



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (02): 477-491.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.056
陈邦学1( ), 徐胜利1, 周能武2(
), 徐胜利1, 周能武2( ), 白权金2, 李超1, 张洪深1
), 白权金2, 李超1, 张洪深1
收稿日期:2019-06-21
修回日期:2020-05-25
出版日期:2021-04-25
发布日期:2021-05-25
通讯作者:
周能武
作者简介:周能武,男,教授级高级工程师,1972年出生,地质矿产勘查专业,从事固体矿产勘查工作。Email: 785296415@qq.com。基金资助:
CHEN Bangxue1( ), XU Shengli1, ZHOU Nengwu2(
), XU Shengli1, ZHOU Nengwu2( ), BAI Quanjin2, LI Chao1, ZHANG Hongshen1
), BAI Quanjin2, LI Chao1, ZHANG Hongshen1
Received:2019-06-21
Revised:2020-05-25
Online:2021-04-25
Published:2021-05-25
Contact:
ZHOU Nengwu
摘要:
采用LA-ICP-MS法分析了塔里木北缘库鲁克塔格一带二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄,获得该二长花岗岩岩体的年龄为(832.3±3.3)Ma(MSWD=2.8,n=24)。岩石地球化学特征显示,二长花岗岩属于准铝质高钾钙碱性系列,为I型花岗岩。微量元素富集大离子亲石元素(LILE)Ba、K、Sr、U等,亏损高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、Ta、Ti、P等;稀土元素总体含量较低(29.88×10-6~63.57×10-6),具有弱Eu正异常(δEu=0.87~1.39),整体配分模式与下地壳一致。结合区域地质背景对岩浆岩地球化学特征进行综合分析,认为二长花岗岩形成于岛弧环境。区域构造演化特征指示832 Ma该区洋壳已经开始俯冲,使得这一地区的地壳加厚,同时地幔柱的上涌加热作用导致古老地壳物质发生部分熔融而形成该期花岗岩。
中图分类号:
陈邦学, 徐胜利, 周能武, 白权金, 李超, 张洪深. 塔里木北缘库鲁克塔格地区新元古代花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 477-491.
CHEN Bangxue, XU Shengli, ZHOU Nengwu, BAI Quanjin, LI Chao, ZHANG Hongshen. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating, Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Neoproterozoic Granite in the Quruqtagh Area,Northern Margin of Tarim Craton,NW China[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 477-491.

图1 欧亚大陆构造简图(a)和塔里木克拉通及周缘地质构造简图(b)(据文献[1])
Fig.1 Simplified tectonic map of the Eurasia (a) and geologic map of the Tarim Craton (b)(after reference [1])
| 点位 | 含量/10-6 | 232Th/ 238U | 1σ | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 21 | 160 | 0.150 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.067 | 0.000 6 | 1.255 5 | 0.011 7 | 0.135 9 | 0.000 7 | 839 | 19 | 826 | 8 | 821 | 4 | |||||||||
| 2 | 63 | 485 | 0.090 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 8 | 0.000 5 | 1.257 1 | 0.010 1 | 0.136 5 | 0.000 8 | 831 | 15 | 827 | 7 | 825 | 5 | |||||||||
| 3 | 41 | 320 | 0.056 2 | 0 | 0.066 1 | 0.000 5 | 1.251 1 | 0.008 9 | 0.137 2 | 0.000 7 | 811 | 15 | 824 | 6 | 829 | 4 | |||||||||
| 4 | 44 | 341 | 0.101 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 5 | 0.000 5 | 1.248 0 | 0.009 2 | 0.136 1 | 0.000 7 | 822 | 15 | 823 | 6 | 823 | 4 | |||||||||
| 5 | 51 | 394 | 0.066 7 | 0 | 0.065 8 | 0.000 5 | 1.248 9 | 0.008 9 | 0.137 7 | 0.000 8 | 800 | 14 | 823 | 6 | 831 | 5 | |||||||||
| 6 | 32 | 248 | 0.067 9 | 0 | 0.066 8 | 0.000 5 | 1.265 8 | 0.009 6 | 0.137 4 | 0.000 7 | 832 | 16 | 831 | 6 | 830 | 4 | |||||||||
| 7 | 18 | 135 | 0.133 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.065 8 | 0.000 7 | 1.256 4 | 0.013 3 | 0.138 4 | 0.000 7 | 801 | 21 | 826 | 9 | 836 | 5 | |||||||||
| 8 | 34 | 258 | 0.055 6 | 0 | 0.065 5 | 0.000 5 | 1.262 6 | 0.009 2 | 0.139 8 | 0.000 7 | 791 | 15 | 829 | 6 | 843 | 4 | |||||||||
| 9 | 29 | 223 | 0.058 6 | 0 | 0.065 9 | 0.000 6 | 1.259 1 | 0.010 9 | 0.138 6 | 0.000 7 | 802 | 18 | 828 | 7 | 837 | 4 | |||||||||
| 10 | 36 | 279 | 0.052 1 | 0 | 0.066 0 | 0.000 5 | 1.263 1 | 0.011 3 | 0.138 9 | 0.000 8 | 805 | 17 | 829 | 7 | 838 | 5 | |||||||||
| 11 | 21 | 154 | 0.155 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.065 8 | 0.000 7 | 1.255 1 | 0.013 2 | 0.138 3 | 0.000 7 | 801 | 22 | 826 | 9 | 835 | 4 | |||||||||
| 12 | 25 | 181 | 0.255 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.065 9 | 0.000 5 | 1.253 9 | 0.009 5 | 0.138 0 | 0.000 7 | 803 | 16 | 825 | 6 | 834 | 4 | |||||||||
| 13 | 27 | 205 | 0.094 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 3 | 0.000 6 | 1.255 2 | 0.010 7 | 0.137 3 | 0.000 7 | 815 | 18 | 826 | 7 | 830 | 4 | |||||||||
| 14 | 39 | 281 | 0.055 0 | 0 | 0.072 2 | 0.000 5 | 1.433 7 | 0.010 3 | 0.144 | 0.000 7 | 992 | 15 | 903 | 7 | 867 | 4 | |||||||||
| 15 | 32 | 248 | 0.060 2 | 0 | 0.066 2 | 0.001 0 | 1.258 8 | 0.019 7 | 0.138 0 | 0.000 7 | 812 | 31 | 827 | 13 | 833 | 5 | |||||||||
| 16 | 29 | 224 | 0.078 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 6 | 0.000 6 | 1.263 3 | 0.011 4 | 0.137 6 | 0.000 7 | 826 | 19 | 829 | 7 | 831 | 4 | |||||||||
| 17 | 30 | 222 | 0.112 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 2 | 0.000 5 | 1.264 9 | 0.010 7 | 0.138 5 | 0.000 7 | 814 | 17 | 830 | 7 | 836 | 4 | |||||||||
| 18 | 24 | 186 | 0.066 7 | 0 | 0.066 9 | 0.000 6 | 1.250 4 | 0.012 0 | 0.135 5 | 0.000 7 | 835 | 19 | 824 | 8 | 819 | 4 | |||||||||
| 19 | 25 | 189 | 0.066 9 | 0 | 0.065 5 | 0.000 8 | 1.266 7 | 0.016 0 | 0.140 2 | 0.000 7 | 791 | 26 | 831 | 10 | 846 | 4 | |||||||||
| 20 | 20 | 148 | 0.196 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 4 | 0.000 6 | 1.246 2 | 0.011 2 | 0.136 0 | 0.000 7 | 820 | 18 | 822 | 7 | 822 | 4 | |||||||||
| 21 | 30 | 230 | 0.058 5 | 0 | 0.066 3 | 0.000 5 | 1.276 8 | 0.009 4 | 0.139 7 | 0.000 7 | 815 | 15 | 835 | 6 | 843 | 4 | |||||||||
| 22 | 40 | 135 | 0.279 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.145 8 | 0.001 1 | 5.146 2 | 0.039 0 | 0.256 0 | 0.001 3 | 2297 | 13 | 1844 | 14 | 1469 | 8 | |||||||||
| 23 | 20 | 152 | 0.107 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 4 | 0.000 7 | 1.260 0 | 0.012 8 | 0.137 6 | 0.000 8 | 819 | 21 | 828 | 8 | 831 | 5 | |||||||||
| 24 | 21 | 163 | 0.077 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 2 | 0.000 6 | 1.268 6 | 0.011 5 | 0.138 9 | 0.000 7 | 813 | 19 | 832 | 8 | 839 | 4 | |||||||||
表1 锆石U-Pb年龄分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating results of samples
| 点位 | 含量/10-6 | 232Th/ 238U | 1σ | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 21 | 160 | 0.150 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.067 | 0.000 6 | 1.255 5 | 0.011 7 | 0.135 9 | 0.000 7 | 839 | 19 | 826 | 8 | 821 | 4 | |||||||||
