



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (03): 418-430.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.017
于立栋1( ), 于学峰2,3,4(
), 于学峰2,3,4( ), 李大鹏2,3,4, 刘强1,2,3,4, 刘家军1, 舒磊2,3,4, 尉鹏飞1,2,3,4
), 李大鹏2,3,4, 刘强1,2,3,4, 刘家军1, 舒磊2,3,4, 尉鹏飞1,2,3,4
收稿日期:2018-09-05
修回日期:2019-12-30
出版日期:2020-07-04
发布日期:2020-07-05
通讯作者:
于学峰
作者简介:于学峰,男,博士,研究员,1962年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事地质矿产研究。Email: xfengy@sohu.com。基金资助:
YU Lidong1( ), YU Xuefeng2,3,4(
), YU Xuefeng2,3,4( ), LI Dapeng2,3,4, LIU Qiang1,2,3,4, LIU Jiajun1, SHU Lei2,3,4, WEI Pengfei1,2,3,4
), LI Dapeng2,3,4, LIU Qiang1,2,3,4, LIU Jiajun1, SHU Lei2,3,4, WEI Pengfei1,2,3,4
Received:2018-09-05
Revised:2019-12-30
Online:2020-07-04
Published:2020-07-05
Contact:
YU Xuefeng
摘要:
鲁西临朐铁寨杂岩体主要由石英二长玢岩和石英二长斑岩组成。为了精确厘定杂岩体的成岩时代和地球化学特征,对石英二长玢岩和石英二长斑岩进行了锆石U-Pb定年、全岩地球化学研究。结果表明,石英二长玢岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为(129.0±1.7) Ma,其含有的继承锆石年龄为(2 520±30) Ma;石英二长斑岩的锆石年龄为(125.0±1.6) Ma。两种侵入岩均具有富硅、富碱和低钙镁的特征,石英二长玢岩比石英二长斑岩的Mg#值高;稀土总量较低,轻重稀土分馏明显,Eu基本无异常;Sr、Ba含量高,Nb、Ta和Ti等高场强元素负异常。岩石地球化学特征表明:鲁西铁寨杂岩体来源为富集地幔部分熔融、同化混染了部分古老的地壳物质,两种岩性的Mg#值差异是磁铁矿分离结晶的结果。早白垩世滞留在地幔过渡带的太平洋板片脱水是岩石圈减薄的诱因,期间产生大量的岩浆岩,表明早白垩世是华北克拉通岩石圈减薄的峰期。
中图分类号:
于立栋, 于学峰, 李大鹏, 刘强, 刘家军, 舒磊, 尉鹏飞. 鲁西临朐铁寨杂岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 418-430.
YU Lidong, YU Xuefeng, LI Dapeng, LIU Qiang, LIU Jiajun, SHU Lei, WEI Pengfei. Zircon U-Pb Chronology, Geochemistry Characteristics of the Tiezhai Complex in Linqu County of Western Shandong and Their Geological Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(03): 418-430.
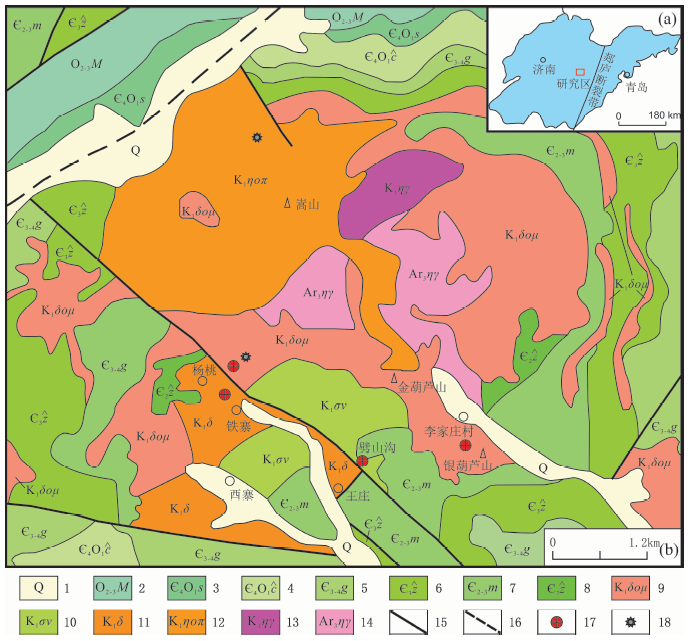
图1 临朐铁寨杂岩体地质简图(据文献[42], 略有修改) 1.第四系;2.奥陶系马家沟群;3.寒武—奥陶系三山子组;4.寒武—奥陶系炒米店组;5.寒武系崮山组;6.寒武系张夏组;7.寒武系馒头组;8.寒武系朱砂洞组;9.早白垩世石英二长玢岩;10.早白垩世橄榄辉长岩;11.早白垩世闪长岩;12.早白垩世石英二长斑岩;13.早白垩世二长花岗岩;14.新太古代二长花岗岩;15.实测断层;16.推测断层;17.金矿床(点);18.采样位置
Fig.1 Geologic sketch of Tiezhai complex in Linqu (modified after reference [42])
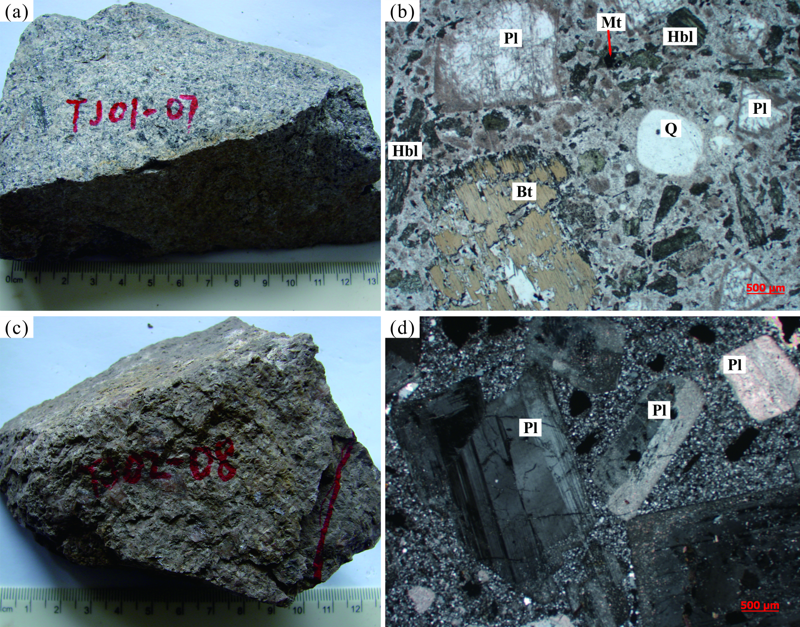
图2 铁寨杂岩体岩相学特征 (a)石英二长玢岩手标本照片;(b)石英二长玢岩单偏光显微照片;(c)石英二长斑岩手标本照片;(d)石英二长斑岩单偏光显微照片;Bt.黑云母;Hbl.角闪石;Mt.磁铁矿;Pl.斜长石;Q.石英
Fig.2 Petrographical characteristics of Tiezhai complex

图3 石英二长玢岩(a)和石英二长斑岩(b)锆石CL图像及年龄(年龄单位:Ma)
Fig.3 CL images of zircons from grey quartz monzonite porphyry (a) and light red quartz monzonite porphyry (b) (age unit: Ma)
| 样号 | 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值(1σ) | 同位素年龄(1σ)/Ma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/ 235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/ 235U | 206Pb/238U | |||||||||
| TZ01- 06 | 1 | 87 | 217 | 0.40 | 0.111 7(0.005 4) | 0.613 2(0.028 3) | 0.040 5(0.001 1) | 1 828(93) | 486(18) | 256(7) | ||||||
| 2 | 172 | 260 | 0.66 | 0.161 1(0.002 9) | 9.599 3(0.192 5) | 0.427 5(0.006 1) | 2 478(31) | 2 397(18) | 2 294(28) | |||||||
| 3 | 15 | 14 | 1.06 | 0.151 9(0.007 5) | 5.527 2(0.285 2) | 0.265 2(0.008 8) | 2 369(85) | 1 905(44) | 1 516(45) | |||||||
| 4 | 56 | 92 | 0.61 | 0.160 9(0.003 1) | 11.178 7(0.236 4) | 0.498 6(0.007 4) | 2 465(33) | 2 538(20) | 2 608(32) | |||||||
| 5 | 117 | 288 | 0.41 | 0.166 5(0.002 9) | 10.725 2(0.217 4) | 0.461 8(0.007 6) | 2 524(29) | 2 500(19) | 2 447(34) | |||||||
| 6 | 95 | 76 | 1.25 | 0.160 2(0.003 4) | 10.481 2(0.232 2) | 0.469 2(0.007 1) | 2 458(37) | 2 478(21) | 2 480(31) | |||||||
| 7 | 579 | 762 | 0.76 | 0.118 6(0.003 2) | 0.928 5(0.029 5) | 0.055 8(0.001 1) | 1 936(48) | 667(16) | 350(7) | |||||||
| 8 | 17 | 75 | 0.23 | 0.159 7(0.004 2) | 9.553 1(0.227 6) | 0.430 4(0.007 1) | 2 454(43) | 2 393(22) | 2 308(32) | |||||||
| 9 | 55 | 54 | 1.03 | 0.164 7(0.004 7) | 11.135 0(0.304 5) | 0.485 6(0.009 6) | 2 506(48) | 2 534(25) | 2 552(42) | |||||||
| 10 | 126 | 221 | 0.57 | 0.050 9(0.003 7) | 0.143 1(0.009 6) | 0.020 9(0.000 5) | 235(170) | 136(9) | 133(3) | |||||||
| 11 | 55 | 126 | 0.44 | 0.162 1(0.003 7) | 10.554 2(0.236 3) | 0.467 1(0.007 8) | 2 477(39) | 2 485(21) | 2 471(34) | |||||||
| 12 | 166 | 185 | 0.90 | 0.056 9(0.004 2) | 0.148 8(0.008 7) | 0.020 1(0.000 5) | 487(163) | 141(8) | 128(3) | |||||||
| 13 | 225 | 367 | 0.61 | 0.050 3(0.002 9) | 0.137 0(0.007 9) | 0.020 1(0.000 4) | 209(131) | 130(7) | 128(3) | |||||||
| 14 | 440 | 334 | 1.32 | 0.173 7(0.002 2) | 11.504 9(0.158 8) | 0.474 8(0.004 9) | 2 594(22) | 2 565(13) | 2 505(22) | |||||||
| 15 | 143 | 183 | 0.78 | 0.164 2(0.002 7) | 10.648 2(0.208 7) | 0.469 1(0.009 7) | 2 499(28) | 2 493(18) | 2 480(42) | |||||||
| 16 | 66 | 88 | 0.75 | 0.152 2(0.004 2) | 4.377 1(0.269 3) | 0.206 5(0.011 6) | 2 372(46) | 1 708(51) | 1 210(62) | |||||||
| 17 | 229 | 308 | 0.74 | 0.050 8(0.003 0) | 0.140 1(0.008 3) | 0.020 3(0.000 4) | 232(139) | 133(7) | 129(2) | |||||||
| 18 | 1 025 | 1 192 | 0.86 | 0.050 6(0.001 5) | 0.140 9(0.004 1) | 0.020 2(0.000 3) | 220(67) | 134(4) | 129(2) | |||||||
| 19 | 87 | 219 | 0.40 | 0.053 2(0.003 9) | 0.143 1(0.009 0) | 0.020 2(0.000 5) | 345(169) | 136(8) | 129(3) | |||||||
