



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (04): 683-696.
李英雷1( ), 徐国1,2, 刘汇川3(
), 徐国1,2, 刘汇川3( ), 白灵麒1, 苏银春1, 刘小女1
), 白灵麒1, 苏银春1, 刘小女1
收稿日期:2016-06-25
修回日期:2017-01-12
出版日期:2017-08-10
发布日期:2017-09-15
通讯作者:
刘汇川,特聘研究员,1986年出生,构造地质学专业,从事区域大地构造研究。Email: liuhuichuan1986@126.com。
作者简介:李英雷,硕士,工程师,1986年出生,构造地质学专业,从事区域地质矿产调查工作。Email: cumtlyl@126.com。
基金资助:
LI Yinglei1( ), XU Guo1,2, LIU Huichuan3(
), XU Guo1,2, LIU Huichuan3( ), BAI Lingqi1, SU Yinchun1, LIU Xiaonü1
), BAI Lingqi1, SU Yinchun1, LIU Xiaonü1
Received:2016-06-25
Revised:2017-01-12
Online:2017-08-10
Published:2017-09-15
摘要:
我国东北地区分布有大量中生代(侏罗纪至白垩纪)火山岩。选取大兴安岭西缘玛尼吐组粗安岩-粗面英安岩-流纹岩为研究对象,研究结果显示它们为高钾钙碱性的火山岩,主量、微量元素含量变化较大,SiO2含量为56.71%~71.85%,Na2O+K2O含量为5.92%~10.18%,Na2O/K2O比值较高,为0.78~1.33,Mg#为30.6~56.4。玛尼吐组火山岩的稀土元素配分图和微量元素蛛网图右倾明显,可见明显的Nb、Ta、Ti、Sr和Eu负异常(Nb*=0.17~0.71,Sr*=0.24~1.15,Eu*=0.49~0.77)。稀土总量较高,为200×10-6~949×10-6。结果分析可知,玛尼吐组火山岩源岩与霍林河火山岩源岩相似,均为混合了少量先存古老地壳的新生基性下地壳。新生基性下地壳部分熔融形成安山质岩浆,并经角闪石+斜长石+钾长石+磷灰石+钛磁铁矿等的分离结晶形成了玛尼吐组粗安岩-粗面英安岩-流纹岩。玛尼吐组火山岩显著的岛弧地球化学特征说明其形成于与太平洋俯冲有关的岛弧环境。
中图分类号:
李英雷, 徐国, 刘汇川, 白灵麒, 苏银春, 刘小女. 大兴安岭西缘玛尼吐组火山岩成因及构造指示[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 683-696.
LI Yinglei, XU Guo, LIU Huichuan, BAI Lingqi, SU Yinchun, LIU Xiaonü. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implication of Volcanic Rocks from Manitu Formation in the Western Great Xing’an Range[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(04): 683-696.
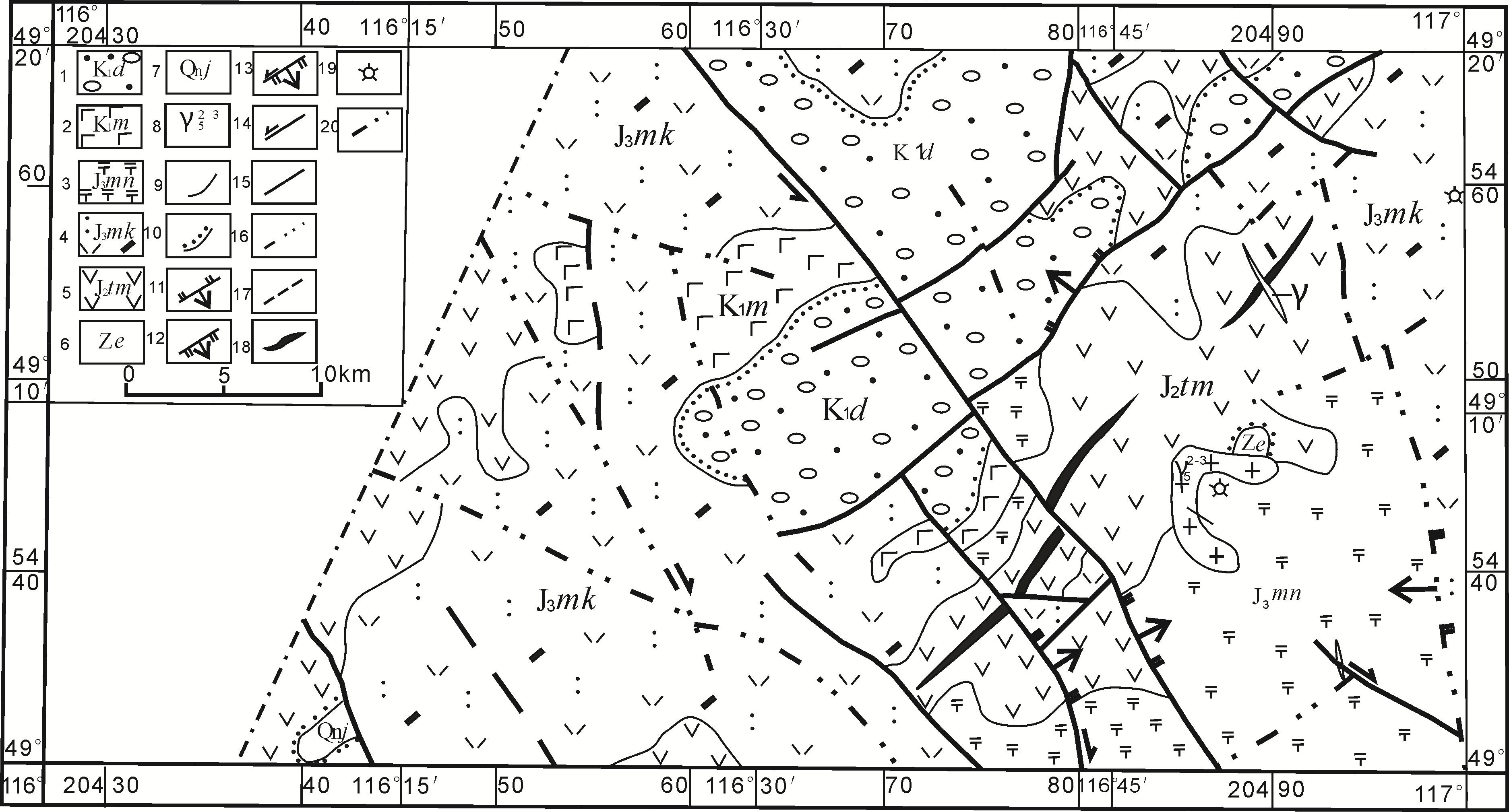
图2 研究区地质图(《根据1:20万西庙幅区调报告》修改) 1.大磨拐河组;2.梅勒图组;3.玛尼吐组;4.满克头鄂博组;5.塔木兰沟组;6.额尔古纳河组;7.佳疙疸组;8.晚侏罗世浅肉红色细粒花岗岩;9.地质界线及侵入接触界限;10.角度不整合界线;11.逆断层;12.正断层;13.平移-正断层;14.平移断层;15.区域性断层;16.航片解译断层;17.实测或推测断层;18.短轴背斜;19.火山喷发中心;20.国界线
Fig.2 Geological map showing the stratigraphic and igneous components of the study area
| 时代 | 旋 回 | 地层单元 | 喷发特征 | 火山喷发产物 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早白 垩世 | 梅勒图旋回 | 梅勒图组(K1m) | 中基性火山熔岩喷溢 | 气孔杏仁状玄武岩、安山玄武岩 |
| 白音高老旋回 | 白音高老组(K1b) | 酸性岩浆爆发 | 流纹岩、流纹质含角砾熔岩、流纹质含角砾凝灰岩、流纹质熔结凝灰岩 | |
| 玛尼吐旋回 | 玛尼吐组(K1mn?) | 中性岩浆间歇性喷溢 | 粗面岩、英安岩、粗安岩、熔结含角砾晶屑凝灰岩、安山质晶屑凝灰岩等 | |
| 晚侏 罗世 | 满克头鄂博旋回 | 满克头鄂博组 (J3mk) | 酸性火山爆发为主,少量熔岩喷溢 | 石泡、球粒流纹岩、流纹质火山角砾、集块岩、角砾凝灰岩、流纹质熔结角砾凝灰岩、沉凝灰岩、流纹岩等 |
| 中侏 罗世 | 塔木兰沟旋回 | 塔木兰沟组(J2tm) | 中基性火山熔岩喷溢 | 杏仁状玄武岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩、玄武质角砾熔岩、安山质凝灰角砾熔岩 |
表1 研究区火山活动旋回划分特征
Table 1 Geological characteristics of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the study area
| 时代 | 旋 回 | 地层单元 | 喷发特征 | 火山喷发产物 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早白 垩世 | 梅勒图旋回 | 梅勒图组(K1m) | 中基性火山熔岩喷溢 | 气孔杏仁状玄武岩、安山玄武岩 |
| 白音高老旋回 | 白音高老组(K1b) | 酸性岩浆爆发 | 流纹岩、流纹质含角砾熔岩、流纹质含角砾凝灰岩、流纹质熔结凝灰岩 | |
| 玛尼吐旋回 | 玛尼吐组(K1mn?) | 中性岩浆间歇性喷溢 | 粗面岩、英安岩、粗安岩、熔结含角砾晶屑凝灰岩、安山质晶屑凝灰岩等 | |
| 晚侏 罗世 | 满克头鄂博旋回 | 满克头鄂博组 (J3mk) | 酸性火山爆发为主,少量熔岩喷溢 | 石泡、球粒流纹岩、流纹质火山角砾、集块岩、角砾凝灰岩、流纹质熔结角砾凝灰岩、沉凝灰岩、流纹岩等 |
| 中侏 罗世 | 塔木兰沟旋回 | 塔木兰沟组(J2tm) | 中基性火山熔岩喷溢 | 杏仁状玄武岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩、玄武质角砾熔岩、安山质凝灰角砾熔岩 |
| 样号 | 岩性 | 时代 | 特征描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GS7802 | 深灰色粗安岩 | J3mn | 深灰色粗安岩,斑状结构,块状-似层状构造;斑晶成分为斜长石,长板状-不规则粒状,粒径0.5~2.0 mm,含量10%~20%,基质隐晶结构,岩石见弱褐铁矿化蚀变 |
| GS7057 | 浅砖红色粗面岩 | J3mn | 浅砖红色,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶成分为灰白色-浅灰红色长石,厚板状-宽板状,见阶梯状解理断口,粒径大小在1.0~6.0 mm之间,弱绿帘石化蚀变,斑晶成分30%。基质隐晶质。弱褐铁矿化 |
| GS06 | 粗安岩 | J3mn | 灰色,具斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶斜长石,自形-半自形板状,粒径多在1~2 mm,多已高岭土化、绿泥石化,含量20%左右,基质为隐晶质,斑晶无定向性,杂乱分布,因长石斑晶脱落,形成晶洞,岩石表面较粗糙 |
| GS14 | 灰紫色粗安岩 | J3mn | 灰紫色,粗面结构,块状构造,矿物成分主要包括钾长石、斜长石、角闪石及部分辉石。斑晶主要由斜长石、钾长石组成,呈短柱状,宽板状,大小2~3 mm,含量20%;基质呈紫红色,矿物成分主要为斜长石,钾长石以及角闪石和少量辉石,钾长石含量约占长石总量30%。岩石节理发育,呈薄板状,厚度约3 cm |
