



现代地质 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (02): 234-245.
李研1,2( ), 王建1(
), 王建1( ), 孙德有1, 陈德兵2, 韩志滨2, 崔家瑞2
), 孙德有1, 陈德兵2, 韩志滨2, 崔家瑞2
收稿日期:2016-05-11
修回日期:2016-10-15
出版日期:2017-04-10
发布日期:2017-04-25
通讯作者:
王 建,男,教授,博士生导师,1963年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事岩石地球化学研究。 Email: 作者简介:李 研,男,硕士研究生,1990年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事岩石地球化学研究。Email: 1483792423@qq.com。
基金资助:
LI Yan1,2( ), WANG Jian1(
), WANG Jian1( ), SUN Deyou1, CHEN Debing2, HAN Zhibin2, CUI Jiarui2
), SUN Deyou1, CHEN Debing2, HAN Zhibin2, CUI Jiarui2
Received:2016-05-11
Revised:2016-10-15
Online:2017-04-10
Published:2017-04-25
摘要:
内蒙古海拉尔北部八大关地区花岗岩以正长花岗岩和二长花岗岩为主,锆石U-Pb定年显示其形成于晚三叠世((212±1.7)~(226.7±1.6) Ma)。岩石为弱过铝质(A/CNK=1.01~1.10),分异指数(DI)介于92.5~95.8之间。岩石大离子亲石元素K和Rb以及LREE相对富集,高场强元素Nb、Ta、P、Ti 和Ba、Sr相对亏损,并显示中等铕负异常(δEu=0.51~0.71)。较低的10 000 Ga/Al值(平均1.91)以及较低的锆石饱和温度(平均683 ℃)等特征显示该花岗岩属于高分异Ⅰ型。锆石的εHf(t)值较高(4.50~10.45),Hf二阶段模式年龄为0.59~0.97 Ga,反映其源区物质为新元古代增生的基性地壳。综合区域其他地质研究成果,认为研究区晚三叠世花岗岩形成于蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋板块俯冲的活动大陆边缘环境。
中图分类号:
李研, 王建, 孙德有, 陈德兵, 韩志滨, 崔家瑞. 内蒙古海拉尔北部八大关地区花岗岩的成岩时代、地球化学特征与成因[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 234-245.
LI Yan, WANG Jian, SUN Deyou, CHEN Debing, HAN Zhibin, CUI Jiarui. Age,Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Granites from Badaguan Area in Northern Hailaer, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(02): 234-245.

图2 八大关地区花岗岩野外和显微结构照片(Q.石英;kf.钾长石;pl.斜长石) a.二长花岗岩(单偏光);b.正长花岗岩(单偏光);c.正长花岗岩野外照片;d.二长花岗岩野外照片
Fig.2 Field and microstructure photographs of granites in Badaguan
| 样品测点 | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 比值 | ±1σ | 比值 | ±1σ | 比值 | ±1σ | 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | ||||||
| Zr3-01 | 0.97 | 0.051 00 | 0.002 22 | 0.253 39 | 0.010 64 | 0.036 04 | 0.000 44 | 229 | 9 | 228 | 3 | ||||
| Zr3-02 | 0.98 | 0.052 96 | 0.001 15 | 0.257 38 | 0.005 20 | 0.035 24 | 0.000 31 | 233 | 4 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-03 | 0.80 | 0.052 90 | 0.001 10 | 0.259 09 | 0.005 02 | 0.035 52 | 0.000 30 | 234 | 4 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-04 | 0.70 | 0.051 27 | 0.001 41 | 0.249 08 | 0.006 52 | 0.035 24 | 0.000 33 | 226 | 5 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-05 | 0.59 | 0.050 57 | 0.004 90 | 0.254 33 | 0.024 03 | 0.036 47 | 0.000 83 | 230 | 19 | 231 | 5 | ||||
| Zr3-07 | 0.75 | 0.052 84 | 0.001 96 | 0.256 38 | 0.009 15 | 0.035 19 | 0.000 39 | 232 | 7 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-09 | 0.79 | 0.050 49 | 0.001 26 | 0.254 29 | 0.006 02 | 0.036 53 | 0.000 33 | 230 | 5 | 231 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-10 | 0.52 | 0.051 18 | 0.001 38 | 0.256 46 | 0.006 59 | 0.036 34 | 0.000 34 | 232 | 5 | 230 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-11 | 0.66 | 0.051 97 | 0.001 63 | 0.255 76 | 0.007 66 | 0.035 69 | 0.000 36 | 231 | 6 | 226 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-12 | 0.92 | 0.050 57 | 0.000 93 | 0.252 22 | 0.004 27 | 0.036 17 | 0.000 30 | 228 | 3 | 229 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-13 | 0.67 | 0.051 56 | 0.001 01 | 0.258 19 | 0.004 69 | 0.036 32 | 0.000 30 | 233 | 4 | 230 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-16 | 0.62 | 0.050 92 | 0.001 30 | 0.254 07 | 0.006 13 | 0.036 18 | 0.000 33 | 230 | 5 | 229 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-17 | 0.79 | 0.051 08 | 0.001 02 | 0.255 28 | 0.004 74 | 0.036 24 | 0.000 30 | 231 | 4 | 229 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-18 | 0.60 | 0.050 76 | 0.001 09 | 0.251 18 | 0.005 03 | 0.035 89 | 0.000 31 | 228 | 4 | 227 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-19 | 1.11 | 0.051 50 | 0.001 27 | 0.249 19 | 0.005 81 | 0.035 09 | 0.000 32 | 226 | 5 | 222 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-20 | 1.13 | 0.051 92 | 0.000 96 | 0.254 64 | 0.004 34 | 0.035 57 | 0.000 29 | 230 | 4 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-01 | 0.86 | 0.050 79 | 0.000 80 | 0.249 07 | 0.003 56 | 0.035 53 | 0.000 29 | 215 | 5 | 224 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-02 | 0.50 | 0.050 49 | 0.001 06 | 0.244 99 | 0.004 81 | 0.035 16 | 0.000 31 | 229 | 5 | 220 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-03 | 0.90 | 0.051 12 | 0.001 67 | 0.247 82 | 0.007 77 | 0.035 13 | 0.000 37 | 226 | 3 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-05 | 0.82 | 0.052 85 | 0.002 13 | 0.258 17 | 0.010 06 | 0.035 40 | 0.000 42 | 221 | 3 | 222 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-06 | 0.83 | 0.057 19 | 0.001 99 | 0.254 76 | 0.008 51 | 0.032 29 | 0.000 36 | 226 | 3 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-07 | 0.79 | 0.051 22 | 0.000 88 | 0.248 85 | 0.003 90 | 0.035 22 | 0.000 29 | 222 | 4 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-08 | 0.93 | 0.052 30 | 0.001 15 | 0.252 78 | 0.005 18 | 0.035 04 | 0.000 30 | 225 | 6 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-09 | 1.25 | 0.051 43 | 0.001 31 | 0.240 67 | 0.005 79 | 0.033 93 | 0.000 31 | 223 | 5 | 226 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-12 | 1.06 | 0.052 53 | 0.001 78 | 0.257 42 | 0.008 35 | 0.035 55 | 0.000 37 | 226 | 3 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-13 | 0.77 | 0.050 62 | 0.002 56 | 0.234 03 | 0.011 45 | 0.033 55 | 0.000 45 | 229 | 4 | 222 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-14 | 0.91 | 0.050 82 | 0.001 46 | 0.236 36 | 0.006 45 | 0.033 75 | 0.000 32 | 219 | 5 | 215 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-15 | 1.21 | 0.050 83 | 0.001 94 | 0.235 78 | 0.008 69 | 0.033 67 | 0.000 37 | 225 | 6 | 216 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-16 | 0.79 | 0.050 79 | 0.000 80 | 0.249 07 | 0.003 56 | 0.035 53 | 0.000 29 | 223 | 7 | 217 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-17 | 0.63 | 0.050 49 | 0.001 06 | 0.244 99 | 0.004 81 | 0.035 16 | 0.000 31 | 233 | 7 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-18 | 0.79 | 0.051 12 | 0.001 67 | 0.247 82 | 0.007 77 | 0.035 13 | 0.000 37 | 214 | 9 | 213 | 3 | ||||