| 20 | 629 | 763 | 0.82 | 0.170 9(0.002 6) | 10.753 4(0.169 7) | 0.453 0(0.006 7) | 2 566(26) | 2 502(15) | 2 409(30) | |||||||
| 21 | 920 | 1 015 | 0.91 | 0.051 6(0.001 8) | 0.143 3(0.005 0) | 0.020 2(0.000 3) | 333(81) | 136(4) | 129(2) | |||||||
| 22 | 92 | 174 | 0.53 | 0.164 8(0.003 9) | 10.937 7(0.394 4) | 0.477 1(0.015 9) | 2 506(40) | 2 518(34) | 2 515(70) | |||||||
| 23 | 176 | 340 | 0.52 | 0.052 4(0.002 6) | 0.147 6(0.007 2) | 0.020 7(0.000 4) | 306(115) | 140(6) | 132(3) | |||||||
| 24 | 133 | 266 | 0.50 | 0.171 0(0.004 1) | 10.836 9(0.255 1) | 0.454 1(0.007 2) | 2 569(40) | 2 509(22) | 2 414(32) | |||||||
| 25 | 11 | 85 | 0.13 | 0.163 6(0.004 6) | 11.142 9(0.305 5) | 0.487 6(0.008 4) | 2 494(42) | 2 535(26) | 2 560(37) | |||||||
| TZ02 -08 | 1 | 108 | 608 | 0.18 | 0.050 4(0.001 9) | 0.141 5(0.005 2) | 0.020 4(0.000 4) | 213(85) | 134(5) | 130(2) | ||||||
| 2 | 194 | 1 207 | 0.16 | 0.047 9(0.001 5) | 0.127 6(0.003 8) | 0.019 3(0.000 3) | 100(72) | 122(3) | 123(2) | |||||||
| 3 | 201 | 1 100 | 0.18 | 0.052 5(0.001 9) | 0.139 8(0.005 1) | 0.019 2(0.000 3) | 309(79) | 133(5) | 122(2) | |||||||
| 4 | 208 | 1 176 | 0.18 | 0.051 0(0.002 2) | 0.131 5(0.006 1) | 0.018 5(0.000 4) | 239(72) | 125(5) | 118(2) | |||||||
| 5 | 78 | 873 | 0.09 | 0.047 9(0.001 8) | 0.128 6(0.005 1) | 0.019 4(0.000 3) | 95(-108) | 123(5) | 124(2) | |||||||
| 6 | 164 | 870 | 0.19 | 0.048 9(0.002 0) | 0.131 6(0.005 5) | 0.019 6(0.000 4) | 146(98) | 126(5) | 125(2) | |||||||
| 7 | 349 | 1 176 | 0.30 | 0.048 4(0.001 8) | 0.128 3(0.004 7) | 0.019 2(0.000 3) | 120(89) | 123(4) | 123(2) | |||||||
| 8 | 135 | 908 | 0.15 | 0.051 4(0.001 8) | 0.136 0(0.005 3) | 0.019 0(0.000 4) | 257(81) | 129(5) | 121(2) | |||||||
| 9 | 115 | 887 | 0.13 | 0.054 1(0.002 1) | 0.138 9(0.005 1) | 0.019 0(0.000 3) | 372(87) | 132(5) | 121(2) | |||||||
| 10 | 55 | 495 | 0.11 | 0.052 1(0.003 1) | 0.135 0(0.009 0) | 0.018 6(0.000 5) | 300(137) | 129(8) | 119(3) | |||||||
| 11 | 118 | 842 | 0.14 | 0.049 8(0.002 0) | 0.135 7(0.005 3) | 0.019 8(0.000 4) | 187(88) | 129(5) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 12 | 84 | 733 | 0.11 | 0.046 1(0.001 9) | 0.126 0(0.005 3) | 0.019 7(0.000 3) | 400(-302) | 120(5) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 13 | 81 | 678 | 0.12 | 0.048 0(0.002 6) | 0.126 0(0.006 8) | 0.019 0(0.000 3) | 98(135) | 120(6) | 122(2) | |||||||
| 14 | 216 | 1 462 | 0.15 | 0.047 3(0.001 8) | 0.127 4(0.005 0) | 0.019 7(0.000 4) | 65(89) | 122(4) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 15 | 25 | 225 | 0.11 | 0.073 6(0.005 7) | 0.292 2(0.029 6) | 0.027 7(0.001 1) | 1 031(162) | 260(23) | 176(7) | |||||||
| 16 | 238 | 937 | 0.25 | 0.047 7(0.002 0) | 0.133 9(0.005 1) | 0.020 4(0.000 4) | 87(102) | 128(5) | 130(2) | |||||||
| 17 | 257 | 1 233 | 0.21 | 0.046 6(0.001 6) | 0.129 3(0.004 3) | 0.020 0(0.000 3) | 32(78) | 123(4) | 127(2) | |||||||
| 18 | 77 | 544 | 0.14 | 0.048 4(0.002 7) | 0.134 1(0.007 1) | 0.020 1(0.000 5) | 120(135) | 128(6) | 128(3) | |||||||
| 19 | 37 | 383 | 0.10 | 0.043 0(0.002 0) | 0.125 0(0.005 5) | 0.021 1(0.000 4) | 120(5) | 135(2) | ||||||||
| 20 | 143 | 1 049 | 0.14 | 0.046 9(0.001 6) | 0.128 0(0.004 3) | 0.019 7(0.000 3) | 43(78) | 122(4) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 21 | 67 | 93 | 0.72 | 0.156 5(0.003 3) | 10.974 5(0.282 1) | 0.503 9(0.010 3) | 2 418(35) | 2 521(24) | 2 630(44) | |||||||
| 22 | 205 | 1 262 | 0.16 | 0.048 4(0.001 6) | 0.130 3(0.004 2) | 0.019 3(0.000 3) | 120(76) | 124(4) | 123(2) | |||||||
| 23 | 110 | 605 | 0.18 | 0.083 3(0.003 9) | 0.325 4(0.019 2) | 0.027 6(0.000 9) | 1 276(91) | 286(15) | 176(6) | |||||||
| 24 | 10 | 1 099 | 0.01 | 0.048 3(0.002 0) | 0.132 8(0.005 8) | 0.019 9(0.000 3) | 122(98) | 127(5) | 127(2) | |||||||
表1 铁寨杂岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 年代学测试结果
Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of Tiezhai complex
| 样号 | 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值(1σ) | 同位素年龄(1σ)/Ma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 232Th | 238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/ 235U | 206Pb/238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/ 235U | 206Pb/238U | |||||||||
| TZ01- 06 | 1 | 87 | 217 | 0.40 | 0.111 7(0.005 4) | 0.613 2(0.028 3) | 0.040 5(0.001 1) | 1 828(93) | 486(18) | 256(7) | ||||||
| 2 | 172 | 260 | 0.66 | 0.161 1(0.002 9) | 9.599 3(0.192 5) | 0.427 5(0.006 1) | 2 478(31) | 2 397(18) | 2 294(28) | |||||||
| 3 | 15 | 14 | 1.06 | 0.151 9(0.007 5) | 5.527 2(0.285 2) | 0.265 2(0.008 8) | 2 369(85) | 1 905(44) | 1 516(45) | |||||||
| 4 | 56 | 92 | 0.61 | 0.160 9(0.003 1) | 11.178 7(0.236 4) | 0.498 6(0.007 4) | 2 465(33) | 2 538(20) | 2 608(32) | |||||||
| 5 | 117 | 288 | 0.41 | 0.166 5(0.002 9) | 10.725 2(0.217 4) | 0.461 8(0.007 6) | 2 524(29) | 2 500(19) | 2 447(34) | |||||||
| 6 | 95 | 76 | 1.25 | 0.160 2(0.003 4) | 10.481 2(0.232 2) | 0.469 2(0.007 1) | 2 458(37) | 2 478(21) | 2 480(31) | |||||||