| 2 | 63 | 485 | 0.090 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 8 | 0.000 5 | 1.257 1 | 0.010 1 | 0.136 5 | 0.000 8 | 831 | 15 | 827 | 7 | 825 | 5 | |||||||||
| 3 | 41 | 320 | 0.056 2 | 0 | 0.066 1 | 0.000 5 | 1.251 1 | 0.008 9 | 0.137 2 | 0.000 7 | 811 | 15 | 824 | 6 | 829 | 4 | |||||||||
| 4 | 44 | 341 | 0.101 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 5 | 0.000 5 | 1.248 0 | 0.009 2 | 0.136 1 | 0.000 7 | 822 | 15 | 823 | 6 | 823 | 4 | |||||||||
| 5 | 51 | 394 | 0.066 7 | 0 | 0.065 8 | 0.000 5 | 1.248 9 | 0.008 9 | 0.137 7 | 0.000 8 | 800 | 14 | 823 | 6 | 831 | 5 | |||||||||
| 6 | 32 | 248 | 0.067 9 | 0 | 0.066 8 | 0.000 5 | 1.265 8 | 0.009 6 | 0.137 4 | 0.000 7 | 832 | 16 | 831 | 6 | 830 | 4 | |||||||||
| 7 | 18 | 135 | 0.133 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.065 8 | 0.000 7 | 1.256 4 | 0.013 3 | 0.138 4 | 0.000 7 | 801 | 21 | 826 | 9 | 836 | 5 | |||||||||
| 8 | 34 | 258 | 0.055 6 | 0 | 0.065 5 | 0.000 5 | 1.262 6 | 0.009 2 | 0.139 8 | 0.000 7 | 791 | 15 | 829 | 6 | 843 | 4 | |||||||||
| 9 | 29 | 223 | 0.058 6 | 0 | 0.065 9 | 0.000 6 | 1.259 1 | 0.010 9 | 0.138 6 | 0.000 7 | 802 | 18 | 828 | 7 | 837 | 4 | |||||||||
| 10 | 36 | 279 | 0.052 1 | 0 | 0.066 0 | 0.000 5 | 1.263 1 | 0.011 3 | 0.138 9 | 0.000 8 | 805 | 17 | 829 | 7 | 838 | 5 | |||||||||
| 11 | 21 | 154 | 0.155 4 | 0.000 1 | 0.065 8 | 0.000 7 | 1.255 1 | 0.013 2 | 0.138 3 | 0.000 7 | 801 | 22 | 826 | 9 | 835 | 4 | |||||||||
| 12 | 25 | 181 | 0.255 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.065 9 | 0.000 5 | 1.253 9 | 0.009 5 | 0.138 0 | 0.000 7 | 803 | 16 | 825 | 6 | 834 | 4 | |||||||||
| 13 | 27 | 205 | 0.094 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 3 | 0.000 6 | 1.255 2 | 0.010 7 | 0.137 3 | 0.000 7 | 815 | 18 | 826 | 7 | 830 | 4 | |||||||||
| 14 | 39 | 281 | 0.055 0 | 0 | 0.072 2 | 0.000 5 | 1.433 7 | 0.010 3 | 0.144 | 0.000 7 | 992 | 15 | 903 | 7 | 867 | 4 | |||||||||
| 15 | 32 | 248 | 0.060 2 | 0 | 0.066 2 | 0.001 0 | 1.258 8 | 0.019 7 | 0.138 0 | 0.000 7 | 812 | 31 | 827 | 13 | 833 | 5 | |||||||||
| 16 | 29 | 224 | 0.078 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 6 | 0.000 6 | 1.263 3 | 0.011 4 | 0.137 6 | 0.000 7 | 826 | 19 | 829 | 7 | 831 | 4 | |||||||||
| 17 | 30 | 222 | 0.112 7 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 2 | 0.000 5 | 1.264 9 | 0.010 7 | 0.138 5 | 0.000 7 | 814 | 17 | 830 | 7 | 836 | 4 | |||||||||
| 18 | 24 | 186 | 0.066 7 | 0 | 0.066 9 | 0.000 6 | 1.250 4 | 0.012 0 | 0.135 5 | 0.000 7 | 835 | 19 | 824 | 8 | 819 | 4 | |||||||||
| 19 | 25 | 189 | 0.066 9 | 0 | 0.065 5 | 0.000 8 | 1.266 7 | 0.016 0 | 0.140 2 | 0.000 7 | 791 | 26 | 831 | 10 | 846 | 4 | |||||||||
| 20 | 20 | 148 | 0.196 6 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 4 | 0.000 6 | 1.246 2 | 0.011 2 | 0.136 0 | 0.000 7 | 820 | 18 | 822 | 7 | 822 | 4 | |||||||||
| 21 | 30 | 230 | 0.058 5 | 0 | 0.066 3 | 0.000 5 | 1.276 8 | 0.009 4 | 0.139 7 | 0.000 7 | 815 | 15 | 835 | 6 | 843 | 4 | |||||||||
| 22 | 40 | 135 | 0.279 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.145 8 | 0.001 1 | 5.146 2 | 0.039 0 | 0.256 0 | 0.001 3 | 2297 | 13 | 1844 | 14 | 1469 | 8 | |||||||||
| 23 | 20 | 152 | 0.107 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 4 | 0.000 7 | 1.260 0 | 0.012 8 | 0.137 6 | 0.000 8 | 819 | 21 | 828 | 8 | 831 | 5 | |||||||||
| 24 | 21 | 163 | 0.077 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.066 2 | 0.000 6 | 1.268 6 | 0.011 5 | 0.138 9 | 0.000 7 | 813 | 19 | 832 | 8 | 839 | 4 | |||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Fe2O3T | FeOT | MnO | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 70.27 | 0.12 | 15.78 | 0.98 | 0.55 | 1.59 | 1.43 | 0.07 | 1.74 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 70.18 | 0.15 | 14.00 | 1.30 | 0.55 | 1.91 | 1.72 | 0.03 | 1.28 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 70.18 | 0.14 | 13.37 | 0.69 | 0.95 | 1.74 | 1.57 | 0.09 | 1.00 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 71.21 | 0.09 | 12.60 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.04 | 1.70 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 69.74 | 0.13 | 14.68 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 1.35 | 1.21 | 0.05 | 0.64 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 69.74 | 0.12 | 14.03 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.83 | 1.65 | 0.05 | 0.64 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 68.68 | 0.15 | 13.63 | 0.52 | 3.00 | 3.85 | 3.47 | 0.02 | 0.95 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | σ | A/CNK | A/NK |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 3.97 | 2.21 | 2.39 | 0.089 | 1.33 | 99.86 | 0.78 | 1.17 | 2.54 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 3.57 | 4.64 | 3.44 | 0.067 | 1.26 | 100.90 | 2.40 | 0.78 | 1.23 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.23 | 4.32 | 3.90 | 0.064 | 3.32 | 100.50 | 2.49 | 0.87 | 1.18 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 1.87 | 4.58 | 3.94 | 0.032 | 3.51 | 100.70 | 2.57 | 0.83 | 1.07 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.23 | 4.50 | 3.89 | 0.051 | 3.18 | 100.90 | 2.63 | 0.94 | 1.26 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.23 | 4.20 | 4.48 | 0.067 | 2.37 | 100.20 | 2.82 | 0.89 | 1.19 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 3.97 | 4.08 | 3.52 | 0.018 | 2.02 | 100.90 | 2.25 | 0.77 | 1.30 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 77.0 | 734 | 1 449 | 7.30 | 0.57 | 112.0 | 3.36 | 0.70 | 1.67 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 66.3 | 895 | 1 641 | 5.51 | 0.35 | 84.7 | 2.55 | 0.63 | 1.30 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 