| GS19 | 灰红色粗面岩 | J3mn | 灰红色,斑状结构或粗面结构,块状构造,矿物成分主要包括钾长石、斜长石、角闪石及部分辉石。斑晶主要由斜长石、钾长石组成,呈短柱状,宽板状,大小2~3 mm,含量20%;基质为斜长石、钾长石,钾长石含量约占长石总量30%。岩石节理发育,呈薄板状,厚度约3 cm |
| GS7912 | 灰色辉石安山岩 | J3mn | 灰色辉石安山岩,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶由斜长石和辉石组成,斜长石呈长条状-集合体粒状,见弱绿帘石化蚀变;辉石,灰褐色,半自形粒状;粒径大小在1.0~5.0 mm之间,斑晶含量占10%~15%,基质由深灰色隐晶质组成,含量约占85% |
| GS7838 | 灰黑色粗安岩 | J3mn | 粗安岩,斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶成分为斜长石,宽板状,见阶梯状断口,粒径大小1.0~4.0 mm,以2.0~3.0 mm为主,见弱绿帘石化蚀变;基质隐晶质结构,弱绿泥石化。斑晶15%,基质85% |
| GS7282 | 粗面安山岩 | J3mn | 灰黑色片理化粗面安山岩,风化面灰褐红-灰黑色,新鲜面灰黑色,斑状结构,基质隐晶质结构,块状构造。斑晶:斜长石呈灰白-微绿色,粒径0.5~2 mm,半自形长板状,含量约17%;透长石,无色透明,半自形板条状,个别星点状,粒径0.2~1.2 mm居多,含量10%。基质由灰黑色隐晶质组成,含量约73% |
| GS7864 | 灰绿色粗安岩 | J3mn | 灰绿色辉石粗安岩,斑状结构,基质间碱结构,块状构造。斑晶斜长石半自形板状,熔蚀麻点状,1~2 mm;钾长石半自形板状,弱泥化,0.5~1 mm;辉石半自形短柱状,1 mm。基质斜长石微晶定向,微晶间分布隐晶质钾长石,少量微晶辉石。斑晶:斜长石15%,钾长石5%,辉石5%。基质:斜长石微晶40%,隐晶质钾长石30%,辉石微晶少量,绿鳞石5% |
| GS7863 | 黑云母粗安岩 | J3mn | 黑云母粗安岩,斑状结构,基质间碱结构,块状构造。斑晶斜长石半自形板状,熔蚀麻点状,弱绢云母化2~4 mm;钾长石半自形板状,弱泥化0.5~1 mm;黑云母片状,弱绿泥石化0.5~1 mm。基质斜长石微晶定向,微晶间冲突隐晶质钾长石及尘点状磁铁矿,黑云母少量。斑晶:斜长石20%,钾长石5%,黑云母5% |
| GS6771 | 粗安岩 | J3mn | 风化面灰褐色,新鲜面深灰绿色,具斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶斜长石,自形-半自形板条状,粒径一般在1~3 mm,个别大者达5 mm,含量30%~35%,普遍泥化、绿泥石化,颗粒表面变污浊;基质为隐晶质,斑晶无定向性,岩石表面较粗糙,见弱褐铁矿化 |
| GS6922 | 紫红色粗安岩 | J3mn | 紫红色粗安岩,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶长板状-宽板状,由斜长石组成,粒径大小1.0~5.0 mm,普遍绿泥石化;基质由紫红色隐晶质组成,此外见黑色团块状暗色物质;斑晶含量约占20%,基质约占80% |
| GS20 | 粗安岩 | J3mn | 风化面灰褐色,新鲜面深灰绿色,具斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶斜长石,自形-半自形板条状,粒径一般在1~5 mm,含量20%~25%,普遍泥化、绿泥石化,颗粒表面变污浊,基质为隐晶质,斑晶无定向性,岩石表面较粗糙 |
表2 本文样品的特征描述
Table 2 Summary of lithology of the representative samples
| 样号 | 岩性 | 时代 | 特征描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GS7802 | 深灰色粗安岩 | J3mn | 深灰色粗安岩,斑状结构,块状-似层状构造;斑晶成分为斜长石,长板状-不规则粒状,粒径0.5~2.0 mm,含量10%~20%,基质隐晶结构,岩石见弱褐铁矿化蚀变 |
| GS7057 | 浅砖红色粗面岩 | J3mn | 浅砖红色,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶成分为灰白色-浅灰红色长石,厚板状-宽板状,见阶梯状解理断口,粒径大小在1.0~6.0 mm之间,弱绿帘石化蚀变,斑晶成分30%。基质隐晶质。弱褐铁矿化 |
| GS06 | 粗安岩 | J3mn | 灰色,具斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶斜长石,自形-半自形板状,粒径多在1~2 mm,多已高岭土化、绿泥石化,含量20%左右,基质为隐晶质,斑晶无定向性,杂乱分布,因长石斑晶脱落,形成晶洞,岩石表面较粗糙 |
| GS14 | 灰紫色粗安岩 | J3mn | 灰紫色,粗面结构,块状构造,矿物成分主要包括钾长石、斜长石、角闪石及部分辉石。斑晶主要由斜长石、钾长石组成,呈短柱状,宽板状,大小2~3 mm,含量20%;基质呈紫红色,矿物成分主要为斜长石,钾长石以及角闪石和少量辉石,钾长石含量约占长石总量30%。岩石节理发育,呈薄板状,厚度约3 cm |
| GS19 | 灰红色粗面岩 | J3mn | 灰红色,斑状结构或粗面结构,块状构造,矿物成分主要包括钾长石、斜长石、角闪石及部分辉石。斑晶主要由斜长石、钾长石组成,呈短柱状,宽板状,大小2~3 mm,含量20%;基质为斜长石、钾长石,钾长石含量约占长石总量30%。岩石节理发育,呈薄板状,厚度约3 cm |
| GS7912 | 灰色辉石安山岩 | J3mn | 灰色辉石安山岩,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶由斜长石和辉石组成,斜长石呈长条状-集合体粒状,见弱绿帘石化蚀变;辉石,灰褐色,半自形粒状;粒径大小在1.0~5.0 mm之间,斑晶含量占10%~15%,基质由深灰色隐晶质组成,含量约占85% |
| GS7838 | 灰黑色粗安岩 | J3mn | 粗安岩,斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶成分为斜长石,宽板状,见阶梯状断口,粒径大小1.0~4.0 mm,以2.0~3.0 mm为主,见弱绿帘石化蚀变;基质隐晶质结构,弱绿泥石化。斑晶15%,基质85% |
| GS7282 | 粗面安山岩 | J3mn | 灰黑色片理化粗面安山岩,风化面灰褐红-灰黑色,新鲜面灰黑色,斑状结构,基质隐晶质结构,块状构造。斑晶:斜长石呈灰白-微绿色,粒径0.5~2 mm,半自形长板状,含量约17%;透长石,无色透明,半自形板条状,个别星点状,粒径0.2~1.2 mm居多,含量10%。基质由灰黑色隐晶质组成,含量约73% |
| GS7864 | 灰绿色粗安岩 | J3mn | 灰绿色辉石粗安岩,斑状结构,基质间碱结构,块状构造。斑晶斜长石半自形板状,熔蚀麻点状,1~2 mm;钾长石半自形板状,弱泥化,0.5~1 mm;辉石半自形短柱状,1 mm。基质斜长石微晶定向,微晶间分布隐晶质钾长石,少量微晶辉石。斑晶:斜长石15%,钾长石5%,辉石5%。基质:斜长石微晶40%,隐晶质钾长石30%,辉石微晶少量,绿鳞石5% |
| GS7863 | 黑云母粗安岩 | J3mn | 黑云母粗安岩,斑状结构,基质间碱结构,块状构造。斑晶斜长石半自形板状,熔蚀麻点状,弱绢云母化2~4 mm;钾长石半自形板状,弱泥化0.5~1 mm;黑云母片状,弱绿泥石化0.5~1 mm。基质斜长石微晶定向,微晶间冲突隐晶质钾长石及尘点状磁铁矿,黑云母少量。斑晶:斜长石20%,钾长石5%,黑云母5% |
