



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (02): 514-522.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.045
收稿日期:2019-01-15
修回日期:2020-06-29
出版日期:2021-04-25
发布日期:2021-05-25
作者简介:李杰,男,1985年出生,硕士,高级工程师,地质工程专业,主要从事区域地质矿产调查研究工作。Email: yinhelijie@163.com。
基金资助:
LI Jie1( ), CONG Diange2,3, GU Yanchun4, TIAN Ying1
), CONG Diange2,3, GU Yanchun4, TIAN Ying1
Received:2019-01-15
Revised:2020-06-29
Online:2021-04-25
Published:2021-05-25
摘要:
查干敖包二长花岗岩位于阿拉善左旗诺尔公苏木查干敖包一带。该岩体是阿拉善地块北缘诺尔公—狼山构造带诺尔公大型复式岩基的主要组成部分。通过LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测年,确定其形成年龄为(278±1)Ma,属早二叠世晚期。二长花岗岩SiO2含量为72.88%~75.44%,全碱(K2O+Na2O)含量平均为8.16%,K2O/Na2O主要介于0.87~1.41之间,Al2O3含量为12.38%~13.98%,铝饱和指数(A/CNK)介于0.88~1.02之间,在AR-SiO2图上落入碱性系列区域。上述特征表明查干敖包二长花岗岩为高硅、富钾、准铝质碱性花岗岩。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化曲线明显右倾,轻稀土元素相对富集(LREE/HREE=4.70~14.66),δEu= 0.18~0.87,平均为0.37,呈中等-较强烈负铕异常。明显亏损Nb、Ta、Ti、P等高场强元素,Sr平均值为94.44×10-6,Yb为3.10×10-6,呈现非常低Sr、高Yb的特征。岩石地球化学特征表明查干敖包二长花岗岩体形成于后碰撞环境,地幔物质底侵作用下的伸展机制可能启动了这次岩浆侵入事件。结合区域资料推断阿拉善地块所代表的华北板块西北缘在早二叠世晚期已经进入后碰撞演化阶段。
中图分类号:
李杰, 丛殿阁, 古艳春, 田颖. 内蒙古阿拉善地块北缘查干敖包一带二长花岗岩锆石定年、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 514-522.
LI Jie, CONG Diange, GU Yanchun, TIAN Ying. Zircon U-Pb Dating, Geochemical Characteristics, and Tectonic Significance of the Chaganobo Monzogranite in the Northern Margin of Alxa Block, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 514-522.
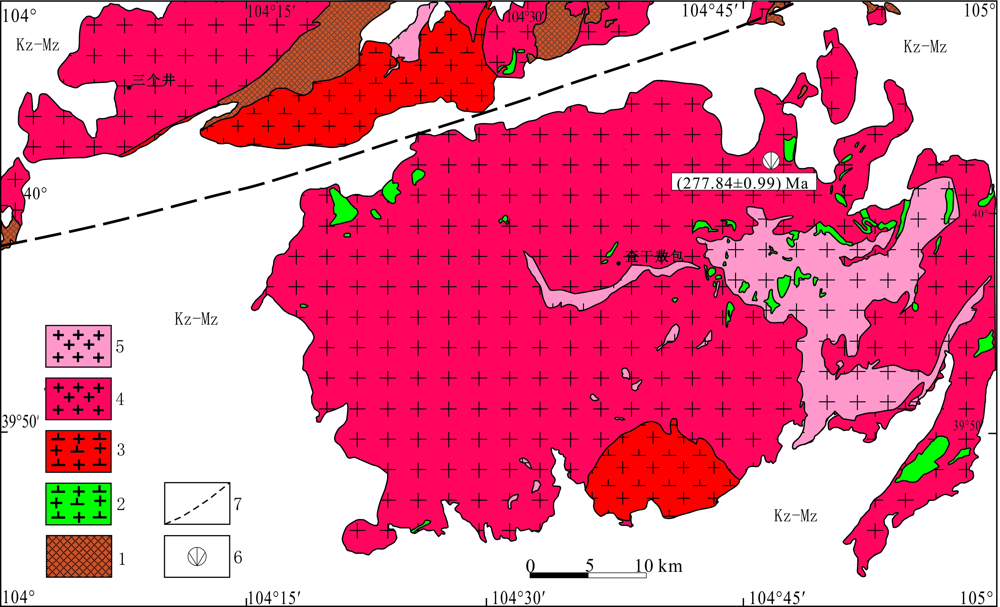
图2 查干敖包一带地质简图(据张维杰等①) 1.前寒武纪变质基底;2.早二叠世基性侵入岩;3.早二叠世花岗闪长岩;4.早二叠世二长花岗岩;5.三叠纪二长花岗岩;6.同位素样品采样位置及U-Pb年龄;7.雅不赖山南缘断裂
Fig.2 Geological sketch map of Chaganobo area (after Zhang Weijie et al.①)

图3 查干敖包二长花岗岩野外特征及显微照片 (a)岩貌及定向包体;(b)岩貌及无定向包体;(c)(d)正交偏光显微照片;kfs.钾长石;Qtz.石英;Bt.黑云母;Pl.斜长石
Fig.3 Monzonitic granite field characteristics and microscopic photos in Chaganobo
| 分析点号 | wB/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 208Pb/ 232Th | 1σ | 232Th/ 238U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||
| WD9016-1 | 27 | 614 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.325 9 | 0.002 4 | 0.053 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.290 6 | 0.000 6 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-2 | 20 | 423 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.323 8 | 0.003 2 | 0.053 3 | 0.000 6 | 0.013 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.565 2 | 0.002 4 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-3 | 69 | 1 481 | 0.039 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.508 6 | 0.004 2 | 0.093 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.021 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.504 0 | 0.007 3 | 249 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-4 | 32 | 797 | 0.037 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.348 9 | 0.004 4 | 0.066 7 | 0.000 6 | 0.015 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.347 4 | 0.001 5 | 240 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-5 | 36 | 804 | 0.044 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.329 3 | 0.002 9 | 0.053 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.016 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.306 6 | 0.000 2 | 283 | 3 | ||
| WD9016-6 | 23 | 491 | 0.044 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.342 1 | 0.002 4 | 0.055 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.014 5 | 0.000 0 | 0.519 5 | 0.001 2 | 281 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-7 | 14 | 298 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.346 4 | 0.006 4 | 0.057 0 | 0.001 0 | 0.015 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.515 8 | 0.002 7 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-8 | 22 | 469 | 0.044 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.324 7 | 0.002 9 | 0.052 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.016 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.367 7 | 0.000 5 | 281 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-9 | 37 | 792 | 0.043 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.336 8 | 0.002 9 | 0.055 8 | 0.000 5 | 0.017 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.390 6 | 0.003 7 | 276 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-10 | 23 | 508 | 0.045 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.333 6 | 0.004 0 | 0.053 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.317 4 | 0.002 1 | 283 | 3 | ||