71.9 | 810 | 1 645 | 8.79 | 0.52 | 86.3 | 2.58 | 0.70 | 1.42 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 58.7 | 469 | 1 859 | 13.00 | 0.50 | 74.6 | 2.27 | 0.97 | 2.93 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 83.5 | 626 | 1 582 | 6.86 | 0.47 | 56.4 | 1.78 | 0.37 | 1.31 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 101.0 | 407 | 1 552 | 6.98 | 0.38 | 51.3 | 1.60 | 0.35 | 1.26 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 95.9 | 498 | 1 487 | 8.53 | 0.62 | 101.0 | 2.88 | 0.76 | 1.68 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | K | Ti | P | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 19 832 | 720 | 388.6 | 11.90 | 21.9 | 2.46 | 8.64 | 1.61 | 0.56 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 28 545 | 900 | 292.5 | 10.50 | 18.9 | 2.16 | 7.28 | 1.35 | 0.59 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32 362 | 840 | 279.4 | 9.47 | 17.2 | 2.03 | 7.07 | 1.48 | 0.50 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 32 694 | 540 | 139.7 | 5.74 | 11.4 | 1.24 | 4.21 | 0.84 | 0.40 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32 279 | 780 | 222.7 | 7.25 | 13.3 | 1.58 | 5.70 | 1.27 | 0.38 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 37 174 | 720 | 292.5 | 8.71 | 15.5 | 1.88 | 6.60 | 1.44 | 0.45 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 29 209 | 900 | 78.6 | 9.61 | 17.6 | 2.16 | 7.21 | 1.61 | 0.53 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 1.51 | 0.26 | 1.52 | 0.34 | 1.17 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.24 | 9.76 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.24 | 0.19 | 1.14 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 6.44 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.55 | 0.26 | 1.50 | 0.31 | 1.06 | 0.17 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 9.34 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 0.58 | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 3.53 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.26 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.15 | 7.93 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.57 | 0.26 | 1.63 | 0.34 | 1.12 | 0.17 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 9.95 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.54 | 0.26 | 1.65 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 0.19 | 1.35 | 0.22 | 10.30 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | ΣREE | LREE/ HREE | δEu | δCe | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | (Ho/ Yb)N | TZr/℃ |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 63.57 | 2.85 | 1.09 | 4.05 | 5.69 | 4.24 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 765.4 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 51.87 | 3.68 | 1.38 | 3.97 | 8.97 | 4.46 | 1.25 | 0.8 | 742.6 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 53.28 | 2.43 | 1.01 | 3.92 | 5.86 | 3.67 | 1.13 | 0.81 | 744.1 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 29.88 | 3.94 | 1.51 | 4.27 | 8.76 | 3.92 | 1.39 | 0.71 | 732.5 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 42.95 | 2.19 | 0.87 | 3.93 | 5.10 | 3.27 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 711.1 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 50.92 | 2.12 | 0.92 | 3.83 | 5.48 | 3.47 | 1.17 | 0.91 | 695.1 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 55.78 | 2.27 | 1.02 | 3.86 | 5.11 | 3.42 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 746.9 |
表2 样品主量(%)、稀土(10-6)和微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2 Major (%) ,rare earth (10-6) and trace element (10-6) analysis results of the samples
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | Fe2O3T | FeOT | MnO | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 70.27 | 0.12 | 15.78 | 0.98 | 0.55 | 1.59 | 1.43 | 0.07 | 1.74 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 70.18 | 0.15 | 14.00 | 1.30 | 0.55 | 1.91 | 1.72 | 0.03 | 1.28 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 70.18 | 0.14 | 13.37 | 0.69 | 0.95 | 1.74 | 1.57 | 0.09 | 1.00 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 71.21 | 0.09 | 12.60 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.04 | 1.70 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 69.74 | 0.13 | 14.68 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 1.35 | 1.21 | 0.05 | 0.64 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 69.74 | 0.12 | 14.03 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.83 | 1.65 | 0.05 | 0.64 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 68.68 | 0.15 | 13.63 | 0.52 | 3.00 | 3.85 | 3.47 | 0.02 | 0.95 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | σ | A/CNK | A/NK |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 3.97 | 2.21 | 2.39 | 0.089 | 1.33 | 99.86 | 0.78 | 1.17 | 2.54 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 3.57 | 4.64 | 3.44 | 0.067 | 1.26 | 100.90 | 2.40 | 0.78 | 1.23 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.23 | 4.32 | 3.90 | 0.064 | 3.32 | 100.50 | 2.49 | 0.87 | 1.18 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 1.87 | 4.58 | 3.94 | 0.032 | 3.51 | 100.70 | 2.57 | 0.83 | 1.07 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.23 | 4.50 | 3.89 | 0.051 | 3.18 | 100.90 | 2.63 | 0.94 | 1.26 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 2.23 | 4.20 | 4.48 | 0.067 | 2.37 | 100.20 | 2.82 | 0.89 | 1.19 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 3.97 | 4.08 | 3.52 | 0.018 | 2.02 | 100.90 | 2.25 | 0.77 | 1.30 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 77.0 | 734 | 1 449 | 7.30 | 0.57 | 112.0 | 3.36 | 0.70 | 1.67 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 66.3 | 895 | 1 641 | 5.51 | 0.35 | 84.7 | 2.55 | 