



现代地质 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (04): 704-717.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.04.07
刘伯崇1( ), 李康宁1,2(
), 李康宁1,2( ), 史海龙1, 蒲万峰1, 汪宏涛1, 王舒恒1
), 史海龙1, 蒲万峰1, 汪宏涛1, 王舒恒1
收稿日期:2017-12-09
修回日期:2018-02-28
出版日期:2018-08-10
发布日期:2018-09-19
通讯作者:
李康宁
作者简介:李康宁,男,工程师,硕士,1986年出生,岩石学专业,从事地质矿产调查与找矿预测工作。Email:379607468@qq.com。基金资助:
LIU Bochong1( ), LI Kangning1,2(
), LI Kangning1,2( ), SHI Hailong1, PU Wanfeng1, WANG Hongtao1, WANG Shuheng1
), SHI Hailong1, PU Wanfeng1, WANG Hongtao1, WANG Shuheng1
Received:2017-12-09
Revised:2018-02-28
Online:2018-08-10
Published:2018-09-19
Contact:
LI Kangning
摘要:
西秦岭甘肃、青海交界一带中生代火山岩较为发育,火山岩组成以安山质、流纹质为主,均为高钾钙碱性火山岩,主、微量元素含量变化较大。SiO2的质量分数为56.67%~78.17%,平均69.78%, Al2O3含量较高(12.77%~17.29%,平均14.64%)。TiO2含量少(0.02%~0.75%,平均0.22%),Na2O/K2O比值较小(0.03%~2.68%,平均0.65%)。轻稀土元素中等富集,重稀土元素相对亏损,稀土元素配分曲线明显右倾,具Eu负异常。安山质火山岩与流纹质火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石配分曲线中重稀土型式明显不同,暗示二者来自不同的源区。微量元素中P、Nb、Ti、Ta等高场强元素(HFS)相对亏损,Th、 Ba、K、Rb等大离子亲石元素相对富集。研究区安山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年结果为(236±1.2)Ma,代表了火山岩的喷发年龄。它们形成于隆务峡蛇绿岩洋壳向南俯冲的活动大陆边缘弧环境,为俯冲洋壳在地幔深部发生高程度部分熔融作用的产物,并在上升过程中受到陆壳物质作用。在岩浆演化过程受部分熔融和分异结晶作用的控制,但安山质火山岩主要受控于分异结晶作用,而流纹质火山岩受部分熔融作用较大。
中图分类号:
刘伯崇, 李康宁, 史海龙, 蒲万峰, 汪宏涛, 王舒恒. 西秦岭甘青交界一带晚三叠世火山岩岩石成因及构造指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 704-717.
LIU Bochong, LI Kangning, SHI Hailong, PU Wanfeng, WANG Hongtao, WANG Shuheng. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Late Triassic Volcanic Rocks at the Gansu-Qinghai Junction in the West Qinling Mountains[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(04): 704-717.

图1 西秦岭同仁—合作地区岩浆岩分布图[6] 1.新近系、第四系;2.白垩系;3.晚三叠世火山岩;4.三叠系;5.石炭系、二叠系;6.花岗岩;7.蛇绿岩;8.断裂;9.岩体名称及年龄;10.地名;11.研究区;12.武山南英云闪长岩-奥长花岗岩-花岗闪长岩岩浆弧;13.同仁—岷县花岗岩-花岗闪长岩岩浆弧;14.同仁—武山—天水蛇绿岩
Fig.1 Map showing the distribution of magmatic rocks in the Tongren-Hezuo area of the West Qinling Mountains[6]
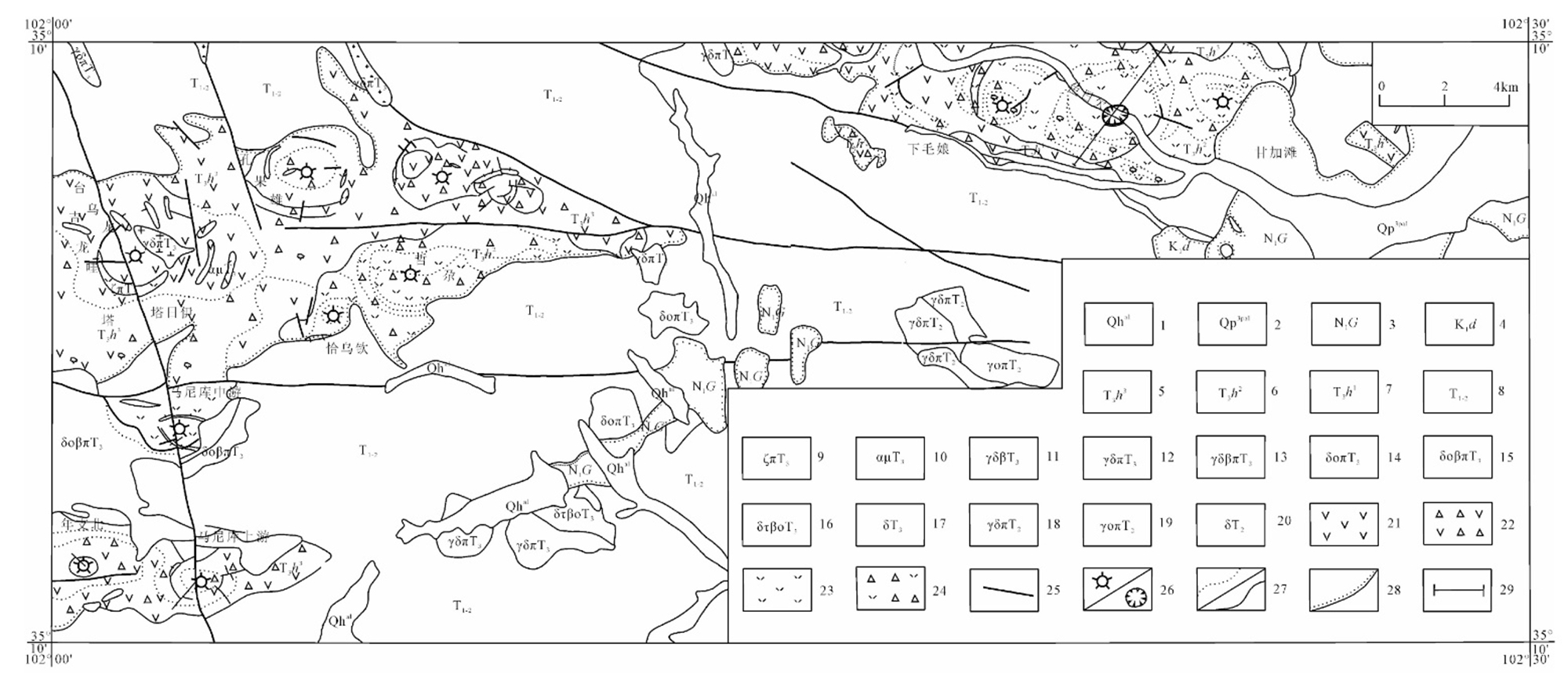
图2 研究区火山岩分布图[10-11] 1.全新世冲积物;2.晚更新世冲洪积物;3.上新世贵德群;4.早白垩世多禾茂组;5.晚三叠世华日组三段;6.晚三叠世华日组二段;7.晚三叠世华日组一段;8.早中三叠世地层;9.晚三叠世英安斑岩;10.晚三叠世安山玢岩;11. 晚三叠世黑云母花岗闪长岩;12. 晚三叠世花岗闪长斑岩;13. 晚三叠世黑云母花岗闪长斑岩;14. 晚三叠世石英闪长玢岩;15. 晚三叠世黑云母石英闪长玢岩;16. 晚三叠世黑云母细晶石英闪长岩;17. 晚三叠世闪长岩;18.中三叠世花岗闪长斑岩;19.中三叠世石英闪长玢岩;20.中三叠世闪长岩;21.安山岩;22.安山质角砾岩;23.英安岩;24.英安质角砾岩;25.断裂;26.火山通道;27. 岩相界线/地质界线;28. 角度不整合接触界线;29.采样剖面位置
Fig.2 Map showing the distribution of Volcanic rocks in the study area

图3 研究区典型火山岩照片 A.安山岩中的气孔构造;B.流纹质角砾集块岩;C.层状凝灰岩;D.层状凝灰岩与英安岩互层;E.蚀变安山岩斜长石斑晶(Pl)被绢云母和方解石集合体代替,仅具假象,基质中斜长石(Pl)具交织结构,正交镜10×10;F.蚀变英安岩斑晶石英(Q)和斜长石(Pl)熔蚀明显,黑云母(Bi)则强烈暗化,正交镜10×2.5;G.蚀变流纹岩方解石(Cal)脉体发育,正交镜10×5;H.蚀变角闪安山玢岩斑晶,包括斜长石(Pl)和角闪石(Hb),正交镜10×2.5
Fig.3 Photographs of typical volcanic rocks in the study area

图4 研究区火山岩分类图解 (a)TAS火山岩分类图解[14];(b)Zr /TiO2-SiO2分类图解[15];(c)AR-SiO2碱率图[16];(d)K2O-SiO2图解[17];数据据表1
Fig.4 Classification diagrams for volcanic rocks in the study area
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | Ba | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安山岩 | 2014Ⅳ-1 | 57.14 | 0.59 | 17.26 | 2.24 | 3.46 | 0.08 | 2.35 | 5.90 | 2.84 | 1.06 | 0.076 | 6.40 | 99.39 | 43.34 | 142 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-2 | 56.67 | 0.61 | 16.12 | 2.06 | 4.71 | 0.11 | 4.22 | 7.32 | 2.27 | 1.56 | 0.069 | 3.45 | 99.17 | 53.40 | 354 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-10 | 59.29 | 0.61 | 15.78 | 0.53 | 5.44 | 0.12 | 3.56 | 4.78 | 2.82 | 3.06 | 0.122 | 2.93 | 99.05 | 51.74 | 775 | |||||
| 灰绿色 角闪安 山玢岩 | 2014Ⅳ-19 | 59.72 | 0.68 | 17.29 | 0.86 | 4.85 | 0.10 | 2.70 | 4.09 | 3.02 | 2.78 | 0.162 | 2.87 | 99.13 | 46.09 | 611 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-20 | 61.05 | 0.75 | 15.18 | 1.00 | 4.02 | 0.09 | 3.01 | 4.26 | 2.93 | 3.24 | 0.128 | 3.58 | 99.23 | 52.17 | 562 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-21 | 61.05 | 0.62 | 16.66 | 0.53 | 4.92 | 0.09 | 1.80 | 4.12 | 3.16 | 2.56 | 0.164 | 3.48 | 99.14 | 37.30 | 562 | |||||