| GS6771 | 粗安岩 | J3mn | 风化面灰褐色,新鲜面深灰绿色,具斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶斜长石,自形-半自形板条状,粒径一般在1~3 mm,个别大者达5 mm,含量30%~35%,普遍泥化、绿泥石化,颗粒表面变污浊;基质为隐晶质,斑晶无定向性,岩石表面较粗糙,见弱褐铁矿化 |
| GS6922 | 紫红色粗安岩 | J3mn | 紫红色粗安岩,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶长板状-宽板状,由斜长石组成,粒径大小1.0~5.0 mm,普遍绿泥石化;基质由紫红色隐晶质组成,此外见黑色团块状暗色物质;斑晶含量约占20%,基质约占80% |
| GS20 | 粗安岩 | J3mn | 风化面灰褐色,新鲜面深灰绿色,具斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶斜长石,自形-半自形板条状,粒径一般在1~5 mm,含量20%~25%,普遍泥化、绿泥石化,颗粒表面变污浊,基质为隐晶质,斑晶无定向性,岩石表面较粗糙 |
| 样号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | 烧失量 | 总量 | Cr | Ni | Co | Li | Rb | Cs | Sr | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS7838 | 56.71 | 16.24 | 7.88 | 5.87 | 3.43 | 2.60 | 3.87 | 1.57 | 0.620 | 0.100 | 1.11 | 100.00 | 95.00 | 38.40 | 22.60 | 13.8 | 75.6 | 1.54 | 761.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS6922 | 60.98 | 15.75 | 6.06 | 4.19 | 2.60 | 3.57 | 3.65 | 1.03 | 0.320 | 0.090 | 1.76 | 100.00 | 43.20 | 26.20 | 15.60 | 22.0 | 134.0 | 3.52 | 580.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7802 | 62.43 | 16.22 | 5.31 | 3.42 | 1.53 | 3.73 | 4.23 | 1.18 | 0.370 | 0.070 | 1.51 | 100.00 | 9.55 | 8.72 | 9.52 | 17.8 | 90.9 | 2.58 | 452.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7863 | 68.52 | 14.54 | 2.02 | 1.36 | 0.45 | 5.72 | 3.38 | 0.46 | 0.074 | 0.040 | 3.43 | 100.00 | 5.13 | 4.73 | 2.49 | 10.1 | 231.0 | 7.30 | 226.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7864 | 62.32 | 16.66 | 5.00 | 3.65 | 0.91 | 4.13 | 3.96 | 1.01 | 0.340 | 0.050 | 1.97 | 100.00 | 49.10 | 23.20 | 13.60 | 17.6 | 133.0 | 4.58 | 555.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7912 | 58.02 | 16.62 | 7.02 | 5.64 | 3.42 | 2.54 | 3.97 | 1.18 | 0.400 | 0.120 | 1.07 | 100.00 | 87.30 | 40.80 | 22.40 | 13.8 | 76.5 | 1.66 | 749.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7057 | 68.6 | 15.77 | 2.58 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 4.64 | 4.22 | 0.58 | 0.150 | 0.060 | 1.99 | 100.00 | 8.58 | 9.45 | 3.49 | 25.7 | 146.0 | 6.46 | 255.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS14 | 66.96 | 16.70 | 2.77 | 2.14 | 0.68 | 4.80 | 4.39 | 0.58 | 0.120 | 0.050 | 0.83 | 100.02 | 12.00 | 7.76 | 3.80 | 21.5 | 180.0 | 6.43 | 445.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS19 | 66.53 | 16.26 | 3.17 | 1.25 | 0.94 | 4.61 | 4.46 | 0.65 | 0.160 | 0.070 | 1.89 | 99.99 | 10.40 | 7.82 | 4.08 | 21.7 | 139.0 | 8.24 | 330.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS6771 | 62.40 | 16.08 | 5.91 | 3.15 | 1.01 | 4.47 | 3.80 | 1.02 | 0.320 | 0.070 | 1.79 | 100.02 | 39.70 | 23.00 | 12.20 | 29.3 | 163.0 | 3.60 | 549.0 | ||||||||||||
| TK08GS20 | 71.85 | 13.76 | 2.24 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 5.58 | 4.40 | 0.55 | 0.054 | 0.040 | 0.95 | 99.99 | 5.52 | 2.91 | 0.68 | 13.4 | 114.0 | 5.43 | 52.2 | ||||||||||||
| GS7282 | 64.08 | 16.12 | 8.37 | 3.32 | 0.87 | 4.38 | 4.11 | 1.00 | 0.310 | 0.082 | 0.84 | 103.482 | 42.50 | 22.40 | 11.50 | 23.3 | 152.0 | 3.83 | 546.0 | ||||||||||||
| 样号 | Ba | V | Sc | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7838 | 755.00 | 144.00 | 13.50 | 1.00 | 331.00 | 8.62 | 1.82 | 9.77 | 53.1 | 77.3 | 14.80 | 59.5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS6922 | 822.00 | 104.00 | 8.60 | 1.16 | 339.00 | 9.56 | 3.07 | 16.60 | 47.4 | 84.2 | 12.20 | 46.6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7802 | 962.00 | 93.60 | 10.90 | 1.19 | 377.00 | 10.10 | 2.53 | 13.60 | 45.3 | 95.3 | 12.10 | 45.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7863 | 641.00 | 17.10 | 9.07 | 1.47 | 413.00 | 12.00 | 5.06 | 17.40 | 35.7 | 68.1 | 8.18 | 29.