0.63 | 1.30 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 71.9 | 810 | 1 645 | 8.79 | 0.52 | 86.3 | 2.58 | 0.70 | 1.42 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 58.7 | 469 | 1 859 | 13.00 | 0.50 | 74.6 | 2.27 | 0.97 | 2.93 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 83.5 | 626 | 1 582 | 6.86 | 0.47 | 56.4 | 1.78 | 0.37 | 1.31 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 101.0 | 407 | 1 552 | 6.98 | 0.38 | 51.3 | 1.60 | 0.35 | 1.26 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 95.9 | 498 | 1 487 | 8.53 | 0.62 | 101.0 | 2.88 | 0.76 | 1.68 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | K | Ti | P | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 19 832 | 720 | 388.6 | 11.90 | 21.9 | 2.46 | 8.64 | 1.61 | 0.56 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 28 545 | 900 | 292.5 | 10.50 | 18.9 | 2.16 | 7.28 | 1.35 | 0.59 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32 362 | 840 | 279.4 | 9.47 | 17.2 | 2.03 | 7.07 | 1.48 | 0.50 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 32 694 | 540 | 139.7 | 5.74 | 11.4 | 1.24 | 4.21 | 0.84 | 0.40 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 32 279 | 780 | 222.7 | 7.25 | 13.3 | 1.58 | 5.70 | 1.27 | 0.38 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 37 174 | 720 | 292.5 | 8.71 | 15.5 | 1.88 | 6.60 | 1.44 | 0.45 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 29 209 | 900 | 78.6 | 9.61 | 17.6 | 2.16 | 7.21 | 1.61 | 0.53 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 1.51 | 0.26 | 1.52 | 0.34 | 1.17 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.24 | 9.76 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.24 | 0.19 | 1.14 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 6.44 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.55 | 0.26 | 1.50 | 0.31 | 1.06 | 0.17 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 9.34 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 0.58 | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 3.53 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 1.40 | 0.26 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.15 | 7.93 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.57 | 0.26 | 1.63 | 0.34 | 1.12 | 0.17 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 9.95 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 1.54 | 0.26 | 1.65 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 0.19 | 1.35 | 0.22 | 10.30 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | ΣREE | LREE/ HREE | δEu | δCe | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | (Gd/ Yb)N | (Ho/ Yb)N | TZr/℃ |
| PM020-2 | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 63.57 | 2.85 | 1.09 | 4.05 | 5.69 | 4.24 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 765.4 |
| PM020-6 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 51.87 | 3.68 | 1.38 | 3.97 | 8.97 | 4.46 | 1.25 | 0.8 | 742.6 |
| PM020-7 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 53.28 | 2.43 | 1.01 | 3.92 | 5.86 | 3.67 | 1.13 | 0.81 | 744.1 |
| PM026-1 | 粗粒花岗二长岩 | 29.88 | 3.94 | 1.51 | 4.27 | 8.76 | 3.92 | 1.39 | 0.71 | 732.5 |
| PM019-3 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 42.95 | 2.19 | 0.87 | 3.93 | 5.10 | 3.27 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 711.1 |
| PM019-4 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 50.92 | 2.12 | 0.92 | 3.83 | 5.48 | 3.47 | 1.17 | 0.91 | 695.1 |
| PM018-1 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 55.78 | 2.27 | 1.02 | 3.86 | 5.11 | 3.42 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 746.9 |
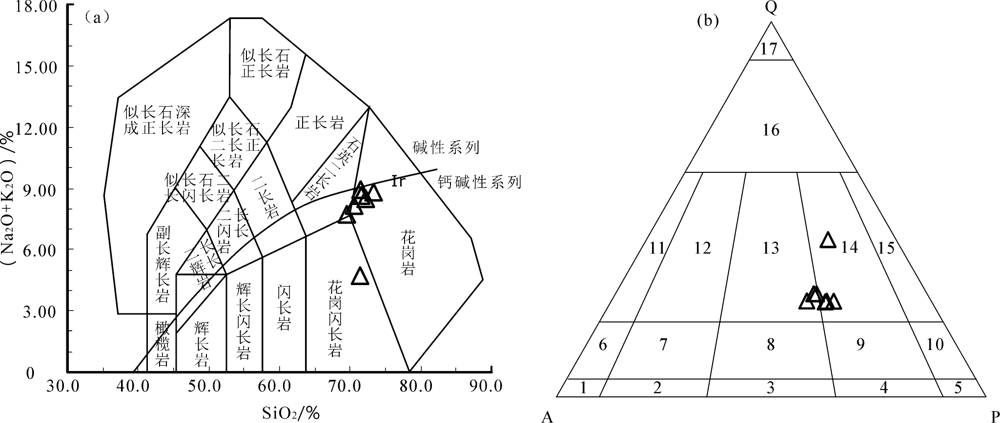
图6 (Na2O+K2O)-SiO2图解((a),底图据参考文献[36])和Q-A-P图解((b),底图据参考文献[37]) 1.碱长正长岩;2.正长岩;3.二长岩;4.二长闪长岩;5.闪长岩;6.石英碱长正长岩;7.石英正长岩;8.石英二长岩;9.石英二长闪长岩;10.石英闪长岩;11.碱长花岗岩;12.正长花岗岩;13.二长花岗岩;14.花岗闪长岩;15.英云闪长岩;16.富石英花岗岩类;17.硅英岩
Fig.6 (Na2O+K2O)-SiO2 diagram ((a), after reference [36]) and Q-A-P diagram ((b),after reference[37])

图7 A/CNK-A/NK图解((a),底图据参考文献[38])和SiO2-K2O图解((b),底图据参考文献[39])
Fig.7 A/CNK-A/NK diagram ((a),base map after reference [38]) and SiO2-K2O diagram ((b),base map after reference [39])
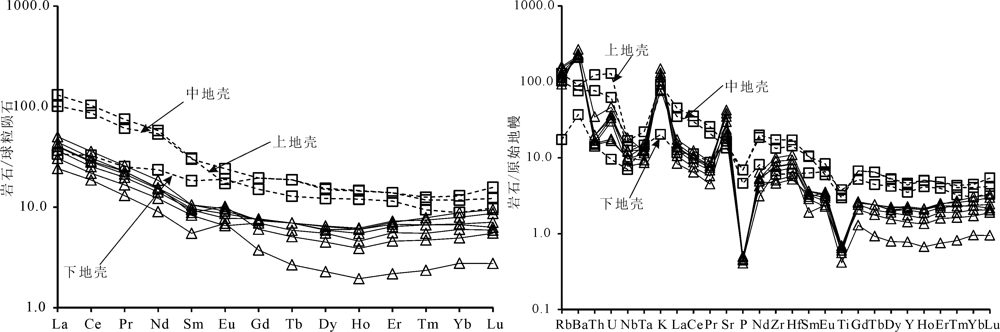
图8 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(上、中、下地壳数据引自参考文献[40],底图据参考文献[41])
Fig.8 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spidergrams (b)(data of the upper,middle and lower crust after reference[40],base map after reference[41])
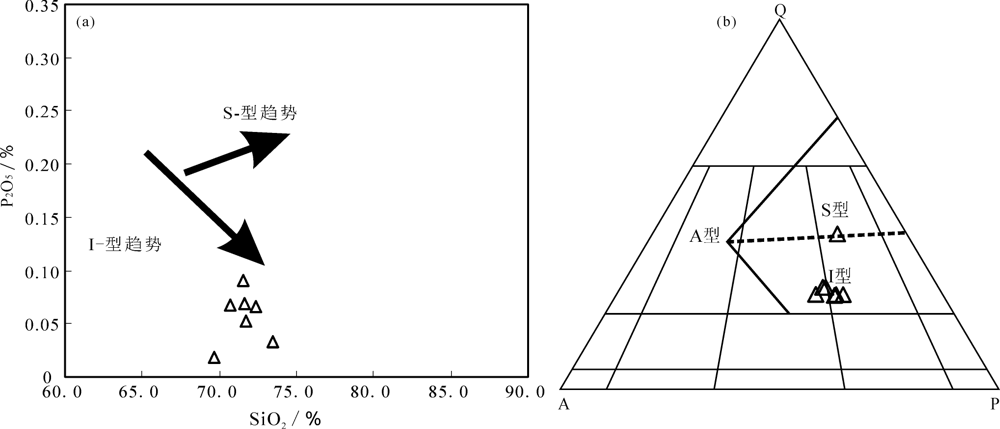
图9 SiO2-P2O5图解((a),底图据参考文献[48])和QAP图解((b),底图据参考文献[49])
Fig.9 SiO2-P2O5 diagram ((a),base map after reference [48]) and QAP diagram ((b),base map after reference [49])
| 地区 | 编号 | 岩性 | 构造环境 | 年龄/Ma | 方法 | 文献 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 铁克里克地区 | 1 | 辉长岩脉 | 伸展 | 802±9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 2 | 花岗岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 815±57 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 3 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 783±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 4 | 变质火山岩 | 汇聚 | 1 021±1 | Ar/Ar,黑云母 | [ | |||
| 5 | 变质火山岩 | 汇聚 | 1 050±1 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | |||
| 阿尔金地区 | 6 | 花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 922±6 | TISM,锆石, U-Pb | [ | ||
| 7 | 变质流纹岩 | 汇聚 | 920±20 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 塔中地区 | 8 | 闪长岩 | 伸展 | 790±22 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | ||
| 9 | 闪长岩 | 伸展 | 754±23 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | |||
| 10 | 闪长岩 | 伸展 | 744±9 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | |||