| WD9016-11 | 32 | 782 | 0.038 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.302 9 | 0.003 5 | 0.057 1 | 0.000 7 | 0.016 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.422 8 | 0.000 7 | 243 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-12 | 41 | 855 | 0.043 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.341 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.056 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.021 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.393 0 | 0.001 4 | 277 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-13 | 36 | 801 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.319 3 | 0.002 0 | 0.052 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.016 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.331 4 | 0.005 9 | 279 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-14 | 34 | 762 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.316 1 | 0.001 9 | 0.052 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.015 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.319 1 | 0.001 1 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-15 | 42 | 906 | 0.043 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.324 7 | 0.002 2 | 0.054 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.015 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.551 2 | 0.001 9 | 273 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-16 | 43 | 926 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.353 3 | 0.002 6 | 0.058 0 | 0.000 8 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.316 9 | 0.000 8 | 279 | 3 | ||
| WD9016-17 | 21 | 474 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.316 2 | 0.002 4 | 0.052 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.351 4 | 0.001 2 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-18 | 25 | 573 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.345 7 | 0.002 4 | 0.056 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.014 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.334 4 | 0.002 6 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-19 | 29 | 716 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.317 7 | 0.002 1 | 0.052 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.012 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.062 8 | 0.000 3 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-20 | 19 | 433 | 0.043 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.333 3 | 0.004 7 | 0.055 4 | 0.000 8 | 0.014 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.279 6 | 0.000 4 | 275 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-21 | 17 | 381 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.321 8 | 0.002 8 | 0.053 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.012 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.448 0 | 0.000 9 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-22 | 39 | 890 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.329 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.054 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.290 7 | 0.001 4 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-23 | 29 | 656 | 0.043 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.326 1 | 0.002 4 | 0.053 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.317 1 | 0.000 9 | 277 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-24 | 59 | 1 315 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.328 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.053 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.016 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.305 5 | 0.002 9 | 279 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-25 | 39 | 881 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.324 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.053 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.013 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.331 9 | 0.001 3 | 279 | 2 | ||