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7864 | 977.00 | 118.00 | 9.54 | 1.09 | 326.00 | 9.22 | 1.13 | 15.10 | 41.6 | 77.6 | 11.30 | 44.4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7912 | 723.00 | 146.00 | 12.20 | 0.72 | 259.00 | 6.97 | 1.41 | 9.24 | 40.1 | 78.8 | 10.70 | 42.1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7057 | 728.00 | 38.50 | 8.39 | 1.33 | 344.00 | 10.20 | 1.16 | 4.45 | 11.3 | 23.2 | 2.82 | 10.8 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS14 | 1 050.00 | 35.80 | 9.49 | 1.32 | 428.00 | 12.00 | 2.84 | 17.80 | 33.3 | 71.6 | 8.52 | 31.8 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS19 | 981.00 | 42.10 | 8.69 | 1.27 | 399.00 | 11.00 | 1.74 | 11.90 | 23.3 | 46.2 | 5.84 | 22.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS6771 | 834.00 | 109.00 | 12.30 | 1.14 | 335.00 | 9.30 | 1.89 | 14.00 | 39.3 | 79.2 | 10.10 | 38.7 | |||||||||||||||||||
| TK08GS20 | 262.00 | 14.70 | 11.90 | 1.72 | 565.00 | 14.20 | 3.04 | 11.00 | 51.0 | 75.0 | 12.50 | 46.5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7282 | 814.00 | 97.10 | 13.90 | 1.15 | 337.00 | 9.35 | 1.74 | 14.60 | 43.7 | 89.3 | 11.20 | 42.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7838 | 10.40 | 2.31 | 8.51 | 1.16 | 5.56 | 0.98 | 2.55 | 0.34 | 2.12 | 0.3 | 24.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS6922 | 8.02 | 1.68 | 6.94 | 0.99 | 5.02 | 0.94 | 2.61 | 0.38 | 2.44 | 0.36 | 24.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7802 | 8.03 | 1.83 | 6.57 | 0.93 | 4.62 | 0.84 | 2.27 | 0.32 | 2.11 | 0.31 | 21.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7863 | 4.80 | 0.72 | 4.28 | 0.64 | 3.47 | 0.68 | 1.98 | 0.32 | 2.16 | 0.34 | 18.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7864 | 8.02 | 1.64 | 6.68 | 0.96 | 4.88 | 0.91 | 2.43 | 0.34 | 2.16 | 0.32 | 23.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7912 | 7.33 | 1.79 | 6.85 | 0.88 | 4.24 | 0.78 | 2.11 | 0.29 | 1.76 | 0.26 | 19.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7057 | 1.84 | 0.41 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 1.31 | 0.27 | 0.76 | 0.12 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 6.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS14 | 5.66 | 1.32 | 4.91 | 0.73 | 3.86 | 0.74 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 2.12 | 0.33 | 18.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS19 | 3.98 | 0.93 | 3.46 | 0.50 | 2.89 | 0.57 | 1.67 | 0.26 | 1.75 | 0.28 | 15.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS6771 | 6.78 | 1.45 | 5.76 | 0.82 | 4.25 | 0.78 | 2.20 | 0.32 | 2.12 | 0.32 | 20.90 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| TK08GS20 | 7.12 | 1.08 | 5.76 | 0.76 | 3.60 | 0.64 | 1.71 | 0.24 | 1.50 | 0.22 | 14.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7282 | 7.68 | 1.53 | 6.84 | 1.00 | 5.25 | 1.01 | 2.86 | 0.42 | 2.74 | 0.41 | 27.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||
表3 玛尼吐组火山岩主量(%)和微量元素(10-6)分析测试结果
Table 3 Major (%) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the volcanic rocks in the Manitu Formation