| 柯坪地区 | 11 | 二长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 601.5±3.4 | 锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 12 | 二长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 677±4 | 锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 库鲁克塔格 | 13 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 636.4±4.5 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 14 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 631.4±3.5 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 15 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 646±3.9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 16 | 煌斑岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 628.7±6.6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 17 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 652.0±7.4 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 18 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 642.8±6.9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 19 | 煌斑岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 634±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 20 | 片麻状花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 933±11 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 21 | 超基性岩墙 | 伸展 | 802.1±6.1 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 22 | 苏长辉长岩 | 伸展 | 760±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 23 | 花岗闪长岩 | 伸展 | 820±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 24 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 795±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 25 | 碳酸岩 | 伸展 | 810±6 | TISM,斜锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 26 | 辉石岩 | 伸展 | 818±11 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 27 | 辉长岩 | 伸展 | 736.5±4.9 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 28 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 734.1±4.1 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 29 | 橄榄辉石岩 | 伸展 | 734.8±3.6 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 30 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 737.3±4.5 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 31 | 凝灰岩 | 伸展 | 755±15 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 32 | 玄武岩 | 伸展 | 725±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 33 | 流纹岩 | 伸展 | 740±7 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 34 | 安山岩 | 伸展 | 616±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 35 | 火山岩 | 伸展 | 739±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 36 | 枕状玄武岩 | 伸展 | 705±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 37 | 斜长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 826±13 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 38 | 辉钼矿 | 830±26 | Re-Os等时线年龄 | [ | ||||
| 39 | 钾长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 816.2±4.6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 40 | 黑云母花岗岩 | 伸展 | 798±3 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 41 | 石英闪长岩 | 伸展 | 754±4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 42 | 黑云母花岗闪长岩 | 伸展 | 790±3 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 43 | 花岗闪长岩 | 伸展 | 785±8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 44 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 806±8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 45 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 798±7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 地区 | 编号 | 岩性 | 构造环境 | 年龄/Ma | 方法 | 文献 | ||
| 库鲁克塔格 | 46 | 花岗质岩墙 | 伸展 | 798±7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 47 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 816±15 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 48 | 闪长岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 773±3 | TISM,斜锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 49 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 776.8±8.9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 50 | 花岗闪长岩 | 汇聚 | 830±5 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 51 | 花岗闪长岩 | 汇聚 | 821±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 52 | 花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 830±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 53 | 花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 834±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 54 | 二云母花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 828±7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 55 | 二云母花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 831±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 56 | 黑云石英正长岩 | 伸展 | 662.4±3.6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 57 | 黑云石英正长岩 | 伸展 | 662.8±6.9 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 58 | 黑云正长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 627.0±4.8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 59 | 黑云正长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 628.8±4.7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 60 | 黑云石英正长岩 | 伸展 | 660.8±5.8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 61 | 钾长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 634.9±3.4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 62 | 黑云角闪片麻岩 | 伸展 | 658.9±3.4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 63 | 流纹岩 | 伸展 | 738.9±5.4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 64 | 正长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 735±10 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 65 | 二长花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 832.3±3.3 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | 本文数据 | |||
表3 塔里木克拉通周缘新元古代地质年代数据
Table 3 Neoproterozoic geological age data from areas around the Tarim Craton