表1 二长花岗岩样品(WD9016)的LA-ICP-MS锆石 U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of monzogranite sample (WD9016)
| 分析点号 | wB/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 208Pb/ 232Th | 1σ | 232Th/ 238U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||
| WD9016-1 | 27 | 614 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.325 9 | 0.002 4 | 0.053 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.290 6 | 0.000 6 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-2 | 20 | 423 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 4 | 0.323 8 | 0.003 2 | 0.053 3 | 0.000 6 | 0.013 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.565 2 | 0.002 4 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-3 | 69 | 1 481 | 0.039 4 | 0.000 3 | 0.508 6 | 0.004 2 | 0.093 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.021 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.504 0 | 0.007 3 | 249 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-4 | 32 | 797 | 0.037 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.348 9 | 0.004 4 | 0.066 7 | 0.000 6 | 0.015 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.347 4 | 0.001 5 | 240 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-5 | 36 | 804 | 0.044 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.329 3 | 0.002 9 | 0.053 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.016 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.306 6 | 0.000 2 | 283 | 3 | ||
| WD9016-6 | 23 | 491 | 0.044 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.342 1 | 0.002 4 | 0.055 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.014 5 | 0.000 0 | 0.519 5 | 0.001 2 | 281 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-7 | 14 | 298 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.346 4 | 0.006 4 | 0.057 0 | 0.001 0 | 0.015 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.515 8 | 0.002 7 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-8 | 22 | 469 | 0.044 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.324 7 | 0.002 9 | 0.052 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.016 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.367 7 | 0.000 5 | 281 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-9 | 37 | 792 | 0.043 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.336 8 | 0.002 9 | 0.055 8 | 0.000 5 | 0.017 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.390 6 | 0.003 7 | 276 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-10 | 23 | 508 | 0.045 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.333 6 | 0.004 0 | 0.053 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.017 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.317 4 | 0.002 1 | 283 | 3 | ||
| WD9016-11 | 32 | 782 | 0.038 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.302 9 | 0.003 5 | 0.057 1 | 0.000 7 | 0.016 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.422 8 | 0.000 7 | 243 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-12 | 41 | 855 | 0.043 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.341 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.056 4 | 0.000 6 | 0.021 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.393 0 | 0.001 4 | 277 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-13 | 36 | 801 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.319 3 | 0.002 0 | 0.052 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.016 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.331 4 | 0.005 9 | 279 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-14 | 34 | 762 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.316 1 | 0.001 9 | 0.052 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.015 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.319 1 | 0.001 1 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-15 | 42 | 906 | 0.043 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.324 7 | 0.002 2 | 0.054 5 | 0.000 3 | 0.015 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.551 2 | 0.001 9 | 273 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-16 | 43 | 926 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.353 3 | 0.002 6 | 0.058 0 | 0.000 8 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.316 9 | 0.000 8 | 279 | 3 | ||
| WD9016-17 | 21 | 474 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.316 2 | 0.002 4 | 0.052 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.351 4 | 0.001 2 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-18 | 25 | 573 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.345 7 | 0.002 4 | 0.056 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.014 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.334 4 | 0.002 6 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-19 | 29 | 716 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.317 7 | 0.002 1 | 0.052 3 | 0.000 2 | 0.012 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.062 8 | 0.000 3 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-20 | 19 | 433 | 0.043 6 | 0.000 3 | 0.333 3 | 0.004 7 | 0.055 4 | 0.000 8 | 0.014 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.279 6 | 0.000 4 | 275 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-21 | 17 | 381 | 0.044 1 | 0.000 3 | 0.321 8 | 0.002 8 | 0.053 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.012 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.448 0 | 0.000 9 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-22 | 39 | 890 | 0.044 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.329 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.054 3 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 3 | 0.000 1 | 0.290 7 | 0.001 4 | 278 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-23 | 29 | 656 | 0.043 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.326 1 | 0.002 4 | 0.053 9 | 0.000 3 | 0.013 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.317 1 | 0.000 9 | 277 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-24 | 59 | 1 315 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.328 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.053 8 | 0.000 4 | 0.016 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.305 5 | 0.002 9 | 279 | 2 | ||
| WD9016-25 | 39 | 881 | 0.044 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.324 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.053 2 | 0.000 2 | 0.013 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.331 9 | 0.001 3 | 279 | 2 | ||
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | 烧失量 | 总量 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D3376-1 | 74.76 | 0.04 | 13.37 | 0.64 | 0.55 | 0.024 | 0.09 | 1.27 | 3.69 | 4.97 | 0.025 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.66 | 100.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3382-2 | 75.26 | 0.04 | 12.83 | 0.79 | 0.53 | 0.034 | 0.18 | 1.23 | 4.09 | 4.42 | 0.047 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 100.