| 样号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | 烧失量 | 总量 | Cr | Ni | Co | Li | Rb | Cs | Sr | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS7838 | 56.71 | 16.24 | 7.88 | 5.87 | 3.43 | 2.60 | 3.87 | 1.57 | 0.620 | 0.100 | 1.11 | 100.00 | 95.00 | 38.40 | 22.60 | 13.8 | 75.6 | 1.54 | 761.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS6922 | 60.98 | 15.75 | 6.06 | 4.19 | 2.60 | 3.57 | 3.65 | 1.03 | 0.320 | 0.090 | 1.76 | 100.00 | 43.20 | 26.20 | 15.60 | 22.0 | 134.0 | 3.52 | 580.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7802 | 62.43 | 16.22 | 5.31 | 3.42 | 1.53 | 3.73 | 4.23 | 1.18 | 0.370 | 0.070 | 1.51 | 100.00 | 9.55 | 8.72 | 9.52 | 17.8 | 90.9 | 2.58 | 452.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7863 | 68.52 | 14.54 | 2.02 | 1.36 | 0.45 | 5.72 | 3.38 | 0.46 | 0.074 | 0.040 | 3.43 | 100.00 | 5.13 | 4.73 | 2.49 | 10.1 | 231.0 | 7.30 | 226.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7864 | 62.32 | 16.66 | 5.00 | 3.65 | 0.91 | 4.13 | 3.96 | 1.01 | 0.340 | 0.050 | 1.97 | 100.00 | 49.10 | 23.20 | 13.60 | 17.6 | 133.0 | 4.58 | 555.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7912 | 58.02 | 16.62 | 7.02 | 5.64 | 3.42 | 2.54 | 3.97 | 1.18 | 0.400 | 0.120 | 1.07 | 100.00 | 87.30 | 40.80 | 22.40 | 13.8 | 76.5 | 1.66 | 749.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS7057 | 68.6 | 15.77 | 2.58 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 4.64 | 4.22 | 0.58 | 0.150 | 0.060 | 1.99 | 100.00 | 8.58 | 9.45 | 3.49 | 25.7 | 146.0 | 6.46 | 255.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS14 | 66.96 | 16.70 | 2.77 | 2.14 | 0.68 | 4.80 | 4.39 | 0.58 | 0.120 | 0.050 | 0.83 | 100.02 | 12.00 | 7.76 | 3.80 | 21.5 | 180.0 | 6.43 | 445.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS19 | 66.53 | 16.26 | 3.17 | 1.25 | 0.94 | 4.61 | 4.46 | 0.65 | 0.160 | 0.070 | 1.89 | 99.99 | 10.40 | 7.82 | 4.08 | 21.7 | 139.0 | 8.24 | 330.0 | ||||||||||||
| GS6771 | 62.40 | 16.08 | 5.91 | 3.15 | 1.01 | 4.47 | 3.80 | 1.02 | 0.320 | 0.070 | 1.79 | 100.02 | 39.70 | 23.00 | 12.20 | 29.3 | 163.0 | 3.60 | 549.0 | ||||||||||||
| TK08GS20 | 71.85 | 13.76 | 2.24 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 5.58 | 4.40 | 0.55 | 0.054 | 0.040 | 0.95 | 99.99 | 5.52 | 2.91 | 0.68 | 13.4 | 114.0 | 5.43 | 52.2 | ||||||||||||
| GS7282 | 64.08 | 16.12 | 8.37 | 3.32 | 0.87 | 4.38 | 4.11 | 1.00 | 0.310 | 0.082 | 0.84 | 103.482 | 42.50 | 22.40 | 11.50 | 23.3 | 152.0 | 3.83 | 546.0 | ||||||||||||
| 样号 | Ba | V | Sc | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7838 | 755.00 | 144.00 | 13.50 | 1.00 | 331.00 | 8.62 | 1.82 | 9.77 | 53.1 | 77.3 | 14.80 | 59.5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS6922 | 822.00 | 104.00 | 8.60 | 1.16 | 339.00 | 9.56 | 3.07 | 16.60 | 47.4 | 84.2 | 12.20 | 46.6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7802 | 962.00 | 93.60 | 10.90 | 1.19 | 377.00 | 10.10 | 2.53 | 13.60 | 45.3 | 95.3 | 12.10 | 45.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7863 | 641.00 | 17.10 | 9.07 | 1.47 | 413.00 | 12.00 | 5.06 | 17.40 | 35.7 | 68.1 | 8.18 | 29.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7864 | 977.00 | 118.00 | 9.54 | 1.09 | 326.00 | 9.22 | 1.13 | 15.10 | 41.6 | 77.6 | 11.30 | 44.4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7912 | 723.00 | 146.00 | 12.20 | 0.72 | 259.00 | 6.97 | 1.41 | 9.24 | 40.1 | 78.8 | 10.70 | 42.1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7057 | 728.00 | 38.50 | 8.39 | 1.33 | 344.00 | 10.20 | 1.16 | 4.45 | 11.3 | 23.2 | 2.82 | 10.8 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS14 | 1 050.00 | 35.80 | 9.49 | 1.32 | 428.00 | 12.00 | 2.84 | 17.80 | 33.3 | 71.6 | 8.52 | 31.8 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS19 | 981.00 | 42.10 | 8.69 | 1.27 | 399.00 | 11.00 | 1.74 | 11.90 | 23.3 | 46.2 | 5.84 | 22.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS6771 | 834.00 | 109.00 | 12.30 | 1.14 | 335.00 | 9.30 | 1.89 | 14.00 | 39.3 | 79.2 | 10.10 | 38.7 | |||||||||||||||||||