| Zr4-19 | 0.97 | 0.050 04 | 0.001 34 | 0.245 92 | 0.006 28 | 0.035 62 | 0.000 34 | 215 | 5 | 214 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-20 | 0.80 | 0.052 85 | 0.002 13 | 0.258 17 | 0.010 06 | 0.035 40 | 0.000 42 | 215 | 7 | 213 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-01 | 0.93 | 0.052 69 | 0.000 78 | 0.242 61 | 0.003 13 | 0.033 52 | 0.000 25 | 223 | 2 | 219 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-02 | 0.96 | 0.058 57 | 0.001 03 | 0.279 42 | 0.004 40 | 0.034 73 | 0.000 28 | 226 | 4 | 220 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-03 | 0.80 | 0.050 79 | 0.001 00 | 0.232 43 | 0.004 21 | 0.033 33 | 0.000 27 | 221 | 3 | 213 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-05 | 1.06 | 0.062 57 | 0.003 99 | 0.309 17 | 0.019 33 | 0.035 84 | 0.000 46 | 212 | 3 | 211 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-09 | 0.52 | 0.051 68 | 0.001 39 | 0.235 71 | 0.006 01 | 0.033 28 | 0.000 31 | 221 | 5 | 215 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-11 | 0.85 | 0.052 39 | 0.001 43 | 0.237 71 | 0.006 16 | 0.033 13 | 0.000 31 | 215 | 5 | 211 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-12 | 0.99 | 0.051 99 | 0.000 95 | 0.246 14 | 0.004 10 | 0.034 58 | 0.000 28 | 208 | 5 | 209 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-13 | 0.62 | 0.064 64 | 0.001 81 | 0.318 47 | 0.008 40 | 0.035 99 | 0.000 36 | 217 | 5 | 210 | 2 | ||||
| ZR4-14 | 0.92 | 0.051 82 | 0.001 10 | 0.240 81 | 0.004 74 | 0.033 96 | 0.000 29 | 223 | 3 | 219 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-16 | 0.94 | 0.054 75 | 0.001 49 | 0.220 75 | 0.005 69 | 0.029 48 | 0.000 28 | 219 | 4 | 215 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-19 | 0.93 | 0.052 69 | 0.000 78 | 0.242 61 | 0.003 13 | 0.033 52 | 0.000 25 | 216 | 4 | 218 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-20 | 0.96 | 0.058 57 | 0.001 03 | 0.279 42 | 0.004 40 | 0.034 73 | 0.000 28 | 213 | 3 | 216 | 2 | ||||
表1 八大关地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating results for granites in Badaguan
| 样品测点 | Th/U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 比值 | ±1σ | 比值 | ±1σ | 比值 | ±1σ | 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | 年龄/Ma | ±1σ | ||||||
| Zr3-01 | 0.97 | 0.051 00 | 0.002 22 | 0.253 39 | 0.010 64 | 0.036 04 | 0.000 44 | 229 | 9 | 228 | 3 | ||||
| Zr3-02 | 0.98 | 0.052 96 | 0.001 15 | 0.257 38 | 0.005 20 | 0.035 24 | 0.000 31 | 233 | 4 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-03 | 0.80 | 0.052 90 | 0.001 10 | 0.259 09 | 0.005 02 | 0.035 52 | 0.000 30 | 234 | 4 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-04 | 0.70 | 0.051 27 | 0.001 41 | 0.249 08 | 0.006 52 | 0.035 24 | 0.000 33 | 226 | 5 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-05 | 0.59 | 0.050 57 | 0.004 90 | 0.254 33 | 0.024 03 | 0.036 47 | 0.000 83 | 230 | 19 | 231 | 5 | ||||
| Zr3-07 | 0.75 | 0.052 84 | 0.001 96 | 0.256 38 | 0.009 15 | 0.035 19 | 0.000 39 | 232 | 7 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-09 | 0.79 | 0.050 49 | 0.001 26 | 0.254 29 | 0.006 02 | 0.036 53 | 0.000 33 | 230 | 5 | 231 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-10 | 0.52 | 0.051 18 | 0.001 38 | 0.256 46 | 0.006 59 | 0.036 34 | 0.000 34 | 232 | 5 | 230 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-11 | 0.66 | 0.051 97 | 0.001 63 | 0.255 76 | 0.007 66 | 0.035 69 | 0.000 36 | 231 | 6 | 226 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-12 | 0.92 | 0.050 57 | 0.000 93 | 0.252 22 | 0.004 27 | 0.036 17 | 0.000 30 | 228 | 3 | 229 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-13 | 0.67 | 0.051 56 | 0.001 01 | 0.258 19 | 0.004 69 | 0.036 32 | 0.000 30 | 233 | 4 | 230 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-16 | 0.62 | 0.050 92 | 0.001 30 | 0.254 07 | 0.006 13 | 0.036 18 | 0.000 33 | 230 | 5 | 229 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-17 | 0.79 | 0.051 08 | 0.001 02 | 0.255 28 | 0.004 74 | 0.036 24 | 0.000 30 | 231 | 4 | 229 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-18 | 0.60 | 0.050 76 | 0.001 09 | 0.251 18 | 0.005 03 | 0.035 89 | 0.000 31 | 228 | 4 | 227 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-19 | 1.11 | 0.051 50 | 0.001 27 | 0.249 19 | 0.005 81 | 0.035 09 | 0.000 32 | 226 | 5 | 222 | 2 | ||||