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9016-1 | 72.88 | 0.17 | 13.98 | 0.52 | 1.53 | 0.039 | 0.50 | 1.94 | 3.38 | 4.30 | 0.064 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 99.83 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9017-1 | 73.50 | 0.07 | 13.04 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.032 | 0.22 | 2.00 | 3.53 | 4.97 | 0.054 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 1.27 | 100.27 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-5-1 | 74.90 | 0.06 | 12.38 | 0.29 | 0.79 | 0.040 | 0.13 | 1.86 | 3.54 | 4.53 | 0.020 | 0.54 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 99.94 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-7-1 | 74.60 | 0.10 | 12.72 | 0.47 | 0.93 | 0.042 | 0.23 | 1.75 | 3.55 | 4.32 | 0.032 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 1.15 | 99.90 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-11-1 | 75.44 | 0.08 | 12.62 | 0.32 | 0.88 | 0.038 | 0.14 | 1.27 | 3.39 | 4.79 | 0.044 | 0.49 | 0.11 | 0.88 | 99.89 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-13-1 | 75.02 | 0.09 | 12.85 | 0.38 | 0.91 | 0.039 | 0.20 | 1.40 | 3.64 | 4.42 | 0.038 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.92 | 99.90 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-15-1 | 74.05 | 0.14 | 13.37 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 0.058 | 0.22 | 1.41 | 4.23 | 3.67 | 0.035 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 99.83 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | A/NK | A/CNK | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||
| D3376-1 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 37.0 | 73.3 | 9.02 | 32.2 | 6.15 | 0.57 | 5.44 | 0.92 | 5.28 | 0.99 | 2.88 | 0.45 | 2.87 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||
| D3382-2 | 1.12 | 0.93 | 30.7 | 58.7 | 7.39 | 25.8 | 5.14 | 0.54 | 4.58 | 0.83 | 5.08 | 1.05 | 3.19 | 0.56 | 3.59 | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||
| WD9016-1 | 1.37 | 1.02 | 31.8 | 55.0 | 6.36 | 20.4 | 2.90 | 0.79 | 2.55 | 0.36 | 1.90 | 0.37 | 1.14 | 0.19 | 1.26 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||
| WD9017-1 | 1.16 | 0.88 | 36.9 | 71.9 | 9.39 | 34.5 | 7.88 | 0.43 | 6.80 | 1.25 | 7.62 | 1.50 | 4.53 | 0.78 | 4.98 | 0.79 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-5-1 | 1.15 | 0.88 | 16.7 | 30.0 | 3.70 | 13.0 | 2.73 | 0.21 | 2.37 | 0.46 | 2.97 | 0.60 | 1.82 | 0.34 | 2.33 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-7-1 | 1.21 | 0.93 | 20.9 | 37.5 | 4.46 | 15.6 | 3.07 | 0.33 | 2.74 | 0.54 | 3.53 | 0.76 | 2.20 | 0.44 | 3.02 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-11-1 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 19.4 | 35.7 | 4.32 | 14.9 | 2.99 | 0.32 | 2.72 | 0.58 | 4.11 | 0.88 | 2.76 | 0.58 | 4.28 | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-13-1 | 1.19 | 0.96 | 23.3 | 43.8 | 5.12 | 17.7 | 3.37 | 0.36 | 3.03 | 0.56 | 3.51 | 0.71 | 2.08 | 0.39 | 2.60 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-15-1 | 1.22 | 0.99 | 32.0 | 63.5 | 7.63 | 27.5 | 4.69 | 0.80 | 3.95 | 0.69 | 4.15 | 0.84 | 2.49 | 0.44 | 2.95 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Ba | Rb | Th | Nb | Ta | Sr | Nd | Zr | Hf | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | δEu | ||||||||||||||||
| D3376-1 | 1 124.0 | 139.0 | 11.50 | 8.26 | 0.565 | 95.7 | 32.2 | 118.0 | 1.73 | 177.46 | 158.20 | 19.26 | 8.21 | 9.25 | 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3382-2 | 787.3 | 138.0 | 19.30 | 9.97 | 0.471 | 76.6 | 25.8 | 216.0 | 2.37 | 147.65 | 128.23 | 19.42 | 6.60 | 6.13 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9016-1 | 908.4 | 108.0 | 9.03 | 4.74 | 0.497 | 225.2 | 20.4 | 132.0 | 1.29 | 125.21 | 117.21 | 8.00 | 14.66 | 18.05 | 0.87 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9017-1 | 195.9 | 234.0 | 22.30 | 14.60 | 1.163 | 48.2 | 34.5 | 331.0 | 3.61 | 189.26 | 161.02 | 28.24 | 5.70 | 5.32 | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-5-1 | 287.9 | 120.0 | 14.40 | 6.56 | 0.637 | 47.2 | 13.0 | 90.2 | 3.74 | 77.57 | 66.29 | 11.27 | 5.88 | 5.15 | 0.24 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-7-1 | 591.8 | 131.0 | 15.40 | 7.05 | 0.927 | 84.6 | 15.6 | 107.1 | 4.26 | 95.61 | 81.92 | 13.69 | 5.98 | 4.97 | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-11-1 | 607.5 | 132.0 | 15.70 | 7.09 | 1.490 | 70.8 | 14.9 | 98.0 | 4.51 | 94.21 | 77.69 | 16.51 | 4.70 | 3.26 | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-13-1 | 604.4 | 131.0 | 12.50 | 7.14 | 0.703 | 75.4 | 17.7 | 103.0 | 4.45 | 106.93 | 93.65 | 13.28 | 7.05 | 6.45 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-15-1 | 1 036.0 | 83.6 | 9.03 | 8.10 | 0.606 | 126.0 | 27.5 | 160.0 | 7.64 | 152.02 | 136.06 | 15.96 | 8.53 | 7.78 | 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||