| 7 | 579 | 762 | 0.76 | 0.118 6(0.003 2) | 0.928 5(0.029 5) | 0.055 8(0.001 1) | 1 936(48) | 667(16) | 350(7) | |||||||
| 8 | 17 | 75 | 0.23 | 0.159 7(0.004 2) | 9.553 1(0.227 6) | 0.430 4(0.007 1) | 2 454(43) | 2 393(22) | 2 308(32) | |||||||
| 9 | 55 | 54 | 1.03 | 0.164 7(0.004 7) | 11.135 0(0.304 5) | 0.485 6(0.009 6) | 2 506(48) | 2 534(25) | 2 552(42) | |||||||
| 10 | 126 | 221 | 0.57 | 0.050 9(0.003 7) | 0.143 1(0.009 6) | 0.020 9(0.000 5) | 235(170) | 136(9) | 133(3) | |||||||
| 11 | 55 | 126 | 0.44 | 0.162 1(0.003 7) | 10.554 2(0.236 3) | 0.467 1(0.007 8) | 2 477(39) | 2 485(21) | 2 471(34) | |||||||
| 12 | 166 | 185 | 0.90 | 0.056 9(0.004 2) | 0.148 8(0.008 7) | 0.020 1(0.000 5) | 487(163) | 141(8) | 128(3) | |||||||
| 13 | 225 | 367 | 0.61 | 0.050 3(0.002 9) | 0.137 0(0.007 9) | 0.020 1(0.000 4) | 209(131) | 130(7) | 128(3) | |||||||
| 14 | 440 | 334 | 1.32 | 0.173 7(0.002 2) | 11.504 9(0.158 8) | 0.474 8(0.004 9) | 2 594(22) | 2 565(13) | 2 505(22) | |||||||
| 15 | 143 | 183 | 0.78 | 0.164 2(0.002 7) | 10.648 2(0.208 7) | 0.469 1(0.009 7) | 2 499(28) | 2 493(18) | 2 480(42) | |||||||
| 16 | 66 | 88 | 0.75 | 0.152 2(0.004 2) | 4.377 1(0.269 3) | 0.206 5(0.011 6) | 2 372(46) | 1 708(51) | 1 210(62) | |||||||
| 17 | 229 | 308 | 0.74 | 0.050 8(0.003 0) | 0.140 1(0.008 3) | 0.020 3(0.000 4) | 232(139) | 133(7) | 129(2) | |||||||
| 18 | 1 025 | 1 192 | 0.86 | 0.050 6(0.001 5) | 0.140 9(0.004 1) | 0.020 2(0.000 3) | 220(67) | 134(4) | 129(2) | |||||||
| 19 | 87 | 219 | 0.40 | 0.053 2(0.003 9) | 0.143 1(0.009 0) | 0.020 2(0.000 5) | 345(169) | 136(8) | 129(3) | |||||||
| 20 | 629 | 763 | 0.82 | 0.170 9(0.002 6) | 10.753 4(0.169 7) | 0.453 0(0.006 7) | 2 566(26) | 2 502(15) | 2 409(30) | |||||||
| 21 | 920 | 1 015 | 0.91 | 0.051 6(0.001 8) | 0.143 3(0.005 0) | 0.020 2(0.000 3) | 333(81) | 136(4) | 129(2) | |||||||
| 22 | 92 | 174 | 0.53 | 0.164 8(0.003 9) | 10.937 7(0.394 4) | 0.477 1(0.015 9) | 2 506(40) | 2 518(34) | 2 515(70) | |||||||
| 23 | 176 | 340 | 0.52 | 0.052 4(0.002 6) | 0.147 6(0.007 2) | 0.020 7(0.000 4) | 306(115) | 140(6) | 132(3) | |||||||
| 24 | 133 | 266 | 0.50 | 0.171 0(0.004 1) | 10.836 9(0.255 1) | 0.454 1(0.007 2) | 2 569(40) | 2 509(22) | 2 414(32) | |||||||
| 25 | 11 | 85 | 0.13 | 0.163 6(0.004 6) | 11.142 9(0.305 5) | 0.487 6(0.008 4) | 2 494(42) | 2 535(26) | 2 560(37) | |||||||
| TZ02 -08 | 1 | 108 | 608 | 0.18 | 0.050 4(0.001 9) | 0.141 5(0.005 2) | 0.020 4(0.000 4) | 213(85) | 134(5) | 130(2) | ||||||
| 2 | 194 | 1 207 | 0.16 | 0.047 9(0.001 5) | 0.127 6(0.003 8) | 0.019 3(0.000 3) | 100(72) | 122(3) | 123(2) | |||||||
| 3 | 201 | 1 100 | 0.18 | 0.052 5(0.001 9) | 0.139 8(0.005 1) | 0.019 2(0.000 3) | 309(79) | 133(5) | 122(2) | |||||||
| 4 | 208 | 1 176 | 0.18 | 0.051 0(0.002 2) | 0.131 5(0.006 1) | 0.018 5(0.000 4) | 239(72) | 125(5) | 118(2) | |||||||
| 5 | 78 | 873 | 0.09 | 0.047 9(0.001 8) | 0.128 6(0.005 1) | 0.019 4(0.000 3) | 95(-108) | 123(5) | 124(2) | |||||||
| 6 | 164 | 870 | 0.19 | 0.048 9(0.002 0) | 0.131 6(0.005 5) | 0.019 6(0.000 4) | 146(98) | 126(5) | 125(2) | |||||||
| 7 | 349 | 1 176 | 0.30 | 0.048 4(0.001 8) | 0.128 3(0.004 7) | 0.019 2(0.000 3) | 120(89) | 123(4) | 123(2) | |||||||
| 8 | 135 | 908 | 0.15 | 0.051 4(0.001 8) | 0.136 0(0.005 3) | 0.019 0(0.000 4) | 257(81) | 129(5) | 121(2) | |||||||
| 9 | 115 | 887 | 0.13 | 0.054 1(0.002 1) | 0.138 9(0.005 1) | 0.019 0(0.000 3) | 372(87) | 132(5) | 121(2) | |||||||
| 10 | 55 | 495 | 0.11 | 0.052 1(0.003 1) | 0.135 0(0.009 0) | 0.018 6(0.000 5) | 300(137) | 129(8) | 119(3) | |||||||
| 11 | 118 | 842 | 0.14 | 0.049 8(0.002 0) | 0.135 7(0.005 3) | 0.019 8(0.000 4) | 187(88) | 129(5) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 12 | 84 | 733 | 0.11 | 0.046 1(0.001 9) | 0.126 0(0.005 3) | 0.019 7(0.000 3) | 400(-302) | 120(5) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 13 | 81 | 678 | 0.12 | 0.048 0(0.002 6) | 0.126 0(0.006 8) | 0.019 0(0.000 3) | 98(135) | 120(6) | 122(2) | |||||||
| 14 | 216 | 1 462 | 0.15 | 0.047 3(0.001 8) | 0.127 4(0.005 0) | 0.019 7(0.000 4) | 65(89) | 122(4) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 15 | 25 | 225 | 0.11 | 0.073 6(0.005 7) | 0.292 2(0.029 6) | 0.027 7(0.001 1) | 1 031(162) | 260(23) | 176(7) | |||||||
| 16 | 238 | 937 | 0.25 | 0.047 7(0.002 0) | 0.133 9(0.005 1) | 0.020 4(0.000 4) | 87(102) | 128(5) | 130(2) | |||||||
| 17 | 257 | 1 233 | 0.21 | 0.046 6(0.001 6) | 0.129 3(0.004 3) | 0.020 0(0.000 3) | 32(78) | 123(4) | 127(2) | |||||||
| 18 | 77 | 544 | 0.14 | 0.048 4(0.002 7) | 0.134 1(0.007 1) | 0.020 1(0.000 5) | 120(135) | 128(6) | 128(3) | |||||||
| 19 | 37 | 383 | 0.10 | 0.043 0(0.002 0) | 0.125 0(0.005 5) | 0.021 1(0.000 4) | 120(5) | 135(2) | ||||||||
| 20 | 143 | 1 049 | 0.14 | 0.046 9(0.001 6) | 0.128 0(0.004 3) | 0.019 7(0.000 3) | 43(78) | 122(4) | 126(2) | |||||||
| 21 | 67 | 93 | 0.72 | 0.156 5(0.003 3) | 10.974 5(0.282 1) | 0.503 9(0.010 3) | 2 418(35) | 2 521(24) | 2 630(44) | |||||||