| Zr3-20 | 1.13 | 0.051 92 | 0.000 96 | 0.254 64 | 0.004 34 | 0.035 57 | 0.000 29 | 230 | 4 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-01 | 0.86 | 0.050 79 | 0.000 80 | 0.249 07 | 0.003 56 | 0.035 53 | 0.000 29 | 215 | 5 | 224 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-02 | 0.50 | 0.050 49 | 0.001 06 | 0.244 99 | 0.004 81 | 0.035 16 | 0.000 31 | 229 | 5 | 220 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-03 | 0.90 | 0.051 12 | 0.001 67 | 0.247 82 | 0.007 77 | 0.035 13 | 0.000 37 | 226 | 3 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-05 | 0.82 | 0.052 85 | 0.002 13 | 0.258 17 | 0.010 06 | 0.035 40 | 0.000 42 | 221 | 3 | 222 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-06 | 0.83 | 0.057 19 | 0.001 99 | 0.254 76 | 0.008 51 | 0.032 29 | 0.000 36 | 226 | 3 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-07 | 0.79 | 0.051 22 | 0.000 88 | 0.248 85 | 0.003 90 | 0.035 22 | 0.000 29 | 222 | 4 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-08 | 0.93 | 0.052 30 | 0.001 15 | 0.252 78 | 0.005 18 | 0.035 04 | 0.000 30 | 225 | 6 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-09 | 1.25 | 0.051 43 | 0.001 31 | 0.240 67 | 0.005 79 | 0.033 93 | 0.000 31 | 223 | 5 | 226 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-12 | 1.06 | 0.052 53 | 0.001 78 | 0.257 42 | 0.008 35 | 0.035 55 | 0.000 37 | 226 | 3 | 223 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-13 | 0.77 | 0.050 62 | 0.002 56 | 0.234 03 | 0.011 45 | 0.033 55 | 0.000 45 | 229 | 4 | 222 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-14 | 0.91 | 0.050 82 | 0.001 46 | 0.236 36 | 0.006 45 | 0.033 75 | 0.000 32 | 219 | 5 | 215 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-15 | 1.21 | 0.050 83 | 0.001 94 | 0.235 78 | 0.008 69 | 0.033 67 | 0.000 37 | 225 | 6 | 216 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-16 | 0.79 | 0.050 79 | 0.000 80 | 0.249 07 | 0.003 56 | 0.035 53 | 0.000 29 | 223 | 7 | 217 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-17 | 0.63 | 0.050 49 | 0.001 06 | 0.244 99 | 0.004 81 | 0.035 16 | 0.000 31 | 233 | 7 | 225 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-18 | 0.79 | 0.051 12 | 0.001 67 | 0.247 82 | 0.007 77 | 0.035 13 | 0.000 37 | 214 | 9 | 213 | 3 | ||||
| Zr4-19 | 0.97 | 0.050 04 | 0.001 34 | 0.245 92 | 0.006 28 | 0.035 62 | 0.000 34 | 215 | 5 | 214 | 2 | ||||
| Zr4-20 | 0.80 | 0.052 85 | 0.002 13 | 0.258 17 | 0.010 06 | 0.035 40 | 0.000 42 | 215 | 7 | 213 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-01 | 0.93 | 0.052 69 | 0.000 78 | 0.242 61 | 0.003 13 | 0.033 52 | 0.000 25 | 223 | 2 | 219 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-02 | 0.96 | 0.058 57 | 0.001 03 | 0.279 42 | 0.004 40 | 0.034 73 | 0.000 28 | 226 | 4 | 220 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-03 | 0.80 | 0.050 79 | 0.001 00 | 0.232 43 | 0.004 21 | 0.033 33 | 0.000 27 | 221 | 3 | 213 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-05 | 1.06 | 0.062 57 | 0.003 99 | 0.309 17 | 0.019 33 | 0.035 84 | 0.000 46 | 212 | 3 | 211 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-09 | 0.52 | 0.051 68 | 0.001 39 | 0.235 71 | 0.006 01 | 0.033 28 | 0.000 31 | 221 | 5 | 215 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-11 | 0.85 | 0.052 39 | 0.001 43 | 0.237 71 | 0.006 16 | 0.033 13 | 0.000 31 | 215 | 5 | 211 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-12 | 0.99 | 0.051 99 | 0.000 95 | 0.246 14 | 0.004 10 | 0.034 58 | 0.000 28 | 208 | 5 | 209 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-13 | 0.62 | 0.064 64 | 0.001 81 | 0.318 47 | 0.008 40 | 0.035 99 | 0.000 36 | 217 | 5 | 210 | 2 | ||||
| ZR4-14 | 0.92 | 0.051 82 | 0.001 10 | 0.240 81 | 0.004 74 | 0.033 96 | 0.000 29 | 223 | 3 | 219 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-16 | 0.94 | 0.054 75 | 0.001 49 | 0.220 75 | 0.005 69 | 0.029 48 | 0.000 28 | 219 | 4 | 215 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-19 | 0.93 | 0.052 69 | 0.000 78 | 0.242 61 | 0.003 13 | 0.033 52 | 0.000 25 | 216 | 4 | 218 | 2 | ||||
| Zr24-20 | 0.96 | 0.058 57 | 0.001 03 | 0.279 42 | 0.004 40 | 0.034 73 | 0.000 28 | 213 | 3 | 216 | 2 | ||||
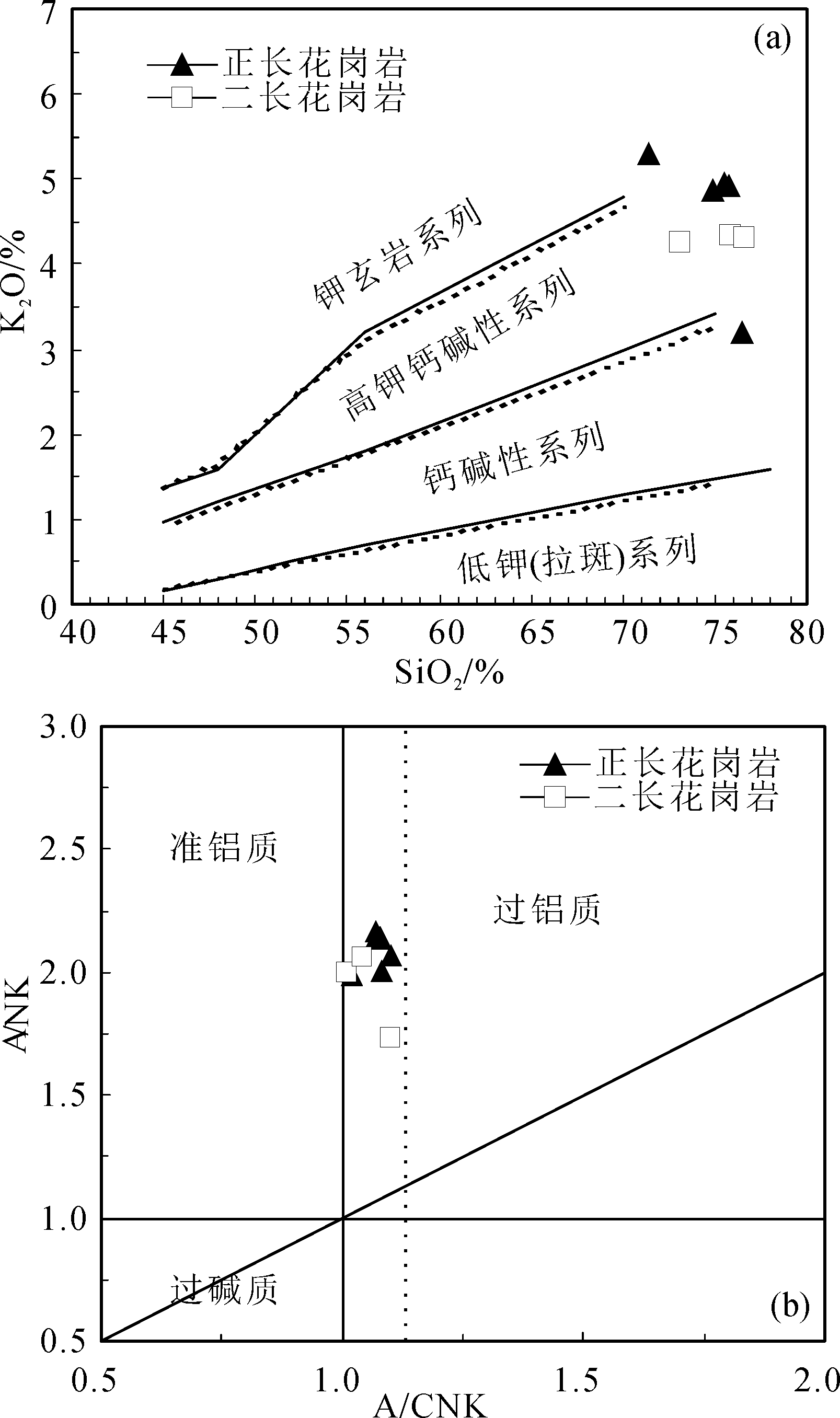
图5 八大关地区花岗岩SiO2-K2O(a)与A/CNK-A/NK图解(b)(底图据参考文献[19])
Fig.5 The SiO2-K2O (a) and A/CNK-A/NK diagrams(b) for granites of Badaguan(base map after reference[19])
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 74.85 | 0.26 | 13.33 | 1.2 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.87 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 71.34 | 0.29 | 15.61 | 0.96 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.37 | 4.71 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 75.82 | 0.26 | 13.12 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 3.82 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 76.41 | 0.15 | 10.86 | 2.49 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.44 | 3.39 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 75.53 | 0.15 | 12.83 | 1.46 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 3.68 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 77.75 | 0.13 | 10.99 | 2.55 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 3.92 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.86 | 0.14 | 11.78 | 2.12 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.62 | 3.67 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.64 | 0.16 | 11.77 | 1.73 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 3.55 |
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | AKI | Mg# |