| 浅灰色 流纹岩 | 2014Ⅳ-7 | 78.17 | 0.03 | 13.96 | 0.71 | 0.95 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 2.28 | 0.036 | 3.23 | 99.72 | 10.07 | 41 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-8 | 75.63 | 0.04 | 13.53 | 0.73 | 1.33 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 1.69 | 4.81 | 0.037 | 1.52 | 99.63 | 11.03 | 375 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-9 | 73.22 | 0.02 | 13.87 | 0.68 | 1.38 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 1.05 | 3.54 | 4.73 | 0.045 | 0.97 | 99.63 | 9.04 | 305 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-11 | 77.03 | 0.02 | 14.87 | 0.64 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 3.96 | 0.020 | 1.96 | 99.73 | 19.05 | 100 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-12 | 73.41 | 0.02 | 14.11 | 0.58 | 1.38 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 1.27 | 1.81 | 4.95 | 0.053 | 1.89 | 99.64 | 11.52 | 284 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-13 | 78.05 | 0.06 | 14.46 | 0.71 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 1.49 | 0.018 | 4.27 | 99.79 | 26.64 | 94 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-16 | 70.97 | 0.08 | 15.06 | 0.83 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 1.05 | 0.20 | 7.78 | 0.022 | 2.73 | 99.61 | 21.13 | 1 250 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-14 | 75.37 | 0.05 | 12.77 | 0.66 | 1.11 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.60 | 2.86 | 4.67 | 0.016 | 1.30 | 99.60 | 14.91 | 988 | |||||
| 流纹质 角砾 (熔)岩 | 2014Ⅳ-3 | 72.91 | 0.09 | 15.39 | 1.19 | 0.89 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 3.05 | 3.98 | 0.025 | 1.68 | 99.66 | 15.37 | 520 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-15 | 74.01 | 0.07 | 14.57 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 6.14 | 0.022 | 2.55 | 99.62 | 18.90 | 1 230 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-4 | 70.41 | 0.12 | 12.97 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 3.76 | 2.02 | 4.62 | 0.051 | 4.01 | 99.57 | 15.31 | 1 200 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-5 | 75.52 | 0.04 | 13.01 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.66 | 1.81 | 4.91 | 0.038 | 1.96 | 99.65 | 13.76 | 457 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-6 | 73.90 | 0.04 | 13.44 | 0.60 | 0.95 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 1.39 | 2.28 | 4.79 | 0.061 | 2.12 | 99.69 | 10.61 | 291 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-18 | 72.05 | 0.04 | 14.23 | 0.93 | 1.61 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 1.27 | 2.27 | 4.72 | 0.019 | 2.2 | 99.60 | 14.30 | 504 | |||||
| 凝灰岩 | 2014Ⅳ-17 | 67.92 | 0.07 | 13.00 | 0.95 | 0.615 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 4.98 | 2.28 | 4.33 | 0.037 | 5.25 | 99.66 | 21.29 | 784 | ||||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Th | Nb | Ta | Sr | Zr | Hf | Eu | Li | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | ||||
| 安山岩 | 2014Ⅳ-1 | 8.48 | 12.4 | 0.62 | 157.0 | 182.0 | 4.80 | 1.000 | 61.8 | 27.1 | 58.9 | 6.28 | 83.8 | 4.62 | 1.00 | 4.01 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-2 | 6.83 | 11.8 | 0.65 | 217.0 | 178.0 | 4.44 | 0.042 | 18.0 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 0.28 | 1.1 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.20 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-10 | 13.00 | 12.1 | 0.72 | 336.0 | 173.0 | 4.64 | 1.140 | 48.6 | 33.3 | 72.6 | 7.66 | 29.2 | 5.44 | 1.14 | 4.88 | |||||
| 灰绿色 角闪安 山玢岩 | 2014Ⅳ-19 | 12.60 | 11.8 | 0.67 | 498.0 | 206.0 | 5.21 | 1.370 | 64.1 | 38.0 | 83.7 | 8.67 | 33.2 | 6.21 | 1.37 | 5.39 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-20 | 18.90 | 14.9 | 0.92 | 240.0 | 266.0 | 7.02 | 1.040 | 67.0 | 41.8 | 93.0 | 9.68 | 36.5 | 6.88 | 1.04 | 6.20 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-21 | 11.30 | 11.0 | 0.68 | 399.0 | 245.0 | 5.92 | 1.310 | 47.8 | 34.7 | 75.7 | 8.14 | 31.0 | 5.87 | 1.31 | 5.17 | |||||
| 浅灰色 流纹岩 | 2014Ⅳ-7 | 10.20 | 17.4 | 1.17 | 43.7 | 64.4 | 3.16 | 0.340 | 49.4 | 19.3 | 48.5 | 5.49 | 20.6 | 5.09 | 0.34 | 2.58 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-8 | 10.60 | 19.3 | 1.17 | 46.5 | 62.9 | 2.88 | 0.330 | 17.4 | 14.3 | 29.0 | 3.17 | 13.1 | 3.89 | 0.33 | 2.67 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-9 | 9.31 | 24.4 | 1.58 | 67.7 | 64.8 | 3.13 | 0.250 | 19.1 | 13.5 | 33.4 | 3.81 | 14.7 | 4.36 | 0.25 | 2.22 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-11 | 11.80 | 20.4 | 1.64 | 14.8 | 61.8 | 3.16 | 0.240 | 13.8 | 15.5 | 37.6 | 4.38 | 16.7 | 4.84 | 0.24 | 3.72 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-12 | 9.88 | 23.7 | 1.63 | 72.1 | 65.1 | 3.10 | 0.300 | 14.1 | 17.5 | 45.7 | 5.21 | 20.3 | 5.91 | 0.30 | 4.43 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-13 | 10.50 | 14.0 | 0.85 | 35.9 | 86.0 | 3.69 | 0.780 | 51.4 | 19.0 | 45.3 | 4.91 | 19.2 | 4.33 | 0.78 | 2.82 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-16 | 44.70 | 14.1 | 0.90 | 57.0 | 93.2 | 3.85 | 0.980 | 40.9 | 20.8 | 48.5 | 5.30 | 21.0 | 4.58 | 0.98 | 2.93 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-14 | 8.45 | 11.8 | 0.64 | 53.1 | 66.9 | 2.83 | 0.730 | 16.7 | 12.0 | 31.4 | 3.33 | 13.2 | 3.31 | 0.73 | 2.13 | |||||