| TK08GS20 | 262.00 | 14.70 | 11.90 | 1.72 | 565.00 | 14.20 | 3.04 | 11.00 | 51.0 | 75.0 | 12.50 | 46.5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| GS7282 | 814.00 | 97.10 | 13.90 | 1.15 | 337.00 | 9.35 | 1.74 | 14.60 | 43.7 | 89.3 | 11.20 | 42.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 样号 | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7838 | 10.40 | 2.31 | 8.51 | 1.16 | 5.56 | 0.98 | 2.55 | 0.34 | 2.12 | 0.3 | 24.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS6922 | 8.02 | 1.68 | 6.94 | 0.99 | 5.02 | 0.94 | 2.61 | 0.38 | 2.44 | 0.36 | 24.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7802 | 8.03 | 1.83 | 6.57 | 0.93 | 4.62 | 0.84 | 2.27 | 0.32 | 2.11 | 0.31 | 21.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7863 | 4.80 | 0.72 | 4.28 | 0.64 | 3.47 | 0.68 | 1.98 | 0.32 | 2.16 | 0.34 | 18.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7864 | 8.02 | 1.64 | 6.68 | 0.96 | 4.88 | 0.91 | 2.43 | 0.34 | 2.16 | 0.32 | 23.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7912 | 7.33 | 1.79 | 6.85 | 0.88 | 4.24 | 0.78 | 2.11 | 0.29 | 1.76 | 0.26 | 19.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7057 | 1.84 | 0.41 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 1.31 | 0.27 | 0.76 | 0.12 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 6.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS14 | 5.66 | 1.32 | 4.91 | 0.73 | 3.86 | 0.74 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 2.12 | 0.33 | 18.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS19 | 3.98 | 0.93 | 3.46 | 0.50 | 2.89 | 0.57 | 1.67 | 0.26 | 1.75 | 0.28 | 15.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS6771 | 6.78 | 1.45 | 5.76 | 0.82 | 4.25 | 0.78 | 2.20 | 0.32 | 2.12 | 0.32 | 20.90 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| TK08GS20 | 7.12 | 1.08 | 5.76 | 0.76 | 3.60 | 0.64 | 1.71 | 0.24 | 1.50 | 0.22 | 14.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GS7282 | 7.68 | 1.53 | 6.84 | 1.00 | 5.25 | 1.01 | 2.86 | 0.42 | 2.74 | 0.41 | 27.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||
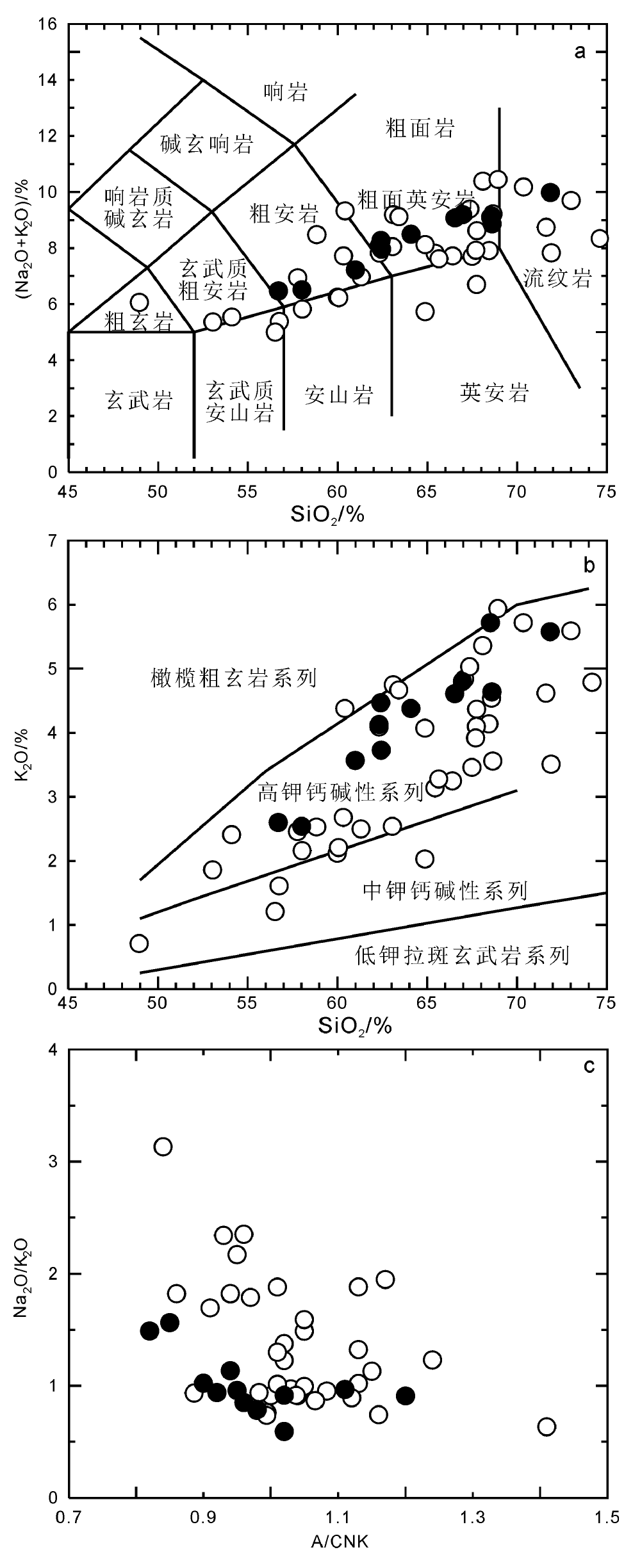
图4 玛尼吐组火山岩TAS(a)、K2O-SiO2(b)和Na2O/K2O-A/CNK(c) 图解 图中黑色圆为本文样品,底图据文献[32-33],空心圆样品来自参考文献[10,35-36,41];A/CNK=(Al2O3/101.96)/((CaO/56.08)+(Na2O/61.98)+(K2O/94.20))
Fig.4 SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)(a), K2O-SiO2 (b) and Na2O/K2O-A/CNK (c) plots of the volcanic rocks
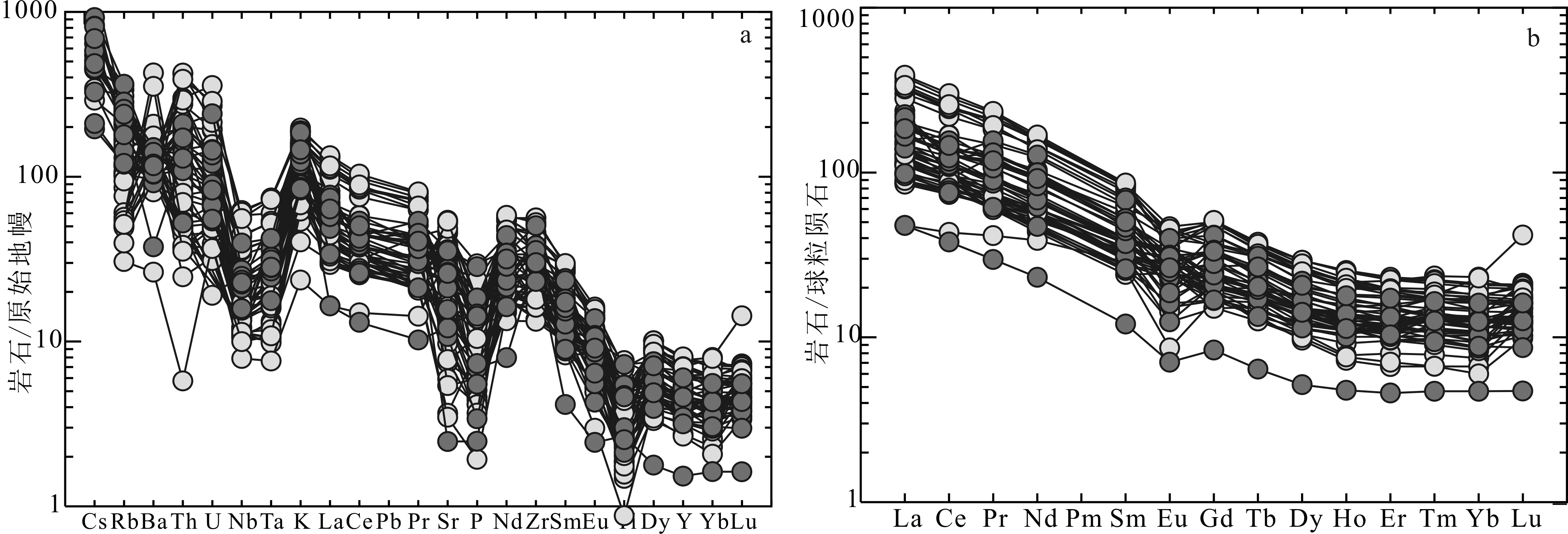
图5 玛尼吐组火山岩微量元素蛛网图和稀土元素配分图 原始地幔和球粒陨石数据参考文献[34]; 图例同图4
Fig.5 Primitive mantle normalized incompatible elemental spidergrams and chondrite normalized REE patterns of the volcanic rocks
| 样品号 | 采样点 | 定年方法 | 年龄/Ma | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS4 | 万宝乡北西 | LA-ICP-MS | 142±1 | 陶传忠等[ |
| GS22-2 | 白辛乡北西 | LA-ICP-MS | 129±3 | 陶传忠等[ |
| 08-41 | 突泉盆地 | 40Ar-39Ar | 138±3 | 李永飞等[ |
| L209 | 弈家沟 | LA-ICP-MS | 147±2 | 杨扬等[ |
| M036-1 | 盆地 | LA-ICP-MS | 158±1 | 孙德有等[ |
| M111-1 | 灵泉盆地 | LA-ICP-MS | 146±2 | 孙德有等[ |
| M080- | 大坝盆地 | LA-ICP-MS | 156±1 | 孙德有等[ |
| N4 | 柴河 | LA-ICP-MS | 135±2 | 李世超等[ |
| D3034-1 | 阿尔山 | LA-ICP-MS | 157±2 | 孙明坤等[ |
| D1204-1 | 阿尔山 | LA-ICP-MS | 152±1 | 孙明坤等[ |
表4 前人已开展的玛尼吐组火山岩同位素定年结果
Table 4 Previous dating results for the volcanic rocks in the Manitu Formation
| 样品号 | 采样点 | 定年方法 | 年龄/Ma | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS4 | 万宝乡北西 | LA-ICP-MS | 142±1 | 陶传忠等[ |
| GS22-2 | 白辛乡北西 | LA-ICP-MS | 129±3 | 陶传忠等[ |
| 08-41 | 突泉盆地 | 40Ar-39Ar | 138±3 | 李永飞等[ |
| L209 | 弈家沟 | LA-ICP-MS | 147±2 | 杨扬等[ |
