHEN B, JAHN B M, WILDE S, et al. Two contrasting paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia, China: petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1): 157-182.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 肖中军, 王振强, 赵春勇, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗北部阿登锡勒大队一带早石炭世高分异I型花岗岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61 (4): 777-786. |
| [39] | 张健, 陈井胜, 李泊洋, 等. 内蒙古塔尔气地区晚古生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素特征[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30 (4): 521-531. |
| [40] | 王瑾. 内蒙古维拉斯托铜多金属矿床矿区花岗岩类年代学与地球化学[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009: 1-68. |
| [41] | 王新宇, 侯青叶, 王瑾, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托矿床花岗岩类SHRIMP年代学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27 (1): 67-78. |
| [42] | LOISELLE M C, WONES D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin(Abstracts with Program), 1979, 11: 1-468. |
| [43] | 胡受奚, 顾连兴, 严正富, 等. 不同类型花岗岩与板块构造的关系及其形成和分布规律[M]//沈阳地质矿产研究所.中国北方花岗岩与成矿作用论文集 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 33-39. |
| [44] | 王德滋, 赵广涛, 邱检生. 中国东部晚中生代A型花岗岩的构造制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 1995, 1 (2): 13-21. |
| [45] | 邵济安, 唐克东, 王成源, 等. 那丹哈达地体的构造特征及演化[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1991 (7): 744-751. |
| [46] | 徐备, 陈斌. 内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构及演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997 27 (3): 227-232. |
| [47] | 黄丁伶, 朱洛婷, 侯青叶, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托矿区花岗岩类地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28 (6): 1122-1137. |
| [48] | 唐克东. 中朝板块北侧褶皱带构造演化及成矿规律[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1992:1-285. |
| [49] | 叶栩松, 廖群安, 葛梦春. 内蒙古锡林浩特、林西地区三叠纪过铝质花岗岩的成因及构造意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30 (3): 57-64. |
| [50] | 王玉净, 樊志勇. 内蒙古西拉木伦河北部蛇绿岩带中二叠纪放射虫的发现及其地质意义[J]. 古生物学报, 1997, 36 (1): 60-71. |
| [51] | ZHANG L, LV X B, LIU G, et al.. Characteristics and genesis of continental back-arc A-type granites in the eastern segment of the Inner Mongolia-Da Hinggan Mountains orogenic belt[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40 (3): 869-884. |
| [1] | 刘建栋, 李五福, 王国良, 董进生, 曹锦山, 李红刚, 赵忠国. 北祁连东段柏木峡—门岗峡地区蛇绿岩的识别及其区域构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 244-258. |
| [2] | 柳志华, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 王佳琳, 刘涛, 王文东, 赵伟, 陈洋. 内蒙古索伦山蛇绿岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 399-417. |
| [3] | 滕超, 张晓飞, 周毅, 冯俊岭, 李树才. 内蒙古锡林浩特小乌兰沟早白垩世二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1003-1014. |
| [4] | 袁建国, 顾玉超, 肖荣阁, 屈云燕, 段凯波, 韩玥. 内蒙古锡林浩特东部地区早白垩世花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 20-32. |
| [5] | 王善辉 , 陈岳龙, 李大鹏. 锡林浩特杂岩中斜长角闪岩锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 1019-1027. |
| [6] | 张承帅, 李莉, 张长青, 王九如. 福建龙岩大洋花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(3): 433-444. |
| [7] | 张春艳 张兴洲 夏庆贺. 吉林中部硅质岩中锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 256-261. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||