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 4.88 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 100.75 | 8.75 | 1.26 | 1.08 | 0.88 | 0.25 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 5.29 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 99.98 | 10.00 | 1.12 | 1.10 | 0.87 | 0.22 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 4.92 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 100.56 | 8.74 | 1.29 | 1.07 | 0.89 | 0.20 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.98 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 101.34 | 7.37 | 1.17 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 0.18 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 4.95 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 101.19 | 8.63 | 1.35 | 1.07 | 0.93 | 0.11 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 2.67 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 101.86 | 6.59 | 0.68 | 1.10 | 0.86 | 0.22 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 4.34 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 101.85 | 8.01 | 1.18 | 1.01 | 0.92 | 0.21 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 4.31 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 101.46 | 5.57 | 1.21 | 1.04 | 0.92 | 0.24 |
表2 八大关地区花岗岩主量元素分析测试结果(wB/%)
Table 2 The compositions of major elements of granites in Badaguan(%)
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 74.85 | 0.26 | 13.33 | 1.2 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.87 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 71.34 | 0.29 | 15.61 | 0.96 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.37 | 4.71 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 75.82 | 0.26 | 13.12 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 3.82 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 76.41 | 0.15 | 10.86 | 2.49 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.44 | 3.39 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 75.53 | 0.15 | 12.83 | 1.46 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 3.68 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 77.75 | 0.13 | 10.99 | 2.55 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 3.92 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 75.86 | 0.14 | 11.78 | 2.12 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.62 | 3.67 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 76.64 | 0.16 | 11.77 | 1.73 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 3.55 |
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | AKI | Mg# |
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 4.88 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 100.75 | 8.75 | 1.26 | 1.08 | 0.88 | 0.25 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 5.29 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 99.98 | 10.00 | 1.12 | 1.10 | 0.87 | 0.22 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 4.92 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 100.56 | 8.74 | 1.29 | 1.07 | 0.89 | 0.20 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 3.98 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 101.34 | 7.37 | 1.17 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 0.18 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 4.95 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 101.19 | 8.63 | 1.35 | 1.07 | 0.93 | 0.11 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 2.67 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 101.86 | 6.59 | 0.68 | 1.10 | 0.86 | 0.22 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 4.34 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 101.85 | 8.01 | 1.18 | 1.01 | 0.92 | 0.21 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 4.31 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 101.46 | 5.57 | 1.21 | 1.04 | 0.92 | 0.24 |
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 28.9 | 57.0 | 6.96 | 24.3 | 4.38 | 0.85 | 3.58 | 0.61 | 3.47 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 23.6 | 49.2 | 5.93 | 20.5 | 3.36 | 0.67 | 2.72 | 0.41 | 2.30 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 52.5 | 72.1 | 8.99 | 32.7 | 5.93 | 0.93 | 4.98 | 0.86 | 5.07 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 40.0 | 71.1 | 8.01 | 25.1 | 3.47 | 0.79 | 3.26 | 0.37 | 1.83 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 29.0 | 58.1 | 7.55 | 25.7 | 5.05 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 0.64 | 3.59 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 42.1 | 71.7 | 8.38 | 25.9 | 3.77 | 0.78 | 3.58 | 0.45 | 2.41 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 40.7 | 74.3 | 8.74 | 27.4 | 4.06 | 0.71 | 3.61 | 0.45 | 2.23 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 35.7 | 61.1 | 7.41 | 24.8 | 3.84 | 0.71 | 3.18 | 0.39 | 1.95 |
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREEE |
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.71 | 2.17 | 0.40 | 2.68 | 0.39 | 136.42 | 122.40 | 14.02 | 8.73 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.45 | 1.33 | 0.23 | 1.48 | 0.26 | 112.37 | 103.19 | 9.18 | 11.24 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 1.02 | 2.98 | 0.51 | 3.34 | 0.48 | 193.13 | 173.88 | 19.25 | 9.03 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.13 | 0.91 | 0.15 | 156.36 | 148.45 | 7.91 | 18.77 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.69 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 2.32 | 0.35 | 140.63 | 126.53 | 14.12 | 8.97 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.42 | 1.42 | 0.22 | 1.61 | 0.25 | 162.89 | 152.54 | 10.35 | 14.74 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.34 | 1.07 | 0.12 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 164.75 | 155.93 | 8.82 | 17.68 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.31 | 1.04 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.16 | 141.66 | 133.54 | 8.12 | 16.44 |