| 流纹质 角砾 (熔)岩 | 2014Ⅳ-3 | 15.00 | 15.5 | 0.94 | 70.9 | 120.0 | 4.53 | 0.980 | 20.5 | 26.6 | 59.3 | 6.59 | 25.3 | 5.33 | 0.98 | 3.61 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-15 | 11.40 | 10.9 | 0.77 | 55.4 | 88.2 | 3.69 | 1.000 | 50.0 | 18.8 | 43.7 | 4.90 | 19.6 | 4.44 | 1.00 | 2.80 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-4 | 19.00 | 13.9 | 0.87 | 214.0 | 126.0 | 4.23 | 1.180 | 31.2 | 51.1 | 108.0 | 11.90 | 44.5 | 8.19 | 1.18 | 6.43 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-5 | 9.32 | 17.8 | 1.14 | 48.4 | 61.0 | 2.82 | 0.400 | 19.8 | 17.6 | 42.8 | 7.97 | 19.0 | 4.94 | 0.40 | 2.59 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-6 | 9.24 | 19.6 | 1.21 | 90.8 | 71.2 | 3.22 | 0.500 | 12.9 | 20.6 | 48.7 | 5.67 | 21.9 | 5.8 | 0.50 | 4.28 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-18 | 7.93 | 15.5 | 0.99 | 64.0 | 65.8 | 3.16 | 0.580 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 87.4 | 2.81 | 11.4 | 3.21 | 0.58 | 2.12 | |||||
| 凝灰岩 | 2014Ⅳ-17 | 10.8 | 11.2 | 0.69 | 114.0 | 83.4 | 3.39 | 0.890 | 20.7 | 16.9 | 36.7 | 4.59 | 18.4 | 4.32 | 0.89 | 2.80 | ||||
| 安山岩 | 2014Ⅳ-1 | 14.80 | 48.4 | 0.60 | 3.52 | 0.70 | 1.91 | 0.300 | 1.960 | 0.280 | 17.40 | 194.98 | 13.68 | 0.69 | 5.87 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-2 | 6.67 | 68.5 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.013 | 0.088 | 0.011 | 1.070 | 6.28 | 8.76 | 0.58 | 5.35 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-10 | 11.7 | 139.0 | 0.68 | 3.82 | 0.74 | 2.02 | 0.300 | 2.100 | 0.300 | 18.50 | 164.18 | 10.06 | 0.66 | 6.12 | ||||||
| 灰绿色 角闪安 山玢岩 | 2014Ⅳ-19 | 5.17 | 114.0 | 0.73 | 3.85 | 0.73 | 1.96 | 0.290 | 1.880 | 0.260 | 17.50 | 186.24 | 11.34 | 0.71 | 6.12 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-20 | 6.46 | 172.0 | 0.89 | 4.96 | 0.97 | 2.64 | 0.390 | 2.660 | 0.360 | 23.60 | 207.97 | 9.91 | 0.48 | 6.08 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-21 | 14.50 | 121.0 | 0.70 | 3.67 | 0.68 | 1.77 | 0.260 | 1.690 | 0.230 | 16.70 | 170.89 | 11.06 | 0.71 | 5.91 | ||||||
| 浅灰色 流纹岩 | 2014Ⅳ-7 | 4.21 | 137.0 | 0.40 | 1.27 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.020 | 0.106 | 0.018 | 3.38 | 104.09 | 20.80 | 0.26 | 3.79 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-8 | 9.63 | 244.0 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.021 | 0.160 | 0.019 | 3.21 | 68.56 | 13.37 | 0.30 | 3.68 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-9 | 6.59 | 255.0 | 0.43 | 1.48 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.220 | 0.160 | 0.020 | 4.33 | 74.94 | 14.23 | 0.22 | 3.10 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-11 | 3.90 | 228.0 | 0.52 | 1.80 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 0.030 | 0.210 | 0.024 | 5.38 | 86.06 | 11.65 | 0.17 | 3.20 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-12 | 9.89 | 312.0 | 0.58 | 1.96 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.028 | 0.220 | 0.027 | 5.64 | 102.69 | 12.22 | 0.17 | 2.96 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-13 | 6.30 | 97.7 | 0.28 | 1.77 | 0.074 | 0.17 | 0.012 | 0.100 | 0.012 | 2.27 | 98.76 | 17.85 | 0.64 | 4.39 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-16 | 9.19 | 368.0 | 0.26 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.009 | 0.092 | 0.013 | 1.52 | 105.26 | 24.65 | 0.76 | 4.54 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-14 | 7.37 | 220.0 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.012 | 0.098 | 0.014 | 1.39 | 68.10 | 15.47 | 0.79 | 3.63 | ||||||