| M036-1 | 盆地 | LA-ICP-MS | 158±1 | 孙德有等[ |
| M111-1 | 灵泉盆地 | LA-ICP-MS | 146±2 | 孙德有等[ |
| M080- | 大坝盆地 | LA-ICP-MS | 156±1 | 孙德有等[ |
| N4 | 柴河 | LA-ICP-MS | 135±2 | 李世超等[ |
| D3034-1 | 阿尔山 | LA-ICP-MS | 157±2 | 孙明坤等[ |
| D1204-1 | 阿尔山 | LA-ICP-MS | 152±1 | 孙明坤等[ |
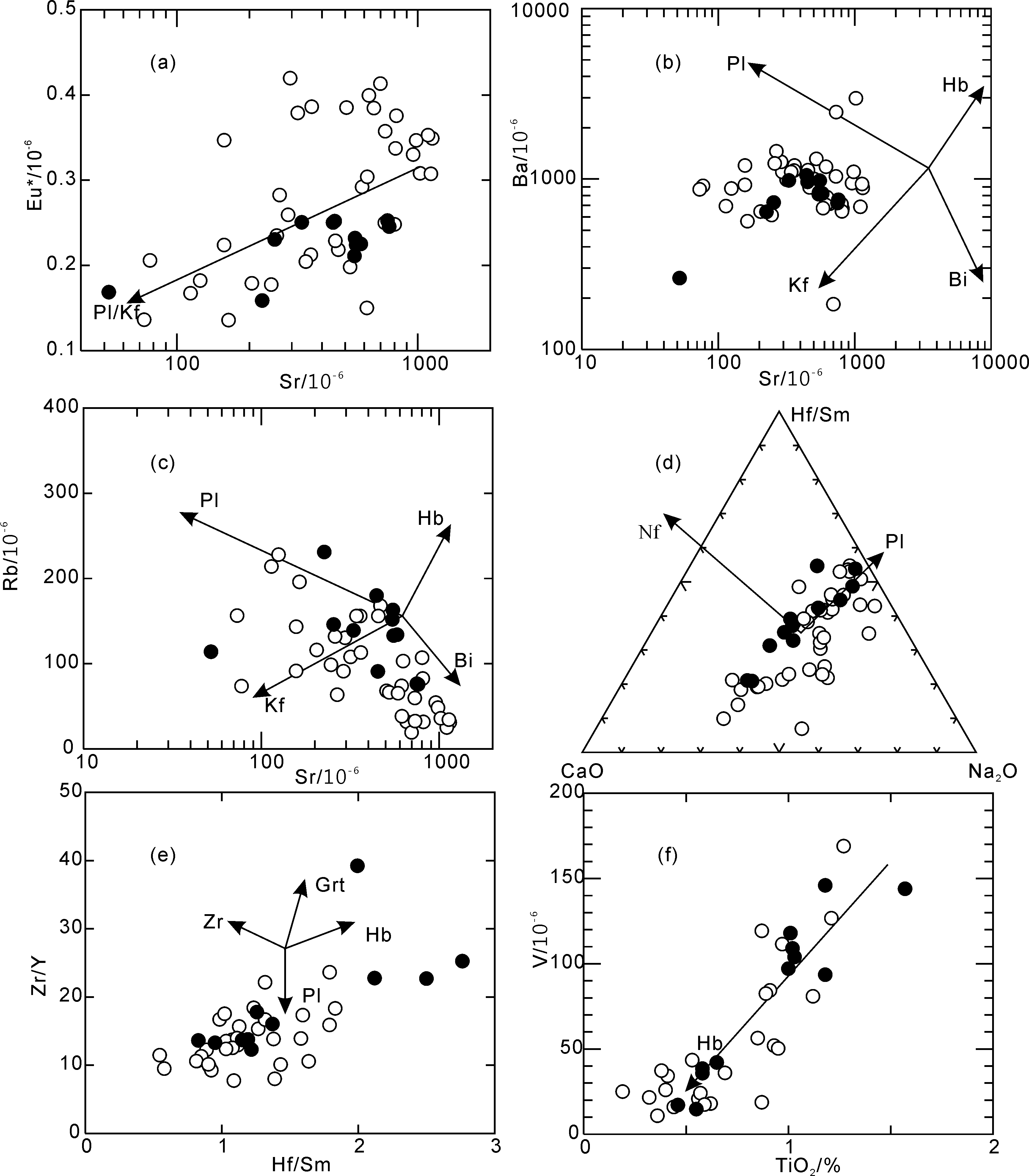
图8 Eu*-Sr (a)、Ba-Sr(b)、Rb-Sr(c)、Hf/Sm-CaO-Na2O(d)、 Zr/Y-Hf/Sm(e)和V-TiO2(f)图解(分离结晶趋势线据参考文献[4,48];Pl.斜长石;Hb.角闪石;Kf.钾性长石;Nf.钠长石;Bt.黑云母;Zr.锆石;Grt.石榴石)
Fig.8 Diagrams of Eu*-Sr(a), Ba-Sr(b), Rb-Sr(c), Hf/Sm-CaO-Na2O(d), Zr/Y-Hf/Sm(e) and V-TiO2 (f)
| [1] | 赵海玲, 邓晋福, 陈发景, 等. 中国东北地区中生代火山岩岩石学特征与盆地形成[J]. 现代地质, 1998, 12(1): 57-63. |
| [2] | 刘德来, 马莉. 中生代东亚大陆边缘构造演化[J]. 现代地质, 1997, 11(4): 37-44. |
| [3] |
WANG F, ZHOU X H, ZHANG L C, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing’an range (NE China): Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 251(1/2): 179-198.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GUO F, FAN W M, LI C W, et al. Early Cretaceous highly positive epsilon(Nd) felsic volcanic rocks from the Hinggan Mountains, NE China: origin and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 98(6): 1395-1411.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZHANG J H, GAO S, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing’an Range, northeastern China: Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3/4): 144-165.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 张昱, 赵焕力, 韩彦东. 大兴安岭北段塔栏沟组玄武岩地球化学及构造背景[J]. 地质与资源, 2005, 14(2): 87-91. |
| [7] | 聂立军, 贾海明, 王聪, 等. 大兴安岭中段白音高老组流纹岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(2): 296-304. |
| [8] | 孔元明. 内蒙古科右中旗地区早白垩世白音高老组酸性火山岩特征及形成的构造背景[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014:1-85. |
| [9] | 金玲, 杨伟红, 杨德明, 等. 内蒙古科右中旗地区梅勒图组安山岩年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(1): 48-58. |
| [10] | 陶传忠, 李伫民, 王大千, 等. 乌兰浩特地区玛尼吐组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2015, 24(2): 102-109. |
| [11] | 张学斌, 周长红, 来林, 等. 锡林浩特东部早白垩世白音高老组岩石地球化学特征、LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(2): 290-302. |
| [12] | 肖中军, 王振强, 吴煜, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗白音乌拉北部白音高老组时代重新厘定——来自LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(9): 1706-1714. |
| [13] | 刘宴文, 邵永旭, 许燕. 内蒙古昌德敖包一带大磨拐河组层序特征及其化石组合[J]. 西部资源, 2015(3): 167-169. |
| [14] | 黄猛. 内蒙古西乌旗地区白音高老组火山岩地球化学特征及其构造环境[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014:1-105. |
| [15] | 姜云鹏. 内蒙古呼伦贝尔北部中生代火山岩地层的划分及其成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013:1-108. |
| [16] | 邵积东, 王慧, 张梅, 等. 内蒙古大地构造单元划分及其地质特征[J]. 西部资源, 2011(2): 51-56. |
| [17] | 王根厚, 张长厚, 王果胜, 等. 辽西地区中生代构造格局及其形成演化[J]. 现代地质, 2001, 15(1): 1-7. |
| [18] | 丁秋红, 李晓海, 姚玉来, 等. 内蒙古扎鲁特旗地区中侏罗统塔木兰沟组的厘定[J]. 地质与资源, 2015, 24(5): 402-407. |
| [19] | 赵忠华, 孙德有, 苟军, 等. 满洲里南部塔木兰沟组火山岩年代学与地球化学[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(6): 1865-1880. |
| [20] | 李鹏川, 李世超, 刘正宏, 等. 内蒙古林西地区满克头鄂博组火山岩形成时代及构造环境[J]. 世界地质, 2016, 35(1): 77-88. |
| [21] | 王刚, 孙国胜, 张超, 等. 内蒙古敖汉旗晚侏罗世满克头鄂博组火山岩地球化学特征及构造背景分析[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(2): 354-361. |
| [22] | 李东瀚, 王晓晗, 杨仲杰. 中侏罗世满克头鄂博组火山岩地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 科技资讯, 2015(17): 211-212. |
| [23] | 张超, 杨伟红, 和钟铧, 等. 大兴安岭中南段塔尔气地区满克头鄂博组流纹岩年代学和地球化学研究[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(2): 255-265. |
| [24] | 林琛. 内蒙古太仆寺旗晚侏罗世火山岩岩石学及成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009:1-118. |
| [25] |
司秋亮, 崔天日, 王恩德, 等. 大兴安岭柴河白音高老组流纹岩锆石U-Pb定年及成因探讨[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(3): 412-415.