表3 八大关地区花岗岩稀土元素分析测试结果(wB/10-6)
Table 3 The compositions of rare earth elements of granites in Badaguan(10-6 )
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 28.9 | 57.0 | 6.96 | 24.3 | 4.38 | 0.85 | 3.58 | 0.61 | 3.47 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 23.6 | 49.2 | 5.93 | 20.5 | 3.36 | 0.67 | 2.72 | 0.41 | 2.30 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 52.5 | 72.1 | 8.99 | 32.7 | 5.93 | 0.93 | 4.98 | 0.86 | 5.07 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 40.0 | 71.1 | 8.01 | 25.1 | 3.47 | 0.79 | 3.26 | 0.37 | 1.83 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 29.0 | 58.1 | 7.55 | 25.7 | 5.05 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 0.64 | 3.59 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 42.1 | 71.7 | 8.38 | 25.9 | 3.77 | 0.78 | 3.58 | 0.45 | 2.41 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 40.7 | 74.3 | 8.74 | 27.4 | 4.06 | 0.71 | 3.61 | 0.45 | 2.23 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 35.7 | 61.1 | 7.41 | 24.8 | 3.84 | 0.71 | 3.18 | 0.39 | 1.95 |
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREEE |
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.71 | 2.17 | 0.40 | 2.68 | 0.39 | 136.42 | 122.40 | 14.02 | 8.73 |
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.45 | 1.33 | 0.23 | 1.48 | 0.26 | 112.37 | 103.19 | 9.18 | 11.24 |
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 1.02 | 2.98 | 0.51 | 3.34 | 0.48 | 193.13 | 173.88 | 19.25 | 9.03 |
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.13 | 0.91 | 0.15 | 156.36 | 148.45 | 7.91 | 18.77 |
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.69 | 2.21 | 0.32 | 2.32 | 0.35 | 140.63 | 126.53 | 14.12 | 8.97 |
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.42 | 1.42 | 0.22 | 1.61 | 0.25 | 162.89 | 152.54 | 10.35 | 14.74 |
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.34 | 1.07 | 0.12 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 164.75 | 155.93 | 8.82 | 17.68 |
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.31 | 1.04 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.16 | 141.66 | 133.54 | 8.12 | 16.44 |
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | Ga | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Sr | Zr | Hf | Y | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 14.40 | 172.0 | 729 | 18.5 | 0.85 | 9.50 | 0.90 | 102.0 | 168.0 | 7.50 | 2.68 | ||||||||||||
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 16.20 | 138.0 | 708 | 14.8 | 0.67 | 11.70 | 0.92 | 79.1 | 183.0 | 8.90 | 1.48 | ||||||||||||
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 15.40 | 177.0 | 656 | 15.4 | 0.93 | 9.61 | 0.75 | 81.9 | 168.0 | 7.84 | 3.34 | ||||||||||||
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 12.90 | 115.0 | 507 | 17.6 | 0.79 | 7.16 | 0.68 | 154.0 | 49.0 | 8.22 | 0.92 | ||||||||||||
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 12.70 | 152.0 | 454 | 16.4 | 1.00 | 10.70 | 0.97 | 78.6 | 115.0 | 8.87 | 2.32 | ||||||||||||
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 9.05 | 58.8 | 374 | 12.6 | 0.78 | 6.75 | 0.67 | 94.1 | 50.0 | 7.45 | 1.61 | ||||||||||||
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 11.50 | 127.0 | 555 | 26.2 | 0.71 | 9.96 | 0.79 | 110.0 | 76.1 | 8.72 | 0.85 | ||||||||||||
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 11.00 | 107.0 | 559 | 22.2 | 0.71 | 8.42 | 0.92 | 117.0 | 63.0 | 9.11 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | δEu | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | Rb/Sr | Sr/Y | Nb/Ta | Zr/Hf | K/Rb | Th/U | Nd/Th | tZr/℃ | ||||||||||||
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.65 | 4.02 | 1.07 | 1.69 | 5.11 | 10.50 | 22.50 | 235 | 21.7 | 1.31 | 730 | ||||||||||||
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.66 | 4.27 | 1.47 | 1.74 | 6.29 | 12.70 | 20.60 | 318 | 22.1 | 1.38 | 736 | ||||||||||||
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.51 | 5.38 | 1.19 | 2.16 | 2.80 | 12.90 | 21.40 | 231 | 16.5 | 2.12 | 717 | ||||||||||||
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.71 | 7.03 | 2.91 | 0.75 | 21.50 | 10.60 | 5.96 | 287 | 22.4 | 1.43 | 648 | ||||||||||||
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.66 | 3.49 | 1.39 | 1.93 | 4.21 | 11.00 | 13.00 | 271 | 16.4 | 1.58 | 702 | ||||||||||||
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.65 | 6.81 | 1.82 | 0.63 | 7.72 | 10.10 | 6.71 | 377 | 16.2 | 2.05 | 651 | ||||||||||||
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.56 | 6.09 | 3.41 | 1.16 | 12.60 | 12.70 | 8.72 | 283 | 37.0 | 1.04 | 663 | ||||||||||||
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.61 | 5.65 | 2.68 | 0.92 | 14.20 | 9.11 | 6.92 | 332 | 31.3 | 1.12 | 657 | ||||||||||||
表4 八大关地区花岗岩微量元素分析测试结果(wB/10-6)
Table 4 The compositions of trace elements of granites in Badaguan (10-6 )