| 22 | 205 | 1 262 | 0.16 | 0.048 4(0.001 6) | 0.130 3(0.004 2) | 0.019 3(0.000 3) | 120(76) | 124(4) | 123(2) | |||||||
| 23 | 110 | 605 | 0.18 | 0.083 3(0.003 9) | 0.325 4(0.019 2) | 0.027 6(0.000 9) | 1 276(91) | 286(15) | 176(6) | |||||||
| 24 | 10 | 1 099 | 0.01 | 0.048 3(0.002 0) | 0.132 8(0.005 8) | 0.019 9(0.000 3) | 122(98) | 127(5) | 127(2) | |||||||
| 样品 编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O/ Na2O | K2O+ Na2O | A/ CNK | A/ NK | AR | Mg# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TZ01-06 | 石英二 长玢岩 | 66.3 | 0.46 | 15.10 | 0.58 | 2.08 | 0.05 | 2.40 | 3.70 | 5.26 | 3.23 | 0.14 | 0.56 | 99.9 | 0.61 | 8.49 | 0.80 | 1.24 | 2.65 | 62 |
| TZ01-07 | 66.4 | 0.46 | 15.30 | 1.62 | 2.11 | 0.05 | 2.30 | 3.20 | 4.94 | 3.11 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 100.0 | 0.63 | 8.05 | 0.88 | 1.33 | 2.54 | 53 | |
| TZ01-13 | 63.9 | 0.55 | 15.70 | 1.88 | 2.41 | 0.06 | 2.70 | 4.50 | 4.55 | 3.30 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 100.1 | 0.73 | 7.85 | 0.82 | 1.42 | 2.27 | 54 | |
| TZ01-14 | 64.3 | 0.54 | 16.00 | 1.51 | 2.59 | 0.06 | 2.70 | 4.20 | 4.64 | 3.32 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 100.3 | 0.72 | 7.96 | 0.85 | 1.42 | 2.30 | 55 | |
| TZ01-15 | 62.0 | 0.56 | 15.80 | 2.35 | 2.62 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 4.30 | 4.67 | 3.55 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 99.0 | 0.76 | 8.22 | 0.82 | 1.37 | 2.38 | 51 | |
| TZ01-16 | 63.3 | 0.53 | 15.90 | 1.83 | 2.43 | 0.05 | 2.70 | 4.20 | 4.67 | 2.98 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 99.1 | 0.64 | 7.65 | 0.86 | 1.46 | 2.23 | 54 | |
| TZ02-08 | 石英二 长斑岩 | 65.0 | 0.27 | 17.60 | 1.27 | 1.37 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 5.45 | 4.79 | 0.07 | 0.97 | 99.4 | 0.88 | 10.24 | 1.01 | 1.24 | 3.24 | 31 |
表2 铁寨杂岩体主量元素分析结果(%)
Table 2 Analytical data of major elements of Tiezhai complex (%)
| 样品 编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O/ Na2O | K2O+ Na2O | A/ CNK | A/ NK | AR | Mg# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TZ01-06 | 石英二 长玢岩 | 66.3 | 0.46 | 15.10 | 0.58 | 2.08 | 0.05 | 2.40 | 3.70 | 5.26 | 3.23 | 0.14 | 0.56 | 99.9 | 0.61 | 8.49 | 0.80 | 1.24 | 2.65 | 62 |
| TZ01-07 | 66.4 | 0.46 | 15.30 | 1.62 | 2.11 | 0.05 | 2.30 | 3.20 | 4.94 | 3.11 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 100.0 | 0.63 | 8.05 | 0.88 | 1.33 | 2.54 | 53 | |
| TZ01-13 | 63.9 | 0.55 | 15.70 | 1.88 | 2.41 | 0.06 | 2.70 | 4.50 | 4.55 | 3.30 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 100.1 | 0.73 | 7.85 | 0.82 | 1.42 | 2.27 | 54 | |
| TZ01-14 | 64.3 | 0.54 | 16.00 | 1.51 | 2.59 | 0.06 | 2.70 | 4.20 | 4.64 | 3.32 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 100.3 | 0.72 | 7.96 | 0.85 | 1.42 | 2.30 | 55 | |
| TZ01-15 | 62.0 | 0.56 | 15.80 | 2.35 | 2.62 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 4.30 | 4.67 | 3.55 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 99.0 | 0.76 | 8.22 | 0.82 | 1.37 | 2.38 | 51 | |
| TZ01-16 | 63.3 | 0.53 | 15.90 | 1.83 | 2.43 | 0.05 | 2.70 | 4.20 | 4.67 | 2.98 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 99.1 | 0.64 | 7.65 | 0.86 | 1.46 | 2.23 | 54 | |
| TZ02-08 | 石英二 长斑岩 | 65.0 | 0.27 | 17.60 | 1.27 | 1.37 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 5.45 | 4.79 | 0.07 | 0.97 | 99.4 | 0.88 | 10.24 | 1.01 | 1.24 | 3.24 | 31 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | Zr | Hf | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TZ01-06 | 石英二 长玢岩 | 69 | 564 | 871 | 4.29 | 1.50 | 0.29 | 5.20 | 133 | 5.29 | 8.1 | 17.9 | 34.9 | 4.94 | 20.5 | 4.02 | 1.21 |
| TZ01-07 | 64 | 640 | 920 | 3.68 | 1.29 | 0.23 | 5.00 | 133 | 4.94 | 7.4 | 13.9 | 28.6 | 3.59 | 18.5 | 2.57 | 0.77 | |
| TZ01-13 | 74 | 831 | 1 081 | 4.52 | 1.47 | 0.50 | 7.60 | 96 | 3.48 | 10.2 | 19.2 | 33.9 | 4.75 | 19.5 | 3.78 | 1.20 | |
| TZ01-14 | 75 | 840 | 1 067 | 4.13 | 1.45 | 0.48 | 7.50 | 86 | 3.28 | 10.2 | 18.1 | 36.4 | 4.82 | 19.4 | 3.73 | 1.10 | |
| TZ01-15 | 72 | 824 | 1 071 | 4.21 | 1.42 | 0.49 | 7.60 | 87 | 3.36 | 10.3 | 20.5 | 35.6 | 4.78 | 19.3 | 3.86 | 1.14 | |
| TZ01-16 | 65 | 834 | 971 | 4.05 | 1.44 | 0.46 | 7.40 | 87 | 3.16 | 10.2 | 19.7 | 35.0 | 4.82 | 20.0 | 3.78 | 1.16 | |
| TZ02-08 | 石英二 长斑岩 | 136 | 724 | 1 589 | 5.22 | 1.96 | 0.48 | 12.10 | 147 | 5.58 | 4.5 | 18.7 | 34.9 | 4.26 | 16.5 | 2.49 | 0.78 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | Sr/Y | δEu | δCe |
| TZ01-06 | 石英二 长玢岩 | 3.12 | 0.42 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 0.82 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 90.9 | 83.6 | 7.29 | 11.5 | 21.4 | 70 | 1.01 | 0.89 |
| TZ01-07 | 2.01 | 0.28 | 1.54 | 0.28 | 0.82 | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.13 | 69.4 | 63.4 | 6.00 | 10.6 | 12.1 | 86 | 1.00 | 0.97 | |
| TZ01-13 | 3.10 | 0.43 | 2.17 | 0.39 | 1.06 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 0.14 | 90.6 | 82.3 | 8.32 | 9.9 | 15.4 | 81 | 1.04 | 0.84 | |