表 2 二长花岗岩样品主量、微量及稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth elements compositions of monzogranite samples
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | 烧失量 | 总量 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D3376-1 | 74.76 | 0.04 | 13.37 | 0.64 | 0.55 | 0.024 | 0.09 | 1.27 | 3.69 | 4.97 | 0.025 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.66 | 100.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3382-2 | 75.26 | 0.04 | 12.83 | 0.79 | 0.53 | 0.034 | 0.18 | 1.23 | 4.09 | 4.42 | 0.047 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 100.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9016-1 | 72.88 | 0.17 | 13.98 | 0.52 | 1.53 | 0.039 | 0.50 | 1.94 | 3.38 | 4.30 | 0.064 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 99.83 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9017-1 | 73.50 | 0.07 | 13.04 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.032 | 0.22 | 2.00 | 3.53 | 4.97 | 0.054 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 1.27 | 100.27 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-5-1 | 74.90 | 0.06 | 12.38 | 0.29 | 0.79 | 0.040 | 0.13 | 1.86 | 3.54 | 4.53 | 0.020 | 0.54 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 99.94 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-7-1 | 74.60 | 0.10 | 12.72 | 0.47 | 0.93 | 0.042 | 0.23 | 1.75 | 3.55 | 4.32 | 0.032 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 1.15 | 99.90 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-11-1 | 75.44 | 0.08 | 12.62 | 0.32 | 0.88 | 0.038 | 0.14 | 1.27 | 3.39 | 4.79 | 0.044 | 0.49 | 0.11 | 0.88 | 99.89 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-13-1 | 75.02 | 0.09 | 12.85 | 0.38 | 0.91 | 0.039 | 0.20 | 1.40 | 3.64 | 4.42 | 0.038 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.92 | 99.90 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-15-1 | 74.05 | 0.14 | 13.37 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 0.058 | 0.22 | 1.41 | 4.23 | 3.67 | 0.035 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 99.83 | ||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | A/NK | A/CNK | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||
| D3376-1 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 37.0 | 73.3 | 9.02 | 32.2 | 6.15 | 0.57 | 5.44 | 0.92 | 5.28 | 0.99 | 2.88 | 0.45 | 2.87 | 0.43 | |||||||||||||||
| D3382-2 | 1.12 | 0.93 | 30.7 | 58.7 | 7.39 | 25.8 | 5.14 | 0.54 | 4.58 | 0.83 | 5.08 | 1.05 | 3.19 | 0.56 | 3.59 | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||
| WD9016-1 | 1.37 | 1.02 | 31.8 | 55.0 | 6.36 | 20.4 | 2.90 | 0.79 | 2.55 | 0.36 | 1.90 | 0.37 | 1.14 | 0.19 | 1.26 | 0.22 | |||||||||||||||
| WD9017-1 | 1.16 | 0.88 | 36.9 | 71.9 | 9.39 | 34.5 | 7.88 | 0.43 | 6.80 | 1.25 | 7.62 | 1.50 | 4.53 | 0.78 | 4.98 | 0.79 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-5-1 | 1.15 | 0.88 | 16.7 | 30.0 | 3.70 | 13.0 | 2.73 | 0.21 | 2.37 | 0.46 | 2.97 | 0.60 | 1.82 | 0.34 | 2.33 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-7-1 | 1.21 | 0.93 | 20.9 | 37.5 | 4.46 | 15.6 | 3.07 | 0.33 | 2.74 | 0.54 | 3.53 | 0.76 | 2.20 | 0.44 | 3.02 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-11-1 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 19.4 | 35.7 | 4.32 | 14.9 | 2.99 | 0.32 | 2.72 | 0.58 | 4.11 | 0.88 | 2.76 | 0.58 | 4.28 | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-13-1 | 1.19 | 0.96 | 23.3 | 43.8 | 5.12 | 17.7 | 3.37 | 0.36 | 3.03 | 0.56 | 3.51 | 0.71 | 2.08 | 0.39 | 2.60 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||
| PM39-15-1 | 1.22 | 0.99 | 32.0 | 63.5 | 7.63 | 27.5 | 4.69 | 0.80 | 3.95 | 0.69 | 4.15 | 0.84 | 2.49 | 0.44 | 2.95 | 0.44 | |||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | Ba | Rb | Th | Nb | Ta | Sr | Nd | Zr | Hf | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | δEu | ||||||||||||||||