| 流纹质 角砾 (熔)岩 | 2014Ⅳ-3 | 3.30 | 181.0 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 0.31 | 0.032 | 0.220 | 0.026 | 3.36 | 129.73 | 22.05 | 0.64 | 4.99 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-15 | 7.62 | 321.0 | 0.25 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 0.15 | 0.012 | 0.110 | 0.016 | 1.58 | 96.94 | 20.55 | 0.81 | 4.23 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-4 | 6.87 | 195.0 | 0.70 | 2.58 | 0.34 | 0.76 | 0.078 | 0.500 | 0.064 | 9.23 | 236.32 | 19.64 | 0.48 | 6.24 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-5 | 5.78 | 236.0 | 0.42 | 1.34 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.020 | 0.160 | 0.021 | 3.65 | 97.63 | 18.84 | 0.31 | 3.56 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-6 | 5.11 | 247.0 | 0.52 | 1.68 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.027 | 0.210 | 0.027 | 4.92 | 110.39 | 14.28 | 0.29 | 3.55 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-18 | 8.44 | 254.0 | 0.21 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.014 | 0.120 | 0.018 | 1.58 | 118.53 | 35.16 | 0.64 | 3.07 | ||||||
| 凝灰岩 | 2014Ⅳ-17 | 5.96 | 208.0 | 0.27 | 0.69 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.010 | 0.082 | 0.012 | 1.71 | 85.86 | 20.16 | 0.73 | 3.91 | |||||
表1 西秦岭甘加一带火山岩主量元素(%)、微量元素(10-6)含量
Table 1 Compositions of major elements (%), trace elements (10-6) of the West Qinling volcanic rocks in Ganjia
| 岩性 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | Mg# | Ba | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安山岩 | 2014Ⅳ-1 | 57.14 | 0.59 | 17.26 | 2.24 | 3.46 | 0.08 | 2.35 | 5.90 | 2.84 | 1.06 | 0.076 | 6.40 | 99.39 | 43.34 | 142 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-2 | 56.67 | 0.61 | 16.12 | 2.06 | 4.71 | 0.11 | 4.22 | 7.32 | 2.27 | 1.56 | 0.069 | 3.45 | 99.17 | 53.40 | 354 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-10 | 59.29 | 0.61 | 15.78 | 0.53 | 5.44 | 0.12 | 3.56 | 4.78 | 2.82 | 3.06 | 0.122 | 2.93 | 99.05 | 51.74 | 775 | |||||
| 灰绿色 角闪安 山玢岩 | 2014Ⅳ-19 | 59.72 | 0.68 | 17.29 | 0.86 | 4.85 | 0.10 | 2.70 | 4.09 | 3.02 | 2.78 | 0.162 | 2.87 | 99.13 | 46.09 | 611 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-20 | 61.05 | 0.75 | 15.18 | 1.00 | 4.02 | 0.09 | 3.01 | 4.26 | 2.93 | 3.24 | 0.128 | 3.58 | 99.23 | 52.17 | 562 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-21 | 61.05 | 0.62 | 16.66 | 0.53 | 4.92 | 0.09 | 1.80 | 4.12 | 3.16 | 2.56 | 0.164 | 3.48 | 99.14 | 37.30 | 562 | |||||
| 浅灰色 流纹岩 | 2014Ⅳ-7 | 78.17 | 0.03 | 13.96 | 0.71 | 0.95 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 2.28 | 0.036 | 3.23 | 99.72 | 10.07 | 41 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-8 | 75.63 | 0.04 | 13.53 | 0.73 | 1.33 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 1.69 | 4.81 | 0.037 | 1.52 | 99.63 | 11.03 | 375 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-9 | 73.22 | 0.02 | 13.87 | 0.68 | 1.38 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 1.05 | 3.54 | 4.73 | 0.045 | 0.97 | 99.63 | 9.04 | 305 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-11 | 77.03 | 0.02 | 14.87 | 0.64 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 3.96 | 0.020 | 1.96 | 99.73 | 19.05 | 100 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-12 | 73.41 | 0.02 | 14.11 | 0.58 | 1.38 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 1.27 | 1.81 | 4.95 | 0.053 | 1.89 | 99.64 | 11.52 | 284 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-13 | 78.05 | 0.06 | 14.46 | 0.71 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 1.49 | 0.018 | 4.27 | 99.79 | 26.64 | 94 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-16 | 70.97 | 0.08 | 15.06 | 0.83 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 1.05 | 0.20 | 7.78 | 0.022 | 2.73 | 99.61 | 21.13 | 1 250 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-14 | 75.37 | 0.05 | 12.77 | 0.66 | 1.11 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.60 | 2.86 | 4.67 | 0.016 | 1.30 | 99.60 | 14.91 | 988 | |||||
| 流纹质 角砾 (熔)岩 | 2014Ⅳ-3 | 72.91 | 0.09 | 15.39 | 1.19 | 0.89 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 3.05 | 3.98 | 0.025 | 1.68 | 99.66 | 15.37 | 520 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-15 | 74.01 | 0.07 | 14.57 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 6.14 | 0.022 | 2.55 | 99.62 | 18.90 | 1 230 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-4 | 70.41 | 0.12 | 12.97 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 3.76 | 2.02 | 4.62 | 0.051 | 4.01 | 99.57 | 15.31 | 1 200 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-5 | 75.52 | 0.04 | 13.01 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.66 | 1.81 | 4.91 | 0.038 | 1.96 | 99.65 | 13.76 | 457 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-6 | 73.90 | 0.04 | 13.44 | 0.60 | 0.95 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 1.39 | 2.28 | 4.79 | 0.061 | 2.12 | 99.69 | 10.61 | 291 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-18 | 72.05 | 0.04 | 14.23 | 0.93 | 1.61 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 1.27 | 2.27 | 4.72 | 0.019 | 2.2 | 99.60 | 14.30 | 504 | |||||