| TZ01-14 | 3.10 | 0.42 | 2.13 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.14 | 0.88 | 0.14 | 91.5 | 83.3 | 8.18 | 10.2 | 14.8 | 82 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| TZ01-15 | 3.08 | 0.46 | 2.24 | 0.37 | 1.05 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 93.5 | 85.1 | 8.41 | 10.1 | 15.5 | 80 | 0.97 | 0.85 | |
| TZ01-16 | 3.05 | 0.44 | 2.11 | 0.36 | 1.03 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 92.6 | 84.4 | 8.15 | 10.4 | 15.8 | 82 | 1.01 | 0.85 | |
| TZ02-08 | 石英二 长斑岩 | 2.00 | 0.23 | 0.96 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 81.1 | 77.0 | 4.13 | 18.7 | 42.7 | 161 | 1.03 | 0.92 |
表3 铁寨杂岩体微量和稀土元素分析结果(10-6)
Table 3 Analytical data of trace and rare earth element contents of Tiezhai complex (10-6)
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Th | U | Ta | Nb | Zr | Hf | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TZ01-06 | 石英二 长玢岩 | 69 | 564 | 871 | 4.29 | 1.50 | 0.29 | 5.20 | 133 | 5.29 | 8.1 | 17.9 | 34.9 | 4.94 | 20.5 | 4.02 | 1.21 |
| TZ01-07 | 64 | 640 | 920 | 3.68 | 1.29 | 0.23 | 5.00 | 133 | 4.94 | 7.4 | 13.9 | 28.6 | 3.59 | 18.5 | 2.57 | 0.77 | |
| TZ01-13 | 74 | 831 | 1 081 | 4.52 | 1.47 | 0.50 | 7.60 | 96 | 3.48 | 10.2 | 19.2 | 33.9 | 4.75 | 19.5 | 3.78 | 1.20 | |
| TZ01-14 | 75 | 840 | 1 067 | 4.13 | 1.45 | 0.48 | 7.50 | 86 | 3.28 | 10.2 | 18.1 | 36.4 | 4.82 | 19.4 | 3.73 | 1.10 | |
| TZ01-15 | 72 | 824 | 1 071 | 4.21 | 1.42 | 0.49 | 7.60 | 87 | 3.36 | 10.3 | 20.5 | 35.6 | 4.78 | 19.3 | 3.86 | 1.14 | |
| TZ01-16 | 65 | 834 | 971 | 4.05 | 1.44 | 0.46 | 7.40 | 87 | 3.16 | 10.2 | 19.7 | 35.0 | 4.82 | 20.0 | 3.78 | 1.16 | |
| TZ02-08 | 石英二 长斑岩 | 136 | 724 | 1 589 | 5.22 | 1.96 | 0.48 | 12.10 | 147 | 5.58 | 4.5 | 18.7 | 34.9 | 4.26 | 16.5 | 2.49 | 0.78 |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | Sr/Y | δEu | δCe |
| TZ01-06 | 石英二 长玢岩 | 3.12 | 0.42 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 0.82 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 90.9 | 83.6 | 7.29 | 11.5 | 21.4 | 70 | 1.01 | 0.89 |
| TZ01-07 | 2.01 | 0.28 | 1.54 | 0.28 | 0.82 | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.13 | 69.4 | 63.4 | 6.00 | 10.6 | 12.1 | 86 | 1.00 | 0.97 | |
| TZ01-13 | 3.10 | 0.43 | 2.17 | 0.39 | 1.06 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 0.14 | 90.6 | 82.3 | 8.32 | 9.9 | 15.4 | 81 | 1.04 | 0.84 | |
| TZ01-14 | 3.10 | 0.42 | 2.13 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.14 | 0.88 | 0.14 | 91.5 | 83.3 | 8.18 | 10.2 | 14.8 | 82 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| TZ01-15 | 3.08 | 0.46 | 2.24 | 0.37 | 1.05 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 93.5 | 85.1 | 8.41 | 10.1 | 15.5 | 80 | 0.97 | 0.85 | |
| TZ01-16 | 3.05 | 0.44 | 2.11 | 0.36 | 1.03 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 92.6 | 84.4 | 8.15 | 10.4 | 15.8 | 82 | 1.01 | 0.85 | |
| TZ02-08 | 石英二 长斑岩 | 2.00 | 0.23 | 0.96 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 81.1 | 77.0 | 4.13 | 18.7 | 42.7 | 161 | 1.03 | 0.92 |
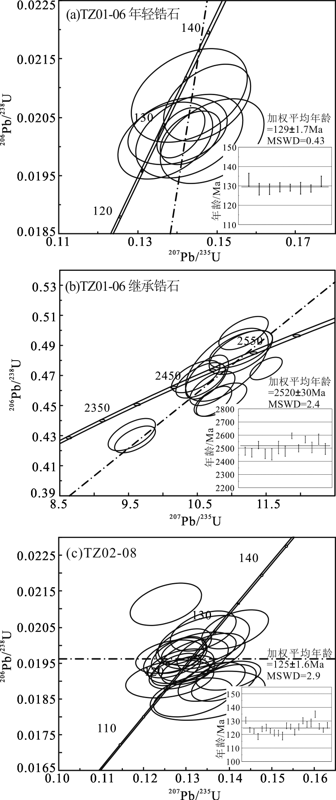
图4 铁寨杂岩体TZ01-06石英二长玢岩(a、b)和TZ02-08石英二长斑岩(c)锆石U-Pb谐和年龄图
Fig.4 Concordia age diagram of younger overgrowths rims of sample TZ01-06(a),concordia age diagram of older overgrowths rims of sample TZ01-06(b),and concordia age diagram of sample TZ02-08(c)
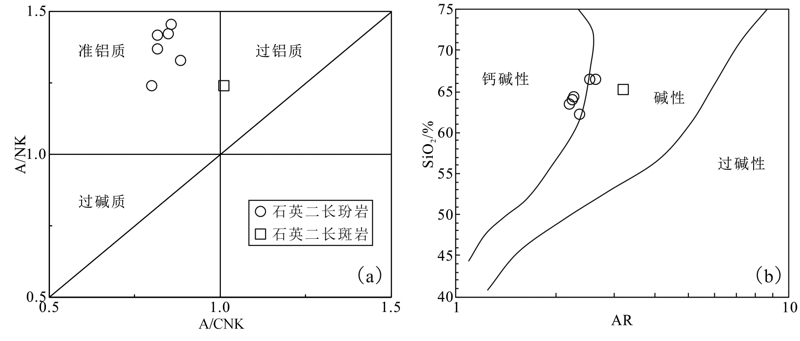
图6 铁寨杂岩体A/CNK-A/NK图解((a),底图据文献[48])和AR-SiO2(碱度率)图解((b),底图据文献[49])
Fig.6 A/CNK-A/NK(a)(base map after reference[48]) and AR-SiO2 (b) (base map after reference[49]) diagrams of Tiezhai complex
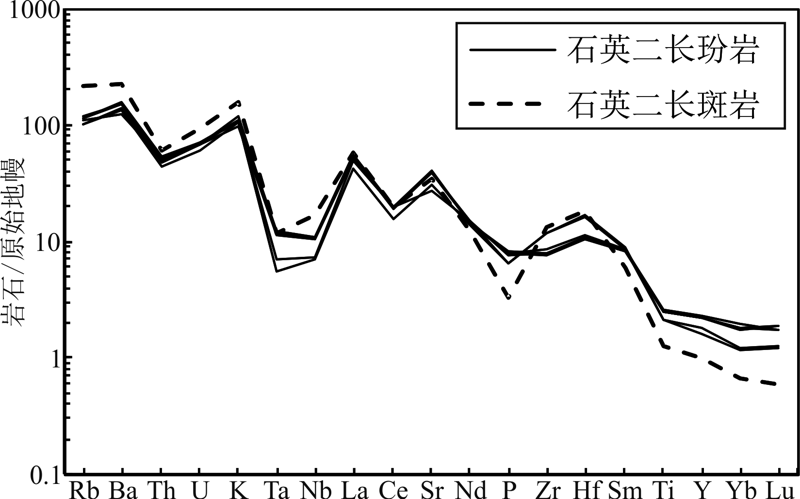
图8 铁寨杂岩体微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(标准化数据引自文献[50])
Fig.8 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns of Tiezhai complex (normalized data after reference [50])
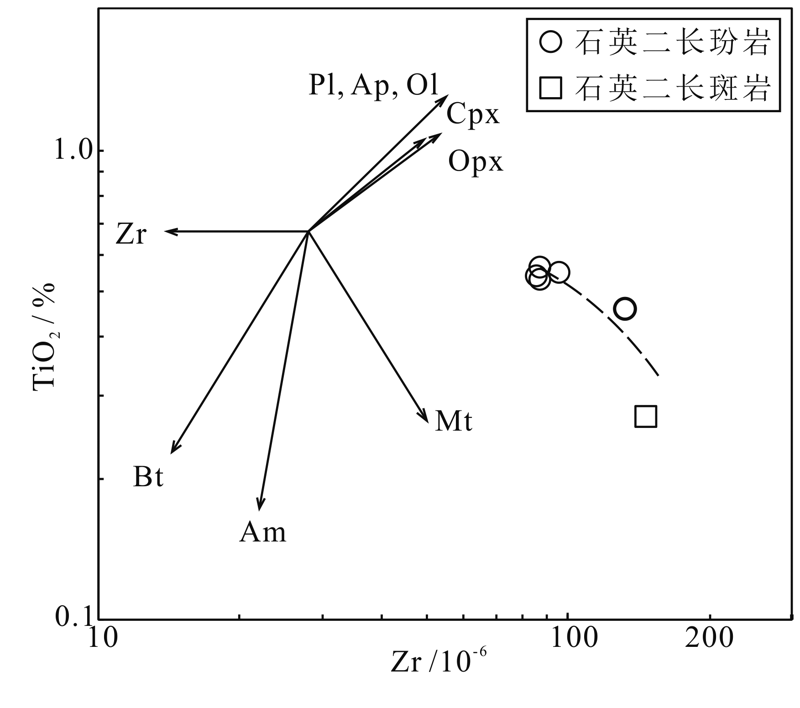
图10 铁寨杂岩体Zr-TiO2分离结晶趋势(底图据文献[59]) Zr.锆石;Bt.黑云母;Am.角闪石;Mt.磁铁矿;Opx.斜方辉石;Cpx.单斜辉石;Pl.斜长石;Ap.磷灰石;Ol.橄榄石
Fig.10 Zr-TiO2 fractionation trends of Tiezhai complex (base map after reference [59])
| [1] | CHEN Y, SU B, GUO S. The Dabie-Sulu orogenic peridotites: Progress and key issues[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015,58(10):1679-1699. |
| [2] | LAN T G, FAN H R, HU F F, et al. Multiple crust-mantle interactions for the destruction of the North China Craton: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic evidence from the Longbaoshan alkaline complex[J]. Lithos, 2011,122(1/2):87-106. |
| [3] | LAN T G, FAN H R, SANTOSH M, et al. Early Jurassic high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic rocks from the Tongshi intrusive complex, eastern North China Craton: Implication for crust-mantle interaction and post-collisional magmatism[J]. Lithos, 2012,140/141:183-199. |
| [4] | LI S R, SANTOSH M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,56:376-414. |
| [5] | MA Q, XU Y G, DENG Y F, et al. Similar crust beneath disrupted and intact cratons: Arguments against lower-crust delamination as a decratonization trigger[J]. Tectonophysics, 2019,750:1-8. |