DOI |
| [26] | 张乐彤, 李世超, 赵庆英, 等. 大兴安岭中段白音高老组火山岩的形成时代及地球化学特征[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(1): 44-54. |
| [27] | 王雄, 陈跃军, 李勇, 等. 大兴安岭中北段塔尔气地区早白垩世白音高老组火山岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(1): 25-33. |
| [28] | 金玲. 内蒙古科右中旗地区梅勒图组火山岩特征及意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014:1-85. |
| [29] | 员庥宇. 大兴安岭中段塔尔气地区中侏罗世花岗岩岩石成因及构造背景[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014:1-75. |
| [30] |
ZHANG J H, GE W C, WU F Y, et al. Large-scale early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing’an Range, northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2): 138-157.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DONG Y, GE W C, YANG H, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks from the Baiyingaolao Formation in the central Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2014, 205: 168-184.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECHEISEN A, et al. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27: 745-750.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
RICKWOOD P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: implication for mantle composition and process[J]. Geological Society, London,Special Publications, 1989, 42(SI): 313-345.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 司秋亮, 崔天日, 唐振, 等. 大兴安岭中段柴河地区玛尼吐组火山岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(2): 389-403. |
| [36] | 孙德有, 苟军, 任云生, 等. 满洲里南部玛尼吐组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(10): 3083-3094. |
| [37] | 王杰, 陈树旺, 丁秋红. 内蒙古突泉盆地中侏罗统万宝组碎屑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、地球化学特征及对源区的制约[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(8): 1224-1235. |
| [38] | 宝音乌力吉, 苏茂荣, 谭强, 等. 内蒙古满洲里西中蒙边境一带中侏罗统万宝组的厘定[J]. 地质与资源, 2011, 20(1): 12-15. |
| [39] | 李永飞, 郜晓勇, 孙守亮. 大兴安岭中段突泉盆地玛尼吐组火山岩地球化学特征与40Ar/39Ar测年[J]. 地质与资源, 2013, 22(6): 444-451. |
| [40] | 杨扬, 高福红, 陈井胜, 等. 赤峰地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(增刊): 257-268. |
| [41] | 李世超, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 等. 大兴安岭中段玛尼吐组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(增刊): 399-407. |
| [42] | 孙明坤, 郝晓飞, 宋海瑞. 浅析内蒙古阿尔山地区玛尼吐组火山岩地球化学特征[R]. 哈尔滨: 中国核学会学术年会, 2013:1-100. |
| [43] | 王瑜. 晚古生代末—中生代内蒙古—燕山地区造山过程中的岩浆热事件与构造演化[J]. 现代地质, 1996, 10(1): 67-76. |
| [44] |
BARTH A P, WOODE J L, TOSDAL R M, et al. Crustal contamination in the petrogenesis of a calc-alkalic rock series-Josephine Mountain intrusion, California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1995, 107(2): 201-212.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
RAPP R P, WARSON E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32-kbar-implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
PECCERILLO A, BARBERIO M R, YIRGU G, et al. Relationships between mafic and peralkaline silicic magmatism in continental rift settings: A petrological, geochemical and isotopic study of the Gedemsa volcano, central Ethiopian rift[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(11): 2003-2032.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
LITVAK V D, POMA S. Geochemistry of mafic Paleocene volcanic rocks in the Valle del Cura region: Implications for the petrogenesis of primary mantle-derived melts over the Pampean flat-slab[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2010, 29(3): 705-716.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
GUO F, FAN W M, LI C W, et al. Multi-stage crust-mantle interaction in SE China: Temporal, thermal and compositional constraints from the Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks in eastern Guangdong-Fujian provinces[J]. Lithos, 2012, 150: 62-84.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
PEARCE J. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19(4): 120-125.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace-element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic-rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
WOOD D A. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary volcanic province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1): 11-30.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李柱, 张德会, 杨帆, 刘向冲. 等距对数比变换及混合分布在区域化探数据分析中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 662-673. |
| [2] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [3] | 陈宇航, 张新涛, 余一欣, 杨帆, 柳永军, 张震, 丁康. 渤中凹陷北部中生界顶面断层破碎带量化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1035-1042. |
| [4] | 杨维刚, 李永胜, 李通元, 张俊, 任鹏飞. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世板块碰撞事件的记录:来自合作地区火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1691-1701. |
| [5] | 陈澍民, 缪宇, 廖驾, 贺前平, 成明, 张珍力, 吴绍安, 章志明. 中拉萨地块南缘孔隆晚白垩世火山岩成因及对地壳演化的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1713-1726. |
| [6] | 赵保具, 张艳飞, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 大兴安岭中段有色金属矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1380-1396. |
| [7] | 潘力, 何青林, 梁生贤, 陈先洁, 陈文, 谢光华, 黎洋, 夏青, 马乾. 基于正演模拟的火山岩重磁响应特征研究:以川西地区二叠系为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1471-1479. |
| [8] | 杨元江, 李成禄, 邓昌州, 李文龙, 张立, 赵忠海, 赵寒冬. 大兴安岭大洋山钼矿成矿岩体地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及构造背景[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1092-1102. |
| [9] | 毛翔, 罗璐, 汪新伟, 国殿斌. 渤海湾盆地新生代火山岩分布特征及其地热勘探潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 858-864. |
| [10] | 王迪, 赵国春, 苏尚国, 李宏星. 大兴安岭南段晚中生代侵入岩时空分布及主脊与东坡岩体特征对比[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 466-482. |
| [11] | 柴云, 赵娟, 李德彪, 马正婷, 安朝, 魏有宁, 王成勇. 南祁连擦勒特地区志留纪巴龙贡嘎尔组火山岩地球化学特征及其地质意义(撤回)[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 64-73. |
| [12] | 周能武, 陈邦学, 邓中飞, 桑明帅, 白权金. 喀拉昆仑火烧云一带早侏罗世双峰式火山岩的发现及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 990-1002. |
| [13] | 许锋, 朱增伍, 李长春, 杨治国. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组长7段厚层熔结凝灰岩特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 389-400. |
| [14] | 徐立明, 王大可, 刘玉, 郑吉林, 张文强, 梁中恺. 大兴安岭北段塔河南部早白垩世侵入岩年代学和地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1212-1226. |
| [15] | 毛艳丽, 王滔, 李鸿睿, 潘中奎. 甘肃省文县刘家坪蓟县系变基性火山岩地球化学特征及构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1254-1262. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||