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | Ga | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Sr | Zr | Hf | Y | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 14.40 | 172.0 | 729 | 18.5 | 0.85 | 9.50 | 0.90 | 102.0 | 168.0 | 7.50 | 2.68 | ||||||||||||
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 16.20 | 138.0 | 708 | 14.8 | 0.67 | 11.70 | 0.92 | 79.1 | 183.0 | 8.90 | 1.48 | ||||||||||||
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 15.40 | 177.0 | 656 | 15.4 | 0.93 | 9.61 | 0.75 | 81.9 | 168.0 | 7.84 | 3.34 | ||||||||||||
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 12.90 | 115.0 | 507 | 17.6 | 0.79 | 7.16 | 0.68 | 154.0 | 49.0 | 8.22 | 0.92 | ||||||||||||
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 12.70 | 152.0 | 454 | 16.4 | 1.00 | 10.70 | 0.97 | 78.6 | 115.0 | 8.87 | 2.32 | ||||||||||||
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 9.05 | 58.8 | 374 | 12.6 | 0.78 | 6.75 | 0.67 | 94.1 | 50.0 | 7.45 | 1.61 | ||||||||||||
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 11.50 | 127.0 | 555 | 26.2 | 0.71 | 9.96 | 0.79 | 110.0 | 76.1 | 8.72 | 0.85 | ||||||||||||
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 11.00 | 107.0 | 559 | 22.2 | 0.71 | 8.42 | 0.92 | 117.0 | 63.0 | 9.11 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||
| 采样点号 | 岩性 | δEu | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | Rb/Sr | Sr/Y | Nb/Ta | Zr/Hf | K/Rb | Th/U | Nd/Th | tZr/℃ | ||||||||||||
| 20106 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.65 | 4.02 | 1.07 | 1.69 | 5.11 | 10.50 | 22.50 | 235 | 21.7 | 1.31 | 730 | ||||||||||||
| 20118 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.66 | 4.27 | 1.47 | 1.74 | 6.29 | 12.70 | 20.60 | 318 | 22.1 | 1.38 | 736 | ||||||||||||
| 20124 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.51 | 5.38 | 1.19 | 2.16 | 2.80 | 12.90 | 21.40 | 231 | 16.5 | 2.12 | 717 | ||||||||||||
| 20406 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.71 | 7.03 | 2.91 | 0.75 | 21.50 | 10.60 | 5.96 | 287 | 22.4 | 1.43 | 648 | ||||||||||||
| Zr3 | 正长花岗岩 | 0.66 | 3.49 | 1.39 | 1.93 | 4.21 | 11.00 | 13.00 | 271 | 16.4 | 1.58 | 702 | ||||||||||||
| Zr4 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.65 | 6.81 | 1.82 | 0.63 | 7.72 | 10.10 | 6.71 | 377 | 16.2 | 2.05 | 651 | ||||||||||||
| 006-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.56 | 6.09 | 3.41 | 1.16 | 12.60 | 12.70 | 8.72 | 283 | 37.0 | 1.04 | 663 | ||||||||||||
| 006-6 | 二长花岗岩 | 0.61 | 5.65 | 2.68 | 0.92 | 14.20 | 9.11 | 6.92 | 332 | 31.3 | 1.12 | 657 | ||||||||||||
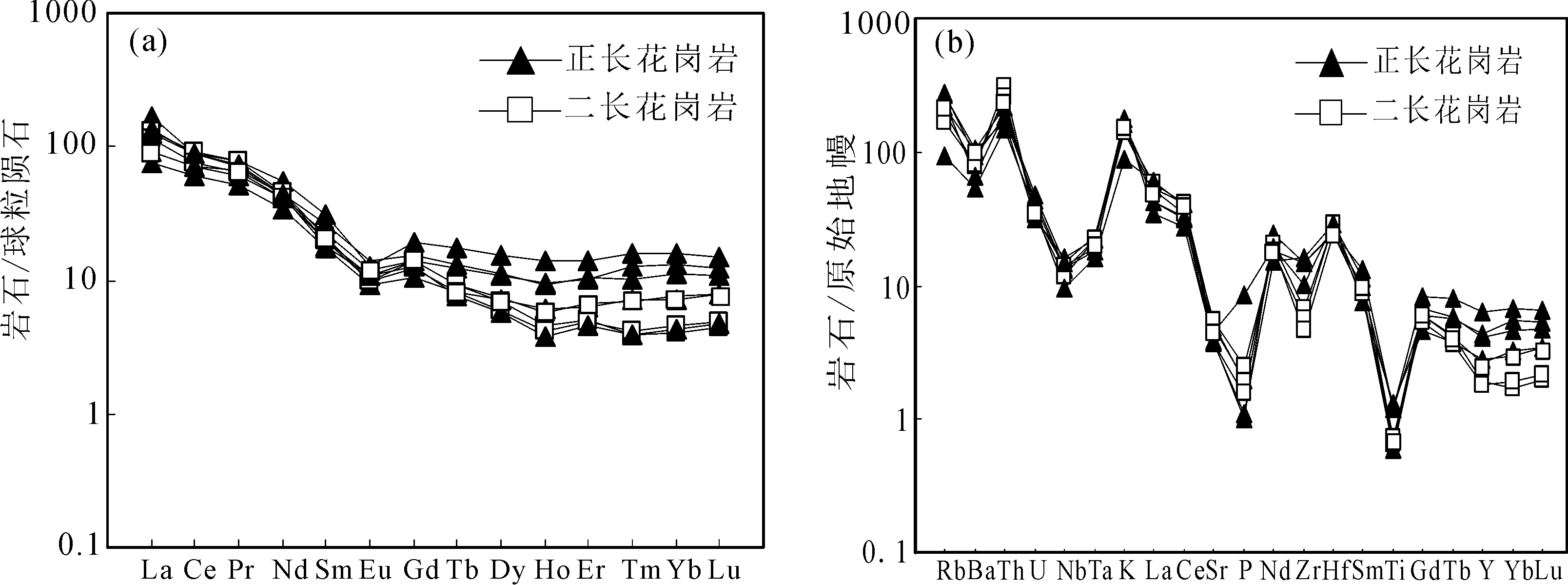
图6 八大关地区花岗岩稀土元素配分模式图(a)[20]和微量元素蛛网图(b)[21]
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution pattern and primitive mantle-normalized spidergram of granites in Badaguan
| 样品测点 | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | ±2σ | εHf (t) | ±2σ | TDM1(Hf)/Ma | TDM2(Hf)/Ma | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3-01 | 0.037 508 | 0.001 618 | 0.282 766 | 0.000 035 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 701 | 971 | -0.95 |
| Zr3-02 | 0.020 352 | 0.000 897 | 0.282 861 | 0.000 027 | 7.97 | 7.97 | 553 | 749 | -0.97 |
| Zr3-03 | 0.044 092 | 0.001 766 | 0.282 880 | 0.000 047 | 8.51 | 8.51 | 539 | 715 | -0.95 |
| Zr3-04 | 0.030 080 | 0.001 271 | 0.282 807 | 0.000 028 | 6.03 | 6.03 | 635 | 873 | -0.96 |
| Zr3-05 | 0.059 907 | 0.002 432 | 0.282 840 | 0.000 036 | 7.02 | 7.02 | 606 | 810 | -0.93 |
| Zr3-06 | 0.060 258 | 0.002 371 | 0.282 792 | 0.000 039 | 5.31 | 5.31 | 677 | 919 | -0.93 |
| Zr3-07 | 0.057 984 | 0.002 321 | 0.282 857 | 0.000 026 | 7.62 | 7.62 | 580 | 772 | -0.93 |
| Zr3-08 | 0.045 652 | 0.001 870 | 0.282 889 | 0.000 038 | 8.84 | 8.84 | 526 | 694 | -0.94 |
| Zr3-09 | 0.048 699 | 0.002 013 | 0.282 902 | 0.000 044 | 9.25 | 9.25 | 510 | 668 | -0.94 |
| Zr3-10 | 0.043 029 | 0.001 781 | 0.282 853 | 0.000 034 | 7.56 | 7.56 | 578 | 776 | -0.95 |
| Zr3-11 | 0.037 352 | 0.001 581 | 0.282 864 | 0.000 038 | 7.97 | 7.97 | 559 | 750 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-01 | 0.044 089 | 0.001 822 | 0.282 830 | 0.000 045 | 6.63 | 1.58 | 611 | 830 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-02 | 0.044 848 | 0.001 854 | 0.282 811 | 0.000 029 | 5.96 | 1.03 | 639 | 873 | -0.94 |
| Zr4-03 | 0.035 888 | 0.001 501 | 0.282 854 | 0.000 027 | 7.52 | 0.95 | 572 | 773 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-04 | 0.039 190 | 0.001 602 | 0.282 904 | 0.000 027 | 9.27 | 0.95 | 501 | 662 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-05 | 0.051 260 | 0.002 023 | 0.282 810 | 0.000 029 | 5.88 | 1.04 | 644 | 878 | -0.94 |
| Zr4-06 | 0.070 644 | 0.002 538 | 0.282 876 | 0.000 025 | 8.13 | 0.89 | 556 | 735 | -0.92 |
| Zr4-07 | 0.033 937 | 0.001 467 | 0.282 937 | 0.000 033 | 10.45 | 1.18 | 452 | 586 | -0.96 |
| Zr4-08 | 0.035 596 | 0.001 514 | 0.282 916 | 0.000 039 | 9.72 | 1.39 | 482 | 633 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-09 | 0.049 393 | 0.001 955 | 0.282 788 | 0.000 084 | 5.11 | 2.98 | 675 | 927 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-01 | 0.037 870 | 0.001 585 | 0.282 819 | 0.000 061 | 6.08 | 2.17 | 624 | 859 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-02 | 0.050 441 | 0.002 087 | 0.282 846 | 0.000 055 | 6.98 | 1.93 | 593 | 802 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-03 | 0.052 199 | 0.002 022 | 0.282 846 | 0.000 030 | 6.98 | 1.05 | 592 | 802 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-04 | 0.045 913 | 0.001 848 | 0.282 845 | 0.000 031 | 7.00 | 1.08 | 590 | 801 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-05 | 0.032 844 | 0.001 230 | 0.282 791 | 0.000 024 | 5.14 | 0.86 | 658 | 919 | -0.96 |