| [6] | SI S K, ZHENG Y P, LIU B H, et al. Structure of the mantle transition zone beneath the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016,116:69-80. |
| [7] | SPENCER C J, ROBERTS N M W, SANTOSH M. Growth, destruction, and preservation of Earth’s continental crust[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017,172:87-106. |
| [8] | TANG Y J, ZHANG H F, SANTOSH M, et al. Differential destruction of the North China Craton: A tectonic perspective[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013,78:71-82. |
| [9] | WANG J, ZHAO D, YAO Z. Crustal and uppermost mantle structure and seismotectonics of North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013,582:177-187. |
| [10] | WANG Y, ZHOU L Y, LIU S F, et al. Post-cratonization deformation processes and tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018,177:320-365. |
| [11] | WINDLEY B F, MARUYAMA S, XIAO W J. Delamination/thinning of sub-continental lithospheric mantle under Eastern China: The role of water and multiple subduction[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010,310(10):1250-1293. |
| [12] | WU K, LING M X, SUN W D, et al. Major transition of continental basalts in the Early Cretaceous: Implications for the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017,470:93-106. |
| [13] | XU W L, YANG D B, GAO S, et al. Geochemistry of peridotite xenoliths in Early Cretaceous high-Mg# diorites from the Central Orogenic Block of the North China Craton: The nature of Mesozoic lithospheric mantle and constraints on lithospheric thinning[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010,270(1/4):257-273. |
| [14] | YANG J H, SUN J F, ZHANG M, et al. Petrogenesis of silica-saturated and silica-undersaturated syenites in the northern North China Craton related to post-collisional and intraplate extension[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012,328:149-167. |
| [15] | ZHAO D P, TIAN Y, LEI J S, et al. Seismic image and origin of the Changbai intraplate volcano in East Asia: Role of big mantle wedge above the stagnant Pacific slab[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2009,173(3/4):197-206. |
| [16] | ZHAO Y, ZHENG J P, XIONG Q, et al. Destruction of the North China Craton triggered by the Triassic Yangtze continental subduction/collision: A review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018,164:72-82. |
| [17] | ZHENG J P, GRIFFIN W L, MA Q, et al. Accretion and reworking beneath the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012,149:61-78. |
| [18] | ZHU G, CHEN Y, JIANG D Z, et al. Rapid change from compression to extension in the North China Craton during the Early Cretaceous: Evidence from the Yunmengshan metamorphic core complex[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015,656:91-110. |
| [19] | ZHU R X, YANG J H, WU F Y. Timing of destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012,149:51-60. |
| [20] | 翟明国, 樊祺诚, 张宏福, 等. 华北东部岩石圈减薄中的下地壳过程:岩浆底侵、置换与拆沉作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(6):1509-1526. |
| [21] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 张广良, 等. 论燕山运动的深部地球动力学本质[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000,6(3):379-388. |
| [22] | 邓晋福, 赵海玲, 莫宣学. 中国大陆根柱构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-20. |
| [23] | ZHANG H F, SUN M, ZHOU X H, et al. Mesozoic lithosphere destruction beneath the North China Craton: evidence from major-, trace-element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopie studies of Fangcheng basalts[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002,144(2):241-253. |
| [24] | ZHANG M, SUDDABY P, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Nature of the lithospheric mantle beneath the eastern part of the Central Asian fold belt: mantle xenolith evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,328(1/2):131-156. |
| [25] | WANG L G, QIU Y M, MCNAUGHTON N J, et al. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the Northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998,13(1/5):275-291. |
| [26] | 巫祥阳, 徐义刚, 马金龙, 等. 鲁西中生代高镁闪长岩的地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2003,27(3):228-236. |
| [27] | 许文良, 王冬艳, 高山, 等. 鲁西中生代金岭闪长岩中纯橄岩和辉石岩包体的发现及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 2003,48(8):790-797. |
| [28] | 许文良, 王冬艳, 王清海, 等. 鲁西中生代闪长岩中两类幔源捕虏体的岩石学和地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2003,19(4):623-636. |
| [29] | 刘建明, 张宏福, 孙景贵, 等. 山东幔源岩浆岩的碳-氧和锶-钕同位素地球化学研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003,33(10):921-930. |
| [30] | 张军, 徐兆文, 李海勇, 等. 山东邹平王家庄铜矿含矿岩体地球化学及成因探讨[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2008,44(6):632-641. |
| [31] | COPE T. Phanerozoic magmatic tempos of North China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017,468:1-10. |