| 凝灰岩 | 2014Ⅳ-17 | 67.92 | 0.07 | 13.00 | 0.95 | 0.615 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 4.98 | 2.28 | 4.33 | 0.037 | 5.25 | 99.66 | 21.29 | 784 | ||||
| 岩性 | 样号 | Th | Nb | Ta | Sr | Zr | Hf | Eu | Li | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | ||||
| 安山岩 | 2014Ⅳ-1 | 8.48 | 12.4 | 0.62 | 157.0 | 182.0 | 4.80 | 1.000 | 61.8 | 27.1 | 58.9 | 6.28 | 83.8 | 4.62 | 1.00 | 4.01 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-2 | 6.83 | 11.8 | 0.65 | 217.0 | 178.0 | 4.44 | 0.042 | 18.0 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 0.28 | 1.1 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.20 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-10 | 13.00 | 12.1 | 0.72 | 336.0 | 173.0 | 4.64 | 1.140 | 48.6 | 33.3 | 72.6 | 7.66 | 29.2 | 5.44 | 1.14 | 4.88 | |||||
| 灰绿色 角闪安 山玢岩 | 2014Ⅳ-19 | 12.60 | 11.8 | 0.67 | 498.0 | 206.0 | 5.21 | 1.370 | 64.1 | 38.0 | 83.7 | 8.67 | 33.2 | 6.21 | 1.37 | 5.39 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-20 | 18.90 | 14.9 | 0.92 | 240.0 | 266.0 | 7.02 | 1.040 | 67.0 | 41.8 | 93.0 | 9.68 | 36.5 | 6.88 | 1.04 | 6.20 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-21 | 11.30 | 11.0 | 0.68 | 399.0 | 245.0 | 5.92 | 1.310 | 47.8 | 34.7 | 75.7 | 8.14 | 31.0 | 5.87 | 1.31 | 5.17 | |||||
| 浅灰色 流纹岩 | 2014Ⅳ-7 | 10.20 | 17.4 | 1.17 | 43.7 | 64.4 | 3.16 | 0.340 | 49.4 | 19.3 | 48.5 | 5.49 | 20.6 | 5.09 | 0.34 | 2.58 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-8 | 10.60 | 19.3 | 1.17 | 46.5 | 62.9 | 2.88 | 0.330 | 17.4 | 14.3 | 29.0 | 3.17 | 13.1 | 3.89 | 0.33 | 2.67 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-9 | 9.31 | 24.4 | 1.58 | 67.7 | 64.8 | 3.13 | 0.250 | 19.1 | 13.5 | 33.4 | 3.81 | 14.7 | 4.36 | 0.25 | 2.22 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-11 | 11.80 | 20.4 | 1.64 | 14.8 | 61.8 | 3.16 | 0.240 | 13.8 | 15.5 | 37.6 | 4.38 | 16.7 | 4.84 | 0.24 | 3.72 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-12 | 9.88 | 23.7 | 1.63 | 72.1 | 65.1 | 3.10 | 0.300 | 14.1 | 17.5 | 45.7 | 5.21 | 20.3 | 5.91 | 0.30 | 4.43 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-13 | 10.50 | 14.0 | 0.85 | 35.9 | 86.0 | 3.69 | 0.780 | 51.4 | 19.0 | 45.3 | 4.91 | 19.2 | 4.33 | 0.78 | 2.82 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-16 | 44.70 | 14.1 | 0.90 | 57.0 | 93.2 | 3.85 | 0.980 | 40.9 | 20.8 | 48.5 | 5.30 | 21.0 | 4.58 | 0.98 | 2.93 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-14 | 8.45 | 11.8 | 0.64 | 53.1 | 66.9 | 2.83 | 0.730 | 16.7 | 12.0 | 31.4 | 3.33 | 13.2 | 3.31 | 0.73 | 2.13 | |||||
| 流纹质 角砾 (熔)岩 | 2014Ⅳ-3 | 15.00 | 15.5 | 0.94 | 70.9 | 120.0 | 4.53 | 0.980 | 20.5 | 26.6 | 59.3 | 6.59 | 25.3 | 5.33 | 0.98 | 3.61 | ||||
| 2014Ⅳ-15 | 11.40 | 10.9 | 0.77 | 55.4 | 88.2 | 3.69 | 1.000 | 50.0 | 18.8 | 43.7 | 4.90 | 19.6 | 4.44 | 1.00 | 2.80 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-4 | 19.00 | 13.9 | 0.87 | 214.0 | 126.0 | 4.23 | 1.180 | 31.2 | 51.1 | 108.0 | 11.90 | 44.5 | 8.19 | 1.18 | 6.43 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-5 | 9.32 | 17.8 | 1.14 | 48.4 | 61.0 | 2.82 | 0.400 | 19.8 | 17.6 | 42.8 | 7.97 | 19.0 | 4.94 | 0.40 | 2.59 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-6 | 9.24 | 19.6 | 1.21 | 90.8 | 71.2 | 3.22 | 0.500 | 12.9 | 20.6 | 48.7 | 5.67 | 21.9 | 5.8 | 0.50 | 4.28 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-18 | 7.93 | 15.5 | 0.99 | 64.0 | 65.8 | 3.16 | 0.580 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 87.4 | 2.81 | 11.4 | 3.21 | 0.58 | 2.12 | |||||
| 凝灰岩 | 2014Ⅳ-17 | 10.8 | 11.2 | 0.69 | 114.0 | 83.4 | 3.39 | 0.890 | 20.7 | 16.9 | 36.7 | 4.59 | 18.4 | 4.32 | 0.89 | 2.80 | ||||
| 安山岩 | 2014Ⅳ-1 | 14.80 | 48.4 | 0.60 | 3.52 | 0.70 | 1.91 | 0.300 | 1.960 | 0.280 | 17.40 | 194.98 | 13.68 | 0.69 | 5.87 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-2 | 6.67 | 68.5 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.013 | 0.088 | 0.011 | 1.070 | 6.28 | 8.76 | 0.58 | 5.35 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-10 | 11.7 | 139.0 | 0.68 | 3.82 | 0.74 | 2.02 | 0.300 | 2.100 | 0.300 | 18.50 | 164.18 | 10.06 | 0.66 | 6.12 | ||||||