| 地区 | 编号 | 岩性 | 构造环境 | 年龄/Ma | 方法 | 文献 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 铁克里克地区 | 1 | 辉长岩脉 | 伸展 | 802±9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 2 | 花岗岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 815±57 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 3 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 783±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 4 | 变质火山岩 | 汇聚 | 1 021±1 | Ar/Ar,黑云母 | [ | |||
| 5 | 变质火山岩 | 汇聚 | 1 050±1 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | |||
| 阿尔金地区 | 6 | 花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 922±6 | TISM,锆石, U-Pb | [ | ||
| 7 | 变质流纹岩 | 汇聚 | 920±20 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 塔中地区 | 8 | 闪长岩 | 伸展 | 790±22 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | ||
| 9 | 闪长岩 | 伸展 | 754±23 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | |||
| 10 | 闪长岩 | 伸展 | 744±9 | Ar/Ar,角闪石 | [ | |||
| 柯坪地区 | 11 | 二长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 601.5±3.4 | 锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 12 | 二长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 677±4 | 锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 库鲁克塔格 | 13 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 636.4±4.5 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 14 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 631.4±3.5 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 15 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 646±3.9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 16 | 煌斑岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 628.7±6.6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 17 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 652.0±7.4 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 18 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 642.8±6.9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 19 | 煌斑岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 634±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 20 | 片麻状花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 933±11 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 21 | 超基性岩墙 | 伸展 | 802.1±6.1 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 22 | 苏长辉长岩 | 伸展 | 760±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 23 | 花岗闪长岩 | 伸展 | 820±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 24 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 795±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 25 | 碳酸岩 | 伸展 | 810±6 | TISM,斜锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 26 | 辉石岩 | 伸展 | 818±11 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 27 | 辉长岩 | 伸展 | 736.5±4.9 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 28 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 734.1±4.1 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 29 | 橄榄辉石岩 | 伸展 | 734.8±3.6 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 30 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 737.3±4.5 | SIMS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 31 | 凝灰岩 | 伸展 | 755±15 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 32 | 玄武岩 | 伸展 | 725±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 33 | 流纹岩 | 伸展 | 740±7 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 34 | 安山岩 | 伸展 | 616±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 35 | 火山岩 | 伸展 | 739±6 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 36 | 枕状玄武岩 | 伸展 | 705±10 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 37 | 斜长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 826±13 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 38 | 辉钼矿 | 830±26 | Re-Os等时线年龄 | [ | ||||
| 39 | 钾长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 816.2±4.6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 40 | 黑云母花岗岩 | 伸展 | 798±3 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 41 | 石英闪长岩 | 伸展 | 754±4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 42 | 黑云母花岗闪长岩 | 伸展 | 790±3 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 43 | 花岗闪长岩 | 伸展 | 785±8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 44 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 806±8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 45 | 花岗岩 | 伸展 | 798±7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 地区 | 编号 | 岩性 | 构造环境 | 年龄/Ma | 方法 | 文献 | ||
| 库鲁克塔格 | 46 | 花岗质岩墙 | 伸展 | 798±7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | ||
| 47 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 816±15 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 48 | 闪长岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 773±3 | TISM,斜锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 49 | 辉绿岩岩墙 | 伸展 | 776.8±8.9 | SHRIMP,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 50 | 花岗闪长岩 | 汇聚 | 830±5 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 51 | 花岗闪长岩 | 汇聚 | 821±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 52 | 花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 830±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 53 | 花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 834±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 54 | 二云母花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 828±7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 55 | 二云母花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 831±6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 56 | 黑云石英正长岩 | 伸展 | 662.4±3.6 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 57 | 黑云石英正长岩 | 伸展 | 662.8±6.9 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 58 | 黑云正长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 627.0±4.8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 59 | 黑云正长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 628.8±4.7 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 60 | 黑云石英正长岩 | 伸展 | 660.8±5.8 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 61 | 钾长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 634.9±3.4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 62 | 黑云角闪片麻岩 | 伸展 | 658.9±3.4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 63 | 流纹岩 | 伸展 | 738.9±5.4 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 64 | 正长花岗岩 | 伸展 | 735±10 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | [ | |||