| [32] | MA Q, XU Y G, ZHENG J P, et al. Coexisting Early Cretaceous high-Mg andesites and Adakitic rocks in the North China Craton: the role of water in intraplate magmatism and cratonic destruction[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2016,57(7):1279-1308. |
| [33] | WANG Q, WYMAN D A, XU J F, et al. Early Cretaceous Adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China: Implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007,71(10):2609-2636. |
| [34] | WANG S J, LI X P, SCHERTL H P, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous andesite dykes in the Sulu orogenic belt, eastern China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2018,113(1):77-97. |
| [35] | 许文良, 王冬艳, 王清海, 等. 华北地块中东部中生代侵入杂岩中角闪石和黑云母的40Ar/39Ar定年:对岩石圈减薄时间的制约 [J]. 地球化学, 2004,33(3):221-231. |
| [36] | 金振奎, 刘泽容, 石占中. 鲁西地区断裂构造类型及其形成机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1999,23(5):1-5. |
| [37] | 孔庆友, 张天祯, 于学峰, 等. 山东矿床[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2006: 19-29. |
| [38] | TANG L, SANTOSH M. Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic terrane assembly and Wilson cycle in the North China Craton: an overview from the central segment of the Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018,182:1-27. |
| [39] | GAO L, LIU S W, SUN G Z, et al. Petrogenesis of late Neoarchean high-K granitoids in the Western Shandong terrane, North China Craton, and their implications for crust-mantle interactions[J]. Precambrian Research, 2018,315:138-161. |
| [40] | 刘玉强, 李洪喜, 黄太岭, 等. 山东省金、铁、煤矿床成矿系列及成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 18-24. |
| [41] | 于立栋. 鲁西临朐铁寨杂岩体地质地球化学特征与动力学背景[J]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. |
| [42] | 王金光, 王立法. 1∶25万潍坊市、青岛市、灵山卫幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 济南: 山东省地质调查院, 2013. |
| [43] | SLáMA J, KOŠLER J, CONDON D J, et al. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,249(1/2):1-35. |
| [44] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for ISOPLOT 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 25-32. |
| [45] | 张万良, 高梦奇, 吕川, 等. 湘赣边界鹿井地区印支早期花岗岩的发现及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018,32(5):863-873. |
| [46] | 高继雷, 赵法强, 李峰, 等. 胶东埠上金矿地球化学特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2015,31(11):20-25. |
| [47] | MIDDLEMOST E A. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224. |
| [48] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [49] | WRIGHT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969,106(4):370-384. |
| [50] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [51] | 许文良, 王清海, 王冬艳, 等. 华北克拉通东部中生代岩石圈减薄的过程与机制: 中生代火成岩和深源捕虏体证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2004,11(3):309-317. |
| [52] | 王世进, 张成基, 杨恩秀, 等. 鲁西地区中生代侵入岩期次划分[J]. 山东国土资源, 2009,25(2):18-23. |
| [53] | WU F Y, LIN J Q, WILDE S A, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005,233(1):103-119. |
| [54] | 罗镇宽, 苗来成. 胶东招莱地区花岗岩和金矿床[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002: 20-57. |
| [55] | 杨承海, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 鲁西上峪辉长—闪长岩的成因:年代学与岩石地球化学证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2008,31(1):44-55. |
| [56] | DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990,347:662-665. |
| [57] | WANG H, XU Z, LU X, et al. Two-types of Early Cretaceous adakitic porphyries from the Luxi terrane, eastern North China Block: Melting of subducted Paleo-Pacific slab and delaminated newly underplated lower crust[J]. Lithos, 2016,240/243:140-154. |
| [58] | YANG H T, SHI J P, YANG D B. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous granodiorite porphyries in Hutouya, western Shandong and their implications for petrogenesis[J]. Global Geology, 2017,20(1):32-39. |
| [59] | PEARCE J. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[M]// THORPE R S. Andesites: Orogenic Andesites and Related Rocks. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1982: 525-548. |
| [60] | RAPP R P, XIAO L, SHIMIZU N. Experimental constraints on the origin of potassium-rich adakites in eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2002,18(3):293-302. |
| [61] | HUANG F, LI S G, DONG F, et al. High-Mg adakitic rocks in the Dabie orogen, central China: Implications for foundering mechanism of lower continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,255(1):1-13. |
| [62] | GAO S, RUDNICK R L, YUAN H L, et al. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton[J]. Nature, 2004,4324:892-897. |
| [63] | 蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 常兆山, 等. 王安镇岩体岩石地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2003,19(1):81-92. |
| [64] | GAO Y F, SANTOSH M, HOU Z Q, et al. High Sr/Y magmas generated through crystal fractionation: Evidence from Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the northern Taihang orogen, North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012,22(1):152-168. |