| Zr24-06 | 0.039 803 | 0.001 552 | 0.282 841 | 0.000 022 | 6.88 | 0.77 | 591 | 808 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-07 | 0.041 609 | 0.001 670 | 0.282 857 | 0.000 029 | 7.44 | 1.03 | 570 | 773 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-08 | 0.039 502 | 0.001 587 | 0.282 878 | 0.000 035 | 8.17 | 1.24 | 539 | 726 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-09 | 0.049 814 | 0.002 000 | 0.282 904 | 0.000 042 | 9.05 | 1.47 | 507 | 670 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-10 | 0.058 361 | 0.002 231 | 0.282 889 | 0.000 027 | 8.50 | 0.95 | 532 | 705 | -0.93 |
表5 八大关地区花岗岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 5 Zircon Hf isotope analysis of granites in Badaguan
| 样品测点 | 176Yb/177Hf | 176Lu/177Hf | 176Hf/177Hf | ±2σ | εHf (t) | ±2σ | TDM1(Hf)/Ma | TDM2(Hf)/Ma | fLu/Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3-01 | 0.037 508 | 0.001 618 | 0.282 766 | 0.000 035 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 701 | 971 | -0.95 |
| Zr3-02 | 0.020 352 | 0.000 897 | 0.282 861 | 0.000 027 | 7.97 | 7.97 | 553 | 749 | -0.97 |
| Zr3-03 | 0.044 092 | 0.001 766 | 0.282 880 | 0.000 047 | 8.51 | 8.51 | 539 | 715 | -0.95 |
| Zr3-04 | 0.030 080 | 0.001 271 | 0.282 807 | 0.000 028 | 6.03 | 6.03 | 635 | 873 | -0.96 |
| Zr3-05 | 0.059 907 | 0.002 432 | 0.282 840 | 0.000 036 | 7.02 | 7.02 | 606 | 810 | -0.93 |
| Zr3-06 | 0.060 258 | 0.002 371 | 0.282 792 | 0.000 039 | 5.31 | 5.31 | 677 | 919 | -0.93 |
| Zr3-07 | 0.057 984 | 0.002 321 | 0.282 857 | 0.000 026 | 7.62 | 7.62 | 580 | 772 | -0.93 |
| Zr3-08 | 0.045 652 | 0.001 870 | 0.282 889 | 0.000 038 | 8.84 | 8.84 | 526 | 694 | -0.94 |
| Zr3-09 | 0.048 699 | 0.002 013 | 0.282 902 | 0.000 044 | 9.25 | 9.25 | 510 | 668 | -0.94 |
| Zr3-10 | 0.043 029 | 0.001 781 | 0.282 853 | 0.000 034 | 7.56 | 7.56 | 578 | 776 | -0.95 |
| Zr3-11 | 0.037 352 | 0.001 581 | 0.282 864 | 0.000 038 | 7.97 | 7.97 | 559 | 750 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-01 | 0.044 089 | 0.001 822 | 0.282 830 | 0.000 045 | 6.63 | 1.58 | 611 | 830 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-02 | 0.044 848 | 0.001 854 | 0.282 811 | 0.000 029 | 5.96 | 1.03 | 639 | 873 | -0.94 |
| Zr4-03 | 0.035 888 | 0.001 501 | 0.282 854 | 0.000 027 | 7.52 | 0.95 | 572 | 773 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-04 | 0.039 190 | 0.001 602 | 0.282 904 | 0.000 027 | 9.27 | 0.95 | 501 | 662 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-05 | 0.051 260 | 0.002 023 | 0.282 810 | 0.000 029 | 5.88 | 1.04 | 644 | 878 | -0.94 |
| Zr4-06 | 0.070 644 | 0.002 538 | 0.282 876 | 0.000 025 | 8.13 | 0.89 | 556 | 735 | -0.92 |
| Zr4-07 | 0.033 937 | 0.001 467 | 0.282 937 | 0.000 033 | 10.45 | 1.18 | 452 | 586 | -0.96 |
| Zr4-08 | 0.035 596 | 0.001 514 | 0.282 916 | 0.000 039 | 9.72 | 1.39 | 482 | 633 | -0.95 |
| Zr4-09 | 0.049 393 | 0.001 955 | 0.282 788 | 0.000 084 | 5.11 | 2.98 | 675 | 927 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-01 | 0.037 870 | 0.001 585 | 0.282 819 | 0.000 061 | 6.08 | 2.17 | 624 | 859 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-02 | 0.050 441 | 0.002 087 | 0.282 846 | 0.000 055 | 6.98 | 1.93 | 593 | 802 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-03 | 0.052 199 | 0.002 022 | 0.282 846 | 0.000 030 | 6.98 | 1.05 | 592 | 802 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-04 | 0.045 913 | 0.001 848 | 0.282 845 | 0.000 031 | 7.00 | 1.08 | 590 | 801 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-05 | 0.032 844 | 0.001 230 | 0.282 791 | 0.000 024 | 5.14 | 0.86 | 658 | 919 | -0.96 |
| Zr24-06 | 0.039 803 | 0.001 552 | 0.282 841 | 0.000 022 | 6.88 | 0.77 | 591 | 808 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-07 | 0.041 609 | 0.001 670 | 0.282 857 | 0.000 029 | 7.44 | 1.03 | 570 | 773 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-08 | 0.039 502 | 0.001 587 | 0.282 878 | 0.000 035 | 8.17 | 1.24 | 539 | 726 | -0.95 |
| Zr24-09 | 0.049 814 | 0.002 000 | 0.282 904 | 0.000 042 | 9.05 | 1.47 | 507 | 670 | -0.94 |
| Zr24-10 | 0.058 361 | 0.002 231 | 0.282 889 | 0.000 027 | 8.50 | 0.95 | 532 | 705 | -0.93 |
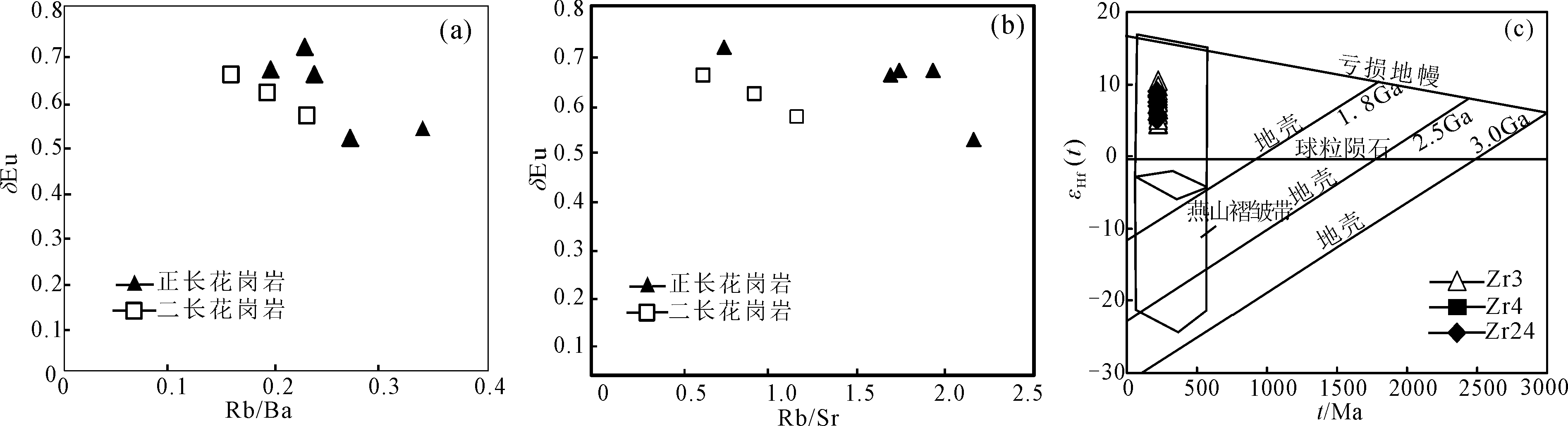
图8 八大关地区花岗岩Rb/Ba-δEu (a)、Rb/Sr-δEu (b)、εHf(t)-t(c)相关图(底图据参考文献[24-25])
Fig.8 The Rb/Ba-δEu (a), Rb/Sr-δEu (b), and εHf(t)-t(c) relationship diagrams for granites of Badaguan
| [1] | KUZMIN M L, ABRAMOVICH G Y, DRIL S L, et al. The Mongolian-Okhotsk suture as the evidence of Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic collisional processes in Central Asia[J]. Abstract of 30th IGC, 1996, 1:261. |
| [2] | ZHAO X X, COE R S. Paleomagnetic constraints on the paleogeography of China: Implications for Gondwanaland[J]. Abstract of 30th IGC, 1996, 1: 231. |
| [3] |
LI J Y. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions: closure of the Paleo-Asian ocean and subduction of the Paleo-pacific plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26: 207-224.