| 灰绿色 角闪安 山玢岩 | 2014Ⅳ-19 | 5.17 | 114.0 | 0.73 | 3.85 | 0.73 | 1.96 | 0.290 | 1.880 | 0.260 | 17.50 | 186.24 | 11.34 | 0.71 | 6.12 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-20 | 6.46 | 172.0 | 0.89 | 4.96 | 0.97 | 2.64 | 0.390 | 2.660 | 0.360 | 23.60 | 207.97 | 9.91 | 0.48 | 6.08 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-21 | 14.50 | 121.0 | 0.70 | 3.67 | 0.68 | 1.77 | 0.260 | 1.690 | 0.230 | 16.70 | 170.89 | 11.06 | 0.71 | 5.91 | ||||||
| 浅灰色 流纹岩 | 2014Ⅳ-7 | 4.21 | 137.0 | 0.40 | 1.27 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.020 | 0.106 | 0.018 | 3.38 | 104.09 | 20.80 | 0.26 | 3.79 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-8 | 9.63 | 244.0 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.021 | 0.160 | 0.019 | 3.21 | 68.56 | 13.37 | 0.30 | 3.68 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-9 | 6.59 | 255.0 | 0.43 | 1.48 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.220 | 0.160 | 0.020 | 4.33 | 74.94 | 14.23 | 0.22 | 3.10 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-11 | 3.90 | 228.0 | 0.52 | 1.80 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 0.030 | 0.210 | 0.024 | 5.38 | 86.06 | 11.65 | 0.17 | 3.20 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-12 | 9.89 | 312.0 | 0.58 | 1.96 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.028 | 0.220 | 0.027 | 5.64 | 102.69 | 12.22 | 0.17 | 2.96 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-13 | 6.30 | 97.7 | 0.28 | 1.77 | 0.074 | 0.17 | 0.012 | 0.100 | 0.012 | 2.27 | 98.76 | 17.85 | 0.64 | 4.39 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-16 | 9.19 | 368.0 | 0.26 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.009 | 0.092 | 0.013 | 1.52 | 105.26 | 24.65 | 0.76 | 4.54 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-14 | 7.37 | 220.0 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.012 | 0.098 | 0.014 | 1.39 | 68.10 | 15.47 | 0.79 | 3.63 | ||||||
| 流纹质 角砾 (熔)岩 | 2014Ⅳ-3 | 3.30 | 181.0 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 0.31 | 0.032 | 0.220 | 0.026 | 3.36 | 129.73 | 22.05 | 0.64 | 4.99 | |||||
| 2014Ⅳ-15 | 7.62 | 321.0 | 0.25 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 0.15 | 0.012 | 0.110 | 0.016 | 1.58 | 96.94 | 20.55 | 0.81 | 4.23 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-4 | 6.87 | 195.0 | 0.70 | 2.58 | 0.34 | 0.76 | 0.078 | 0.500 | 0.064 | 9.23 | 236.32 | 19.64 | 0.48 | 6.24 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-5 | 5.78 | 236.0 | 0.42 | 1.34 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.020 | 0.160 | 0.021 | 3.65 | 97.63 | 18.84 | 0.31 | 3.56 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-6 | 5.11 | 247.0 | 0.52 | 1.68 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.027 | 0.210 | 0.027 | 4.92 | 110.39 | 14.28 | 0.29 | 3.55 | ||||||
| 2014Ⅳ-18 | 8.44 | 254.0 | 0.21 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.014 | 0.120 | 0.018 | 1.58 | 118.53 | 35.16 | 0.64 | 3.07 | ||||||
| 凝灰岩 | 2014Ⅳ-17 | 5.96 | 208.0 | 0.27 | 0.69 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.010 | 0.082 | 0.012 | 1.71 | 85.86 | 20.16 | 0.73 | 3.91 | |||||
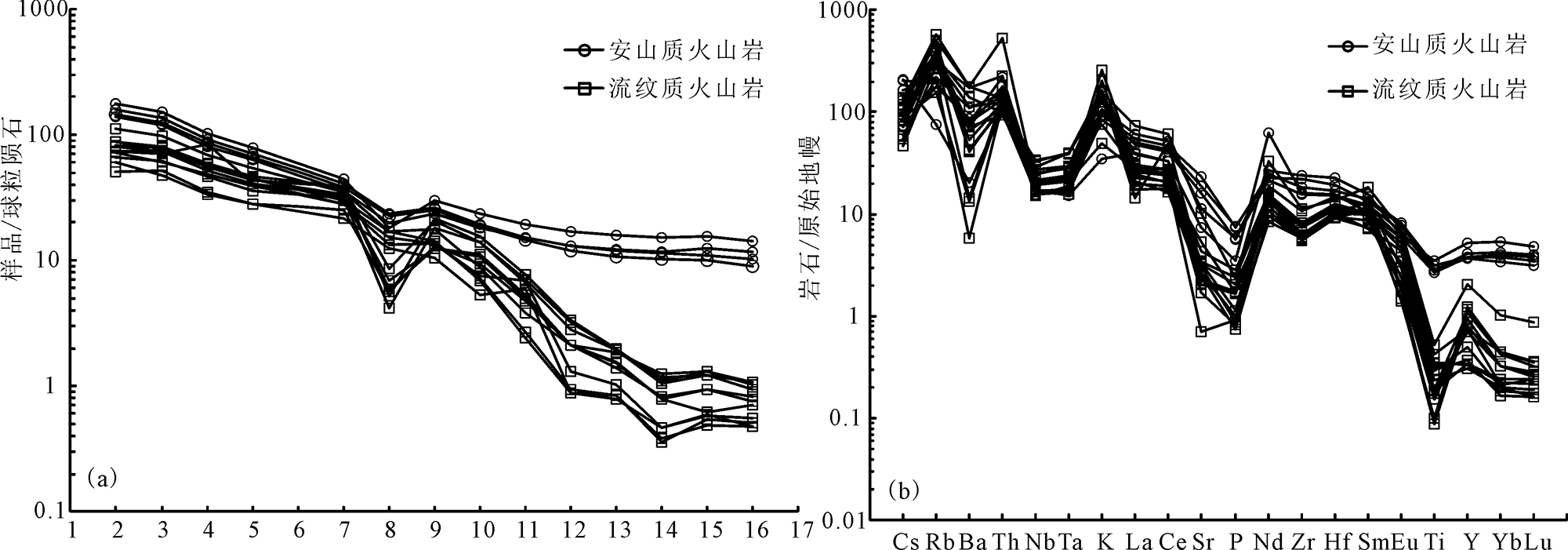
图5 研究区火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)[18]
Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE pattern (a)and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spider diagram (b) [18] for the West Qinling volcanic rocks
| 数据类别 | 编号 | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th | 1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Pb同 位素分 析数据 | 3 | 0.054 17 | 0.002 28 | 0.287 22 | 0.008 87 | 0.038 46 | 0.000 54 | 0.012 44 | 0.000 23 |
| 4 | 0.054 74 | 0.002 51 | 0.287 26 | 0.010 24 | 0.038 06 | 0.000 56 | 0.012 09 | 0.000 23 | |
| 5 | 0.051 88 | 0.002 76 | 0.242 50 | 0.010 74 | 0.033 90 | 0.000 54 | 0.010 81 | 0.000 24 | |
| 9 | 0.050 40 | 0.003 00 | 0.252 19 | 0.013 03 | 0.036 30 | 0.000 62 | 0.011 86 | 0.000 34 | |
| 10 | 0.0553 10 | 0.002 18 | 0.290 39 | 0.007 91 | 0.038 08 | 0.000 52 | 0.012 89 | 0.000 22 | |
| 14 | 0.051 34 | 0.002 20 | 0.269 97 | 0.008 60 | 0.038 14 | 0.000 54 | 0.012 50 | 0.000 28 | |
| 15 | 0.053 10 | 0.004 23 | 0.278 24 | 0.020 44 | 0.038 02 | 0.000 76 | 0.012 35 | 0.000 52 | |