| D3376-1 | 1 124.0 | 139.0 | 11.50 | 8.26 | 0.565 | 95.7 | 32.2 | 118.0 | 1.73 | 177.46 | 158.20 | 19.26 | 8.21 | 9.25 | 0.29 | ||||||||||||||||
| D3382-2 | 787.3 | 138.0 | 19.30 | 9.97 | 0.471 | 76.6 | 25.8 | 216.0 | 2.37 | 147.65 | 128.23 | 19.42 | 6.60 | 6.13 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9016-1 | 908.4 | 108.0 | 9.03 | 4.74 | 0.497 | 225.2 | 20.4 | 132.0 | 1.29 | 125.21 | 117.21 | 8.00 | 14.66 | 18.05 | 0.87 | ||||||||||||||||
| WD9017-1 | 195.9 | 234.0 | 22.30 | 14.60 | 1.163 | 48.2 | 34.5 | 331.0 | 3.61 | 189.26 | 161.02 | 28.24 | 5.70 | 5.32 | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-5-1 | 287.9 | 120.0 | 14.40 | 6.56 | 0.637 | 47.2 | 13.0 | 90.2 | 3.74 | 77.57 | 66.29 | 11.27 | 5.88 | 5.15 | 0.24 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-7-1 | 591.8 | 131.0 | 15.40 | 7.05 | 0.927 | 84.6 | 15.6 | 107.1 | 4.26 | 95.61 | 81.92 | 13.69 | 5.98 | 4.97 | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-11-1 | 607.5 | 132.0 | 15.70 | 7.09 | 1.490 | 70.8 | 14.9 | 98.0 | 4.51 | 94.21 | 77.69 | 16.51 | 4.70 | 3.26 | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-13-1 | 604.4 | 131.0 | 12.50 | 7.14 | 0.703 | 75.4 | 17.7 | 103.0 | 4.45 | 106.93 | 93.65 | 13.28 | 7.05 | 6.45 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| PM39-15-1 | 1 036.0 | 83.6 | 9.03 | 8.10 | 0.606 | 126.0 | 27.5 | 160.0 | 7.64 | 152.02 | 136.06 | 15.96 | 8.53 | 7.78 | 0.56 | ||||||||||||||||
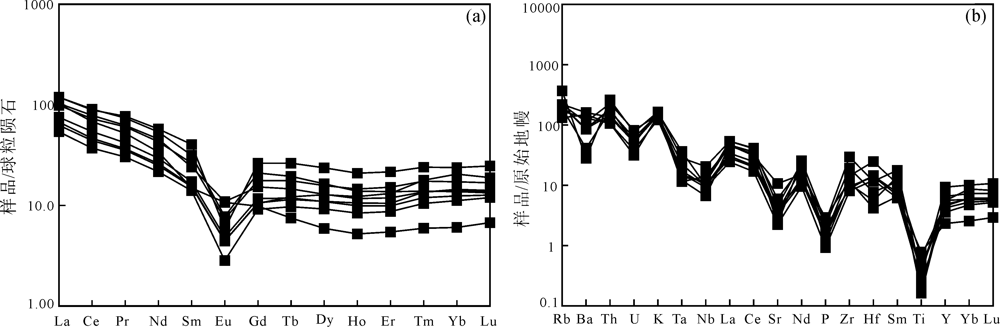
图6 查干敖包二长花岗岩样品稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergrams (b) of monzogranite samples in Chaganaobao
| 地层或岩性 | 测定方法 | 年龄1/Ma | 年龄2/Ma |
|---|---|---|---|
| 巴彦乌拉山岩组 | 锆石离子探针 | 446 | 281 |
| 祖宗毛道组 | 锆石离子探针 | 482 | 266 |
| 黑云斜长角闪岩 | 角闪石39Ar-40Ar | 升温坪288 Ma,等时线年龄288 Ma | |
| 斜长角闪岩中 | 角闪石39Ar-40Ar | 升温坪277 Ma,等时线年龄288 Ma |
表3 前寒武纪变质基底古生代构造热事件
Table 3 Paleozoic tectonic thermal events in the Precambrian metamorphic basement
| 地层或岩性 | 测定方法 | 年龄1/Ma | 年龄2/Ma |
|---|---|---|---|
| 巴彦乌拉山岩组 | 锆石离子探针 | 446 | 281 |
| 祖宗毛道组 | 锆石离子探针 | 482 | 266 |
| 黑云斜长角闪岩 | 角闪石39Ar-40Ar | 升温坪288 Ma,等时线年龄288 Ma | |
| 斜长角闪岩中 | 角闪石39Ar-40Ar | 升温坪277 Ma,等时线年龄288 Ma |
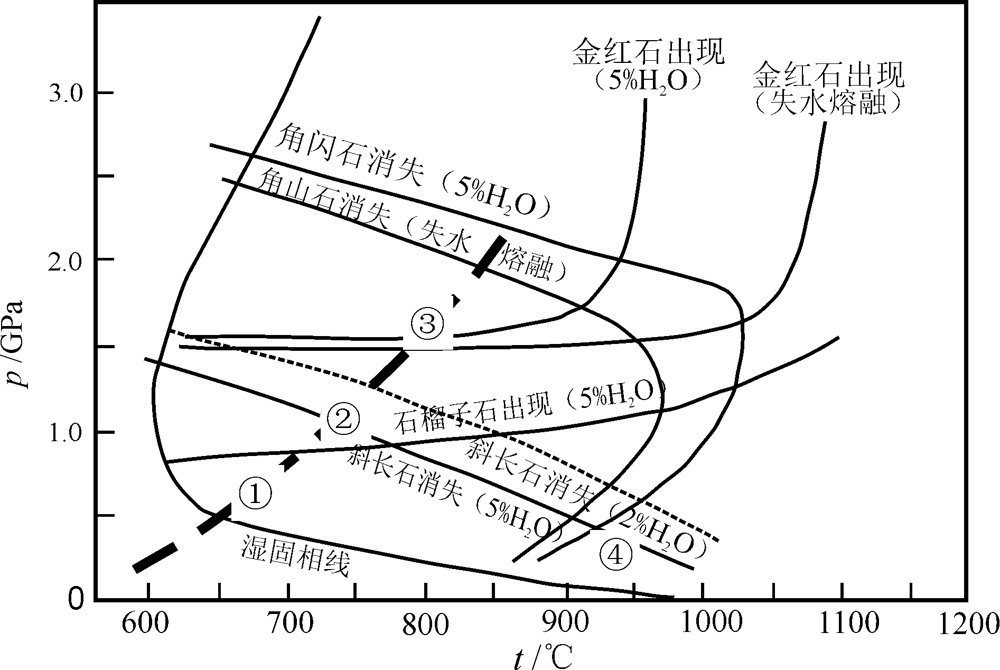
图7 玄武岩部分熔融实验[16,19-20] ①石榴子石稳定区,熔出的花岗岩具有高Sr低Yb的特点;②石榴子石+斜长石稳定区,为低Sr低Yb型花岗岩分布区;③斜长石稳定区,相当于低Sr高Yb型;④斜长石稳定区,但处于非常低压和高温条件下,形成的花岗岩具有非常低Sr高Yb的特点
Fig.7 Partial melting experiments of basalt[16,19-20]

图8 二长花岗岩(Y+Nb)-Rb构造环境判别图解(底图据Pearce 等[25]) syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;WPG.板内花岗岩;post-COLG.后碰撞花岗岩;VAG.火山弧花岗岩;ORG.洋脊花岗岩
Fig. 8 (Y+Nb)-Rb diagram for discriminating the tectonic setting of monzogranite (after Pearce et al.[25])
| [1] | 吴泰然, 何国琦. 内蒙古阿拉善地块北缘的构造单元划分及各单元的基本特征[J]. 地质学报, 1993,67(2):97-108. |
| [2] | 王廷印, 王金荣, 王士政. 阿拉善北部恩格尔乌苏蛇绿混杂岩带的发现及其构造意义[J]. 兰州大学学报, 1992,28(2):194-196. |
| [3] | 王廷印, 王金荣, 王士政, 等. 阿拉善北部查干础鲁—霍尔森蛇绿混杂岩带地质地球化学特征[J]. 甘肃地质学报, 1993,2(1):46-53. |
| [4] | 吴泰然, 何国琦. 阿拉善地块北缘的蛇绿混杂岩带及其大地构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 1992,6(3):286-296. |
| [5] | 王廷印, 王士政, 王金荣. 阿拉善地区古生代陆壳的形成和演化[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 1994: 107-112. |
| [6] | 张云, 孙立新, 张天福, 等. 内蒙古狼山地区乌花辉长岩的年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成:对地幔源区特征和岩石成因的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020,34(3):450-465. |
| [7] | 王廷印, 高军平, 王金荣, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善北部地区碰撞期和后造山期岩浆作用[J]. 地质学报, 1998,72(2):126-137. |
| [8] | 耿元生, 周喜文. 阿拉善地区新元古代岩浆事件及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010,29(6):779-795. |
| [9] |
LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,257(1/2):34-43.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 30-32. |
| [11] | 邱家骧. 应用岩浆岩岩石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1991: 160-161. |
| [12] | 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质岩系形成时代的初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 2007,34(2):251-261. |