| 65 | 二长花岗岩 | 汇聚 | 832.3±3.3 | LA-ICP-MS,锆石,U-Pb | 本文数据 | |||
| [1] |
GE R, ZHU W, ZHENG B, et al. Early Pan-African magmatism in the Tarim Craton: Insights from zircon U-Pb-Lu-Hf isotope and geochemistry of granitoids in the Korla area, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012,212/213(8):117-138.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 张传林, 赵宇, 郭坤一, 等. 青藏高原北缘首次获得格林威尔期造山事件同位素年龄值[J]. 地质科学, 2003,38(4):535-538. |
| [3] | 张传林, 杨淳, 沈加林, 等. 西昆仑北缘新元古代片麻状花岗岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2003,49(3):239-244. |
| [4] | 张传林, 李怀坤, 王洪燕. 塔里木地块前寒武纪地质研究进展评述[J]. 地质论评, 2012,58(5):923-936. |
| [5] |
ZHANG C L, LI Z X, LI X H, et al. Neoproterozoic bimodal intrusive complex in the Southwestern Tarim Block, Northwest China: Age, geochemistry, and implications for the rifting of Rodinia[J]. International Geology Review, 2006,48(2):112-128.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG C L, LI X H, LI Z X, et al. Neoproterozoic ultramafic-mafic-carbonatite complex and granitoids in Quruqtagh of northeastern Tarim Block, Western China: Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007,152(3/4):149-169.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG C L, YANG D S, WANG H Y, et al. Neoproterozoic mafic dykes and basalts in the southern margin of Tarim, northwest China: Age, geochemistry and geodynamic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010,84(3):549-562.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GE R F, ZHU W B, WILDE S A, et al. Neoproterozoic to Paleozoic long-lived accretionary orogeny in the northern Tarim Craton[J]. Tectonics, 2014,33(3):302-329.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 王海培, 郭瑞清, 朱志新, 等. 塔里木北缘库鲁克塔格地区南华纪花岗质火山—侵入杂岩岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2016,51(1):239-261. |
| [10] | GEHRELS G E, YIN A, WANG X F. Magmatic history of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2003,108(9):2423. |
| [11] | 张志诚, 郭召杰, 冯志硕, 等. 阿尔金索尔库里地区元古代流纹岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(2):597-606. |
| [12] | 邓兴梁, 舒良树, 朱文斌, 等. 新疆兴地断裂带前寒武纪构造-岩浆-变形作用特征及其年龄[J]. 岩石学报, 2008,24(12):2800-2808. |
| [13] |
ZHU W B, ZHANG Z Y, SHU L S, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Neoproterozoic Korla mafic dykes in the northern Tarim Block, NW China: implications for the long-lasting breakup process of Rodinia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2008,165(5):887-890.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
XU B, JIAN P, ZHENG H F, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Neoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the Tarim Block of northwest China: implications for the breakup of Rodinia supercontinent and Neoproterozoic glaciations[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005,136(2):107-123.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
XU B, XIAO S H, ZOU H B, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age constraints on Neoproterozoic Quruqtagh diamictites in NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009,168(3/4):247-258.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHANG Z Y, ZHU W B, SHU L S, et al. Neoproterozoic ages of the Kuluketage diabase dyke swarm in Tarim, NW China, and its relationship to the breakup of Rodinia[J]. Geological Magazine, 2009,146(1):150-154.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 高林志, 王宗起, 许志琴, 等. 塔里木盆地库鲁克塔格地区新元古代冰碛岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄新证据[J]. 地质通报, 2010,29(增):205-213. |
| [18] |
LONG X P, YUAN C, SUN M, et al. Archean crustal evolution of the northern Tarim craton, NW China: Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010,180(3/4):272-284.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LONG X P, YUAN C, SUN M, et al. Reworking of the Tarim Craton by underplating of mantle plume-derived magmas: Evidence from Neoproterozoic granitoids in the Kuluketage area, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2011,187(1/2):1-14.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 罗金海, 车自成, 张小莉, 等. 塔里木盆地东北部新元古代花岗质岩浆活动及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011,85(4):467-474. |
| [21] |
ZHANG C L, LI Z X, LI X H, et al. Neoproterozoic mafic dyke swarms at the northern margin of the Tarim Block, NW China: Age, geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009,35(2):167-179.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG C L, YANG D S, WANG H Y, et al. Neoproterozoic mafic-ultramafic layered intrusion in Quruqtagh of northeastern Tarim Block, NW China: Two phases of mafic igneous activity with different mantle sources[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011,19(1):177-190.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG C L, ZOU H B, WANG H Y, et al. Multiple phases of the Neoproterozoic igneous activity in Quruqtagh of the northeastern Tarim Block, NW China: Interaction between plate subduction and mantle plume?[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012,222/223:488-502.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 何登发, 袁航, 李涤, 等. 吐格尔明背斜核部花岗岩的年代学、地球化学与构造环境及其对塔里木地块北缘古生代伸展聚敛旋回的揭示[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(1):133-146. |
| [25] |