| 16 | 0.080 48 | 0.004 56 | 0.417 03 | 0.020 01 | 0.037 59 | 0.000 69 | 0.016 48 | 0.000 47 | |
| U-Pb同 位素表 面年龄 数据 | 3 | 377.8 | 91.42 | 256.4 | 6.99 | 243.3 | 3.35 | 249.8 | 4.67 |
| 4 | 401.6 | 99.12 | 256.4 | 8.08 | 240.8 | 3.50 | 243.0 | 4.61 | |
| 5 | 280.0 | 117.21 | 220.5 | 8.78 | 214.9 | 3.35 | 217.3 | 4.73 | |
| 9 | 213.2 | 132.43 | 228.4 | 10.56 | 229.8 | 3.84 | 238.2 | 6.77 | |
| 10 | 424.6 | 85.35 | 258.9 | 6.22 | 240.9 | 3.22 | 258.9 | 4.32 | |
| 14 | 256.2 | 95.43 | 242.7 | 6.87 | 241.3 | 3.34 | 251.1 | 5.57 | |
| 15 | 332.8 | 170.86 | 249.3 | 16.24 | 240.5 | 4.73 | 248.1 | 10.28 | |
| 16 | 1 208.7 | 107.68 | 353.9 | 14.34 | 237.9 | 4.30 | 330.4 | 9.29 |
表2 西秦岭安山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素分析有效数据表
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of the West Qinling andesite
| 数据类别 | 编号 | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 208Pb/232Th | 1σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Pb同 位素分 析数据 | 3 | 0.054 17 | 0.002 28 | 0.287 22 | 0.008 87 | 0.038 46 | 0.000 54 | 0.012 44 | 0.000 23 |
| 4 | 0.054 74 | 0.002 51 | 0.287 26 | 0.010 24 | 0.038 06 | 0.000 56 | 0.012 09 | 0.000 23 | |
| 5 | 0.051 88 | 0.002 76 | 0.242 50 | 0.010 74 | 0.033 90 | 0.000 54 | 0.010 81 | 0.000 24 | |
| 9 | 0.050 40 | 0.003 00 | 0.252 19 | 0.013 03 | 0.036 30 | 0.000 62 | 0.011 86 | 0.000 34 | |
| 10 | 0.0553 10 | 0.002 18 | 0.290 39 | 0.007 91 | 0.038 08 | 0.000 52 | 0.012 89 | 0.000 22 | |
| 14 | 0.051 34 | 0.002 20 | 0.269 97 | 0.008 60 | 0.038 14 | 0.000 54 | 0.012 50 | 0.000 28 | |
| 15 | 0.053 10 | 0.004 23 | 0.278 24 | 0.020 44 | 0.038 02 | 0.000 76 | 0.012 35 | 0.000 52 | |
| 16 | 0.080 48 | 0.004 56 | 0.417 03 | 0.020 01 | 0.037 59 | 0.000 69 | 0.016 48 | 0.000 47 | |
| U-Pb同 位素表 面年龄 数据 | 3 | 377.8 | 91.42 | 256.4 | 6.99 | 243.3 | 3.35 | 249.8 | 4.67 |
| 4 | 401.6 | 99.12 | 256.4 | 8.08 | 240.8 | 3.50 | 243.0 | 4.61 | |
| 5 | 280.0 | 117.21 | 220.5 | 8.78 | 214.9 | 3.35 | 217.3 | 4.73 | |
| 9 | 213.2 | 132.43 | 228.4 | 10.56 | 229.8 | 3.84 | 238.2 | 6.77 | |
| 10 | 424.6 | 85.35 | 258.9 | 6.22 | 240.9 | 3.22 | 258.9 | 4.32 | |
| 14 | 256.2 | 95.43 | 242.7 | 6.87 | 241.3 | 3.34 | 251.1 | 5.57 | |
| 15 | 332.8 | 170.86 | 249.3 | 16.24 | 240.5 | 4.73 | 248.1 | 10.28 | |
| 16 | 1 208.7 | 107.68 | 353.9 | 14.34 | 237.9 | 4.30 | 330.4 | 9.29 |

图9 西秦岭火山岩Rb/30-Hf-3×Ta(a)、Rb-(Y+Nb)(b)构造环境判别图解[27-28]
Fig.9 Tectonic discrimination diagrams of Rb/30-Hf-3×Ta(a)and Rb vs.(Y+Nb)(b) of the West Qinling volcanic rocks[27-28]
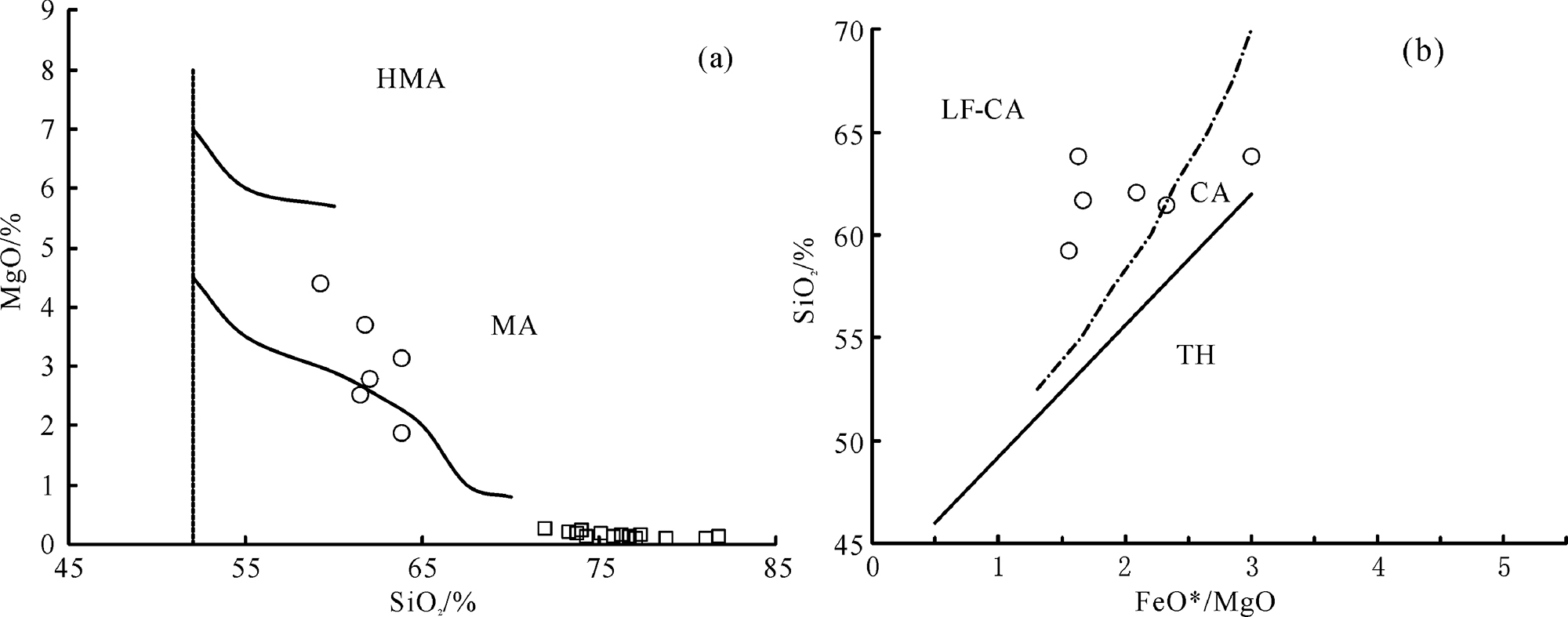
图10 西秦岭高镁/镁安山岩SiO2-MgO(a)、SiO2-FeO*/MgO(b) 判别图解[29-30]
Fig.10 SiO2 vs.MgO(a) and SiO2 vs.FeO*/MgO(b) discrimination diagrams of the West Qinling (high)-Mg andesite[29-30]

图11 研究区流纹质/安山质火山岩形成示意图(据文献[29-30]修改)
Fig.11 Schematic diagram showing formation of the West Qinling andesitic and rhyolitic volcanic rocks(Modified after reference[29-30])
| [1] | 任纪舜, 张正坤, 牛宝贵, 等. 论秦岭造山带——中朝与扬子陆块的拼合过程[M]// 叶连俊, 钱祥麟, 张国伟. 秦岭造山带学术讨论会论文选集. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1991:99-110. |
| [2] | 张旗, 殷先明, 殷勇, 等. 西秦岭与埃达克岩和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的金铜成矿及找矿问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(12) :3103-3122. |
| [3] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1):1-10. |
| [4] | 闫臻. 西秦岭晚古生代弧前盆地沉积与成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 2002:20-50. |
| [5] | 张国伟, 张宗清, 董云鹏, 等. 秦岭造山带主要构造岩石地层单元的构造性质及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(2):101-113. |
| [6] | 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带结构造山过程及动力学[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 2002:1-263. |
| [7] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 李继亮. 造山带沉积盆地构造原型恢复[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27 (12) :2001-2013. |
| [8] | 秦江锋. 秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩类成因机制及深部动力学背景[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2010:1-30. |
| [9] | 王志鹏. 松潘-阿坝和西秦岭三叠系砂岩组分特征及其构造意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自科科学版), 2009, 36 (5) :465-474. |
| [10] | 李注苍, 李永军, 齐建宏, 等. 西秦岭下三叠统华日组火山岩地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 西北地质, 2016, 19(1):26-32. |
| [11] | 李康宁. 西秦岭多哇地区晚三叠世火山岩石学、地球化学特征及构造环境分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016:1-67. |
| [12] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79.