DOI URL |
| [4] | MENG E, XU W L, PEI F P, et al. Chronology of Late Paleozoic volcanism in eastern southeastern margin of Jiamusi massif and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(8):1231-1245. |
| [5] |
MENG E, XU W L, PEI F P, et al. Detrital-zircon geochronology of Late Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in eastern Heilongjiang province, NE China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the eastern segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 485: 42-51.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 葛文春, 林强, 李献华, 等. 大兴安岭北部伊列克得组玄武岩的地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2000, 10(3):14-18. |
| [7] | 葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 等. 大兴安岭中生代两类流纹岩成因的地球化学研究[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25 (2):172-178. |
| [8] | 葛文春, 李献华, 林强, 等. 呼伦湖早白垩世碱性流纹岩的地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36 (2): 176-183. |
| [9] | 林强, 葛文春, 曹林, 等. 大兴安岭中生代双峰式火山岩的地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(3):208-222. |
| [10] |
WANG F, ZHOU X H, ZHANG L C, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing’an Range (NE China): Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 251: 179-198.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
XU W L, JI W Q, PEI F P, et al. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, NE China: Chronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34: 392-402.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41: 1-30.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 许文良, 葛文春, 裴福萍, 等. 东北地区中生代火山作用的年代学格架及其构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(增刊):286-287. |
| [14] |
MENG Q R. What drove Late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract?[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 369(3/4): 155-174.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China(1): Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003, 66: 241-273.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 苏永江, 等. 蒙古国额尔登特特大型铜-钼矿床年代学与成因研究[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3):289-306. |
| [17] | 陈志广, 张连昌, 卢百志, 等. 内蒙古太平川铜钼矿成矿斑岩时代地球化学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(5): 1437-1449. |
| [18] | 吕长禄, 徐东海, 李新鹏, 等. 黑龙江太平岭早侏罗世花岗岩成因及壳幔混合作用[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 634-646. |
| [19] |
RICHWOOD P C. Boundary lines with petrologic diagrams which use oxides major and minor element[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22:247-263.
DOI URL |
| [20] | BOYNTON W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[M]//HENDERSONP. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Developments in Geochemistry. Amsterdam, New York: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114. |
| [21] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]//SAUNDER A D, NORRY M J. Magmatism in Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society, 1989: 313-345. |
| [22] |
BELOUSOVA E A, O’REILLY W G, GRIFFIN W L, et al. Igneous zircon: trace-element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143: 602-622.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95: 407-419.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 曹康, 许继峰, 陈建林, 等. 云南普朗大型斑岩型铜矿含矿斑岩成因及其成矿意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(2):307-322. |
| [25] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, SHAO J A, et al. Constraints on the timing of uplift of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt,North China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 246:336-352.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 杨帆, 肖荣阁, 李娜, 等. 内蒙古宝音图钼矿床花岗岩稀土元素地球化学特征及花岗岩成因[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4):831-840. |
| [27] | 武鹏飞, 孙德有, 王天豪, 等. 延边和龙地区闪长岩的年代学、地球化学特征及岩石成因研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2013, 19(4): 600-610. |
| [28] | 李蓉, 孙德有, 苟军, 等. 张广才岭北部苇河花岗岩基的地球化学特征与岩石成因[J]. 世界地质, 2012, 31(3): 462-470. |
| [29] | 敬海鑫, 孙德有, 苟军, 等. 兴凯地块南部花岗岩年代学、地球化学及Hf同位素特征[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6): 982-994. |
| [30] | 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 张广才岭帽儿山组双峰式火山岩成因:年代学与地球化学证据[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30(4):508-520. |
| [31] | 徐美君, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 小兴安岭中部早侏罗世花岗质岩石的年代学与地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):354-368. |
| [32] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 等. 西拉木伦河—长春—延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间——来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004, 34(2):174-181. |
| [33] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. |
| [34] | 佘宏全, 李进文, 向安平, 等. 大兴安岭中北段原岩锆石U-Pb测年及其与区域构造演化关系[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):571-594. |
| [35] | 曾维顺, 周建波, 董策, 等. 蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋俯冲的记录:额尔古纳地区八大关变质杂岩的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(6):1948-1960. |
| [36] | 侯召硕. 内蒙古额尔古纳地区八大关铜钼矿床成因与构造背景[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014:42-45. |
| [37] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B L, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25:956-983.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [3] | 张舒, 张赞赞, 胡召齐, 施立胜, 周涛发, 吴明安, 杜建国. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区花岗岩型铀矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1435-1448. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [6] | 席振, 马德成, 李欢, 高光明, 向夏楠. 新疆东昆仑土窑洞地区新元古代早期侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1609-1623. |
| [7] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 滕超, 张学斌, 杨欣杰, 来林, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古西乌旗早泥盆世I型石英闪长岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1624-1633. |
| [8] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [9] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [10] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [11] | 徐立明, 刘涛, 郑吉林. 大兴安岭北段阿里河镇早白垩世高分异花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 613-626. |
| [12] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [13] | 张国宾, 孔金贵, 吴子杰, 冯玥, 何云龙, 陈兴凯. 蒙古—鄂霍次克洋早侏罗世构造演化:来自大兴安岭北段新立屯地区花岗岩的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [14] | 刘金宝, 朱洛婷, 李龙雪, 侯青叶. 内蒙古艾力格庙地区卫境岩体的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 419-432. |
| [15] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||