| [13] | 叶珂, 张磊, 王涛, 等. 阿拉善雅布赖山二叠纪中酸性岩浆岩年代学、地球化学、锆石Hf同位素特征及构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016,35(6):901-928. |
| [14] | 史兴俊, 童英, 王涛, 等. 内蒙古西部阿拉善地区哈里努登花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012,31(5):662-670. |
| [15] | 张永清, 韩建刚, 胡凤翔. 内蒙古阿拉善盟巴音诺日公地区中三叠世花岗岩特征及构造意义[J]. 内蒙古地质, 2002(4):15-20. |
| [16] | 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(9):2249-2269. |
| [17] | 徐克勤, 胡受奚, 孙明志, 等. 论花岗岩的成因系列——以华南中生代花岗岩为例[J]. 地质学报, 1983,57(2):107-118. |
| [18] |
GREEN T H. Island arc and continent-building magmatism-A review of petrogenic models based on experimental petrology and geochemistry[J]. Tectonophysics, 1980,63(1/2/3/4):367-385.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩按照压力的分类[J]. 地质通报, 2006,25(11):1274-1278. |
| [20] | 张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 等. 造山前、造山和造山后花岗岩的识别[J]. 地质通报, 2008,27(1):1-18. |
| [21] | 张磊, 史兴俊, 张建军, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善北部陶豪托西圈辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2013,32(10):1536-1547. |
| [22] | 肖进, 孙萍, 徐琳. 阿拉善北部诺尔公地区早二叠世辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 西部资源, 2016,47(4):55-60. |
| [23] | 张建军, 王涛, 张招崇, 等. 华北地块北缘西段巴音诺尔公—狼山地区牙马图岩体的岩浆混合成因——岩相学和元素地球化学证据[J]. 地质论评, 2012,58(1):53-66. |
| [24] | 李杰. 内蒙古阿拉善地区雅布赖—巴音诺尔公晚古生代侵入岩特征及其大地构造意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012: 1-54. |
| [25] |
KAY R W, MAHLBURG-KAY S. Creation and destruction of the lower continental crust[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1991,80(2):259-278.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
KAY R W, MAHLBURG-KAY S, Delamination and delamination magmatism[J]. Tectonophysics, 1993(1/2/3/4),219:177-189.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 张文, 吴泰然, 贺元凯, 等. 甘肃北山西涧泉子富碱高钾花岗岩体的锆石LA-ICP-MS定年及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010,29(6):719-731. |
| [28] | 童英, 王涛, 洪大卫, 等. 北疆及邻区石炭—二叠纪花岗岩时空分布特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010,29(6):619-641. |
| [29] | 王涛, 童英, 李舢, 等. 阿尔泰造山带花岗岩时空演变、构造环境及地壳生长意义——以中国阿尔泰为例[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010,29(6):595-618. |
| [30] | 程新彬, 王玮, 魏波, 等. 内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗查干敖包花岗岩体时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(3):508-520. |
| [31] |
XIONG X L, ADAM J, GREEN T H. Rutile stability and rutile/ melt HF-SF partitioning during partial melting of hydrous basalt: implications for TTG genesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005,218(3/4):339-359.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [3] | 苏惠, 曾认宇, 甘德斌, 严杰. 阿拉善北大山地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1580-1596. |
| [4] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [5] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623. |
| [6] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 滕超, 张学斌, 杨欣杰, 来林, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古西乌旗早泥盆世I型石英闪长岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1624-1633. |
| [7] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [8] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [9] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| [10] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [11] | 刘金宝, 朱洛婷, 李龙雪, 侯青叶. 内蒙古艾力格庙地区卫境岩体的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 419-432. |
| [12] | 杨帆, 陈岳龙, 于洋. 鲁西地区新太古代晚期正长-二长花岗岩成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1155-1172. |
| [13] | 李柱, 张德会, 张荣臻, 沈存利, 焦世豪, 李林, 朱鹏龙. 内蒙古那仁乌拉早白垩世高分异花岗岩年代学及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 848-861. |
| [14] | 张宏辉, 谢财富, 陈凯, 袁永盛, 余杨忠, 张沥元, 陈贵仁, 李鸿, 詹华思, 石海涛, 蔡泉宇, 于一帆. 粤西北大桂山岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、岩石成因及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 862-875. |
| [15] | 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 王建田, 王利鹏, 赵鹏飞. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 876-897. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||