DOI URL |
| [13] | LUDWIG K R. Users Manual for Isoplot/Ex(rev.30):A Geochronologica Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkrley: Berkrley Geochronology Center, 2003:1-55. |
| [14] | LE MAIRE R W. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1989:193. |
| [15] |
WINCHESTER J A, FLOYD P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20:325-343.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WRIGHT J B A. Simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geology Magazine, 1969, 106(4):370-384.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
PECERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area,northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotope systematic of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等. 利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):77-88. |
| [20 ] |
LI Xiaowei, MO Xuanxue, YU Xuehui, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of the early Mesozoic pyroxene andesites in the Maixiu Area,West Qinling, China: Products of subduction or syn-collision[J]. Lithos, 2013, 172/173:158-174.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 邓晋福, 路凤香, 鄂莫岚. 汉诺坝玄武岩岩浆起源及上升的p-t路线[J]. 地质论评, 1987, 33(4):317-32. |
| [22] |
ALLEGRE C J, MINSTER J F. Quantitative method of trace element behavior in magmatic processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 38:1-25.
DOI URL |
| [23] | WEAVER B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions:trace element and isotopic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104:3810. |
| [24] | 龙晓平, 孙敏, 袁超, 等. 东准噶尔石炭系火山岩的形成机制及其对准噶尔洋盆闭合时限的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(1):31-40. |
| [25] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[M]// HOLLABDH D, TUREKIANK K. TheCrust Vol. 3 Treatise on Geochemistry. Oxford: Elsevier-Pergamon, 2003:1-64. |
| [26] | LASSITER J C, DEPAOLO D J. Plume/lithosphere interaction in the generation of continental and oceanic flood basalts: Chemical and isotopic constraints[M]//MAHONEY J. Large Igneous Provinces:Continental,Oceanic and Planetary Flood Volcanism:Geophysical Monography 100. Washington D.C: American Geophysical Union, 1997: 335-355. |
| [27] | HARRIS N B, PEARCE J A, YINDLE A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[M]// COWARDM P, REISA C. Collision Tectonics. London: Geological Society of London, 1986:67-81. |
| [28] |
PEARCE J A. Sources and setting of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19:120-125.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 等. 岩浆弧火成岩构造组合与洋陆转换[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(3):473-484. |
| [30] | 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等. 高镁安山岩/闪长岩类(HMA)和镁安山岩/闪长岩类(MA):与洋俯冲作用相关的两类典型的火成岩类[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4):1112-1118. |
| [31] | 甘成势, 王岳军, 张玉芝, 等. 右江盆地晚侏罗世钾玄质高镁安山岩的厘定及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32 (11) :3281-3294. |
| [32] | 代富强, 赵子福, 郑永飞. 板片-地幔相互作用:大别造山带碰撞后安山质火山岩成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(增刊1):15-20. |
| [33] | 王绘清, 朱云海, 林启祥, 等. 青海尖扎—同仁地区隆务峡蛇绿岩的形成时代及意义——来自辉长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(1) :86-92. |
| [34] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 李继亮, 等. 西秦岭楔的构造属性及其增生造山过程[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(6):1808-1828. |
| [35] | 张克信, 朱云海, 林启祥, 等. 青海同仁县隆务峡地区首次发现镁铁质-超镁铁质岩带[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(6):661-667. |
| [36] | YIN Hongfu, ZHANG Kexin, FENG Qinglai. The archipelagic ocean system of eastern Eurasian Tethys[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(l):230-236. |
| [37] |
ZHANG Kexin, HUANG Jichun, YIN Hongfu, et al. Application of radiolarians and other fossils in non-Smithstrata:Exemplified by the Animaqing mélange belt in eastern Kunlun Mountains[J]. Science in China(Series D), 2000, 43(4):364-374.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 马德成, 席振, 高光明, 李欢. 新疆祁漫塔格花土沟地区中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 599-612. |
| [2] | 陈宇航, 张新涛, 余一欣, 杨帆, 柳永军, 张震, 丁康. 渤中凹陷北部中生界顶面断层破碎带量化研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1035-1042. |
| [3] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [4] | 胡博心, 周鸿飞, 屈海浪, 曹易刚, 白会良, 王凌童, 王立新, 杨昭克, 李元申. 陕西铧厂沟金矿南矿带构造叠加晕特征及深部找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1515-1522. |
| [5] | 高银虎, 尹刚, 龚泽强, 郭明春. 甘肃两当湘潭子金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| [6] | 缪广, 董国臣, 屈海浪, 刘舒飞, 艾忠林, 史鹏亮, 曹雪峰. 西秦岭大店沟金矿成矿流体演化及矿床成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1565-1575. |
| [7] | 第鹏飞, 汤庆艳, 刘聪, 宋宏, 张家和, 刘东晓, 王玉玺, 蒲万峰. 西秦岭夏河—合作地区早子沟和加甘滩金矿床石英微量元素特征及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1608-1621. |
| [8] | 任廷仙, 李小伟, 王可, 葛涵云, 关瑞. 西秦岭碌础坝石英闪长岩-花岗闪长岩的地球化学、矿物学研究及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1651-1676. |
| [9] | 严镜, 刘景显, 蒲万峰, 魏学平, 李智斌. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世构造属性:来自将其那梁侵入杂岩体的年代学及地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1677-1690. |
| [10] | 杨维刚, 李永胜, 李通元, 张俊, 任鹏飞. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世板块碰撞事件的记录:来自合作地区火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1691-1701. |
| [11] | 陈澍民, 缪宇, 廖驾, 贺前平, 成明, 张珍力, 吴绍安, 章志明. 中拉萨地块南缘孔隆晚白垩世火山岩成因及对地壳演化的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1713-1726. |
| [12] | 潘力, 何青林, 梁生贤, 陈先洁, 陈文, 谢光华, 黎洋, 夏青, 马乾. 基于正演模拟的火山岩重磁响应特征研究:以川西地区二叠系为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1471-1479. |
| [13] | 寇少磊, 魏立勇, 张振, 李国英, 郑鑫, 路宗悦, 杨瀚文, 孟五一. 西秦岭中段日多玛岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1245-1260. |
| [14] | 毛翔, 罗璐, 汪新伟, 国殿斌. 渤海湾盆地新生代火山岩分布特征及其地热勘探潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 858-864. |
| [15] | 蔺新望, 王星, 陈光庭, 赵端昌, 赵江林. 新疆北部阿尔泰山东段泥盆纪岩浆活动及侵位方式的探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 514-531. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||