| [65] | GAO Y F, SANTOSH M, WEI R H, et al. Origin of high Sr/Y magmas from the northern Taihang Mountains: Implications for Mesozoic porphyry copper mineralization in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013,78(12):143-159. |
| [66] | ZHANG H D, LIU J C, WANG J Y, et al. Petrology, geochronology and geochemistry characteristics of Wang’anzhen complex in the northern Taihang Mountain and their geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016,32(3):727-745. |
| [67] | JIANG N, LIU Y S, ZHOU W G, et al. Derivation of Mesozoic adakitic magmas from ancient lower crust in the North China craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007,71(10):2591-2608. |
| [68] | CHEN B, JAHN B M, SUZUKI K. Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os isotopic constraints on the origin of high-Mg adakitic rocks from the North China Craton: Tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 2013,41(1):91-94. |
| [69] | ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, DAVIS G A, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatism and deformation in the North China Craton: Implications for lithospheric thinning and decratonization[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014,131:49-87. |
| [70] | ZHENG J P. Comparison of mantle-derived material from different spatiotemporal settings: Implications for destructive and accretional processes of the North China Craton[J]. Science Bulletin, 2009,54(19):3397-3416. |
| [71] | COPE T, RITTS B D, DARBY B J, et al. Late Paleozoic sedimentation on the northern margin of the North China Block: Implications for regional tectonics and climate change[J]. International Geology Review, 2010,47(3):270-296. |
| [72] | YANG J H, WU F Y, SHAO J A, et al. Constraints on the timing of uplift of the Yanshan Fold and Thrust Belt, North China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006,246(3/4):336-352. |
| [73] | ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, YANG Z Y, et al. The 1.35Ga diabase sills from the northern North China Craton: Implications for breakup of the Columbia (Nuna) supercontinent[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009,288(3/4):588-600. |
| [74] | ZHENG J, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Mineral chemistry of peridotites from Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lithosphere: Constraints on mantle evolution beneath Eastern China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006,47(11):2233-2256. |
| [75] | 路凤香, 韩柱国, 郑建平, 等. 辽宁复县地区古生代岩石圈地幔特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 1991,10(增):2-20. |
| [76] | 郑建平. 中国东部地幔置换作用与中新生代岩石圈减薄[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1999: 1-126. |
| [77] | ZHU R X, FAN H R, LI J W, et al. Decratonic gold deposits[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015,58(9):1523-1537. |
| [78] | ZHAO D P, OHTANI E. Deep slab subduction and dehydration and their geodynamic consequences: Evidence from seismology and mineral physics[J]. Gondwana Research, 2009,16(3/4):401-413. |
| [79] | NIU Y. Generation and evolution of basaltic magmas: some basic concepts and a new view on the origin of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basaltic volcanism in eastern China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005,11(1):9-46. |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [3] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [4] | 任程昊, 佘宏全, 柯昌辉, 孙衍东, 周群茂, 焦天龙, 李保亮. 福建平和钟腾铜矿床成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1447-1464. |
| [5] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 王晓丽, 严溶, 路远发. 西藏日喀则蛇绿岩镁铁质岩石Re-Os同位素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1503-1512. |
| [6] | 杨帆, 陈岳龙, 于洋. 鲁西地区新太古代晚期正长-二长花岗岩成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1155-1172. |
| [7] | 刘建栋, 李五福, 王国良, 董进生, 曹锦山, 李红刚, 赵忠国. 北祁连东段柏木峡—门岗峡地区蛇绿岩的识别及其区域构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 244-258. |
| [8] | 谢亘, 喻光明, 路英川, 冯欣, 田光昊, 王然, 王建. 华北克拉通南缘小秦岭地区花岗质片麻岩年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1702-1712. |
| [9] | 张志平, 钟康惠, 单树成, 郑鑫, 黄浩震, 严钊. 新特提斯洋晚白垩世演化特点:来自泽当共国日二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1194-1205. |
| [10] | 王玉平, 吴文彬, 刘永俊, 李海洋, 王晓亮, 李超. 辽东岫岩地区晚侏罗世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(04): 955-967. |
| [11] | 何泽宇, 申俊峰, 张善明, 刘俊, 杜佰松. 内蒙古乌海桌子山花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 523-534. |
| [12] | 饶世成, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 石康兴, 祝佳萱, 陈奇, 段泓羽, 李朋伟. 豫西熊耳山地区五丈山岩体成因与构造意义:岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1230-1244. |
| [13] | 岳相元, 杨波, 周雄, 龚大兴, 叶亚康, 谭红旗, 周玉, 朱志敏. 川西地区热达门石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征:岩石成因与构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 1015-1024. |
| [14] | 朱伯鹏, 秦纪华, 何斌, 张汉青, 吴晓贵. 阿尔泰巴利尔斯河一带岩体LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 680-691. |
| [15] | 翁凯, 马中平, 张雪. 西准噶尔谢米斯台地区双峰式火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 692-703. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||