SHU L S, DENG X L, ZHU W B, et al. Precambrian tectonic evolution of the Tarim Block, NW China: New geochronological insights from the Quruqtagh domain[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011,42(5):774-790.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
CAO X F, LÜ X B, LEI J H, et al. The Age of the Neoproterozoic Dapingliang Skarn Copper Deposit in Kuruketage, NW China[J]. Resource Geology, 2010,60(4):397-403.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
CAO X, LÜ X, LIU S, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon dating, geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Dapingliang Neoproterozoic granites at Kuluketage block, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2011,186(1/2/3/4):205-219.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
GUO Z J, YIN A, ROBINSON A, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of deep-drill-core samples from the basement of the central Tarim basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005,25(1):45-56.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 魏永峰, 邓泽锦, 李建兵, 等. 西南天山木扎尔特群长英质岩地球化学特征及U-Pb年龄的地学意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2010,28(2):125-129. |
| [30] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report204Pb[J]. Chemical geology, 2002,192(1/2):59-79
DOI URL |
| [31] | 王岚, 杨理勤, 王亚平, 等. 锆石LA-ICP-MS原位微区U-Pb定年及微量元素的同时测定[J]. 地球学报, 2012,33(5):763-772. |
| [32] | WILLIAMS I S. U-Th-Pb geochronology by ion microprobe[J]. Reviews in Economic Geology, 1998,7(1):1-35 |
| [33] | LUDWIG K R. Using Isoplot/Ex Version 2.01: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkelay: Berkelay Geochronological Center Special Publication, 1999: 151-181. |
| [34] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004,49(16):1589-1604. |
| [35] | 钟玉芳, 马昌前, 佘振兵. 锆石地球化学特征及地质应用研究综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006,25(1):27-34. |
| [36] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
STRECKEISEN A. To each plutonic rock its proper name[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1976,12(1):1-33.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976,58(1):63-81.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989,22(4):247-263.
DOI URL |
| [40] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003,3:1-64. |
| [41] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGHW F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(6):1217-1238. |
| [43] | 张旗, 周国庆. 中国蛇绿岩[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. |
| [44] | 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等. 福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008,24(11):2468-2484. |
| [45] | 王汝成, 赵广涛, 王德滋, 等. A型花岗岩中流体的分异聚集:副矿物证据[J]. 科学通报, 2000,45(7):771-775. |
| [46] | 张旗, 冉皞, 李承东. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012,31(4):621-626. |
| [47] |
BONIN B. From orogenic to anorogenic settings: evolution of granitoid suites after a major orogenesis[J]. Geological Journal, 1990,25(3/4):261-270.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
EBY G N. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990,26(1/2):115-134.
DOI URL |
| [49] | CHAPPELL B W. Two contrasting granite types[J]. PacificGeology, 1974,8:173-174. |
| [50] | 刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 等. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003,9(4):573-591. |
| [51] | 王德滋, 刘昌实, 沈渭洲, 等. 桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J]. 岩石学报, 1993,9(1):44-54. |
| [52] | 王珍珍, 刘栋, 赵志丹, 等. 冈底斯带南部桑日高分异 I 型花岗岩的岩石成因及其动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017,33(8):2479-2493. |
| [53] |
RICHARDS J P. Magmatic to hydrothermal metal fluxes in convergent and collided margins[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011,40(1):1-26.
DOI URL |
| [54] | 王永文, 颜丹平, 刘红旭, 等. 西天山伊犁地块北缘桦木沟高分异I型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015,29(3):529-541. |
| [55] |
MARTIN H, SMITHIES R H, RAPP R, et al. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: relationships and some implications for crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 2005,79(1):1-24.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
PEARCE JULIAN A, HARRIS NIGEL B W, TINDLE A G . Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25(4):956-983.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [3] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [4] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623. |
| [5] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 滕超, 张学斌, 杨欣杰, 来林, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古西乌旗早泥盆世I型石英闪长岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1624-1633. |
| [6] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [7] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [8] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| [9] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [10] | 刘金宝, 朱洛婷, 李龙雪, 侯青叶. 内蒙古艾力格庙地区卫境岩体的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 419-432. |
| [11] | 杨帆, 陈岳龙, 于洋. 鲁西地区新太古代晚期正长-二长花岗岩成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1155-1172. |
| [12] | 李柱, 张德会, 张荣臻, 沈存利, 焦世豪, 李林, 朱鹏龙. 内蒙古那仁乌拉早白垩世高分异花岗岩年代学及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 848-861. |
| [13] | 张宏辉, 谢财富, 陈凯, 袁永盛, 余杨忠, 张沥元, 陈贵仁, 李鸿, 詹华思, 石海涛, 蔡泉宇, 于一帆. 粤西北大桂山岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、岩石成因及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 862-875. |
| [14] | 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 王建田, 王利鹏, 赵鹏飞. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 876-897. |
| [15] | 李王鹏, 王毅, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 刘少峰, 杨伟利, 蔡习尧, 聂海宽, 钱涛, 李晓剑. 塔里木地块西北缘阿克苏地区新元古代冰碛岩年代与冰期事件[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 27-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||